合成生物学 ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (4): 470-480.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-011
合成生物学在探索生物图案形成基本原理中的应用与展望
周楠1, 夏婷颖2, 黄建东1,2
- 1.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,中国科学院深圳合成生物学创新研究院定量工程生物学重点实验室,广东 深圳 518055
2.香港大学李嘉诚医学院,生物医学学院,香港 999077
-
收稿日期:2020-02-29修回日期:2020-03-17出版日期:2020-08-31发布日期:2020-10-09 -
通讯作者:黄建东 -
作者简介:周楠(1987-),男,博士,助理研究员,研究方向为合成生物学。E-mail:nan.zhou@siat.ac.cn
黄建东(1965-),男,博士,教授,研究方向为合成生物学、肿瘤免疫治疗和传染病疫苗。E-mail:jdhuang@hku.hk -
基金资助:深圳孔雀项目(KQTD2015033117210153);深圳市科技计划项目基础研究(学科布局)(JCYJ20170413154523577)
Applications and prospects of synthetic biology in exploring the basic principles of biological pattern formation
ZHOU Nan1, XIA Tingying2, HUANG Jiandong1,2
- 1.CAS Key Laboratory of Quantitative Engineering Biology,Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
2.School of Biomedical Sciences,Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine,The University of Hong Kong,Hong Kong 999077,China
-
Received:2020-02-29Revised:2020-03-17Online:2020-08-31Published:2020-10-09 -
Contact:HUANG Jiandong
摘要:
自然界中不同生物图案形成的背后是否存在普遍规律,是生物学最基本的科学问题之一。然而,生物系统的复杂性给归纳、理解和验证潜在的普遍规律带来了极大挑战。合成生物学采用自下而上的工程策略,利用功能明确的基因元件构建定量可控的合成体系,为解析生物图案形成的基本原理带来了新的契机。本文围绕合成生物学在生物图案形成研究中的应用,重点阐述了利用合成生物系统验证成形素浓度梯度模型和反应-扩散模型等现有生物图案形成理论的研究进展,并总结了合成生物学在探索生物图案尺寸调控、周期性生物图案形成和多细胞结构产生新机制中的重要贡献。最后提出对合成系统的研究与发育生物学的进一步交互有望拓展对自然生物图案形成的认知,并指出合成生物图案今后在生物材料制造、再生医学和组织工程等领域的应用价值和前景。
中图分类号:
引用本文
周楠, 夏婷颖, 黄建东. 合成生物学在探索生物图案形成基本原理中的应用与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(4): 470-480.
ZHOU Nan, XIA Tingying, HUANG Jiandong. Applications and prospects of synthetic biology in exploring the basic principles of biological pattern formation[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(4): 470-480.

图1 生物图案形成的理论模型[23]note:(The left panel shows the activator and inhibitor which are two interacting morphogens involved in the reaction-diffusion model. The activator activates the synthesis of itself and the inhibitor,whereas the inhibitor suppresses the synthesis of the activator. The diffusion rate of the activator is much higher than that of the inhibitor; the middle panel shows oscillations with fixed wavelength resulted from the reaction and diffusion of the two morphogens; the right panel shows different types of Turing patterns by the simulation of the reaction-diffusion model)
Fig. 1 Theoretical models for biological pattern formation[23]
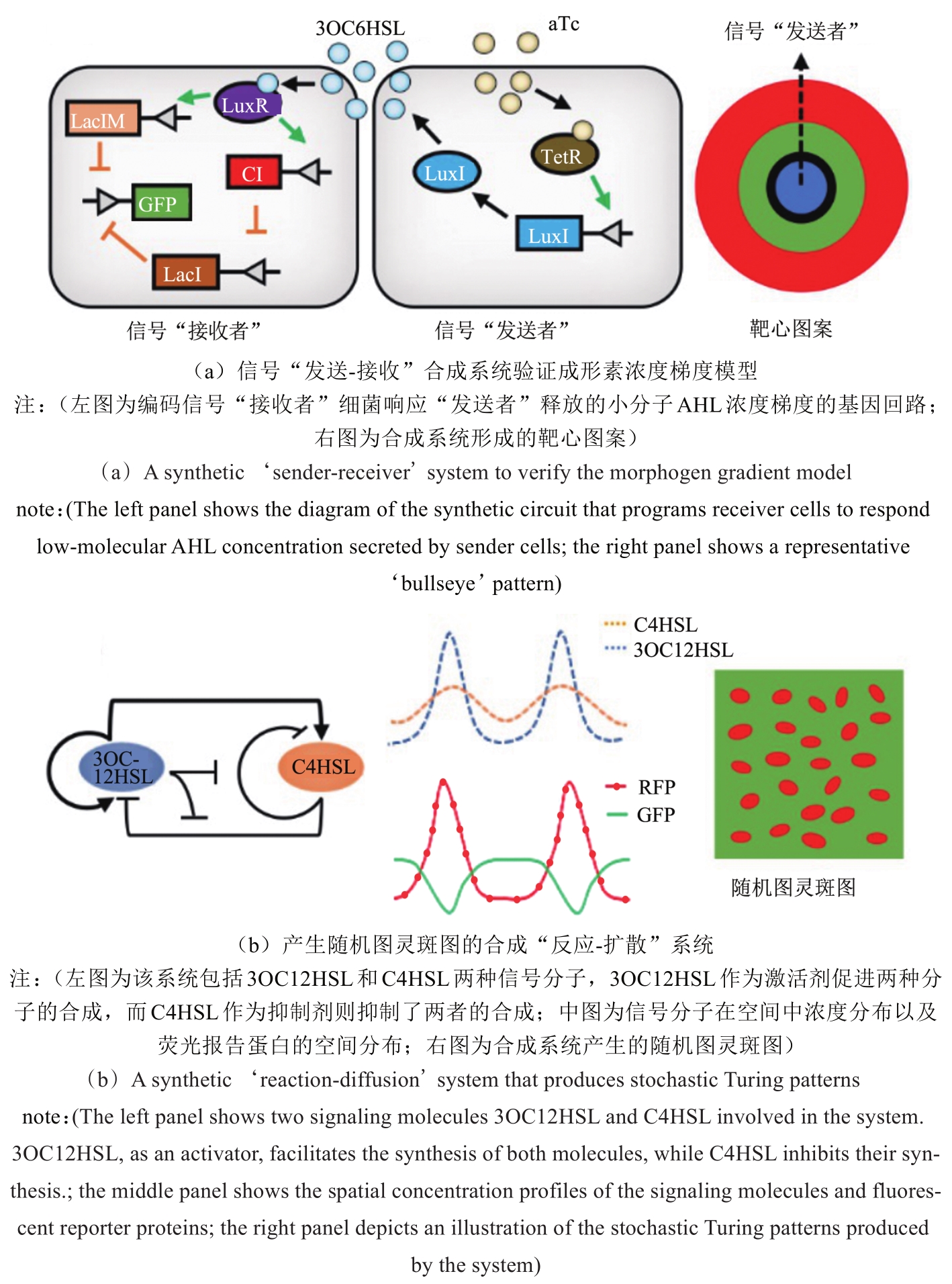
图2 利用合成生物学验证现有生物图案形成理论的经典案例[33,39]
Fig. 2 Representative studies in the application of synthetic biology to verify existing theories for pattern formation[33,39]
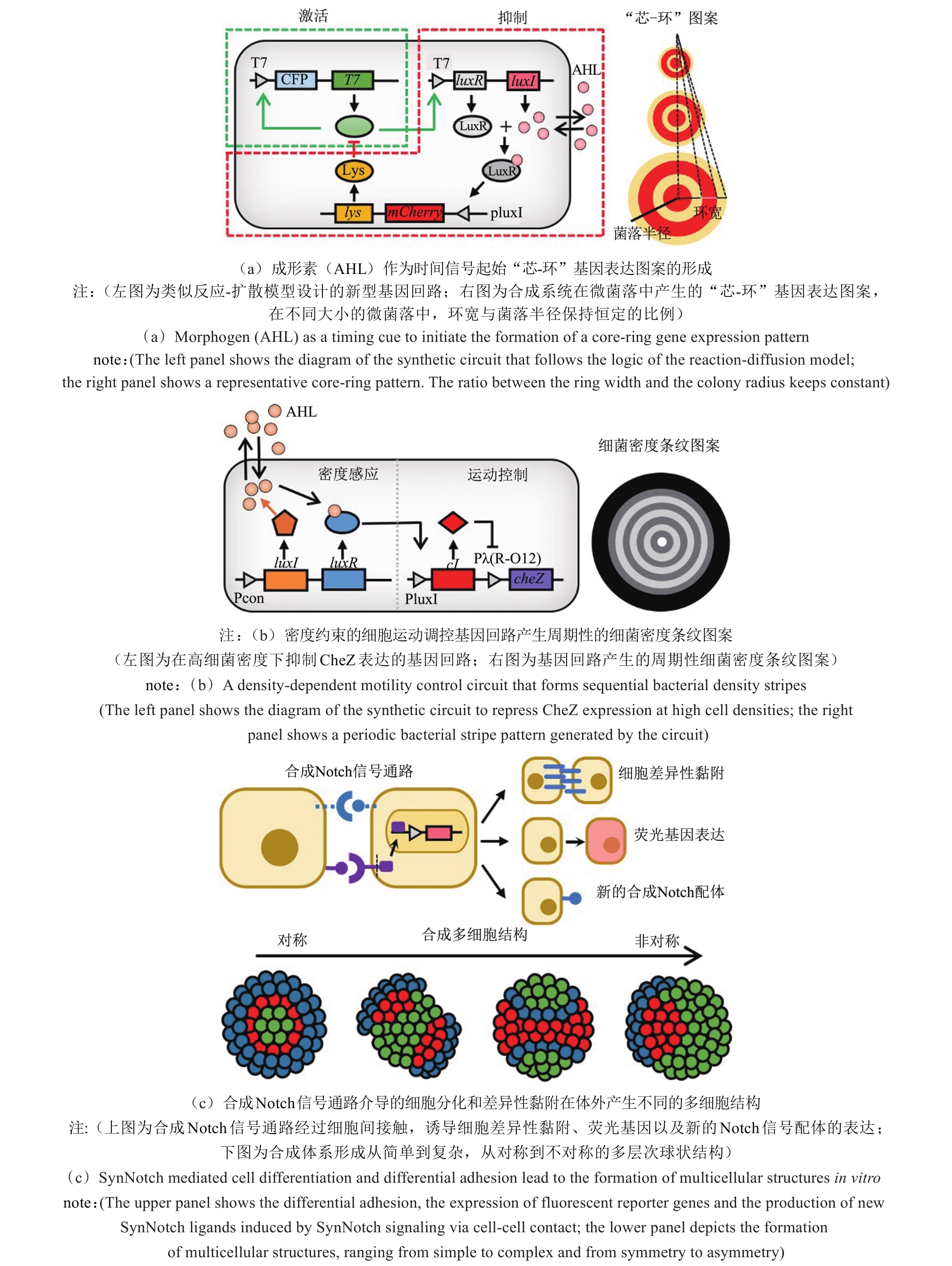
图3 利用合成生物学探索生物图案形成新机制的经典案例[40-41,43,49]
Fig. 3 Representative studies in the application of synthetic biology to explore novel mechanisms for biological pattern formation[40-41,43,49]
| 1 | CANTON B, LABNO A, ENDY D. Refinement and standardization of synthetic biological parts and devices[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2008, 26(7): 787-793. |
| 2 | CAMERON D E, BASHOR C J, COLLINS J J. A brief history of synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews: Microbiology, 2014, 12(5): 381-390. |
| 3 | GARDNER T S, CANTOR C R, COLLINS J J. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 339-342. |
| 4 | ELOWITZ M B, LEIBLER S. A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators[J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 335-338. |
| 5 | GUET C C, ELOWITZ M B, HSING W, et al. Combinatorial synthesis of genetic networks[J]. Science, 2002, 296(5572): 1466-1470. |
| 6 | ASIMOV I. A short history of chemistry[M]. New South Wales: Doubleday, 1965. |
| 7 | KOCH A, MEINHARDT H. Biological pattern formation: from basic mechanisms to complex structures[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1994, 66(4): 1481. |
| 8 | LAWRENCE P A, MORATA G. Developmental biology. Lighting up Drosophila[J]. Nature, 1992, 356(6365): 107-108. |
| 9 | WATANABE M, KONDO S. Changing clothes easily: connexin41.8 regulates skin pattern variation[J]. Pigment Cell Melanoma Research, 2012, 25(3): 326-330. |
| 10 | MADERSPACHER F, NUSSLEIN-VOLHARD C. Formation of the adult pigment pattern in zebrafish requires leopard and obelix dependent cell interactions[J]. Development, 2003, 130(15): 3447-3457. |
| 11 | KUMAR N M, GILULA N B. The gap junction communication channel[J]. Cell, 1996, 84(3): 381-388. |
| 12 | MALLARINO R, HENEGAR C, MIRASIERRA M, et al. Developmental mechanisms of stripe patterns in rodents[J]. Nature, 2016, 539(7630): 518-523. |
| 13 | WOLPERT L. Positional information and the spatial pattern of cellular differentiation[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 1969, 25(1): 1-47. |
| 14 | STRUHL G, STRUHL K, MACDONALD P M. The gradient morphogen bicoid is a concentration-dependent transcriptional activator[J]. Cell, 1989, 57(7): 1259-1273. |
| 15 | DRIEVER W, NUSSLEIN-VOLHARD C. A gradient of bicoid protein in Drosophila embryos [J]. Cell, 1988, 54(1): 83-93. |
| 16 | GURDON J B, HARGER P, MITCHELL A, et al. Activin signalling and response to a morphogen gradient[J]. Nature, 1994, 371(6497): 487-492. |
| 17 | HEEMSKERK J, DINARDO S. Drosophila hedgehog acts as a morphogen in cellular patterning[J]. Cell, 1994, 76(3): 449-460. |
| 18 | KIECKER C, NIEHRS C. A morphogen gradient of Wnt/beta-catenin signalling regulates anteroposterior neural patterning in Xenopus [J]. Development, 2001, 128(21): 4189-4201. |
| 19 | WARTLICK O, KICHEVA A, GONZALEZ-GAITAN M. Morphogen gradient formation[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2009, 1(3): A001255. |
| 20 | DESSAUD E, YANG L L, HILL K, et al. Interpretation of the sonic hedgehog morphogen gradient by a temporal adaptation mechanism[J]. Nature, 2007, 450(7170): 717-720. |
| 21 | VUILLEUMIER R, SPRINGHORN A, PATTERSON L, et al. Control of Dpp morphogen signalling by a secreted feedback regulator[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2010, 12(6): 611-617. |
| 22 | REEVES G T, STATHOPOULOS A. Graded dorsal and differential gene regulation in the Drosophila embryo [J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2009, 1(4): A000836. |
| 23 | IBANES M, IZPISUA BELMONTE J C. Theoretical and experimental approaches to understand morphogen gradients[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2008, 4: 176. |
| 24 | WATANABE M, KONDO S. Is pigment patterning in fish skin determined by the Turing mechanism?[J]. Trends in Genetics, 2015, 31(2): 88-96. |
| 25 | YAMAGUCHI M, YOSHIMOTO E, KONDO S. Pattern regulation in the stripe of zebrafish suggests an underlying dynamic and autonomous mechanism[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(12): 4790-4793. |
| 26 | TURING A M. The chemical basis of morphogenesis [J]. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 1952, 52(1/2): 153-197. |
| 27 | MEINHARDT H, GIERER A. Pattern formation by local self-activation and lateral inhibition[J]. Bioessays, 2000, 22(8): 753-760. |
| 28 | MEINHARDT H, GIERER A. Applications of a theory of biological pattern formation based on lateral inhibition[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 1974, 15(2): 321-346. |
| 29 | MAINI P K, MYERSCOUGH M R, WINTERS K H, et al. Bifurcating spatially heterogeneous solutions in a chemotaxis model for biological pattern generation[J]. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 1991, 53(5): 701-719. |
| 30 | SWINDALE N V. A model for the formation of ocular dominance stripes[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 1980, 208(1171): 243-264. |
| 31 | KONDO S, MIURA T. Reaction-diffusion model as a framework for understanding biological pattern formation[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5999): 1616-1620. |
| 32 | ECONOMOU A D, OHAZAMA A, PORNTAVEETUS T, et al. Periodic stripe formation by a Turing mechanism operating at growth zones in the mammalian palate[J]. Nature Genetics, 2012, 44(3): 348. |
| 33 | BASU S, GERCHMAN Y, COLLINS C H, et al. A synthetic multicellular system for programmed pattern formation[J]. Nature, 2005, 434(7037): 1130-1134. |
| 34 | SOHKA T, HEINS R A, PHELAN R M, et al. An externally tunable bacterial band-pass filter[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(25): 10135-10140. |
| 35 | KONG W, BLANCHARD A E, LIAO C, et al. Engineering robust and tunable spatial structures with synthetic gene circuits[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(2): 1005-1014. |
| 36 | SCHAERLI Y, MUNTEANU A, GILI M, et al. A unified design space of synthetic stripe-forming networks[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4905. |
| 37 | SEKINE R, SHIBATA T, EBISUYA M. Synthetic mammalian pattern formation driven by differential diffusivity of Nodal and Lefty[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 5456. |
| 38 | MULLER P, ROGERS K W, JORDAN B M, et al. Differential diffusivity of Nodal and Lefty underlies a reaction-diffusion patterning system[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6082): 721-724. |
| 39 | KARIG D, MARTINI K M, LU T, et al. Stochastic Turing patterns in a synthetic bacterial population[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(26): 6572-6577. |
| 40 | PAYNE S, LI B, CAO Y, et al. Temporal control of self-organized pattern formation without morphogen gradients in bacteria[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2013, 9: 697. |
| 41 | CAO Y, RYSER M D, PAYNE S, et al. Collective space-sensing coordinates pattern scaling in engineered bacteria[J]. Cell, 2016, 165(3): 620-630. |
| 42 | LIU C, FU X, HUANG J D. Synthetic biology: a new approach to study biological pattern formation[J]. Quantitative Biology, 2013, 1(4): 246-252. |
| 43 | LIU C, FU X, LIU L, et al. Sequential establishment of stripe patterns in an expanding cell population[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6053): 238-241. |
| 44 | GILMOUR D, REMBOLD M, LEPTIN M. From morphogen to morphogenesis and back[J]. Nature, 2017, 541(7637): 311-320. |
| 45 | ABERCROMBIE M. Contact inhibition and malignancy[J]. Nature, 1979, 281(5729): 259-262. |
| 46 | POLIAKOV A, COTRINA M, WILKINSON D G. Diverse roles of eph receptors and ephrins in the regulation of cell migration and tissue assembly[J]. Developmental Cell, 2004, 7(4): 465-480. |
| 47 | STEINBERG M S. Differential adhesion in morphogenesis: a modern view[J]. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 2007, 17(4): 281-286. |
| 48 | CACHAT E, LIU W, MARTIN K C, et al. 2-and 3-dimensional synthetic large-scale de novo patterning by mammalian cells through phase separation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 20664. |
| 49 | TODA S, BLAUCH L R, TANG S K Y, et al. Programming self-organizing multicellular structures with synthetic cell-cell signaling[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6398): 156-162. |
| 50 | YAMANAKA H, KONDO S. In vitro analysis suggests that difference in cell movement during direct interaction can generate various pigment patterns in vivo [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(5): 1867-1872. |
| 51 | THEVENEAU E, STEVENTON B, SCARPA E, et al. Chase-and-run between adjacent cell populations promotes directional collective migration[J]. Nature Cell Biology. 2013, 15(7): 763-772. |
| 52 | XIONG L, CAO Y, COOPER R, et al. Flower-like patterns in multi-species bacterial colonies[J]. eLife, 2020, 9. |
| 53 | CURATOLO A I, ZHOU N, ZHAO Y,et al. Cooperative pattern formation in multi-component bacterial systems through reciprocal motility regulation[J]. Nature Physics, 2020. DOI: 10.1038/s41567-020-0964-z . |
| 54 | 邓子新. 合成生物学趁最好时代,建物致知,建物致用[J]. 生命科学, 2019, 31(4): 323-324 |
| DENG Z X. Synthetic biology takes advantage of the golden age, building to know, building to use[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2019, 31(4): 323-324. | |
| 55 | 赵国屏. 合成生物学: 开启生命科学 “会聚” 研究新时代[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(11): 1135-1149 |
| ZHAO G P. Synthetic biology: unsealing the convergence era of life science research[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(11): 1135-1149. | |
| 56 | DAVIES J. Using synthetic biology to explore principles of development[J]. Development, 2017, 144(7): 1146-1158. |
| 57 | CAO Y, FENG Y, RYSER M D, et al. Programmable assembly of pressure sensors using pattern-forming bacteria[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2017, 35(11): 1087. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [12] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [13] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [14] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [15] | 查文龙, 卜兰, 訾佳辰. 中药药效成分群的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
