Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (1): 29-43.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-063
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
The application of biological reverse engineering in synthetic biology
CHEN Xinmao, OUYANG Qi
- School of Physics, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
-
Received:2020-05-06Revised:2020-05-16Online:2020-07-07Published:2020-02-29 -
Contact:OUYANG Qi
生物逆向工程设计在合成生物学中的应用
陈欣懋, 欧阳颀
- 北京大学物理学院,北京 100871
-
通讯作者:欧阳颀 -
作者简介:陈欣懋(1994-),女,博士研究生,研究方向为定量系统生物学和合成生物学。E-mail: xmaochen@pku.edu.cn
欧阳颀(1955-),男,博士,教授,中国科学院院士,研究方向为定量系统生物学、生物网络动力学、生物系统中的非线性问题、生物微流体技术。E-mail: qi@pku.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(11774011)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CHEN Xinmao, OUYANG Qi. The application of biological reverse engineering in synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 29-43.
陈欣懋, 欧阳颀. 生物逆向工程设计在合成生物学中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(1): 29-43.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2020-063
| Time | SK | Cdc2 | Ste9 | Rum1 | Slp1 | Cdc2* | Wee1 | Cdc25 | PP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Tab. 1 Biological pathway of fission yeast cell cycle network [55]
| Time | SK | Cdc2 | Ste9 | Rum1 | Slp1 | Cdc2* | Wee1 | Cdc25 | PP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | IDEKER T, THORSSON V, RANISH J A, et al. Integrated genomic and proteomic analyses of a systematically perturbed metabolic network[J]. Science, 2001, 292(5518): 929-934. |
| 2 | BARABÁSI A, CRANDALL R E. Linked: the new science of networks[J]. American Journal of Physics, 2002, 71(4): 243-270. |
| 3 | WOLKENHAUER O. Systems biology: the reincarnation of systems theory applied in biology?[J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2001, 2(3): 258-270. |
| 4 | BORNHOLDT S. Less is more in modeling large genetic networks[J]. Science, 2005, 310(5747): 449-451. |
| 5 | FRIEDMAN N. Inferring cellular networks using probabilistic graphical models[J]. Science, 2004, 303(5659): 799-805. |
| 6 | SAEZ‐RODRIGUEZ J, ALEXOPOULOS L G, EPPERLEIN J, et al. Discrete logic modelling as a means to link protein signaling networks with functional analysis of mammalian signal transduction[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2009, 5(1): e331. |
| 7 | BASSO K, MARGOLIN A A, STOLOVITZKY G, et al. Reverse engineering of regulatory networks in human B cells[J]. Nature Genetics, 2005, 37(4): 382-390. |
| 8 | ZOPPOLI P, MORGANELLA S, CECCARELLI M. TimeDelay-ARACNE: reverse engineering of gene networks from time-course data by an information theoretic approach[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2010, 11(1): 154-169. |
| 9 | YEUNG M K S, TEGNÉR J, COLLINS J J. Reverse engineering gene networks using singular value decomposition and robust regression[J]. PNAS, 2002, 99(9): 6163-6168. |
| 10 | TEGNER J, YEUNG M K S, HASTY J, et al. Reverse engineering gene networks: integrating genetic perturbations with dynamical modeling[J]. PNAS, 2003, 100(10): 5944-5949. |
| 11 | BONGARD J, LIPSON H. Automated reverse engineering of nonlinear dynamical systems[J]. PNAS, 2007, 104(24): 9943-9948. |
| 12 | D’HAESELEER P, LIANG S, SOMOGYI R. Genetic network inference: from co-expression clustering to reverse engineering[J]. Bioinformatics, 2000, 16(8): 707-726. |
| 13 | GARDNER T S, FAITH J J. Reverse-engineering transcription control networks [J]. Physics of Life Reviews, 2005, 2(1): 65-88. |
| 14 | VILLAVERDE A F, BANGA J R. Reverse engineering and identification in systems biology: strategies, perspectives and challenges[J]. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2014, 11(91): 20130505. |
| 15 | SLUSARCZYK A L, LIN A, WEISS R. Foundations for the design and implementation of synthetic genetic circuits[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2012, 13(6): 406-420. |
| 16 | CANTON B, LABNO A, ENDY D. Refinement and standardization of synthetic biological parts and devices[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2008, 26(7): 787-793. |
| 17 | ENDY D. Foundations for engineering biology[J]. Nature, 2005, 438(7067): 449-453. |
| 18 | ELOWITZ M B, LEIBLER S. A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators[J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 335-338. |
| 19 | GARDNER T S, CANTOR C R, Collins J J. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 339-342. |
| 20 | BASHOR C J, HORWITZ A A, PEISAJOVICH S G, et al. Rewiring cells: synthetic biology as a tool to interrogate the organizational principles of living systems[J]. Annual Review of Biophysics, 2010, 39: 515-537. |
| 21 | MAYO A E, SETTY Y, SHAVIT S, et al. Plasticity of the cis-regulatory input function of a gene[J]. PLoS Biology, 2006, 4(4):555-561. |
| 22 | ANDERSON J C, VOIGT C A, ARKIN A P. Environmental signal integration by a modular AND gate[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2007, 3(1): e133. |
| 23 | TAMSIR A, TABOR J J, VOIGT C A. Robust multicellular computing using genetically encoded NOR gates and chemical ‘wires’[J]. Nature, 2011, 469(7329): 212-215. |
| 24 | MOON T S, LOU C, TAMSIR A, et al. Genetic programs constructed from layered logic gates in single cells[J]. Nature, 2012, 491(7423): 249-253. |
| 25 | LOU C, LIU X, NI M, et al. Synthesizing a novel genetic sequential logic circuit: a push‐on push‐off switch[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2010, 6(1): e350. |
| 26 | WANG B, KITNEY R I, JOLY N, et al. Engineering modular and orthogonal genetic logic gates for robust digital-like synthetic biology[J]. Nature Communications, 2011, 2(1): 1-9. |
| 27 | BALAGADDÉ F K, SONG H, OZAKI J, et al. A synthetic Escherichia coli predator-prey ecosystem[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2008, 4(1): e187. |
| 28 | MARTIN V J J, PITERA D J, WITHERS S T, et al. Engineering a mevalonate pathway in Escherichia coli for production of terpenoids[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2003, 21(7): 796-802. |
| 29 | RO D K, PARADISE E M, OUELLET M, et al. Production of the antimalarial drug precursor artemisinic acid in engineered yeast[J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7086): 940-943. |
| 30 | ZHANG H, LIN M, SHI H, et al. Programming a Pavlovian-like conditioning circuit in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 1-10. |
| 31 | MATSUURA S, ONO H, KAWASAKI S, et al. Synthetic RNA-based logic computation in mammalian cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-8. |
| 32 | LIU W, CREMER J, LI D, et al. An evolutionarily stable strategy to colonize spatially extended habitats[J]. Nature, 2019, 575(7784): 664-668. |
| 33 | BASHOR C J, PATEL N, CHOUBEY S, et al. Complex signal processing in synthetic gene circuits using cooperative regulatory assemblies[J]. Science, 2019, 364(6440): 593-597. |
| 34 | SHAO Y, LU N, WU Z, et al. Creating a functional single-chromosome yeast[J]. Nature, 2018, 560(7718): 331-335. |
| 35 | MCKAY M D, BECKMAN R J, Conover W J. A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code[J]. Technometrics, 2000, 42(1): 55-61. |
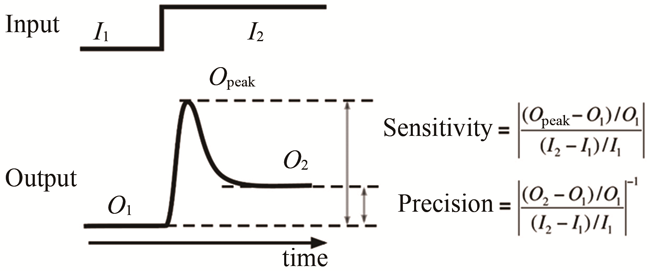
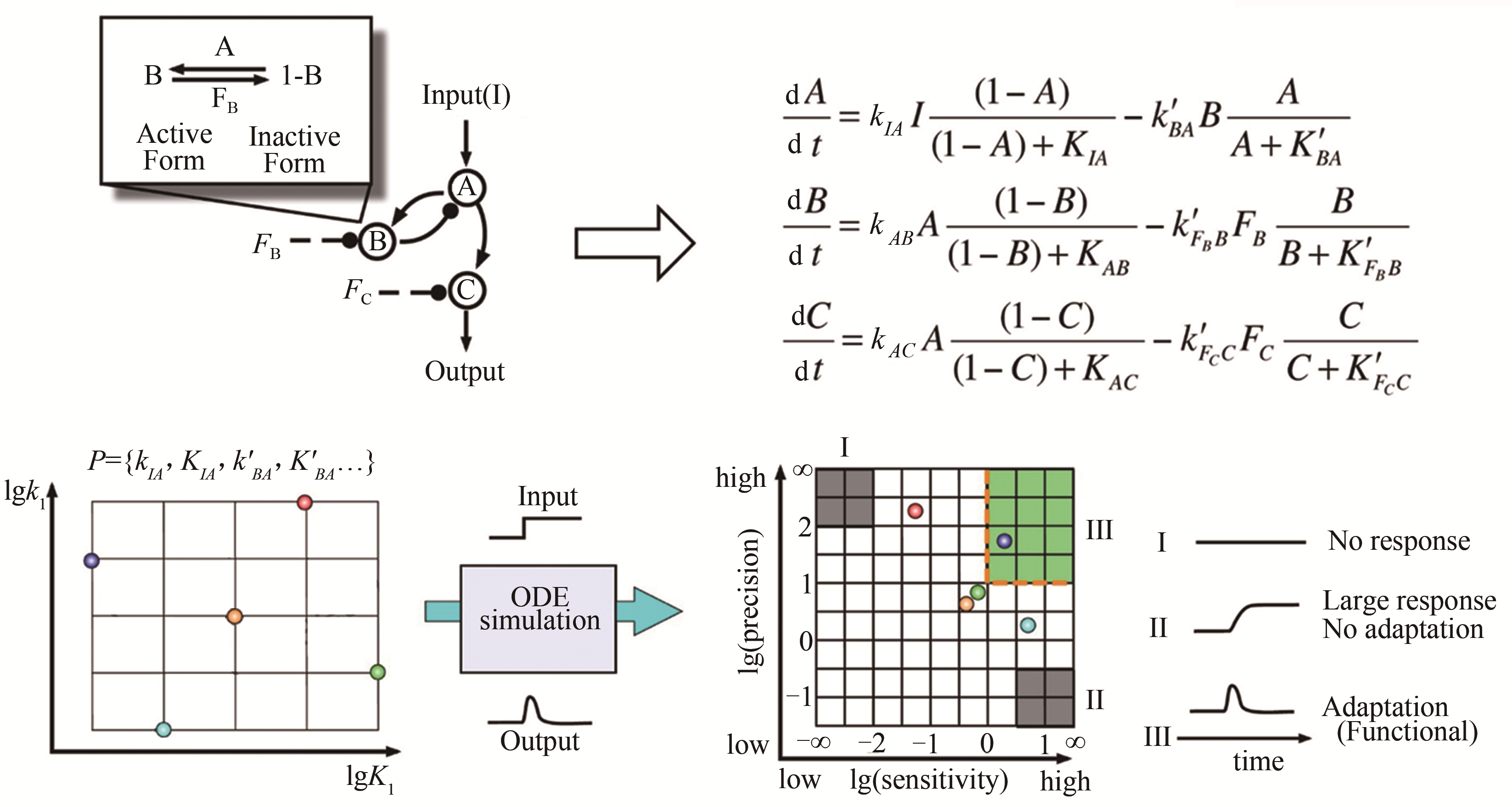
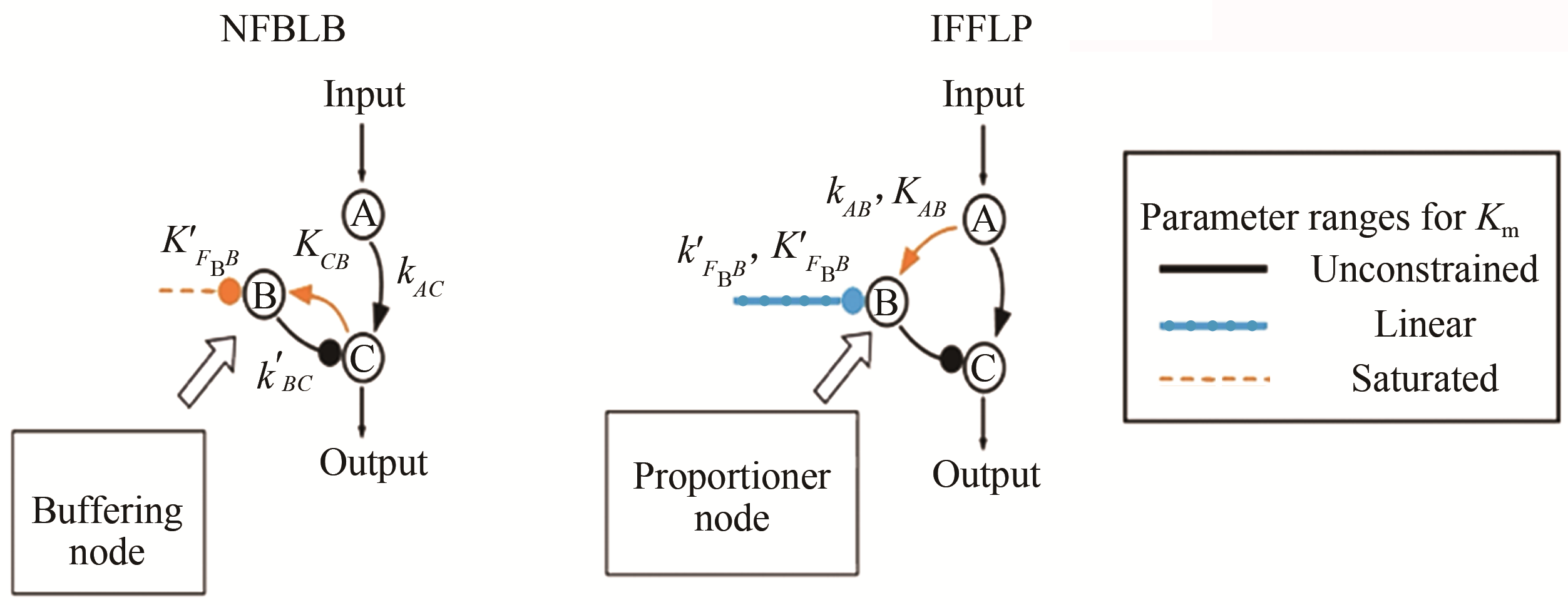
| 36 | MA W, TRUSINA A, El-SAMAD H, et al. Defining network topologies that can achieve biochemical adaptation[J]. Cell, 2009, 138(4): 760-773. |
| 37 | MA W, LAI L, OUYANG Q, et al. Robustness and modular design of the Drosophila segment polarity network[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2006, 2(1): e70. |
| 38 | YAN L, OUYANG Q, WANG H. Dose-response aligned circuits in signaling systems[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(4): e34727. |
| 39 | CHAU A H, WALTER J M, GERARDIN J, et al. Designing synthetic regulatory networks capable of self-organizing cell polarization[J]. Cell, 2012, 151(2): 320-332. |
| 40 | ZHENG M M, SHAO B, OUYANG Q. Identifying network topologies that can generate turing pattern[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2016, 408: 88-96. |
| 41 | WU L, OUYANG Q, WANG H. Robust network topologies for generating oscillations with temperature-independent periods[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(2): e0171263. |
| 42 | GERARDIN J, REDDY N R, LIM W A. The design principles of biochemical timers: circuits that discriminate between transient and sustained stimulation[J]. Cell Systems, 2019, 9(3): 297-308. |
| 43 | GUET C C, ELOWITZ M B, HSING W, et al. Combinatorial synthesis of genetic networks[J]. Science, 2002, 296(5572): 1466-1470. |
| 44 | MANGAN S, ALON U. Structure and function of the feed-forward loop network motif[J]. PNAS, 2003, 100(21): 11980-11985. |
| 45 | WHITAKER W R, DAVIS S A, ARKIN A P, et al. Engineering robust control of two-component system phosphotransfer using modular scaffolds[J]. PNAS, 2012, 109(4): 18090-18095. |
| 46 | 习静怡. 生物网络逆向工程的子网络合并法以及生物系统中的量子热力学[D]. 北京:北京大学, 2017. |
| XI J Y. Sub-network combination in biological network reverse engineering and quantum thermodynamics in biological systems[D]. Beijing: Peking University, 2017. | |
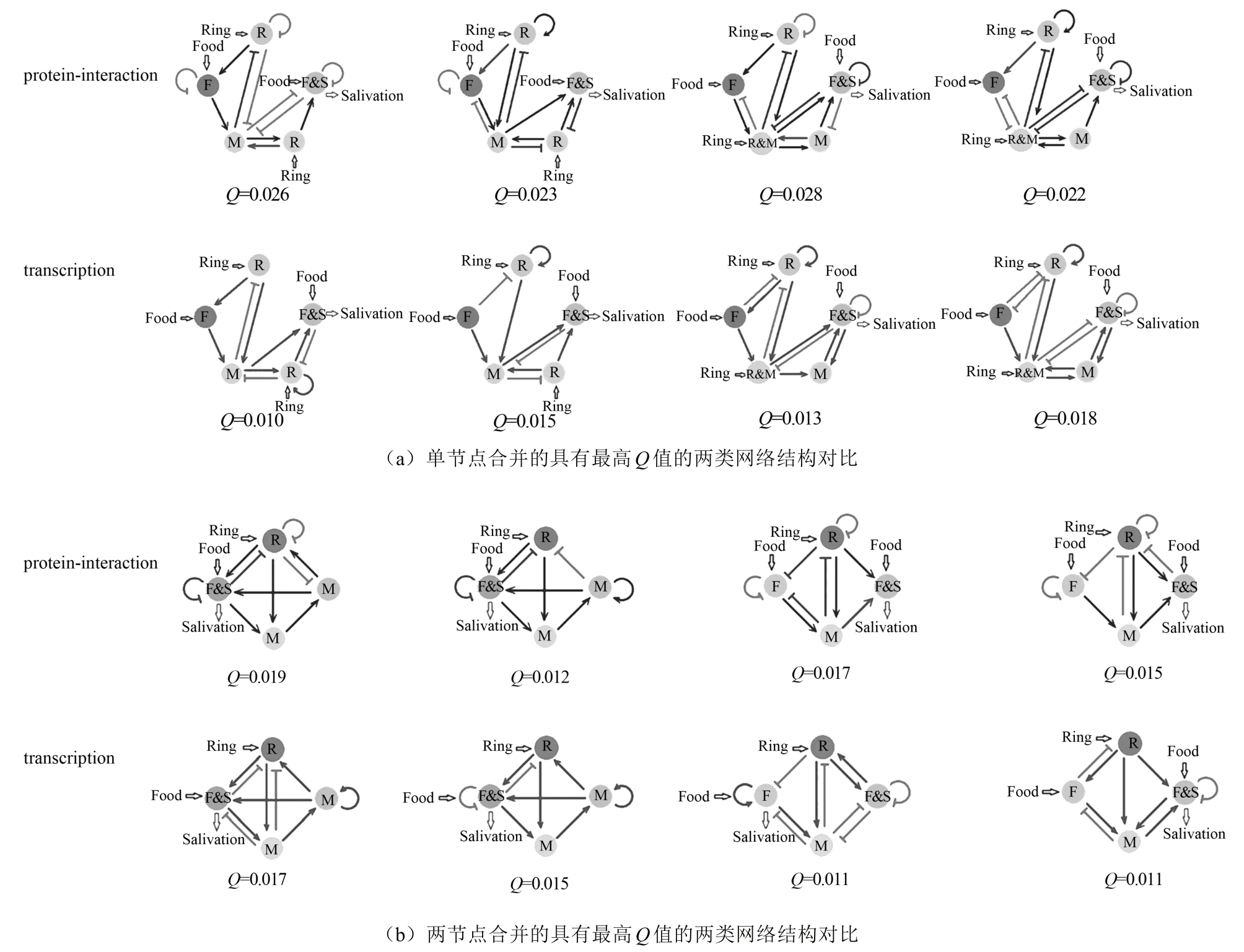
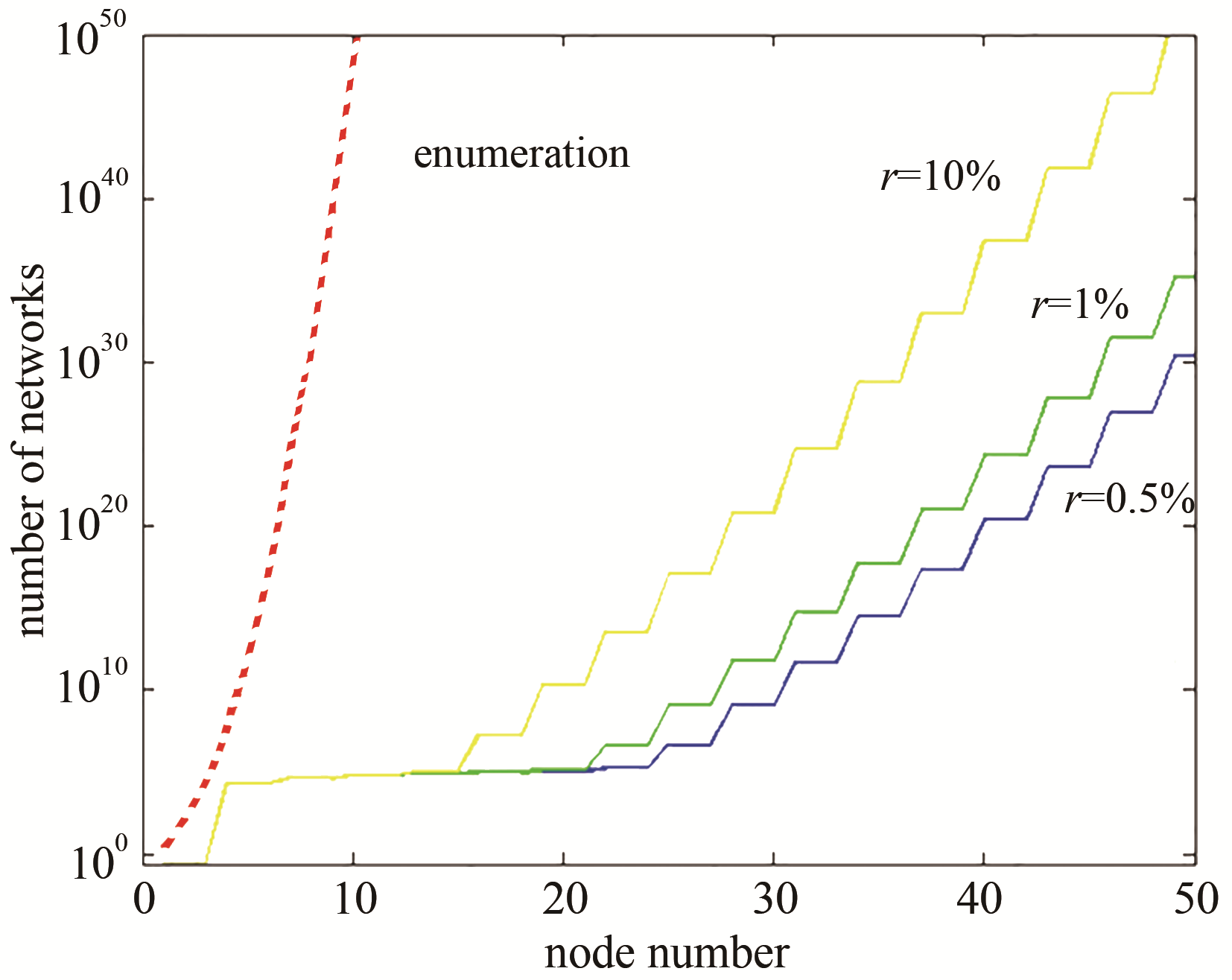
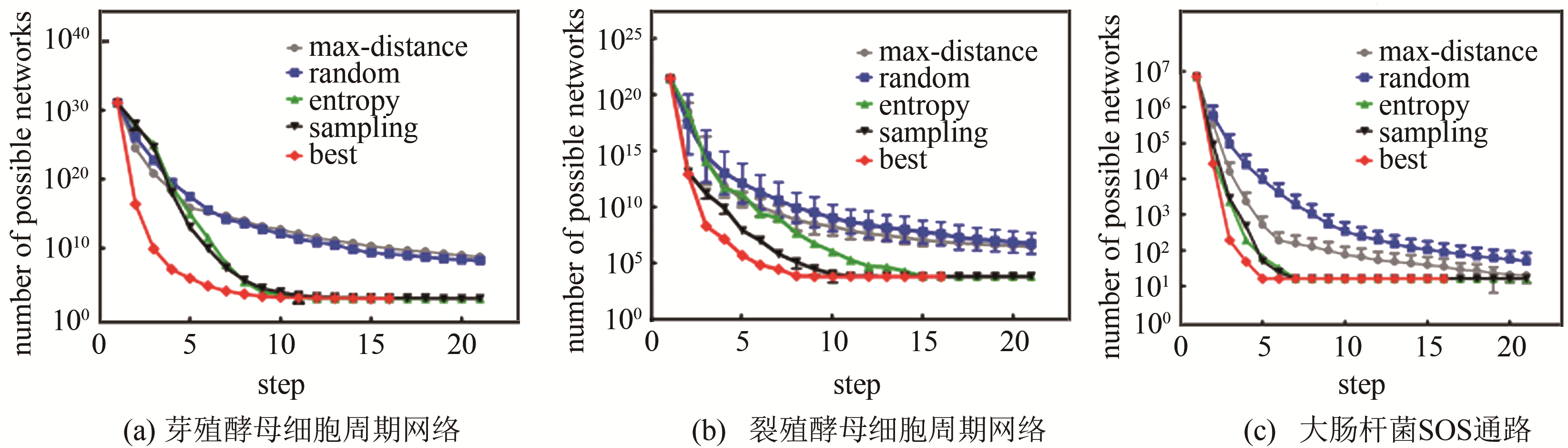
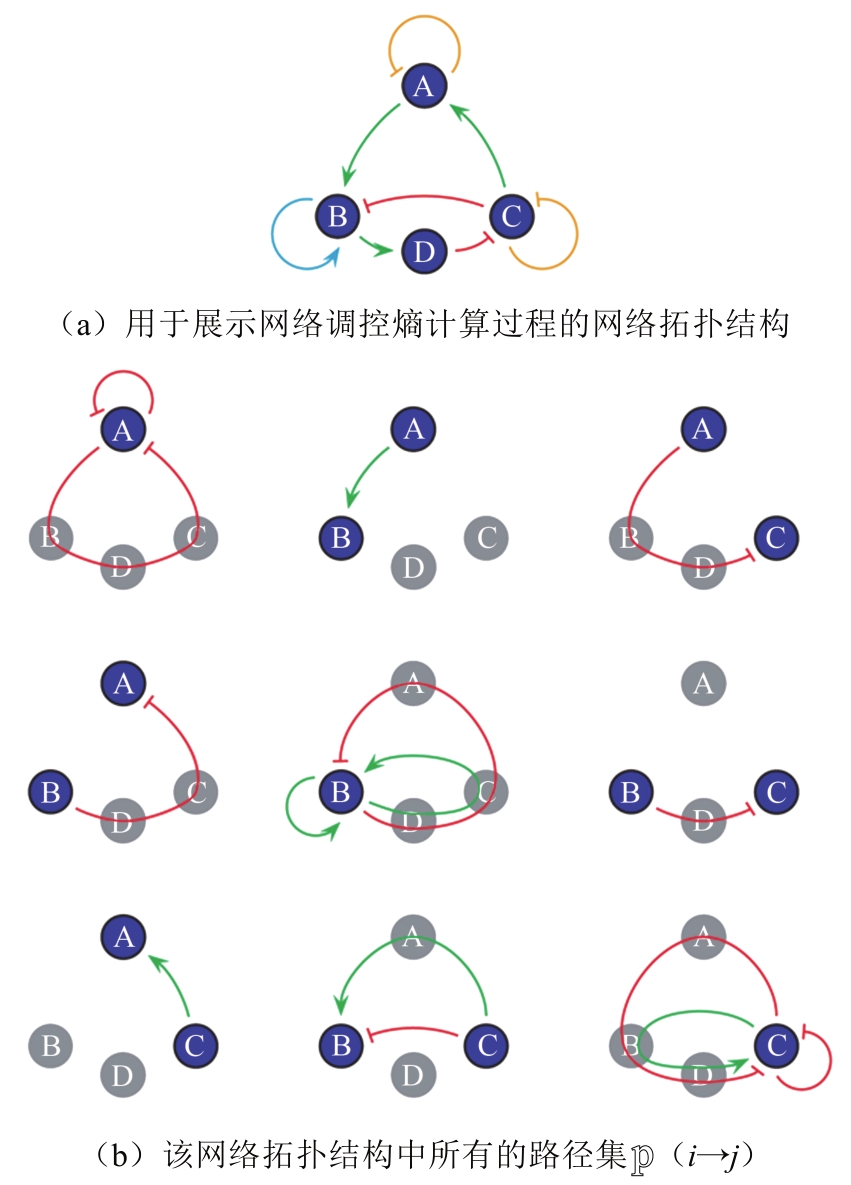
| 47 | XI J Y, OUYANG Q. Using sub-network combinations to scale up an enumeration method for determining the network structures of biological functions[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(12): e0168214. |
| 48 | WU L, WANG H, OUYANG Q. Constructing network topologies for multiple signal-encoding functions[J]. BMC Systems Biology, 2019, 13(1): 6. |
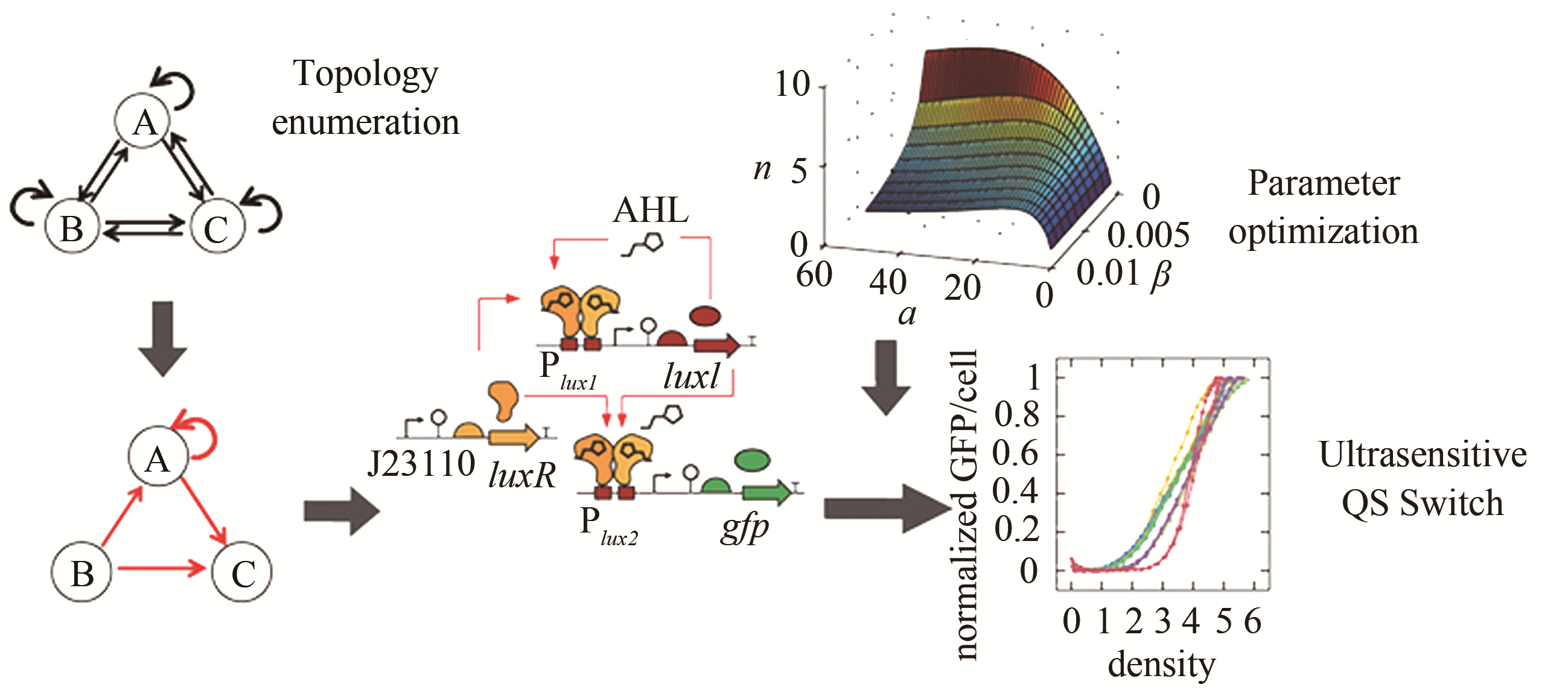
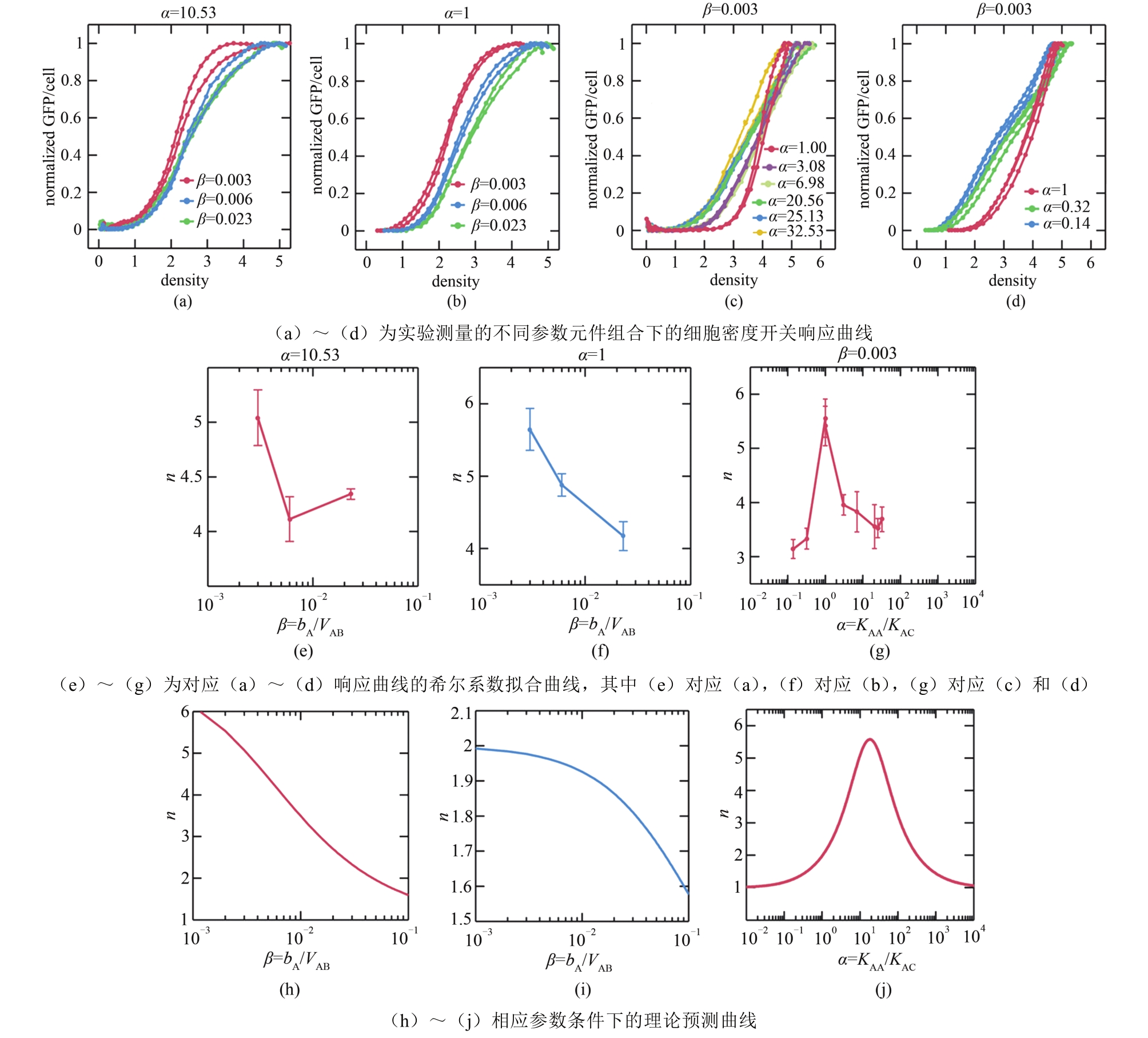
| 49 | ZENG W, DU P, LOU Q, et al. Rational design of an ultrasensitive quorum-sensing switch[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(8): 1445-1452. |
| 50 | 曾维倩.基于逆向工程的超敏细胞密度开关的理性设计[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 2017. |
| ZENG W Q. Rational design of an ultrasensitive cell density switch based on reverse engineering[D]. Beijing: Peking University, 2017. | |
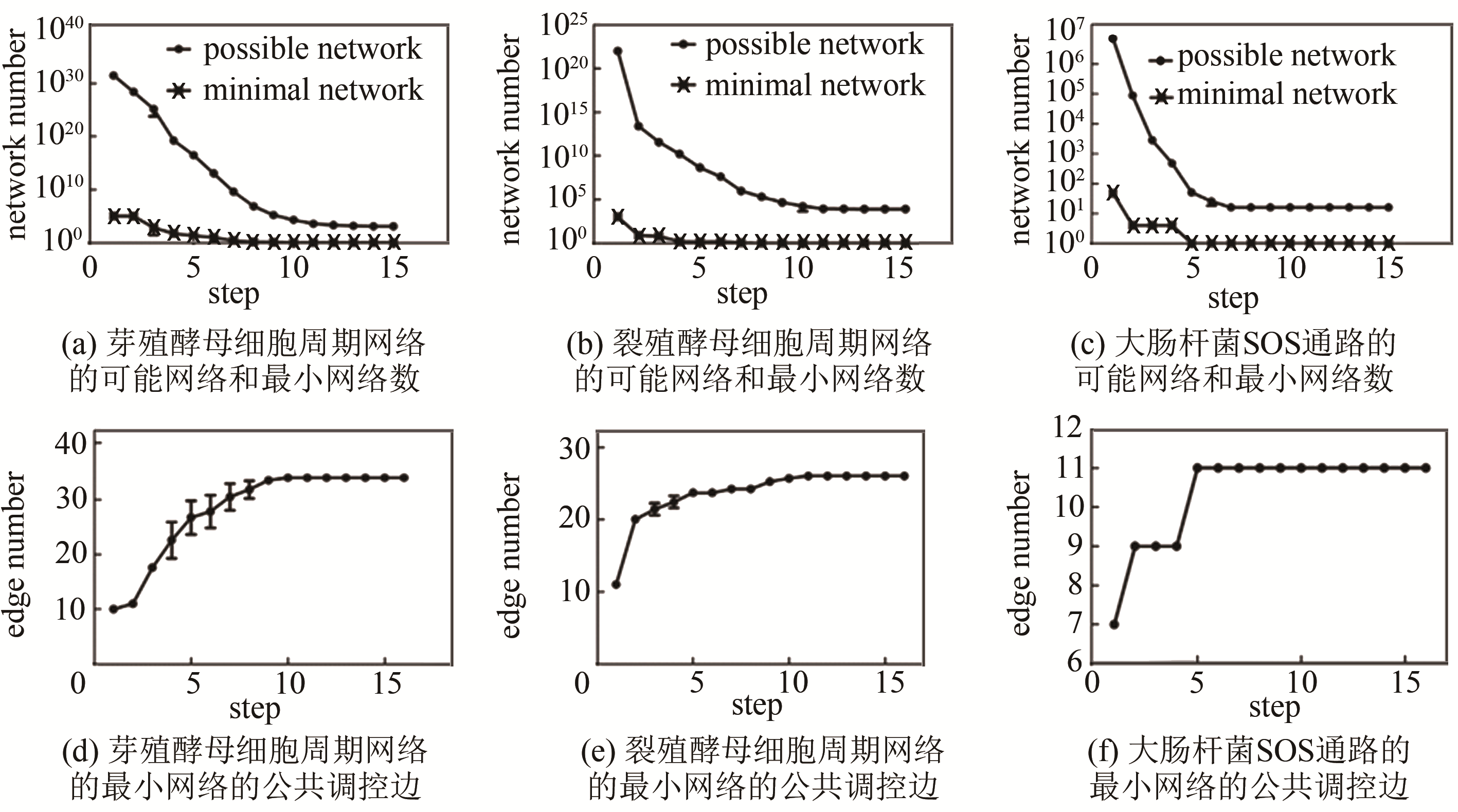
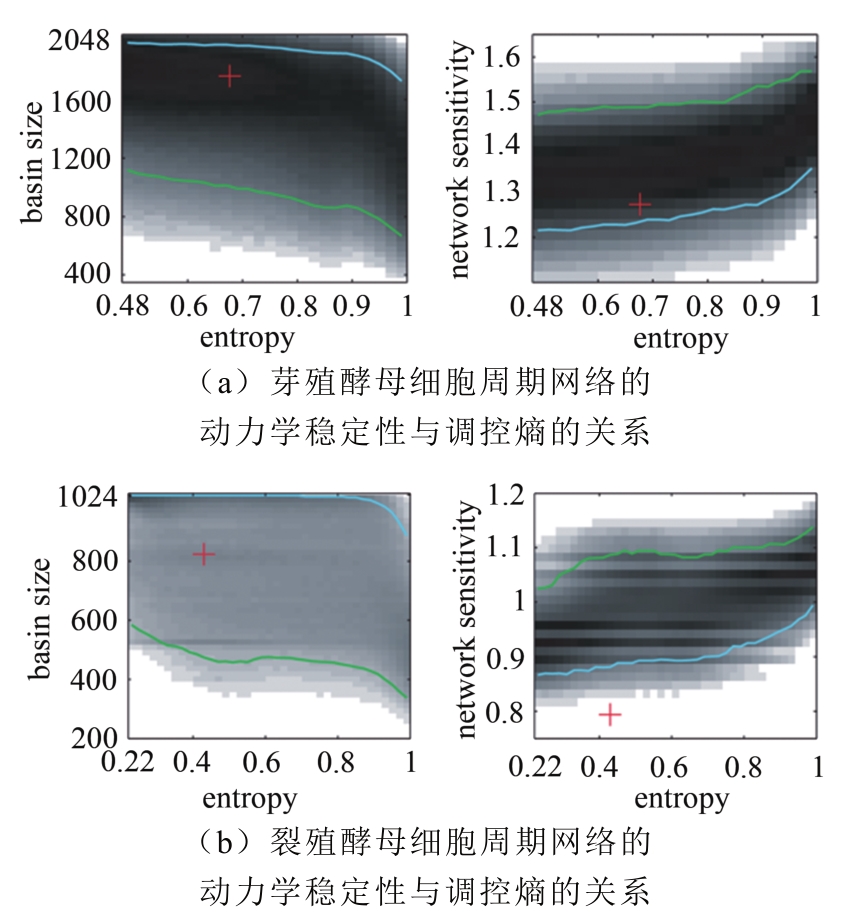
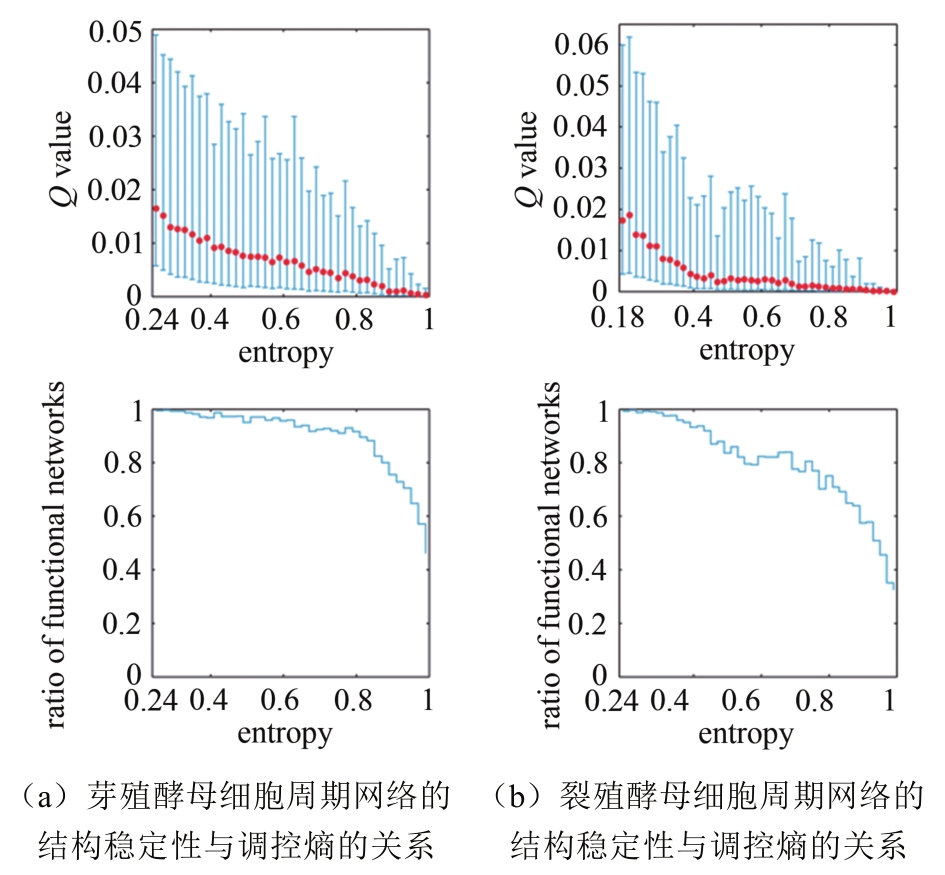
| 51 | LI F, LONG T, LU Y, et al. The yeast cell-cycle network is robustly designed[J]. PNAS, 2004, 101(14): 4781-4786. |
| 52 | WANG G, DU C, CHEN H, et al. Process-based network decomposition reveals backbone motif structure[J]. PNAS, 2010, 107(23): 10478-10483. |
| 53 | 张晓萌.布尔网络动力学研究及其反向工程[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 2011. |
| ZHANG X M. Dynamics and reverse engineering of Boolean network[D]. Beijing: Peking University, 2011. | |
| 54 | ZHANG X, SHAO B, WU Y, et al. A reverse engineering approach to optimize experiments for the construction of biological regulatory networks[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(9): e75931. |
| 55 | SHAO B, WU J, TIAN B, et al. Minimum network constraint on reverse engineering to develop biological regulatory networks[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2015, 380: 9-15. |
| 56 | WU Y, ZHANG X, YU J, et al. Identification of a topological characteristic responsible for the biological robustness of regulatory networks[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2009, 5(7): e1000442. |
| 57 | 邵斌.生物网络逆向工程及其应用[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 2016. |
| SHAO B. Biological network reverse engineering and its applications[D]. Beijing: Peking University, 2016. | |
| 58 | SHAO B, LIU X, ZHANG D, et al. From Boolean network model to continuous model helps in design of functional circuits[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(6):e0128630. |
| 59 | 张浩千.细菌转录调控线路的精准制造[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 2016. |
| ZHANG H Q. High-precision manufacturing of transcriptional regulatory circuits in bacteria [D]. Beijing: Peking University, 2016. | |
| 60 | ZONG Y Q, ZHANG H M, LYU C, et al. Insulated transcriptional elements enable precise design of genetic circuits[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 1-13. |
| [1] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [12] | CAI Bingyu, TAN Xiangtian, LI Wei. Advances in synthetic biology for engineering stem cell [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [13] | XIE Huang, ZHENG Yilei, SU Yiting, RUAN Jingyi, LI Yongquan. An overview on reconstructing the biosynthetic system of actinomycetes for polyketides production [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [14] | ZHA Wenlong, BU Lan, ZI Jiachen. Advances in synthetic biology for producing potent pharmaceutical ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| [15] | HUI Zhen, TANG Xiaoyu. Applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 editing system in the study of microbial natural products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||