合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (1): 53-76.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-028
人工调控受体聚集的化学合成生物学策略及应用
袁燕燕, 陈慧芳, 杨思慧, 王洪辉, 聂舟
- 湖南大学,化学生物传感与化学计量学国家重点实验室,化学化工学院,生物学院,生物大分子化学生物学湖南省重点实验室,湖南 长沙 410082
-
收稿日期:2023-04-06修回日期:2023-06-08出版日期:2024-02-29发布日期:2024-03-20 -
通讯作者:王洪辉,聂舟 -
作者简介:袁燕燕 (1998—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为化学手段调控细胞行为和命运。 E-mail:S201101026 @hnu.edu.cn王洪辉 (1980—),男,副教授,博士生导师。研究方向为细胞受体信号转导机制和调控细胞功能的合成生物学新方法。 E-mail:wanghonghui@hnu.edu.cn聂舟 (1982—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向:①基于功能蛋白质和核酸的生物传感新方法;②调控细胞行为和命运的化学生物学和合成生物学新策略。 E-mail:niezhou@hnu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2020YFA0907500);国家自然科学基金(22177030)
Engineering artificial receptor cluster: chemical synthetic biology strategies and emerging applications
YUAN Yanyan, CHEN Huifang, YANG Sihui, WANG Honghui, NIE Zhou
- State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics,College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,College of Biology,Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Biomacromolecular Chemical Biology,Hunan University,Changsha 410082,Hunan,China
-
Received:2023-04-06Revised:2023-06-08Online:2024-02-29Published:2024-03-20 -
Contact:WANG Honghui, NIE Zhou
摘要:
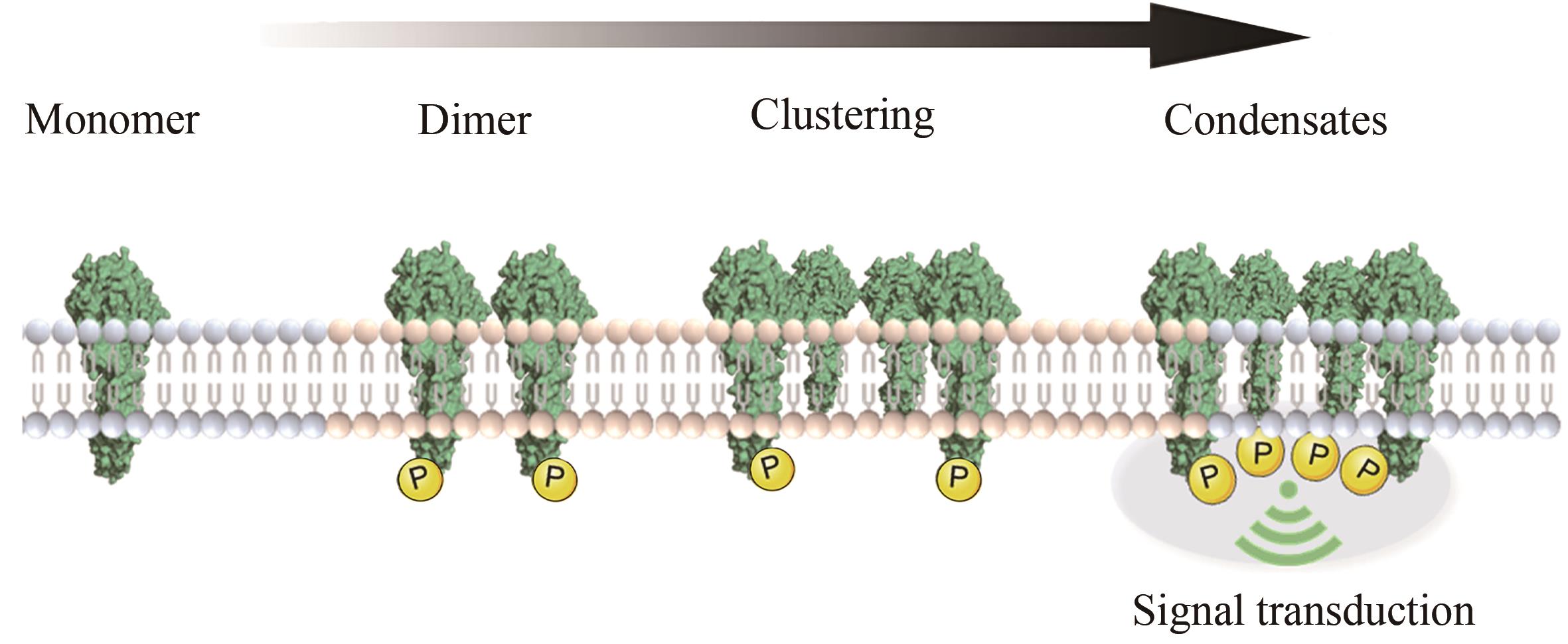
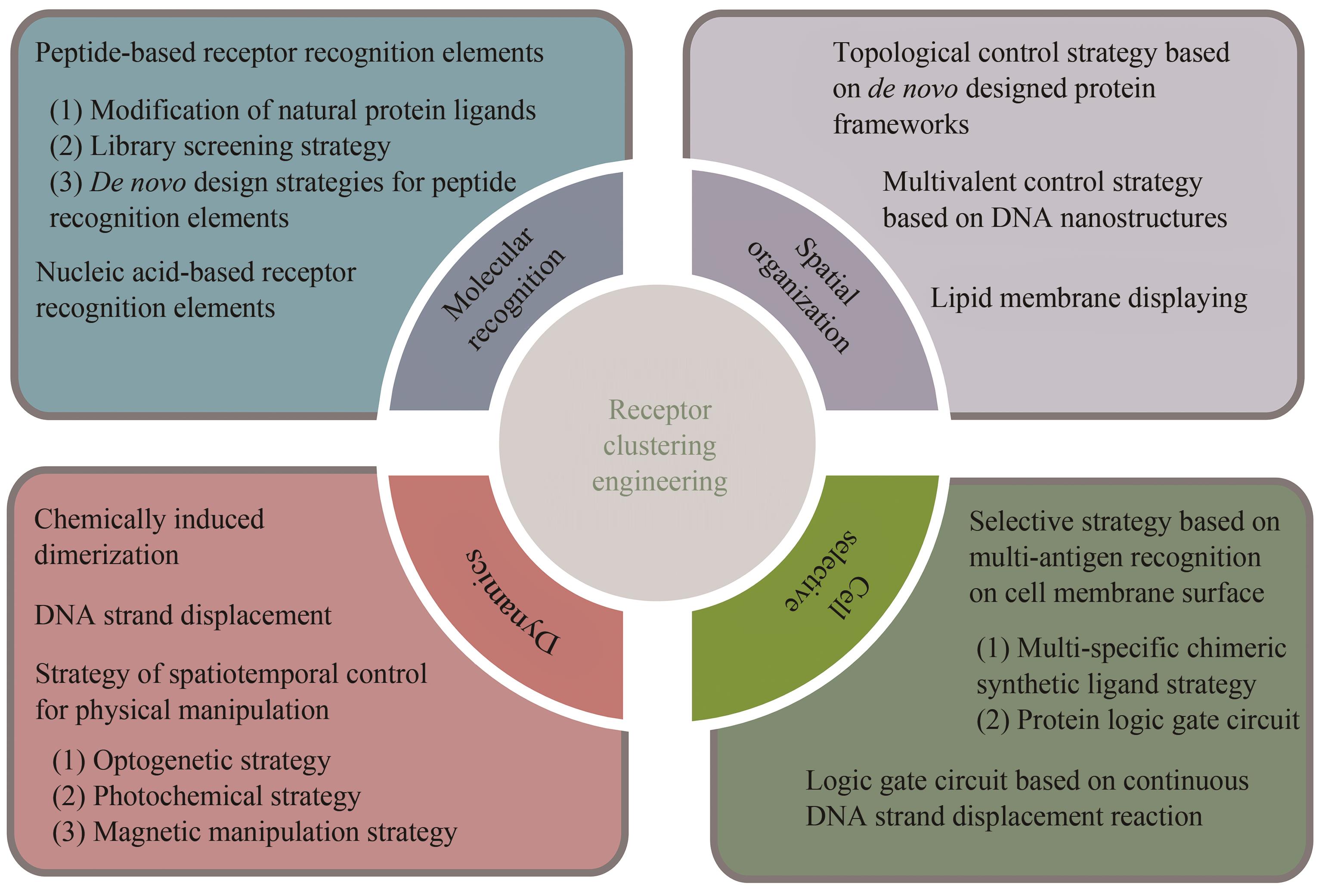
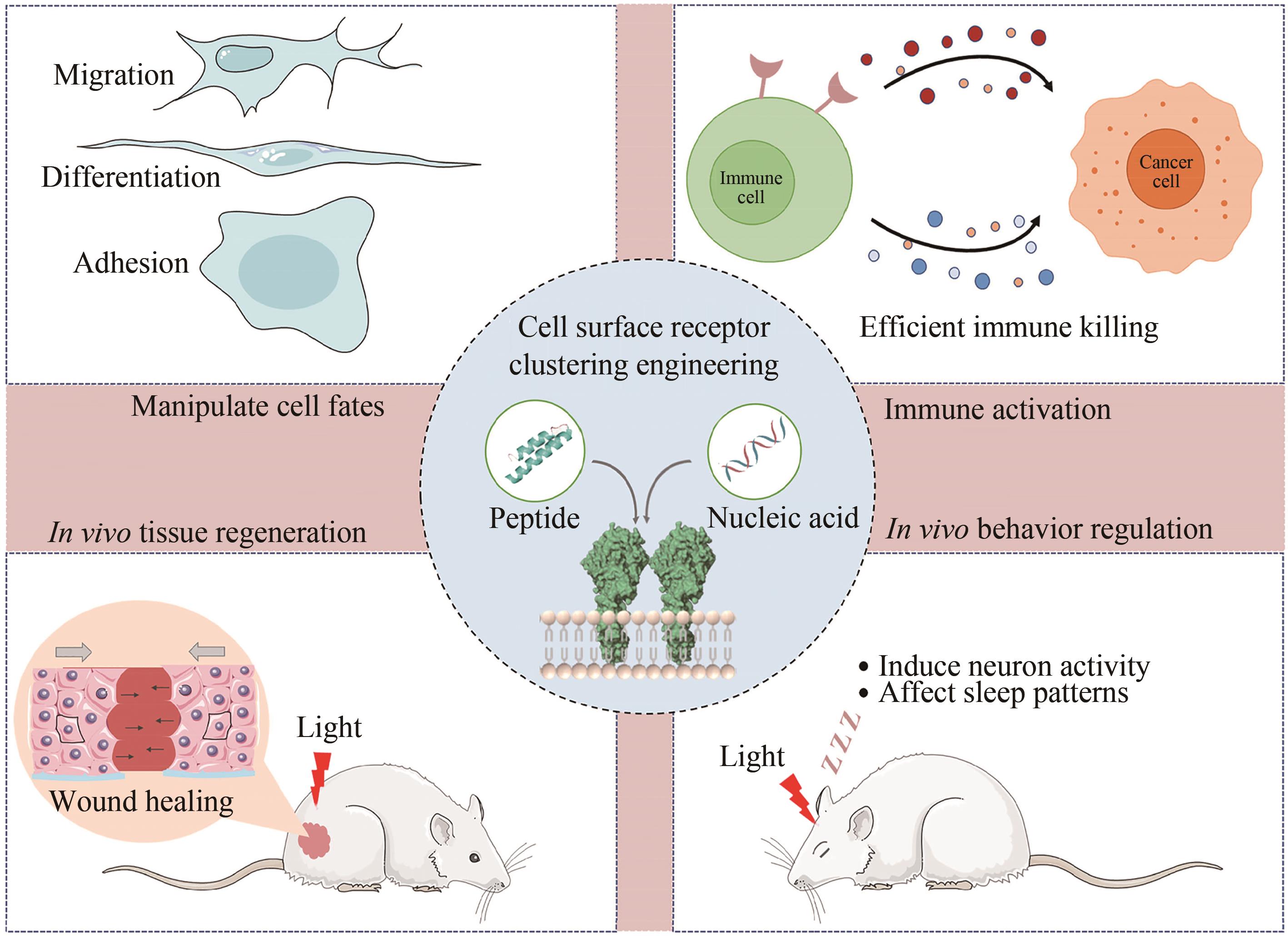
细胞表面受体的聚集和激活在多种生物过程中发挥着重要作用,如细胞迁移、增殖、凋亡和分化。鉴于受体介导的细胞功能对健康和疾病的广泛相关性,研究人员一直致力于探究细胞受体信号传递和激活的生物化学和生物物理学机制,进而在其基础上开发多样的分子工程策略操纵受体信号和细胞功能。随着化学合成生物学的快速发展,一系列分子工程工具被开发出来用于理性控制受体,使得人工受体激活更加简单、精准和多样化。本综述首先总结了涉及调节受体聚集控制的关键功能元件,包括分子识别、空间组织、动态和细胞选择性元件。随后介绍了这些高度可控的功能模块在动态聚集、特定响应性、时空分辨和高细胞选择性的精准控制受体聚集分子工具的最新研究进展。此外强调了多种人工控制受体聚集的精准激活策略在细胞表型和命运操纵、免疫激活和活体组织修复方面的新兴应用。最后,本文从作用机理、元件工程、临床局限性、体内长效性等多个角度概述人工受体聚集策略当前面临的挑战和缺点。同时,本文也对其在疾病治疗领域的潜在应用进行了前瞻性的展望。
中图分类号:
引用本文
袁燕燕, 陈慧芳, 杨思慧, 王洪辉, 聂舟. 人工调控受体聚集的化学合成生物学策略及应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 53-76.
YUAN Yanyan, CHEN Huifang, YANG Sihui, WANG Honghui, NIE Zhou. Engineering artificial receptor cluster: chemical synthetic biology strategies and emerging applications[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 53-76.
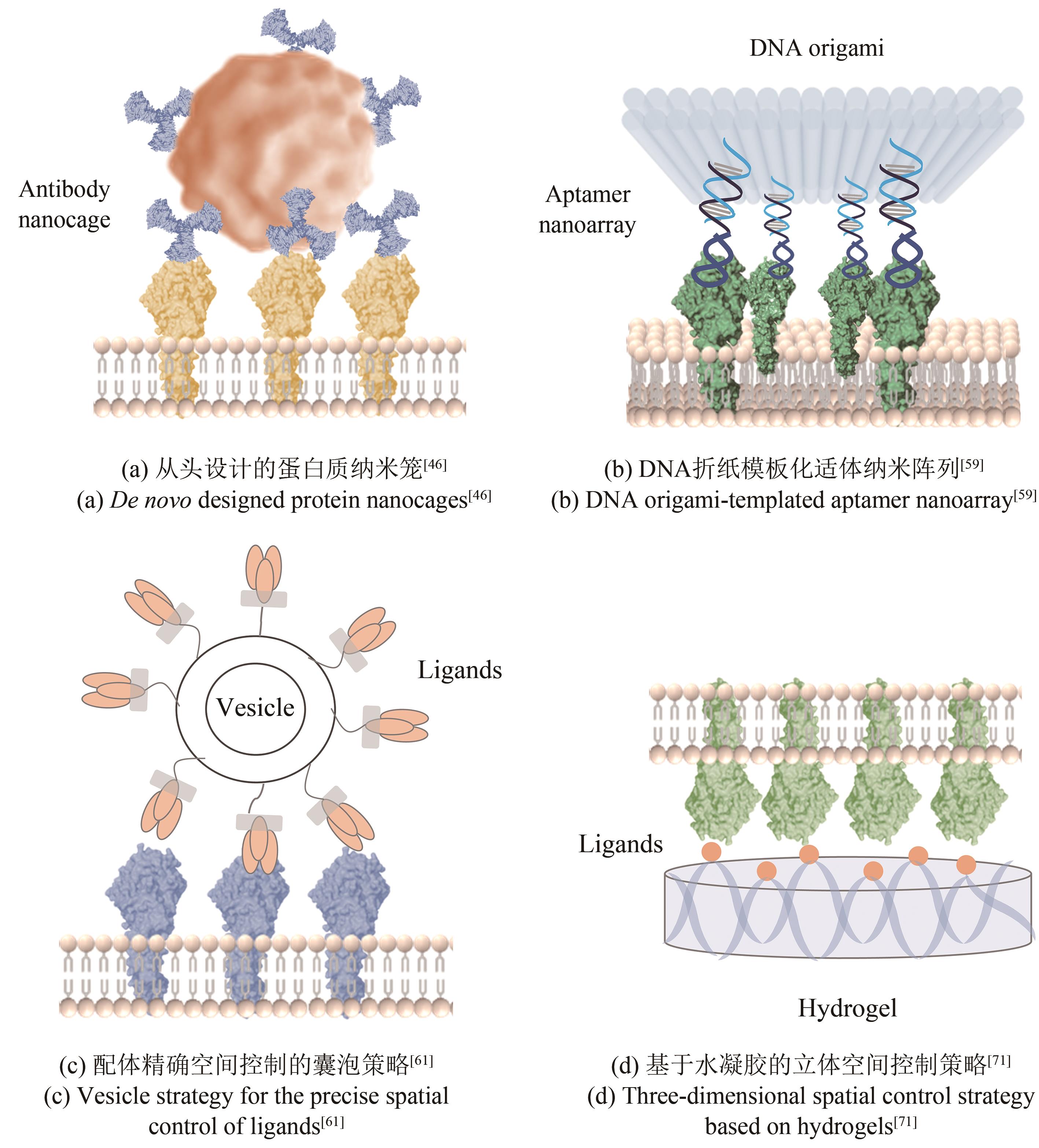
| 空间组织元件 | 纳米精度 | 优势 | 局限性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 基于从头设计蛋白框架的拓扑控制策略 | 15~40 nm[ | 可定制蛋白质框架形状和功能特征,精确指定配体结构和化合价 | 技术门槛和生产成本高, |
| 基于DNA纳米结构的多价控制策略 | 14.3~200 nm[ | 易于合成,易于修饰,可精确控制几何形状,配体修饰位点具有特异性,能够准确定义不同配体的数比和分布模式 | 可溶性免疫信号配体以及疏水性有效载荷并不容易掺入DNA纳米结构中,体内稳定性有待提高 |
| 基于囊泡的工程策略 | Not test | 高生物相容性、低毒性、低免疫原性、易于修饰 | 尺寸和形状难以精确控制,存在容量限制 |
| 基于支持的脂质双层策略 | 40~120 nm[ | 具有维度和横向迁移率等关键特征,可与光学工具结合进行高时空分辨研究 | 一般需要固体衬底,生产工艺复杂 |
| 基于水凝胶的立体空间控制策略 | 49、135 nm[ | 组成成分明确,物理和化学性质(例如基质弹性、配体密度和孔隙率)可以独立控制,优异的防污性能 | 易溶胀,配体定位难以精确控制,体内 |
表1 受体聚集空间组织元件的纳米精度比较
Table 1 Comparison for the spatial organization elements of cell surface receptors at of nanometer scale
| 空间组织元件 | 纳米精度 | 优势 | 局限性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 基于从头设计蛋白框架的拓扑控制策略 | 15~40 nm[ | 可定制蛋白质框架形状和功能特征,精确指定配体结构和化合价 | 技术门槛和生产成本高, |
| 基于DNA纳米结构的多价控制策略 | 14.3~200 nm[ | 易于合成,易于修饰,可精确控制几何形状,配体修饰位点具有特异性,能够准确定义不同配体的数比和分布模式 | 可溶性免疫信号配体以及疏水性有效载荷并不容易掺入DNA纳米结构中,体内稳定性有待提高 |
| 基于囊泡的工程策略 | Not test | 高生物相容性、低毒性、低免疫原性、易于修饰 | 尺寸和形状难以精确控制,存在容量限制 |
| 基于支持的脂质双层策略 | 40~120 nm[ | 具有维度和横向迁移率等关键特征,可与光学工具结合进行高时空分辨研究 | 一般需要固体衬底,生产工艺复杂 |
| 基于水凝胶的立体空间控制策略 | 49、135 nm[ | 组成成分明确,物理和化学性质(例如基质弹性、配体密度和孔隙率)可以独立控制,优异的防污性能 | 易溶胀,配体定位难以精确控制,体内 |
| 1 | TRUSOLINO L, BERTOTTI A, COMOGLIO P M. MET signalling: principles and functions in development, organ regeneration and cancer[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2010, 11(12): 834-848. |
| 2 | BLUME-JENSEN P, HUNTER T. Oncogenic kinase signalling[J]. Nature, 2001, 411(6835): 355-365. |
| 3 | CAI K, ZHANG X W, BAI X C. Cryo-electron microscopic analysis of single-pass transmembrane receptors[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2022, 122(17): 13952-13988. |
| 4 | LEMMON M A, SCHLESSINGER J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases[J]. Cell, 2010, 141(7): 1117-1134. |
| 5 | CASE L B, DITLEV J A, ROSEN M K. Regulation of transmembrane signaling by phase separation[J]. Annual Review of Biophysics, 2019, 48: 465-494. |
| 6 | SÁNCHEZ M F, TAMPÉ R. Ligand-independent receptor clustering modulates transmembrane signaling: a new paradigm[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2023, 48(2): 156-171. |
| 7 | LIAO W, LIN J X, LEONARD W J. IL-2 family cytokines: new insights into the complex roles of IL-2 as a broad regulator of T helper cell differentiation[J]. Current Opinion in Immunology, 2011, 23(5): 598-604. |
| 8 | WENG X, MAXWELL-WARBURTON S, HASIB A, et al. The membrane receptor CD44: novel insights into metabolism[J]. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2022, 33(5): 318-332. |
| 9 | KODIS E J, SMINDAK R J, KEFAUVER J M, et al. First messengers[M/OL]//.Wiley, 2012[2023-02-01]. . |
| 10 | MORSUT L, ROYBAL K T, XIONG X, et al. Engineering customized cell sensing and response behaviors using synthetic Notch receptors[J]. Cell, 2016, 164(4): 780-791. |
| 11 | ZHU I, LIU R, GARCIA J M, et al. Modular design of synthetic receptors for programmed gene regulation in cell therapies[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(8): 1431-1443.e16. |
| 12 | SILVA D A, YU S, ULGE U Y, et al. De novo design of potent and selective mimics of IL-2 and IL-15[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7738): 186-191. |
| 13 | CHIARABELLI C, STANO P, LUISI P L. Chemical approaches to synthetic biology[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2009, 20(4): 492-497. |
| 14 | CHIARABELLI C, LUISI P L. Chemical synthetic biology[J]. Science Progress, 2014, 97(1): 48-61. |
| 15 | MORAGA I, WERNIG G, WILMES S, et al. Tuning cytokine receptor signaling by re-orienting dimer geometry with surrogate ligands[J]. Cell, 2015, 160(6): 1196-1208. |
| 16 | SPANGLER J B, MORAGA I, MENDOZA J L, et al. Insights into cytokine-receptor interactions from cytokine engineering[J]. Annual Review of Immunology, 2015, 33: 139-167. |
| 17 | WILMES S, BEUTEL O, LI Z, et al. Receptor dimerization dynamics as a regulatory valve for plasticity of typeⅠinterferon signaling[J]. The Journal of Cell Biology, 2015, 209(4): 579-593. |
| 18 | WANG Y J, XUE P, CAO M F, et al. Directed evolution: methodologies and applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(20): 12384-12444. |
| 19 | MO F, YU Z Y, LI P, et al. An engineered IL-2 partial agonist promotes CD8+ T cell stemness[J]. Nature, 2021, 597(7877): 544-548. |
| 20 | HO C C M, CHHABRA A, STARKL P, et al. Decoupling the functional pleiotropy of stem cell factor by tuning c-kit signaling[J]. Cell, 2017, 168(6): 1041-1052.e18. |
| 21 | KIM A R, ULIRSCH J C, WILMES S, et al. Functional selectivity in cytokine signaling revealed through a pathogenic EPO mutation[J]. Cell, 2017, 168(6): 1053-1064.e15. |
| 22 | JANES P W, VAIL M E, GAN H K, et al. Antibody targeting of Eph receptors in cancer[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2020, 13(5): 88. |
| 23 | CARLES-KINCH K, KILPATRICK K E, STEWART J C, et al. Antibody targeting of the EphA2 tyrosine kinase inhibits malignant cell behavior[J]. Cancer Research, 2002, 62(10): 2840-2847. |
| 24 | SUN H, HU N, WANG J H. Application of microfluidic technology in antibody screening[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 17(8): e2100623. |
| 25 | SHI R, SHAN C, DUAN X M, et al. A human neutralizing antibody targets the receptor-binding site of SARS-CoV-2[J]. Nature, 2020, 584(7819): 120-124. |
| 26 | BHUSHAN B, GRANATA D, KAAS C S, et al. An integrated platform approach enables discovery of potent, selective and ligand-competitive cyclic peptides targeting the GIP receptor[J]. Chemical Science, 2022, 13(11): 3256-3262. |
| 27 | GOTO Y, SUGA H. The RaPID platform for the discovery of pseudo-natural macrocyclic peptides[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2021, 54(18): 3604-3617. |
| 28 | MIHARA E, WATANABE S, BASHIRUDDIN N K, et al. Lasso-grafting of macrocyclic peptide pharmacophores yields multi-functional proteins[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 1543. |
| 29 | HUANG P S, BOYKEN S E, BAKER D. The coming of age of de novo protein design[J]. Nature, 2016, 537(7620): 320-327. |
| 30 | CAO L X, GORESHNIK I, COVENTRY B, et al. De novo design of picomolar SARS-CoV-2 miniprotein inhibitors[J]. Science, 2020, 370(6515): 426-431. |
| 31 | KUHLMAN B, DANTAS G, IRETON G C, et al. Design of a novel globular protein fold with atomic-level accuracy[J]. Science, 2003, 302(5649): 1364-1368. |
| 32 | ALFORD R F, LEAVER-FAY A, JELIAZKOV J R, et al. The Rosetta all-atom energy function for macromolecular modeling and design[J]. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2017, 13(6): 3031-3048. |
| 33 | LU P L, MIN D, DIMAIO F, et al. Accurate computational design of multipass transmembrane proteins[J]. Science, 2018, 359(6379): 1042-1046. |
| 34 | THOMSON A R, WOOD C W, BURTON A J, et al. Computational design of water-soluble α-helical barrels[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6208): 485-488. |
| 35 | BRUNETTE T, PARMEGGIANI F, HUANG P S, et al. Exploring the repeat protein universe through computational protein design[J]. Nature, 2015, 528(7583): 580-584. |
| 36 | HUANG B, XU Y, HU X H, et al. A backbone-centred energy function of neural networks for protein design[J]. Nature, 2022, 602(7897): 523-528. |
| 37 | CAO L X, COVENTRY B, GORESHNIK I, et al. Design of protein-binding proteins from the target structure alone[J]. Nature, 2022, 605(7910): 551-560. |
| 38 | HOSSEINZADEH P, WATSON P R, CRAVEN T W, et al. Anchor extension: a structure-guided approach to design cyclic peptides targeting enzyme active sites[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 3384. |
| 39 | WIRAJA C, YEO D, LIO D, et al. Aptamer technology for tracking cells' status & function[J]. Molecular and Cellular Therapies, 2014, 2(1): 33. |
| 40 | ZHOU J H, ROSSI J. Aptamers as targeted therapeutics: current potential and challenges[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2017, 16(3): 181-202. |
| 41 | TAKAHASHI M. Aptamers targeting cell surface proteins[J]. Biochimie, 2018, 145: 63-72. |
| 42 | OHUCHI S. Cell-SELEX technology[J]. BioResearch Open Access, 2012, 1(6): 265-272. |
| 43 | CAMORANI S, CRESCENZI E, FEDELE M, et al. Oligonucleotide aptamers against tyrosine kinase receptors: prospect for anticancer applications[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Reviews on Cancer, 2018, 1869(2): 263-277. |
| 44 | HAHN U. SDA and IDA—two aptamers to inhibit cancer cell adhesion[J]. Biochimie, 2018, 145: 84-90. |
| 45 | ZUMRUT H E, ARA M N, MAIO G E, et al. Ligand-guided selection of aptamers against T-cell receptor-cluster of differentiation 3 (TCR-CD3) expressed on Jurkat.E6 cells[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2016, 512: 1-7. |
| 46 | DIVINE R, DANG H V, UEDA G, et al. Designed proteins assemble antibodies into modular nanocages[J]. Science, 2021, 372(6537): eabd9994. |
| 47 | SHAW A, LUNDIN V, PETROVA E, et al. Spatial control of membrane receptor function using ligand nanocalipers[J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(8): 841-846. |
| 48 | CAI H G, MULLER J, DEPOIL D, et al. Full control of ligand positioning reveals spatial thresholds for T cell receptor triggering[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2018, 13(7): 610-617. |
| 49 | YE K, WANG X, CAO L P, et al. Matrix stiffness and nanoscale spatial organization of cell-adhesive ligands direct stem cell fate[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(7): 4720-4729. |
| 50 | MOHAN K, UEDA G, KIM A R, et al. Topological control of cytokine receptor signaling induces differential effects in hematopoiesis[J]. Science, 2019, 364(6442): eaav7532. |
| 51 | WANG S S, ELLINGTON A D. Pattern generation with nucleic acid chemical reaction networks[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(10): 6370-6383. |
| 52 | TSENG C Y, WANG W X, DOUGLAS T R, et al. Engineering DNA nanostructures to manipulate immune receptor signaling and immune cell fates[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2022, 11(4): 2101844. |
| 53 | SEEMAN N C. Nucleic acid junctions and lattices[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 1982, 99(2): 237-247. |
| 54 | HE Y, TIAN Y, CHEN Y, et al. Sequence symmetry as a tool for designing DNA nanostructures[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2005, 44(41): 6694-6696. |
| 55 | DOUGLAS S M, DIETZ H, LIEDL T, et al. Self-assembly of DNA into nanoscale three-dimensional shapes[J]. Nature, 2009, 459(7245): 414-418. |
| 56 | WEI B, DAI M J, YIN P. Complex shapes self-assembled from single-stranded DNA tiles[J]. Nature, 2012, 485(7400): 623-626. |
| 57 | SEEMAN N C, SLEIMAN H F. DNA nanotechnology[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2018, 3: 17068. |
| 58 | HONG F, ZHANG F, LIU Y, et al. DNA origami: scaffolds for creating higher order structures[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(20): 12584-12640. |
| 59 | WANG M, YANG D L, LU Q, et al. Spatially reprogramed receptor organization to switch cell behavior using a DNA origami-templated aptamer nanoarray[J]. Nano Letters, 2022, 22(21): 8445-8454. |
| 60 | LAI R C, YEO R W Y, TAN K H, et al. Exosomes for drug delivery—a novel application for the mesenchymal stem cell[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2013, 31(5): 543-551. |
| 61 | NAKASE I, UENO N, KATAYAMA M, et al. Receptor clustering and activation by multivalent interaction through recognition peptides presented on exosomes[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(2): 317-320. |
| 62 | OHNO S, TAKANASHI M, SUDO K, et al. Systemically injected exosomes targeted to EGFR deliver antitumor microRNA to breast cancer cells[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2013, 21(1): 185-191. |
| 63 | RICHTER M, VADER P, FUHRMANN G. Approaches to surface engineering of extracellular vesicles[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2021, 173: 416-426. |
| 64 | LUO Z W, LI F X Z, LIU Y W, et al. Aptamer-functionalized exosomes from bone marrow stromal cells target bone to promote bone regeneration[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(43): 20884-20892. |
| 65 | DI IORIO D, LU Y, MEULMAN J, et al. Recruitment of receptors at supported lipid bilayers promoted by the multivalent binding of ligand-modified unilamellar vesicles[J]. Chemical Science, 2020, 11(12): 3307-3315. |
| 66 | DI IORIO D, HUSKENS J. Surface modification with control over ligand density for the study of multivalent biological systems[J]. ChemistryOpen, 2020, 9(1): 53-66. |
| 67 | SALAITA K, NAIR P M, PETIT R S, et al. Restriction of receptor movement alters cellular response: physical force sensing by EphA2[J]. Science, 2010, 327(5971): 1380-1385. |
| 68 | YANG D Y. Recent advances in hydrogels[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2022, 34(5): 1987-1989. |
| 69 | WEN H, XIAO W W, BISWAS S, et al. Alginate hydrogel modified with a ligand interacting with α3β1 integrin receptor promotes the differentiation of 3D neural spheroids toward oligodendrocytes in vitro [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(6): 5821-5833. |
| 70 | KWON M Y, WANG C, GALARRAGA J H, et al. Influence of hyaluronic acid modification on CD44 binding towards the design of hydrogel biomaterials[J]. Biomaterials, 2019, 222: 119451. |
| 71 | YOSHIDA D, TERAMOTO A. The use of 3-D culture in peptide hydrogel for analysis of discoidin domain receptor 1-collagen interaction[J]. Cell Adhesion & Migration, 2007, 1(2): 92-98. |
| 72 | CHEN X Y, LAI N C H, WEI K C, et al. Biomimetic presentation of cryptic ligands via single-chain nanogels for synergistic regulation of stem cells[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(4): 4027-4035. |
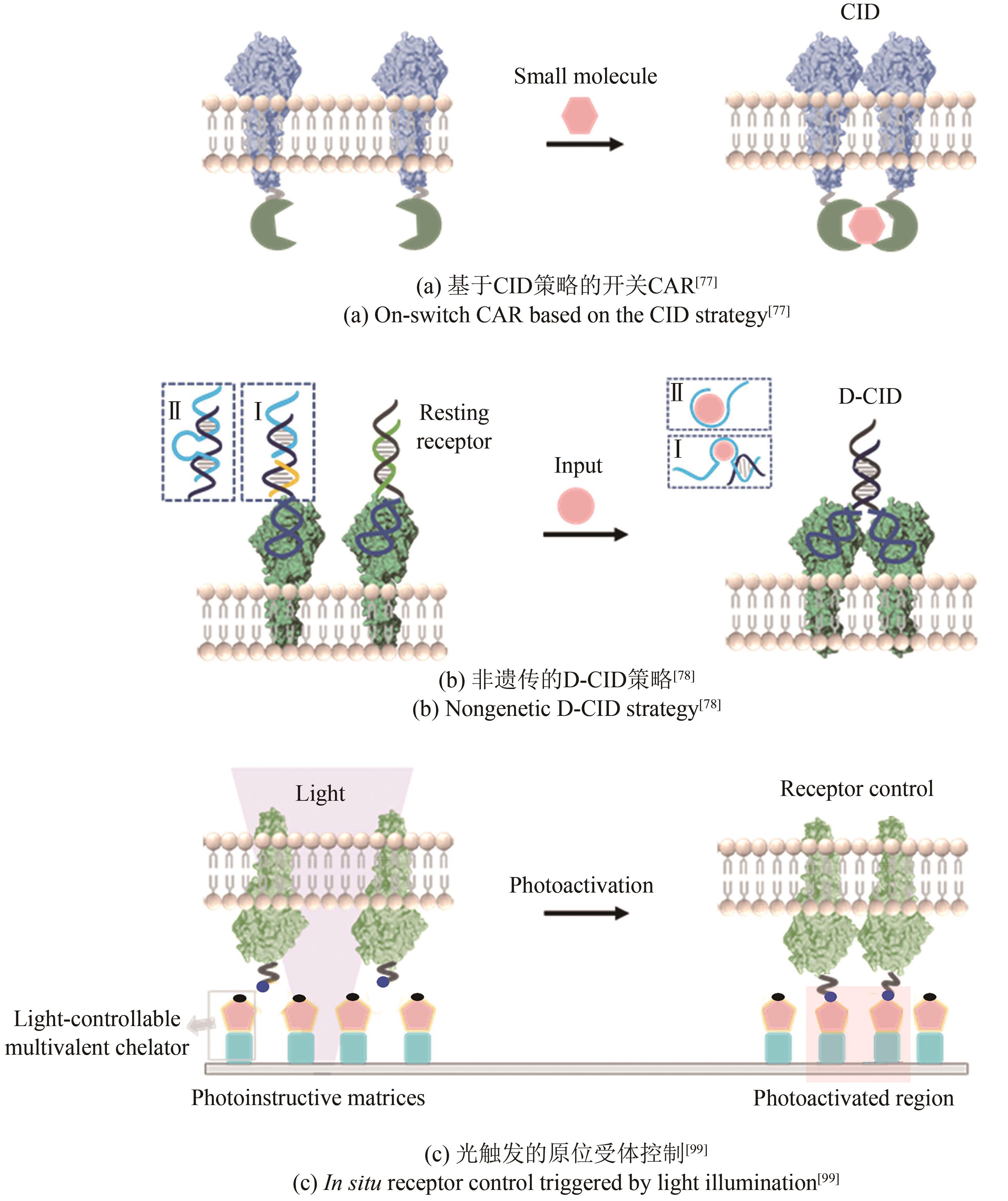
| 73 | DEROSE R, MIYAMOTO T, INOUE T. Manipulating signaling at will: chemically-inducible dimerization (CID) techniques resolve problems in cell biology[J]. Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology, 2013, 465(3): 409-417. |
| 74 | FEGAN A, WHITE B, CARLSON J C T, et al. Chemically controlled protein assembly: techniques and applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2010, 110(6): 3315-3336. |
| 75 | SPENCER D M, WANDLESS T J, SCHREIBER S L, et al. Controlling signal transduction with synthetic ligands[J]. Science, 1993, 262(5136): 1019-1024. |
| 76 | CLACKSON T, YANG W, ROZAMUS L W, et al. Redesigning an FKBP-ligand interface to generate chemical dimerizers with novel specificity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1998, 95(18): 10437-10442. |
| 77 | WU C Y, ROYBAL K T, PUCHNER E M, et al. Remote control of therapeutic T cells through a small molecule-gated chimeric receptor[J]. Science, 2015, 350(6258): aab4077. |
| 78 | LI H, WANG M, SHI T H, et al. A DNA-mediated chemically induced dimerization (D-CID) nanodevice for nongenetic receptor engineering to control cell behavior[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(32): 10226-10230. |
| 79 | SOLOVEICHIK D, SEELIG G, WINFREE E. DNA as a universal substrate for chemical kinetics[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(12): 5393-5398. |
| 80 | SIMMEL F C, YURKE B, SINGH H R. Principles and applications of nucleic acid strand displacement reactions[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(10): 6326-6369. |
| 81 | LI F, TANG Y N, TRAYNOR S M, et al. Kinetics of proximity-induced intramolecular DNA strand displacement[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 88(16): 8152-8157. |
| 82 | JOESAAR A, YANG S, BÖGELS B, et al. DNA-based communication in populations of synthetic protocells[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2019, 14(4): 369-378. |
| 83 | TAYLOR M J, HUSAIN K, GARTNER Z J, et al. A DNA-based T cell receptor reveals a role for receptor clustering in ligand discrimination[J]. Cell, 2017, 169(1): 108-119.e20. |
| 84 | YANG X Q, YANG L J, YANG D L, et al. In situ DNA self-assembly on the cell surface drives unidirectional clustering of membrane proteins for the modulation of cell behaviors[J]. Nano Letters, 2022, 22(8): 3410-3416. |
| 85 | WANG Z M, XIE S T, WU L M, et al. Aptamer-functionalized nanodevices for dynamic manipulation of membrane receptor signaling in living cells[J]. Nano Letters, 2022, 22(19): 7853-7859. |
| 86 | O'BANION C P, LAWRENCE D S. Optogenetics: a primer for chemists[J]. ChemBioChem, 2018, 19(12): 1201-1216. |
| 87 | BOYDEN E S, ZHANG F, BAMBERG E, et al. Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity[J]. Nature Neuroscience, 2005, 8(9): 1263-1268. |
| 88 | TAN P, HE L, HUANG Y, et al. Optophysiology: illuminating cell physiology with optogenetics[J]. Physiological Reviews, 2022, 102(3): 1263-1325. |
| 89 | GOGLIA A G, TOETTCHER J E. A bright future: optogenetics to dissect the spatiotemporal control of cell behavior[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2019, 48: 106-113. |
| 90 | LIU Q Y, DEITERS A. Optochemical control of deoxyoligonucleotide function via a nucleobase-caging approach[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2014, 47(1): 45-55. |
| 91 | COURTNEY T, DEITERS A. Recent advances in the optical control of protein function through genetic code expansion[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2018, 46: 99-107. |
| 92 | AMATRUDO J M, OLSON J P, AGARWAL H K, et al. Caged compounds for multichromic optical interrogation of neural systems[J]. European Journal of Neuroscience, 2015, 41(1): 5-16. |
| 93 | LI W H, ZHENG G H. Photoactivatable fluorophores and techniques for biological imaging applications[J]. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 2012, 11(3): 460-471. |
| 94 | VOß S, KLEWER L, WU Y W. Chemically induced dimerization: reversible and spatiotemporal control of protein function in cells[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2015, 28: 194-201. |
| 95 | GAUTIER A, GAURON C, VOLOVITCH M, et al. How to control proteins with light in living systems[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2014, 10(7): 533-541. |
| 96 | KLÁN P, ŠOLOMEK T, BOCHET C G, et al. Photoremovable protecting groups in chemistry and biology: reaction mechanisms and efficacy[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113(1): 119-191. |
| 97 | WAGNER N, STEPHAN M, HÖGLINGER D, et al. A click cage: organelle-specific uncaging of lipid messengers[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(40): 13339-13343. |
| 98 | BARDHAN A, DEITERS A. Development of photolabile protecting groups and their application to the optochemical control of cell signaling[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2019, 57: 164-175. |
| 99 | SÁNCHEZ M F, ELS-HEINDL S, BECK-SICKINGER A G, et al. Photoinduced receptor confinement drives ligand-independent GPCR signaling[J]. Science, 2021, 371(6536): eabb7657. |
| 100 | DEL SOL-FERNÃNDEZ S, MARTINEZ-VICENTE P, GOMOLLON-ZUECO P, et al. Magnetogenetics: remote activation of cellular functions triggered by magnetic switches[J]. Nanoscale, 2022, 14(6): 2091-2118. |
| 101 | MUHAMED I, CHOWDHURY F, MARUTHAMUTHU V. Biophysical tools to study cellular mechanotransduction[J]. Bioengineering, 2017, 4(4): 12. |
| 102 | KHATUA C, MIN S H, JUNG H J, et al. In situ magnetic control of macroscale nanoligand density regulates the adhesion and differentiation of stem cells[J]. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(6): 4188-4196. |
| 103 | LODE H N, XIANG R, BECKER J C, et al. Immunocytokines: a promising approach to cancer immunotherapy[J]. Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 1998, 80(3):277-292. |
| 104 | DE LUCA R, SOLTERMANN A, PRETTO F, et al. Potency-matched dual cytokine-antibody fusion proteins for cancer therapy[J]. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 2017, 16(11): 2442-2451. |
| 105 | YEN M, REN J M, LIU Q X, et al. Facile discovery of surrogate cytokine agonists[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(8): 1414-1430.e19. |
| 106 | SINGH A. Designing protein logic gates[J]. Nature Methods, 2020, 17(6): 565. |
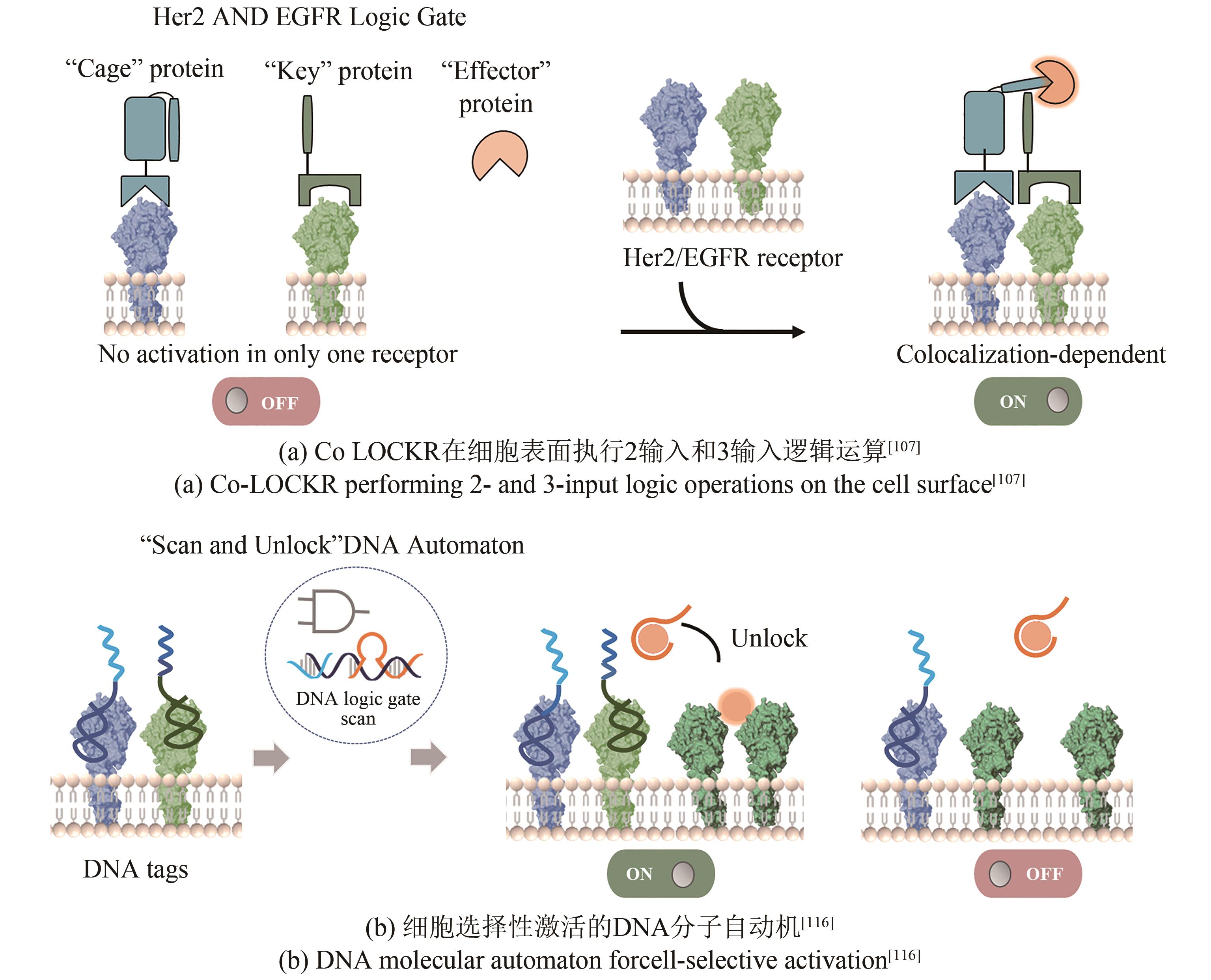
| 107 | LAJOIE M J, BOYKEN S E, SALTER A I, et al. Designed protein logic to target cells with precise combinations of surface antigens[J]. Science, 2020, 369(6511): 1637-1643. |
| 108 | QUIJANO-RUBIO A, BHUIYAN A M, YANG H L, et al. A split, conditionally active mimetic of IL-2 reduces the toxicity of systemic cytokine therapy[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2023, 41(4): 532-540. |
| 109 | VISHWESHWARAIAH Y L, CHEN J X, CHIRASANI V R, et al. Two-input protein logic gate for computation in living cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 6615. |
| 110 | QIAN L L, WINFREE E. Scaling up digital circuit computation with DNA strand displacement cascades[J]. Science, 2011, 332(6034): 1196-1201. |
| 111 | SEELIG G, SOLOVEICHIK D, ZHANG D Y, et al. Enzyme-free nucleic acid logic circuits[J]. Science, 2006, 314(5805): 1585-1588. |
| 112 | QIN W W, CHEN L, WANG Z R, et al. Bioinspired DNA nanointerface with anisotropic aptamers for accurate capture of circulating tumor cells[J]. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(19): 2000647. |
| 113 | CHANG X, ZHANG C, LV C, et al. Construction of a multiple-aptamer-based DNA logic device on live cell membranes via associative toehold activation for accurate cancer cell identification[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(32): 12738-12743. |
| 114 | LIANG H, CHEN S, LI P P, et al. Nongenetic approach for imaging protein dimerization by aptamer recognition and proximity-induced DNA assembly[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(12): 4186-4190. |
| 115 | XIAO M S, LAI W, YU H Z, et al. Assembly pathway selection with DNA reaction circuits for programming multiple cell-cell interactions[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(9): 3448-3454. |
| 116 | ZHANG J H, QIU Z Y, FAN J H, et al. Scan and unlock: a programmable DNA molecular automaton for cell-selective activation of ligand-based signaling[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(12): 6733-6743. |
| 117 | LI R, LI T T, LU G Z, et al. Programming cell-surface signaling by phase-separation-controlled compartmentalization[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2022, 18(12): 1351-1360. |
| 118 | SHELBY S A, CASTELLO-SERRANO I, WISSER K C, et al. Membrane phase separation drives responsive assembly of receptor signaling domains[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2023, 19(6): 750-758. |
| 119 | ITO K, SAKAI K, SUZUKI Y, et al. Artificial human Met agonists based on macrocycle scaffolds[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 6373. |
| 120 | BEN-SASSON A J, WATSON J L, SHEFFLER W, et al. Design of biologically active binary protein 2D materials[J]. Nature, 2021, 589(7842): 468-473. |
| 121 | WU Y C, HUANG J, HE H, et al. Logic nanodevice-mediated receptor assembly for nongenetic regulation of cell behavior in tumor-like microenvironment[J]. Nano Letters, 2023, 23(5): 1801-1809. |
| 122 | JIN Y, LEE J U, CHUNG E, et al. Magnetic control of axon navigation in reprogrammed neurons[J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(9): 6517-6523. |
| 123 | LIU Y Y, CHEUNG L H, MARKS J W, et al. Recombinant single-chain antibody fusion construct targeting human melanoma cells and containing tumor necrosis factor[J]. International Journal of Cancer, 2004, 108(4): 549-557. |
| 124 | BI S Y, CHEN W, FANG Y Y, et al. Cancer cell-selective membrane receptor clustering driven by VEGF secretion for in vivo therapy[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(9): 5041-5052. |
| 125 | UEKI R, UEKI A, KANDA N, et al. Oligonucleotide-based mimetics of hepatocyte growth factor[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(2): 579-582. |
| 126 | UEKI R, ATSUTA S, UEKI A, et al. Nongenetic reprogramming of the ligand specificity of growth factor receptors by bispecific DNA aptamers[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(19): 6554-6557. |
| 127 | UEKI R, WATANABE Y, AKIYAMA M, et al. CiD agonists: circular DNA-based agonists for the fine-tuning of receptor signaling [EB/OL]. ChemRxiv, 2022[2023-02-01]. . |
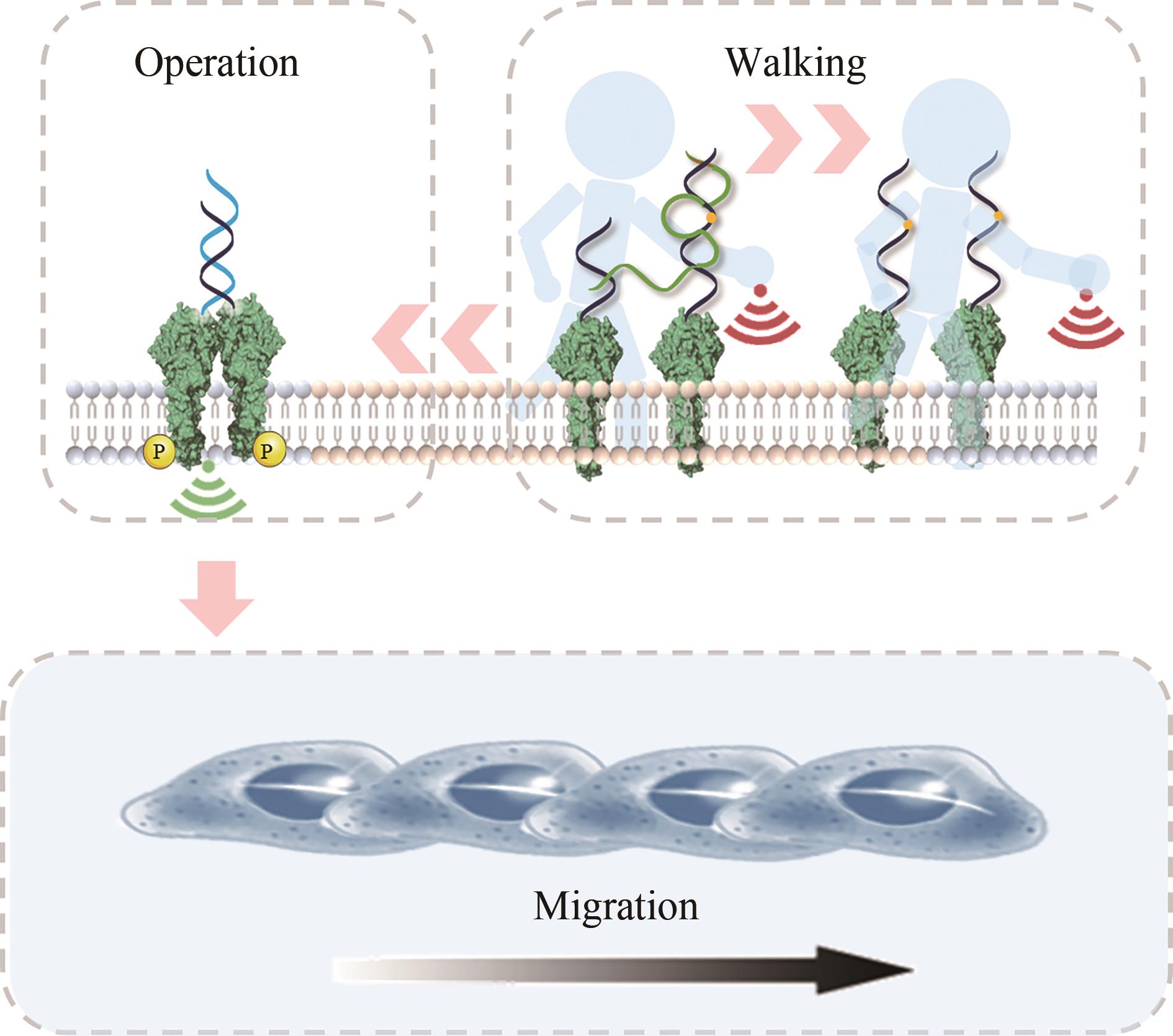
| 128 | LI H, GAO J, CAO L, et al. A DNA molecular robot that autonomously walks on the cell membrane to drive cell motility[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(50): 26087-26095. |
| 129 | GIANCOTTI F G, RUOSLAHTI E. Integrin signaling[J]. Science, 1999, 285(5430): 1028-1032. |
| 130 | MASSIA S P, HUBBELL J A. An RGD spacing of 440 nm is sufficient for integrin alpha V beta 3-mediated fibroblast spreading and 140 nm for focal contact and stress fiber formation[J]. Journal of Cell Biology, 1991, 114(5): 1089-1100. |
| 131 | ARNOLD M, CAVALCANTI-ADAM E A, GLASS R, et al. Activation of integrin function by nanopatterned adhesive interfaces[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2004, 5(3): 383-388. |
| 132 | SCHVARTZMAN M, PALMA M, SABLE J, et al. Nanolithographic control of the spatial organization of cellular adhesion receptors at the single-molecule level[J]. Nano Letters, 2011, 11(3): 1306-1312. |
| 133 | HE J H, SHEN R J, LIU Q, et al. RGD nanoarrays with nanospacing gradient selectively induce orientation and directed migration of endothelial and smooth muscle cells[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(33): 37436-37446. |
| 134 | ZHANG K X, DENG R J, SUN Y P, et al. Reversible control of cell membrane receptor function using DNA nano-spring multivalent ligands[J]. Chemical Science, 2017, 8(10): 7098-7105. |
| 135 | O'SULLIVAN D, SANIN D E, PEARCE E J, et al. Metabolic interventions in the immune response to cancer[J]. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2019, 19(5): 324-335. |
| 136 | LI M, YU Y. Innate immune receptor clustering and its role in immune regulation[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 2021, 134(4): jcs249318. |
| 137 | LI M, WANG H M, LI W Q, et al. Macrophage activation on "phagocytic synapse" arrays: spacing of nanoclustered ligands directs TLR1/2 signaling with an intrinsic limit[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(49): eabc8482. |
| 138 | BROWNLIE R J, ZAMOYSKA R. T cell receptor signalling networks: branched, diversified and bounded[J]. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2013, 13(4): 257-269. |
| 139 | DONG R, AKSEL T, CHAN W P, et al. DNA origami patterning of synthetic T cell receptors reveals spatial control of the sensitivity and kinetics of signal activation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(40): e2109057118. |
| 140 | LIU Z, LIU Y, CHANG Y, et al. Nanoscale optomechanical actuators for controlling mechanotransduction in living cells[J]. Nature Methods, 2016, 13(2): 143-146. |
| 141 | LIU Y, BLANCHFIELD L, MA V P Y, et al. DNA-based nanoparticle tension sensors reveal that T-cell receptors transmit defined pN forces to their antigens for enhanced fidelity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(20): 5610-5615. |
| 142 | LIU Y, GALIOR K, MA V P Y, et al. Molecular tension probes for imaging forces at the cell surface[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2017, 50(12): 2915-2924. |
| 143 | BROCKMAN J M, SALAITA K. Mechanical proofreading: a general mechanism to enhance the fidelity of information transfer between cells[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2019, 7: 14. |
| 144 | WOSCZYNA M N, RANDO T A. A muscle stem cell support group: coordinated cellular responses in muscle regeneration[J]. Developmental Cell, 2018, 46(2): 135-143. |
| 145 | CHAMBERS R L, MCDERMOTT J C. Molecular basis of skeletal muscle regeneration[J]. Canadian Journal of Applied Physiology, 1996, 21(3): 155-184. |
| 146 | CHATTOPADHYAY S, TEIXEIRA L B C, KIESSLING L L, et al. Bifunctional peptide that anneals to damaged collagen and clusters TGF-β receptors enhances wound healing[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2022, 17(2): 314-321. |
| 147 | KWEE B J, MOONEY D J. Biomaterials for skeletal muscle tissue engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2017, 47: 16-22. |
| 148 | WANG M, HE F, LI H, et al. Near-infrared light-activated DNA-agonist nanodevice for nongenetically and remotely controlled cellular signaling and behaviors in live animals[J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(4): 2603-2613. |
| 149 | MICHALOPOULOS G K. Hepatostat: liver regeneration and normal liver tissue maintenance[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(4): 1384-1392. |
| 150 | LIANG H, YAN Z K, TONG Y H, et al. Circular bivalent aptamers enhance the activation of the regenerative signaling pathway for repairing liver injury in vivo [J]. Chemical Communications, 2023, 59(12): 1621-1624. |
| 151 | LEOPOLD A V, THANKACHAN S, YANG C, et al. A general approach for engineering RTKs optically controlled with far-red light[J]. Nature Methods, 2022, 19(7): 871-880. |
| 152 | XIE S T, WANG Z M, FU T, et al. Engineering aptamers with selectively enhanced biostability in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(31): e202201220. |
| 153 | YANG C, ZHAO H T, SUN Y, et al. Programmable manipulation of oligonucleotide-albumin interaction for elongated circulation time[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022, 50(6): 3083-3095. |
| [1] | 孙扬, 陈立超, 石艳云, 王珂, 吕丹丹, 徐秀美, 张立新. 作物光合作用合成生物学的策略与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-16. |
| [2] | 钟奶才, 陈缘, 潘文锋, 苏小凤, 廖景文, 钟近艺. 等离子体微生物育种技术在生物制造中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-17. |
| [3] | 狄泽燕, 周铄, 杨铭方, 刘昕, 陈瑶. 功能框架材料在一碳生物转化中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-18. |
| [4] | 张成辛. 基于文本数据挖掘的蛋白功能预测的机遇与挑战[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-14. |
| [5] | 姜源旭, 范盈盈, 魏平. 生物振荡的设计原理与人工合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-15. |
| [6] | 黄姝涵, 马赫, 罗云孜. 生物合成红景天苷的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-16. |
| [7] | 李倩, James E. Ferrell, 陈于平. 细胞质浓度:细胞生物学的老问题、新参数[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-18. |
| [8] | 姜百翼, 钱珑. 活细胞记录器在细胞谱系追踪中的应用和前景[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, (): 1-17. |
| [9] | 温艳华, 刘合栋, 曹春来, 巫瑞波. 蛋白质工程在医药产业中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 65-86. |
| [10] | 仲泉周, 单依怡, 裴清云, 金艳芸, 王艺涵, 孟璐远, 王歆韵, 张雨鑫, 刘坤媛, 王慧中, 冯尚国. 生物合成法生产α-熊果苷的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 118-135. |
| [11] | 张以恒, 陈雪梅, 石婷. 生物制造的市本率(PC值):定义与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 8-17. |
| [12] | 刘晓悦, 王盼娣, 吴刚, 刘芳. 基因工程辅助萝卜硫苷在十字花科作物中的高效生物合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 136-156. |
| [13] | 任家卫, 张金鹏, 徐国强, 张晓梅, 许正宏, 张晓娟. 大肠杆菌中终止子对下游转录单元基因表达的影响[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 213-227. |
| [14] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [15] | 郑益坤, 郑婕, 胡国鹏. 光遗传学工具在学习记忆中的应用研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 87-104. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||