合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (6): 1404-1418.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-032
生物高纯精草:高光学纯L-草铵膦生物制造的创新与发展
程峰1,2, 邹树平1,2, 徐建妙1,2, 汤恒1,2, 薛亚平1,2, 郑裕国1,2
- 1.浙江工业大学生物工程学院,全省生物有机合成重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310014
2.浙江工业大学,手性生物制造国家地方联合工程研究中心,浙江 杭州 310014
-
收稿日期:2024-04-02修回日期:2024-06-25出版日期:2024-12-31发布日期:2025-01-10 -
通讯作者:薛亚平 -
作者简介:程峰 (1986—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为工业酶创制与手性生物合成。 E-mail:fengcheng@zjut.edu.cn薛亚平 (1975—),男,教授,博士生导师,手性生物制造国家地方联合工程研究中心副主任。研究方向为绿色生物制造。 E-mail:xyp@zjut.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFC2102000);国家优秀青年基金(22222811)
BioHPP®: a benchmark of biomanufacturing for high optically pure L-phosphinothricin
CHENG Feng1,2, ZOU Shuping1,2, XU Jianmiao1,2, TANG Heng1,2, XUE Yaping1,2, ZHENG Yuguo1,2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Synthesis of Zhejiang Province,College of Biotechnology and Bioengineering,Zhejiang University of Technology,Hangzhou 310014,Zhejiang,China
2.The National and Local Joint Engineering Research Center for Biomanufacturing of Chiral Chemicals,Zhejiang University of Technology,Hangzhou 310014,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2024-04-02Revised:2024-06-25Online:2024-12-31Published:2025-01-10 -
Contact:XUE Yaping
摘要:
草铵膦是全球三大除草剂之一,具有广谱、高活性、非选择性等特点,市场前景被广泛看好。然而,草铵膦具有两种对映异构体(
中图分类号:
引用本文
程峰, 邹树平, 徐建妙, 汤恒, 薛亚平, 郑裕国. 生物高纯精草:高光学纯L-草铵膦生物制造的创新与发展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1404-1418.
CHENG Feng, ZOU Shuping, XU Jianmiao, TANG Heng, XUE Yaping, ZHENG Yuguo. BioHPP®: a benchmark of biomanufacturing for high optically pure L-phosphinothricin[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1404-1418.
| 条目 | 热裂解-ACA工艺(“气相合成”) | 铝法-Strecker工艺(“铝法合成”) | 格氏-Strecker工艺(“格氏合成”) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 连续化程度 | 完全连续化 | 半连续化 | 间歇化 |
| 工艺特点 | 连续化程度高 对反应器装置要求高 | 工艺简单 易燃易爆,使用剧毒氰化物,分离纯化困难 | 工艺简单 易燃易爆,使用剧毒氰化物,分离纯化困难 |
| 三废排放 | 固废量少,可用来制备高附加值产品 | 固废量大 | 废水量大 |
| 生产成本 | 5万~6万 元/吨 | 6万~7万 元/吨 | 7万~8万元/吨 |
表1 D,L-草铵膦三种生产工艺比较
Table 1 Comparison of three production processes for D,L-PPT
| 条目 | 热裂解-ACA工艺(“气相合成”) | 铝法-Strecker工艺(“铝法合成”) | 格氏-Strecker工艺(“格氏合成”) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 连续化程度 | 完全连续化 | 半连续化 | 间歇化 |
| 工艺特点 | 连续化程度高 对反应器装置要求高 | 工艺简单 易燃易爆,使用剧毒氰化物,分离纯化困难 | 工艺简单 易燃易爆,使用剧毒氰化物,分离纯化困难 |
| 三废排放 | 固废量少,可用来制备高附加值产品 | 固废量大 | 废水量大 |
| 生产成本 | 5万~6万 元/吨 | 6万~7万 元/吨 | 7万~8万元/吨 |
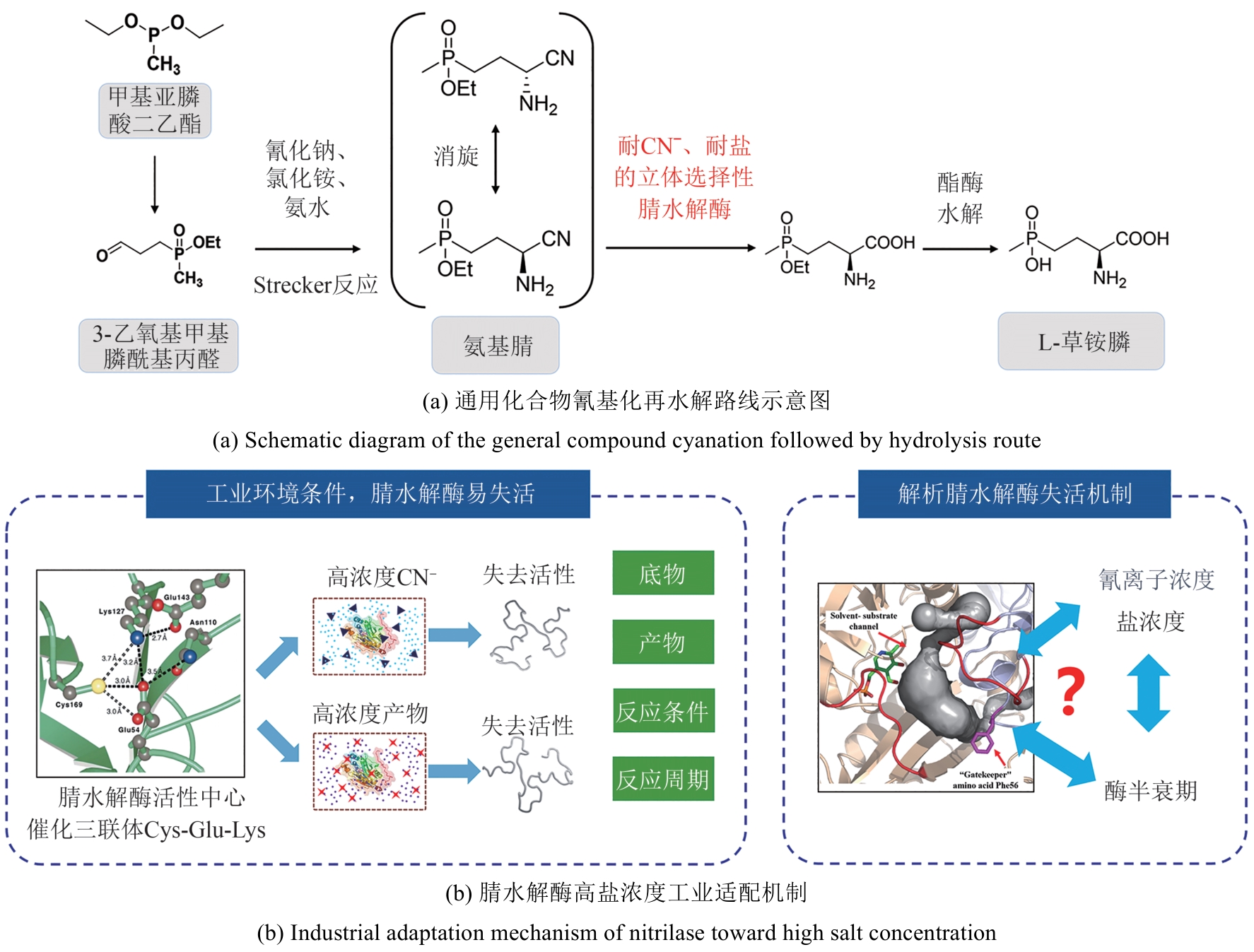
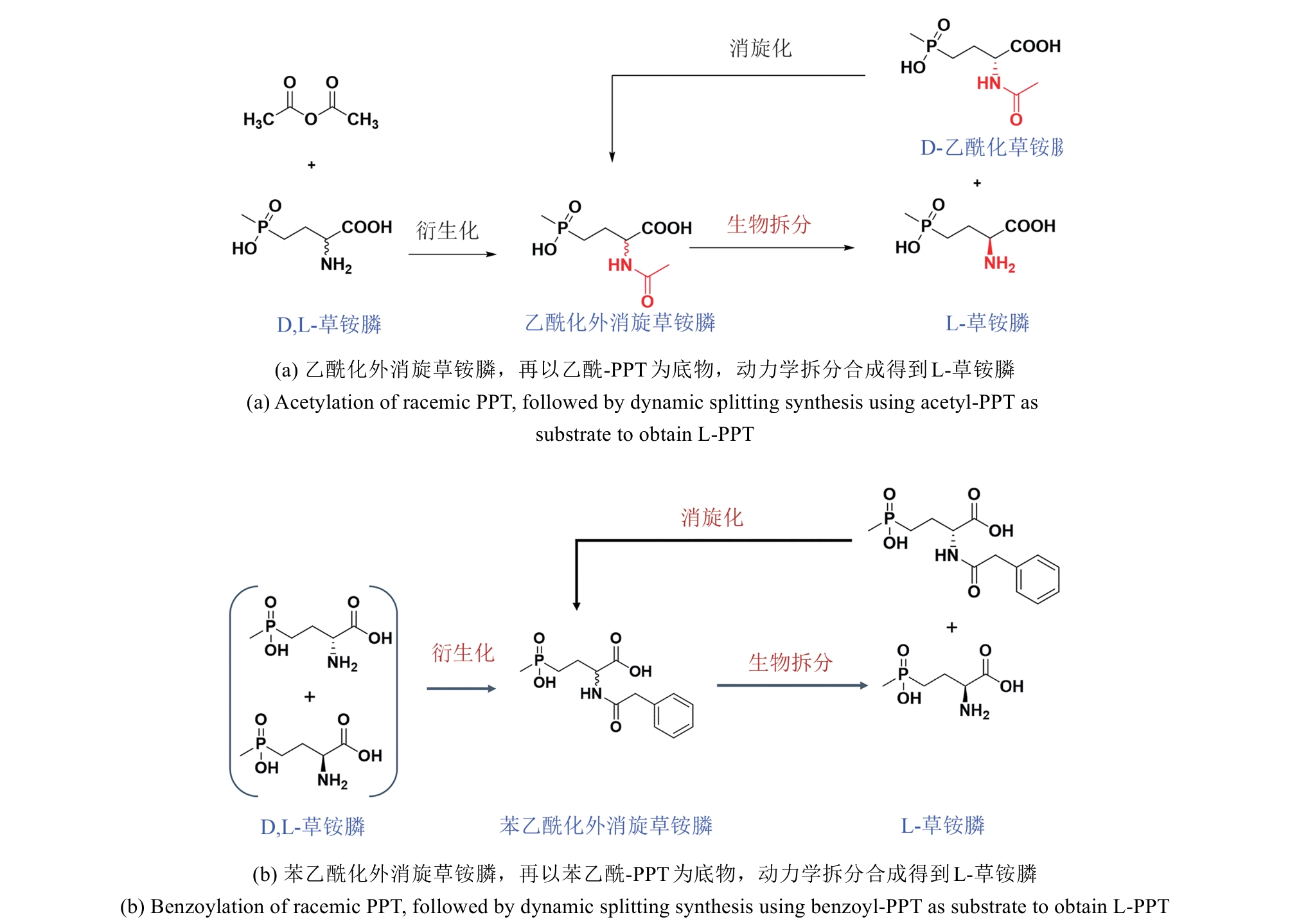
图4 通用化合物氰基化再水解路线合成L-草铵膦路线图与腈水解酶工业适配
Fig. 4 Diagram of L-PPT synthesis route via cyanation and hydrolysis of general compounds and industrial adaptation of nitrilase
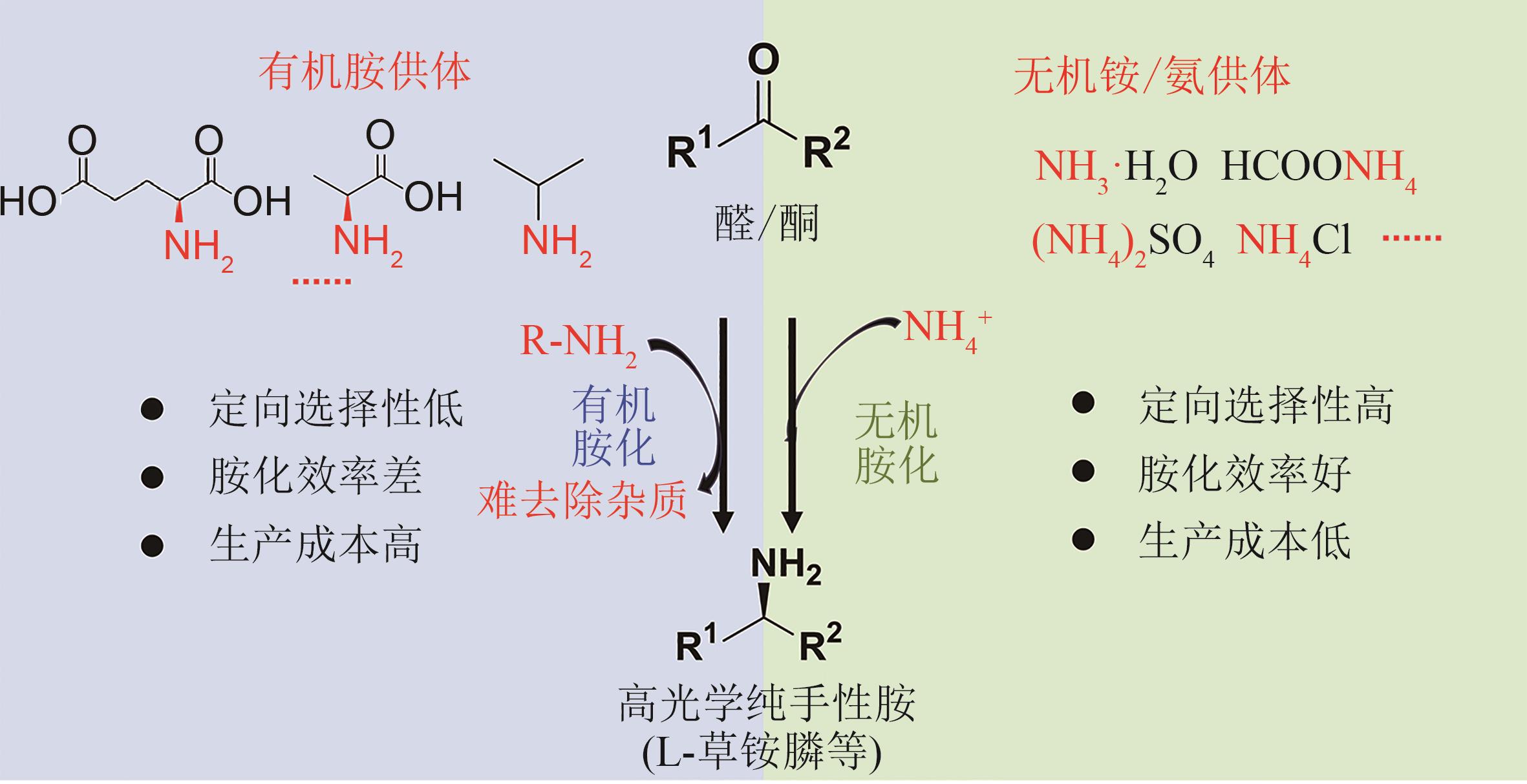
| 条目 | 通用化合物氰基化再水解路线 | 外消旋 混旋体合成-去消旋化路线 | 从常用化学品合成 | 从头合成高丝氨酸再化学合成路线 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物拆分 | 生物有机胺胺化 | 生物无机氨胺化 | 生物无机氨胺化 | 生物有机胺胺化 | |||
生物 催化剂 | 腈水解酶等 | 酰化酶、酰胺酶等 | 氧化酶/多个转氨酶 | 脱氢酶等 | 转氨酶 | 生物发酵 | |
| 供体 | 无 | 无 | 3~4倍当量有机胺 | 无机氨 | 无机氨 | 2~4倍当量有机胺 | 有机膦 |
| 底物 | 氨基腈 | 草铵膦衍生物 | 潜手性酮 | 葡萄糖 | |||
转化率 产物e.e.值 | 86% >99% | <50% >99% | 90%~99% >99% | 100% >99% | <100% >99% | 90%~99% >99% | >99% |
分离 纯化 | 容易 | 容易 | 困难 | 容易 | 容易 | 困难 | 容易 |
| (原粉、水剂) | (原粉、水剂) | (水剂) | (原粉、水剂) | (原粉、水剂) | (水剂) | (原粉、水剂) | |
表2 L-草铵膦四大技术路线比较
Table 2 Comparison of four technical routes for L-PPT
| 条目 | 通用化合物氰基化再水解路线 | 外消旋 混旋体合成-去消旋化路线 | 从常用化学品合成 | 从头合成高丝氨酸再化学合成路线 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物拆分 | 生物有机胺胺化 | 生物无机氨胺化 | 生物无机氨胺化 | 生物有机胺胺化 | |||
生物 催化剂 | 腈水解酶等 | 酰化酶、酰胺酶等 | 氧化酶/多个转氨酶 | 脱氢酶等 | 转氨酶 | 生物发酵 | |
| 供体 | 无 | 无 | 3~4倍当量有机胺 | 无机氨 | 无机氨 | 2~4倍当量有机胺 | 有机膦 |
| 底物 | 氨基腈 | 草铵膦衍生物 | 潜手性酮 | 葡萄糖 | |||
转化率 产物e.e.值 | 86% >99% | <50% >99% | 90%~99% >99% | 100% >99% | <100% >99% | 90%~99% >99% | >99% |
分离 纯化 | 容易 | 容易 | 困难 | 容易 | 容易 | 困难 | 容易 |
| (原粉、水剂) | (原粉、水剂) | (水剂) | (原粉、水剂) | (原粉、水剂) | (水剂) | (原粉、水剂) | |
| 酶类 | 国际酶学编号 | 辅酶再生底物 | 辅酶再生产物 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDH | EC 1.2.1.2 | 甲酸(铵) | CO2和水 | 副产物CO2无毒具挥发性易于分离 | 催化效率低,底物亲和力差,具NAD+特异性 |
| GDH | EC 1.1.1.47 | 葡萄糖 | 葡萄糖酸 | 催化活力高,辅底物价格低廉 | 副产物易溶于水难以分离,反应pH降低需要调控 |
| ADH | EC 1.1.1.1-2 | 异丙醇 | 丙酮 | 催化活力较高,副产物沸点低,易除去 | 反应可逆,副产物可能会影响酶活 |
表3 辅酶再生酶的分类及特点
Table 3 Classification and characteristics of coenzyme regeneration enzymes
| 酶类 | 国际酶学编号 | 辅酶再生底物 | 辅酶再生产物 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDH | EC 1.2.1.2 | 甲酸(铵) | CO2和水 | 副产物CO2无毒具挥发性易于分离 | 催化效率低,底物亲和力差,具NAD+特异性 |
| GDH | EC 1.1.1.47 | 葡萄糖 | 葡萄糖酸 | 催化活力高,辅底物价格低廉 | 副产物易溶于水难以分离,反应pH降低需要调控 |
| ADH | EC 1.1.1.1-2 | 异丙醇 | 丙酮 | 催化活力较高,副产物沸点低,易除去 | 反应可逆,副产物可能会影响酶活 |
| 1 | HOERLEIN G. Glufosinate (phosphinothricin), a natural amino acid with unexpected herbicidal properties[M/OL]//WARE G W. Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. New York: Springer New York, 1994, 138: 73-145 [2024-04-01]. . |
| 2 | TAKANO H K, DAYAN F E. Glufosinate-ammonium: a review of the current state of knowledge[J]. Pest Management Science, 2020, 76(12): 3911-3925. |
| 3 | BAYER E, GUGEL K H, HÄGELE K, et al. Metabolic products of microorganisms. 98. Phosphinothricin and phosphinothricyl-alanyl-analine[J]. Helvetica Chimica Acta, 1972, 55(1): 224-239. |
| 4 | ZHOU C Z, LUO X X, CHEN N Y, et al. C-P natural products as next-generation herbicides: chemistry and biology of glufosinate[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68(11): 3344-3353. |
| 5 | XUE Y P, CAO C H, ZHENG Y G. Enzymatic asymmetric synthesis of chiral amino acids[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(4): 1516-1561. |
| 6 | CHENG F, LI H, ZHANG K, et al. Tuning amino acid dehydrogenases with featured sequences for L-phosphinothricin synthesis by reductive amination[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2020, 312: 35-43. |
| 7 | 李嘉宁, 赵静喃, 孟庆伟. 草铵膦制备工艺研究进展[J]. 农药, 2020, 59(12): 859-866. |
| LI J N, ZHAO J N, MENG Q W. Progress in synthesis of glufosinate[J]. Agrochemicals, 2020, 59(12): 859-866. | |
| 8 | 范立攀, 杨达, 史秀肖, 等. 一种连续化生产草铵膦的工艺与设备: CN111659330B[P]. 2021-05-07. |
| FAN L P, YANG D, SHI X X, ET AL. PROCESS AND EQUIPMENT FOR CONTINUOUS PRODUCTION OF GLUFOSINATE: CN111659330B[P]. 2021-05-07. | |
| 9 | 朱凤香, 吴永刚, 沈德隆. 甲基二氯化膦的合成方法[J]. 农药, 2002, 41(5): 46-47, 45. |
| ZHU F X, WU Y G, SHEN D L. Synthesis methods of CH3PCl2 [J]. Agrochemicals, 2002, 41(5): 46-47, 45. | |
| 10 | MAIER L, RIST G, LEA P J. Synthesis and properties of phosphinothricin derivatives[J]. Phosphorus and Sulfur and the Related Elements, 1983, 18(1/2/3): 349-352. |
| 11 | 周曙光, 秦龙, 姜胜宝, 等. 一种草甘膦与草铵膦的联产技术: CN113201013B[P]. 2022-03-29. |
| ZHOU S H, QIN L, JIANG S B, ET AL. A CO-PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGY OF GLYPHOSATE AND GLUFOSINATE: CN113201013B[P]. 2022-03-29. | |
| 12 | TAKEMATSU T, KONNAL M, TACHIBANA K, et al. Herbicidal Compositions: US4265654[P]. 1981-05-05. |
| 13 | BERIAULT J N, HORSMAN G P, DEVINE M D. Phloem transport of D,L-glufosinate and acetyl-L-glufosinate in glufosinate-resistant and-susceptible Brassica napus [J]. Plant Physiology, 1999, 121(2): 619-628. |
| 14 | 范立攀, 史秀肖, 唐兴敏, 等. D-草铵膦的除草活性研究[J]. 世界农药, 2022, 44(3): 53-56. |
| FAN L P, SHI X X, TANG X M, et al. The herbicidal activity of D-glufosinate[J]. World Pesticide, 2022, 44(3): 53-56. | |
| 15 | 董文凯, 柴洪伟, 解银萍, 等. 化学法合成精草铵膦的研究进展[J]. 现代农药, 2016, 15(5): 26-29. |
| DONG W K, CHAI H W, XIE Y P, et al. Progress in chemosynthesis of glufosinate-P[J]. Modern Agrochemicals, 2016, 15(5): 26-29. | |
| 16 | SURESH A, SHRAVAN RAMGOPAL D, PANCHAMOORTHY GOPINATH K, et al. Recent advancements in the synthesis of novel thermostable biocatalysts and their applications in commercially important chemoenzymatic conversion processes[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 323: 124558. |
| 17 | LIU H L, YI P H, WU J M, et al. Identification of a novel thermostable transaminase and its application in L-phosphinothricin biosynthesis[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2024, 108(1): 184. |
| 18 | 徐建妙, 李方龙, 郑裕国, 等. 一种手性N-苯乙酰氨基酸及其衍生物的消旋方法: CN109456220B[P]. 2021-10-08. |
| XU J M, LI F L, ZHENG Y G, et al. A METHOD FOR RACEMIZING CHIRAL N-BENZOYL AMINO ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES: CN109456220B[P]. 2021-10-08. | |
| 19 | 薛亚平, 程峰, 曹成浩, 等. 一种生物酶法去消旋化制备L-草铵膦的方法、草铵膦脱氢酶突变体及应用: CN111363775B[P]. 2022-08-05. |
| XUE Y P, CHENG F, CAO C H, et al. METHOD FOR ENANTIOSELECTIVE PREPARATION OF L-GLUFOSINATE USING BIOCATALYSIS, MUTANT OF GLUFOSINATE DEHYDROGENASE, AND APPLICATION THEREOF: CN111363775B[P]. 2022-08-05. | |
| 20 | 薛亚平, 程峰, 李恒, 等. 一种氨基酸脱氢酶突变体及其在合成l-草铵膦中的应用: CN109609474B[P]. 2020-07-28. |
| XUE Y P, CHENG F, LI H, et al. AMINO ACID DEHYDROGENASE MUTANT AND ITS APPLICATION IN SYNTHESIZING L-GLUFOSINATE: CN109609474B[P]. 2020-07-28. | |
| 21 | 薛亚平, 程峰, 王柳玉, 等. 一种D-氨基酸氧化酶突变体及其应用: CN109576236B[P]. 2019-12-17. |
| XUE YAPING, CHENG FENG, WANG LIUYU, et al. D-AMINO ACID OXIDASE MUTANT AND ITS APPLICATION: CN109576236B[P]. 2019-12-17. | |
| 22 | 薛亚平, 毛杰, 程峰, 等. L-草铵膦粉剂的制备方法: CN112028931B[P]. 2021-05-11. |
| XUE Y P, MAO J, CHENG F, et al. METHOD FOR PREPARING L-GLUFOSINATE POWDER: CN112028931B[P]. 2021-05-11. | |
| 23 | 薛亚平, 郑裕国, 曹成浩, 等. 一种利用化学-酶法生产L-草铵膦的方法: CN108690854B[P]. 2022-03-18. |
| XUE Y P, ZHENG Y G, CAO C H, et al. METHOD FOR PRODUCING L-GLUFOSINATE USING CHEMICAL-ENZYMATIC APPROACH: CN108690854B[P]. 2022-03-18. | |
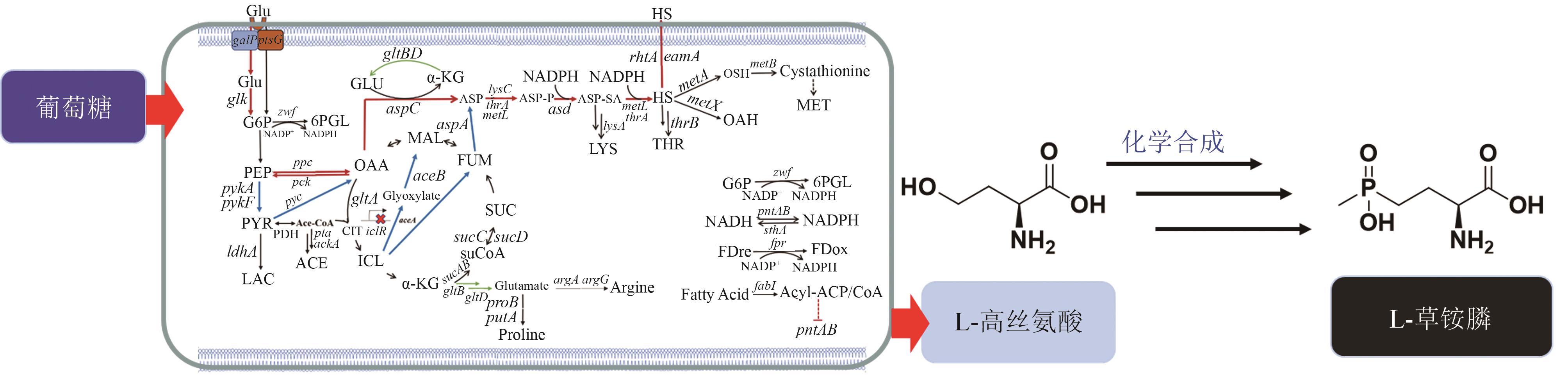
| 24 | 张博, 姚臻豪, 柳志强, 等. 代谢工程改造大肠杆菌生产L-高丝氨酸[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37(4): 1287-1297. |
| ZHANG B, YAO Z H, LIU Z Q, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for L-homoserine production[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37(4): 1287-1297. | |
| 25 | 程峰, 张铧月, 薛亚平, 等. 天冬氨酸氧化酶突变体、工程菌及其在氧化-还原偶联制备精草铵膦中的应用: CN111909907B[P]. 2022-05-24. |
| CHENG F, ZHANG H Y, XUE Y P, et al. MUTANT OF ASPARTATE OXIDASE, ENGINEERED BACTERIA, AND THEIR APPLICATION IN THE OXIDATIVE-REDUCTIVE COUPLING SYNTHESIS OF GLUFOSINATE: CN111909907B[P]. 2022-05-24. | |
| 26 | KANG X M, CAI X, LIU Z Q, et al. Identification and characterization of an amidase from Leclercia adecarboxylata for efficient biosynthesis of L-phosphinothricin[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 289: 121658. |
| 27 | LIN C P, MAO Y, ZHENG R C, et al. Highly efficient chemoenzymatic synthesis of L-phosphinothricin from N-phenylacetyl-D,L-phosphinothricin by a robust immobilized amidase[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68(49): 14549-14554. |
| 28 | WU Z M, XIE F, ZHENG W, et al. Structure-oriented engineering of amidase: modification of twisted access tunnel for efficient synthesis of 2-chloronicotinic acid[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(13): 9078-9089. |
| 29 | WANG L Y, TANG H, ZHU H L, et al. Enhancement of the substrate specificity of D-amino acid oxidase based on tunnel-pocket engineering[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2023, 120(12): 3557-3569. |
| 30 | 王华磊, 魏东芝, 吴承骏, 等. 利用生物多酶偶联法制备L-草铵膦的方法: CN112410383B[P]. 2022-07-12. |
| WANG H L, WEI D Z, WU C J, et al. METHOD FOR PREPARING L-GLUFOSINATE USING BI-ENZYMATIC COUPLING: CN112410383B[P]. 2022-07-12. | |
| 31 | CHENG F, LI J M, ZHOU S P, et al. A single-transaminase-catalyzed biocatalytic cascade for efficient asymmetric synthesis of l-phosphinothricin[J]. ChemBioChem, 2021, 22(2): 345-348. |
| 32 | ZHOU H S, MENG L J, YIN X J, et al. Biocatalytic asymmetric synthesis of L-phosphinothricin using a one-pot three enzyme system and a continuous substrate fed-batch strategy[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2020, 589: 117239. |
| 33 | XUE Y P, CHENG F, LI H, et al. Amino acid dehydrogenase mutant and application in synthesis of L-glufosinate-ammonium thereof: US11408016B2[P]. 2021-03-11. |
| 34 | XUE Y P, CHENG F, WU D, et al. Machine learning gene mining method and phosphinothricin dehydrogenase mutant for amino translocation: US11781117B2[P]. 2022-06-30. |
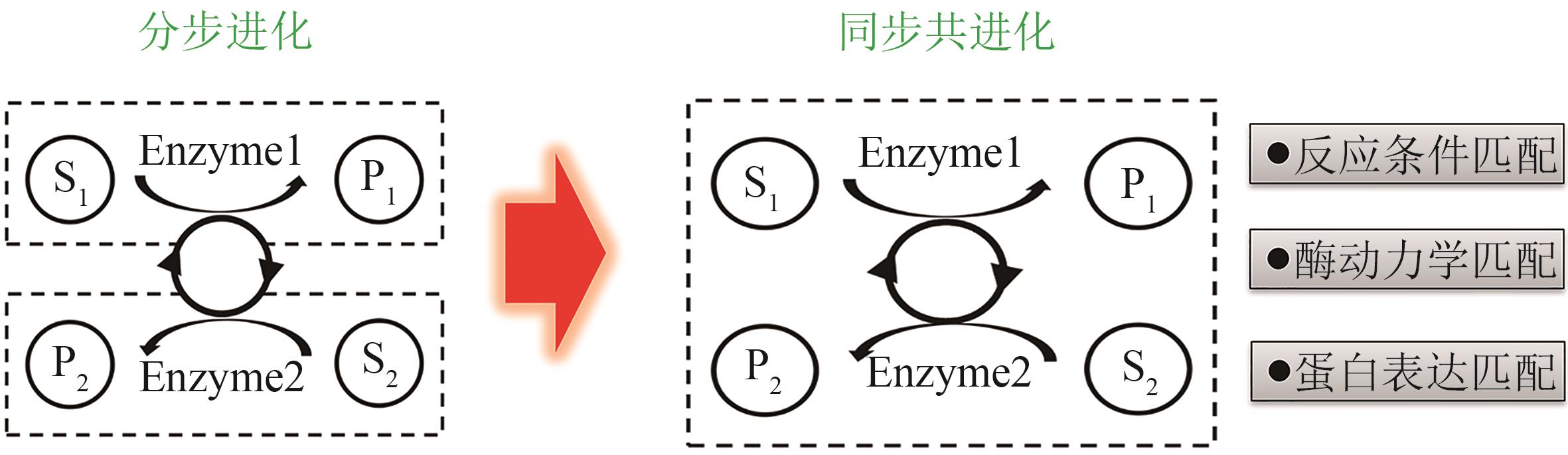
| 35 | CHENG F, LI Q H, ZHANG H Y, et al. Simultaneous directed evolution of coupled enzymes for efficient asymmetric synthesis of L-phosphinothricin[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2021, 87(5): e02563-20. |
| 36 | 程峰, 李清华, 李恒, 等. NAD(P)H依赖型氧化还原酶不对称还原胺化制备手性胺的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2020, 36(9): 1794-1816. |
| CHENG F, LI Q H, LI H, et al. NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductases for synthesis of chiral amines by asymmetric reductive amination of ketones[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2020, 36(9): 1794-1816. | |
| 37 | CAO C H, GONG H, DONG Y, et al. Enzyme cascade for biocatalytic deracemization of D,L-phosphinothricin[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 325: 372-379. |
| 38 | 薛亚平, 郑裕国, 吕胜芝, 等. 粘质沙雷氏菌及其应用: CN107118977B[P]. 2020-02-21. |
| XUE Y P, ZHENG Y G, LV S Z, et al. VISCOUS Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its application: CN107118977B[P]. 2020-02-21. | |
| 39 | ALBIZATI K F, KAMBOURAKIS S, GRUBBS A, et al. Process of producing phosphinothricin employing nitrilases: US09683001B2[P]. 2017-06-20. |
| 40 | LIU Z Q, DONG L Z, CHENG F, et al. Gene cloning, expression, and characterization of a nitrilase from Alcaligenes faecalis ZJUTB10[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2011, 59(21): 11560-11570. |
| 41 | YIN X J, LIU Y Y, MENG L J, et al. Rational molecular engineering of glutamate dehydrogenases for enhancing asymmetric reductive amination of bulky α-keto acids[J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2019, 361(4): 803-812. |
| 42 | CHENG F, ZHANG J M, JIANG Z T, et al. Development of an NAD(H)-driven biocatalytic system for asymmetric synthesis of chiral amino acids[J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2022, 364(8): 1450-1459. |
| 43 | 汤恒, 韩鑫, 邹树平, 等. 多酶催化体系在医药化学品合成中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 559-576. |
| TANG H, HAN X, ZOU S P, et al. Application of multi-enzyme catalytic system in the synthesis of pharmaceutical chemicals[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(4): 559-576. | |
| 44 | 吴淑可, 周颐, 王文, 等. 从单酶催化到多酶级联催化——从王义翘教授在酶技术领域的贡献说开去[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 543-558. |
| WU S K, ZHOU Y, WANG W, et al. From single-enzyme catalysis to multienzyme cascade: inspired from Professor Daniel I.C. Wang’s pioneer work in enzyme technology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(4): 543-558. | |
| 45 | 牛坤, 高利平, 葛丽蓉, 等. 大肠杆菌代谢工程改造合成L-高丝氨酸及其衍生物研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(12): 4385-4402. |
| NIU K, GAO L P, GE L R, et al. Advances in the biosynthesis of L-homoserine and its derivatives by metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli [J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 38(12): 4385-4402. | |
| 46 | MU Q X, ZHANG S S, MAO X J, et al. Highly efficient production of L-homoserine in Escherichia coli by engineering a redox balance route[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2021, 67: 321-329. |
| 47 | 刘鹏. 生物合成L-高丝氨酸及其衍生物的细胞工厂构建[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2020. |
| LIU P. construction of cell factories for bioproduction of L-homoserine and its derivatives[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2020. | |
| 48 | CAO C H, CHENG F, XUE Y P, et al. Efficient synthesis of L-phosphinothricin using a novel aminoacylase mined from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2020, 135: 109493. |
| 49 | TONG X D, EL-ZAHAB B, ZHAO X Y, et al. Enzymatic synthesis of L-lactic acid from carbon dioxide and ethanol with an inherent cofactor regeneration cycle[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2011, 108(2): 465-469. |
| 50 | KIM S, LEE S Y, ANJONG T F, et al. Artificial photocatalytic system using polydiacetylene-(-NH-phen)Ru(bpy)2 for cofactor regeneration and CO2 reduction[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(50): 28407-28414. |
| 51 | ZHANG Z B, LI J J, JI M B, et al. Encapsulation of multiple enzymes in a metal-organic framework with enhanced electro-enzymatic reduction of CO2 to methanol[J]. Green Chemistry, 2021, 23(6): 2362-2371. |
| 52 | GOLDBERG K, SCHROER K, LÜTZ S, et al. Biocatalytic ketone reduction—a powerful tool for the production of chiral alcohols—partⅠ: processes with isolated enzymes[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2007, 76(2): 237-248. |
| 53 | NAGAO T, MITAMURA T, WANG X H, et al. Cloning, nucleotide sequences, and enzymatic properties of glucose dehydrogenase isozymes from Bacillus megaterium IAM1030[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1992, 174(15): 5013-5020. |
| 54 | 李凌凌, 吕早生, 吴敏, 等. 重组的葡萄糖脱氢酶催化辅酶的再生性质[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(3): 112-115, 132. |
| LI L L, LÜ Z S, WU M, et al. Cofactor regeneration of recombinant glucose dehydrogenase[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(3): 112-115, 132. | |
| 55 | VAN DER DONK W A, ZHAO H M. Recent developments in pyridine nucleotide regeneration[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2003, 14(4): 421-426. |
| 56 | ALPDAĞTAŞ S, YÜCEL S, KAPKAÇ H A, et al. Discovery of an acidic, thermostable and highly NADP+ dependent formate dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus buchneri NRRL B-30929[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2018, 40(7): 1135-1147. |
| 57 | ÖZGÜN G P, ORDU E B, TÜTÜNCÜ H E, et al. Site saturation mutagenesis applications on Candida methylica formate dehydrogenase[J]. Scientifica, 2016, 2016: 4902450. |
| 58 | CHENG F, WEI L, WANG C J, et al. Switching the cofactor preference of formate dehydrogenase to develop an NADPH-dependent biocatalytic system for synthesizing chiral amino acids[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(23): 9009-9019. |
| 59 | AN J H, NIE Y, XU Y. Structural insights into alcohol dehydrogenases catalyzing asymmetric reductions[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2019, 39(3): 366-379. |
| 60 | HOLLMANN F, OPPERMAN D J, PAUL C E. Biocatalytic reduction reactions from a chemist’s perspective[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(11): 5644-5665. |
| 61 | MATSUDA T, YAMAGISHI Y, KOGUCHI S, et al. An effective method to use ionic liquids as reaction media for asymmetric reduction by Geotrichum candidum [J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2006, 47(27): 4619-4622. |
| 62 | STAMPFER W, KOSJEK B, FABER K, et al. Biocatalytic asymmetric hydrogen transfer employing Rhodococcus ruber DSM44541[J]. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2003, 68(2): 402-406. |
| 63 | XU J M, WU Z S, ZHAO K J, et al. IPTG-induced high protein expression for whole-cell biosynthesis of L-phosphinothricin[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2023, 18(9): e2300027. |
| [1] | 温艳华, 刘合栋, 曹春来, 巫瑞波. 蛋白质工程在医药产业中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 65-86. |
| [2] | 刘宽庆, 张以恒. 木质素的生物降解和生物利用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1264-1278. |
| [3] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [4] | 雷航彬, 何宁, 李斐煊, 董玲玲, 王世珍. 氢化酶固定化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1485-1497. |
| [5] | 王子渊, 杨立荣, 吴坚平, 郑文隆. 酶促合成手性氨基酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1319-1349. |
| [6] | 董玲玲, 李斐煊, 雷航彬, 宋启迪, 王世珍. 仿生分区室固定化多酶体系[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1518-1529. |
| [7] | 李庚, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 过氧化物酶的重组表达和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1498-1517. |
| [8] | 张阿磊, 魏国光, 张弛, 陈磊, 周奚, 刘伟, 陈可泉. 几丁质资源生物降解和高值转化的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1279-1299. |
| [9] | 李怡霏, 陈艾, 孙俊松, 张以恒. 体外多酶分子机器产氢应用中的氢酶研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1461-1484. |
| [10] | 付雨, 钟芳锐. 化学原理驱动的光生物不对称催化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1021-1049. |
| [11] | 郑梦梦, 刘犇犇, 林芝, 瞿旭东. 重要甾体化合物的化学酶法合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 941-959. |
| [12] | 程晓雷, 刘天罡, 陶慧. 萜类化合物的非常规生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1050-1071. |
| [13] | 杨皓然, 叶发荣, 黄平, 王平. 糖蛋白合成的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1072-1101. |
| [14] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [15] | 程中玉, 李付琸. 基于P450选择性氧化的天然产物化学-酶法合成进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 960-980. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||