合成生物学 ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (4): 577-597.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-008
环脂肽生物合成的研究进展
侯正杰, 孙慧中, 白松, 陈新月, 曹春阳, 程景胜
- 教育部合成生物学前沿科学中心,系统生物学教育部重点实验室,天津大学化工学院,天津 300350
-
收稿日期:2021-01-20修回日期:2021-04-03出版日期:2021-08-31发布日期:2021-09-10 -
通讯作者:程景胜 -
作者简介:侯正杰 (1995—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为生物制药、代谢工程与合成生物学。E-mail:hou_zj@tju.edu.cn程景胜 (1972—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为生物制药、合成生物学与系统生物技术等。E-mail:jscheng@tju.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0902200);国家自然科学基金面上项目(21878224)
Research progress of cyclic lipopeptide biosynthesis
HOU Zhengjie, SUN Huizhong, BAI Song, CHEN Xinyue, CAO Chunyang, CHENG Jingsheng
- Frontiers Science Center for Synthetic Biology and Key Laboratory of Systems Bioengineering (Ministry of Education),School of Chemical Engineering and Technology,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300350,China
-
Received:2021-01-20Revised:2021-04-03Online:2021-08-31Published:2021-09-10 -
Contact:CHENG Jingsheng
摘要:
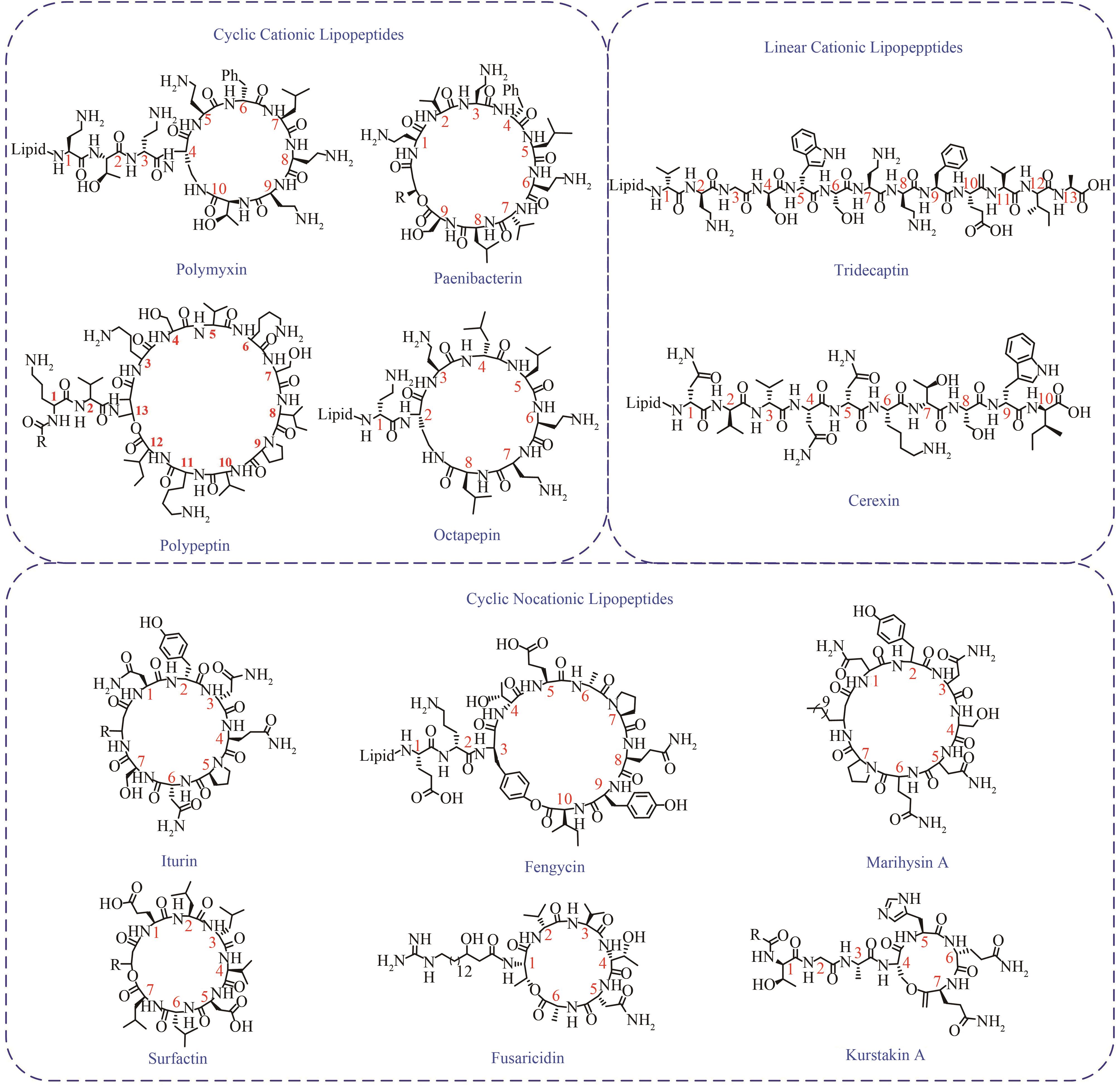
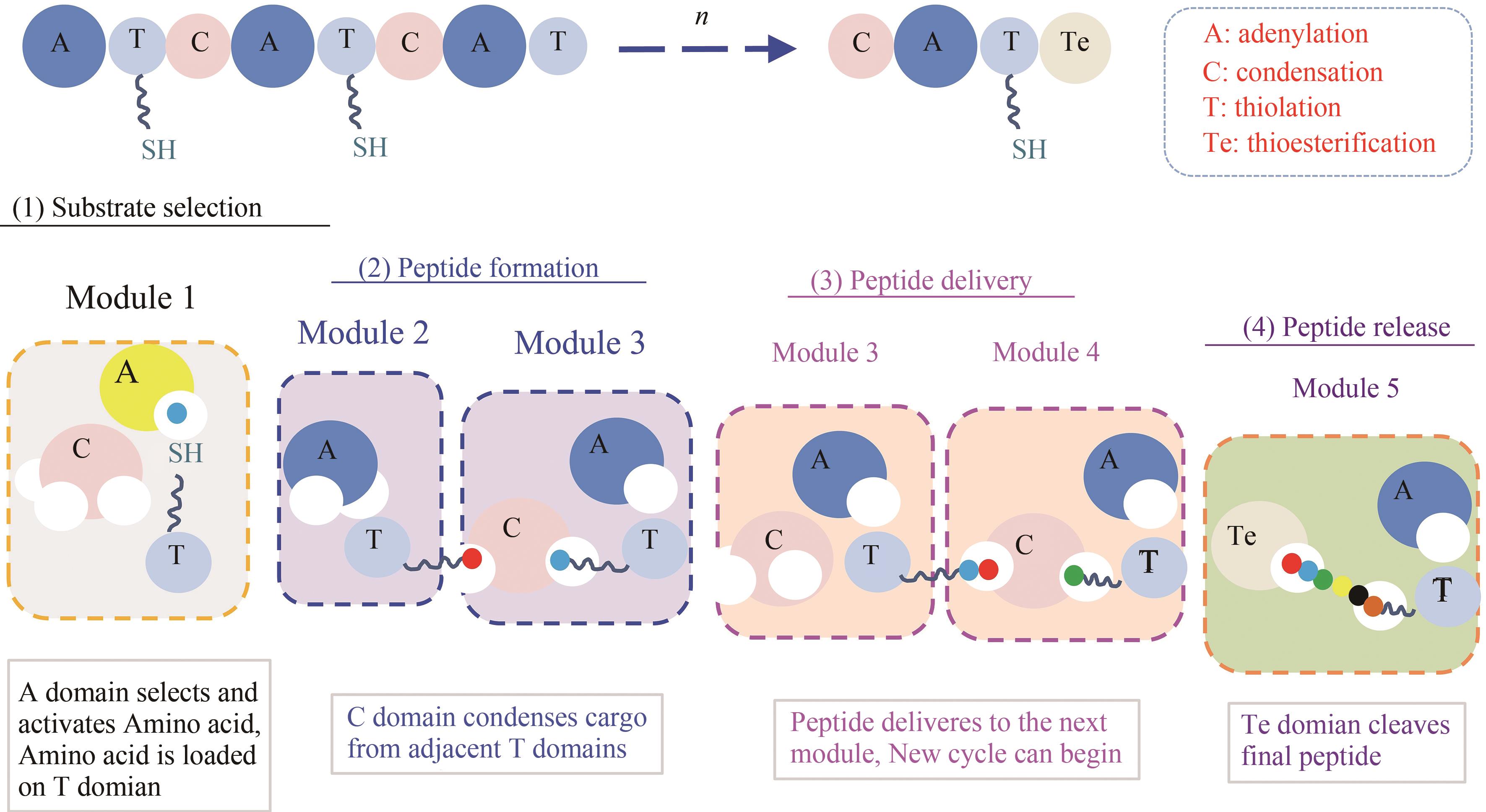
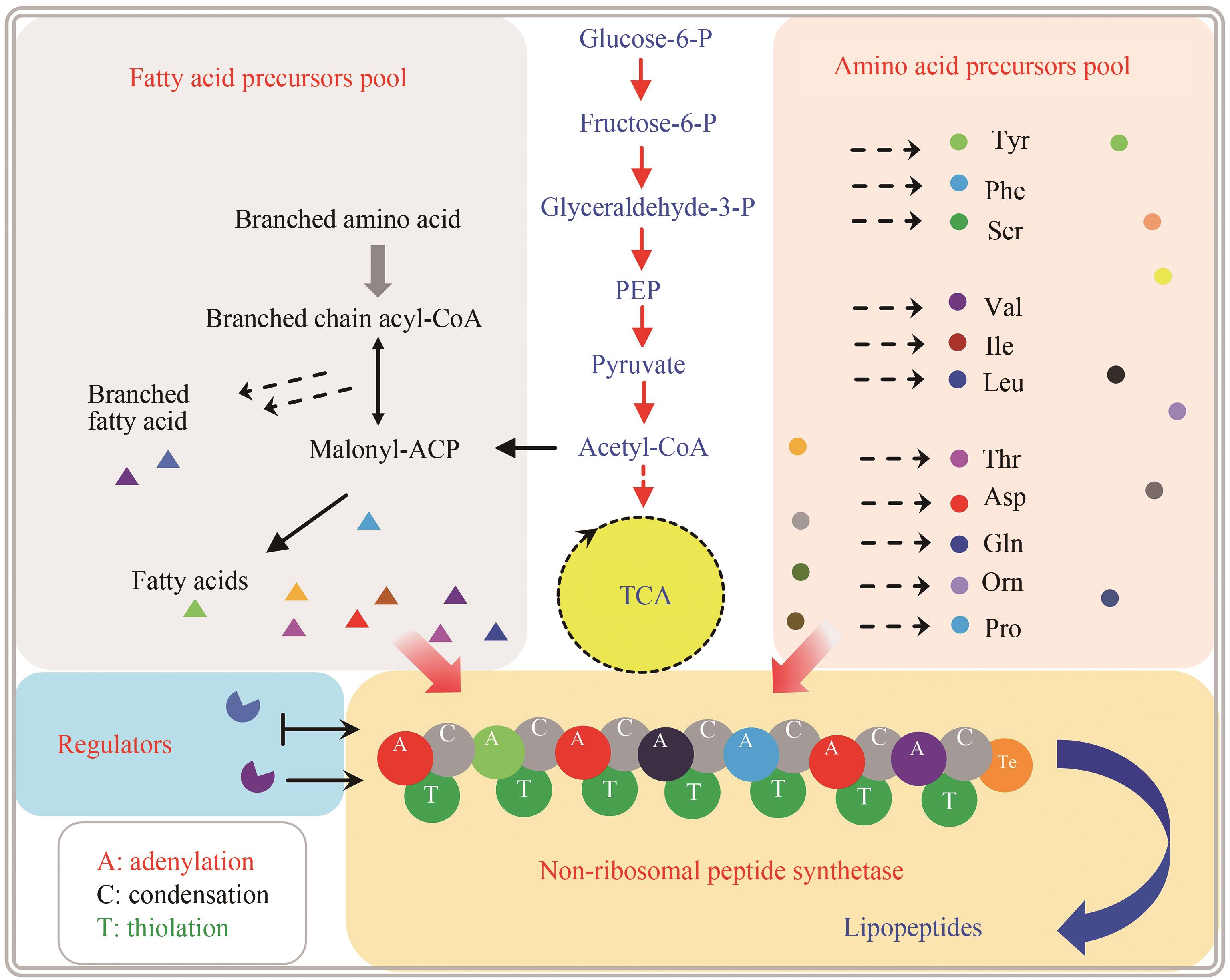
环脂肽化合物是一类结构新颖的环状肽类,其两亲性的物化特性决定了其独特的生物活性,可作为抗生素、生物表面活性剂等。在生物防治、药物开发、环境修复和疾病治疗等方面广泛应用,具有迫切的市场需求和广阔的发展前景。环脂肽类天然产物主要由非核糖体肽合成途径合成,由于环脂肽合成复杂的代谢网络和前体需求、专一且严格的合成途径、多种同系物的共存,制约着环脂肽合成的微生物开发和产品价值提升。本文主要介绍了来源于细菌界的环脂肽类物质的结构特性,非核糖体肽合成途径及非核糖体肽合成酶(non-ribosomal peptide synthetase,NRPS)的结构域特点,天然产物底盘菌株开发现状,通过基因工程、代谢工程方法进行同系物调控和生物合成策略,混菌对脂肽生物合成的影响,以及合成生物学在脂肽合成中的应用。随着合成生物技术的迅速发展和运用,环脂肽类天然产物的微生物合成也有望实现“质”和“量”的提升,以及促进新型脂肽的开发。
中图分类号:
引用本文
侯正杰, 孙慧中, 白松, 陈新月, 曹春阳, 程景胜. 环脂肽生物合成的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(4): 577-597.
HOU Zhengjie, SUN Huizhong, BAI Song, CHEN Xinyue, CAO Chunyang, CHENG Jingsheng. Research progress of cyclic lipopeptide biosynthesis[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(4): 577-597.
| 脂肽 | 方法 | 结果 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| actinomycin | N-甲基缬氨酸活化结构域替换 | 导致催化非甲基化和N-甲基化酰基二肽的合成 | [ |
| bacillibactin | DhbE-A结构域突变、文库筛选 | 3-羟基苯甲酸和2-氨基苯甲酸酰基化的bacillibactin | [ |
| bacitracin | Cy结构域插入 | 产生新的杂环二肽 | [ |
| CDA | CdaPS3-A结构域点突变 | 产生含Gln、mGln的CDA变体 | [ |
| clorobiocin | 调控相关酶表达 | 表达卤化酶HrmQ导致形成两个有5-氯吡咯的clorobiocin衍生物 | [ |
| daptomycin | DptBC引入新的模块 | 21种改造菌产生超过60种新型物质 | [ |
| enterobactin | EntF-AThr结构域替换、定向进化 | 产生中间体,得到两种不同的NRPS变体,酶活性和产物产量提高了10倍 | [ |
| fusaricidins | FusA-A3结构域点突变 | 增加了fusaricidin类似物(LI-F07)的量 | [ |
| gramicidin | GrsA-Aphe结构域替换 | 将编码不同特异性的亚结构域移植到GrsA-Aphe结构域中,所有嵌合体表达 | [ |
| luminmide | A结构域点突变 | luminmide B在几种突变体中变得显著丰富(超过90%) | [ |
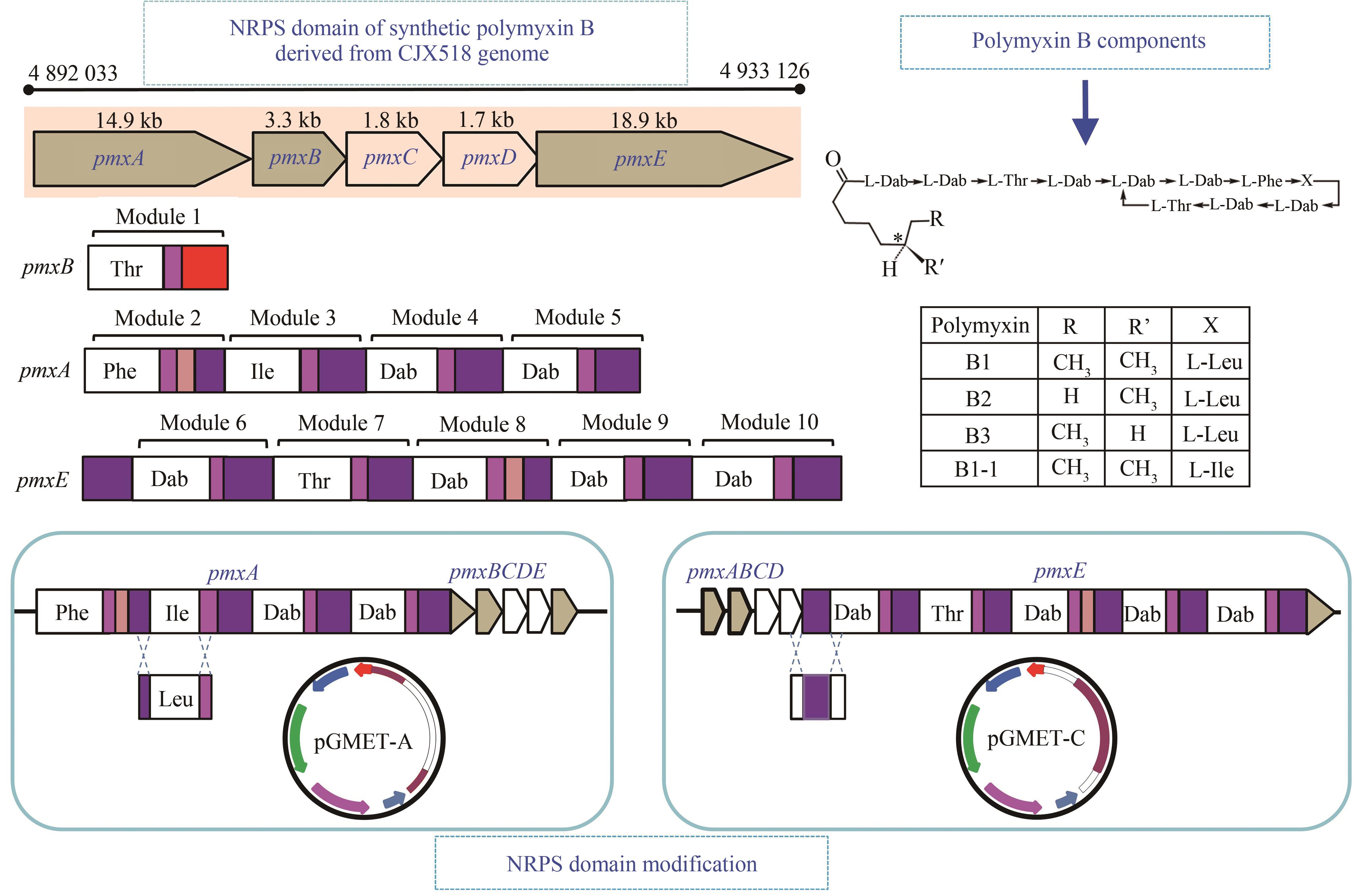
| polymyxin | PmxA-ALeu与PmxA-Athr替换 | 通过替换polymyxin A的A结构域合成polymyxin B、D、P | [ |
| pyoverdine | PvdD-C/A结构域替换 | 产生变短或者被修饰的多肽 | [ |
| pyoverdine | PvdD-T结构域替换 | 产生了两个重组pyoverdine | [ |
| surfactin | SrfAC-Aleu结构域替换 | 得到surfactin结构中亮氨酸改变的5种surfactin类似物 | [ |
| surfactin | SrfA模块的替换 | 创建一个完全活跃的杂交酶,以高产率形成一个新的肽 | [ |
| surfactin | SrfAA-AGlu点突变与模块的替换 | 产生未知的七肽Asn5表面活性素 | [ |
| surfactin | SrfAA-Aleu模块删除 | 产生缺少一个亮氨基酸的表面活性素变体 | [ |
| tyrocidine | TE结构域替换 | 来源不同的TE结构域都可以水解二肽 | [ |
| tyrocidine | 模块融合 | 合成不同三肽 | [ |
表1 脂肽合成域改造调控相关研究
Tab. 1 Studies on regulation and modification of lipopeptide synthesis domain
| 脂肽 | 方法 | 结果 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| actinomycin | N-甲基缬氨酸活化结构域替换 | 导致催化非甲基化和N-甲基化酰基二肽的合成 | [ |
| bacillibactin | DhbE-A结构域突变、文库筛选 | 3-羟基苯甲酸和2-氨基苯甲酸酰基化的bacillibactin | [ |
| bacitracin | Cy结构域插入 | 产生新的杂环二肽 | [ |
| CDA | CdaPS3-A结构域点突变 | 产生含Gln、mGln的CDA变体 | [ |
| clorobiocin | 调控相关酶表达 | 表达卤化酶HrmQ导致形成两个有5-氯吡咯的clorobiocin衍生物 | [ |
| daptomycin | DptBC引入新的模块 | 21种改造菌产生超过60种新型物质 | [ |
| enterobactin | EntF-AThr结构域替换、定向进化 | 产生中间体,得到两种不同的NRPS变体,酶活性和产物产量提高了10倍 | [ |
| fusaricidins | FusA-A3结构域点突变 | 增加了fusaricidin类似物(LI-F07)的量 | [ |
| gramicidin | GrsA-Aphe结构域替换 | 将编码不同特异性的亚结构域移植到GrsA-Aphe结构域中,所有嵌合体表达 | [ |
| luminmide | A结构域点突变 | luminmide B在几种突变体中变得显著丰富(超过90%) | [ |
| polymyxin | PmxA-ALeu与PmxA-Athr替换 | 通过替换polymyxin A的A结构域合成polymyxin B、D、P | [ |
| pyoverdine | PvdD-C/A结构域替换 | 产生变短或者被修饰的多肽 | [ |
| pyoverdine | PvdD-T结构域替换 | 产生了两个重组pyoverdine | [ |
| surfactin | SrfAC-Aleu结构域替换 | 得到surfactin结构中亮氨酸改变的5种surfactin类似物 | [ |
| surfactin | SrfA模块的替换 | 创建一个完全活跃的杂交酶,以高产率形成一个新的肽 | [ |
| surfactin | SrfAA-AGlu点突变与模块的替换 | 产生未知的七肽Asn5表面活性素 | [ |
| surfactin | SrfAA-Aleu模块删除 | 产生缺少一个亮氨基酸的表面活性素变体 | [ |
| tyrocidine | TE结构域替换 | 来源不同的TE结构域都可以水解二肽 | [ |
| tyrocidine | 模块融合 | 合成不同三肽 | [ |
| 外源添加 | 目标脂肽 | 影响 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 肉豆蔻酸、十五烷酸、棕榈酸等烷酸 | iturin、fengycin、 surfactin | 脂肽合成基因的转录水平上调,碳链长度为奇数的烷酸对脂肽产生靶基因上调的影响大于碳链长度为偶数的烷酸 | [ |
| 棕榈酸 | iturin A | 通过引入棕榈酸酯的烷基来促进iturin A的形成 | [ |
| 碳源、氮源和氨基酸 | C14 iturin W、 C15 iturin W | 除淀粉外,碳源能显著提高C14 iturin W的产量,尤其是山梨醇,但不同碳源使C15 iturin W产量受到抑制;氮源除了硫酸铵外,对C14 iturin W的产量都有促进,而C15 iturin W的产量除胰蛋白胨外都略有抑制;不同氨基酸对C14 iturin W和C15 iturin W的影响很大且不同 | [ |
| 酪氨酸、谷氨酰胺、天冬酰胺和脯氨酸、丝氨酸 | iturin A | 复合氨基酸的产量最高,天冬酰胺和脯氨酸的加入略微提高iturin A产量,丝氨酸可显著促进合成 | [ |
| 异亮氨酸、缬氨酸 | bacillomycin F | 促进枯草芽孢杆菌产生bacillomycin F | [ |
| L-亮氨酸、D-亮氨酸 | surfactin | L-Leu使surfactin产量显著增加,添加D-Leu后surfactin产量急剧下降 | [ |
| 碳源、金属离子 | surfactin | 不同碳源的添加(木糖除外)对表面活性素同系物的相对产量无显著影响;不同碳源的添加对不同脂肪酸链长的分子基团的比例有影响;金属离子的加入可能选择性地影响了脂肽第5位AME5残基的氨基酸序列 | [ |
| 亚铁离子 | iturin A | 通过添加亚铁离子提高了解淀粉芽孢杆菌产iturin A的能力 | [ |
| 锰和铁盐 | surfactin | 提高了surfactin的产量 | [ |
| 氧化锌纳米颗粒 | surfactin、iturin | 增加脂肽surfactin和iturin的合成,增强菌株的抗真菌活性 | [ |
表2 外源添加调控脂肽合成相关研究
Tab. 2 Studies on regulation of lipopeptide synthesis by exogenous addition
| 外源添加 | 目标脂肽 | 影响 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 肉豆蔻酸、十五烷酸、棕榈酸等烷酸 | iturin、fengycin、 surfactin | 脂肽合成基因的转录水平上调,碳链长度为奇数的烷酸对脂肽产生靶基因上调的影响大于碳链长度为偶数的烷酸 | [ |
| 棕榈酸 | iturin A | 通过引入棕榈酸酯的烷基来促进iturin A的形成 | [ |
| 碳源、氮源和氨基酸 | C14 iturin W、 C15 iturin W | 除淀粉外,碳源能显著提高C14 iturin W的产量,尤其是山梨醇,但不同碳源使C15 iturin W产量受到抑制;氮源除了硫酸铵外,对C14 iturin W的产量都有促进,而C15 iturin W的产量除胰蛋白胨外都略有抑制;不同氨基酸对C14 iturin W和C15 iturin W的影响很大且不同 | [ |
| 酪氨酸、谷氨酰胺、天冬酰胺和脯氨酸、丝氨酸 | iturin A | 复合氨基酸的产量最高,天冬酰胺和脯氨酸的加入略微提高iturin A产量,丝氨酸可显著促进合成 | [ |
| 异亮氨酸、缬氨酸 | bacillomycin F | 促进枯草芽孢杆菌产生bacillomycin F | [ |
| L-亮氨酸、D-亮氨酸 | surfactin | L-Leu使surfactin产量显著增加,添加D-Leu后surfactin产量急剧下降 | [ |
| 碳源、金属离子 | surfactin | 不同碳源的添加(木糖除外)对表面活性素同系物的相对产量无显著影响;不同碳源的添加对不同脂肪酸链长的分子基团的比例有影响;金属离子的加入可能选择性地影响了脂肽第5位AME5残基的氨基酸序列 | [ |
| 亚铁离子 | iturin A | 通过添加亚铁离子提高了解淀粉芽孢杆菌产iturin A的能力 | [ |
| 锰和铁盐 | surfactin | 提高了surfactin的产量 | [ |
| 氧化锌纳米颗粒 | surfactin、iturin | 增加脂肽surfactin和iturin的合成,增强菌株的抗真菌活性 | [ |
| 多黏菌素 | AA-3 | AA-6 | AA-7 | 脂肪酰基尾巴 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| polymyxins A | ||||
| P-A1 | D-Dab | D-Leu | L-Thr | 6-MOA |
| P-A2 | D-Dab | D-Leu | L-Thr | 6-MHA |
| polymyxin B | ||||
| P-B1 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Leu | 6-MOA |
| P-B2 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Leu | 6-MHA |
| P-B3 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Leu | OA |
| P-B4 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Leu | HA |
| P-B5 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Leu | NA |
| P-B6 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Leu | 3-OH-6-MOA |
| Ile-P-B1 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Ile | 6-MOA |
| polymyxin C | ||||
| P-C | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Thr | 6-MOA |
| polymyxin D | ||||
| P-D1 | D-Ser | D-Leu | L-Thr | 6-MOA |
| P-D2 | D-Ser | D-Leu | L-Thr | 6-MHA |
| polymyxin E | ||||
| P-E1 | L-Dab | D-Leu | D-Leu | 6-MOA |
| P-E2 | L-Dab | D-Leu | D-Leu | 6-MHA |
| P-E3 | L-Dab | D-Leu | D-Leu | OA |
| P-E4 | L-Dab | D-Leu | D-Leu | HA |
| P-E7 | L-Dab | D-Leu | D-Leu | 7-MOA |
| Ile-P-E1 | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Ile | 6-MOA |
| Ile-P-E2 | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Ile | 6-MHA |
| Ile-P-E8 | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Ile | 7-MNA |
| Nval-E1 | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Nval | 6-MOA |
| Val-E1 | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Val | 6-MOA |
| Val-E2 | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Val | 6-MHA |
| polymyxin M | ||||
| P-M | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Thr | 6-MOA |
| polymyxin P | ||||
| P-P1 | D-Dab | D-Phe | L-Thr | 6-MOA |
| P-P2 | D-Dab | D-Phe | L-Thr | 6-MHA |
表3 多黏菌素同系物化学结构
Tab. 3 Chemical structure of polymyxin homologues
| 多黏菌素 | AA-3 | AA-6 | AA-7 | 脂肪酰基尾巴 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| polymyxins A | ||||
| P-A1 | D-Dab | D-Leu | L-Thr | 6-MOA |
| P-A2 | D-Dab | D-Leu | L-Thr | 6-MHA |
| polymyxin B | ||||
| P-B1 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Leu | 6-MOA |
| P-B2 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Leu | 6-MHA |
| P-B3 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Leu | OA |
| P-B4 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Leu | HA |
| P-B5 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Leu | NA |
| P-B6 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Leu | 3-OH-6-MOA |
| Ile-P-B1 | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Ile | 6-MOA |
| polymyxin C | ||||
| P-C | L-Dab | D-Phe | L-Thr | 6-MOA |
| polymyxin D | ||||
| P-D1 | D-Ser | D-Leu | L-Thr | 6-MOA |
| P-D2 | D-Ser | D-Leu | L-Thr | 6-MHA |
| polymyxin E | ||||
| P-E1 | L-Dab | D-Leu | D-Leu | 6-MOA |
| P-E2 | L-Dab | D-Leu | D-Leu | 6-MHA |
| P-E3 | L-Dab | D-Leu | D-Leu | OA |
| P-E4 | L-Dab | D-Leu | D-Leu | HA |
| P-E7 | L-Dab | D-Leu | D-Leu | 7-MOA |
| Ile-P-E1 | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Ile | 6-MOA |
| Ile-P-E2 | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Ile | 6-MHA |
| Ile-P-E8 | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Ile | 7-MNA |
| Nval-E1 | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Nval | 6-MOA |
| Val-E1 | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Val | 6-MOA |
| Val-E2 | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Val | 6-MHA |
| polymyxin M | ||||
| P-M | L-Dab | D-Leu | L-Thr | 6-MOA |
| polymyxin P | ||||
| P-P1 | D-Dab | D-Phe | L-Thr | 6-MOA |
| P-P2 | D-Dab | D-Phe | L-Thr | 6-MHA |
| 表面活性素 | AA-2 | AA-4 | AA-7 | 脂肪酰基尾巴 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| surfactin | L-Leu | L-Val | L-Leu | C11, C12 |
| Ala4-surfactin | L-Leu | L-Ala | L-Leu | C11, C12 |
| Leu4-surfactin | L-Leu | L-Leu | L-Leu | C12 |
| Ile4-surfactin | L-Leu | L-Ile | L-Leu | C12 |
| Val7-surfactin | L-Leu | L-Val | L-Val | C11, C12, C13, C14 |
| Ile7-surfactin | L-Leu | L-Val | L-Ile | C11, C12, C13, C14 |
| Ile2,4-surfactin | L-Ile | L-Ile | L-Leu | C12 |
| Val2,7-surfactin | L-Val | L-Val | L-Val | C10~C12 |
| Val2,Ile7-surfactin | L-Val | L-Val | L-Ile | C10~C12 |
| Ile2,Val7-surfactin | L-Ile | L-Val | L-Val | C10~C12 |
| Ile2,4,7-surfactin | L-Ile | L-Ile | L-Ile | C12 |
表4 表面活性素同系物化学结构
Tab. 4 Chemical structure of surfactin homologues
| 表面活性素 | AA-2 | AA-4 | AA-7 | 脂肪酰基尾巴 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| surfactin | L-Leu | L-Val | L-Leu | C11, C12 |
| Ala4-surfactin | L-Leu | L-Ala | L-Leu | C11, C12 |
| Leu4-surfactin | L-Leu | L-Leu | L-Leu | C12 |
| Ile4-surfactin | L-Leu | L-Ile | L-Leu | C12 |
| Val7-surfactin | L-Leu | L-Val | L-Val | C11, C12, C13, C14 |
| Ile7-surfactin | L-Leu | L-Val | L-Ile | C11, C12, C13, C14 |
| Ile2,4-surfactin | L-Ile | L-Ile | L-Leu | C12 |
| Val2,7-surfactin | L-Val | L-Val | L-Val | C10~C12 |
| Val2,Ile7-surfactin | L-Val | L-Val | L-Ile | C10~C12 |
| Ile2,Val7-surfactin | L-Ile | L-Val | L-Val | C10~C12 |
| Ile2,4,7-surfactin | L-Ile | L-Ile | L-Ile | C12 |
| 丰原素 | AA-3 | AA-4 | AA-6 | AA-9 | AA-10 | 脂肪酰基尾巴 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fengycin | ||||||
| fengycin A | D-Tyr | D-Thr | D-Ala | L-Allo-Thr | L-Ile | C14~C18 |
| fengycin A2 | D-Tyr | D-Thr | D-Ala | L-Allo-Thr | L-Val | C14~C18 |
| fengycin B | D-Tyr | D-Thr | D-Val | L-Allo-Thr | L-Ile | C14~C18 |
| fengycin B2 | D-Tyr | D-Thr | D-Val | L-Allo-Thr | L-Val | C14~C18 |
| fengycin C | D-Tyr | D-Allo-Thr | D-Val | D-Allo-Thr | L-Ile | C14~C18 |
| fengycin S | D-Tyr | D-Ser | D-Val | L-Allo-Thr | L-Ile | C14~C18 |
| Plipastain | ||||||
| Plipastain A | L-Tyr | D-Allo-Thr | D-Ala | D-Tyr | L-Ile | C14~C18 |
| Plipastain B | L-Tyr | D-Allo-Thr | D-Val | D-Tyr | L-Ile | C14~C18 |
表5 丰原素同系物化学结构
Tab. 5 Chemical structure of fengycin homologues
| 丰原素 | AA-3 | AA-4 | AA-6 | AA-9 | AA-10 | 脂肪酰基尾巴 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fengycin | ||||||
| fengycin A | D-Tyr | D-Thr | D-Ala | L-Allo-Thr | L-Ile | C14~C18 |
| fengycin A2 | D-Tyr | D-Thr | D-Ala | L-Allo-Thr | L-Val | C14~C18 |
| fengycin B | D-Tyr | D-Thr | D-Val | L-Allo-Thr | L-Ile | C14~C18 |
| fengycin B2 | D-Tyr | D-Thr | D-Val | L-Allo-Thr | L-Val | C14~C18 |
| fengycin C | D-Tyr | D-Allo-Thr | D-Val | D-Allo-Thr | L-Ile | C14~C18 |
| fengycin S | D-Tyr | D-Ser | D-Val | L-Allo-Thr | L-Ile | C14~C18 |
| Plipastain | ||||||
| Plipastain A | L-Tyr | D-Allo-Thr | D-Ala | D-Tyr | L-Ile | C14~C18 |
| Plipastain B | L-Tyr | D-Allo-Thr | D-Val | D-Tyr | L-Ile | C14~C18 |
| 达托霉素 | 直链氨基酸部分 | 环链氨基酸部分 | 脂肪酰侧链 |
|---|---|---|---|
| daptomycin | Trp-D-Asn-Asp | Thr-Gly-Om-Asp-D-Ala-Asp-Gly-D-Ser-3MeGlu-Kyn | n-decanoyl |
| A21978C1 | Trp-D-Asn-Asp | Thr-Gly-Om-Asp-D-Ala-Asp-Gly-D-Ser-3MeGlu-Kyn | anteiso-undecanoyl |
| A21978C2 | Trp-D-Asn-Asp | Thr-Gly-Om-Asp-D-Ala-Asp-Gly-D-Ser-3MeGlu-Kyn | iso-dodecanoyl |
| A21978C3 | Trp-D-Asn-Asp | Thr-Gly-Om-Asp-D-Ala-Asp-Gly-D-Ser-3MeGlu-Kyn | anteiso-tridecanoyl |
表6 达托霉素及其同系物
Tab. 6 Schematic diagram of daptomycin and its homologues
| 达托霉素 | 直链氨基酸部分 | 环链氨基酸部分 | 脂肪酰侧链 |
|---|---|---|---|
| daptomycin | Trp-D-Asn-Asp | Thr-Gly-Om-Asp-D-Ala-Asp-Gly-D-Ser-3MeGlu-Kyn | n-decanoyl |
| A21978C1 | Trp-D-Asn-Asp | Thr-Gly-Om-Asp-D-Ala-Asp-Gly-D-Ser-3MeGlu-Kyn | anteiso-undecanoyl |
| A21978C2 | Trp-D-Asn-Asp | Thr-Gly-Om-Asp-D-Ala-Asp-Gly-D-Ser-3MeGlu-Kyn | iso-dodecanoyl |
| A21978C3 | Trp-D-Asn-Asp | Thr-Gly-Om-Asp-D-Ala-Asp-Gly-D-Ser-3MeGlu-Kyn | anteiso-tridecanoyl |
| 伊枯草菌素 | AA-1 | AA-4 | AA-5 | AA-6 | 脂肪酰基尾巴 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iturin A | L-Asn/Asp | L-Gln | L-Pro | D-Asn | C13~C17 |
| bacillomycin | L-Asn/Asp | L-Pro/Gln/Ser | L-Gln/Pro/Glu | D-Ser/Asn | C13~C17 |
| mixirins | L-Asn | L-Gln | L-Ser | D-Asn | C13~C17 |
| mojawensin | L-Asn | L-Gln | L-Pro | D-Asn | C13~C17 |
表7 伊枯草素同系物化学结构
Tab. 7 Chemical structure of iturin homologues
| 伊枯草菌素 | AA-1 | AA-4 | AA-5 | AA-6 | 脂肪酰基尾巴 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iturin A | L-Asn/Asp | L-Gln | L-Pro | D-Asn | C13~C17 |
| bacillomycin | L-Asn/Asp | L-Pro/Gln/Ser | L-Gln/Pro/Glu | D-Ser/Asn | C13~C17 |
| mixirins | L-Asn | L-Gln | L-Ser | D-Asn | C13~C17 |
| mojawensin | L-Asn | L-Gln | L-Pro | D-Asn | C13~C17 |
| 1 | LIU H-W, BEGLEY T P. Comprehensive natural products III: chemistry and biology [M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2020. |
| 2 | MARTÍNEZ-NÚÑEZ M A, RODRÍGUEZ-ESCAMILLA Z. Mining the Yucatan Coastal microbiome for the identification of non-ribosomal peptides synthetase (NRPS) genes [J]. Toxins, 2020, 12(6):349. |
| 3 | SCHNEIDER T, MÜLLER A, MIESS H, et al. Cyclic lipopeptides as antibacterial agents-potent antibiotic activity mediated by intriguing mode of actions [J]. International Journal of Medical Microbiology, 2014, 304(1): 37-43. |
| 4 | FELNAGLE E A, JACKSON E E, CHAN Y A, et al. Nonribosomal peptide synthetases involved in the production of medically relevant natural products [J]. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 2008, 5(2): 191-211. |
| 5 | NATION R L, LI J, CARS O, et al. Framework for optimisation of the clinical use of colistin and polymyxin B: the Prato polymyxin consensus [J]. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 2015, 15(2): 225-234. |
| 6 | LIU Y Y, WANG Y, WALSH T R, et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: a microbiological and molecular biological study [J]. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 2016, 16(2): 161-168. |
| 7 | DI PILATO V, ARENA F, TASCINI C, et al. mcr-1.2, A new mcr variant carried on a transferable plasmid from a colistin-resistant KPC carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae strain of sequence type 512 [J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2016, 60(9):5612-5615. |
| 8 | BRINK A J, RICHARDS G A, COLOMBO G, et al. Multicomponent antibiotic substances produced by fermentation: implications for regulatory authorities, critically ill patients and generics [J]. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 2014, 43(1):1-6. |
| 9 | VELKOV T, GALLARDO-GODOY A, SWARBRICK J D, et al. Structure, function, and biosynthetic origin of octapeptin antibiotics active against extensively drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria [J]. Cell Chemical Biology, 2018, 25(4):380-391.e5. |
| 10 | ZEITLINGER M A, DERENDORF H, MOUTON J W, et al. Protein binding: do we ever learn?[J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2011, 55(7): 3067-3074. |
| 11 | SIRIWARDENA T N, STACH M, HE R, et al. Lipidated peptide dendrimers killing multidrug-resistant bacteria [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(1): 423-432. |
| 12 | BALTZ R H. Combinatorial biosynthesis of cyclic lipopeptide antibiotics: a model for synthetic biology to accelerate the evolution of secondary metabolite biosynthetic pathways [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2014, 3(10):748–758. |
| 13 | INÈS M, DHOUHA G. Lipopeptide surfactants: production, recovery and pore forming capacity [J]. Peptides, 2015, 71:100-112. |
| 14 | TALLY F P, DEBRUIN M F. Development of daptomycin for Gram-positive infections [J]. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 2000, 46(4): 523-526. |
| 15 | TRIMBLE M J, MLYNÁRČIK P, KOLÁŘ M, et al. Polymyxin: Alternative mechanisms of action and resistance [J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine, 2016, 6(10): a025288. |
| 16 | KÜGLER J H, LE ROES-HILL M, SYLDATK C, et al. Surfactants tailored by the class Actinobacteria[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2015, 6:212. |
| 17 | ONGENA M, JACQUES P. Bacillus lipopeptides: versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol [J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2008, 16(3):115–125. |
| 18 | GROSS H, LOPER J E. Genomics of secondary metabolite production by Pseudomonas spp [J]. Natural Product Reports, 2009, 26(11): 1408-1446. |
| 19 | BANAT I M, FRANZETTI A, GANDOLFI I, et al. Microbial biosurfactants production, applications and future potential [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 87(2): 427-444. |
| 20 | COCHRANE S A, VEDERAS J C. Lipopeptides from Bacillus and Paenibacillus spp. a gold mine of antibiotic candidates [J]. Medicinal Research Reviews, 2016, 36(1): 4-31. |
| 21 | MARAHIEL M A. A structural model for multimodular NRPS assembly lines [J]. Natural Product Reports, 2016, 33(2): 136-140. |
| 22 | ZHANG F L, WANG Y K, JIANG Q, et al. Substrate selection of adenylation domains for nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) in bacillamide C biosynthesis by marine Bacillus atrophaeus C89 [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2018, 45(5): 335-344. |
| 23 | BUMPUS S B, EVANS B S, THOMAS P M, et al. A proteomics approach to discovering natural products and their biosynthetic pathways [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2009, 27(10): 951-956. |
| 24 | MEIER J L, NIESSEN S, HOOVER H S, et al. An orthogonal active site identification system (OASIS) for proteomic profiling of natural product biosynthesis [J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2009, 4(11): 948-957. |
| 25 | ISHIKAWA F, TANABE G. Chemical strategies for visualizing and analyzing endogenous nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) megasynthetases [J]. Chembiochem, 2019, 20(16): 2032-2040. |
| 26 | 肖丽萍,邓子新,刘天罡. 链霉菌底盘细胞的开发现状及其应用[J]. 微生物学报, 2016, 56(3): 441-453. |
| XIAO L P, DENG Z X, LIU T G. Progress in developing and applying Streptomyces chassis - a review [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2016, 56(3): 441-453. | |
| 27 | 卜庆廷. 基于恰塔努加链霉菌的聚酮类底盘细胞构建与评估[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. |
| BU Q T. Construction and evaluation of polyketide chassis derived from Streptomyces chattanoogensis [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019. | |
| 28 | GEYS R, SOETAERT W, BOGAERT I VAN. Biotechnological opportunities in biosurfactant production [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2014, 30: 66-72. |
| 29 | KOSARIC N, VARDAR-SUKAN F. Biosurfactants: production and applications [M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2014. |
| 30 | KOMATSU M, KOMATSU K, KOIWAI H, et al. Engineered Streptomyces avermitilis host for heterologous expression of biosynthetic gene cluster for secondary metabolites [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2013, 2(7): 384-396. |
| 31 | LIU Q, XIAO L P, ZHOU Y J, et al. Development of Streptomyces sp. FR-008 as an emerging chassis [J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2016, 1(3): 207-214. |
| 32 | TAN B, ZHANG Q B, ZHU Y G, et al. Deciphering biosynthetic enzymes leading to 4-chloro-6-methyl-5,7-dihydroxyphenylglycine, a non-proteinogenic amino acid in totopotensamides [J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2020, 15(3): 766-773. |
| 33 | BALTZ R H. Correction to: synthetic biology, genome mining, and combinatorial biosynthesis of NRPS‑derived antibiotics: a perspective [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2018, 45(7): 651-655. |
| 34 | ZHANG M M, WANG Y, ANG E L, et al. Engineering microbial hosts for production of bacterial natural products [J]. Natural Product Reports, 2016, 33(8): 963-987. |
| 35 | WANG X, ZHOU H B, CHEN H N, et al. Discovery of recombinases enables genome mining of cryptic biosynthetic gene clusters in Burkholderiales species [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(18): E4255-E4263. |
| 36 | ZHI Y, WU Q, XU Y. Genome and transcriptome analysis of surfactin biosynthesis in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MT45 [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 40976. |
| 37 | WU Q, ZHI Y, XU Y. Systematically engineering the biosynthesis of a green biosurfactant surfactin by Bacillus subtilis 168[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 52: 87-97. |
| 38 | HÜHNER E, BACKHAUS K, KRAUT R, et al. Production of α-keto carboxylic acid dimers in yeast by overexpression of NRPS-like genes from Aspergillus terreus [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(4): 1663-1672. |
| 39 | NAH H J, PYEON H R, KANG S H, et al. Cloning and heterologous expression of a large-sized natural product biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces species [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 394. |
| 40 | HACKER C, CAI X, KEGLER C, et al. Structure-based redesign of docking domain interactions modulates the product spectrum of a rhabdopeptide-synthesizing NRPS [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 4366. |
| 41 | BALTZ R H. Synthetic biology, genome mining, and combinatorial biosynthesis of NRPS-derived antibiotics: a perspective [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2018, 45(7): 635-649. |
| 42 | GRADY E N, MACDONALD J, LIU L D, et al. Current knowledge and perspectives of Paenibacillus: a review[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15(1):203. |
| 43 | TAMBADOU F, CARADEC T, GAGEZ A L, et al. Characterization of the colistin (polymyxin E1 and E2) biosynthetic gene cluster [J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2015, 197(4): 521-532. |
| 44 | KWA A L, LIM T P, LOW J G, et al. Pharmacokinetics of polymyxin B1 in patients with multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections [J]. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease, 2008, 60(2): 163-167. |
| 45 | HE H, LI J C, NATION R L, et al. Pharmacokinetics of four different brands of colistimethate and formed colistin in rats[J]. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 2013, 68(10): 2311-2317. |
| 46 | SIVANESAN S, ROBERTS K, WANG J P, et al. Pharmacokinetics of the individual major components of polymyxin B and colistin in rats [J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2017, 80(1): 225-229. |
| 47 | ROBERTS K D, AZAD M A K, WANG J P, et al. Antimicrobial activity and toxicity of the major lipopeptide components of polymyxin B and colistin: last-line antibiotics against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria [J]. ACS Infectious Diseases, 2015, 1(11): 568-575. |
| 48 | MEDEMA M H, CIMERMANCIC P, SALI A, et al. A systematic computational analysis of biosynthetic gene cluster evolution: lessons for engineering biosynthesis [J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2014, 10(12):e1004016. |
| 49 | YAN F, BURGARD C, POPOFF A, et al. Synthetic biology approaches and combinatorial biosynthesis towards heterologous lipopeptide production [J]. Chemical Science, 2018, 9(38): 7510-7519. |
| 50 | MINGEOT-LECLERCQ M P, TULKENS P M, DENAMUR S, et al. Novel polymyxin derivatives are less cytotoxic than polymyxin B to renal proximal tubular cells [J]. Peptides, 2012, 35(2): 248-252. |
| 51 | VAARA M, SADER H S, RHOMBERG P R, et al. Antimicrobial activity of the novel polymyxin derivative NAB739 tested against Gram-negative pathogens [J]. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 2013, 68(3): 636-639. |
| 52 | SCHAUWECKER F, PFENNIG F, GRAMMEL N, et al. Construction and in vitro analysis of a new bi-modular polypeptide synthetase for synthesis of N-methylated acyl peptides [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2000, 7(4): 287-297. |
| 53 | ZHANG K, NELSON K M, BHURIPANYO K, et al. Engineering the substrate specificity of the DhbE adenylation domain by yeast cell surface display [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2013, 20(1): 92-101. |
| 54 | DUERFAHRT T, EPPELMANN K, MÜLLER R, et al. Rational design of a bimodular model system for the investigation of heterocyclization in nonribosomal peptide biosynthesis[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2004, 11(2): 261-271. |
| 55 | THIRLWAY J, LEWIS R, NUNNS L, et al. Introduction of a non-natural amino acid into a nonribosomal peptide antibiotic by modification of adenylation domain specificity [J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2012, 51(29): 7181-7184. |
| 56 | HEIDE L, WESTRICH L, ANDERLE C, et al. Use of a halogenase of hormaomycin biosynthesis for formation of new clorobiocin analogues with 5-chloropyrrole moieties [J]. ChembioChem, 2008, 9(12): 1992-1999. |
| 57 | NGUYEN K T, RITZ D, GU J-Q, et al. Combinatorial biosynthesis of novel antibiotics related to daptomycin [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(46): 17462-17467. |
| 58 | FISCHBACH M A, LAI J R, ROCHE E D, et al. Directed evolution can rapidly improve the activity of chimeric assembly-line enzymes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(29): 11951-11956. |
| 59 | HAN J W, KIM E Y, LEE J M, et al. Site-directed modification of the adenylation domain of the fusaricidin nonribosomal peptide synthetase for enhanced production of fusaricidin analogs [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2012, 34(7): 1327-1334. |
| 60 | KRIES H, NIQUILLE D L, HILVERT D. A subdomain swap strategy for reengineering nonribosomal peptides [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2015, 22(5): 640-648. |
| 61 | BIAN X Y, PLAZA A, YAN F, et al. Rational and efficient site-directed mutagenesis of adenylation domain alters relative yields of luminmide derivatives in vivo [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2015, 112(7): 1343-1353. |
| 62 | KIM S Y, PARK S Y, CHOI S K, et al. Biosynthesis of polymyxins B, E, and P using genetically engineered polymyxin synthetases in the surrogate host Bacillus subtilis [J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 25(7): 1015-1025. |
| 63 | CALCOTT M J, OWEN J G, LAMONT I L, et al. Biosynthesis of novel Pyoverdines by domain substitution in a nonribosomal peptide synthetase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 80(18): 5723-5731. |
| 64 | CALCOTT M J, ACKERLEY D F. Portability of the thiolation domain in recombinant pyoverdine non-ribosomal peptide synthetases [J]. BMC Microbiology, 2015, 15: 162. |
| 65 | STACHELHAUS T, SCHNEIDER A, MARAHIEL M A. Rational design of peptide antibiotics by targeted replacement of bacterial and fungal domains [J]. Science, 1995, 269(5220): 69-72. |
| 66 | YAKIMOV M M, GIULIANO L, TIMMIS K N, et al. Recombinant acylheptapeptide lichenysin: high level of production by Bacillus subtilis cells [J]. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2000, 2(2): 217-224. |
| 67 | EPPELMANN K, STACHELHAUS T, MARAHIEL M A. Exploitation of the selectivity-conferring code of nonribosomal peptide synthetases for the rational design of novel peptide antibiotics [J]. Biochemistry, 2002, 41(30): 9718-9726. |
| 68 | MOOTZ H D, KESSLER N, LINNE U, et al. Decreasing the ring size of a cyclic nonribosomal peptide antibiotic by in-frame module deletion in the biosynthetic genes [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(37): 10980-10981. |
| 69 | SCHWARZER D, MOOTZ H D, MARAHIEL M A. Exploring the impact of different thioesterase domains for the design of hybrid peptide synthetases [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2001, 8(10): 997-1010. |
| 70 | MOOTZ H D, SCHWARZER D, MARAHIEL M A. Construction of hybrid peptide synthetases by module and domain fusions [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2000, 97(11): 5848-5853. |
| 71 | ZHAO H B, SHAO D Y, JIANG C M, et al. Biological activity of lipopeptides from Bacillus [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(15): 5951-5960. |
| 72 | COUTTE F, LECOUTURIER D, DIMITROV K, et al. Microbial lipopeptide production and purification bioprocesses, current progress and future challenges [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 12(7): 1600566. |
| 73 | WANG M M, YU H M, SHEN Z Y. Antisense RNA-based strategy for enhancing surfactin production in Bacillus subtilis TS1726 via overexpression of the unconventional biotin carboxylase II to enhance ACCase activity [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(2): 251-256. |
| 74 | DANG Y L, ZHAO F J, LIU X S, et al. Enhanced production of antifungal lipopeptide iturin A by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LL3 through metabolic engineering and culture conditions optimization [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18(1): 1-14. |
| 75 | XU Y X, CAI D B, ZHANG H, et al. Enhanced production of iturin A in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens by genetic engineering and medium optimization [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2020, 90: 50-57. |
| 76 | HUANG X W, MA T M, TIAN J, et al. wblA, a pleiotropic regulatory gene modulating morphogenesis and daptomycin production in Streptomyces roseosporus [J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2017, 123(3): 669-677. |
| 77 | STEVENS B W, JOSKA T M, ANDERSON A C. Progress toward re-engineering non-ribosomal peptide synthetase proteins: a potential new source of pharmacological agents [J]. Drug Development Research, 2005, 66(1): 9-18. |
| 78 | UGURU G C, MILNE C, BORG M, et al. Active-site modifications of adenylation domains lead to hydrolysis of upstream nonribosomal peptidyl thioester intermediates [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(16): 5032-5033. |
| 79 | BELSHAW P J, WALSH C T, STACHELHAUS T. Aminoacyl-CoAs as probes of condensation domain selectivity in nonribosomal peptide synthesis [J]. Science, 1999, 284(5413): 486-489. |
| 80 | ACKERLEY D F, LAMONT I L. Characterization and genetic manipulation of peptide synthetases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 in order to generate novel pyoverdines [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2004, 11(7): 971-980. |
| 81 | DE FERRA F, RODRIGUEZ F, TORTORA O, et al. Engineering of peptide synthetases. Key role of the thioesterase-like domain for efficient production of recombinant peptides [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1997, 272(40): 25304-25309. |
| 82 | DUERFAHRT T, DOEKEL S, SONKE T, et al. Construction of hybrid peptide synthetases for the production of α-l-aspartyl-l-phenylalanine, a precursor for the high-intensity sweetener aspartame [J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 2003, 270(22): 4555-4563. |
| 83 | BUTZ D, SCHMIEDERER T, HADATSCH B, et al. Module extension of a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase of the glycopeptide antibiotic balhimycin produced by Amycolatopsis balhimycina [J]. ChemBioChem, 2008, 9(8): 1195-1200. |
| 84 | CHOOI Y H, TANG Y. Adding the lipo to lipopeptides: do more with less [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2010, 17(8): 791-793. |
| 85 | SHAHEEN M, LI J, ROSS A C, et al. Paenibacillus polymyxa PKB1 produces variants of polymyxin B-type antibiotics [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2011, 18(12): 1640-1648. |
| 86 | NIU B, VATER J, RUECKERT C, et al. Polymyxin P is the active principle in suppressing phytopathogenic Erwinia spp. by the biocontrol rhizobacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa M-1 [J]. BMC Microbiology, 2013, 13(1): 1-13. |
| 87 | GALEA C A, HAN M L, ZHU Y, et al. Characterization of the polymyxin D synthetase biosynthetic cluster and product profile of Paenibacillus polymyxa ATCC 10401 [J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2017, 80(5): 1264-1274. |
| 88 | BLOUDOFF K, RODIONOV D, SCHMEING T M. Crystal structures of the first condensation domain of CDA synthetase suggest conformational changes during the synthetic cycle of nonribosomal peptide synthetases [J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2013, 425(17): 3137-3150. |
| 89 | MÜLLER A, WENZEL M, STRAHL H, et al. Daptomycin inhibits cell envelope synthesis by interfering with fluid membrane microdomains [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(45): E7077-E7086. |
| 90 | BALTZ R H, MIAO V, WRIGLEY S K. Natural products to drugs: daptomycin and related lipopeptide antibiotics [J]. Natural Product Reports, 2005, 22(6): 717-741. |
| 91 | LIU T Q, ZHU N Y, ZHONG C, et al. Effect of N-methylated and fatty acid conjugation on analogs of antimicrobial peptide Anoplin [J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2020, 152: 105453. |
| 92 | DHALI D, COUTTE F, ARIAS A A, et al. Genetic engineering of the branched fatty acid metabolic pathway of Bacillus subtilis for the overproduction of surfactin C14 isoform [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 12(7): 1600574. |
| 93 | LIU Q, FAN W J, ZHAO Y J, et al. Probing and engineering the fatty acyl substrate selectivity of starter condensation domains of nonribosomal peptide synthetases in lipopeptide biosynthesis [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 15(2): e1900175. |
| 94 | FAN W J, LIU H, LIU P P, et al. Characterization of protein interaction surface on fatty acyl selectivity of starter condensation domain in lipopeptide biosynthesis[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(2): 653-660. |
| 95 | NGUYEN K T, HE X W, ALEXANDER D C, et al. Genetically engineered lipopeptide antibiotics related to A54145 and daptomycin with improved properties [J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2010, 54(4): 1404-1413. |
| 96 | HANSEN D B, BUMPUS S B, ARON Z D, et al. The loading module of mycosubtilin: an adenylation domain with fatty acid selectivity [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(20): 6366-6367. |
| 97 | DING L S, GUO W B, CHEN X H. Exogenous addition of alkanoic acids enhanced production of antifungal lipopeptides in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Pc3[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(13): 5367-5377. |
| 98 | ZHOU D Y, HU F X, LIN J Z, et al. Genome and transcriptome analysis of Bacillus velezensis BS-37, an efficient surfactin producer from glycerol, in response to D-/L-leucine [J]. MicrobiologyOpen, 2019, 8(8): e00794. |
| 99 | WU J Y, LIAO J H, SHIEH C J, et al. Kinetic analysis on precursors for iturin A production from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BPD1 [J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2018, 126(5): 630-635. |
| 100 | KATO H, NISHIYAMA H, NAKAO K, et al. Pressor effects of orally administered beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents in consciou spontaneously hypertensive rats [J]. Japanese Journal of Pharmacology, 1976, 26(6): 772-775. |
| 101 | BARTAL A, VIGNESHWARI A, BÓKA B, et al. Effects of different cultivation parameters on the production of surfactin variants by a Bacillus subtilis strain [J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(10): 2675. |
| 102 | LYHS U, KATZAV M, ISOHANNI P, et al. The temporal, PFGE and resistance pattern associations suggest that poultry products are only a minor source of human infections in western Finland [J]. Food Microbiology, 2010, 27(2): 311-315. |
| 103 | LIN H-Y, RAO Y, WU W-S, et al. Ferrous ion enhanced lipopeptide antibiotic iturin A production from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B128 [J]. International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 2007, 2: 123-132. |
| 104 | COOPER D G, MACDONALD C R, DUFF S J, et al. Enhanced production of surfactin form Bacillus subtilis by continous product removal and metal cation additions[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,1981, 42(3):408-412. |
| 105 | BESSON F, M-L HOURDOU, MICHEL G. Studies on the biosynthesis of iturin, an antibiotic of Bacillus subtilis, and alipopeptide containing β-hydroxy fatty acids [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 1990, 1036(2): 101-106. |
| 106 | ZHOU S N, LIU G, ZHENG R K, et al. Structural and functional insights into iturin W, a novel lipopeptide produced by the deep-sea bacterium Bacillus sp. strain wsm-1 [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2020, 86(21): e01597-20. |
| 107 | BESSON F, HOURDOU M L. Effect of amino acids on the biosynthesis of β-amino acids, constituents of bacillomycins F [J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 1987, 40(2): 221-223. |
| 108 | RAVI A, NANDAYIPURATH V V T, RAJAN S, et al. Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticle supplementation on the enhanced production of surfactin and iturin lipopeptides of endophytic Bacillus sp. Fcl1 and its ameliorated antifungal activity [J]. Pest Management Science, 2021, 77(2): 1035-1041. |
| 109 | YUAN Y, XU Q M, YU S C, et al. Control of the polymyxin analog ratio by domain swapping in the nonribosomal peptide synthetase of Paenibacillus polymyxa [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2020, 47(6/7): 551-562. |
| 110 | KRAAS F I, HELMETAG V, WITTMANN M, et al. Functional dissection of surfactin synthetase initiation module reveals insights into the mechanism of lipoinitiation [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2010, 17(8): 872-880. |
| 111 | SCHNEIDER A, STACHELHAUS T, MARAHIEL M A. Targeted alteration of the substrate specificity of peptide synthetases by rational module swapping [J]. Molecular and General Genetics MGG, 1998, 257(3): 308-318. |
| 112 | JIANG J, GAO L, BIE X M, et al. Identification of novel surfactin derivatives from NRPS modification of Bacillus subtilis and its antifungal activity against Fusarium moniliforme [J]. BMC Microbiology, 2016, 16(1): 1-14. |
| 113 | SIEBER S A, MARAHIEL M A. Learning from nature's drug factories: nonribosomal synthesis of macrocyclic peptides [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2003, 185(24): 7036-7043. |
| 114 | VILLEGAS-ESCOBAR V, CEBALLOS I, MIRA J J, et al. fengycin C produced by Bacillus subtilis EA-CB0015 [J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2013, 76(4):503–509. |
| 115 | SANG-CHEOL L, KIM S H, PARK I H, et al. Isolation, purification, and characterization of novel fengycin S from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LSC04 degrading-crude oil [J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2010, 15(2): 246-253. |
| 116 | GAO L, GUO J P, FAN Y, et al. Module and individual domain deletions of NRPS to produce plipastatin derivatives in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17(1): 84. |
| 117 | GONG A D, LI H P, YUAN Q S, et al. Antagonistic mechanism of iturin A and plipastatin A from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens S76-3 from wheat spikes against Fusarium graminearum [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(2): e0116871. |
| 118 | MA Z W, HU J C. Plipastatin A1 produced by a marine sediment-derived Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SH-B74 contributes to the control of gray mold disease in tomato [J]. 3 Biotech, 2018, 8(2): 1-10. |
| 119 | GAO L, LIU H X, MA Z, et al. Translocation of the thioesterase domain for the redesign of plipastatin synthetase [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:38467. |
| 120 | TAYLOR S D, PALMER M. The action mechanism of daptomycin [J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2016, 24(24): 6253-6268. |
| 121 | BALTZ R H. Biosynthesis and genetic engineering of lipopeptides in Streptomyces roseosporus [M]// Complex enzymes in microbial natural product biosynthesis, part a: overview articles and peptides. Elsevier, 2009: 511-531. |
| 122 | HUBER F M, PIEPER R L, TIETZ A J. The formation of daptomycin by supplying decanoic acid to Streptomyces roseosporus cultures producing the antibiotic complex A21978C [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 1988, 7(4): 283-292. |
| 123 | KAWAGOE Y, SHIRAISHI S, KONDO H, et al. Cyclic lipopeptide iturin A structure-dependently induces defense response in Arabidopsis plants by activating SA and JA signaling pathways [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2015, 460(4): 1015-1020. |
| 124 | 罗帅. 达托霉素优质高效生物合成的调控机制研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. |
| LUO S. The regulatory mechanisms of daptomycin in biosynthesis in high-quality and efficiency [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018. | |
| 125 | ONAKA H, MORI Y, IGARASHI Y, et al. Mycolic acid-containing bacteria induce natural-product biosynthesis in Streptomyces species [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(2): 400-406. |
| 126 | ALVES A R, SEQUEIRA A M, CUNHA Â. Increase in bacterial biosurfactant production by co-cultivation with biofilm-forming bacteria [J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2019, 69(1): 79-86. |
| 127 | WOŹNIAK-KARCZEWSKA M, MYSZKA K, SZNAJDROWSKA A, et al. Isolation of rhamnolipids-producing cultures from faeces: influence of interspecies communication on the yield of rhamnolipid congeners [J]. New Biotechnology, 2017, 36: 17-25. |
| 128 | WU Q, NI M, DOU K, et al. Co-culture of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ACCC11060 and Trichoderma asperellum GDFS1009 enhanced pathogen-inhibition and amino acid yield [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17(1): 155. |
| 129 | MNIF I, MNIF S, SAHNOUN R, et al. Biodegradation of diesel oil by a novel microbial consortium: comparison between co-inoculation with biosurfactant-producing strain and exogenously added biosurfactants [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(19): 14852-14861. |
| 130 | GÖTZE S, HERBST-IRMER R, KLAPPER M, et al. Structure, biosynthesis, and biological activity of the cyclic lipopeptide Anikasin [J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2017, 12(10): 2498-2502. |
| 131 | GOERING A W, LI J, MCCLURE R A, et al. In vitro reconstruction of nonribosomal peptide biosynthesis directly from DNA using cell-free protein synthesis [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(1): 39-44. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [12] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [13] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [14] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [15] | 查文龙, 卜兰, 訾佳辰. 中药药效成分群的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||