合成生物学 ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (1): 92-102.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-036
微生物药物的合成生物学研究进展
饶聪1, 云轩1, 虞沂1, 邓子新1,2
- 1.武汉大学药学院,组合生物合成与新药发现教育部重点实验室,湖北 武汉 430071
2.上海交通大学生命科学技术学院,微生物代谢国家重点实验室,上海 200240
-
收稿日期:2020-03-26修回日期:2020-04-19出版日期:2020-02-29发布日期:2020-07-07 -
通讯作者:虞沂,邓子新 -
作者简介:饶聪(1996-),男,硕士研究生。
虞沂(1978—),男,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为天然产物化学生物学。E-mail: yu_yi@whu.edu.cn
邓子新(1957—),男,中国科学院院士,第三世界科学院(TWAS)院士,美国微生物科学院院士,2020年当选全球工业微生物学会(GIM)首届主席,主要从事放线菌遗传学及抗生素生物合成的化学生物学、合成生物学研究。E-mail:zxdeng@sjtu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0900400);国家自然科学基金(31870035)
Recent progress of synthetic biology applications in microbial pharmaceuticals research
RAO Cong1, YUN Xuan1, YU Yi1, DENG Zixin1,2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery (Ministry of Education), School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei, China
2.State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism, School of Life Science & Biotechnology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
-
Received:2020-03-26Revised:2020-04-19Online:2020-02-29Published:2020-07-07 -
Contact:YU Yi, DENG Zixin
摘要:
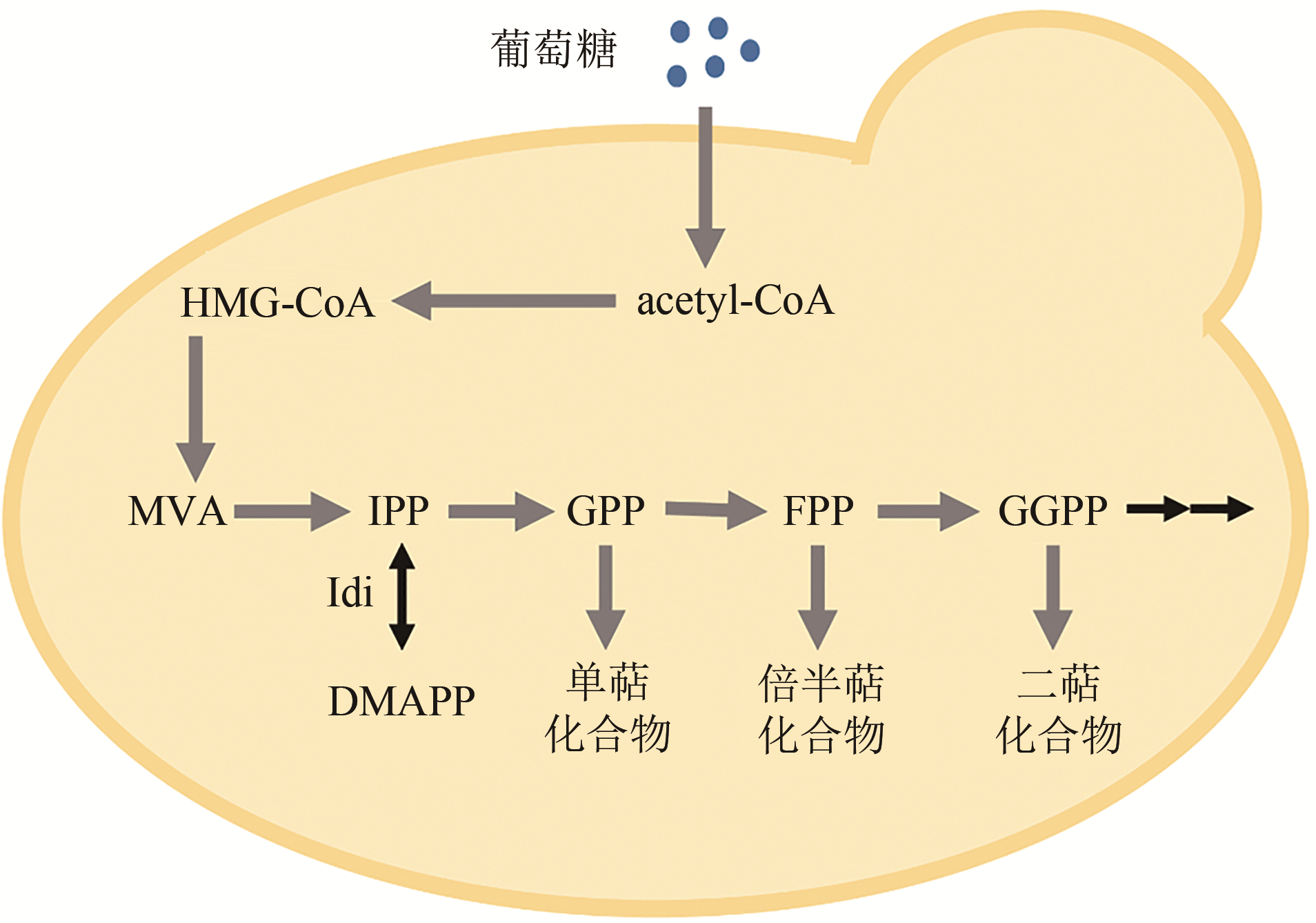
微生物天然产物一直都是新型生物药物创新的主要源泉,是目前开发临床抗菌、抗肿瘤、免疫抑制剂等药物的重要资源。随着临床耐药菌的日益增多,新型病原菌和病毒的不断出现,以及新骨架天然产物挖掘难度的增加,新型微生物药物的开发正面临着巨大挑战。作为21世纪生命医学领域催动原创突破和学科交叉融合的前沿学科,合成生物学的崛起为解决药物研发困境提供了新的思路和方法,它可以突破天然药物发现的瓶颈,设计新的生物合成途径,产生更多天然药物及类似物。本文综述了近五年来合成生物学在微生物药物研究领域的技术革新,及其在氨基糖苷类抗生素、核苷类抗生素、核糖体肽、萜类以及聚酮类化合物等5大类微生物天然药物的发掘、生物合成以及新结构创制等方面的应用。
中图分类号:
引用本文
饶聪, 云轩, 虞沂, 邓子新. 微生物药物的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(1): 92-102.
RAO Cong, YUN Xuan, YU Yi, DENG Zixin. Recent progress of synthetic biology applications in microbial pharmaceuticals research[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 92-102.
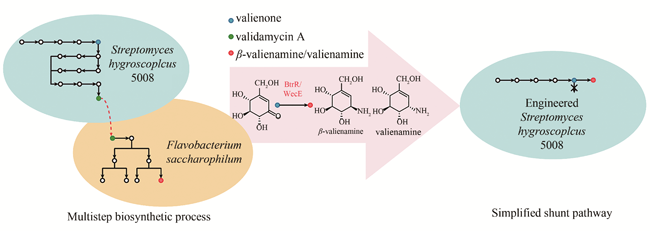
图1 Valienamine天然多步合成途径及改造后的简化合成途径
Fig. 1 The natural multistep biosynthetic pathway of valienamine, and the simplified biosynthetic pathway after modification

图3 喹啉酸及其类似物喂养工程菌SL3052产生siomycin及其类似物
Fig. 3 The engineered strain SL3052 fed with quinolinic acid and its analogues, leading to the production of siomycin and its analogues
| 1 | NEWMAN David J, CRAGG Gordon M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019[J]. Journal of Natural Product, 2020, 83 (3): 770-803. |
| 2 | BERDY J. Thoughts and facts about antibiotics: where we are now and where we are heading[J]. Journal of Antibiotics, 2012, 65(8): 385-395. |
| 3 | KELWICK R, MACDONALD J T, WEBB A J, et al. Developments in the tools and methodologies of synthetic biology[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2014, 2: 60. |
| 4 | MUKHERJEE S, STAMATIS D, BERTSCH J, et al. Genomes OnLine database (GOLD) v.7: updates and new features[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47 (D1): 649-659. |
| 5 | SMANSKI M J, ZHOU H, CLAESEN J, et al. Synthetic biology to access and expand nature’s chemical diversity[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016,14 (3):135-149. |
| 6 | BLIN Kai, PASCAL ANDREU Victòria, DE LOS SANTOS Emmanuel L C, et al. The antiSMASH database version 2: a comprehensive resource on secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 47 (D1): 625-630. |
| 7 | NAVARRO MU OZ Jorge C, SELEM MOJICA Nelly, MULLOWNEY Michael W, et al. A computational framework for systematic exploration of biosynthetic diversity from large-scale genomic data[J]. bioRxiv., 2018: 445270.DOI: 10.110/445270 |
| 8 | Gökcen ERASLAN, Žiga AVSEC, GAGNEUR Julien, et al. Deep learning: new computational modelling techniques for genomics[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2019, 20 (7): 389-403. |
| 9 | TIETZ Jonathan I, SCHWALEN Christopher J, PATEL Parth S, et al. A new genome-mining tool redefines the lasso peptide biosynthetic landscape[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2017, 13 (5): 470-478. |
| 10 | HU Qiannan, DENG Zhe, HU Huanan, et al. RxnFinder: biochemical reaction search engines using molecular structures, molecular fragments and reaction similarity[J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27 (17): 2465-2467. |
| 11 | CHENG Xingxiang, SUN Dandan, ZHANG Dachuan, et al. RxnBLAST: molecular scaffold and reactive chemical environment feature extractor for biochemical reactions[J]. Bioinformatics, 2020,36(9): 2946-2947. |
| 12 | ZHANG Tong, TIAN Yu, YUAN Le, et al. Bio2Rxn: sequence-based enzymatic reaction predictions by a consensus strategy[J]. Bioinformatics, 2020. DOI: 10.1093/bio in formatics/baa135 . |
| 13 | TU Weizhong, ZHANG Haoran, LIU Juan, et al. BioSynther: a customized biosynthetic potential explorer[J]. Bioinformatics, 2015, 32 (3): 472-473. |
| 14 | DING Shaozhen, LIAO Xiaoping, TU Weizhong, et al. EcoSynther: a customized platform to explore biosynthetic potential in E. coli [J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2017, 12 (11), 2823-2829. |
| 15 | HAMEDIRAD Mohammad, CHAO Ran, WEISBERG Scott, et al. Towards a fully automated algorithm driven platform for biosystems design[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10 (1): 5150. |
| 16 | HERRMANN S, SIEGL T, LUZHETSKA M, et al. Site-specific recombination strategies for engineering actinomycete genomes[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 78 (6): 1804-1812. |
| 17 | JIANG W, BIKARD D, COX D, et al. RNA-guided editing of bacterial genomes using CRISPR-Cas systems[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31 (3): 233-239. |
| 18 | JINEK M, CHYLINSKI K, FONFARA I, et al. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity[J]. Science, 2012, 337 (6096): 816-821. |
| 19 | COBB Ryan E, WANG Yajie, ZHAO Huimin. High-efficiency multiplex genome editing of streptomyces species using an engineered CRISPR/Cas system[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4 (6): 723-728. |
| 20 | ZHANG M M, WONG F T, WANG Y, et al. CRISPR-Cas9 strategy for activation of silent Streptomyces biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2017, 13: 607-609. |
| 21 | WANG Hailong, LI Zhen, JIA Ruonan, et al. RecET direct cloning and Redαβ recombineering of biosynthetic gene clusters, large operons or single genes for heterologous expression[J]. Nature Protocols, 2016, 11 (7): 1175-1190. |
| 22 | BU Qingting, YU Pin, WANG Jue, et al. Rational construction of genome-reduced and high-efficient industrial Streptomyces chassis based on multiple comparative genomic approaches[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18 (1): 16. |
| 23 | KALLIFIDAS Dimitris, JIANG Guangde, DING Yousong, et al. Rational engineering of Streptomyces albus J1074 for the overexpression of secondary metabolite gene clusters[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17 (1): 25. |
| 24 | LUO X, REITER M A, D'ESPAUX L,et al. Complete biosynthesis of cannabinoids and their unnatural analogues in yeast[J]. Nature, 2019, 567 (7746): 123-126. |
| 25 | JUNG W S, LEE S K, HONG J S, et al. Heterologous expression of tylosin polyketide synthase and production of a hybrid bioactive macrolide in Streptomyces venezuelae [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 72 (4): 763-769. |
| 26 | PADDON C J, WESTFALL P J, PITERA D J, et al. High-level semi-synthetic production of the potent antimalarial artemisinin[J]. Nature, 2013, 496 (7446): 528-532. |
| 27 | LI Sicong, GUO Junhong, REVA Anna, et al. Methyltransferases of gentamicin biosynthesis[J]. PNAS, 2018, 115 (6): 1340. |
| 28 | BURY Priscila dos Santos, HUANG Fanglu, LI Sicong, et al. Structural basis of the selectivity of GenN, an aminoglycoside N-methyltransferase involved in gentamicin biosynthesis[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2017, 12 (11): 2779-2787. |
| 29 | TAO Weixin, CHEN Li, ZHAO Chunhua, et al. In vitro packaging mediated one-step targeted cloning of natural product pathway[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8 (9): 1991-1997. |
| 30 | CUI Li, ZHU Ying, GUAN Xiaoqing, et al. De novo biosynthesis of β-valienamine in engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus 5008[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5 (1): 15-20. |
| 31 | CUI Li, WEI Xiaodong, WANG Xinran, et al. A validamycin shunt pathway for valienamine synthesis in engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus 5008[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(2), 294-303. |
| 32 | ZHAO Q, LUO Y, ZHANG X, et al. A severe leakage of intermediates to shunt products in acarbose biosynthesis[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11 (1): 1468. |
| 33 | CHEN Wenqing, QI Jianzhao, WU Pan, et al. Natural and engineered biosynthesis of nucleoside antibiotics in Actinomycetes[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2016, 43 (2): 401-417. |
| 34 | QI Jianzhao, WAN Dan, MA Hongmin, et al. Deciphering carbamoylpolyoxamic acid biosynthesis reveals unusual acetylation cycle associated with tandem reduction and sequential hydroxylation[J]. Cell Chemical Biology, 2016, 23 (8): 935-944. |
| 35 | CHEN Wenqing, LI Yan, LI Jie, et al. An unusual UMP C-5 methylase in nucleoside antibiotic polyoxin biosynthesis[J]. Protein & Cell, 2016, 7 (9): 673-683. |
| 36 | WU Pan, WAN Dan, XU Gudan, et al. An unusual Protector-Protégé strategy for the biosynthesis of purine nucleoside antibiotics[J]. Cell Chemical Biology, 2017, 24 (2): 171-181. |
| 37 | ZHANG Meng, ZHANG Peichao, XU Gudan, et al. Comparative investigation into formycin A and pyrazofurin A biosynthesis reveals branch pathways for the construction of C-nucleoside scaffolds[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2019. DOI:10.1128/AEM.01971-19 . |
| 38 | LIU Yan, GONG Rong, LIU Xiaoqin, et al. Discovery and characterization of the tubercidin biosynthetic pathway from Streptomyces tubercidicus NBRC 13090[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17 (1): 131. |
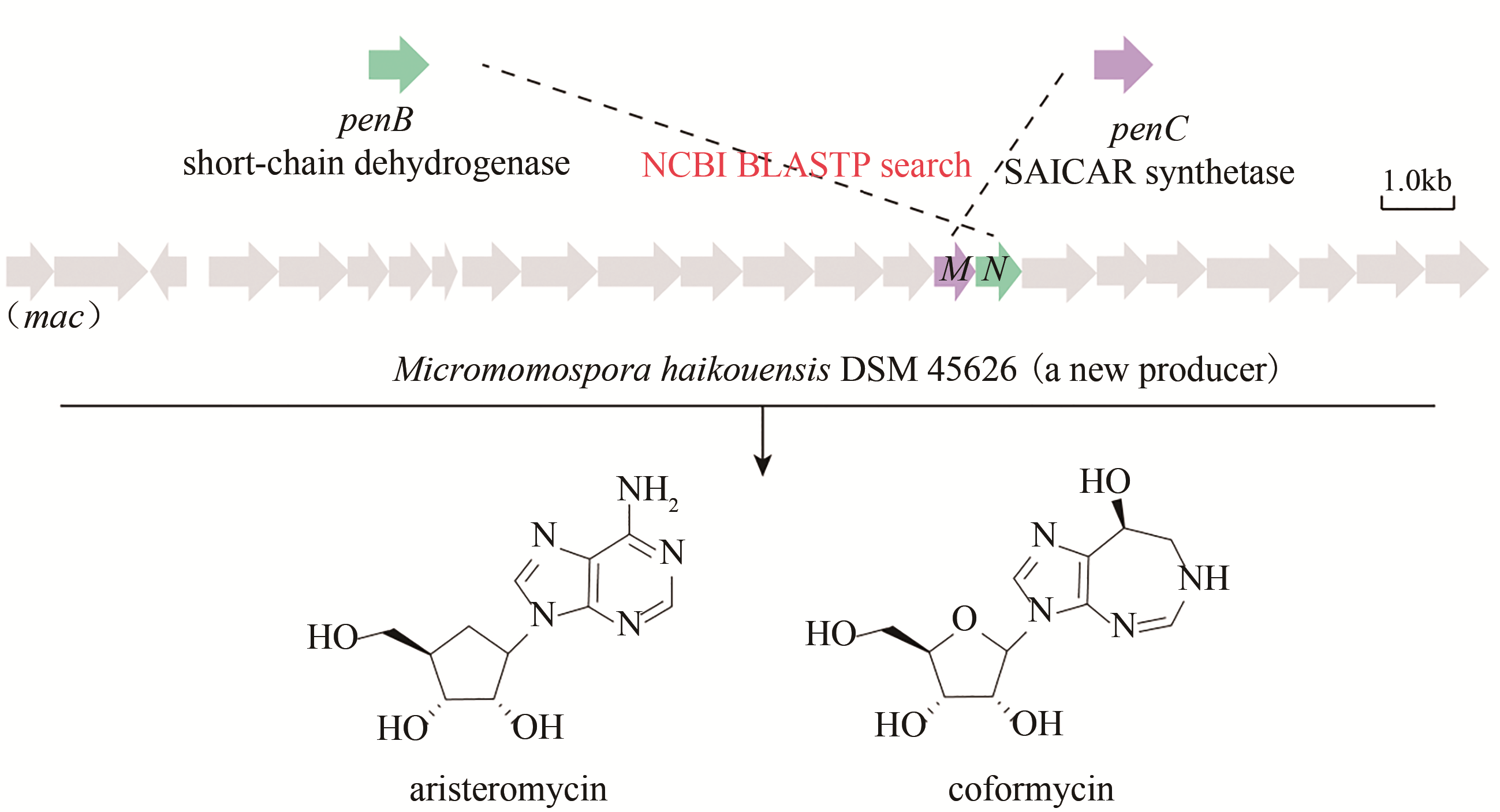
| 39 | XU Gudan, KONG Liyuan, GONG Rong, et al. Coordinated biosynthesis of the purine nucleoside antibiotics aristeromycin and coformycin in actinomycetes[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84 (22).DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01860-18 . |
| 40 | ZHANG Yi, CHEN Manyun, BRUNER Steven D, et al. Heterologous production of microbial ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 1801. |
| 41 | ZHENG Qingfei, FANG Hui, LIU Wen. Post-translational modifications involved in the biosynthesis of thiopeptide antibiotics[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2017, 15 (16): 3376-3390. |
| 42 | QIU Yanping, DU Yanan, WANG Shoufeng, et al. Radical S-adenosylmethionine protein NosN forms the side ring system of nosiheptide by functionalizing the polythiazolyl peptide S-conjugated indolic moiety[J]. Organic Letters, 2019, 21 (5): 1502-1505. |
| 43 | LIU Jingyu, LIN Zhi, CHEN Hua, et al. Biosynthesis of the central piperidine nitrogen heterocycle in series a thiopeptides[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 37 (1): 35-41. |
| 44 | WANG Jian, LIN Zhi, BAI Xuebing, et al. Optimal design of thiostrepton-derived thiopeptide antibiotics and their potential application against oral pathogens[J]. Organic Chemistry Frontiers, 2019, 6 (8): 1194-1199. |
| 45 | MO Tianlu, LIU Wanqiu, JI Wenjuan, et al. Biosynthetic insights into Linaridin natural products from genome mining and Precursor peptide mutagenesis[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2017, 12 (6): 1484-1488. |
| 46 | BIAN Guangkai, HAN Yichao, HOU Anwei, et al. Releasing the potential power of terpene synthases by a robust precursor supply platform[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 42: 1-8. |
| 47 | BIAN Guangkai, HOU Anwei, YUAN Yujie, et al. Metabolic engineering-based rapid characterization of a sesquiterpene cyclase and the skeletons of Fusariumdiene and Fusagramineol from Fusarium graminearum [J]. Organic Letters, 2018, 20 (6): 1626-1629. |
| 48 | CHENG S, LIU X, JIANG G, et al. Orthogonal engineering of biosynthetic pathway for efficient production of Limonene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8 (5): 968-975. |
| 49 | KANG Wei, MA Tian, LIU Min, et al. Modular enzyme assembly for enhanced cascade biocatalysis and metabolic flux[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10 (1): 1-11. |
| 50 | WANG Weishan, LI Shanshan, LI Zilong, et al. Harnessing the intracellular triacylglycerols for titer improvement of polyketides in Streptomyces [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38 (1): 76-83. |
| 51 | YOU Di, WANG Miaomiao, YIN Bincheng, et al. Precursor supply for Erythromycin biosynthesis: Engineering of propionate assimilation pathway based on propionylation modification[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8 (2): 371-380. |
| 52 | PALAZZOTTO E, TONG Y, LEE S Y, et al. Synthetic biology and metabolic engineering of actinomycetes for natural product discovery[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37 (6): 107366. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 仲泉周, 单依怡, 裴清云, 金艳芸, 王艺涵, 孟璐远, 王歆韵, 张雨鑫, 刘坤媛, 王慧中, 冯尚国. 生物合成法生产α-熊果苷的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 118-135. |
| [7] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [11] | 刘益宁, 蒲伟, 杨金星, 王钰. ω-氨基酸与内酰胺的生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1350-1366. |
| [12] | 李庚, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 过氧化物酶的重组表达和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1498-1517. |
| [13] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [14] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [15] | 程晓雷, 刘天罡, 陶慧. 萜类化合物的非常规生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1050-1071. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||