Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (4): 779-807.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-060
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Rewiring and application of Yarrowia lipolytica chassis cell
SUN Meili, WANG Kaifeng, LU Ran, JI Xiaojun
- State Key Laboratory of Materials-Oriented Chemical Engineering,College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering,Nanjing Tech University,Nanjing 211816,Jiangsu,China
-
Received:2022-11-02Revised:2022-12-12Online:2023-09-14Published:2023-08-31 -
Contact:JI Xiaojun
解脂耶氏酵母底盘细胞的工程改造及应用
孙美莉, 王凯峰, 陆然, 纪晓俊
- 南京工业大学生物与制药工程学院,材料化学工程国家重点实验室,江苏 南京 211816
-
通讯作者:纪晓俊 -
作者简介:孙美莉 (1990—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为代谢工程与合成生物学。E-mail:meilisun@njtech.edu.cn纪晓俊 (1982—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为代谢工程与合成生物学。E-mail:xiaojunji@njtech.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFC2101100);国家自然科学基金优秀青年科学基金(21922806);江苏省重点研发计划(BE2020782);英国皇家学会牛顿高级学者基金(NAF\R1\20118)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SUN Meili, WANG Kaifeng, LU Ran, JI Xiaojun. Rewiring and application of Yarrowia lipolytica chassis cell[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): 779-807.
孙美莉, 王凯峰, 陆然, 纪晓俊. 解脂耶氏酵母底盘细胞的工程改造及应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 779-807.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2022-060

Fig. 1 Schematic representation for various compounds synthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica chassis cell(The same type of products are labeled with dots using the same color) Cit—citrate; ICit—isocitrate; α-KG—α-ketoglutaric acid; Suc—succinate; Mal—malic acid; TAG—triacylglyceride; MIT—mitochondria; ER—endoplasmic reticulum; LB—lipid body
| 表征的启动子强度排序 | 表征方法 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| pEXP1> pTEF> pGPD > pGPAT> pYAT1 >pXPR2 > pFBA1 | 报告蛋白:绿色荧光蛋白 分析:流式细胞仪 | [ |
| pCTR1 > pTEF > pCTR2 | 报告蛋白:β-半乳糖苷酶 分析:紫外-可见分光光度计 | [ |
| pTEFin>php4d > pTEF | 报告蛋白:β-半乳糖苷酶 分析:分光光度计 | [ |
| pTEF> pGAP > pACL2 > pICL > pIDH2 > pFAS1 > pDGA1 > pFAS2 > pZWF1 > pPOX4 > pACC1 > pIDP2 | 报告蛋白: 荧光素酶 分析:酶标仪 | [ |
| pFBAin> pFBA> pTDH1 > pGPM1= pTEF | 报告蛋白:β-葡萄糖醛酸酶 分析:荧光微孔板读数仪 | [ |
Table 1 Comparison of strength and characterization of promoters
| 表征的启动子强度排序 | 表征方法 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| pEXP1> pTEF> pGPD > pGPAT> pYAT1 >pXPR2 > pFBA1 | 报告蛋白:绿色荧光蛋白 分析:流式细胞仪 | [ |
| pCTR1 > pTEF > pCTR2 | 报告蛋白:β-半乳糖苷酶 分析:紫外-可见分光光度计 | [ |
| pTEFin>php4d > pTEF | 报告蛋白:β-半乳糖苷酶 分析:分光光度计 | [ |
| pTEF> pGAP > pACL2 > pICL > pIDH2 > pFAS1 > pDGA1 > pFAS2 > pZWF1 > pPOX4 > pACC1 > pIDP2 | 报告蛋白: 荧光素酶 分析:酶标仪 | [ |
| pFBAin> pFBA> pTDH1 > pGPM1= pTEF | 报告蛋白:β-葡萄糖醛酸酶 分析:荧光微孔板读数仪 | [ |
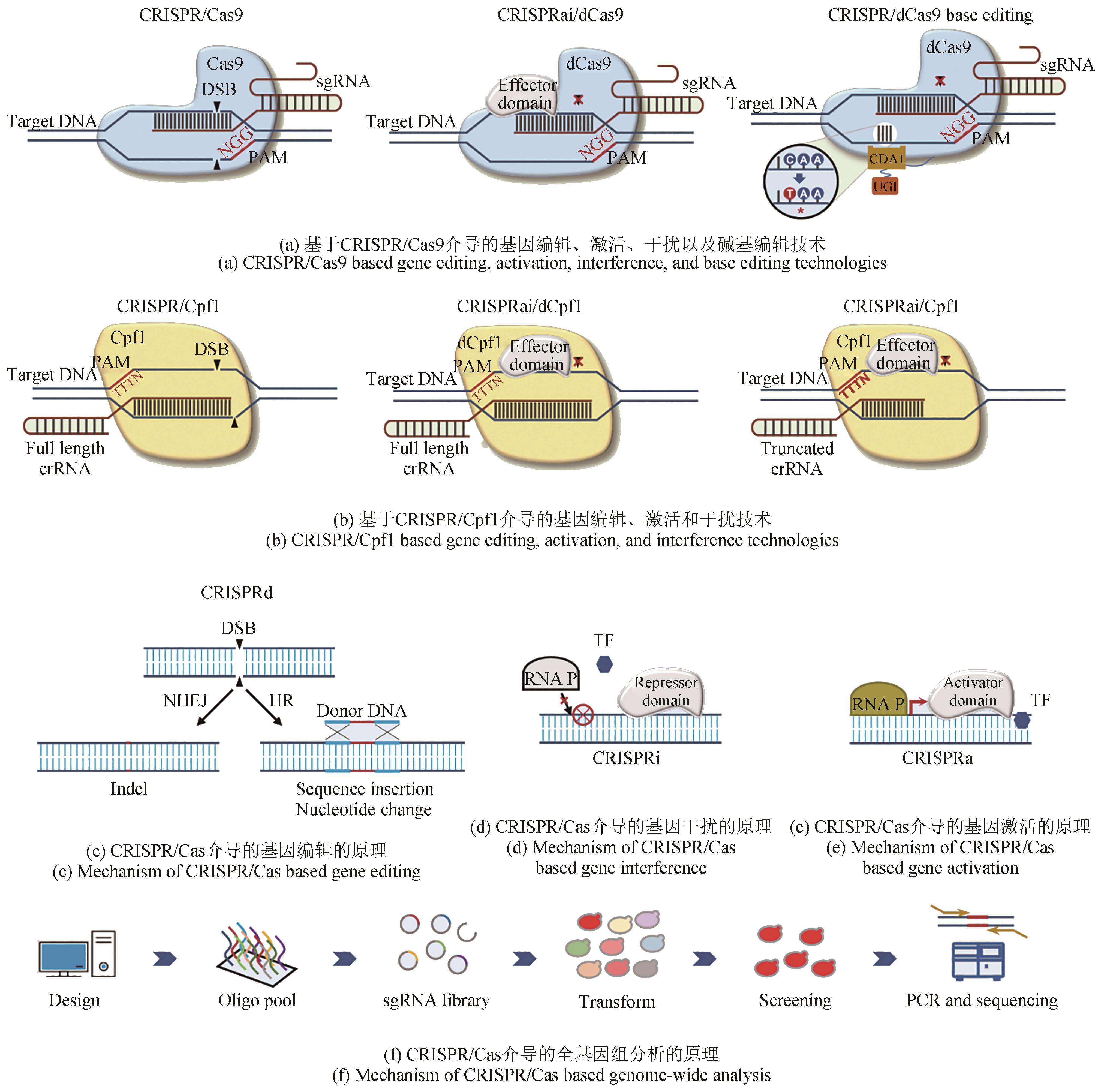
Fig. 2 CRISPR/Cas based genome-editingtechnologies applied in Yarrowia lipolyticaCRISPRa—CRISPR/Cas based gene activation; CRISPRd—CRISPR/Cas based gene editing; CRISPRi—CRISPR/Cas based gene interference; crRNA—CRISPR RNA; DSB—DNA double strand breaks; HR—homologyrecombination; NHEJ—non-homologous endjoining; PAM—protospacer adjacent motif; RNA P—RNA polymerase; sgRNA—single-guide RNA; TF—transcription factor
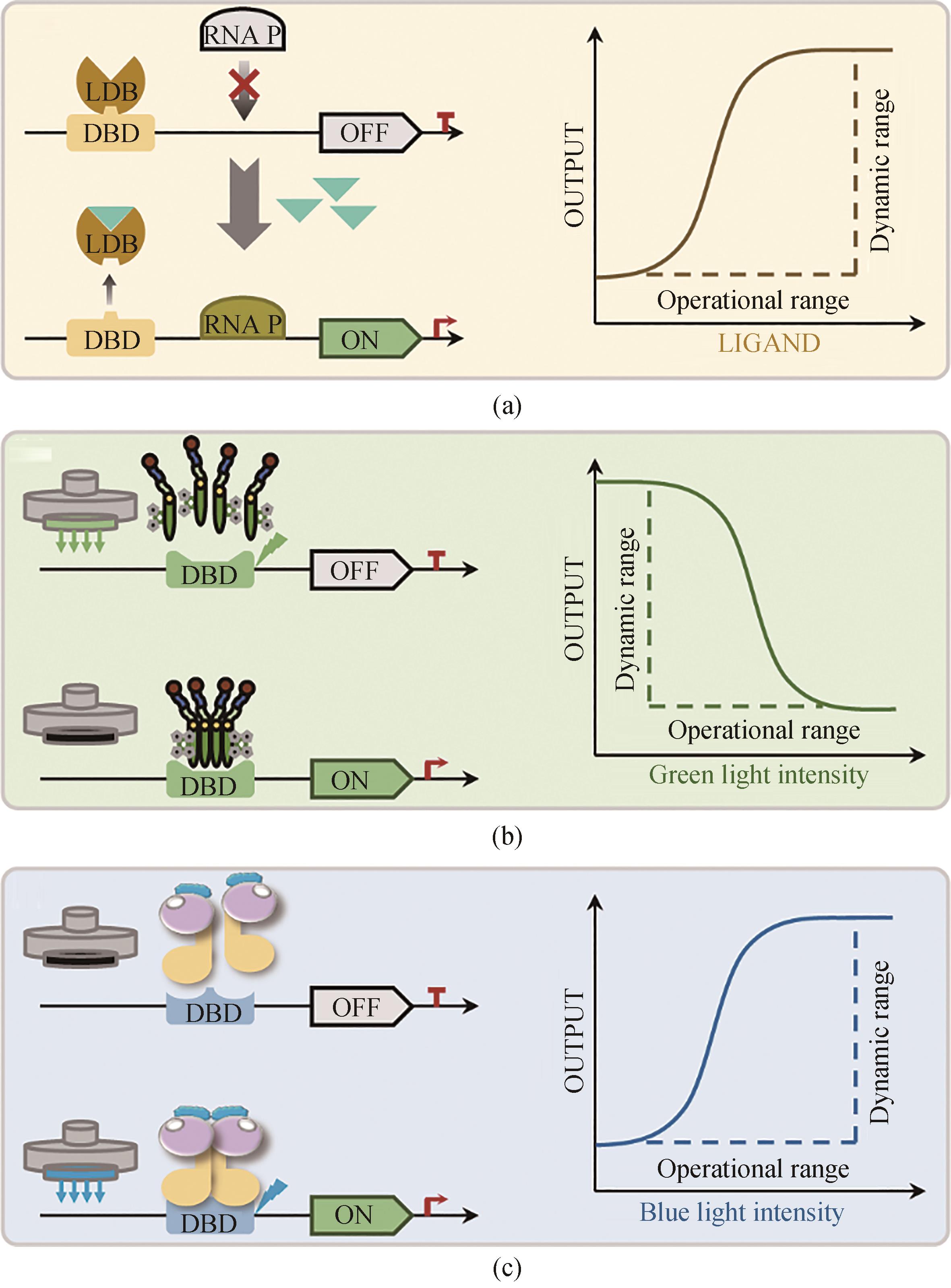
Fig. 3 Dynamic regulation of gene circuits through biosensors in Yarrowia lipolytica(a) Mechanism of the metabolites response biosensor,"ON" mode represents turning on the gene expression in the presence of the response metabolites,and "OFF" mode represents turning off the gene expression in theabsence of the response metabolites; (b) Mechanism of the green light response biosensor,"ON" mode represents turning on the gene expression in the dark condition;and "OFF" mode represents turning off the gene expression under the green light; (c) Mechanism of the blue light response biosensor, "ON" mode represents turning on the gene expression under the blue light, and "OFF" mode represents turning off the gene expression inthe dark condition.DBD—DNA binding domain; LDB—ligand binding domain; RNA P—RNA polymerase
| 模型名称 | 基因数 | 代谢物数 | 反应数 | 代谢区室数 | 准确性 | 年份 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iNL895 | 895 | 1847 | 1989 | 16 | 0.65 | 2012 | [ |
| iYL619_PCP | 619 | 849 | 1142 | 2 | 0.83 | 2012 | [ |
| iMK735 | 735 | 1111 | 1336 | 8 | 0.80 | 2015 | [ |
| iYali4 | 901 | 1683 | 1985 | 16 | Not determined | 2016 | [ |
| iYL_2.0 | 645 | 1083 | 1471 | 4 | 0.97 | 2017 | [ |
| iYLI647 | 647 | 1119 | 1347 | 8 | 0.80 | 2018 | [ |
| iYli21 | 1058 | 1868 | 2285 | 16 | 0.86 | 2022 | [ |
Table 2 Summary of the different GEMs available for Yarrowia lipolytica
| 模型名称 | 基因数 | 代谢物数 | 反应数 | 代谢区室数 | 准确性 | 年份 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iNL895 | 895 | 1847 | 1989 | 16 | 0.65 | 2012 | [ |
| iYL619_PCP | 619 | 849 | 1142 | 2 | 0.83 | 2012 | [ |
| iMK735 | 735 | 1111 | 1336 | 8 | 0.80 | 2015 | [ |
| iYali4 | 901 | 1683 | 1985 | 16 | Not determined | 2016 | [ |
| iYL_2.0 | 645 | 1083 | 1471 | 4 | 0.97 | 2017 | [ |
| iYLI647 | 647 | 1119 | 1347 | 8 | 0.80 | 2018 | [ |
| iYli21 | 1058 | 1868 | 2285 | 16 | 0.86 | 2022 | [ |
| 种类 | 产品 | 生产规模 | 生产水平 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机酸 | 柠檬酸 | 1L 生物反应器 | 97.1 g/L | [ |
| 异柠檬酸 | 1L 生物反应器 | 136.7 g/L | [ | |
| 琥珀酸 | 1L 生物反应器 | 101.4 g/L | [ | |
| 衣康酸 | 5L 生物反应器 | 22.03 g/L | [ | |
| α-酮戊二酸 | 3L 生物反应器 | 67.4 g/L | [ | |
| 丙酮酸 | 3L 生物反应器 | 39.1 g/L | [ | |
| 萜烯类 | 柠檬烯 | 摇瓶 | 35.9 mg/L | [ |
| α-法尼烯 | 1L 生物反应器 | 25.55 g/L | [ | |
| β-法尼烯 | 摇瓶 | 955 mg/L | [ | |
| α-葎草烯 | 5L 生物反应器 | 3.2 g/L | [ | |
| (-)-α-红没药醇 | 5L 生物反应器 | 4.4 g/L | [ | |
| 脱落酸 | 摇瓶 | 263.5 mg/L | [ | |
| 赤霉素3 | 摇瓶 | 17.29 mg/L | [ | |
| 赤霉素4 | 摇瓶 | 12.81 mg/L | [ | |
| 角鲨烯 | 摇瓶 | 731.18 mg/L | [ | |
| 桦木酸 | 摇瓶 | 51.87 mg/L | [ | |
| 人参皂苷CK | 5L 生物反应器 | 161.8 mg/L | [ | |
| 番茄红素 | 3L 生物反应器 | 17.6 g/L | [ | |
| β-胡萝卜素 | 5L 生物反应器 | 6.5 g/L | [ | |
| 虾青素 | 摇瓶 | 858 mg/L | [ | |
| 功能糖及糖醇类 | 赤藓糖醇 | 3L生物反应器 | 148 g/L | [ |
| D-苏糖醇 | 摇瓶 | 112 g/L | [ | |
| 木糖醇 | 摇瓶 | 53.2 g/L | [ | |
| 2′-岩藻糖基乳糖 | 2L 生物反应器 | 24 g/L | [ | |
| 异麦芽酮糖 | 10L 生物反应器 | 572.1 g/L | [ | |
| 海藻糖 | 3L 生物反应器 | 219 g/L | [ | |
| 脂肪酸及衍生物类 | 奇数链脂肪酸(C15~C19) | 摇瓶 | 1.87 g/L | [ |
| (10E,12Z)十八碳二烯酸 | 5L 生物反应器 | 4 g/L | [ | |
| 油酸 | 5L 生物反应器 | 46.23 g/L | [ | |
| α-亚麻酸 | 2L 生物反应器 | 1.42 g/L | [ | |
| γ-亚麻酸 | 摇瓶 | 71.6 mg/L | [ | |
| 花生四烯酸 | 摇瓶 | 118.1 mg/L | [ | |
| 二十碳五烯酸 | 摇瓶 | 占总脂肪酸的56.6% | [ | |
| 二十二碳六烯酸 | 1L 生物反应器 | 350 mg/L | [ | |
| 环丙烷脂肪酸(C17、C19) | 5L 生物反应器 | 7.49 g/L | [ | |
| 10-甲基支链脂肪酸 | 1L 生物反应器 | 1.2 g/L | [ | |
| 蓖麻油酸 | 摇瓶 | 12 g/L | [ | |
| 甲基酮 | 0.5L 生物反应器 | 314.8 mg/L | [ | |
| 聚羟基脂肪酸酯 | 摇瓶 | 占细胞干重7.3% | [ | |
| γ-癸内酯 | 300L 生物反应器 | 12.3 g/L | [ | |
| δ-癸内酯 | 摇瓶 | 1.9 g/L | [ | |
| γ-十二内酯 | 1L 生物反应器 | 282 mg/L | [ | |
| 烷(烯)烃 | 摇瓶 | 1.47 g/L | [ | |
| 烯烃 | 摇瓶 | 554.4 mg/L | [ | |
| 聚酮类和黄酮类 | 三乙酸内酯 | 3L 生物反应器 | (35.9±3.9) g/L | [ |
| 白藜芦醇 | 5L 生物反应器 | 430 mg/L | [ | |
| 柚皮素 | 3L 生物反应器 | 898 mg/L | [ | |
| 圣草酚 | 摇瓶 | 134.2 mg/L | [ | |
| 氨基酸衍生物类 | 2-苯乙醇 | 摇瓶 | 2669.54 mg/L | [ |
| 对香豆酸 | 摇瓶 | (593.53 ± 28.75) mg/L | [ | |
| 紫杆菌素 | 摇瓶 | (366.30 ± 28.99) mg/L | [ | |
| 犬尿酸 | 5L 生物反应器 | 培养液:68 mg/L 生物量:542 mg/kg | [ | |
| 麦角硫因 | 1L 生物反应器 | 1.63 g/L | [ |
Table 3 Representative application examples of engineered Y. lipolytica chassis cell
| 种类 | 产品 | 生产规模 | 生产水平 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机酸 | 柠檬酸 | 1L 生物反应器 | 97.1 g/L | [ |
| 异柠檬酸 | 1L 生物反应器 | 136.7 g/L | [ | |
| 琥珀酸 | 1L 生物反应器 | 101.4 g/L | [ | |
| 衣康酸 | 5L 生物反应器 | 22.03 g/L | [ | |
| α-酮戊二酸 | 3L 生物反应器 | 67.4 g/L | [ | |
| 丙酮酸 | 3L 生物反应器 | 39.1 g/L | [ | |
| 萜烯类 | 柠檬烯 | 摇瓶 | 35.9 mg/L | [ |
| α-法尼烯 | 1L 生物反应器 | 25.55 g/L | [ | |
| β-法尼烯 | 摇瓶 | 955 mg/L | [ | |
| α-葎草烯 | 5L 生物反应器 | 3.2 g/L | [ | |
| (-)-α-红没药醇 | 5L 生物反应器 | 4.4 g/L | [ | |
| 脱落酸 | 摇瓶 | 263.5 mg/L | [ | |
| 赤霉素3 | 摇瓶 | 17.29 mg/L | [ | |
| 赤霉素4 | 摇瓶 | 12.81 mg/L | [ | |
| 角鲨烯 | 摇瓶 | 731.18 mg/L | [ | |
| 桦木酸 | 摇瓶 | 51.87 mg/L | [ | |
| 人参皂苷CK | 5L 生物反应器 | 161.8 mg/L | [ | |
| 番茄红素 | 3L 生物反应器 | 17.6 g/L | [ | |
| β-胡萝卜素 | 5L 生物反应器 | 6.5 g/L | [ | |
| 虾青素 | 摇瓶 | 858 mg/L | [ | |
| 功能糖及糖醇类 | 赤藓糖醇 | 3L生物反应器 | 148 g/L | [ |
| D-苏糖醇 | 摇瓶 | 112 g/L | [ | |
| 木糖醇 | 摇瓶 | 53.2 g/L | [ | |
| 2′-岩藻糖基乳糖 | 2L 生物反应器 | 24 g/L | [ | |
| 异麦芽酮糖 | 10L 生物反应器 | 572.1 g/L | [ | |
| 海藻糖 | 3L 生物反应器 | 219 g/L | [ | |
| 脂肪酸及衍生物类 | 奇数链脂肪酸(C15~C19) | 摇瓶 | 1.87 g/L | [ |
| (10E,12Z)十八碳二烯酸 | 5L 生物反应器 | 4 g/L | [ | |
| 油酸 | 5L 生物反应器 | 46.23 g/L | [ | |
| α-亚麻酸 | 2L 生物反应器 | 1.42 g/L | [ | |
| γ-亚麻酸 | 摇瓶 | 71.6 mg/L | [ | |
| 花生四烯酸 | 摇瓶 | 118.1 mg/L | [ | |
| 二十碳五烯酸 | 摇瓶 | 占总脂肪酸的56.6% | [ | |
| 二十二碳六烯酸 | 1L 生物反应器 | 350 mg/L | [ | |
| 环丙烷脂肪酸(C17、C19) | 5L 生物反应器 | 7.49 g/L | [ | |
| 10-甲基支链脂肪酸 | 1L 生物反应器 | 1.2 g/L | [ | |
| 蓖麻油酸 | 摇瓶 | 12 g/L | [ | |
| 甲基酮 | 0.5L 生物反应器 | 314.8 mg/L | [ | |
| 聚羟基脂肪酸酯 | 摇瓶 | 占细胞干重7.3% | [ | |
| γ-癸内酯 | 300L 生物反应器 | 12.3 g/L | [ | |
| δ-癸内酯 | 摇瓶 | 1.9 g/L | [ | |
| γ-十二内酯 | 1L 生物反应器 | 282 mg/L | [ | |
| 烷(烯)烃 | 摇瓶 | 1.47 g/L | [ | |
| 烯烃 | 摇瓶 | 554.4 mg/L | [ | |
| 聚酮类和黄酮类 | 三乙酸内酯 | 3L 生物反应器 | (35.9±3.9) g/L | [ |
| 白藜芦醇 | 5L 生物反应器 | 430 mg/L | [ | |
| 柚皮素 | 3L 生物反应器 | 898 mg/L | [ | |
| 圣草酚 | 摇瓶 | 134.2 mg/L | [ | |
| 氨基酸衍生物类 | 2-苯乙醇 | 摇瓶 | 2669.54 mg/L | [ |
| 对香豆酸 | 摇瓶 | (593.53 ± 28.75) mg/L | [ | |
| 紫杆菌素 | 摇瓶 | (366.30 ± 28.99) mg/L | [ | |
| 犬尿酸 | 5L 生物反应器 | 培养液:68 mg/L 生物量:542 mg/kg | [ | |
| 麦角硫因 | 1L 生物反应器 | 1.63 g/L | [ |
| 1 | XU X H, LIU Y F, DU G C, et al. Microbial chassis development for natural product biosynthesis[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 779-796. |
| 2 | LIU J Y, WU X, YAO M D, et al. Chassis engineering for microbial production of chemicals: from natural microbes to synthetic organisms[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 66: 105-112. |
| 3 | LIU H H, JI X J, HUANG H. Biotechnological applications of Yarrowia lipolytica: past, present and future[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2015, 33(8): 1522-1546. |
| 4 | PARK Y K, LEDESMA AMARO R. What makes Yarrowia lipolytica well suited for industry?[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2023, 41(2): 242-254. |
| 5 | MADZAK C. Yarrowia lipolytica strains and their biotechnological applications: how natural biodiversity and metabolic engineering could contribute to cell factories improvement[J]. Journal of Fungi, 2021, 7(7): 548. |
| 6 | ABDEL-MAWGOUD A M, MARKHAM K A, PALMER C M, et al. Metabolic engineering in the host Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 50: 192-208. |
| 7 | MARKHAM K A, ALPER H S. Synthetic biology expands the industrial potential of Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2018, 36(10): 1085-1095. |
| 8 | WANG K F, SHI T Q, LIN L, et al. Advances in synthetic biology tools paving the way for the biomanufacturing of unusual fatty acids using the Yarrowia lipolytica chassis[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2022, 59: 107984. |
| 9 | WANG J P, LEDESMA-AMARO R, WEI Y J, et al. Metabolic engineering for increased lipid accumulation in Yarrowia lipolytica—a review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 313: 123707. |
| 10 | MA Y R, WANG K F, WANG W J, et al. Advances in the metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for the production of terpenoids[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 281: 449-456. |
| 11 | MUHAMMAD A, FENG X D, RASOOL A, et al. Production of plant natural products through engineered Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2020, 43: 107555. |
| 12 | 徐鹏. 纪念王义翘教授:解脂耶氏酵母替代植物油脂的技术瓶颈及展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 509-527. |
| XU P. In memory of Prof. Daniel I.C. Wang: engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for the production of plant-based lipids: technical constraints and perspectives for a sustainable cellular agriculture economy[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(4): 509-527. | |
| 13 | ZINJARDE S, APTE M, MOHITE P, et al. Yarrowia lipolytica and pollutants: interactions and applications[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2014, 32(5): 920-933. |
| 14 | LEDESMA AMARO R, NICAUD J M. Metabolic engineering for expanding the substrate range of Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2016, 34(10): 798-809. |
| 15 | SUN M L, SHI T Q, LIN L, et al. Advancing Yarrowia lipolytica as a superior biomanufacturing platform by tuning gene expression using promoter engineering[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 347: 126717. |
| 16 | DAVIDOW L S, O'DONNELL M M, KACZMAREK F S, et al. Cloning and sequencing of the alkaline extracellular protease gene of Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1987, 169(10): 4621-4629. |
| 17 | MÜLLER S, SANDAL T, KAMP-HANSEN P, et al. Comparison of expression systems in the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Hansenula polymorpha, Klyveromyces lactis, Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Yarrowia lipolytica. Cloning of two novel promoters from Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Yeast, 1998, 14(14): 1267-1283. |
| 18 | TRASSAERT M, VANDERMIES M, CARLY F, et al. New inducible promoter for gene expression and synthetic biology in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2017, 16(1): 141. |
| 19 | JURETZEK T, WANG H J, NICAUD J M, et al. Comparison of promoters suitable for regulated overexpression of β-galactosidase in the alkane-utilizing yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2000, 5(5): 320-326. |
| 20 | WONG L, ENGEL J, JIN E Q, et al. YaliBricks, a versatile genetic toolkit for streamlined and rapid pathway engineering in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Metabolic Engineering Communications, 2017, 5: 68-77. |
| 21 | KAMINENI A, CHEN S Y, CHIFAMBA G, et al. Promoters for lipogenesis-specific downregulation in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2020, 20(5): foaa035. |
| 22 | XIONG X C, CHEN S L. Expanding toolbox for genes expression of Yarrowia lipolytica to include novel inducible, repressible, and hybrid promoters[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(8): 2208-2213. |
| 23 | HONG S P, SEIP J, WALTERS-POLLAK D, et al. Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica to express secretory invertase with strong FBA1IN promoter[J]. Yeast, 2012, 29(2): 59-72. |
| 24 | XUE Z X, ZHU Q Q. Ammonium transporter promoter for gene expression in oleaginous yeast: US08323960B2[P]. 2012-12-04. |
| 25 | BLAZECK J, LIU L Q, REDDEN H, et al. Tuning gene expression in Yarrowia lipolytica by a hybrid promoter approach[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(22): 7905-7914. |
| 26 | TAI M, STEPHANOPOULOS G. Engineering the push and pull of lipid biosynthesis in oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for biofuel production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2013, 15: 1-9. |
| 27 | GEISBERG J V, MOQTADERI Z, FAN X C, et al. Global analysis of mRNA isoform half-lives reveals stabilizing and destabilizing elements in yeast[J]. Cell, 2014, 156(4): 812-824. |
| 28 | WAGNER J M, ALPER H S. Synthetic biology and molecular genetics in non-conventional yeasts: current tools and future advances[J]. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 2016, 89: 126-136. |
| 29 | CURRAN K A, MORSE N J, MARKHAM K A, et al. Short synthetic terminators for improved heterologous gene expression in yeast[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(7): 824-832. |
| 30 | BARTH G, GAILLARDIN C. Yarrowia lipolytica[M/OL]//Nonconventional Yeasts in Biotechnology: a handbook. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1996: 313-388 [2022-11-01]. . |
| 31 | LE DALL M T, NICAUD J M, GAILLARDIN C. Multiple-copy integration in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Current Genetics, 1994, 26(1): 38-44. |
| 32 | BLAZECK J, HILL A, LIU L Q, et al. Harnessing Yarrowia lipolytica lipogenesis to create a platform for lipid and biofuel production[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 3131. |
| 33 | KERKHOVEN E J, KIM Y M, WEI S W, et al. Leucine biosynthesis is involved in regulating high lipid accumulation in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. mBio, 2017, 8(3): e00857-e00817. |
| 34 | BOEKE J D, TRUEHEART J, NATSOULIS G, et al. 5-Fluoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics[M/OL]//Methods in enzymology. New York: Academic Press, 1987: 164-175 [2022-11-01]. . |
| 35 | FICKERS P, LE DALL M T, GAILLARDIN C, et al. New disruption cassettes for rapid gene disruption and marker rescue in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2003, 55(3): 727-737. |
| 36 | CELIŃSKA E, BORKOWSKA M, KORPYS-WOŹNIAK P, et al. Optimization of Yarrowia lipolytica-based consolidated biocatalyst through synthetic biology approach: transcription units and signal peptides shuffling[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(13): 5845-5859. |
| 37 | LARROUDE M, TRABELSI H, NICAUD J M, et al. A set of Yarrowia lipolytica CRISPR/Cas9 vectors for exploiting wild-type strain diversity[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2020, 42(5): 773-785. |
| 38 | HESLOT H. Genetics and genetic engineering of the industrial yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [M/OL]//Applied molecular genetics. Berlin: Springer, 1990: 43-73 [2022-11-01]. . |
| 39 | FOURNIER P, ABBAS A, CHASLES M, et al. Colocalization of centromeric and replicative functions on autonomously replicating sequences isolated from the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1993, 90(11): 4912-4916. |
| 40 | VERNIS L, ABBAS A, CHASLES M, et al. An origin of replication and a centromere are both needed to establish a replicative plasmid in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 1997, 17(4): 1995-2004. |
| 41 | LIU L Q, OTOUPAL P, PAN A, et al. Increasing expression level and copy number of a Yarrowia lipolytica plasmid through regulated centromere function[J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2014, 14(7): 1124-1127. |
| 42 | LOPEZ C, CAO M F, YAO Z Y, et al. Revisiting the unique structure of autonomously replicating sequences in Yarrowia lipolytica and its role in pathway engineering[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2021, 105(14): 5959-5972. |
| 43 | CUI Z Y, ZHENG H H, JIANG Z N, et al. Identification and characterization of the mitochondrial replication origin for stable and episomal expression in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(4): 826-835. |
| 44 | GUO Z P, BORSENBERGER V, CROUX C, et al. An artificial chromosome ylAC enables efficient assembly of multiple genes in Yarrowia lipolytica for biomanufacturing[J]. Communications Biology, 2020, 3(1): 199. |
| 45 | MADZAK C, TRÉTON B, BLANCHIN-ROLAND S. Strong hybrid promoters and integrative expression/secretion vectors for quasi-constitutive expression of heterologous proteins in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2000, 2(2): 207-216. |
| 46 | NICAUD J M. Yarrowia lipolytica[J]. Yeast, 2012, 29(10): 409-418. |
| 47 | LARROUDE M, ROSSIGNOL T, NICAUD J M, et al. Synthetic biology tools for engineering Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2018, 36(8): 2150-2164. |
| 48 | DING Y, WANG K F, WANG W J, et al. Increasing the homologous recombination efficiency of eukaryotic microorganisms for enhanced genome engineering[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(11): 4313-4324. |
| 49 | JI Q C, MAI J, DING Y, et al. Improving the homologous recombination efficiency of Yarrowia lipolytica by grafting heterologous component from Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Metabolic Engineering Communications, 2020, 11: e00152. |
| 50 | BARTH G. Yarrowia lipolytica: biotechnological Applications[M/OL]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2013[2022-11-01]. . |
| 51 | PIGNÈDE G, WANG H J, FUDALEJ F, et al. Autocloning and amplification of LIP2 in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 66(8): 3283-3289. |
| 52 | BORDES F, FUDALEJ F, DOSSAT V, et al. A new recombinant protein expression system for high-throughput screening in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2007, 70(3): 493-502. |
| 53 | CUI Z Y, ZHENG H H, ZHANG J H, et al. A CRISPR/Cas9-mediated, homology-independent tool developed for targeted genome integration in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2021, 87(6): e02666-20. |
| 54 | BAI Q Y, CHENG S, ZHANG J L, et al. Establishment of genomic library technology mediated by non-homologous end joining mechanism in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2021, 64(12): 2114-2128. |
| 55 | CUI Z Y, JIANG X, ZHENG H H, et al. Homology-independent genome integration enables rapid library construction for enzyme expression and pathway optimization in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2019, 116(2): 354-363. |
| 56 | LIU Y H, JIANG X, CUI Z Y, et al. Engineering the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for production of α-farnesene[J].Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2019, 12(1): 296. |
| 57 | LI Y W, YANG C L, SHEN Q, et al. YALIcloneNHEJ: an efficient modular cloning toolkit for NHEJ integration of multigene pathway and terpenoid production in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 9: 816980. |
| 58 | PLAGENS A, TJADEN B, HAGEMANN A, et al. Characterization of the CRISPR/cas subtype I-A system of the hyperthermophilic crenarchaeon thermoproteus tenax[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2012, 194(10): 2491-2500. |
| 59 | SHI T Q, HUANG H, KERKHOVEN E J, et al. Advancing metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica using the CRISPR/Cas system[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(22): 9541-9548. |
| 60 | DARVISHI F, ARIANA M, MARELLA E R, et al. Advances in synthetic biology of oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for producing non-native chemicals[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(14): 5925-5938. |
| 61 | SCHWARTZ C M, HUSSAIN M S, BLENNER M, et al. Synthetic RNA polymeraseⅢpromoters facilitate high-efficiency CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(4): 356-359. |
| 62 | HOLKENBRINK C, DAM M I, KILDEGAARD K R, et al. EasyCloneYALI: CRISPR/Cas9-based synthetic toolbox for engineering of the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 13(9): e1700543. |
| 63 | GAO S L, TONG Y Y, WEN Z Q, et al. Multiplex gene editing of the Yarrowia lipolytica genome using the CRISPR-Cas9 system[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2016, 43(8): 1085-1093. |
| 64 | GAO D F, SMITH S, SPAGNUOLO M, et al. Dual CRISPR-Cas9 cleavage mediated gene excision and targeted integration in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 13(9): e1700590. |
| 65 | MA J B, GU Y, MARSAFARI M, et al. Synthetic biology, systems biology, and metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica toward a sustainable biorefinery platform[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2020, 47(9/10): 845-862. |
| 66 | YANG Z L, EDWARDS H, XU P. CRISPR-Cas12a/Cpf1-assisted precise, efficient and multiplexed genome-editing in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Metabolic Engineering Communications, 2020, 10: e00112. |
| 67 | MA H H, TU L C, NASERI A, et al. Multiplexed labeling of genomic loci with dCas9 and engineered sgRNAs using CRISPRainbow[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2016, 34(5): 528-530. |
| 68 | SCHWARTZ C, FROGUE K, RAMESH A, et al. CRISPRi repression of nonhomologous end-joining for enhanced genome engineering via homologous recombination in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2017, 114(12): 2896-2906. |
| 69 | ZHANG J L, PENG Y Z, LIU D, et al. Gene repression via multiplex gRNA strategy in Y. lipolytica [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17(1): 62. |
| 70 | SCHWARTZ C, WHEELDON I. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing and transcriptional control in Yarrowia lipolytica [M]//Synthetic Biology. New York, NY: Springer New York, 2018: 327-345. |
| 71 | RAMESH A, ONG T, GARCIA J A, et al. Guide RNA engineering enables dual purpose CRISPR-Cpf1 for simultaneous gene editing and gene regulation in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(4): 967-971. |
| 72 | SHIMATANI Z, KASHOJIYA S, TAKAYAMA M, et al. Targeted base editing in rice and tomato using a CRISPR-Cas9 cytidine deaminase fusion[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2017, 35(5): 441-443. |
| 73 | BAE S J, PARK B G, KIM B G, et al. Multiplex gene disruption by targeted base editing of Yarrowia lipolytica genome using cytidine deaminase combined with the CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 15(1): e1900238. |
| 74 | SCHWARTZ C, CHENG J F, EVANS R, et al. Validating genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 function improves screening in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 55: 102-110. |
| 75 | LUPISH B, HALL J, SCHWARTZ C, et al. Genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screen reveals a persistent null-hyphal phenotype that maintains high carotenoid production in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2022, 119(12): 3623-3631. |
| 76 | BAISYA D, RAMESH A, SCHWARTZ C, et al. Genome-wide functional screens enable the prediction of high activity CRISPR-Cas9 and-Cas12a guides in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 922. |
| 77 | JURETZEK T, LE DALL M T, MAUERSBERGER S, et al. Vectors for gene expression and amplification in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Yeast, 2001, 18(2): 97-113. |
| 78 | WANG K F, SHI T Q, WANG J P, et al. Engineering the lipid and fatty acid metabolism in Yarrowia lipolytica for sustainable production of high oleic oils[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(4): 1542-1554. |
| 79 | LV Y K, EDWARDS H, ZHOU J W, et al. Combining 26S rDNA and the Cre-loxP system for iterative gene integration and efficient marker curation in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(3): 568-576. |
| 80 | ZHOU Q H, JIAO L C, LI W J, et al. A novel cre/lox-based genetic tool for repeated, targeted and markerless gene integration in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(19): 10739. |
| 81 | SCHMID-BERGER N, SCHMID B, BARTH G. Ylt1, a highly repetitive retrotransposon in the genome of the dimorphic fungus Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1994, 176(9): 2477-2482. |
| 82 | BULANI S I, MOLELEKI L, ALBERTYN J, et al. Development of a novel rDNA based plasmid for enhanced cell surface display on Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. AMB Express, 2012, 2(1): 27. |
| 83 | NICAUD J M, MADZAK C, VAN DEN BROEK P, et al. Protein expression and secretion in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2002, 2(3): 371-379. |
| 84 | MADZAK C, GAILLARDIN C, BECKERICH J M. Heterologous protein expression and secretion in the non-conventional yeast Yarrowia lipolytica: a review[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2004, 109(1/2): 63-81. |
| 85 | ZHAO Y, LIU S Q, LU Z H, et al. Hybrid promoter engineering strategies in Yarrowia lipolytica: isoamyl alcohol production as a test study[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2021, 14(1): 149. |
| 86 | BARTH G, GAILLARDIN C. Physiology and genetics of the dimorphic fungus Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 1997, 19(4): 219-237. |
| 87 | JUNEAU K, MIRANDA M, HILLENMEYER M E, et al. Introns regulate RNA and protein abundance in yeast[J]. Genetics, 2006, 174(1): 511-518. |
| 88 | MEKOUAR M, BLANC-LENFLE I, OZANNE C, et al. Detection and analysis of alternative splicing in Yarrowia lipolytica reveal structural constraints facilitating nonsense-mediated decay of intron-retaining transcripts[J]. Genome Biology, 2010, 11(6): R65. |
| 89 | PELLIZZA L, SMAL C, RODRIGO G, et al. Codon usage clusters correlation: towards protein solubility prediction in heterologous expression systems in E. coli [J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 10618. |
| 90 | GASMI N, FUDALEJ F, KALLEL H, et al. A molecular approach to optimize hIFN α2b expression and secretion in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2011, 89(1): 109-119. |
| 91 | DE POURCQ K, VERVECKEN W, DEWERTE I, et al. Engineering the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for the production of therapeutic proteins homogeneously glycosylated with Man8GlcNAc2 and Man5GlcNAc2 [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2012, 11: 53. |
| 92 | 于政, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 等. 动态调控策略在代谢工程中的应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(4): 440-453. |
| YU Z, SHEN X L, SUN X X, et al. Application of dynamic regulation strategies in metabolic engineering[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(4): 440-453. | |
| 93 | QIU C X, ZHAI H T, HOU J. Biosensors design in yeast and applications in metabolic engineering[J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2019, 19(8): foz082. |
| 94 | WAN X, MARSAFARI M, XU P. Engineering metabolite-responsive transcriptional factors to sense small molecules in eukaryotes: current state and perspectives[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18(1): 61. |
| 95 | PARK B G, KIM J, KIM E J, et al. Application of random mutagenesis and synthetic FadR promoter for de novo production of ω-hydroxy fatty acid in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2021, 9: 624838. |
| 96 | LV Y K, GU Y, XU J L, et al. Coupling metabolic addiction with negative autoregulation to improve strain stability and pathway yield[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 61: 79-88. |
| 97 | CHO E J, TRINH L T P, SONG Y H, et al. Bioconversion of biomass waste into high value chemicals[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 298: 122386. |
| 98 | ISIKGOR F H, BECER C R J P C. Lignocellulosic biomass: a sustainable platform for the production of bio-based chemicals and polymers[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2015, 6(25): 4497-4559. |
| 99 | SUN T, YU Y Z, WANG K F, et al. Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica to produce fuels and chemicals from xylose: a review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 337: 125484. |
| 100 | WEI W P, SHANG Y Z, ZHANG P, et al. Engineering prokaryotic transcriptional activator XylR as a xylose-inducible biosensor for transcription activation in yeast[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(5): 1022-1029. |
| 101 | WEI W P, ZHANG P, SHANG Y Z, et al. Metabolically engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for the biosynthesis of naringenin from a mixture of glucose and xylose[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 314: 123726. |
| 102 | QIU X L, XU P, ZHAO X R, et al. Combining genetically-encoded biosensors with high throughput strain screening to maximize erythritol production in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 60: 66-76. |
| 103 | 张萍, 魏文平, 周英, 等. 解脂耶氏酵母中光控表达系统的构建及其应用研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(5): 778-791. |
| ZHANG P, WEI W P, ZHOU Y, et al. Construction of a light-controlled expression system and its application in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(5): 778-791. | |
| 104 | WANG Z Q, YAN Y J, ZHANG H J. A single-component blue light-induced system based on EL222 in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(11): 6344. |
| 105 | KERKHOVEN E J. Advances in constraint-based models: methods for improved predictive power based on resource allocation constraints[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2022, 68: 102168. |
| 106 | BORDBAR A, MONK J M, KING Z A, et al. Constraint-based models predict metabolic and associated cellular functions[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2014, 15(2): 107-120. |
| 107 | MAIA P, ROCHA M, ROCHA I. In silico constraint-based strain optimization methods: the quest for optimal cell factories[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 2016, 80(1): 45-67. |
| 108 | PARK B G, KIM M, KIM J, et al. Systems biology for understanding and engineering of heterotrophic oleaginous microorganisms[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 12(1): 1600104. |
| 109 | LOIRA N, DULERMO T, NICAUD J M, et al. A genome-scale metabolic model of the lipid-accumulating yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. BMC Systems Biology, 2012, 6: 35. |
| 110 | PAN P C, HUA Q. Reconstruction and in silico analysis of metabolic network for an oleaginous yeast, Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(12): e51535. |
| 111 | KAVŠČEK M, BHUTADA G, MADL T, et al. Optimization of lipid production with a genome-scale model of Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. BMC Systems Biology, 2015, 9: 72. |
| 112 | KERKHOVEN E J, POMRANING K R, BAKER S E, et al. Regulation of amino-acid metabolism controls flux to lipid accumulation in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Npj Systems Biology and Applications, 2016, 2: 16005. |
| 113 | AUNG H W, HENRY S A, WALKER L P. Revising the representation of fatty acid, glycerolipid, and glycerophospholipid metabolism in the consensus model of yeast metabolism[J]. Industrial Biotechnology, 2013, 9(4): 215-228. |
| 114 | DUARTE N C, HERRGÅRD M J, PALSSON B Ø. Reconstruction and validation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae IND750, a fully compartmentalized genome-scale metabolic model[J]. Genome Research, 2004, 14(7): 1298-1309. |
| 115 | WEI S S, JIAN X X, CHEN J, et al. Reconstruction of genome-scale metabolic model of Yarrowia lipolytica and its application in overproduction of triacylglycerol[J]. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 2017, 4: 51. |
| 116 | MISHRA P, LEE N R, LAKSHMANAN M, et al. Genome-scale model-driven strain design for dicarboxylic acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. BMC Systems Biology, 2018, 12(): 12. |
| 117 | ZHANG C, JI B Y, MARDINOGLU A, et al. Logical transformation of genome-scale metabolic models for gene level applications and analysis[J]. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(14): 2324-2331. |
| 118 | JIAN X X, ZHOU S G, ZHANG C, et al. In silico identification of gene amplification targets based on analysis of production and growth coupling[J]. Biosystems, 2016, 145: 1-8. |
| 119 | MISHRA P, LEE N R, LAKSHMANAN M, et al. Genome-scale model-driven strain design for dicarboxylic acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. BMC systems biology, 2018, 12(2): 9-20. |
| 120 | KIM M, PARK B G, KIM E J, et al. In silico identification of metabolic engineering strategies for improved lipid production in Yarrowia lipolytica by genome-scale metabolic modeling[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2019, 12: 187. |
| 121 | GUO Y F, SU L Q, LIU Q, et al. Dissecting carbon metabolism of Yarrowia lipolytica type strain W29 using genome-scale metabolic modelling[J]. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20: 2503-2511. |
| 122 | KUBICEK C P, MIKUS M, SCHUSTER A, et al. Metabolic engineering strategies for the improvement of cellulase production by Hypocrea jecorina [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2009, 2: 19. |
| 123 | WARD O P. Production of recombinant proteins by filamentous fungi[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2012, 30(5): 1119-1139. |
| 124 | KIM H, YOO S J, KANG H A. Yeast synthetic biology for the production of recombinant therapeutic proteins[J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2015, 15(1): 1-16. |
| 125 | WOLF K. Nonconventional yeasts in biotechnology: a handbook[M/OL]. Heidelberg: Springer Berlin, 2012[2022-11-01]. . |
| 126 | CELIŃSKA E, BORKOWSKA M, BIAŁAS W. Enhanced production of insect raw-starch-digesting alpha-amylase accompanied by high erythritol synthesis in recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica fed-batch cultures at high-cell-densities[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2017, 52: 78-85. |
| 127 | OUEPHANIT C, BOONVITTHYA N, THEERACHAT M, et al. Efficient expression and secretion of endo-1,4-β-xylanase from Penicillium citrinum in non-conventional yeast Yarrowia lipolytica directed by the native and the preproLIP2 signal peptides[J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2019, 160: 1-6. |
| 128 | GUO Z P, DUQUESNE S, BOZONNET S, et al. Expressing accessory proteins in cellulolytic Yarrowia lipolytica to improve the conversion yield of recalcitrant cellulose[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2017, 10: 298. |
| 129 | DERAKSHAN F K, DARVISHI F, DEZFULIAN M, et al. Expression and characterization of glucose oxidase from Aspergillus niger in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Molecular Biotechnology, 2017, 59(8): 307-314. |
| 130 | PARK Y K, VANDERMIES M, SOUDIER P, et al. Efficient expression vectors and host strain for the production of recombinant proteins by Yarrowia lipolytica in process conditions[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18(1): 167. |
| 131 | CUI W, WANG Q, ZHANG F, et al. Direct conversion of inulin into single cell protein by the engineered Yarrowia lipolytica carrying inulinase gene[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2011, 46(7): 1442-1448. |
| 132 | KRISS S, ZANE G, ZANE K, et al. Waste cooking oil as substrate for single cell protein production by yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Environmental and Climate Technologies, 2020, 24(3): 457-469. |
| 133 | YANG R, CHEN Z, HU P, et al. Two-stage fermentation enhanced single-cell protein production by Yarrowia lipolytica from food waste[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 361: 127677. |
| 134 | GASMI N, AYED A, AMMAR B B H, et al. Development of a cultivation process for the enhancement of human interferon alpha 2b production in the oleaginous yeast, Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2011, 10: 90. |
| 135 | GASMI N, AYED A, NICAUD J M, et al. Design of an efficient medium for heterologous protein production in Yarrowia lipolytica: case of human interferon alpha 2b[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2011, 10: 38. |
| 136 | PARK J N, SONG Y, CHEON S A, et al. Essential role of YlMPO1, a novel Yarrowia lipolytica homologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae MNN4, in mannosylphosphorylation of N- and O-linked glycans[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(4): 1187-1195. |
| 137 | SOONG Y H V, LIU N, YOON S, et al. Cellular and metabolic engineering of oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica for bioconversion of hydrophobic substrates into high-value products[J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2019, 19(6): 423-443. |
| 138 | YUZBASHEVA E Y, AGRIMI G, YUZBASHEV T V, et al. The mitochondrial citrate carrier in Yarrowia lipolytica: its identification, characterization and functional significance for the production of citric acid[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 54: 264-274. |
| 139 | YUZBASHEVA E Y, SCARCIA P, YUZBASHEV T V, et al. Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for the selective and high-level production of isocitric acid through manipulation of mitochondrial dicarboxylate-tricarboxylate carriers[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2021, 65: 156-166. |
| 140 | JIANG Z N, CUI Z Y, ZHU Z W, et al. Engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica transporters for high-efficient production of biobased succinic acid from glucose[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2021, 14(1): 145. |
| 141 | ZHAO C, CUI Z Y, ZHAO X Y, et al. Enhanced itaconic acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica via heterologous expression of a mitochondrial transporter MTT[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(5): 2181-2192. |
| 142 | ZENG W Z, DU G C, CHEN J, et al. A high-throughput screening procedure for enhancing α-ketoglutaric acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica by random mutagenesis[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2015, 50(10): 1516-1522. |
| 143 | ZENG W Z, FANG F, LIU S, et al. Comparative genomics analysis of a series of Yarrowia lipolytica WSH-Z06 mutants with varied capacity for α-ketoglutarate production[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 239: 76-82. |
| 144 | ZENG W Z, ZHANG H L, XU S, et al. Biosynthesis of keto acids by fed-batch culture of Yarrowia lipolytica WSH-Z06[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 243: 1037-1043. |
| 145 | ZHANG G, WANG H, ZHANG Z, et al. Metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for terpenoids production: advances and perspectives[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2022, 42(4): 618-633. |
| 146 | MAI J, LI W J, LEDESMA-AMARO R, et al. Engineering plant sesquiterpene synthesis into yeasts: a review[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2021, 69(33): 9498-9510. |
| 147 | LI W J, CUI L W, MAI J, et al. Advances in metabolic engineering paving the way for the efficient biosynthesis of terpenes in yeasts[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2022, 70(30): 9246-9261. |
| 148 | GOTO T, TAKAHASHI N, HIRAI S, et al. Various terpenoids derived from herbal and dietary plants function as PPAR modulators and regulate carbohydrate and lipid metabolism[J]. PPAR Research, 2010, 2010: 483958. |
| 149 | PANG Y R, ZHAO Y K, LI S L, et al. Engineering the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica to produce limonene from waste cooking oil[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2019, 12: 241. |
| 150 | ARNESEN J A, KILDEGAARD K R, CERNUDA PASTOR M, et al. Yarrowia lipolytica strains engineered for the production of terpenoids[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020, 8: 945. |
| 151 | GUO Q, SHI T Q, PENG Q Q, et al. Harnessing Yarrowia lipolytica peroxisomes as a subcellular factory for α-humulene overproduction [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2021, 69(46): 13831-13837. |
| 152 | MA Y R, LI W J, MAI J, et al. Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for sustainable production of the chamomile sesquiterpene (-)-α-bisabolol[J]. Green Chemistry, 2021, 23(2): 780-787. |
| 153 | KILDEGAARD K R, ARNESEN J A, ADIEGO-PÉREZ B, et al. Tailored biosynthesis of gibberellin plant hormones in yeast[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2021, 66: 1-11. |
| 154 | TANG W Y, WANG D P, TIAN Y, et al. Metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for improving squalene production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 323: 124652. |
| 155 | JIN C C, ZHANG J L, SONG H, et al. Boosting the biosynthesis of betulinic acid and related triterpenoids in Yarrowia lipolytica via multimodular metabolic engineering[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18(1): 77. |
| 156 | MA Y S, LIU N, GREISEN P, et al. Removal of lycopene substrate inhibition enables high carotenoid productivity in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 572. |
| 157 | LARROUDE M, CELINSKA E, BACK A, et al. A synthetic biology approach to transform Yarrowia lipolytica into a competitive biotechnological producer of β-carotene[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2018, 115(2): 464-472. |
| 158 | MA Y S, LI J B, HUANG S W, et al. Targeting pathway expression to subcellular organelles improves astaxanthin synthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2021, 68: 152-161. |
| 159 | MA T, SHI B, YE Z L, et al. Lipid engineering combined with systematic metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for high-yield production of lycopene[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 52: 134-142. |
| 160 | MENG Y H, SHAO X X, WANG Y, et al. Extension of cell membrane boosting squalene production in the engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2020, 117(11): 3499-3507. |
| 161 | LUO Z S, LIU N, LAZAR Z, et al. Enhancing isoprenoid synthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica by expressing the isopentenol utilization pathway and modulating intracellular hydrophobicity[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 61: 344-351. |
| 162 | GUO X Y, SUN J, LI D S, et al. Heterologous biosynthesis of (+)-nootkatone in unconventional yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 137: 125-131. |
| 163 | ARNESEN J A, JACOBSEN I H, DANNOW DYEKJÆR J, et al. Production of abscisic acid in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2022, 22(1): foac015. |
| 164 | LI D S, WU Y F, ZHANG C B, et al. Production of triterpene ginsenoside compound K in the non-conventional yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2019, 67(9): 2581-2588. |
| 165 | BILAL M, XU S, IQBAL H M N, et al. Yarrowia lipolytica as an emerging biotechnological chassis for functional sugars biosynthesis[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2021, 61(4): 535-552. |
| 166 | JANEK T, DOBROWOLSKI A, BIEGALSKA A, et al. Characterization of erythrose reductase from Yarrowia lipolytica and its influence on erythritol synthesis[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2017, 16(1): 118. |
| 167 | MIROŃCZUK A M, BIEGALSKA A, DOBROWOLSKI A. Functional overexpression of genes involved in erythritol synthesis in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2017, 10: 77. |
| 168 | CHI P, WANG S Q, GE X M, et al. Efficient D-threitol production by an engineered strain of Yarrowia lipolytica overexpressing xylitol dehydrogenase gene from Scheffersomyces stipitis [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 149: 107259. |
| 169 | BENAHMED A G, GASMI A, ARSHAD M, et al. Health benefits of xylitol[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(17): 7225-7237. |
| 170 | PRABHU A A, THOMAS D J, LEDESMA-AMARO R, et al. Biovalorisation of crude glycerol and xylose into xylitol by oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2020, 19(1): 121. |
| 171 | BODE L. Human milk oligosaccharides: every baby needs a sugar mama[J]. Glycobiology, 2012, 22(9): 1147-1162. |
| 172 | HOLLANDS K, BARON C M, GIBSON K J, et al. Engineering two species of yeast as cell factories for 2′-fucosyllactose [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 52: 232-242. |
| 173 | ZHANG P, WANG Z P, SHENG J, et al. High and efficient isomaltulose production using an engineered Yarrowia lipolytica strain[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 265: 577-580. |
| 174 | LI N, WANG H W, LI L J, et al. Integrated approach to producing high-purity trehalose from maltose by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica displaying trehalose synthase (TreS) on the cell surface[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2016, 64(31): 6179-6187. |
| 175 | 王凯峰, 王金鹏, 韦萍, 等. 代谢工程改造解脂耶氏酵母生产脂肪酸及其衍生物[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 351-365. |
| WANG K F, WANG J P, WEI P, et al. Metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica to produce fatty acids and their derivatives[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 351-365. | |
| 176 | XU J Y, LIU N, QIAO K J, et al. Application of metabolic controls for the maximization of lipid production in semicontinuous fermentation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(27): E5308-E5316. |
| 177 | LEDESMA AMARO R, DULERMO R, NIEHUS X, et al. Combining metabolic engineering and process optimization to improve production and secretion of fatty acids[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 38: 38-46. |
| 178 | LU R, SHI T Q, LIN L, et al. Advances in metabolic engineering of yeasts for the production of fatty acid-derived hydrocarbon fuels [J]. Green Chemical Engineering, 2022,3(4): 289-303. |
| 179 | RIGOUIN C, CROUX C, BORSENBERGER V, et al. Increasing medium chain fatty acids production in Yarrowia lipolytica by metabolic engineering[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17(1): 142. |
| 180 | HANKO E K R, DENBY C M, SÀNCHEZ I NOGUÉ V, et al. Engineering β-oxidation in Yarrowia lipolytica for methyl ketone production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 48: 52-62. |
| 181 | HADDOUCHE R, POIRIER Y, DELESSERT S, et al. Engineering polyhydroxyalkanoate content and monomer composition in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica by modifying the β-oxidation multifunctional protein[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2011, 91(5): 1327-1340. |
| 182 | GUO Y Q, SONG H L, WANG Z Y, et al. Expression of POX2 gene and disruption of POX3 genes in the industrial Yarrowia lipolytica on the γ-decalactone production[J]. Microbiological Research, 2012, 167(4): 246-252. |
| 183 | LI H B, ALPER H S. Producing biochemicals in Yarrowia lipolytica from xylose through a strain mating approach[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 15(2): e1900304. |
| 184 | XUE Z X, SHARPE P L, HONG S P, et al. Production of omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid by metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(8): 734-740. |
| 185 | GEMPERLEIN K, DIETRICH D, KOHLSTEDT M, et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica employing designed myxobacterial PUFA synthases[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 4055. |
| 186 | SUN M L, MADZAK C, LIU H H, et al. Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for efficient γ-linolenic acid production[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 117: 172-180. |
| 187 | LIU H H, MADZAK C, SUN M L, et al. Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for arachidonic acid production through rapid assembly of metabolic pathway[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 119: 52-58. |
| 188 | LIU H H, ZENG S Y, SHI T Q, et al. A Yarrowia lipolytica strain engineered for arachidonic acid production counteracts metabolic burden by redirecting carbon flux towards intracellular fatty acid accumulation at the expense of organic acids secretion[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 128: 201-209. |
| 189 | LIU H H, WANG C, LU X Y, et al. Improved production of arachidonic acid by combined pathway engineering and synthetic enzyme fusion in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2019, 67(35): 9851-9857. |
| 190 | XIE D M, JACKSON E N, ZHU Q. Sustainable source of omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid from metabolically engineered Yarrowia lipolytica: from fundamental research to commercial production[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(4): 1599-1610. |
| 191 | PARK Y K, DULERMO T, LEDESMA-AMARO R, et al. Optimization of odd chain fatty acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2018, 11: 158. |
| 192 | PARK Y K, LEDESMA-AMARO R, NICAUD J M. De novo biosynthesis of odd-chain fatty acids in Yarrowia lipolytica enabled by modular pathway engineering[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020, 7: 484. |
| 193 | TANG S Y, QIAN S, AKINTERINWA O, et al. Screening for enhanced triacetic acid lactone production by recombinant Escherichia coli expressing a designed triacetic acid lactone reporter[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(27): 10099-10103. |
| 194 | SAUNDERS L P, BOWMAN M J, MERTENS J A, et al. Triacetic acid lactone production in industrial Saccharomyces yeast strains[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2015, 42(5): 711-721. |
| 195 | MARKHAM K A, PALMER C M, CHWATKO M, et al. Rewiring Yarrowia lipolytica toward triacetic acid lactone for materials generation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(9): 2096-2101 |
| 196 | YU J, LANDBERG J, SHAVAREBI F, et al. Bioengineering triacetic acid lactone production in Yarrowia lipolytica for pogostone synthesis[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2018, 115(9): 2383-2388. |
| 197 | LIU H, MARSAFARI M, WANG F, et al. Engineering acetyl-CoA metabolic shortcut for eco-friendly production of polyketides triacetic acid lactone in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 56: 60-68. |
| 198 | TRANTAS E A, KOFFAS M A G, XU P, et al. When plants produce not enough or at all: metabolic engineering of flavonoids in microbial hosts[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 7. |
| 199 | PALMER C M, MILLER K K, NGUYEN A, et al. Engineering 4-coumaroyl-CoA derived polyketide production in Yarrowia lipolytica through a β-oxidation mediated strategy[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 57: 174-181. |
| 200 | HE Q, SZCZEPAŃSKA P, YUZBASHEV T, et al. De novo production of resveratrol from glycerol by engineering different metabolic pathways in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Metabolic Engineering Communications, 2020, 11: e00146. |
| 201 | LV Y K, MARSAFARI M, KOFFAS M, et al. Optimizing oleaginous yeast cell factories for flavonoids and hydroxylated flavonoids biosynthesis[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(11): 2514-2523. |
| 202 | ZHOU S H, LYU Y B, LI H Z, et al. Fine-tuning the (2S)-naringenin synthetic pathway using an iterative high-throughput balancing strategy[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2019, 116(6): 1392-1404. |
| 203 | KALLSCHEUER N, VOGT M, STENZEL A, et al. Construction of a Corynebacterium glutamicum platform strain for the production of stilbenes and (2S)-flavanones[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 38: 47-55. |
| 204 | GAO S, LYU Y B, ZENG W Z, et al. Efficient biosynthesis of (2S)-naringenin from p-coumaric acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68(4): 1015-1021. |
| 205 | FOWLER Z L, GIKANDI W W, KOFFAS M A G. Increased malonyl coenzyme A biosynthesis by tuning the Escherichia coli metabolic network and its application to flavanone production[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75(18): 5831-5839. |
| 206 | AMOR I L B, HEHN A, GUEDONE E, et al. Biotransformation of naringenin to eriodictyol by Saccharomyces cerevisiea functionally expressing flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase[J]. Natural Product Communications, 2010, 5(12): 1893-1898. |
| 207 | CELIŃSKA E, KUBIAK P, BIAŁAS W, et al. Yarrowia lipolytica: the novel and promising 2-phenylethanol producer[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2013, 40(3/4): 389-392. |
| 208 | CELIŃSKA E, OLKOWICZ M, GRAJEK W. L-Phenylalanine catabolism and 2-phenylethanol synthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica—mapping molecular identities through whole-proteome quantitative mass spectrometry analysis[J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2015, 15(5): fov041. |
| 209 | GU Y, MA J B, ZHU Y L, et al. Refactoring ehrlich pathway for high-yield 2-phenylethanol production in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(3): 623-633. |
| 210 | GU Y, MA J B, ZHU Y L, et al. Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica as a chassis for de novo synthesis of five aromatic-derived natural products and chemicals[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(8): 2096-2106. |
| 211 | TONG Y J, ZHOU J W, ZHANG L, et al. A golden-gate based cloning toolkit to build violacein pathway libraries in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021, 10(1): 115-124. |
| 212 | WRÓBEL-KWIATKOWSKA M, TURSKI W, KOCKI T, et al. An efficient method for production of kynurenic acid by Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Yeast, 2020, 37(9/10): 541-547. |
| 213 | WRÓBEL-KWIATKOWSKA M, TURSKI W, JUSZCZYK P, et al. Improved production of kynurenic acid by Yarrowia lipolytica in media containing different honeys[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(22): 9424. |
| 214 | VAN DER HOEK S A, RUSNÁK M, JACOBSEN I H, et al. Engineering ergothioneine production in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. FEBS Letters, 2022, 596(10): 1356-1364. |
| 215 | PARK Y K, BORDES F, LETISSE F, et al. Engineering precursor pools for increasing production of odd-chain fatty acids in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Metabolic Engineering Communications, 2021, 12: e00158. |
| 216 | ZHANG B X, CHEN H Q, LI M, et al. Genetic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for enhanced production of trans-10, cis-12 conjugated linoleic acid[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2013, 12: 70. |
| 217 | IMATOUKENE N, BACK A, NONUS M, et al. Fermentation process for producing CFAs using Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2020, 47(4): 403-412. |
| 218 | BLITZBLAU H G, CONSIGLIO A L, TEIXEIRA P, et al. Production of 10-methyl branched fatty acids in yeast[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2021, 14(1): 12. |
| 219 | BEOPOULOS A, VERBEKE J, BORDES F, et al. Metabolic engineering for ricinoleic acid production in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(1): 251-262. |
| 220 | RABENHORST J, GATFIELD I. Method of producing γ-decalactone using Yarrowia lipolytica strain HR 145 (DSM 12397): US06451565B1[P]. 2002-09-17. . |
| 221 | KANG W R, SEO M J, AN J U, et al. Production of δ-decalactone from linoleic acid via 13-hydroxy-9(Z)-octadecenoic acid intermediate by one-pot reaction using linoleate 13-hydratase and whole Yarrowia lipolytica cells[J].Biotechnology Letters, 2016, 38(5): 817-823. |
| 222 | MARELLA E R, DAHLIN J, DAM M I, et al. A single-host fermentation process for the production of flavor lactones from non-hydroxylated fatty acids[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 61: 427-436. |
| 223 | LI J B, MA Y S, LIU N, et al. Synthesis of high-titer alka(e)nes in Yarrowia lipolytica is enabled by a discovered mechanism[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 6198. |
| 224 | YANG K X, QIAO Y G, LI F, et al. Subcellular engineering of lipase dependent pathways directed towards lipid related organelles for highly effectively compartmentalized biosynthesis of triacylglycerol derived products in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 55: 231-238. |
| [1] | YING Hanjie, LIU Dong, WANG Zhenyu, SHEN Tao, ZHUANG Wei, ZHU Chenjie. Exploring industrial biomanufacturing and the goal of “carbon neutrality” [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 1-7. |
| [2] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [3] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job, CHEN Xuemei, SHI Ting. Price to Cost-of-raw-materials Ratio (PC) of biomanufacturing: definition and application [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 8-17. |
| [8] | ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. The enlightenment of the Chinese philosophy “Tao-Fa-Shu-Qi” to industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1231-1241. |
| [9] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [10] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [11] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [12] | ZHAO Liang, LI Zhenshuai, FU Liping, LYU Ming, WANG Shi’an, ZHANG Quan, LIU Licheng, LI Fuli, LIU Ziyong. Progress in biomanufacturing of lipids and single cell protein from one-carbon compounds [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [13] | LIU Jianming, ZHANG Chijian, ZHANG Bing, ZENG Anping. Clostridium pasteurianum as an industrial chassis for efficient production of 1,3-propanediol: from metabolic engineering to fermentation and product separation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1386-1403. |
| [14] | CHENG Feng, ZOU Shuping, XU Jianmiao, TANG Heng, XUE Yaping, ZHENG Yuguo. BioHPP®: a benchmark of biomanufacturing for high optically pure L-phosphinothricin [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1404-1418. |
| [15] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||