合成生物学 ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (2): 158-173.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-017
甲醇生物转化的机遇与挑战
高教琪1,2, 周雍进1,2
- 1.中国科学院大连化学物理研究所生物技术研究部,辽宁 大连 116023
2.大连市能源生物技术重点实验室,辽宁 大连 116023
-
收稿日期:2020-03-05修回日期:2020-03-23出版日期:2020-04-30发布日期:2020-08-04 -
作者简介:高教琪(1989—),男,博士,助理研究员,主要从事多形汉逊酵母甲醇生物转化及产物合成研究。E-mail:jqgao@dicp.ac.cn
周雍进(1984—),男,博士,研究员,主要从事基于合成生物学工具开发的甲醇生物转化与天然产物合成研究。E-mail:zhouyongjin@dicp.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金青年项目(21808216);国家自然科学基金优秀青年基金项目(21922812);中国科学院大连化学物理研究所BioChE-X项目(BioChE-X201801)
Advances in methanol bio-transformation
GAO Jiaoqi1,2, ZHOU Yongjin1,2
- 1.Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian 116023, Liaoning, China
2.Dalian Key Laboratory of Energy Biotechnology, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, CAS, Dalian 116023, Liaoning, China
-
Received:2020-03-05Revised:2020-03-23Online:2020-04-30Published:2020-08-04
摘要:
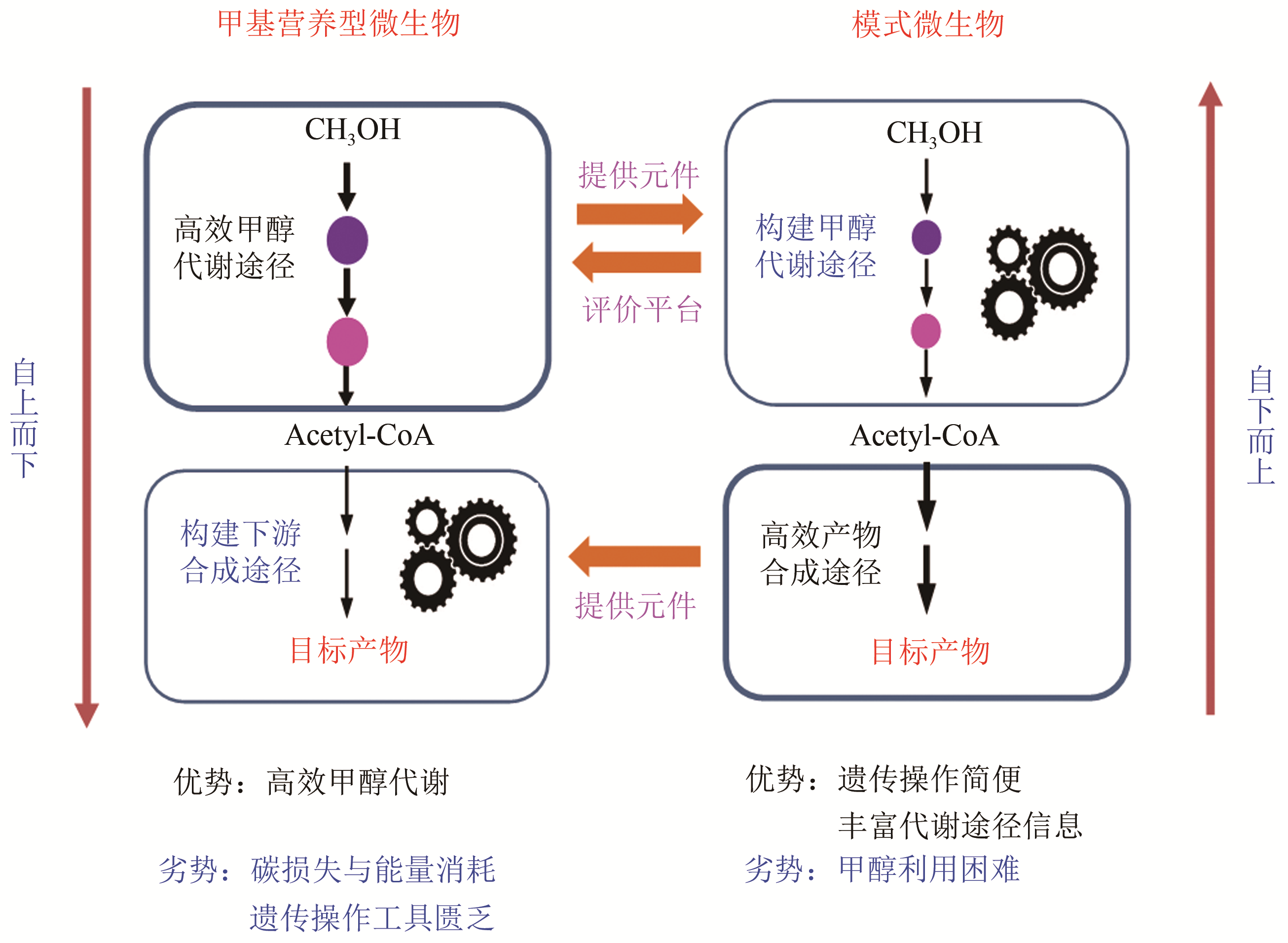
甲醇以其易储存和易运输等特性,成为极具应用潜力的原料。除了传统的基于合成气(CO,H2,CO2)和化学催化的甲醇合成,甲烷氧化(化学法和生物法)和CO2加氢技术逐步成熟,特别是CO2加氢技术将有望实现甲醇可持续洁净合成。甲醇生物转化有望进一步拓展现有甲醇转化路线,推动我国煤炭资源洁净利用以及CO2利用。本文详细综述了国内外甲醇生物炼制研究进展:①以甲基营养型微生物,包括细菌和甲醇酵母,为宿主构建细胞工厂实现氨基酸以及平台化合物等合成;②在模式微生物中构建甲醇代谢途径实现甲醇利用与转化。通过天然/人工甲基营养型代谢途径相互借鉴,采用代谢工程与合成生物学策略,提高甲醇利用效率、底物与产物耐受能力,将推动甲醇生物转化、拓展生物炼制原料供应路线。
中图分类号:
引用本文
高教琪, 周雍进. 甲醇生物转化的机遇与挑战[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(2): 158-173.
GAO Jiaoqi, ZHOU Yongjin. Advances in methanol bio-transformation[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(2): 158-173.
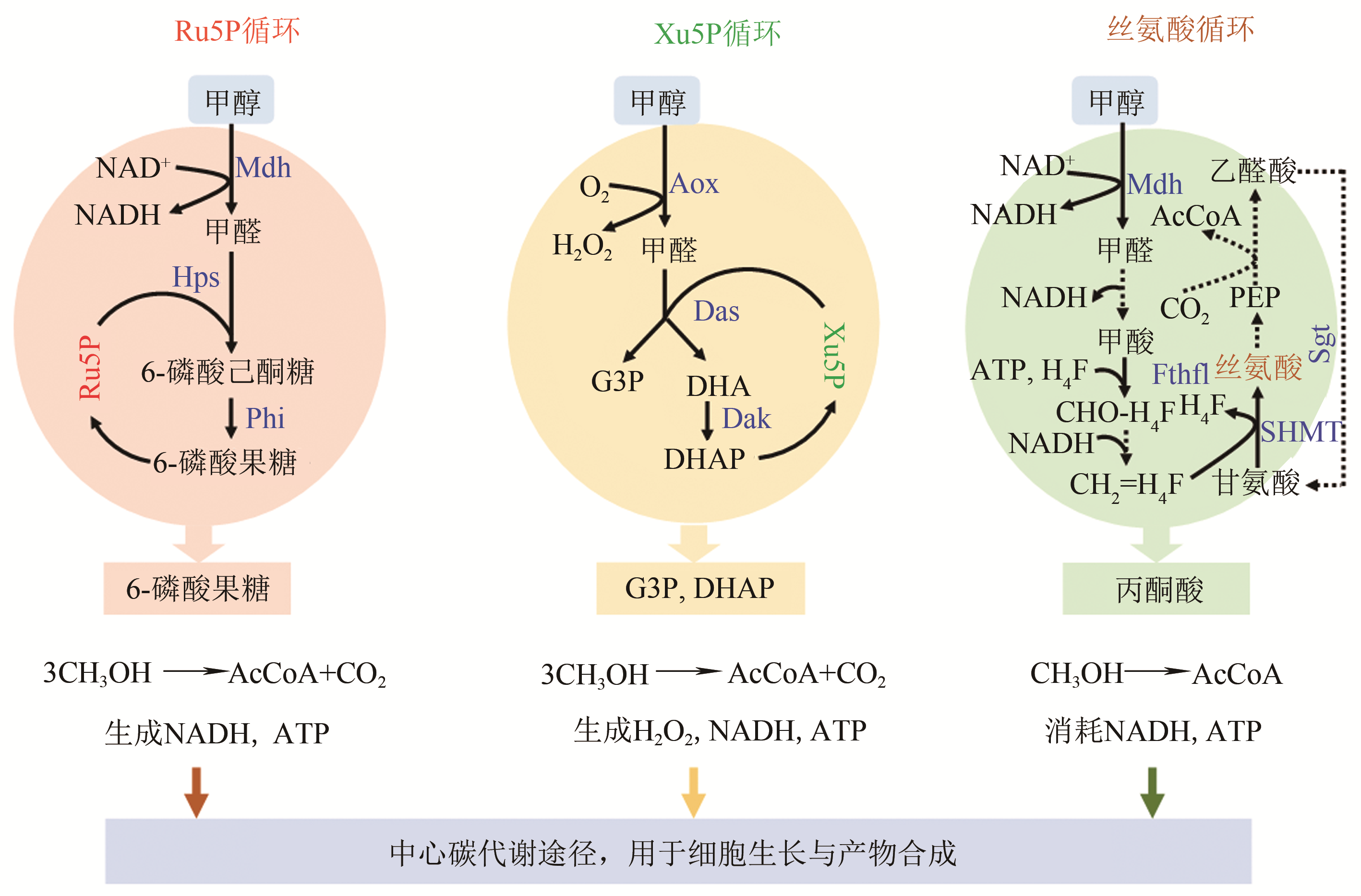
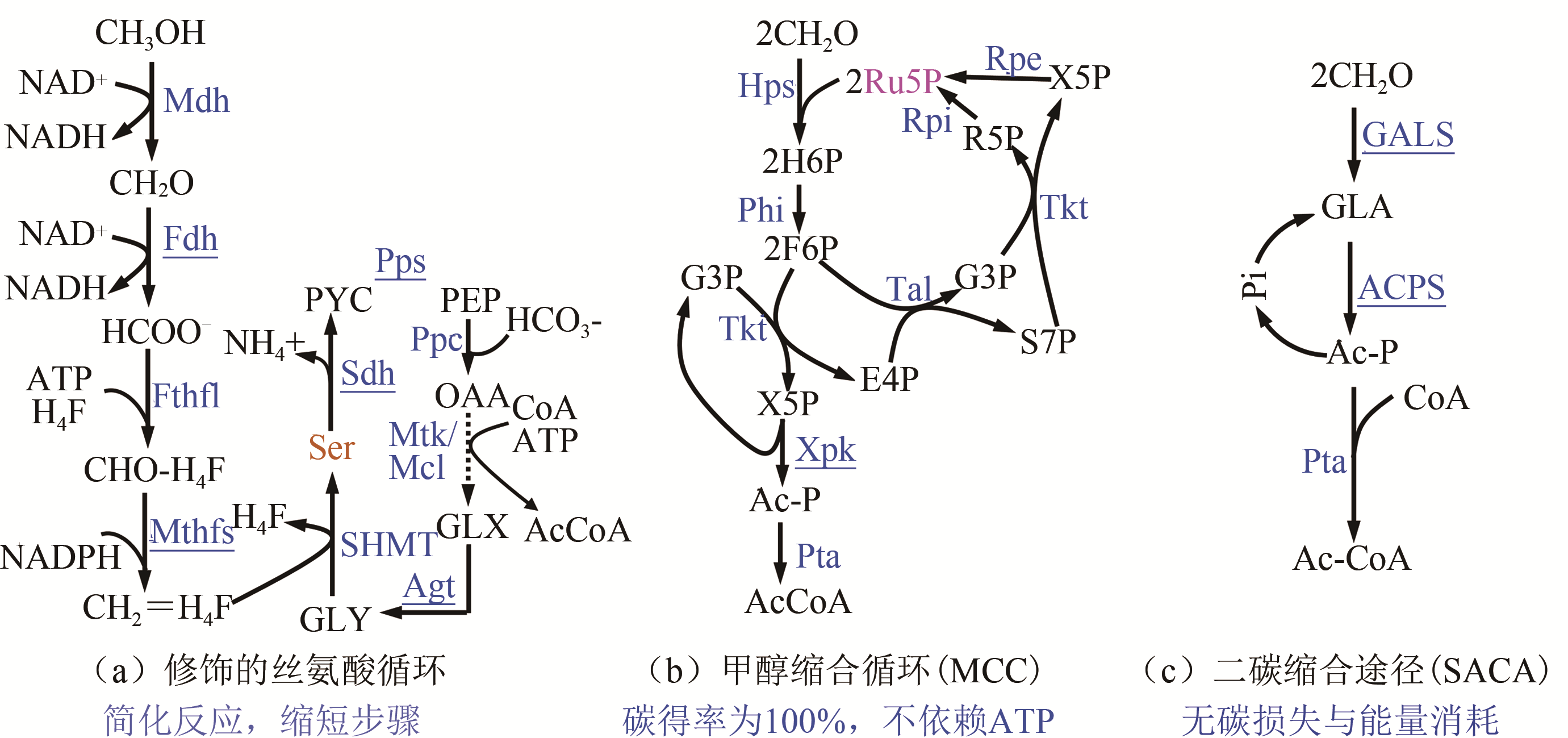
图2 天然甲醇代谢途径(Ru5P, 核酮糖-5-磷酸;Xu5P, 木酮糖-5-磷酸;G3P, 3-磷酸甘油醛;DHA, 二羟丙酮;DHAP, 磷酸二羟丙酮;PEP, 磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸;AcCoA, 乙酰辅酶A;Mdh, 甲醇脱氢酶;Hps, 3-乙酮糖-6-磷酸合成酶;Phi, 6-磷酸-3-己酮糖异构酶;Aox, 醇氧化酶;Das, 二羟丙酮合酶;Dak, 二羟丙酮激酶;Fthfl, 甲酸THF连接酶;SHMT, 丝氨酸羟甲基转移酶;Sgt, 丝氨酸-乙醛酸转氨酶)
Fig. 2 Native metabolic pathways for methanol assimilation
| 宿主 | 培养基 | 产物 | 产量 | 备注 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲醇芽孢杆菌 | 甲醇,酵母粉, 基础盐培养基 | L-谷氨酸 | 69.0g/L | 批式补料 | [ |
| 甲醇芽孢杆菌 | 甲醇,酵母粉, 基础盐培养基 | L-赖氨酸 | 11.0g/L | 批式补料 | [ |
| 甲醇芽孢杆菌 | 甲醇,酵母粉, 基础盐培养基 | γ-氨基丁酸 | 9.0g/L | 批式补料 | [ |
| 甲醇芽孢杆菌 | 甲醇,酵母粉, 基础盐培养基 | 尸胺 | 10.2g/L | 批式补料 | [ |
| 扭脱甲基杆菌 | 甲醇, 基础盐培养基 | 甲羟戊酸 | 2.3g/L | ALE &批式补料 | [ |
| 扭脱甲基杆菌 | 甲醇,琥珀酸, 基础盐培养基 | 3-羟基丙酸 | 91.0mg/L | 摇瓶 | [ |
| 扭脱甲基杆菌 | 甲醇, 基础盐培养基 | 2-羟基丁酸 | 2.1g/L | 批式补料 | [ |
| 扭脱甲基杆菌 | 甲醇, 基础盐培养基 | 1-丁醇 | 25.5mg/L | ALE & 摇瓶 | [ |
| 扭脱甲基杆菌 | 甲醇, 基础盐培养基 | α-葎草烯 | 1.7g/L | 摇瓶 两相发酵 | [ |
| 巴斯德毕赤酵母 | 甲醇, 基础盐培养基 | 莫那克林J、洛伐他汀 | 60.0mg/L 14.4mg/L | 摇瓶 | [ |
| 巴斯德毕赤酵母 | 甲醇, YPD培养基 | D-乳酸 | 3.5g/L | 试管 | [ |
| 多形汉逊酵母 | 甲醇 基础盐培养基 | 谷胱甘肽 | 约1.3g/L | 批式补料 | [ |
表1 天然甲基营养型细胞工厂构建
Tab. 1 Construction of cell factories in native methylotrophs
| 宿主 | 培养基 | 产物 | 产量 | 备注 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲醇芽孢杆菌 | 甲醇,酵母粉, 基础盐培养基 | L-谷氨酸 | 69.0g/L | 批式补料 | [ |
| 甲醇芽孢杆菌 | 甲醇,酵母粉, 基础盐培养基 | L-赖氨酸 | 11.0g/L | 批式补料 | [ |
| 甲醇芽孢杆菌 | 甲醇,酵母粉, 基础盐培养基 | γ-氨基丁酸 | 9.0g/L | 批式补料 | [ |
| 甲醇芽孢杆菌 | 甲醇,酵母粉, 基础盐培养基 | 尸胺 | 10.2g/L | 批式补料 | [ |
| 扭脱甲基杆菌 | 甲醇, 基础盐培养基 | 甲羟戊酸 | 2.3g/L | ALE &批式补料 | [ |
| 扭脱甲基杆菌 | 甲醇,琥珀酸, 基础盐培养基 | 3-羟基丙酸 | 91.0mg/L | 摇瓶 | [ |
| 扭脱甲基杆菌 | 甲醇, 基础盐培养基 | 2-羟基丁酸 | 2.1g/L | 批式补料 | [ |
| 扭脱甲基杆菌 | 甲醇, 基础盐培养基 | 1-丁醇 | 25.5mg/L | ALE & 摇瓶 | [ |
| 扭脱甲基杆菌 | 甲醇, 基础盐培养基 | α-葎草烯 | 1.7g/L | 摇瓶 两相发酵 | [ |
| 巴斯德毕赤酵母 | 甲醇, 基础盐培养基 | 莫那克林J、洛伐他汀 | 60.0mg/L 14.4mg/L | 摇瓶 | [ |
| 巴斯德毕赤酵母 | 甲醇, YPD培养基 | D-乳酸 | 3.5g/L | 试管 | [ |
| 多形汉逊酵母 | 甲醇 基础盐培养基 | 谷胱甘肽 | 约1.3g/L | 批式补料 | [ |
| 宿主 | 途径 | 基因 | 培养基 | 表征 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大肠杆菌 | RuMP | BmMdh2, BmHps, BmPhi | 13C甲醇+核糖 | 40%标记C进入中心碳代谢 | [ |
| RuMP | BmMdh2, MlHps, MlPhi | 13C甲醇+葡糖酸盐 | 24%甲醇进入中心代谢物,甲醇代谢速率加快 | [ | |
| RuMP | BsMdh, BmHps, BmPhi | 1g/L酵母粉+甲醇 | 1g甲醇转化生物量0.29g(DCW),39% 甲醇C进入TCA循环,实现柚皮素合成 | [ | |
| RuMP | BmMdh, BmHps, BmPhi | 葡萄糖,酵母粉,甲醇 | 琥珀酸得率提高7.7%,甲醇消耗 0.38~0.45 g/L | [ | |
| 丝氨酸 | Mdh, Fdh, Fthfl, Mthfs, Mtk/Mcl, Agx1, SdaA, GlyA | 13C甲醇+木糖 | 25%丙酮酸标记,甲醇消耗0.70mmol/(L·h·OD) | [ | |
| SACA | BsMDH, GALS, ACPS, PTA | LB+甲醇 | 甲醇转化生物量0.03gDCW/g甲醇 | [ | |
| MCC | BmMDH, McHps, MlPhi, BaFpk, BsPta | — | 13C标记证明循环发挥功能,无细胞体系合成乙醇和丁醇 | [ | |
| 谷氨酸棒状杆菌 | RuMP | BmMdh, BshxlA, BshxlB | 甲醇+核糖 | 比生长速率0.18h-1,13C标记 | [ |
| RuMP | BsMdh, BmHps, BmPhi | 甲醇+木糖 | 比生长速率0.03h-1,63%标记13C进入代谢 | [ | |
| 酿酒酵母 | XuMP | Aox, Cat, Das, Dak | 甲醇+酵母粉 | 生物量增长12%,甲醇消耗2.4 g/L | [ |
表2 人工构建甲基营养型酵母
Tab. 2 Construction of artificial methylotrophs
| 宿主 | 途径 | 基因 | 培养基 | 表征 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大肠杆菌 | RuMP | BmMdh2, BmHps, BmPhi | 13C甲醇+核糖 | 40%标记C进入中心碳代谢 | [ |
| RuMP | BmMdh2, MlHps, MlPhi | 13C甲醇+葡糖酸盐 | 24%甲醇进入中心代谢物,甲醇代谢速率加快 | [ | |
| RuMP | BsMdh, BmHps, BmPhi | 1g/L酵母粉+甲醇 | 1g甲醇转化生物量0.29g(DCW),39% 甲醇C进入TCA循环,实现柚皮素合成 | [ | |
| RuMP | BmMdh, BmHps, BmPhi | 葡萄糖,酵母粉,甲醇 | 琥珀酸得率提高7.7%,甲醇消耗 0.38~0.45 g/L | [ | |
| 丝氨酸 | Mdh, Fdh, Fthfl, Mthfs, Mtk/Mcl, Agx1, SdaA, GlyA | 13C甲醇+木糖 | 25%丙酮酸标记,甲醇消耗0.70mmol/(L·h·OD) | [ | |
| SACA | BsMDH, GALS, ACPS, PTA | LB+甲醇 | 甲醇转化生物量0.03gDCW/g甲醇 | [ | |
| MCC | BmMDH, McHps, MlPhi, BaFpk, BsPta | — | 13C标记证明循环发挥功能,无细胞体系合成乙醇和丁醇 | [ | |
| 谷氨酸棒状杆菌 | RuMP | BmMdh, BshxlA, BshxlB | 甲醇+核糖 | 比生长速率0.18h-1,13C标记 | [ |
| RuMP | BsMdh, BmHps, BmPhi | 甲醇+木糖 | 比生长速率0.03h-1,63%标记13C进入代谢 | [ | |
| 酿酒酵母 | XuMP | Aox, Cat, Das, Dak | 甲醇+酵母粉 | 生物量增长12%,甲醇消耗2.4 g/L | [ |
| 1 | DALENA F, SENATORE A, BASILE M, et al. Advances in methanol production and utilization, with particular emphasis toward hydrogen generation via membrane reactor technology[J]. Membranes, 2018, 8(4): 98. |
| 2 | OLAH G A. Beyond oil and gas: the methanol economy[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2005, 44(18): 2636-2639. |
| 3 | TIAN P, WEI Y, YE M, et al. Methanol to olefins (MTO): from fundamentals to commercialization[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(3): 1922-1938. |
| 4 | ZENG A P. New bioproduction systems for chemicals and fuels: needs and new development[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37: 11. |
| 5 | PFEIFENSCHNEIDER J, BRAUTASET T, WENDISCH V F. Methanol as carbon substrate in the bio‐economy: metabolic engineering of aerobic methylotrophic bacteria for production of value‐added chemicals[J]. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 2017, 11(4): 719-731. |
| 6 | BOZZANO G, MANENTI F. Efficient methanol synthesis: Perspectives, technologies and optimization strategies[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2016, 56: 71-105. |
| 7 | ZHOU Y J, KERKHOVEN E J, NIELSEN J. Barriers and opportunities in bio-based production of hydrocarbons[J]. Nature Energy, 2018, 3(11): 925-935. |
| 8 | SCHRADER J, SCHILLING M, HOLTMANN D, et al. Methanol-based industrial biotechnology: current status and future perspectives of methylotrophic bacteria[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2009, 27(2): 107-115. |
| 9 | OLAH G A. Towards oil independence through renewable methanol chemistry[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(1): 104-107. |
| 10 | KNöZINGER H, WEITKAMP J. Handbook of heterogeneous catalysis [M]. New York:Wiley-VCH, 1997. |
| 11 | BERTAU M, OFFERMANNS H, PLASS L, et al. Methanol: the basic chemical and energy feedstock of the future[M]. Berlin:Springer, 2014. |
| 12 | YANG Y, XU J, LIU Z, et al. Progress in coal chemical technologies of China[J]. Reviews in Chemical Engineering, 2019, 36(1): 21-66. |
| 13 | CHEJNE F, HERNANDEZ J. Modelling and simulation of coal gasification process in fluidised bed[J]. Fuel, 2002, 81(13): 1687-1702. |
| 14 | DAI J, SAAYMAN J, GRACE J R, et al. Gasification of woody biomass[J]. Annual Review of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 2015, 6: 77-99. |
| 15 | TROP P, ANICIC B, GORICANEC D. Production of methanol from a mixture of torrefied biomass and coal[J]. Energy, 2014, 77: 125-132. |
| 16 | ZHANG X, ZHONG L, GUO Q, et al. Influence of the calcination on the activity and stability of the Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst in liquid phase methanol synthesis[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(7): 1348-1352. |
| 17 | 石磊, 张婉莹, 王玉鑫. 低温甲醇合成研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(9): 3333-3340. |
| SHI L, ZHANG W Y, WANG Y X. Research developments of low-temperature methanol synthesis[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(9): 3333-3340. | |
| 18 | SILVA M J DA. Synthesis of methanol from methane: Challenges and advances on the multi-step (syngas) and one-step routes (DMTM)[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2016, 145:42-61. |
| 19 | HUANG W, ZHANG S, TANG Y, et al. Low‐temperature transformation of methane to methanol on Pd1O4 single sites anchored on the internal surface of microporous silicate[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(43): 13441-13445. |
| 20 | GRUNDNER S, MARKOVITS M A, LI G, et al. Single-site trinuclear copper oxygen clusters in mordenite for selective conversion of methane to methanol[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 7546. |
| 21 | JIN Z, WANG L, ZUIDEMA E, et al. Hydrophobic zeolite modification for in situ peroxide formation in methane oxidation to methanol[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6474): 193-197. |
| 22 | SAZINSKY M H, LIPPARD S J. Methane monooxygenase: functionalizing methane at iron and copper[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 205-256. |
| 23 | HWANG I Y, LEE S H, CHOI Y S, et al. Biocatalytic conversion of methane to methanol as a key step for development of methane-based biorefineries[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 24(12): 1597-1605. |
| 24 | DUAN C, LUO M, XING X. High-rate conversion of methane to methanol by Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(15): 7349-7353. |
| 25 | KAHN B. The world passes 400 PPM threshold. Permanently[R]. Princeton: Climate Central, 2016. |
| 26 | LI W, WANG H, JIANG X, et al. A short review of recent advances in CO2 hydrogenation to hydrocarbons over heterogeneous catalysts[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(14): 7651-7669. |
| 27 | NAVARRO R, SANCHEZ-SANCHEZ M, ALVAREZ-GALVAN M, et al. Hydrogen production from renewable sources: biomass and photocatalytic opportunities[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2009, 2(1): 35-54. |
| 28 | YOON Y, HALL A S, SURENDRANATH Y. Tuning of silver catalyst mesostructure promotes selective carbon dioxide conversion into fuels[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(49): 15282-15286. |
| 29 | LI K, PENG B, PENG T. Recent advances in heterogeneous photocatalytic CO2 conversion to solar fuels[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(11): 43. |
| 30 | KATTEL S, RAMíREZ P J, CHEN J G, et al. Active sites for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol on Cu/ZnO catalysts[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6331): 1296-1299. |
| 31 | RUI N, WANG Z, SUN K, et al. CO2 hydrogenation to methanol over Pd/In2O3: effects of Pd and oxygen vacancy[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 218: 488-497. |
| 32 | SUN K, FAN Z, YE J, et al. Hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol over In2O3 catalyst[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2015, 12: 1-6. |
| 33 | LI H, WANG L, DAI Y, et al. Synergetic interaction between neighbouring platinum monomers in CO2 hydrogenation[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2018, 13(5): 411. |
| 34 | WANG Y, KATTEL S, GAO W, et al. Exploring the ternary interactions in Cu-ZnO-ZrO2 catalysts for efficient CO2 hydrogenation to methanol[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1166. |
| 35 | SHIH C F, ZHANG T, LI J, et al. Powering the future with liquid sunshine[J]. Joule, 2018, 2(10): 1925-1949. |
| 36 | WITTHOFF S, MüHLROTH A, MARIENHAGEN J, et al. C1 metabolism in Corynebacterium glutamicum: an endogenous pathway for oxidation of methanol to carbon dioxide[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2013, 79(22): 6974-6983. |
| 37 | KROG A, HEGGESET T M, MüLLER J E, et al. Methylotrophic Bacillus methanolicus encodes two chromosomal and one plasmid born NAD+ dependent methanol dehydrogenase paralogs with different catalytic and biochemical properties[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(3): E59188. |
| 38 | HEGGESET T M, KROG A, BALZER S, et al. Genome sequence of thermotolerant Bacillus methanolicus: features and regulation related to methylotrophy and production of L-lysine and L-glutamate from methanol[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 78(15): 5170-5181. |
| 39 | BRAUTASET T, JAKOBSEN Ø M, DEGNES K F, et al. Bacillus methanolicus pyruvate carboxylase and homoserine dehydrogenase I and II and their roles for L-lysine production from methanol at 50oC[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 87(3): 951-964. |
| 40 | IRLA M, NÆRDAL I, BRAUTASET T, et al. Methanol-based γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) production by genetically engineered Bacillus methanolicus strains[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2017, 106: 12-20. |
| 41 | IRLA M, HEGGESET T, NAERDAL I, et al. Genome-based genetic tool development for Bacillus methanolicus: theta-and rolling circle-replicating plasmids for inducible gene expression and application to methanol-based cadaverine production[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, 7: 1481. |
| 42 | CUI L Y, WANG S S, GUAN C G, et al. Breeding of methanol‐tolerant Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 by atmospheric and room temperature plasma mutagenesis combined with adaptive laboratory evolution[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 13(6): 1700679. |
| 43 | YANG Y M, CHEN W J, YANG J, et al. Production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid in engineered Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 and its reassimilation through a reductive route[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2017, 16(1): 179. |
| 44 | ROHDE M T, TISCHER S, HARMS H, et al. Production of 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid from methanol by Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 expressing (R)-3-hydroxybutyryl coenzyme A-isomerizing enzymes[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2017, 83(3): E02622-E02616. |
| 45 | HU B, YANG Y M, BECK D A, et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 adapted for 1-butanol tolerance[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2016, 9(1): 84. |
| 46 | SONNTAG F, KRONER C, LUBUTA P, et al. Engineering Methylobacterium extorquens for de novo synthesis of the sesquiterpenoid α-humulene from methanol[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 32: 82-94. |
| 47 | LIU Y, TU X, XU Q, et al. Engineered monoculture and co-culture of methylotrophic yeast for de novo production of monacolin J and lovastatin from methanol[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 45: 189-199. |
| 48 | YAMADA R, OGURA K, KIMOTO Y, et al. Toward the construction of a technology platform for chemicals production from methanol: D-lactic acid production from methanol by an engineered yeast Pichia pastoris [J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 35(2): 37. |
| 49 | UBIYVOVK V M, ANANIN V M, MALYSHEV A Y, et al. Optimization of glutathione production in batch and fed-batch cultures by the wild-type and recombinant strains of the methylotrophic yeast Hansenula polymorpha DL-1[J]. BMC Biotechnology, 2011, 11(1): 8. |
| 50 | OCHSNER A M, SONNTAG F, BUCHHAUPT M, et al. Methylobacterium extorquens: methylotrophy and biotechnological applications[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(2): 517-534. |
| 51 | RAVIN N V, ELDAROV M A, KADNIKOV V V, et al. Genome sequence and analysis of methylotrophic yeast Hansenula polymorpha DL1[J]. BMC Genomics, 2013, 14(1): 837. |
| 52 | BRAUTASET T, JAKOBSEN Ø M, FLICKINGER M C, et al. Plasmid-dependent methylotrophy in thermotolerant Bacillus methanolicus [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2004, 186(5): 1229-1238. |
| 53 | YU H, LIAO J C. A modified serine cycle in Escherichia coli coverts methanol and CO2 to two-carbon compounds[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-10. |
| 54 | MÜLLER J E, MEYER F, LITSANOV B, et al. Engineering Escherichia coli for methanol conversion[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 28: 190-201. |
| 55 | GREEN P N, ARDLEY J K. Review of the genus Methylobacterium and closely related organisms: a proposal that some Methylobacterium species be reclassified into a new genus, Methylorubrum gen. nov[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2018, 68(9): 2727-2748. |
| 56 | ZHAO L, CHANG W C, XIAO Y, et al. Methylerythritol phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2013, 82: 497-530. |
| 57 | PEÑA D A, GASSER B, ZANGHELLINI J, et al. Metabolic engineering of Pichia pastoris [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 50: 2-15. |
| 58 | SCHWARZHANS J P, LUTTERMANN T, GEIER M, et al. Towards systems metabolic engineering in Pichia pastoris [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2017, 35(6): 681-710. |
| 59 | YANG Z, ZHANG Z. Engineering strategies for enhanced production of protein and bio-products in Pichia pastoris: a review[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2018, 36(1): 182-195. |
| 60 | XUE Y, KONG C, SHEN W, et al. Methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris as a chassis organism for polyketide synthesis via the full citrinin biosynthetic pathway[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 242: 64-72. |
| 61 | 刘爽, 高教琪, 薛闯, 等. 多形汉逊酵母提高生长性能的培养基优化[J]. 生物加工过程, 2020, 18(1): 116-125. |
| LIU S, GAO J Q, XUE C, et al. Medium optimization for growth of Ogataea polymorpha [J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2020, 18(1): 116-125. | |
| 62 | VORONOVSKY A Y, ROHULYA O V, ABBAS C A, et al. Development of strains of the thermotolerant yeast Hansenula polymorpha capable of alcoholic fermentation of starch and xylan[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2009, 11(4/5): 234-242. |
| 63 | BOGORAD I W, CHEN C T, THEISEN M K, et al. Building carbon-carbon bonds using a biocatalytic methanol condensation cycle[J]. PNAS, 2014, 111(45): 15928-15933. |
| 64 | LU X, LIU Y, YANG Y, et al. Constructing a synthetic pathway for acetyl-coenzyme A from one-carbon through enzyme design[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1-10. |
| 65 | 陈阳, 杨雪, 袁倩倩, 等. 一碳化合物利用新途径的设计和体外构建[J]. 生物加工过程, 2017, 15(5): 86-92. |
| CHEN Y, YANG X, YUAN Q Q, et al. A computationally designed pathway for one carbon compounds utilization and its in vitro construction[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2017, 15(5): 86-92. | |
| 66 | CAI P, GAO J, ZHOU Y. CRISPR-mediated genome editing in non-conventional yeasts for biotechnological applications[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18(1): 63. |
| 67 | WANG L, DENG A, ZHANG Y, et al. Efficient CRISPR-Cas9 mediated multiplex genome editing in yeasts[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2018, 11(1): 1-16. |
| 68 | JUERGENS H, VARELA J A, GORTER DE VRIES A R, et al. Genome editing in Kluyveromyces and Ogataea yeasts using a broad-host-range Cas9/gRNA co-expression plasmid[J]. FEMS Yeast Research, 2018, 18(3): foy012. |
| 69 | NUMAMOTO M, MAEKAWA H, KANEKO Y. Efficient genome editing by CRISPR/Cas9 with a tRNA-sgRNA fusion in the methylotrophic yeast Ogataea polymorpha [J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2017, 124(5): 487-492. |
| 70 | WENINGER A, FISCHER J E, RASCHMANOVá H, et al. Expanding the CRISPR/Cas9 toolkit for Pichia pastoris with efficient donor integration and alternative resistance markers[J]. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 2018, 119(4): 3183-3198. |
| 71 | WENINGER A, HATZL A M, SCHMID C, et al. Combinatorial optimization of CRISPR/Cas9 expression enables precision genome engineering in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 235: 139-149. |
| 72 | ZHANG W, ZHANG T, SONG M, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for high yield production of succinic acid driven by methanol[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(12): 2803-2811. |
| 73 | WHITAKER W B, JONES J A, BENNETT R K, et al. Engineering the biological conversion of methanol to specialty chemicals in Escherichia coli [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 39: 49-59. |
| 74 | MEYER F, KELLER P, HARTL J, et al. Methanol-essential growth of Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-10. |
| 75 | TUYISHIME P, WANG Y, FAN L, et al. Engineering Corynebacterium glutamicum for methanol-dependent growth and glutamate production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 49: 220-231. |
| 76 | LEßMEIER L, PFEIFENSCHNEIDER J, CARNICER M, et al. Production of carbon-13-labeled cadaverine by engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum using carbon-13-labeled methanol as co-substrate[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(23): 10163-10176. |
| 77 | DAI Z, GU H, ZHANG S, et al. Metabolic construction strategies for direct methanol utilization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245: 1407-1412. |
| 78 | 周文娟, 刘娇, 李庆刚,等 赖氨酸工业发展的机遇与挑战 [J]. 生物产业技术, 2019, 1: 12. |
| ZHOU W J, LIU J, LI Q G, et al. Opportunities and challenges in the development of lysine industry[J]. Biotechnology & Business, 2019, 1: 12. | |
| 79 | BARITUGO K A G, KIM H T, DAVID Y C, et al. Recent advances in metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum as a potential platform microorganism for biorefinery[J]. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 2018, 12(5): 899-925. |
| 80 | 高教琪, 段兴鹏, 周雍进. 酵母细胞工厂生产脂肪酸及其衍生物[J]. 生物加工过程, 2018, 16(1): 19-30. |
| GAO J Q, DUAN X P, ZHOU Y J. Production of fatty acids and their derivatives by yeast cell factories[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2018, 16(1): 19-30. | |
| 81 | YASOKAWA D, MURATA S, IWAHASHI Y, et al. Toxicity of methanol and formaldehyde towards Saccharomyces cerevisiae as assessed by DNA microarray analysis[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2010, 160(6): 1685-1698. |
| 82 | PRICE J V, CHEN L, WHITAKER W B, et al. Scaffoldless engineered enzyme assembly for enhanced methanol utilization[J]. PNAS, 2016, 113(45): 12691-12696. |
| 83 | 王千, 程健, 江会锋. 新基因起源: 从自然进化到人工设计[J]. 生物工程学报, 2017, 33(3): 324-330. |
| WANG Q, CHENG J, JIANG H F. Origin of new genes: from evolution to design[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 33(3): 324-330. | |
| 84 | WOOLSTON B M, KING J R, REITER M, et al. Improving formaldehyde consumption drives methanol assimilation in engineered E. coli [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-12. |
| 85 | GONZALEZ J E, BENNETT R K, PAPOUTSAKIS E T, et al. Methanol assimilation in Escherichia coli is improved by coutilization of threonine and deletion of leucine-responsive regulatory protein[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 45: 67-74. |
| 86 | CHEN C T, CHEN F Y H, BOGORAD I W, et al. Synthetic methanol auxotrophy of Escherichia coli for methanol-dependent growth and production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 49: 257-266. |
| 87 | BENNETT R K, GONZALEZ J E, WHITAKER W B, et al. Expression of heterologous non-oxidative pentose phosphate pathway from Bacillus methanolicus and phosphoglucose isomerase deletion improves methanol assimilation and metabolite production by a synthetic Escherichia coli methylotroph[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 45: 75-85. |
| 88 | HE H, EDLICH-MUTH C, LINDNER S N, et al. Ribulose monophosphate shunt provides nearly all biomass and energy required for growth of E. coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(6): 1601-1611. |
| 89 | ROHLHILL J, SANDOVAL N R, PAPOUTSAKIS E T. Sort-seq approach to engineering a formaldehyde-inducible promoter for dynamically regulated Escherichia coli growth on methanol[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(8): 1584-1595. |
| 90 | HAMMER S K, AVALOS J L. Harnessing yeast organelles for metabolic engineering[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2017, 13(8): 823. |
| 91 | SANDBERG T E, SALAZAR M J, WENG L L, et al. The emergence of adaptive laboratory evolution as an efficient tool for biological discovery and industrial biotechnology[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 56: 1-16. |
| 92 | 曲戈, 赵晶, 郑平, 等 定向进化技术的最新进展 [J]. 生物工程学报, 2018, 34(1): 1-11. |
| QU G, ZHAO J, ZHENG P, et al. Recent advances in directed evolution[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2018, 34(1): 1-11. |
| [1] | 郭姝媛, 张倩楠, 姑丽克孜·买买提热夏提, 杨一群, 于涛. 液体生物燃料合成与炼制的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 18-44. |
| [2] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [3] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | 赵亮, 李振帅, 付丽平, 吕明, 王士安, 张全, 刘立成, 李福利, 刘自勇. 生物转化一碳化合物原料产油脂与单细胞蛋白研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [11] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [12] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [13] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [14] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [15] | 禹伟, 高教琪, 周雍进. 一碳生物转化合成有机酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1169-1188. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||