合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (5): 1189-1210.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-001
负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用
郑皓天1,2, 李朝风1,2, 刘良叙1,2, 王嘉伟1,2, 李恒润1,2, 倪俊1,2
- 1.上海交通大学生命科学技术学院,微生物代谢国家重点实验室,上海 200240
2.上海交通大学张江高等研究院,上海 201203
-
收稿日期:2024-01-02修回日期:2024-04-16出版日期:2024-10-31发布日期:2024-11-20 -
通讯作者:倪俊 -
作者简介:郑皓天 (2000—),男,硕士研究生。研究方向为人工光合群落和光合细胞工厂的设计与优化。 E-mail:zhenghtjames@sjtu.edu.cn倪俊 (1987—),男,副教授,博士生导师。研究方向为合成生物学;人工光合群落;多酶级联组装;负碳生物合成等。 E-mail:tearroad@sjtu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(32071418);国家重点研发计划(2019YFA0904603)
Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community
ZHENG Haotian1,2, LI Chaofeng1,2, LIU Liangxu1,2, WANG Jiawei1,2, LI Hengrun1,2, NI Jun1,2
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism,School of Life Science and Technology,Shanghai Jiaotong University,Shanghai 200240,China
2.Zhangjiang Institute for Advanced Study,Shanghai Jiaotong University,Shanghai 201203,China
-
Received:2024-01-02Revised:2024-04-16Online:2024-10-31Published:2024-11-20 -
Contact:NI Jun
摘要:
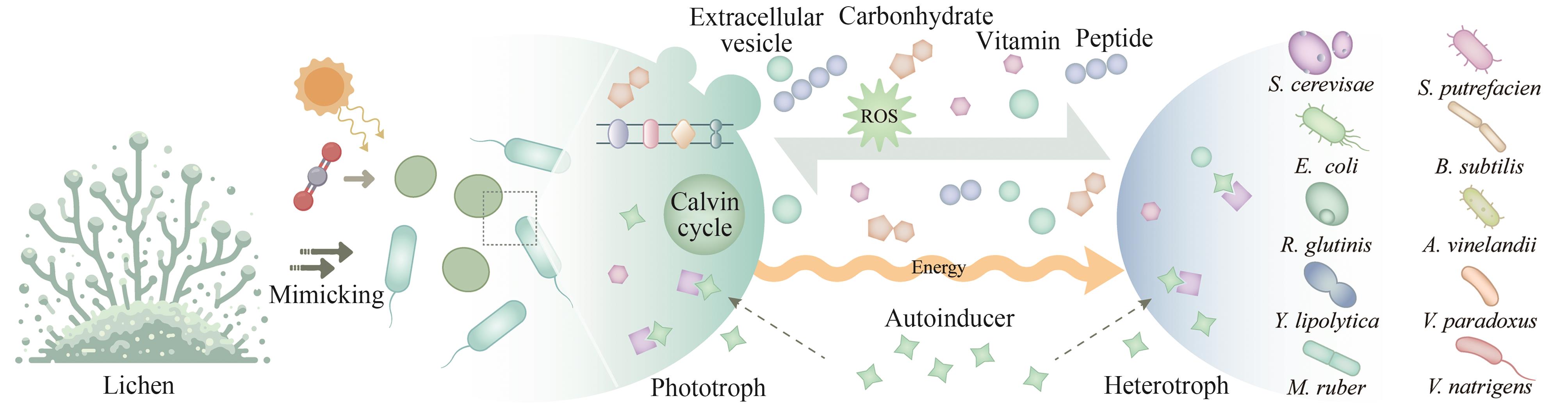
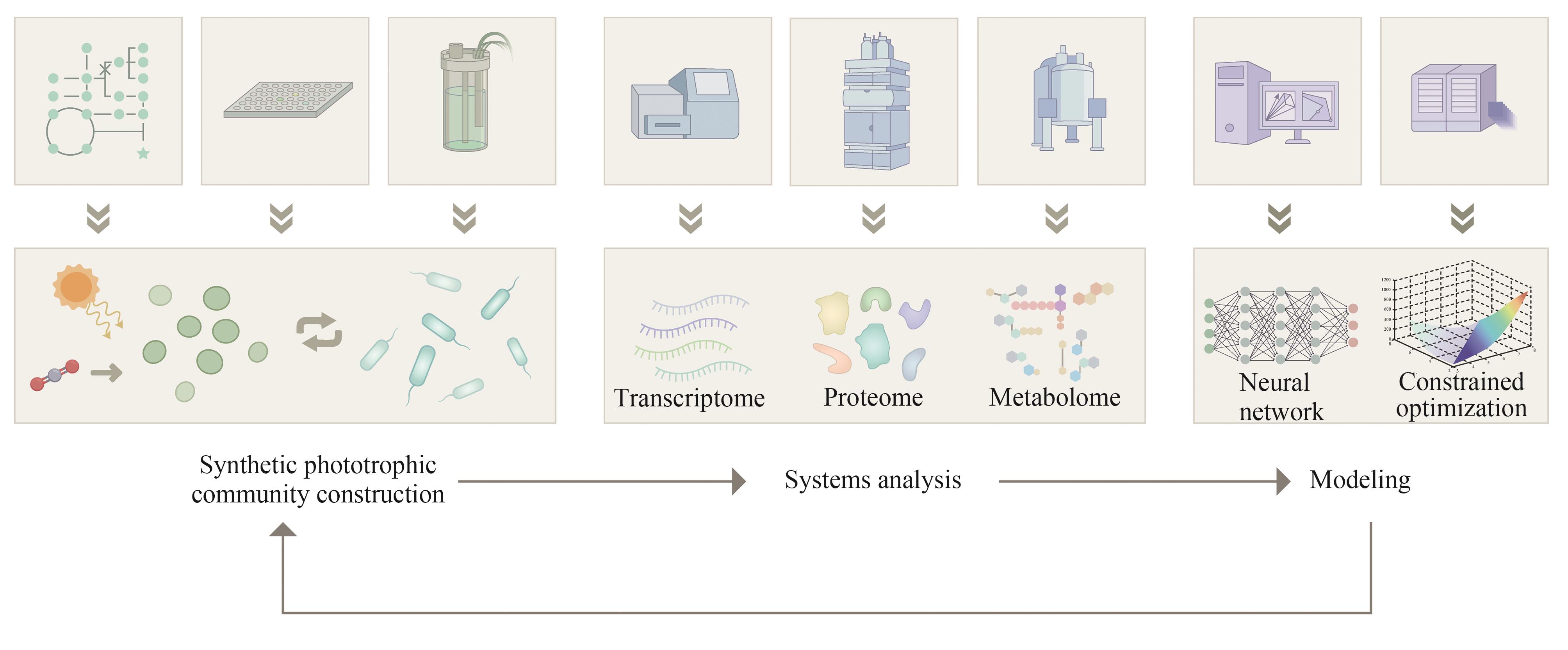
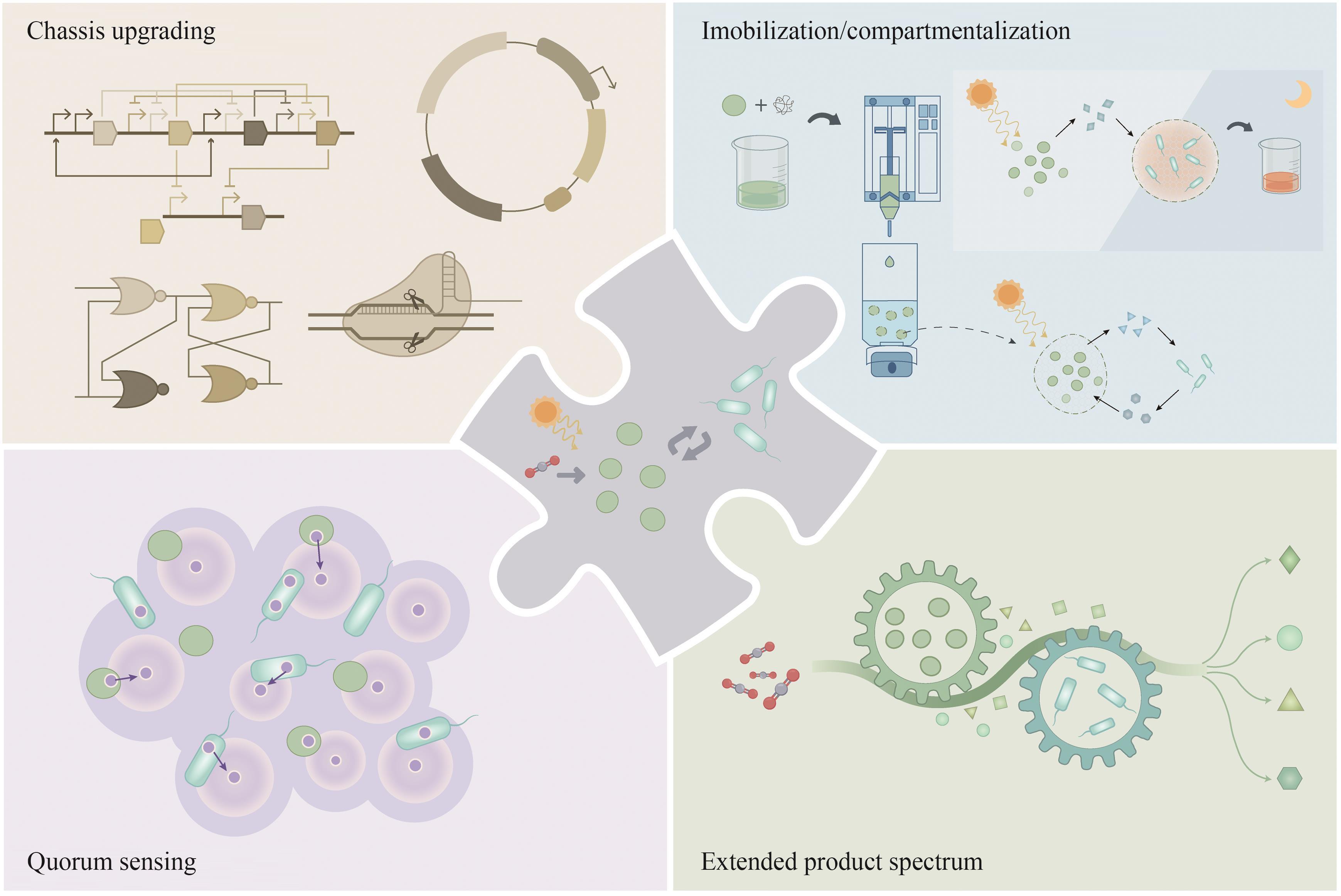
CO2生物转化技术的开发为解决能源转型和气候变化问题提供了可能。人工光合群落是由密切协作的光合自养微生物与异养微生物组成的新一代生物炼制平台,能够通过群落成员间的互利代谢分工,高效地利用光能将CO2直接转化为生物质和多种化学品,是实现负碳生物制造的潜在途径之一,因其在适用性和鲁棒性方面的优势受到了广泛的关注。近年来,随着系统生物学研究和合成生物技术的快速发展,多种研究策略被用于人工光合群落的设计与优化,取得了长远的进展,促进了对光合群落生产的理解。本文综述了光合群落的互作机制、独到优势和系统生物学研究方法,着重介绍人工光合群落的底盘升级、固定化/区室化技术、加强内部多层次调控等设计与优化策略以及在不同领域的应用进展。在此基础上,探讨了进一步将人工光合群落规模化应用所面临的光合效率和中间碳水化合物限制以及外源生物污染等潜在挑战,对纳米半导体材料杂合、物种间精细互作关系调控、基于多组学数据的群落模型构建等未来的改造方向和研究策略进行了展望。
中图分类号:
引用本文
郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210.
ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210.
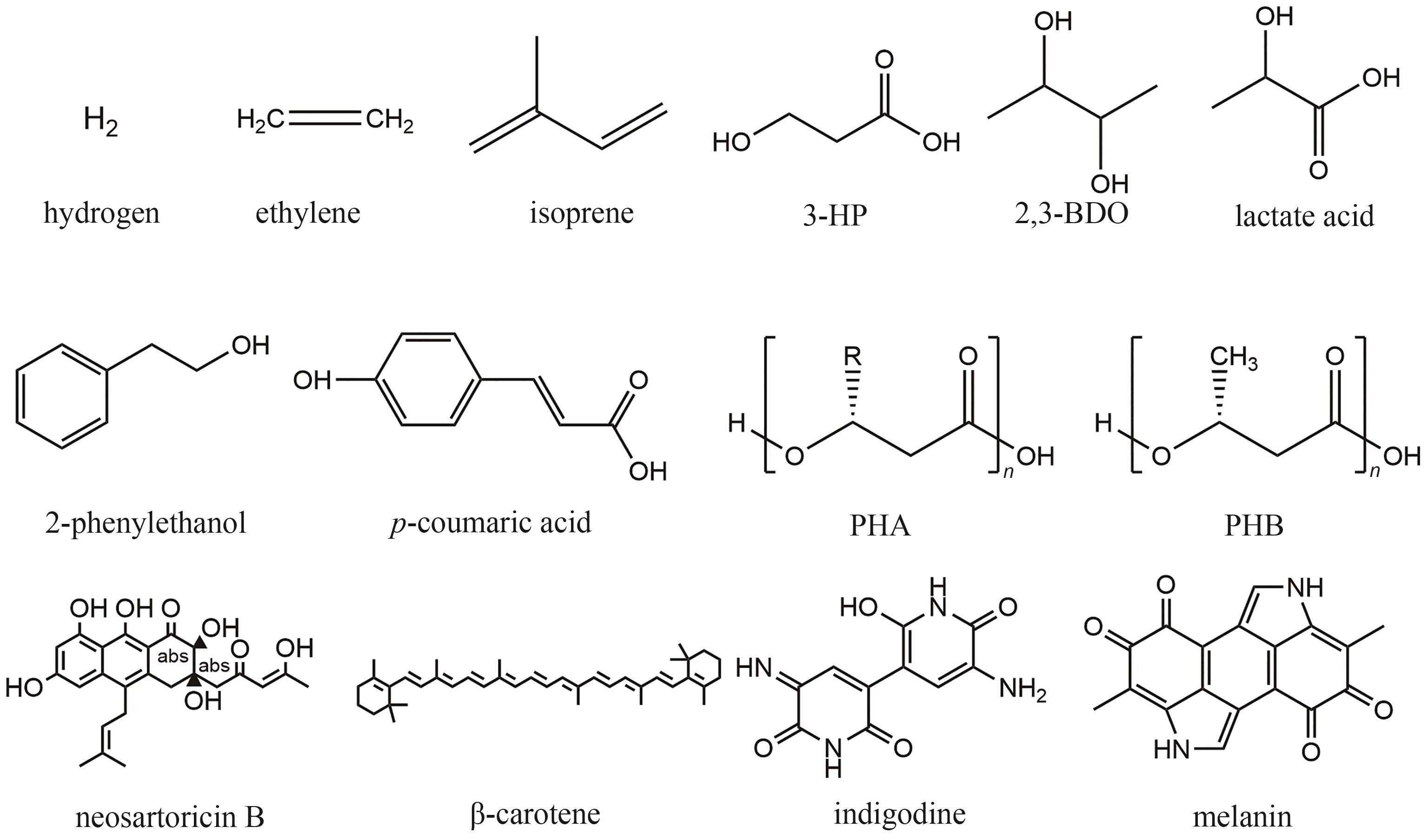
| 自养微生物 | 异养微生物 | 中间碳 | 产物 | 滴度/(mg/L) | 产率/[mg/(L·d)] | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | S. cerevisiae | 蔗糖 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | A. vinelandii | 蔗糖 | PHB | < 40 | < 8 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | H. boliviensis | 蔗糖 | PHB | 未指明 | 28.3 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | R. glutinis | 蔗糖 | 游离脂肪酸 | 39 | 1.2 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | P. putida | 蔗糖 | PHA | 156 | 9.8 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | S. cerevisiae | 蔗糖 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | PHB | < 1 | < 0.15 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | B. subtilis | 蔗糖 | α-淀粉酶 | 未指明 | 未指明 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | P. putida | 蔗糖 | PHA;降解2,4-DNT | 5.1 | 5.1 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | P. putida | 蔗糖 | HMF转化为FDCA | 约750 | 约250 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | Y. lipolytica | 蔗糖 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | B. subtilis | 蔗糖 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 异戊二烯 | 400 | 15.4 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | P. putida | 蔗糖 | PHA | 393 | 42.1 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 乙烯 | 1.2 | 0.6 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 异戊二烯 | 0.051 | 0.026 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | V. natriegens | 蔗糖 | 乳酸 | 313.3 | 52.2 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | V. natriegens | 蔗糖 | 2,3-丁二醇 | 137.3 | 22.9 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | V. natriegens | 蔗糖 | 对香豆酸 | 24.7 | 4.1 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | V. natriegens | 蔗糖 | 黑色素 | 9.1 | 1.5 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | A. nidulans | 蔗糖 | Neosartoricin B | 0.2 | 0.05 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 构建方法开发 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 匹配度预测 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 群体感应工具箱开发 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus UTEX 2973 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 3-羟基丙酸 | 68.3 | 9.8 | [ |
| S. elongatus UTEX 2973 | P. putida | 蔗糖 | 天然蓝色素 | 7500 | 1250 | [ |
| S. elongatus UTEX 2973 | Y. lipolytica | 蔗糖 | β-胡萝卜素 | 1300 | 260 | [ |
| Synechococcus sp. WH7803 | R. pomeroyi | 光合产物 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 | S. putrefaciens | 光合产物 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 | M. alcaliphilum | 光合产物 | 甲烷降解 | — | — | [ |
| T. elongates PKUAC-SCTE542 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 乙烯 | 1.5 | 0.74 | [ |
| T. elongates PKUAC-SCTE542 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 异戊二烯 | 0.027 | 0.013 | [ |
| T. elongatus BP-1 | M. ruber | 光合产物 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| Nostoc sp. PCC 6720 | A. nidulans | 光合产物 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| Nostoc sp. PCC 7413 | A. niger | 光合产物 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| Nostocaceae sp. SAB-B866 | P. cypripedii | 光合产物 | 促进植物生长 | — | — | [ |
| Nostocaceae sp. SAB-B866 | P. putida | 光合产物 | 促进植物生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. hyalinum | 废水内源微生物 | 光合产物 | 废水处理 | — | — | [ |
| P. keutzingium | 活性污泥微生物 | 光合产物 | 氢气;废水处理 | 89.9 | 14.9 | [ |
| T. obliquus IS2 | V. paradoxus | 光合产物 | 废水处理 | — | — | [ |
| Chlorella sp. GY-H4 | S. cerevisiae | 光合产物 | 苯乙醇 | 2130 | 710 | [ |
表1 基于自养/异养微生物对的合成生物群落
Table 1 Synthetic consortia consisting of phototroph/heterotroph pairs
| 自养微生物 | 异养微生物 | 中间碳 | 产物 | 滴度/(mg/L) | 产率/[mg/(L·d)] | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | S. cerevisiae | 蔗糖 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | A. vinelandii | 蔗糖 | PHB | < 40 | < 8 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | H. boliviensis | 蔗糖 | PHB | 未指明 | 28.3 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | R. glutinis | 蔗糖 | 游离脂肪酸 | 39 | 1.2 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | P. putida | 蔗糖 | PHA | 156 | 9.8 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | S. cerevisiae | 蔗糖 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | PHB | < 1 | < 0.15 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | B. subtilis | 蔗糖 | α-淀粉酶 | 未指明 | 未指明 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | P. putida | 蔗糖 | PHA;降解2,4-DNT | 5.1 | 5.1 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | P. putida | 蔗糖 | HMF转化为FDCA | 约750 | 约250 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | Y. lipolytica | 蔗糖 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | B. subtilis | 蔗糖 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 异戊二烯 | 400 | 15.4 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | P. putida | 蔗糖 | PHA | 393 | 42.1 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 乙烯 | 1.2 | 0.6 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 异戊二烯 | 0.051 | 0.026 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | V. natriegens | 蔗糖 | 乳酸 | 313.3 | 52.2 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | V. natriegens | 蔗糖 | 2,3-丁二醇 | 137.3 | 22.9 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | V. natriegens | 蔗糖 | 对香豆酸 | 24.7 | 4.1 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | V. natriegens | 蔗糖 | 黑色素 | 9.1 | 1.5 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | A. nidulans | 蔗糖 | Neosartoricin B | 0.2 | 0.05 | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 构建方法开发 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 匹配度预测 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus PCC 7942 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 群体感应工具箱开发 | — | — | [ |
| S. elongatus UTEX 2973 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 3-羟基丙酸 | 68.3 | 9.8 | [ |
| S. elongatus UTEX 2973 | P. putida | 蔗糖 | 天然蓝色素 | 7500 | 1250 | [ |
| S. elongatus UTEX 2973 | Y. lipolytica | 蔗糖 | β-胡萝卜素 | 1300 | 260 | [ |
| Synechococcus sp. WH7803 | R. pomeroyi | 光合产物 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 | S. putrefaciens | 光合产物 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 | M. alcaliphilum | 光合产物 | 甲烷降解 | — | — | [ |
| T. elongates PKUAC-SCTE542 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 乙烯 | 1.5 | 0.74 | [ |
| T. elongates PKUAC-SCTE542 | E. coli | 蔗糖 | 异戊二烯 | 0.027 | 0.013 | [ |
| T. elongatus BP-1 | M. ruber | 光合产物 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| Nostoc sp. PCC 6720 | A. nidulans | 光合产物 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| Nostoc sp. PCC 7413 | A. niger | 光合产物 | 促进生长 | — | — | [ |
| Nostocaceae sp. SAB-B866 | P. cypripedii | 光合产物 | 促进植物生长 | — | — | [ |
| Nostocaceae sp. SAB-B866 | P. putida | 光合产物 | 促进植物生长 | — | — | [ |
| S. hyalinum | 废水内源微生物 | 光合产物 | 废水处理 | — | — | [ |
| P. keutzingium | 活性污泥微生物 | 光合产物 | 氢气;废水处理 | 89.9 | 14.9 | [ |
| T. obliquus IS2 | V. paradoxus | 光合产物 | 废水处理 | — | — | [ |
| Chlorella sp. GY-H4 | S. cerevisiae | 光合产物 | 苯乙醇 | 2130 | 710 | [ |
| 1 | CESTELLOS-BLANCO S, ZHANG H, KIM J M, et al. Photosynthetic semiconductor biohybrids for solar-driven biocatalysis[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2020, 3: 245-255. |
| 2 | LIAO J C, MI L, PONTRELLI S, et al. Fuelling the future: microbial engineering for the production of sustainable biofuels[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(5): 288-304. |
| 3 | LIU Z H, WANG K, CHEN Y, et al. Third-generation biorefineries as the means to produce fuels and chemicals from CO2 [J]. Nature Catalysis, 2020, 3: 274-288. |
| 4 | CASE A E, ATSUMI S. Cyanobacterial chemical production[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 231: 106-114. |
| 5 | GLEIZER S, BEN-NISSAN R, BAR-ON Y M, et al. Conversion of Escherichia coli to generate all biomass carbon from CO2 [J]. Cell, 2019, 179(6): 1255-1263.e12. |
| 6 | VENKATA MOHAN S, MODESTRA J A, AMULYA K, et al. A circular bioeconomy with biobased products from CO2 sequestration[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2016, 34(6): 506-519. |
| 7 | KASHYAP M, CHAKRABORTY S, KUMARI A, et al. Strategies and challenges to enhance commercial viability of algal biorefineries for biofuel production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 387: 129551. |
| 8 | AHIRWAR A, DAS S, DAS S, et al. Photosynthetic microbial fuel cell for bioenergy and valuable production: a review of circular bio-economy approach[J]. Algal Research, 2023, 70: 102973. |
| 9 | ERDEM E, MALIHAN-YAP L, ASSIL-COMPANIONI L, et al. Photobiocatalytic oxyfunctionalization with high reaction rate using a Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase from Burkholderia xenovorans in metabolically engineered cyanobacteria[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(1): 66-72. |
| 10 | MASCIA F, PEREIRA S B, PACHECO C C, et al. Light-driven hydroxylation of testosterone by Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 expressing the heterologous CYP450 monooxygenase CYP110D1[J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(16): 6156-6167. |
| 11 | TAN C L, TAO F, XU P. Direct carbon capture for the production of high-performance biodegradable plastics by cyanobacterial cell factories[J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(11): 4470-4483. |
| 12 | WANG Q K, YU Z Y, WEI D, et al. Mixotrophic Chlorella pyrenoidosa as cell factory for ultrahigh-efficient removal of ammonium from catalyzer wastewater with valuable algal biomass coproduction through short-time acclimation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 333: 125151. |
| 13 | ZHU B J, WEI D, POHNERT G. The thermoacidophilic red alga Galdieria sulphuraria is a highly efficient cell factory for ammonium recovery from ultrahigh-NH4+ industrial effluent with co-production of high-protein biomass by photo-fermentation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 438: 135598. |
| 14 | BAI W, RANAIVOARISOA T O, SINGH R, et al. n-Butanol production by Rhodopseudomonas palustris TIE-1[J]. Communications Biology, 2021, 4(1): 1257. |
| 15 | LI M J, XIA Q Q, LV S Z, et al. Enhanced CO2 capture for photosynthetic lycopene production in engineered Rhodopseudomonas palustris, a purple nonsulfur bacterium[J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(19): 7500-7518. |
| 16 | DEMAY J, BERNARD C, REINHARDT A, et al. Natural products from cyanobacteria: focus on beneficial activities[J]. Marine Drugs, 2019, 17(6): 320. |
| 17 | TAN C L, XU P, TAO F. Carbon-negative synthetic biology: challenges and emerging trends of cyanobacterial technology[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40(12): 1488-1502. |
| 18 | KNOOT C J, UNGERER J, WANGIKAR P P, et al. Cyanobacteria: promising biocatalysts for sustainable chemical production[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2018, 293(14): 5044-5052. |
| 19 | OPEL F, SIEBERT N A, KLATT S, et al. Generation of synthetic shuttle vectors enabling modular genetic engineering of cyanobacteria[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(5): 1758-1771. |
| 20 | DERUYCK B, NGUYEN K H THI, DECAESTECKER E, et al. Modeling the impact of rotifer contamination on microalgal production in open pond, photobioreactor and thin layer cultivation systems[J]. Algal Research, 2019, 38: 101398. |
| 21 | STUART R K, MAYALI X, LEE J Z, et al. Cyanobacterial reuse of extracellular organic carbon in microbial mats[J]. The ISME Journal, 2016, 10(5): 1240-1251. |
| 22 | SENEVIRATNE G, INDRASENA I K. Nitrogen fixation in lichens is important for improved rock weathering[J]. Journal of Biosciences, 2006, 31(5): 639-643. |
| 23 | ZUÑIGA C, LI C T, YU G, et al. Environmental stimuli drive a transition from cooperation to competition in synthetic phototrophic communities[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2019, 4(12): 2184-2191. |
| 24 | KRATZL F, KREMLING A, PFLÜGER-GRAU K. Streamlining of a synthetic co-culture towards an individually controllable one-pot process for polyhydroxyalkanoate production from light and CO2 [J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2022, 23(1): e2100156. |
| 25 | WEISS T L, YOUNG E J, DUCAT D C. A synthetic, light-driven consortium of cyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria enables stable polyhydroxybutyrate production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 44: 236-245. |
| 26 | ZHANG L, CHEN L, DIAO J J, et al. Construction and analysis of an artificial consortium based on the fast-growing cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973 to produce the platform chemical 3-hydroxypropionic acid from CO2 [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2020, 13: 82. |
| 27 | WANG L, ZHANG X, TANG C W, et al. Engineering consortia by polymeric microbial swarmbots[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 3879. |
| 28 | LI C F, WANG R Y, WANG J W, et al. A highly compatible phototrophic community for carbon-negative biosynthesis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(2): e202215013. |
| 29 | ZHAO R Y, SENGUPTA A, TAN A X, et al. Photobiological production of high-value pigments via compartmentalized co-cultures using Ca-alginate hydrogels[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 22163. |
| 30 | SHU W S, HUANG L N. Microbial diversity in extreme environments[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2022, 20(4): 219-235. |
| 31 | SCHIPPERS A, NERETIN L N, KALLMEYER J, et al. Prokaryotic cells of the deep sub-seafloor biosphere identified as living bacteria[J]. Nature, 2005, 433(7028): 861-864. |
| 32 | CASTENHOLZ R W. The effect of sulfide on the blue-green algae of hot springsⅡ. Yellowstone National Park[J]. Microbial Ecology, 1977, 3(2): 79-105. |
| 33 | THOMAS D N, DIECKMANN G S. Antarctic Sea ice: a habitat for extremophiles[J]. Science, 2002, 295(5555): 641-644. |
| 34 | TANG Y Z, KOCH F, GOBLER C J. Most harmful algal bloom species are vitamin B1 and B12 auxotrophs[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(48): 20756-20761. |
| 35 | XIONG Q, HU L X, LIU Y S, et al. Microalgae-based technology for antibiotics removal: from mechanisms to application of innovational hybrid systems[J]. Environment International, 2021, 155: 106594. |
| 36 | KUMARI M, GHOSH P, SWATI, et al. Development of artificial consortia of microalgae and bacteria for efficient biodegradation and detoxification of lindane[J]. Bioresource Technology Reports, 2020, 10: 100415. |
| 37 | MOHSENPOUR S F, HENNIGE S, WILLOUGHBY N, et al. Integrating micro-algae into wastewater treatment: a review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 752: 142168. |
| 38 | SANTOS C A, REIS A. Microalgal symbiosis in biotechnology[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(13): 5839-5846. |
| 39 | PARK Y, JE K W, LEE K, et al. Growth promotion of Chlorella ellipsoidea by co-inoculation with Brevundimonas sp. isolated from the microalga[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2008, 598(1): 219-228. |
| 40 | BUCHAN A, LECLEIR G R, GULVIK C A, et al. Master recyclers: features and functions of bacteria associated with phytoplankton blooms[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2014, 12(10): 686-698. |
| 41 | JAMES C C, BARTON A D, ALLEN L Z, et al. Influence of nutrient supply on plankton microbiome biodiversity and distribution in a coastal upwelling region[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 2448. |
| 42 | SEYMOUR J R, AMIN S A, RAINA J B, et al. Zooming in on the phycosphere: the ecological interface for phytoplankton-bacteria relationships[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2017, 2: 17065. |
| 43 | MISHRA A, KAVITA K, JHA B. Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances produced by micro-algae Dunaliella salina [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2011, 83(2): 852-857. |
| 44 | VAN OOSTENDE N, MOERDIJK-POORTVLIET T C W, BOSCHKER H T S, et al. Release of dissolved carbohydrates by Emiliania huxleyi and formation of transparent exopolymer particles depend on algal life cycle and bacterial activity[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2013, 15(5): 1514-1531. |
| 45 | WICKER R J, DANESHVAR E, KUMAR GUPTA A, et al. Hybrid planktonic-biofilm cultivation of a Nordic mixed-species photosynthetic consortium: a pilot study on carbon capture and nutrient removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 471: 144585. |
| 46 | COLE J J. Interactions between bacteria and algae in aquatic ecosystems[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 1982, 13: 291-314. |
| 47 | ŽITNIK M, ŠUNTA U, GODIČ TORKAR K, et al. The study of interactions and removal efficiency of Escherichia coli in raw blackwater treated by microalgae Chlorella vulgaris [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 238: 117865. |
| 48 | FOSTER R A, KUYPERS M M M, VAGNER T, et al. Nitrogen fixation and transfer in open ocean diatom-cyanobacterial symbioses[J]. The ISME Journal, 2011, 5(9): 1484-1493. |
| 49 | THOMPSON A W, FOSTER R A, KRUPKE A, et al. Unicellular cyanobacterium symbiotic with a single-celled eukaryotic alga[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6101): 1546-1550. |
| 50 | SYLVAN J B, DORTCH Q, NELSON D M, et al. Phosphorus limits phytoplankton growth on the Louisiana shelf during the period of hypoxia formation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(24): 7548-7553. |
| 51 | CARRIÓN O, LI C Y, PENG M, et al. DMSOP-cleaving enzymes are diverse and widely distributed in marine microorganisms[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2023, 8(12): 2326-2337. |
| 52 | BRINKHOFF T, BACH G, HEIDORN T, et al. Antibiotic production by a Roseobacter clade-affiliated species from the German Wadden Sea and its antagonistic effects on indigenous isolates[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70(4): 2560-2565. |
| 53 | SEYEDSAYAMDOST M R, CARR G, KOLTER R, et al. Roseobacticides: small molecule modulators of an algal-bacterial symbiosis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(45): 18343-18349. |
| 54 | LIU H L, ZHOU Y Y, XIAO W J, et al. Shifting nutrient-mediated interactions between algae and bacteria in a microcosm: evidence from alkaline phosphatase assay[J]. Microbiological Research, 2012, 167(5): 292-298. |
| 55 | GURUNG T B, URABE J, NAKANISHI M. Regulation of the relationship between phytoplankton Scenedesmus acutus and heterotrophic bacteria by the balance of light and nutrients[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 1999, 17: 27-35. |
| 56 | LIU L, HALL G, CHAMPAGNE P. Effects of environmental factors on the disinfection performance of a wastewater stabilization pond operated in a temperate climate[J]. Water, 2015, 8(1): 5. |
| 57 | VASKER B, BEN-ZION M, KINEL-TAHAN Y, et al. Computerized optimization of microalgal photosynthesis and growth[J]. Applied Phycology, 2021, 2(1): 22-30. |
| 58 | CHO K H, WOLNY J, KASE J A, et al. Interactions of E. coli with algae and aquatic vegetation in natural waters[J]. Water Research, 2022, 209: 117952. |
| 59 | CROFT M T, LAWRENCE A D, RAUX-DEERY E, et al. Algae acquire vitamin B12 through a symbiotic relationship with bacteria[J]. Nature, 2005, 438(7064): 90-93. |
| 60 | AMIN S A, GREEN D H, HART M C, et al. Photolysis of iron-siderophore chelates promotes bacterial-algal mutualism[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(40): 17071-17076. |
| 61 | DURHAM B P, SHARMA S, LUO H W, et al. Cryptic carbon and sulfur cycling between surface ocean plankton[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(2): 453-457. |
| 62 | PAERL R W, BOUGET F Y, LOZANO J C, et al. Use of plankton-derived vitamin B1 precursors, especially thiazole-related precursor, by key marine picoeukaryotic phytoplankton[J]. The ISME Journal, 2017, 11(3): 753-765. |
| 63 | TORTELL P D, MALDONADO M T, GRANGER J, et al. Marine bacteria and biogeochemical cycling of iron in the oceans[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 1999, 29(1): 1-11. |
| 64 | YAO S, LYU S, AN Y, et al. Microalgae-bacteria symbiosis in microalgal growth and biofuel production: a review[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2019, 126(2): 359-368. |
| 65 | HOPKINSON B M, MOREL F M M. The role of siderophores in iron acquisition by photosynthetic marine microorganisms[J]. BioMetals, 2009, 22(4): 659-669. |
| 66 | RAINA J B, LAMBERT B S, PARKS D H, et al. Chemotaxis shapes the microscale organization of the ocean’s microbiome[J]. Nature, 2022, 605(7908): 132-138. |
| 67 | CHEN S S, CHEN J, ZHANG L L, et al. Biophotoelectrochemical process co-driven by dead microalgae and live bacteria[J]. The ISME Journal, 2023, 17(5): 712-719. |
| 68 | MUKHERJEE S, BASSLER B L. Bacterial quorum sensing in complex and dynamically changing environments[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2019, 17(6): 371-382. |
| 69 | FEDERLE M J. Autoinducer-2-based chemical communication in bacteria: complexities of interspecies signaling[M/OL]// COLLIN M, SCHUCH R. Contributions to microbiology: bacterial sensing and signaling. Basel: Karger, 2009, 16: 18-32 [2023-12-01]. . |
| 70 | ZHOU J, LYU Y H, RICHLEN M, et al. Quorum sensing is a language of chemical signals and plays an ecological role in algal-bacterial interactions[J]. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 2016, 35(2): 81-105. |
| 71 | JI X Y, JIANG M Q, ZHANG J B, et al. The interactions of algae-bacteria symbiotic system and its effects on nutrients removal from synthetic wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 247: 44-50. |
| 72 | ZHOU D D, ZHANG C F, FU L, et al. Responses of the microalga Chlorophyta sp. to bacterial quorum sensing molecules (N-acylhomoserine lactones): aromatic protein-induced self-aggregation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(6): 3490-3498. |
| 73 | PAPENFORT K, BASSLER B L. Quorum sensing signal-response systems in Gram-negative bacteria[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(9): 576-588. |
| 74 | CHOI H, MASCUCH S J, VILLA F A, et al. Honaucins A-C, potent inhibitors of inflammation and bacterial quorum sensing: synthetic derivatives and structure-activity relationships[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2012, 19(5): 589-598. |
| 75 | BORGES A, SIMÕES M. Quorum sensing inhibition by marine bacteria[J]. Marine Drugs, 2019, 17(7): 427. |
| 76 | ZHANG B, LI W, GUO Y, et al. Microalgal-bacterial consortia: from interspecies interactions to biotechnological applications[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 118: 109563. |
| 77 | KANAGASABHAPATHY M, YAMAZAKI G, ISHIDA A, et al. Presence of quorum-sensing inhibitor-like compounds from bacteria isolated from the brown alga Colpomenia sinuosa [J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2009, 49(5): 573-579. |
| 78 | KOKARAKIS E J, RILLEMA R, DUCAT D C, et al. Developing cyanobacterial quorum sensing toolkits: toward interspecies coordination in mixed autotroph/heterotroph communities[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2023, 12(1): 265-276. |
| 79 | RIQUELME C E, ISHIDA Y. Chemotaxis of bacteria to extracellular products of marine bloom algae[J]. The Journal of General and Applied Microbiology, 1988, 34(5): 417-423. |
| 80 | LI X J, CAI F S, LUAN T G, et al. Pyrene metabolites by bacterium enhancing cell division of green alga Selenastrum capricornutum [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 689: 287-294. |
| 81 | ALLEN A E, DUPONT C L, OBORNÍK M, et al. Evolution and metabolic significance of the urea cycle in photosynthetic diatoms[J]. Nature, 2011, 473(7346): 203-207. |
| 82 | LI T T, LI C T, BUTLER K, et al. Mimicking lichens: incorporation of yeast strains together with sucrose-secreting cyanobacteria improves survival, growth, ROS removal, and lipid production in a stable mutualistic co-culture production platform[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2017, 10: 55. |
| 83 | FEDESON D T, SAAKE P, CALERO P, et al. Biotransformation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene in a phototrophic co-culture of engineered Synechococcus elongatus and Pseudomonas putida [J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2020, 13(4): 997-1011. |
| 84 | CUI Y X, RASUL F, JIANG Y, et al. Construction of an artificial consortium of Escherichia coli and cyanobacteria for clean indirect production of volatile platform hydrocarbons from CO2 [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13: 965968. |
| 85 | KRATZL F, URBAN M, PANDHAL J, et al. Pseudomonas putida as saviour for troubled Synechococcus elongatus in a synthetic co-culture-interaction studies based on a multi-OMICs approach[J]. Communications Biology, 2024, 7: 452. |
| 86 | 国陶红, 宋馨宇, 陈磊, 等. 人工微生物混菌系统机制解析中的组学应用及进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(2): 460-477. |
| GUO T H, SONG X Y, CHEN L, et al. Using OMICS technologies to analyze the mechanisms of synthetic microbial co-culture systems: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 38(2): 460-477. | |
| 87 | LIU H, CAO Y J, GUO J, et al. Study on the isoprene-producing co-culture system of Synechococcus elongates-Escherichia coli through omics analysis[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2021, 20(1): 6. |
| 88 | NAIR S, ZHANG Z H, LI H M, et al. Inherent tendency of Synechococcus and heterotrophic bacteria for mutualism on long-term coexistence despite environmental interference[J]. Science Advances, 2022, 8(39): eabf4792. |
| 89 | ZHANG Z H, NAIR S, TANG L L, et al. Long-term survival of Synechococcus and heterotrophic bacteria without external nutrient supply after changes in their relationship from antagonism to mutualism[J]. mBio, 2021, 12(4): e0161421. |
| 90 | MA J J, GUO T H, REN M J, et al. Cross-feeding between cyanobacterium Synechococcus and Escherichia coli in an artificial autotrophic-heterotrophic coculture system revealed by integrated omics analysis[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels and Bioproducts, 2022, 15(1): 69. |
| 91 | LIU H, XIAN M, CAO Y J, et al. Omics integration for in-depth understanding of the low-carbon co-culture platform system of Chlorella vulgaris-Escherichia coli [J]. Algal Research, 2023, 75: 103252. |
| 92 | BECKER S A, FEIST A M, MO M L, et al. Quantitative prediction of cellular metabolism with constraint-based models: the COBRA Toolbox[J]. Nature Protocols, 2007, 2(3): 727-738. |
| 93 | KUMAR M, JI B Y, ZENGLER K, et al. Modelling approaches for studying the microbiome[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2019, 4(8): 1253-1267. |
| 94 | ANTONAKOUDIS A, BARBOSA R, KOTIDIS P, et al. The era of big data: genome-scale modelling meets machine learning[J]. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18: 3287-3300. |
| 95 | CHIU H C, LEVY R, BORENSTEIN E. Emergent biosynthetic capacity in simple microbial communities[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2014, 10(7): e1003695. |
| 96 | ZUÑIGA C, LI T T, GUARNIERI M T, et al. Synthetic microbial communities of heterotrophs and phototrophs facilitate sustainable growth[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3803. |
| 97 | LLOYD C J, KING Z A, SANDBERG T E, et al. The genetic basis for adaptation of model-designed syntrophic co-cultures[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2019, 15(3): e1006213. |
| 98 | GARCÍA-JIMÉNEZ B, GARCÍA J L, NOGALES J. FLYCOP: metabolic modeling-based analysis and engineering microbial communities[J]. Bioinformatics, 2018, 34(17): i954-i963. |
| 99 | THOMMES M, WANG T Y, ZHAO Q, et al. Designing metabolic division of labor in microbial communities[J]. mSystems, 2019, 4(2): e00263-18. |
| 100 | KARKARIA B D, FEDOREC A J H, BARNES C P. Automated design of synthetic microbial communities[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 672. |
| 101 | SAKKOS J K, SANTOS-MERINO M, KOKARAKIS E J, et al. Predicting partner fitness based on spatial structuring in a light-driven microbial community[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2023, 19(5): e1011045. |
| 102 | DUCAT D C, AVELAR-RIVAS J A, WAY J C, et al. Rerouting carbon flux to enhance photosynthetic productivity[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 78(8): 2660-2668. |
| 103 | SMITH M J, FRANCIS M B. A designed A. vinelandii-S. elongatus coculture for chemical photoproduction from air, water, phosphate, and trace metals[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(9): 955-961. |
| 104 | LÖWE H, HOBMEIER K, MOOS M, et al. Photoautotrophic production of polyhydroxyalkanoates in a synthetic mixed culture of Synechococcus elongatus cscB and Pseudomonas putida cscAB [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2017, 10: 190. |
| 105 | HAYS S G, YAN L L W, SILVER P A, et al. Synthetic photosynthetic consortia define interactions leading to robustness and photoproduction[J]. Journal of Biological Engineering, 2017, 11: 4. |
| 106 | LIN T Y, WEN R C, SHEN C R, et al. Biotransformation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid by a syntrophic consortium of engineered Synechococcus elongatus and Pseudomonas putida [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 15(6): e1900357. |
| 107 | FENG J, LI J W, LIU D X, et al. Generation and comprehensive analysis of Synechococcus elongatus-Aspergillus nidulans co-culture system for polyketide production[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels and Bioproducts, 2023, 16(1): 32. |
| 108 | SINGH A K, DUCAT D C. Generation of stable, light-driven co-cultures of cyanobacteria with heterotrophic microbes[M/OL]//ZURBRIGGEN M D. Methods in molecular biology: plant synthetic biology. New York: Humana, 2022, 2379: 277-291 [2023-12-01]. . |
| 109 | CHRISTIE-OLEZA J A, SOUSONI D, LLOYD M, et al. Nutrient recycling facilitates long-term stability of marine microbial phototroph-heterotroph interactions[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2017, 2: 17100. |
| 110 | BELIAEV A S, ROMINE M F, SERRES M, et al. Inference of interactions in cyanobacterial-heterotrophic co-cultures via transcriptome sequencing[J]. The ISME Journal, 2014, 8(11): 2243-2255. |
| 111 | HILL E A, CHRISLER W B, BELIAEV A S, et al. A flexible microbial co-culture platform for simultaneous utilization of methane and carbon dioxide from gas feedstocks[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 228: 250-256. |
| 112 | BERNSTEIN H C, MCCLURE R S, THIEL V, et al. Indirect interspecies regulation: transcriptional and physiological responses of a Cyanobacterium to heterotrophic partnership[J]. mSystems, 2017, 2(2): e00181-16. |
| 113 | JIANG L Q, LI T T, JENKINS J, et al. Evidence for a mutualistic relationship between the cyanobacteria Nostoc and fungi Aspergilli in different environments[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(14): 6413-6426. |
| 114 | LI T T, JIANG L Q, HU Y F, et al. Creating a synthetic lichen: mutualistic co-culture of fungi and extracellular polysaccharide-secreting cyanobacterium Nostoc PCC 7413[J]. Algal Research, 2020, 45: 101755. |
| 115 | TORIBIO A J, SUÁREZ-ESTRELLA F, JURADO M M, et al. Design and validation of cyanobacteria-rhizobacteria consortia for tomato seedlings growth promotion[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 13150. |
| 116 | WU L, QUAN L H, DENG Z K, et al. Performance of a biocrust cyanobacteria-indigenous bacteria (BCIB) co-culture system for nutrient capture and transfer in municipal wastewater[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 888: 164236. |
| 117 | MOHAMMED AL NUAIMI M, JAVED M A, EL-TARABILY K A, et al. Biohydrogen production of a halophytic cyanobacteria Phormidium keutzingium and activated sludge co-culture using different carbon substrates and saline concentrations[J]. Energy Conversion and Management: X, 2023, 20: 100487. |
| 118 | PERERA I A, ABINANDAN S, PANNEERSELVAN L, et al. Co-culturing of microalgae and bacteria in real wastewaters alters indigenous bacterial communities enhancing effluent bioremediation[J]. Algal Research, 2022, 64: 102705. |
| 119 | GAO H, WANG H X, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Design and optimization of artificial light-driven microbial consortia for the sustainable growth and biosynthesis of 2-phenylethanol[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 466: 143050. |
| 120 | RUFFING A M, KALLAS T. Editorial: cyanobacteria: the green E. coli [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2016, 4: 7. |
| 121 | HU Q, SOMMERFELD M, JARVIS E, et al. Microalgal triacylglycerols as feedstocks for biofuel production: perspectives and advances[J]. The Plant Journal, 2008, 54(4): 621-639. |
| 122 | LIN P C, ZHANG F Z, PAKRASI H B. Enhanced production of sucrose in the fast-growing cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 390. |
| 123 | YU J J, LIBERTON M, CLIFTEN P F, et al. Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973, a fast growing cyanobacterial chassis for biosynthesis using light and CO2 [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 8132. |
| 124 | LI S B, SUN T, XU C X, et al. Development and optimization of genetic toolboxes for a fast-growing cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 48: 163-174. |
| 125 | TAN X M, HOU S W, SONG K, et al. The primary transcriptome of the fast-growing Cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus UTEX 2973[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2018, 11: 218. |
| 126 | LÖWE H, SCHMAUDER L, HOBMEIER K, et al. Metabolic engineering to expand the substrate spectrum of Pseudomonas putida toward sucrose[J]. Microbiology Open, 2017, 6(4): e00473. |
| 127 | LIU J Z, WU Y H, WU C X, et al. Advanced nutrient removal from surface water by a consortium of attached microalgae and bacteria: a review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 241: 1127-1137. |
| 128 | YU W, ZENG Y, WANG Z H, et al. Solar-powered multi-organism symbiont mimic system for beyond natural synthesis of polypeptides from CO2 and N2 [J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(11): eadf6772. |
| 129 | ALNAHHAS R N, SADEGHPOUR M, CHEN Y, et al. Majority sensing in synthetic microbial consortia[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3659. |
| 130 | KONG W T, MELDGIN D R, COLLINS J J, et al. Designing microbial consortia with defined social interactions[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(8): 821-829. |
| 131 | KYLILIS N, TUZA Z A, STAN G B, et al. Tools for engineering coordinated system behaviour in synthetic microbial consortia[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 2677. |
| 132 | KIM J K, CHEN Y, HIRNING A J, et al. Long-range temporal coordination of gene expression in synthetic microbial consortia[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(11): 1102-1109. |
| 133 | ROELL G W, ZHA J, CARR R R, et al. Engineering microbial consortia by division of labor[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18(1): 35. |
| 134 | LI Z H, WANG X N, ZHANG H R. Balancing the non-linear rosmarinic acid biosynthetic pathway by modular co-culture engineering[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 54: 1-11. |
| 135 | WANG X, LIU W, XIN C P, et al. Enhanced limonene production in cyanobacteria reveals photosynthesis limitations[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(50): 14225-14230. |
| 136 | RICHARDSON K N, BLACK W B, LI H. Aldehyde production in crude lysate- and whole cell-based biotransformation using a noncanonical redox cofactor system[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(15): 8898-8903. |
| 137 | LI C F, YIN L J, WANG J W, et al. Light-driven biosynthesis of volatile, unstable and photosensitive chemicals from CO2 [J]. Nature Synthesis, 2023, 2: 960-971. |
| 138 | WANG H, ZHANG W, CHEN L, et al. The contamination and control of biological pollutants in mass cultivation of microalgae[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 128: 745-750. |
| 139 | FUCHS G. Alternative pathways of carbon dioxide fixation: insights into the early evolution of life?[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2011, 65: 631-658. |
| 140 | KUMAR M, SUNDARAM S, GNANSOUNOU E, et al. Carbon dioxide capture, storage and production of biofuel and biomaterials by bacteria: a review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 247: 1059-1068. |
| 141 | WŁODARCZYK A, SELÃO T T, NORLING B, et al. Newly discovered Synechococcus sp. PCC 11901 is a robust cyanobacterial strain for high biomass production[J]. Communications Biology, 2020, 3(1): 215. |
| 142 | ZHANG S S, SUN J H, FENG D D, et al. Unlocking the potentials of cyanobacterial photosynthesis for directly converting carbon dioxide into glucose[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 3425. |
| 143 | ZHU Z, JIANG J H, FA Y. Overcoming the biological contamination in microalgae and cyanobacteria mass cultivations for photosynthetic biofuel production[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(22): 5220. |
| 144 | SING S FON, ISDEPSKY A, BOROWITZKA M A, et al. Pilot-scale continuous recycling of growth medium for the mass culture of a halotolerant Tetraselmis sp. in raceway ponds under increasing salinity: a novel protocol for commercial microalgal biomass production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 161: 47-54. |
| 145 | BACELLAR MENDES L B, VERMELHO A B. Allelopathy as a potential strategy to improve microalgae cultivation[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2013, 6(1): 152. |
| 146 | SINGH J S, KUMAR A, RAI A N, et al. Cyanobacteria: a precious bio-resource in agriculture, ecosystem, and environmental sustainability[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, 7: 529. |
| 147 | SELÃO T T, WŁODARCZYK A, NIXON P J, et al. Growth and selection of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 using alternative nitrogen and phosphorus sources[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 54: 255-263. |
| 148 | GIFUNI I, POLLIO A, SAFI C, et al. Current bottlenecks and challenges of the microalgal biorefinery[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2019, 37(3): 242-252. |
| 149 | HOBISCH M, SPASIC J, MALIHAN-YAP L, et al. Internal illumination to overcome the cell density limitation in the scale-up of whole-cell photobiocatalysis[J]. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(15): 3219-3225. |
| 150 | PRABHA S, VIJAY A K, PAUL R R, et al. Cyanobacterial biorefinery: towards economic feasibility through the maximum valorization of biomass[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 814: 152795. |
| 151 | JODLBAUER J, ROHR T, SPADIUT O, et al. Biocatalysis in green and blue: cyanobacteria[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2021, 39(9): 875-889. |
| 152 | LIN Y L, SHI J Y, FENG W, et al. Periplasmic biomineralization for semi-artificial photosynthesis[J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(29): eadg5858. |
| 153 | PI S S, YANG W J, FENG W, et al. Solar-driven waste-to-chemical conversion by wastewater-derived semiconductor biohybrids[J]. Nature Sustainability, 2023, 6: 1673-1684. |
| 154 | HU Q S, HU H T, CUI L, et al. Ultrafast electron transfer in Au-cyanobacteria hybrid for solar to chemical production[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2023, 8(1): 677-684. |
| 155 | LIANG J, CHEN Z, YIN P Q, et al. Efficient semi-artificial photosynthesis of ethylene by a self-assembled InP-cyanobacterial biohybrid system[J]. ChemSusChem, 2023, 16(20): e202300773. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [11] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [12] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [13] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [14] | 查文龙, 卜兰, 訾佳辰. 中药药效成分群的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| [15] | 惠真, 唐啸宇. CRISPR/Cas9编辑系统在微生物天然产物研究中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||