合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (1): 38-52.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-016
基于细菌双组分系统的生物传感器的研究进展
赵静宇, 张健, 祁庆生, 王倩
- 山东大学,国家糖工程技术研究中心,微生物技术国家重点实验室,山东 青岛 266237
-
收稿日期:2023-02-22修回日期:2023-07-01出版日期:2024-02-29发布日期:2024-03-20 -
通讯作者:祁庆生,王倩 -
作者简介:赵静宇 (1998—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为微生物代谢工程与合成生物学。 E-mail:1504362801@qq.com祁庆生 (1966—),男,教授,山东大学微生物技术国家重点实验室副主任。研究方向为代谢工程与合成生物学,废弃塑料降解及生物可降解塑料的合成等。 E-mail:qiqingsheng@sdu.edu.cn王倩 (1983—),女,博士,教授。研究方向为微生物代谢工程与合成生物学。 E-mail:qiqi20011983@gmail.com -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“合成生物学专项”(2019YFA0904900);国家自然科学基金面上项目(32270089)
Research progress in biosensors based on bacterial two-component systems
ZHAO Jingyu, ZHANG Jian, QI Qingsheng, WANG Qian
- National Glycoengineeing Research Center,State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology,Shandong University,Qingdao 266237,Shandong,China
-
Received:2023-02-22Revised:2023-07-01Online:2024-02-29Published:2024-03-20 -
Contact:QI Qingsheng, WANG Qian
摘要:
细菌双组分系统能够感知和响应细胞内外的物理、化学和生物刺激,通过耦合传感和调节机制从而引起一系列的细胞反应,是一个普遍存在的信号转导通路家族。当前越来越多的合成生物学家已开始利用双组分系统的特异属性来工程化设计微生物传感系统,并应用于光遗传学、材料科学、肠道微生物组工程、生物炼制和土壤改良等领域。本综述重点介绍了开发基于双组分系统的生物传感器的最新研究进展以及在各个领域中的潜在应用。同时探讨了如何运用新的工程方法提高双组分系统传感器性能的可靠性,包括遗传重构、DNA结合结构域交换、检测阈值调节和磷酸化串扰隔离,以及如何根据特定应用的要求定制双组分系统信号特性。在未来,研究者可以将这些方法与大规模的基因合成、高通量筛选相结合,以加速和帮助发现更多未确定特征输入的双组分系统,并开发新的对广泛的刺激做出反应的基因编码生物传感器,拓展双组分生物传感器在不同领域的应用。
中图分类号:
引用本文
赵静宇, 张健, 祁庆生, 王倩. 基于细菌双组分系统的生物传感器的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 38-52.
ZHAO Jingyu, ZHANG Jian, QI Qingsheng, WANG Qian. Research progress in biosensors based on bacterial two-component systems[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 38-52.
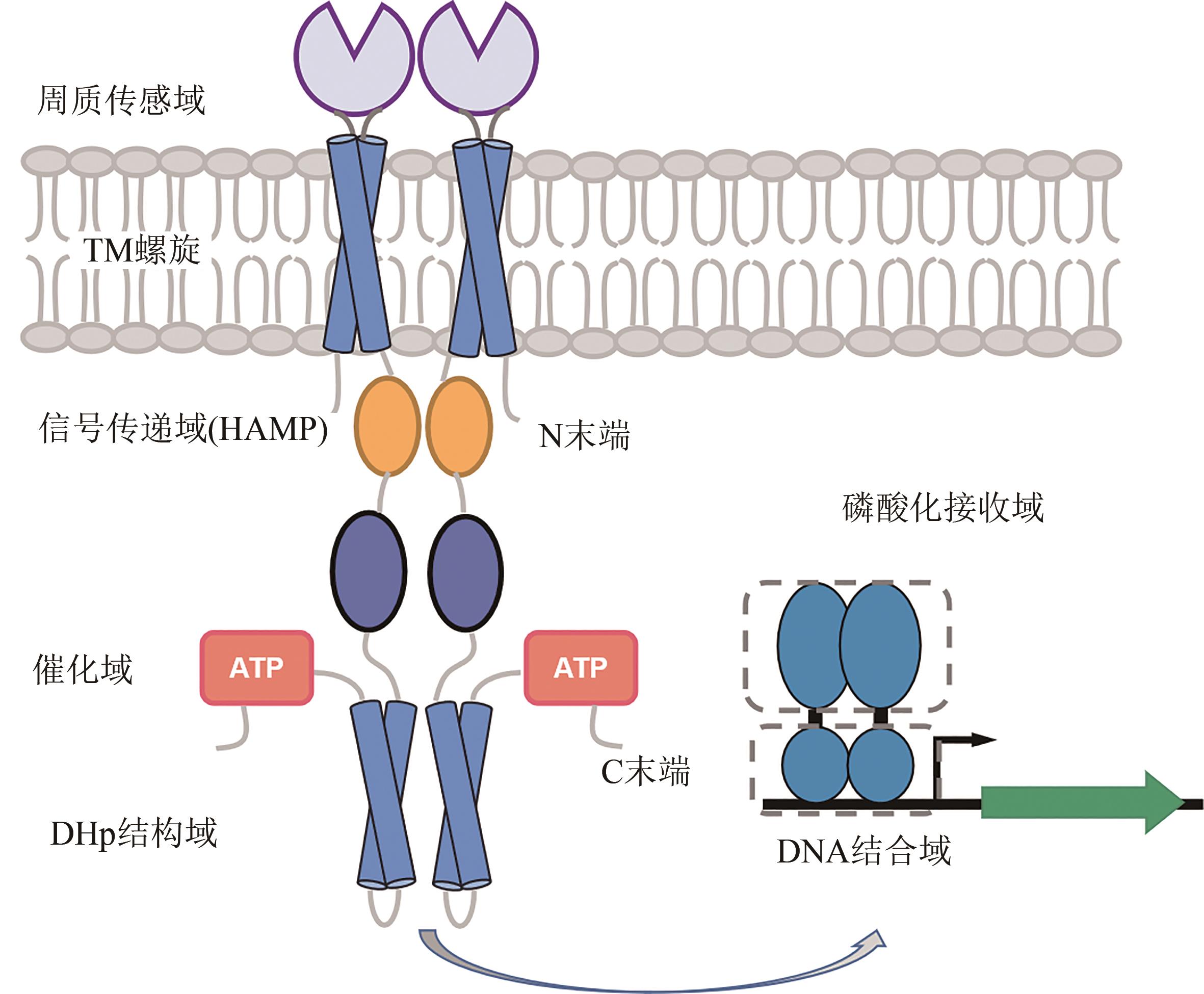
图1 细菌双组分调控系统的结构[双组分系统包括传感器组氨酸激酶(SK)和应答调节器(RR)两部分。典型的SK通常是同源二聚体,由N末端胞质结构域、周质传感器结构域、两个跨膜螺旋、信号传递域(HAMP)、催化域、二聚/组氨酸磷酸化转移结构域(DHp结构域)和C末端结构域组成。应答调节器(RR)包括N末端磷酸化接收域和C末端DNA结合域两部分]
Fig. 1 Structure of bacterial two-component regulatory systems[The two-component systems consist of two parts: histidine kinase (SK) for sensing and the response regulator (RR). A typical SK is a homodimer consisting of the N-terminal cytosolic domain, the periplasmic sensor domain, two transmembrane (TM) helixes, the signal transport domain, the catalytic domain, the dimeric/histidine phosphorylation transfer domain (DHp), and the C-terminal domain. RR consists of two parts: phosphorylated receiving domain and DNA-binding domain]
| 输入 | 天然宿主 | SK | RR | 输出 启动子 | 表现特点 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 光 | ||||||
| 紫外光 | 聚球藻PCC6803 | UirS | UirR | P csiR1 | 激活5倍 | [ |
| 蓝光 | 枯草芽孢杆菌, 日本血吸虫 | YF1 | FixJ | P fixK2 | 嵌合体与pDusk系统偶联时激活460倍 | [ |
| 绿光 | 聚球藻PCC6803 | CcaSmini#10 | CcaR | P cpcG2-172 | 激活600倍 | [ |
| 红光 | 聚球藻PCC6803 大肠杆菌 | Cph8* | OmpR | P ompF112 | 抑制80倍 | [ |
| 近红外光 | 大豆根瘤菌 | BphP1 | PpsR2 | PBr_ crtE | 激活2倍 | [ |
| pH | ||||||
| 酸性pH(<6.2) | 奥奈登斯链球菌 枯草芽孢杆菌 | SO-4387 | SO_4388REC-PsdRDBD 137 | P psdA110 | 用于检测小鼠的肠道炎症 | [ |
| 金属离子 | ||||||
| As3+(胞外) | 根癌土壤杆菌 | AioS | AioR | P aioB | 需要 AioX 内膜辅助蛋白 | [ |
| Ca2+(胞外) | 铜绿假单胞菌PAO1 | CarS | CarR | P carO | CARS与PhoQ有关 | [ |
| Cu+(胞外) | 大肠杆菌 | CusS | CusR | P cusC | 也被Ag+激活 | [ |
| Cu2+(胞内和胞外) | 聚球藻PCC6803 | CopS | CopR | P couM | CopS位于类囊体膜 | [ |
| Cu2+(胞外) | 黄曲霉 | CorS | CorR | P couA | — | [ |
| Fe2+,Fe3+(胞外) | 黏质沙雷氏菌 | RssA | RssB | P pvcA | 活性受天然产物2-异氰基-6,7-二羟基香豆素调节 | [ |
| K+(胞内及胞外) | 大肠杆菌 | KdpD | KdpE | P kdpF | K+抑制 | [ |
| U | 月柄杆菌 | UzcS | UzcR | P urcA | 通过与门耦合到UrpRS提高了灵敏度和特异性 | [ |
| Zn2+ | 大肠杆菌 | ZraS | ZraR | P zraP | P zraP 依赖σ54 | [ |
| 养分可利用性 | ||||||
| 硫代硫酸盐 | S. halifaxensis | ThsS | ThsR | P phsA342 | 成比例地被与DSS诱导的小鼠结肠炎症所激活 | [ |
| 连四硫酸盐 | S. baltica | TtrS | TtrR | P ttrB185-269 | 动态范围为100倍 | [ |
| 硝酸盐 | 大肠杆菌 | NarX | NarLREC-YdflDBD 131 | P ydfJ115 | 在枯草芽孢杆菌中被激活1300倍 | [ |
| 三甲胺氮氧化物(TMAO) | 大肠杆菌 | TorS | TorRREC-PsdRDBD137 | P psdA110 | DBD交换消除了O2对天然输出启动子的交叉抑制。需要周质TorT辅助蛋白 | [ |
| 氧化剂 | ||||||
| O2,H2O2,NO | 金黄色葡萄球菌 | AirS | AirR | P crtO | AirS需要一个[2Fe-2S]2+簇 | [ |
| 小分子代谢物 | ||||||
| α-酮戊二酸 (细胞外) | 铜绿假单胞菌PAO1 | MifS | MitR | P PA5530 | 激活10倍。对L-谷氨酸有微弱的响应 | [ |
| 丁醇 | 乙酰丁酸单胞菌 | BtrK | BtrR | P btrT | 参与丁醇的耐受性 | [ |
| 柠檬酸 | 肺炎克雷伯氏菌 | CitA | CitB | P citC | 需厌氧条件 | [ |
| 岩藻糖 | 大肠杆菌 | FusK | FusR | P z0461 | 岩藻糖抑制转录输出 | [ |
| 富马酸 | 大肠杆菌 | DcuSZ | OmpR | P ompC | 激活2倍 | [ |
| 葡萄糖-6-磷酸 | 大肠杆菌 | UhpB | UhpA | P uhpT99 | 需要UhpC内膜辅助蛋白 | [ |
| L-谷氨酸 | 铜绿假单胞菌PAO1 | AauS | AauR | P aatJ | 被L-天冬氨酸、谷氨酰胺和天冬酰胺微弱激活 | [ |
| 血红素(细胞外) | 金黄色葡萄球菌 | HssS | HssR | P hrtA | 激活100倍以上 | [ |
| 吲哚 | 大肠杆菌 | BaeS | BaeR | P arcD | CpxAR TCS的存在放大了对吲哚的响应 | [ |
| 苹果酸 | 枯草芽孢杆菌 | YufL | YufM | P maeN381 | 激活100倍 | [ |
| 甲醇 | 脱氮假单胞菌 大肠杆菌 | FlhS-EnvZ | OmpR | P ompC | 激活2倍 | [ |
| 丙酮酸(细胞外) | 大肠杆菌 | BtsS | BtsR | P yjiY | 泌尿道感染期间在泌尿致病性大肠杆菌中被激活 | [ |
| D-木糖(细胞外) | 拜氏梭菌 | LytS | YesN | P xylF | 外膜转运蛋白XylFⅡ识别D-木糖 | [ |
| 苯乙烯 | 假单胞菌菌株Y2 | StyS | StyR | P styA | [ | |
| 细菌间通信信号 | ||||||
| CaI-1[(S)-3羟基十三烷-4-酮] | 霍乱弧菌 | CqsS | LuxO | P tpqrr4 | 需要中间磷酸转移蛋白LuxU | [ |
| CSP(能力刺激肽) | 格登链球菌 | ComD | ComE | P comC | [ | |
| ComX(胞外信息素) | 枯草芽孢杆菌 | ComP | ComA | P srfA | [ | |
| 抗生素 | ||||||
| β-内酰胺 | 霍乱弧菌 | VxrA | VxrB | P murJ | 通常由细胞被膜损伤激活 | [ |
| 线霉菌素(膜内) | 枯草芽孢杆菌 | LnrJ | LnrK | P lnrL | 还可以检测到抗真菌多烯两性霉素B | [ |
| 万古霉素(胞外) | 腔血链球菌 | VanS | VanR | P vanJ | 磷酸化的VanR也激活VanSR操纵子 | [ |
| 抗菌肽 | ||||||
| 口腔致病菌变形链球菌产生的抗菌肽(胞外) | 链球菌A12 | PcfK | PcfR | P pcfF | 大约激活100倍 | [ |
| 杆菌肽(胞外) | 枯草芽孢杆菌 | LiaS | LiaR | P lial(opt) | 激活1000倍。需要辅膜蛋白LiaF | [ |
| Nisin(胞外) | 乳酸乳杆菌 | NisK | NisR | P nisA | 激活1000倍 | [ |
| 枯草蛋白(细胞外) | 枯草芽孢杆菌 | SpaK | SpaR | P spaS | 激活110倍 | [ |
| 低聚糖 | ||||||
| 阿拉伯半乳聚糖 | 双歧杆菌 | BT0267 | BT0267 | P BT0268 | BT0267是一种杂交的TCS,其中SK和RR融合在一起 | [ |
| 硫酸软骨素 | 双歧杆菌 | BT3334 | BT3334 | P BT3324 | BT3334是一种杂交的双组分系统 | [ |
| 黏蛋白多糖 | 铜绿假单胞菌 | GacS | GacA | P rsmY | 黏蛋白多聚糖是通过辅助组氨酸激酶rets感受到的 | [ |
| 双歧杆菌 | BT0366 | BT0366 | P BT0365 | BT0366是一种杂交的双组分系统 | [ | |
| 蛋白质 | ||||||
| PilA | 铜绿假单胞菌 | PilS | PilR | P pilA | PilA是主要的Ⅳ型菌毛蛋白 | [ |
| 宿主信号 | ||||||
| 哺乳动物感染过程中产生的抗菌肽、二价阳离子限制和酸性pH | 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌 | PhoQ | PhoP | P virK | — | [ |
| 肾上腺素,去甲肾上腺素 | 大肠杆菌 O157:H7 | QseC | QseB | P flhD | 被肾上腺素激活2倍,去甲肾上腺素抑制1.5倍 | [ |
| 吲哚-3-乙酸 (生长素) | P. phytofirmans PsJN | lacS | lacR1 | P iacA | 二氧吲哚-3-乙酸放大信号 | [ |
| 2-异戊烯基腺嘌呤(细胞分裂素) | X. campestris | PcrK | PcrR | P ctrA | 激活3倍 | [ |
| 植物伤口中存在的酚类物质、单糖和酸性pH | 根癌农杆菌 | VirA | VirG | P vir | 对单糖的感应需要周质辅助蛋白ChvE | [ |
| 反式玉米素(细胞分裂素) | 拟南芥, 大肠杆菌 | AQ4* | PhoP4* | P mgrB | AQ4*为拟南芥AHK4和大肠杆菌PhoQ的传感域嵌体,经改造与所有大肠杆菌双组分系统绝缘,可防止磷酸化串扰 | [ |
表1 基于双组分系统设计和构建的生物传感器
Table 1 Biosensors designed and developed based on bacterial two-component systems
| 输入 | 天然宿主 | SK | RR | 输出 启动子 | 表现特点 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 光 | ||||||
| 紫外光 | 聚球藻PCC6803 | UirS | UirR | P csiR1 | 激活5倍 | [ |
| 蓝光 | 枯草芽孢杆菌, 日本血吸虫 | YF1 | FixJ | P fixK2 | 嵌合体与pDusk系统偶联时激活460倍 | [ |
| 绿光 | 聚球藻PCC6803 | CcaSmini#10 | CcaR | P cpcG2-172 | 激活600倍 | [ |
| 红光 | 聚球藻PCC6803 大肠杆菌 | Cph8* | OmpR | P ompF112 | 抑制80倍 | [ |
| 近红外光 | 大豆根瘤菌 | BphP1 | PpsR2 | PBr_ crtE | 激活2倍 | [ |
| pH | ||||||
| 酸性pH(<6.2) | 奥奈登斯链球菌 枯草芽孢杆菌 | SO-4387 | SO_4388REC-PsdRDBD 137 | P psdA110 | 用于检测小鼠的肠道炎症 | [ |
| 金属离子 | ||||||
| As3+(胞外) | 根癌土壤杆菌 | AioS | AioR | P aioB | 需要 AioX 内膜辅助蛋白 | [ |
| Ca2+(胞外) | 铜绿假单胞菌PAO1 | CarS | CarR | P carO | CARS与PhoQ有关 | [ |
| Cu+(胞外) | 大肠杆菌 | CusS | CusR | P cusC | 也被Ag+激活 | [ |
| Cu2+(胞内和胞外) | 聚球藻PCC6803 | CopS | CopR | P couM | CopS位于类囊体膜 | [ |
| Cu2+(胞外) | 黄曲霉 | CorS | CorR | P couA | — | [ |
| Fe2+,Fe3+(胞外) | 黏质沙雷氏菌 | RssA | RssB | P pvcA | 活性受天然产物2-异氰基-6,7-二羟基香豆素调节 | [ |
| K+(胞内及胞外) | 大肠杆菌 | KdpD | KdpE | P kdpF | K+抑制 | [ |
| U | 月柄杆菌 | UzcS | UzcR | P urcA | 通过与门耦合到UrpRS提高了灵敏度和特异性 | [ |
| Zn2+ | 大肠杆菌 | ZraS | ZraR | P zraP | P zraP 依赖σ54 | [ |
| 养分可利用性 | ||||||
| 硫代硫酸盐 | S. halifaxensis | ThsS | ThsR | P phsA342 | 成比例地被与DSS诱导的小鼠结肠炎症所激活 | [ |
| 连四硫酸盐 | S. baltica | TtrS | TtrR | P ttrB185-269 | 动态范围为100倍 | [ |
| 硝酸盐 | 大肠杆菌 | NarX | NarLREC-YdflDBD 131 | P ydfJ115 | 在枯草芽孢杆菌中被激活1300倍 | [ |
| 三甲胺氮氧化物(TMAO) | 大肠杆菌 | TorS | TorRREC-PsdRDBD137 | P psdA110 | DBD交换消除了O2对天然输出启动子的交叉抑制。需要周质TorT辅助蛋白 | [ |
| 氧化剂 | ||||||
| O2,H2O2,NO | 金黄色葡萄球菌 | AirS | AirR | P crtO | AirS需要一个[2Fe-2S]2+簇 | [ |
| 小分子代谢物 | ||||||
| α-酮戊二酸 (细胞外) | 铜绿假单胞菌PAO1 | MifS | MitR | P PA5530 | 激活10倍。对L-谷氨酸有微弱的响应 | [ |
| 丁醇 | 乙酰丁酸单胞菌 | BtrK | BtrR | P btrT | 参与丁醇的耐受性 | [ |
| 柠檬酸 | 肺炎克雷伯氏菌 | CitA | CitB | P citC | 需厌氧条件 | [ |
| 岩藻糖 | 大肠杆菌 | FusK | FusR | P z0461 | 岩藻糖抑制转录输出 | [ |
| 富马酸 | 大肠杆菌 | DcuSZ | OmpR | P ompC | 激活2倍 | [ |
| 葡萄糖-6-磷酸 | 大肠杆菌 | UhpB | UhpA | P uhpT99 | 需要UhpC内膜辅助蛋白 | [ |
| L-谷氨酸 | 铜绿假单胞菌PAO1 | AauS | AauR | P aatJ | 被L-天冬氨酸、谷氨酰胺和天冬酰胺微弱激活 | [ |
| 血红素(细胞外) | 金黄色葡萄球菌 | HssS | HssR | P hrtA | 激活100倍以上 | [ |
| 吲哚 | 大肠杆菌 | BaeS | BaeR | P arcD | CpxAR TCS的存在放大了对吲哚的响应 | [ |
| 苹果酸 | 枯草芽孢杆菌 | YufL | YufM | P maeN381 | 激活100倍 | [ |
| 甲醇 | 脱氮假单胞菌 大肠杆菌 | FlhS-EnvZ | OmpR | P ompC | 激活2倍 | [ |
| 丙酮酸(细胞外) | 大肠杆菌 | BtsS | BtsR | P yjiY | 泌尿道感染期间在泌尿致病性大肠杆菌中被激活 | [ |
| D-木糖(细胞外) | 拜氏梭菌 | LytS | YesN | P xylF | 外膜转运蛋白XylFⅡ识别D-木糖 | [ |
| 苯乙烯 | 假单胞菌菌株Y2 | StyS | StyR | P styA | [ | |
| 细菌间通信信号 | ||||||
| CaI-1[(S)-3羟基十三烷-4-酮] | 霍乱弧菌 | CqsS | LuxO | P tpqrr4 | 需要中间磷酸转移蛋白LuxU | [ |
| CSP(能力刺激肽) | 格登链球菌 | ComD | ComE | P comC | [ | |
| ComX(胞外信息素) | 枯草芽孢杆菌 | ComP | ComA | P srfA | [ | |
| 抗生素 | ||||||
| β-内酰胺 | 霍乱弧菌 | VxrA | VxrB | P murJ | 通常由细胞被膜损伤激活 | [ |
| 线霉菌素(膜内) | 枯草芽孢杆菌 | LnrJ | LnrK | P lnrL | 还可以检测到抗真菌多烯两性霉素B | [ |
| 万古霉素(胞外) | 腔血链球菌 | VanS | VanR | P vanJ | 磷酸化的VanR也激活VanSR操纵子 | [ |
| 抗菌肽 | ||||||
| 口腔致病菌变形链球菌产生的抗菌肽(胞外) | 链球菌A12 | PcfK | PcfR | P pcfF | 大约激活100倍 | [ |
| 杆菌肽(胞外) | 枯草芽孢杆菌 | LiaS | LiaR | P lial(opt) | 激活1000倍。需要辅膜蛋白LiaF | [ |
| Nisin(胞外) | 乳酸乳杆菌 | NisK | NisR | P nisA | 激活1000倍 | [ |
| 枯草蛋白(细胞外) | 枯草芽孢杆菌 | SpaK | SpaR | P spaS | 激活110倍 | [ |
| 低聚糖 | ||||||
| 阿拉伯半乳聚糖 | 双歧杆菌 | BT0267 | BT0267 | P BT0268 | BT0267是一种杂交的TCS,其中SK和RR融合在一起 | [ |
| 硫酸软骨素 | 双歧杆菌 | BT3334 | BT3334 | P BT3324 | BT3334是一种杂交的双组分系统 | [ |
| 黏蛋白多糖 | 铜绿假单胞菌 | GacS | GacA | P rsmY | 黏蛋白多聚糖是通过辅助组氨酸激酶rets感受到的 | [ |
| 双歧杆菌 | BT0366 | BT0366 | P BT0365 | BT0366是一种杂交的双组分系统 | [ | |
| 蛋白质 | ||||||
| PilA | 铜绿假单胞菌 | PilS | PilR | P pilA | PilA是主要的Ⅳ型菌毛蛋白 | [ |
| 宿主信号 | ||||||
| 哺乳动物感染过程中产生的抗菌肽、二价阳离子限制和酸性pH | 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌 | PhoQ | PhoP | P virK | — | [ |
| 肾上腺素,去甲肾上腺素 | 大肠杆菌 O157:H7 | QseC | QseB | P flhD | 被肾上腺素激活2倍,去甲肾上腺素抑制1.5倍 | [ |
| 吲哚-3-乙酸 (生长素) | P. phytofirmans PsJN | lacS | lacR1 | P iacA | 二氧吲哚-3-乙酸放大信号 | [ |
| 2-异戊烯基腺嘌呤(细胞分裂素) | X. campestris | PcrK | PcrR | P ctrA | 激活3倍 | [ |
| 植物伤口中存在的酚类物质、单糖和酸性pH | 根癌农杆菌 | VirA | VirG | P vir | 对单糖的感应需要周质辅助蛋白ChvE | [ |
| 反式玉米素(细胞分裂素) | 拟南芥, 大肠杆菌 | AQ4* | PhoP4* | P mgrB | AQ4*为拟南芥AHK4和大肠杆菌PhoQ的传感域嵌体,经改造与所有大肠杆菌双组分系统绝缘,可防止磷酸化串扰 | [ |
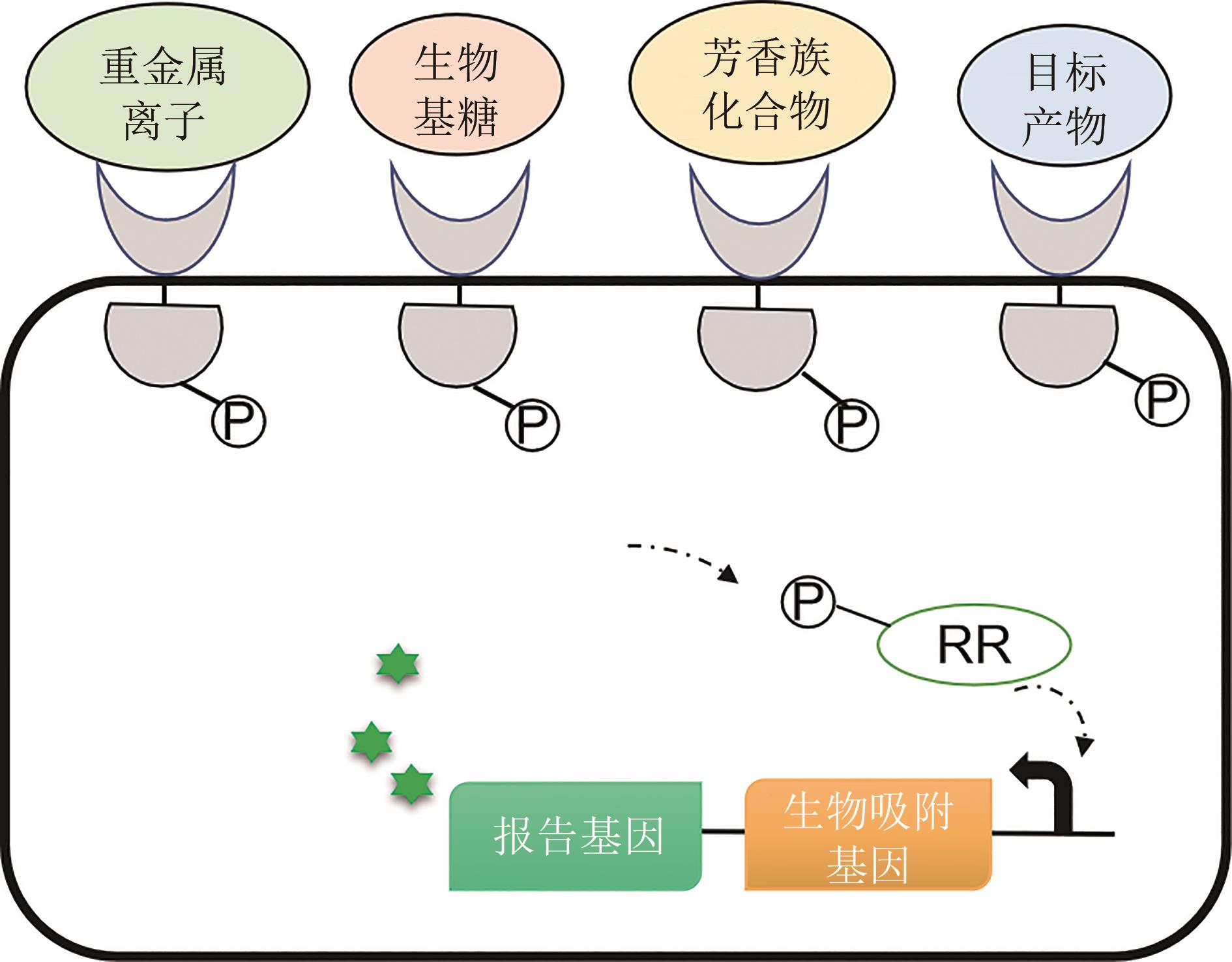
图3 双组分生物传感器在生物修复和微生物生物炼制中的应用(双组分系统可被设计为对重金属离子、生物基糖、芳香族化合物及目标化学品响应的基因编码的生物传感器)
Fig. 3 Applications of bacterial two-component biosensors in microbial bioremediation and biorefinery.(Bacterial two-component systems can be designed to genetically encode biosensors in response to heavy metal ions, sugars, aromatic compounds, and other targeted chemicals)

图4 双组分系统在疾病检测中的应用(将霍乱弧菌TcpP胆酸盐传感模块融合到CadC的DBD在大肠杆菌内构建了响应胆酸盐的生物传感器;将sfGFP置于双组分系统ThsS/ThsR的控制下构建了响应肠道内硫代硫酸盐的生物传感器)
Fig. 4 Applications of bacterial two-component systems in disease detection(The V. cholerae TcpP cholate sensing module is fused to the DBD of CadC to build a TCS in response to bile salt. A biosensor that responds to intestinal thiosulfate is constructed by placing sfGFP under the control of ThsS/ThsR)
| 47 | LOCKEY C, EDWARDS R J, ROPER D I, et al. The extracellular domain of two-component system sensor kinase VanS from Streptomyces coelicolor binds vancomycin at a newly identified binding site[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 5727. |
| 48 | LEE K, KASPAR J R, ROJAS-CARREÑO G, et al. A single system detects and protects the beneficial oral bacterium Streptococcus sp. A12 from a spectrum of antimicrobial peptides[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2021, 116(1): 211-230. |
| 49 | TOYMENTSEVA A A, SCHRECKE K, SHARIPOVA M R, et al. The LIKE system, a novel protein expression toolbox for Bacillus subtilis based on the liaI promoter[J].Microbial Cell Factories, 2012, 11: 143. |
| 50 | WOLF D, MASCHER T. The applied side of antimicrobial peptide-inducible promoters from Firmicutes bacteria: expression systems and whole-cell biosensors[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(11): 4817-4829. |
| 51 | MIMEE M, TUCKER A C, VOIGT C A, et al. Programming a human commensal bacterium, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, to sense and respond to stimuli in the murine gut microbiota[J]. Cell Systems, 2015, 1(1): 62-71. |
| 52 | WANG B X, WHEELER K M, CADY K C, et al. Mucin glycans signal through the sensor kinase RetS to inhibit virulence-associated traits in pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Current Biology, 2021, 31(1): 90-102.e7. |
| 53 | N D Ⅲ SCHWALM, TOWNSEND G E Ⅱ, GROISMAN E A. Multiple signals govern utilization of a polysaccharide in the gut bacterium Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron [J]. mBio, 2016, 7(5): e01342-16. |
| 54 | KILMURY S L N, BURROWS L L. Type Ⅳ pilins regulate their own expression via direct intramembrane interactions with the sensor kinase PilS[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(21): 6017-6022. |
| 55 | RICHARDS S M, STRANDBERG K L, CONROY M, et al. Cationic antimicrobial peptides serve as activation signals for the Salmonella Typhimurium PhoPQ and PmrAB regulons in vitro and in vivo [J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2012, 2: 102. |
| 56 | CLARKE M B, HUGHES D T, ZHU C R, et al. The QseC sensor kinase: a bacterial adrenergic receptor[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(27): 10420-10425. |
| 57 | DONOSO R, LEIVA-NOVOA P, ZÚÑIGA A, et al. Biochemical and genetic bases of indole-3-acetic acid (auxin phytohormone) degradation by the plant-growth-promoting rhizobacterium Paraburkholderia phytofirmans PsJN[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2017, 83(1): e01991-16. |
| 58 | WANG F F, CHENG S T, WU Y, et al. A bacterial receptor PcrK senses the plant hormone cytokinin to promote adaptation to oxidative stress[J]. Cell Reports, 2017, 21(10): 2940-2951. |
| 59 | LIN Y H, DANIEL PIERCE B, FANG F, et al. Role of the VirA histidine autokinase of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in the initial steps of pathogenesis[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2014, 5: 195. |
| 60 | MCCLUNE C J, ALVAREZ-BUYLLA A, VOIGT C A, et al. Engineering orthogonal signalling pathways reveals the sparse occupancy of sequence space[J]. Nature, 2019, 574(7780): 702-706. |
| 61 | MIMEE M, NADEAU P, HAYWARD A, et al. An ingestible bacterial-electronic system to monitor gastrointestinal health[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6391): 915-918. |
| 62 | DUTTA A, RUDRA P, BANIK S K, et al. Evidence of robustness in a two-component system using a synthetic circuit[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2020, 202(4): e00672-19. |
| 63 | LANDRY B P, PALANKI R, DYULGYAROV N, et al. Phosphatase activity tunes two-component system sensor detection threshold[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1433. |
| 64 | PODGORNAIA A I, LAUB M T. Determinants of specificity in two-component signal transduction[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2013, 16(2): 156-162. |
| 65 | LAZAR J T, TABOR J J. Bacterial two-component systems as sensors for synthetic biology applications[J]. Current Opinion in Systems Biology, 2021, 28: 100398. |
| 66 | GREBE T W, STOCK J. Bacterial chemotaxis: the five sensors of a bacterium[J]. Current Biology, 1998, 8(5): R154-R157. |
| 67 | WHITAKER W R, DAVIS S A, ARKIN A P, et al. Engineering robust control of two-component system phosphotransfer using modular scaffolds[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(44): 18090-18095. |
| 68 | GAO R, BOUILLET S, STOCK A M. Structural basis of response regulator function[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2019, 73: 175-197. |
| 69 | HANSEN J, MAILAND E, SWAMINATHAN K K, et al. Transplantation of prokaryotic two-component signaling pathways into mammalian cells[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(44): 15705-15710. |
| 70 | MAZÉ A, BENENSON Y. Artificial signaling in mammalian cells enabled by prokaryotic two-component system[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2020, 16(2): 179-187. |
| 71 | RAVIKUMAR S, YOO I K, LEE S Y, et al. A study on the dynamics of the zraP gene expression profile and its application to the construction of zinc adsorption bacteria[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2011, 34(9): 1119-1126. |
| 72 | Dı́AZ E, PRIETO M A. Bacterial promoters triggering biodegradation of aromatic pollutants[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2000, 11(5): 467-475. |
| 73 | RUTTER J W, DEKKER L, FEDOREC A J H, et al. Engineered acetoacetate-inducible whole-cell biosensors based on the AtoSC two-component system[J]. Biotechnology Biengineering, 2021, 118(11); 4278-4289. |
| 74 | SKERKER J M, PERCHUK B S, SIRYAPORN A, et al. Rewiring the specificity of two-component signal transduction systems[J]. Cell, 2008, 133(6): 1043-1054. |
| 1 | BOURRET R B, SILVERSMITH R E. Two-component signal transduction[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2010, 13(2): 113-115. |
| 2 | ULRICH L E, ZHULIN I B. The MiST2 database: a comprehensive genomics resource on microbial signal transduction[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 38(): D401-D407. |
| 3 | 杨璐, 吴楠, 白茸茸, 等. 基因回路型全细胞微生物传感器的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6): 1061-1080. |
| YANG L, WU N, BAI R R, et al. Design, optimization and application of whole-cell microbial biosensors with engineered genetic circuits[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6): 1061-1080. | |
| 4 | MEYER A J, SEGALL-SHAPIRO T H, GLASSEY E, et al. Escherichia coli "Marionette" strains with 12 highly optimized small-molecule sensors[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(2): 196-204. |
| 5 | 吴一凡, 林晟豪, 许文涛. 小分子靶标的核糖开关生物传感器研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2022, 12(2): 168-175. |
| WU Y F, LIN S H, XU W T. Research progress of riboswitch biosensors for small molecule target[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(2): 168-175. | |
| 6 | RAVIKUMAR S, BAYLON M G, PARK S J, et al. Engineered microbial biosensors based on bacterial two-component systems as synthetic biotechnology platforms in bioremediation and biorefinery[J].Microbial Cell Factories, 2017, 16: 62. |
| 7 | RAVIKUMAR S, YOO I K, LEE S Y, et al. Construction of copper removing bacteria through the integration of two-component system and cell surface display[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2011, 165(7): 1674-1681. |
| 8 | ANTUNES M S, MOREY K J, SMITH J J, et al. Programmable ligand detection system in plants through a synthetic signal transduction pathway[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(1): e16292. |
| 9 | LIM H G, JANG S, JANG S, et al. Design and optimization of genetically encoded biosensors for high-throughput screening of chemicals[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2018, 54: 18-25. |
| 10 | 杨慧勤. 富马酸响应型双组分生物传感器的设计与优化[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2022. |
| YANG H Q. Design and optimization of fumaric acid responsive two-component biosensor[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2022. | |
| 11 | RAVIKUMAR S, DAVID Y, PARK S J, et al. A chimeric two-component regulatory system-based Escherichia coli biosensor engineered to detect glutamate[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2018, 186(2): 335-349. |
| 12 | RAMAKRISHNAN P, TABOR J J. Repurposing Synechocystis PCC6803 UirS-UirR as a UV-violet/green photoreversible transcriptional regulatory tool in E. coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(7): 733-740. |
| 13 | OHLENDORF R, VIDAVSKI R R, ELDAR A, et al. From dusk till dawn: one-plasmid systems for light-regulated gene expression[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2012, 416(4): 534-542. |
| 14 | ONG N T, TABOR J J. A miniaturized Escherichia coli green light sensor with high dynamic range[J]. ChemBioChem, 2018, 19(12): 1255-1258. |
| 15 | SCHMIDL S R, SHETH R U, WU A, et al. Refactoring and optimization of light-switchable Escherichia coli two-component systems[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2014, 3(11): 820-831. |
| 16 | ONG N T, OLSON E J, TABOR J J. Engineering an E. coli near-infrared light sensor[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(1): 240-248. |
| 17 | CARTWRIGHT I M, DOWDELL A S, LANIS J M, et al. Mucosal acidosis elicits a unique molecular signature in epithelia and intestinal tissue mediated by GPR31-induced CREB phosphorylation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(20): e2023871118. |
| 18 | LIU G H, LIU M Y, KIM E H, et al. A periplasmic arsenite-binding protein involved in regulating arsenite oxidation[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 14(7): 1624-1634. |
| 19 | GURAGAIN M, KING M M, WILLIAMSON K S, et al. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 two-component regulator CarSR regulates calcium homeostasis and calcium-induced virulence factor production through its regulatory targets CarO and CarP[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2016, 198(6): 951-963. |
| 20 | GUDIPATY S A, LARSEN A S, RENSING C, et al. Regulation of Cu(I)/Ag(I) efflux genes in Escherichia coli by the sensor kinase CusS[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2012, 330(1): 30-37. |
| 21 | GINER-LAMIA J, LÓPEZ-MAURY L, REYES J C, et al. The CopRS two-component system is responsible for resistance to copper in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803[J]. Plant Physiology, 2012, 159(4): 1806-1818. |
| 22 | SÁNCHEZ-SUTIL M C, MARCOS-TORRES F J, PÉREZ J, et al. Dissection of the sensor domain of the copper-responsive histidine kinase CorS from Myxococcus xanthus [J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2016, 8(3): 363-370. |
| 23 | LIN C S, TSAI Y H, CHANG C J, et al. An iron detection system determines bacterial swarming initiation and biofilm formation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 36747. |
| 24 | GANESH I, RAVIKUMAR S, LEE S H, et al. Engineered fumarate sensing Escherichia coli based on novel chimeric two-component system[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2013, 168(4): 560-566. |
| 25 | PARK D M, TAFFET M J. Combinatorial sensor design in Caulobacter crescentus for selective environmental uranium detection[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(4): 807-817. |
| 26 | PETIT-HÄRTLEIN I, ROME K, DE ROSNY E, et al. Biophysical and physiological characterization of ZraP from Escherichia coli, the periplasmic accessory protein of the atypical ZraSR two-component system[J]. The Biochemical Journal, 2015, 472(2): 205-216. |
| 27 | DAEFFLER K N M, GALLEY J D, SHETH R U, et al. Engineering bacterial thiosulfate and tetrathionate sensors for detecting gut inflammation[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2017, 13(4): 923. |
| 28 | SCHMIDL S R, EKNESS F, SOFJAN K, et al. Rewiring bacterial two-component systems by modular DNA-binding domain swapping[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(7): 690-698. |
| 29 | SUN F, JI Q J, JONES M B, et al. AirSR, a [2Fe-2S] cluster-containing two-component system, mediates global oxygen sensing and redox signaling in staphylococcus aureus[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(1): 305-314. |
| 30 | SARWAR Z, WANG M X, LUNDGREN B R, et al. MifS, a DctB family histidine kinase, is a specific regulator of α-ketoglutarate response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1[J]. Microbiology, 2020, 166(9): 867-879. |
| 31 | YANG Y P, LANG N N, ZHANG L, et al. A novel regulatory pathway consisting of a two-component system and an ABC-type transporter contributes to butanol tolerance in Clostridium acetobutylicum [J].Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(11): 5011-5023. |
| 32 | YAMAMOTO K, MATSUMOTO F, OSHIMA T, et al. Anaerobic regulation of citrate fermentation by CitAB in Escherichia coli [J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 2008, 72(11): 3011-3014. |
| 33 | PACHECO A R, CURTIS M M, RITCHIE J M, et al. Fucose sensing regulates bacterial intestinal colonization[J]. Nature, 2012, 492(7427): 113-117. |
| 34 | SELVAMANI V, GANESH I, MARUTHAMUTHU M K, et al. Engineering chimeric two-component system into Escherichia coli from Paracoccus denitrificans to sense methanol[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2017, 22(3): 225-230. |
| 35 | OLEKHNOVICH I N, KADNER R J. Mutational scanning and affinity cleavage analysis of UhpA-binding sites in the Escherichia coli uhpT promoter[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2002, 184(10): 2682-2691. |
| 36 | LUNDGREN B R, SHOYTUSH J M, SCHEEL R A, et al. Utilization of L-glutamate as a preferred or sole nutrient in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 depends on genes encoding for the enhancer-binding protein AauR, the sigma factor RpoN and the transporter complex AatJQMP[J].BMC Microbiology, 2021, 21(1): 83. |
| 37 | HIRAKAWA H, INAZUMI Y, MASAKI T, et al. Indole induces the expression of multidrug exporter genes in Escherichia coli [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2005, 55(4): 1113-1126. |
| 38 | TANAKA K, KOBAYASHI K, OGASAWARA N. The Bacillus subtilis YufLM two-component system regulates the expression of the malate transporters MaeN (YufR) and YflS, and is essential for utilization of malate in minimal medium[J]. Microbiology, 2003, 149(9): 2317-2329. |
| 39 | BEHR S, KRISTOFICOVA I, WITTING M, et al. Identification of a high-affinity pyruvate receptor in Escherichia coli [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 1388. |
| 40 | SUN Z, CHEN Y X, YANG C, et al. A novel three-component system-based regulatory model for D-xylose sensing and transport in Clostridium beijerinckii [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2015, 95(4): 576-589. |
| 41 | VELASCO A, ALONSO S, GARCÍA J L, et al. Genetic and functional analysis of the styrene catabolic cluster of Pseudomonas sp. strain Y2[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1998, 180(5): 1063-1071. |
| 42 | JAYARAMAN P, HOLOWKO M B, YEOH J W, et al. Repurposing a two-component system-based biosensor for the killing of Vibrio cholerae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(7): 1403-1415. |
| 43 | DAVEY L, HALPERIN S A, LEE S F. Mutation of the thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase SdbA activates the CiaRH two-component system, leading to bacteriocin expression shutdown in streptococcus gordonii[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2016, 198(2): 321-331. |
| 44 | GUAN C R, CUI W J, CHENG J T, et al. Construction and development of an auto-regulatory gene expression system in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 150. |
| 45 | SHIN J H, CHOE D, RANSEGNOLA B, et al. A multifaceted cellular damage repair and prevention pathway promotes high-level tolerance to β-lactam antibiotics[J]. EMBO Reports, 2021, 22(2): e51790. |
| 46 | REVILLA-GUARINOS A, DÜRR F, POPP P F, et al. Amphotericin B specifically induces the two-component system LnrJK: development of a novel whole-cell biosensor for the detection of amphotericin-like polyenes[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 2022. |
| [1] | 郭姝媛, 张倩楠, 姑丽克孜·买买提热夏提, 杨一群, 于涛. 液体生物燃料合成与炼制的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 18-44. |
| [2] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [3] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | 郑益坤, 郑婕, 胡国鹏. 光遗传学工具在学习记忆中的应用研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 87-104. |
| [7] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [8] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [9] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [10] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [11] | 赵亮, 李振帅, 付丽平, 吕明, 王士安, 张全, 刘立成, 李福利, 刘自勇. 生物转化一碳化合物原料产油脂与单细胞蛋白研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [12] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [13] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [14] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [15] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

