合成生物学 ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (1): 71-83.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-054
合成生物技术制备脂肪族二元胺的研究进展
王昕, 王静, 陈可泉, 欧阳平凯
- 南京工业大学生物与制药工程学院,材料化学工程国家重点实验室,江苏省国家先进材料协同创新中心,江苏 南京 211816
-
收稿日期:2020-04-20修回日期:2020-05-06出版日期:2020-02-29发布日期:2020-07-07 -
通讯作者:欧阳平凯 -
作者简介:王昕(1988—),女,博士,副教授。研究方向为生物催化。E-mail:xinwang1988@njtech.edu.cn
欧阳平凯(1945—),男,教授,中国工程院院士。研究方向为生物催化。E-mail:ouyangpk@njtech.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0901500)
Research progress in bioproduction of aliphatic diamines by synthetic biotechnology
WANG Xin, WANG Jing, CHEN Kequan, OUYANG Pingkai
- College of Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, State Key Laboratory of Materials-Oriented Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu National Synergetic Innovation Center for Advance Material, Nanjing 211816, Jiangsu, China
-
Received:2020-04-20Revised:2020-05-06Online:2020-02-29Published:2020-07-07 -
Contact:OUYANG Pingkai
摘要:
合成生物学作为发展迅速的一门交叉学科,为构建高效的微生物细胞工厂、促进生物基产品的产业化制备提供了强有力的工具。二元胺作为一种重要的聚合单体,广泛应用于聚酯、聚氨酯、聚酰胺等高分子材料的合成中。本文针对C3~C5脂肪族二元胺(1,5-戊二胺、1,3-丙二胺、1,4-丁二胺)的生物合成,从途径设计与构建、关键结构元件的设计和改造、调控元件的挖掘与优化、辅因子合成和转运调控等模块的优化和系统集成等方面,综述了利用合成生物学策略改造大肠杆菌和谷氨酸棒状杆菌合成二元胺的现状,并从非粮生物质的利用和生物合成过程中CO2的再循环利用两个方面阐述了提高二元胺合成过程中原子经济性的研究概况,展望了如何利用合成生物技术进一步优化二元胺合成细胞的性能,以促进生物基二元胺的产业化生产。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王昕, 王静, 陈可泉, 欧阳平凯. 合成生物技术制备脂肪族二元胺的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(1): 71-83.
WANG Xin, WANG Jing, CHEN Kequan, OUYANG Pingkai. Research progress in bioproduction of aliphatic diamines by synthetic biotechnology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 71-83.
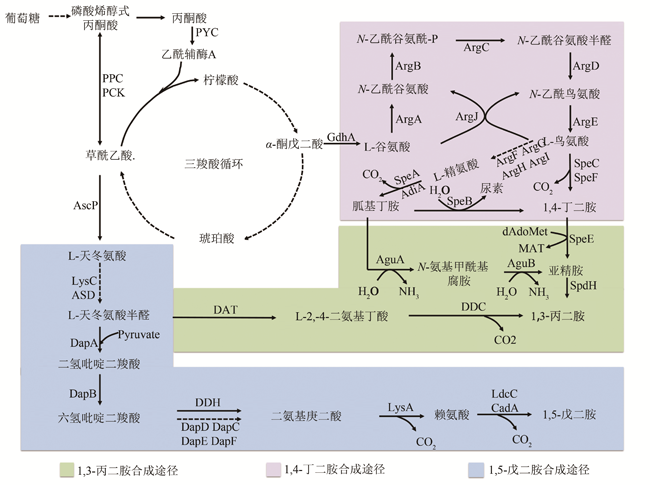
图1 C3~C5脂肪族二元胺的生物合成途径[8,9,10,11,12,13](实线箭头为一步代谢途径,虚线箭头为一步以上代谢途径。绿色为1,3-丙二胺合成途径,紫色为1,4-丁二胺合成途径,蓝色为1,5-戊二胺合成途径)
Fig. 1 The biosynthetic pathway of the aliphatic diamines with 3~5 carbon atoms (The solid arrows indicate one-step metabolic pathways, and the dotted arrows indicate multiple-step metabolic pathways. The green square represents the synthetic pathway of 1,3-propanediamine, the purple square represents the synthetic pathway of 1,4-butanediamine synthesis route, and the blue square represents the synthetic pathway of 1,5-pentanediamine)
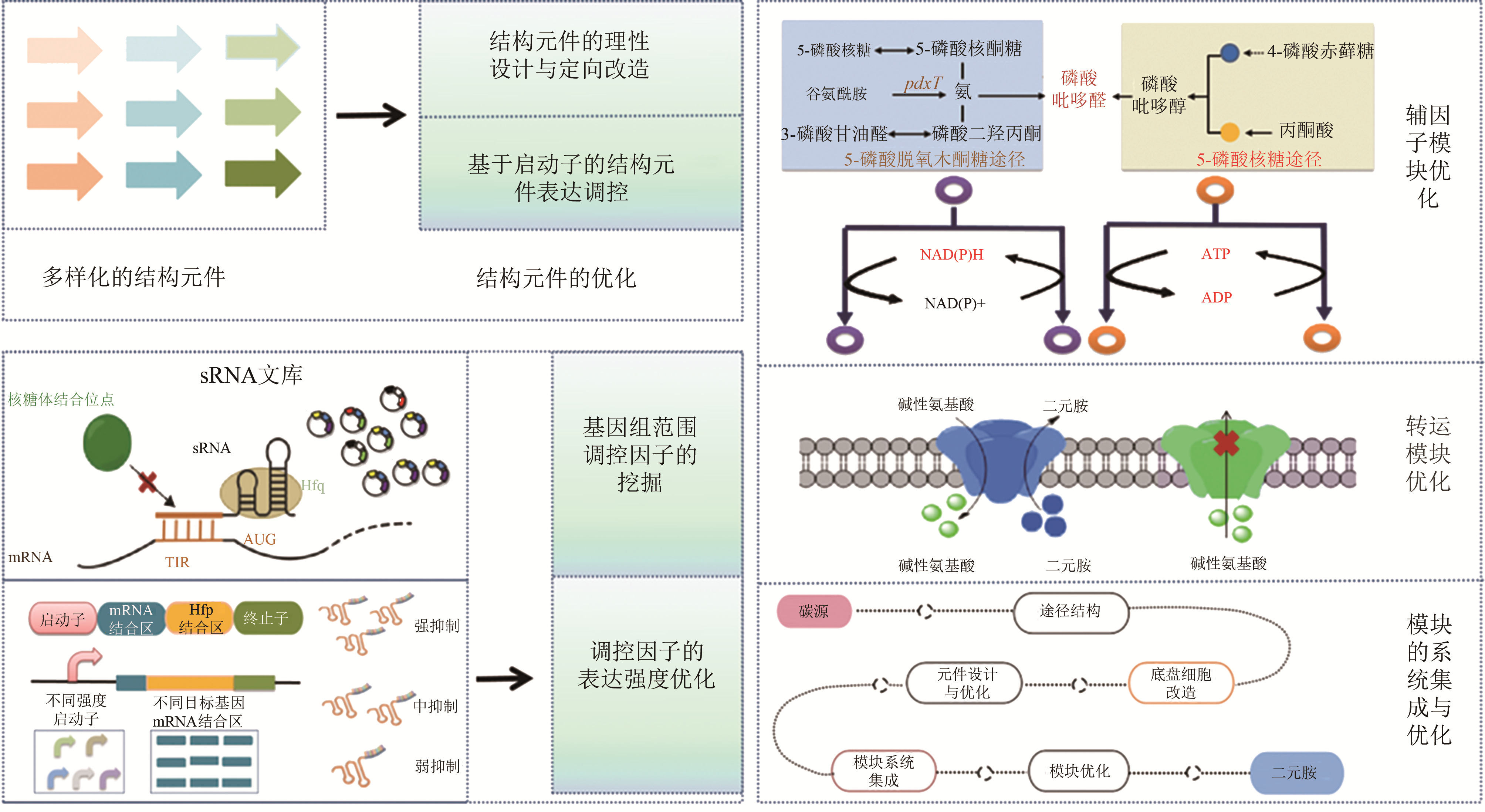
图2 二元胺合成细胞的优化策略 [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48]
Fig. 2 The engineering strategy for the optimization of diamine synthetic cells[14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48]
| 产品 | 宿主 | 改造策略 | 产量 /g·L-1 | 产率/g·g-1 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1,5- 戊二胺 | 大肠杆菌 | 过表达赖氨酸脱羧酶元件cadA 过表达dapA基因增强前体赖氨酸合成 敲除1,5-戊二胺利用途径基因speE、speG、ygjG和 puuA 抑制调控元件murE的表达 | 12.6 | — | [ |
| 谷氨酸棒状杆菌 | 高强度表达E.coli 来源的赖氨酸脱羧酶元件ldcC 敲除赖氨酸分泌蛋白lysE | 103.78 | 0.303 | [ | |
1,4- 丁二胺 | 大肠杆菌 | 敲除产物降解途径基因 speE、speG、puuA 敲除前体鸟氨酸降解途径基因argI 敲除全局转录因子 rpoS 过表达合成途径基因speC、argE、argC、argB、argH、speF和argD 过表达1,4-丁二胺分泌蛋白potE 下调argF和glnA的表达水平 | 42.3 | 0.26 | [ |
| 谷氨酸棒状杆菌 | 异源表达 E. coli 来源的鸟氨酸脱羧酶speC 敲除前体鸟氨酸利用途径基因argF和argR 精确调控argF的表达水平 | 19 | 0.16 | [ | |
1,3- 丙二胺 | 大肠杆菌 | 表达不动杆菌属来源的dat和ddc组装1,3-丙二胺合成途径 过表达thrA和lysC突变体增强天冬氨酸半醛合成 过表达ppc和aspC增强前体天冬氨酸的合成 敲除pfkA增强胞内NADPH的供给 | 13.06 | 0.1 | [ |
表1 不同宿主合成C3~C5脂肪族二元胺最高水平对比
Tab. 1 The highest production level of aliphatic diamines with 3~5 carbon atoms by different hosts
| 产品 | 宿主 | 改造策略 | 产量 /g·L-1 | 产率/g·g-1 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1,5- 戊二胺 | 大肠杆菌 | 过表达赖氨酸脱羧酶元件cadA 过表达dapA基因增强前体赖氨酸合成 敲除1,5-戊二胺利用途径基因speE、speG、ygjG和 puuA 抑制调控元件murE的表达 | 12.6 | — | [ |
| 谷氨酸棒状杆菌 | 高强度表达E.coli 来源的赖氨酸脱羧酶元件ldcC 敲除赖氨酸分泌蛋白lysE | 103.78 | 0.303 | [ | |
1,4- 丁二胺 | 大肠杆菌 | 敲除产物降解途径基因 speE、speG、puuA 敲除前体鸟氨酸降解途径基因argI 敲除全局转录因子 rpoS 过表达合成途径基因speC、argE、argC、argB、argH、speF和argD 过表达1,4-丁二胺分泌蛋白potE 下调argF和glnA的表达水平 | 42.3 | 0.26 | [ |
| 谷氨酸棒状杆菌 | 异源表达 E. coli 来源的鸟氨酸脱羧酶speC 敲除前体鸟氨酸利用途径基因argF和argR 精确调控argF的表达水平 | 19 | 0.16 | [ | |
1,3- 丙二胺 | 大肠杆菌 | 表达不动杆菌属来源的dat和ddc组装1,3-丙二胺合成途径 过表达thrA和lysC突变体增强天冬氨酸半醛合成 过表达ppc和aspC增强前体天冬氨酸的合成 敲除pfkA增强胞内NADPH的供给 | 13.06 | 0.1 | [ |
| 1 | JIANG Y, LOOS K. Enzymatic synthesis of biobased polyesters and polyamides [J]. Polymers, 2016, 8(7): 243. |
| 2 | WINNACKER M, RIEGER B. Biobased polyamides: recent advances in basic and applied research [J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2016, 37(17): 1391-1413. |
| 3 | GILBERT M. Aliphatic polyamides [M]. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinermann, 2017. |
| 4 | 李秀峥, 李澜鹏, 曹长海, 等. 生物基聚酰胺及其单体研究进展 [J]. 工程塑料应用, 2018(7): 138-142. |
| LI X Z, LI L P, CAO C H, et al. Research progress of bio-based polyamide and its monomer [J]. Engineering Plastics Application, 2018(7): 138-142. | |
| 5 | MA W, CAO W, ZHANG H, et al. Enhanced cadaverine production from l-lysine using recombinant Escherichia coli co-overexpressing CadA and CadB [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2015, 37(4): 799-806. |
| 6 | KIM H T, BARITUGO K A, OH Y H, et al. High-level conversion of l-lysine into cadaverine by Escherichia coli whole cell biocatalyst expressing Hafnia alvei l-lysine decarboxylase [J]. Polymers, 2019, 11(7): 1184. |
| 7 | SEO S W, YANG J, MIN B E, et al. Synthetic biology: tools to design microbes for the production of chemicals and fuels [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2013, 31(6): 811-817. |
| 8 | WENDISCH V F, MINDT M, PÉREZ-GARCÍA F. Biotechnological production of mono- and diamines using bacteria: recent progress, applications, and perspectives [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(8): 3583-3594. |
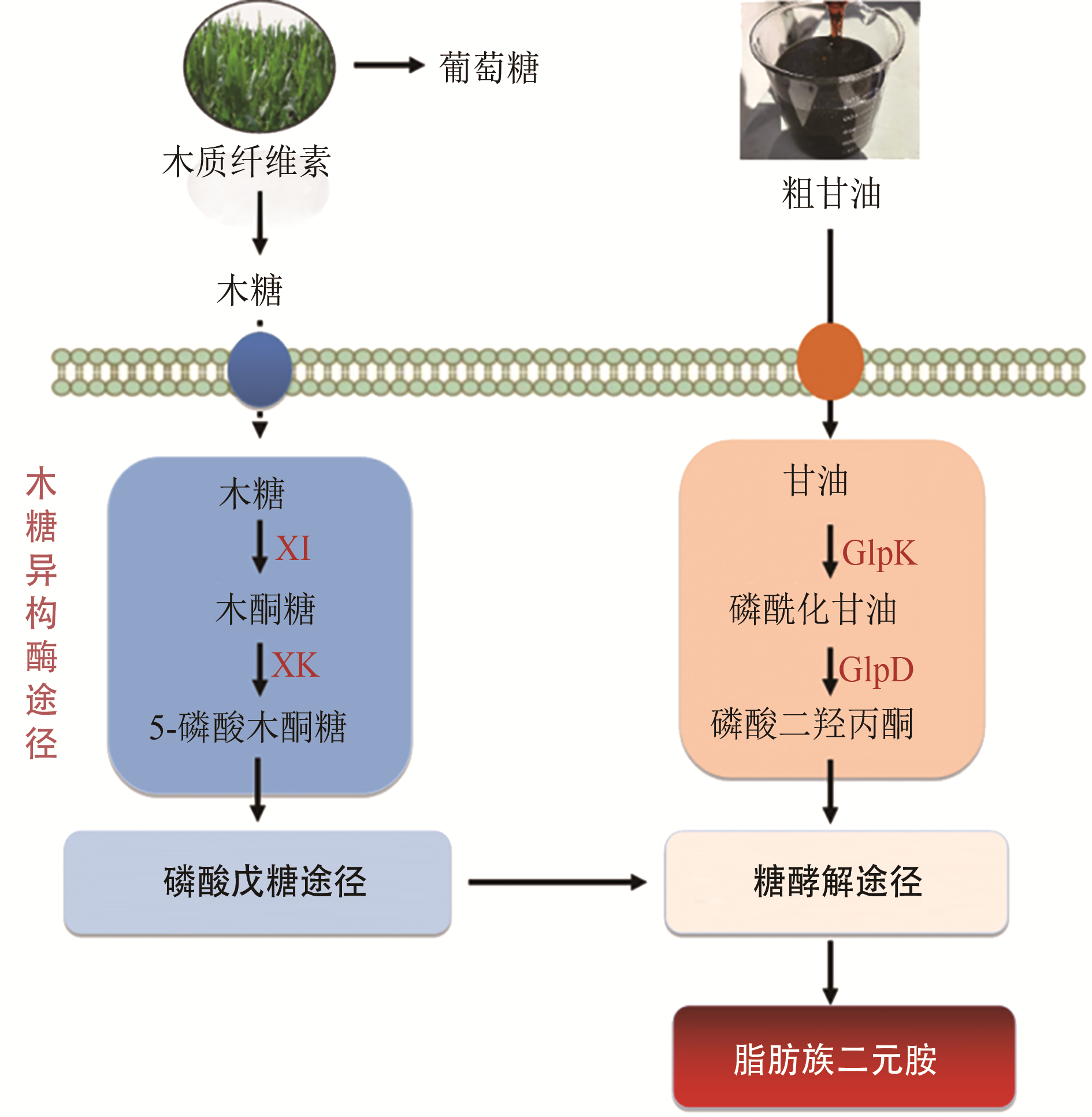
| 9 | LI Z, LIU J Z. Transcriptomic changes in response to putrescine production in metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 1-11. |
| 10 | SCHNEIDER J, WENDISCH V F. Putrescine production by engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 88(4): 859-868. |
| 11 | JENSEN J V K, EBERHARDT D, WENDISCH V F. Modular pathway engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for production of the glutamate-derived compounds ornithine, proline, putrescine, citrulline, and arginine [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2015, 214: 85-94. |
| 12 | ZHAN M, KAN B, DONG J, et al. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for improved l-arginine synthesis by enhancing NADPH supply [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 46(1): 45-54. |
| 13 | CHAE T U, KIM W J, CHOI S, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of 1,3-diaminopropane, a three carbon diamine [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 1-13. |
| 14 | QIAN Z G, XIA X X, LEE S Y. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of cadaverine: a five carbon diamine [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2011, 108(1): 93-103. |
| 15 | QIAN Z G, XIA X X, LEE S Y. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of putrescine: a four carbon diamine [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2009, 104(4): 651-662. |
| 16 | MIMITSUKA T, SAWAI H, HATSU M, et al. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for cadaverine fermentation [J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 2007, 71(9): 2130-2135. |
| 17 | KIND S, JEONG W K, SCHRÖDER H, et al. Identification and elimination of the competing N-acetyldiaminopentane pathway for improved production of diaminopentane by Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(15): 5175-5180. |
| 18 | NGUYEN A Q D, SCHNEIDER J, WENDISCH V F. Elimination of polyamine N-acetylation and regulatory engineering improved putrescine production by Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2015, 201: 75-85. |
| 19 | YAMAMOTO S, TSUZAKI Y, TOUGOU K, et al. Purification and characterization of L-2,4-diaminobutyrate decarboxylase from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus [J]. Journal of General Microbiology, 1992, 138(7): 1461-1465. |
| 20 | YAMAMOTO S, MUTOH N, IKAI H, et al. Occurrence of a novel L-2,4-diaminobutyrate decarboxylase activity in some species of Enterobacteriaceae, and purification and characterization of the enzymes of Enterobacter aerogenes and Serratia marcescens [J]. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1996,19(10): 1298-1303. |
| 21 | IKAI H, YAMAMOTO S. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene encoding a novel L-2,4-diaminobutyratedecarboxylase of Acinetobacter baumannii [J] FEMS Microbiology Letters, 1994, 124(2): 225-228. |
| 22 | NAKAO H, TAKEUCHI K, SHINODA S, et al. L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid decarboxylase activity responsible for the formation of 1,3-diaminopropane in Enterobacter aerogenes [J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 1990, 70(1): 61-66. |
| 23 | BLETHEN S L, BOEKER E A, SNELL E E. Argenine decarboxylase from Escherichia coli. I. purification and specificity for substrates and coenzyme [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1968, 243(8):1671-1677. |
| 24 | WU W H, MORRIS D R. Biosynthetic arginine decarboxylase from Escherichia coli: purification and properties [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1973,248(5): 1687-1695. |
| 25 | GOLDEMBERG S H. Lysine decarboxylase mutants of Escherichia coli: evidence for two enzyme forms [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1980, 141(3): 1428-1431. |
| 26 | KIKUCHI Y, KOJIMA H, TANAKA T, et al. Characterization of a second lysine decarboxylase isolated from Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1997, 179(14): 4486-4492. |
| 27 | LEMONNIER M, LANE D. Expression of the second lysine decarboxylate gene of Escherichia coli [J]. Microbiology, 1998, 144(3): 751-760. |
| 28 | SABO D L, BOEKER E A, BYERS B, et al. Purification and physical properties of inducible Escherichia coli lysine decarboxylase [J]. Biochemistry, 1974, 13(4): 662-670. |
| 29 | YAMAMOTO Y, MIWA Y, MIYOSHI K, et al. The Escherichia coli ldcC gene encodes another lysine decarboxylase, probably a constitutive enzyme [J]. Genes and Genetic Systems, 1997, 72(3): 167-172. |
| 30 | LI Z, SHEN Y P, JIANG X L, et al. Metabolic evolution and a comparative omics analysis of Corynebacterium glutamicum for putrescine production[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 45(2): 123-139. |
| 31 | WANG C, ZHANG K, ZHONG J C, et al. Directed evolution and mutagenesis of lysine decarboxylase from Hafnia alvei AS1.1009 to improve its activity toward efficient cadaverine production[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2015, 20(3): 439-446. |
| 32 | HONG E Y, LEE S G, PARK B J, et al. Simultaneously enhancing the stability and catalytic activity of multimeric lysine decarboxylase CadA by engineering interface regions for enzymatic production of cadaverine at high concentration of lysine [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 12(11): 1700268. |
| 33 | CHOI H, KYEONG H H, CHOI J M, et al. Rational design of ornithine decarboxylase with high catalytic activity for the production of putrescine [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(17): 7483-7490. |
| 34 | HONG E Y, KIM J Y, UPADHYAY R, et al. Rational engineering of ornithine decarboxylase with greater selectivity for ornithine over lysine through protein network analysis[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2018, 281: 175-182. |
| 35 | OH Y H, CHOI J W, KIM E Y, et al. Construction of synthetic promoter-based expression cassettes for the production of cadaverine in recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2015, 176(7): 2065-2075. |
| 36 | KIM H T, BARITUGO K A, OH Y H, et al. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the high-level production of cadaverine that can be used for the synthesis of biopolyamide 510 [J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, 2018, 6(4): 5296-5305. |
| 37 | SCHNEIDER J, EBERHARDT D, WENDISCH V F. Improving putrescine production by Corynebacterium glutamicum by fine-tuning ornithine transcarbamoylase activity using a plasmid addiction system [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 95(1): 169-178. |
| 38 | NA D, YOO S M, CHUNG H, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli using synthetic small regulatory RNAs[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(2): 170-174. |
| 39 | NOH M, YOO S M, KIM W J, et al. Gene expression knockdown by modulating synthetic small RNA expression in Escherichia coli [J]. Cell Systems, 2017, 5(4): 418-426. |
| 40 | LIANG J, HAN Q, TAN Y, et al. Current advances on structure-function relationships of pyridoxal 5′-phosphate dependent enzymes [J]. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 2019(6): 4. |
| 41 | FITZPATRICK T B, AMRHEIN N, KAPPES B, et al. Two independent routes of de novo vitamin B6 biosynthesis: not that different after all [J]. Biochemical Journal, 2007, 407(1): 1-13. |
| 42 | FITZPATRICK T B, MOCCAND C, ROUX C. Vitamin B6 biosynthesis: charting the mechanistic landscape [J]. ChemBioChem, 2010, 11(9): 1185-1193. |
| 43 | ROSENBERG J, ISCHEBECK T, COMMICHAU F M. Vitamin B6 metabolism in microbes and approaches for fermentative production [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2017, 35(1): 31-40. |
| 44 | RASCHLE T, AMRHEIN N, FITZPATRICK T B. On the two components of pyridoxal 5′-phosphate synthase from Bacillus subtilis [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2005, 280(37): 32291-32300. |
| 45 | TATSUO H, KEIKO I, MASAAKI T. Recombinant microorganism for the production of vitamin B6: US528891 [P]. 2005-10-19. |
| 46 | MA W, CAO W, ZHANG B, et al. Engineering a pyridoxal 5′-phosphate supply for cadaverine production by using Escherichia coli whole-cell biocatalysis [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 1-10. |
| 47 | LI M, LI D, HUANG Y, et al. Improving the secretion of cadaverine in Corynebacterium glutamicum by cadaverine-lysine antiporter [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 41(4): 701-709. |
| 48 | KIND S, KREYE S, WITTMANN C. Metabolic engineering of cellular transport for overproduction of the platform chemical 1,5-diaminopentane in Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2011, 13(5): 617-627. |
| 49 | KIND S, NEUBAUER S, BECKER J, et al. From zero to hero-production of bio-based nylon from renewable resources using engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2014, 25: 113-123. |
| 50 | ARISTIDOU A, PENTTIL A M. Metabolic engineering applications to renewable resource utilization [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2000, 11: 187-198. |
| 51 | CHOI J W, JEON E J, JEONG K J. Recent advances in engineering Corynebacterium glutamicum for utilization of hemicellulosic biomass [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2019, 57: 17-24. |
| 52 | MEISWINKEL T M, GOPINATH V, LINDNER S N, et al. Accelerated pentose utilization by Corynebacterium glutamicum for accelerated production of lysine, glutamate, ornithine and putrescine [J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2013, 6(2): 131-140. |
| 53 | BUSCHKE N, SCHRODER H, WITTMANN C. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for production of 1,5-diaminopentane from hemicellulose [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2011, 6(3): 306-317. |
| 54 | BUSCHKE N, BECKER J, SCHAFER R, et al. Systems metabolic engineering of xylose-utilizing Corynebacterium glutamicum for production of 1,5-diaminopentane [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2013, 8(5): 557-570. |
| 55 | CHEN Z, LIU D. Toward glycerol biorefinery: metabolic engineering for the production of biofuels and chemicals from glycerol [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2016, 9(1): 1-15. |
| 56 | BECKERS V, POBLETE-CASTRO I, TOMASCH J, et al. Integrated analysis of gene expression and metabolic fluxes in PHA-producing Pseudomonas putida grown on glycerol [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15(1): 1-18. |
| 57 | GAO C, YANG X, WANG H, et al. Robust succinic acid production from crude glycerol using engineered Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2016, 9(1): 1-11. |
| 58 | MEISWINKEL T M, RITTMANN D, LINDNER S N, et al. Crude glycerol-based production of amino acids and putrescine by Corynebacterium glutamicum [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 145: 254-258. |
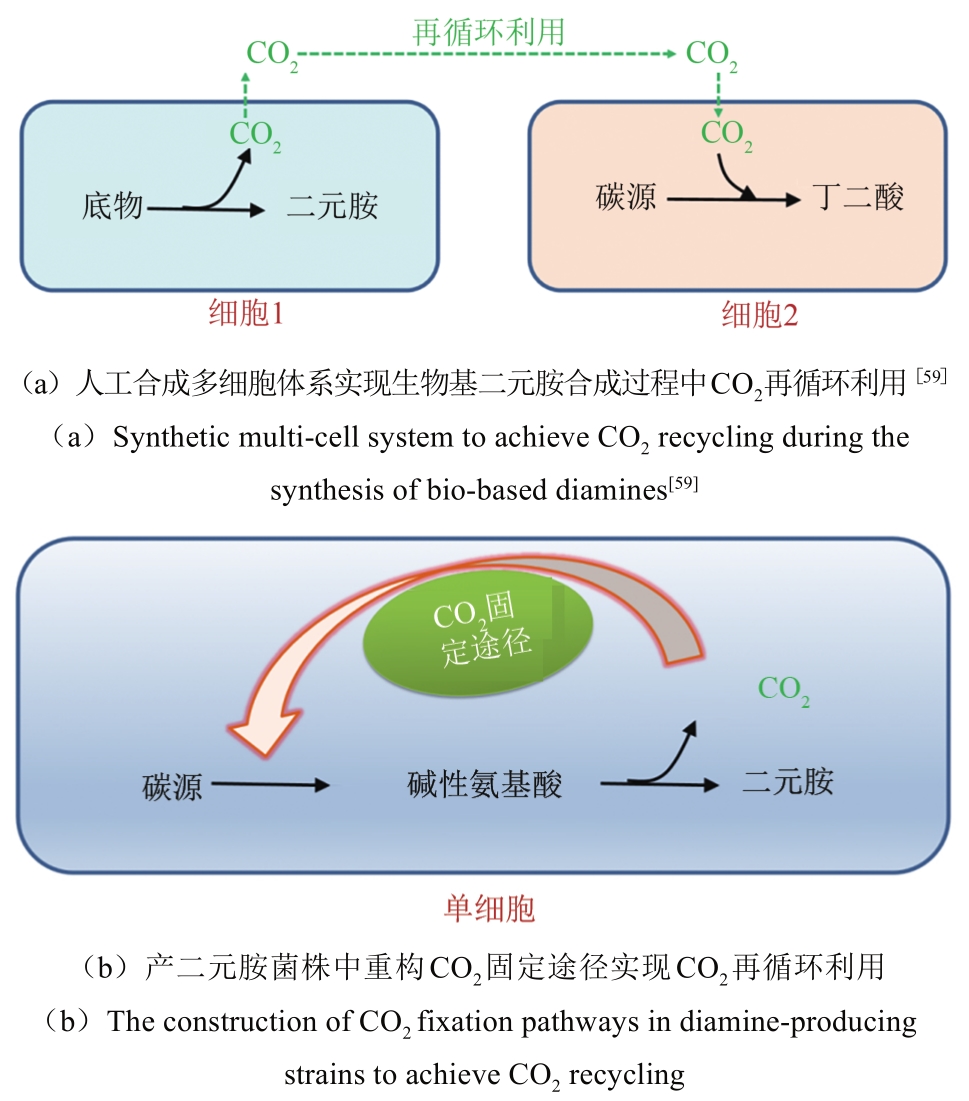
| 59 | WANG J, MAO J, TIAN W, et al. Coproduction of succinic acid and cadaverine using lysine as a neutralizer and CO2 donor with l-lysine decarboxylase overexpressed: Escherichia coli AFP111 [J]. Green Chemistry, 2018, 20(12): 2880-2887. |
| 60 | CLAASSENS N J, SOUSA D Z, SANTOS V A P M DOS, et al. Harnessing the power of microbial autotrophy [J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(11):692-706. |
| 61 | GUADALUPE-MEDINA V, WISSELINK H W, LUTTIK M A, et al. Carbon dioxide fixation by Calvin-cycle enzymes improves ethanol yield in yeast [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2013, 6(1):125. |
| 62 | HU G, ZHOU J, CHEN X, et al. Engineering synergetic CO2-fixing pathways for malate production [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47:496-504. |
| 63 | LIMSUWUN K, JONES P G. Spermidine acetyltransferase is required to prevent spermidine toxicity at low temperatures in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2000, 182(19):5373-5380. |
| 64 | KATINKA M, COSSART P, SIBILLI L, et al. Nucleotide sequence of the thrA gene of Escherichia coli [J]. PNAS, 1980, 77: 5730-5733. |
| 65 | HU G, LI Y, YE C, et al. Engineering microorganisms for enhanced CO2 sequestration [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2019, 37(5): 532-547. |
| 66 | GONG F, ZHU H, ZHANG Y, et al. Biological carbon fixation: from natural to synthetic [J]. 2018, 28:221-227. |
| 67 | PLEGARIA J S, KERFELD C A. Engineering nanoreactors using bacterial microcompartment architectures [J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2018, 51:1-7. |
| 68 | WANG S Z, ZHANG Y H, REN H, et al. Strategies and perspectives of assembling multi-enzyme systems [J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2017, 37(8):1-14. |
| 69 | PRICE J V, CHEN L, WHITAKER W B, et al. Scaffoldless engineered enzyme assembly for enhanced methanol utilization [J]. PNAS, 2016, 113(45): 12691-12696. |
| 70 | KUMAR M, SUNDARAM S, GNANSOUNOU E, et al. Carbon dioxide capture, storage and production of biofuel and biomaterials by bacteria: a review [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 247: 1059-1068. |
| 71 | TURMO A, GONZALEZ-ESQUER C R, Kerfeld C A. Carboxysomes: metabolic modules for CO2 fixation [J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2017, 364(18):176. |
| [1] | 应汉杰, 柳东, 王振宇, 沈涛, 庄伟, 朱晨杰. 工业生物制造与“碳中和”目标探讨[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 1-7. |
| [2] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [3] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [11] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [12] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [13] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [14] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [15] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||