合成生物学 ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (3): 319-336.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-028
基于合成生物学策略的酶蛋白元件规模化挖掘
张建志, 付立豪, 唐婷, 张嵩亚, 朱静, 李拓, 王子宁, 司同
- 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,深圳合成生物学创新研究院,中国科学院定量工程生物学重点实验室,广东 深圳 518055
-
收稿日期:2020-03-17修回日期:2020-04-29出版日期:2020-06-30发布日期:2020-09-29 -
通讯作者:司同 -
作者简介:张建志(1988—),男,博士,助理研究员,研究方向为合成生物学、代谢工程。E-mail:zhangjz@siat.ac.cn
司同(1987—),男,博士,研究员,研究方向为合成生物学。E-mail:tong.si@siat.ac.cn -
基金资助:深圳合成生物学创新研究院主题项目(ZTXM20190002)
Scalable mining of proteins for biocatalysis via synthetic biology
ZHANG Jianzhi, FU Lihao, TANG Ting, ZHANG Songya, ZHU Jing, LI Tuo, WANG Zining, SI Tong
- CAS keylaboratory of Quantitative Engineering Biology,Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2020-03-17Revised:2020-04-29Online:2020-06-30Published:2020-09-29 -
Contact:SI Tong
摘要:
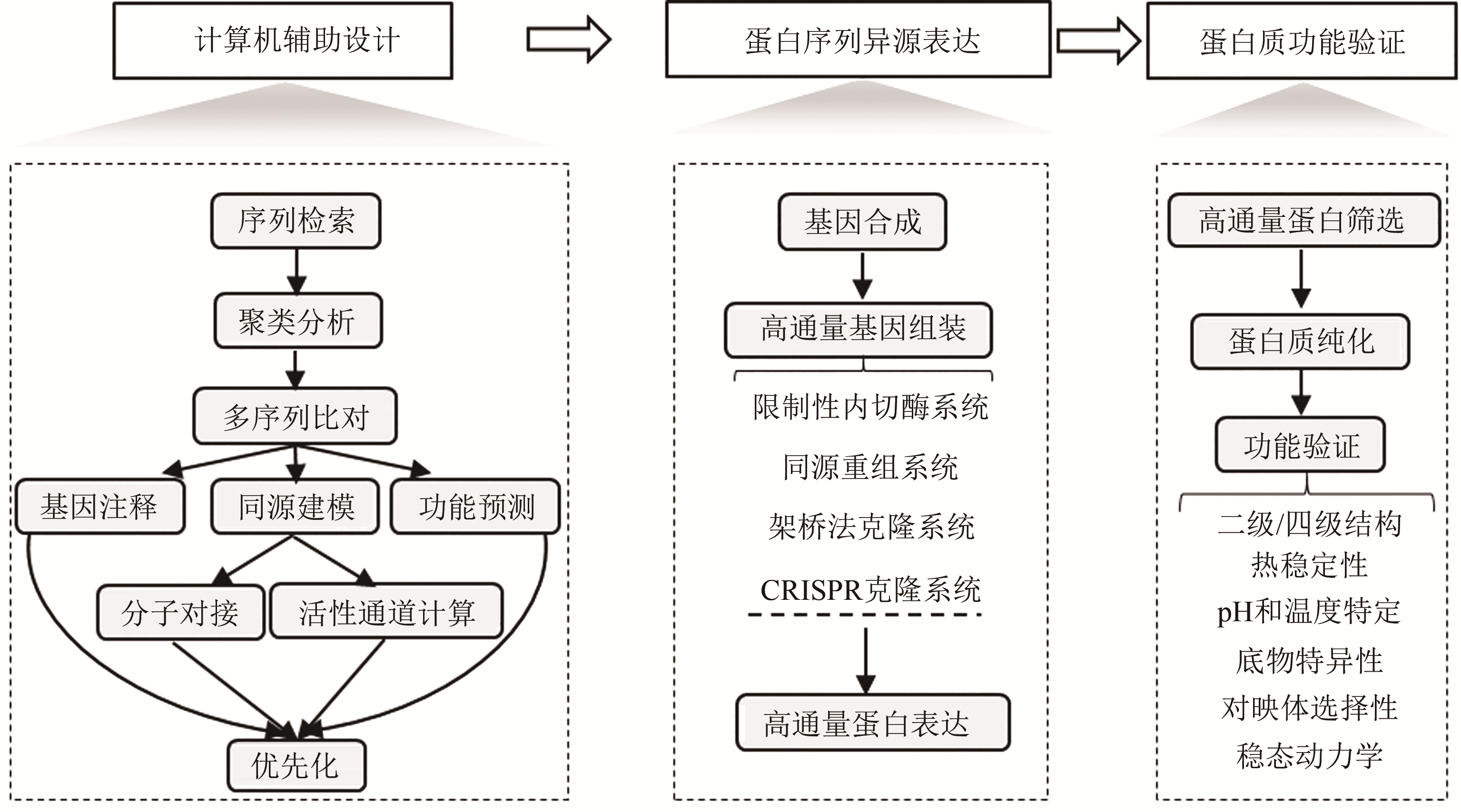
生物制造以人工生物体系为催化剂合成工业化学品、药物和功能材料,具有低碳循环、绿色清洁等特征。酶蛋白是构建生物催化系统的重要功能单元,然而,由于缺乏准确预测序列-功能关系的方法,目前酶的理性设计仍面临巨大挑战。因此,需要利用合成生物学工程化的思路和手段,从自然界中大规模挖掘新的酶蛋白元件,相关研究不但可以为开发工业酶制剂和构建细胞合成代谢提供优质元件,而且有利于快速获得酶蛋白序列-结构-功能间的对应关系,为建立预测与设计模型提供基础。本文针对酶元件工程化挖掘的关键技术进行综述:介绍了计算机辅助设计的算法和软件,用于将数据库中海量的酶蛋白序列按照实验目的进行聚类分析和优先化排序;总结了规模化合成组装、异源表达和功能筛选酶蛋白元件的高通量实验技术;讨论了如何综合利用计算与实验手段,系统性探索酶家族成员的催化性能。未来,通过综合计算机辅助设计、自动化合成生物构建、高通量测试等方法,设计和建设高度集成的工程化研究平台,成为实现对酶蛋白资源进行系统化的研究和挖掘的重要方向。
中图分类号:
引用本文
张建志, 付立豪, 唐婷, 张嵩亚, 朱静, 李拓, 王子宁, 司同. 基于合成生物学策略的酶蛋白元件规模化挖掘[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(3): 319-336.
ZHANG Jianzhi, FU Lihao, TANG Ting, ZHANG Songya, ZHU Jing, LI Tuo, WANG Zining, SI Tong. Scalable mining of proteins for biocatalysis via synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(3): 319-336.
| 蛋白质序列数据库 | 基本信息 |
|---|---|
Uniprot https://www.uniprot.org/ | 信息最丰富、资源最广的蛋白质数据库。由Swiss-Prot、TrEMBL和PIR-PSD三大数据库的数据组合而成 |
NCBI https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ | |
| Conserved Domains | 蛋白质保守结构域数据库,是关于蛋白质功能单元注释的资源 |
| Protein | 包含GenBank,RefSeq,TPA,SwissProt,RIP,PDB等数据库中的序列 |
| Protein cluster | 包括完整的原核生物基因组和叶绿体基因组编码的RefSeq蛋白质序列 |
| Structure | 数据来源于PDB的蛋白质结构数据库,并将结构数据链接到书目信息、序列数据库和NCBI的Taxonomy中,运用3D结构浏览器和Cn3D,可以从Entrez获得分子间相互作用的图像 |
PDB http://www.rcsb.org/ | 生物大分子(如蛋白质和核酸)数据库,包括由全世界生物学家和生物化学家上传的蛋白质或核酸的X射线晶体衍射或者NMR核磁共振结构数据。从PDB的网站上,可以通过蛋白质的编号查找到相应的3D结构,并通过PyMol、RasMol、Chimera、VMD、Swiss-PdbViewer等软件查看、编辑 |
InterPro http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/ | 整合了CATH、CDD、PRINTS、Pfam等多个数据库,并去掉冗余数据,对蛋白质家族预测、结构域和结合位点预测进行注释 |
Brenda https://www.brenda-enzymes.org/ | 包括酶促反应、特异性、动力学参数、结构和稳定性等蛋白质功能数据及基因组序列信息 |
BKMS-react http://bkm-react.tu-bs.de/ | 包括酶促反应、动力学参数、实验条件和代谢途径等信息 |
EzCatDb http://ezcatdb.cbrc.jp/EzCatDB/ | 包括酶促反应、辅因子、中间代谢产物、催化活性结构域和结构等信息 |
M-CSAb https://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/m-csa/browse/ | 对催化残基、辅助因子和反应机理的注释 |
FireProt https://loschmidt.chemi.muni.cz/fireprotdb/ | 包括序列突变后导致的热稳定性变化数据 |
ProTherm https://www.iitm.ac.in/bioinfo/ProTherm/ | 包括序列突变后导致的热稳定性变化数据 |
eSOL http://tanpaku.org/tp-esol/index.php?lang=en | 基于蛋白质翻译和离心条件推测蛋白质溶解度 |
SoluProtMut https://loschmidt.chemi.muni.cz/soluprotmutdb/ | 包括序列突变后导致的溶解性变化数据 |
TargetTrack http://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.821654 | 蛋白质溶解性数据库 |
ProtaBank https://protabank.org/ | 包括各种突变后的蛋白质序列信息 |
hPDB http://hackage.haskell.org/package/hPDB | 可动态展示生物大分子立体结构 |
KEGG https://www.kegg.jp/ | 整合基因组、化学和系统功能信息的数据库。把从已经完整测序的基因组中得到的基因目录与更高级别的细胞、物种和生态系统水平的系统功能关联起来 |
PMD http://www.proteinmicroarray.cn/ | 蛋白质突变数据库 |
Pfam http://pfam.xfam.org/ | 蛋白质家族数据库,蛋白质家族以多序列比对和隐马尔科夫模型的形式表示 |
FIGFAMs http://blog.theseed.org/servers | 基于人工注释的来源于不同细菌,古菌等生物的蛋白质序列构成,同功能蛋白质组合为相应的集合 |
PRINTS http://bioinf.man.ac.uk/dbbrowser/PRINTS | 蛋白质Motif数据库 |
CATH http://cathdb.info/ | 以蛋白质结构域层次组织的包含类型(C)、架构(A)、拓扑学(T)和同源超家族的数据库 |
SCOP http://scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/ | 蛋白质结构分类 |
CCDC https://ccdc.cam.ac.uk/ | 剑桥晶体中心数据库 |
SWISS-3DIMAGE http://us.expasy.org/sw3d/ | 蛋白质及其他生物分子的三维图像 |
BioMagResBank http://www.bmrb.wisc.edu/ | 蛋白质、氨基酸和核苷酸的核磁共振数据库 |
SWISS-MODEL Repository http://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/ | 自动产生蛋白质模型的数据库 |
PROTOMAP https://www.scripps.edu/cravatt/protomap/ | Swiss-Prot蛋白质自动分类系统 |
iProClass http://pir.georgetown.edu/iproclass/ | 蛋白质分类数据库 |
TIGRFAM http://www.tigr.org/TIGRFAMs/ | 蛋白质家族数据库 |
OWL http://www.bioinf.man.ac.uk/dbbrowser/OWL/ | 非冗余蛋白序列数据库,由SWISS-PROT、PIR、GenBank(由其编码序列翻译而成的氨基酸序列)和NRL-3D一级序列数据库集合而成 |
3DID http://3did.irbbarcelona.org | 包括3D结构已知的蛋白质的互作信息 |
DOMINE http://manticore.niehs.nih.gov/cgi-bin/Domine | 蛋白质结构域互作数据库 |
PiSite http://pisite.hgc.jp | 以PDB为基础,可在蛋白序列中搜寻互作位点 |
Binding MOAD http://www.BindingMOAD.org | 提供蛋白质-配体晶体结构数据信息 |
Phospho.ELM http://phospho.elm.eu.org | 蛋白质磷酸化位点数据库 |
STITCH http://stitch.embl.de/ | 蛋白质-化合物作用网数据库 |
Reactome http://www.reactome.org | 人体生命活动路径与过程数据库,提供生化过程网络图,并对参与其中的蛋白质分子有详细注解,与其他数据库如UniPort、KEGG、OMIM等建立了广泛的交叉应用 |
UniHI http://www.unihi.org | 人体蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用数据库 |
Bionemo http://bionemo.bioinfo.cnio.es | 包括与生物降解代谢相关的蛋白质、基因数据,包括蛋白序列、结构域、结构;基因序列、调控元件、转录单元等信息。除此之外还包括生物降解的代谢路径图、相关生化反应等 |
CAZy http://www.cazy.org/ | 碳水化合物活性酶数据库,包括能够合成或者分解复杂碳水化合物的酶类 |
LED http://www.led.uni-stuttgart.de/ | 脂肪酶工程数据库,整合了脂肪酶的结构域序列信息 |
MEROPS https://www.ebi.ac.uk/merops/ | 肽酶数据库,同时也包括一些蛋白质类肽酶抑制剂的信息 |
PLANT-PIs http://plantpis.ba.itb.cnr.it/ | 植物蛋白酶抑制剂及相关基因信息 |
PROSPER https://prosper.erc.monash.edu.au | 基于序列预测24个不同蛋白酶家族的催化底物和切割位点 |
CPDB 140.113.15.73/~lab/deprecated/cpdb-2009/ | 利什曼原虫中半胱氨酸蛋白酶注释数据库 |
SABIO-RK http://sabio.h-its.org/ | 包括生化反应动力学参数的数据库 |
表1 酶元件资源数据库及链接
Tab. 1 Enzyme resource database and their corresponding links
| 蛋白质序列数据库 | 基本信息 |
|---|---|
Uniprot https://www.uniprot.org/ | 信息最丰富、资源最广的蛋白质数据库。由Swiss-Prot、TrEMBL和PIR-PSD三大数据库的数据组合而成 |
NCBI https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ | |
| Conserved Domains | 蛋白质保守结构域数据库,是关于蛋白质功能单元注释的资源 |
| Protein | 包含GenBank,RefSeq,TPA,SwissProt,RIP,PDB等数据库中的序列 |
| Protein cluster | 包括完整的原核生物基因组和叶绿体基因组编码的RefSeq蛋白质序列 |
| Structure | 数据来源于PDB的蛋白质结构数据库,并将结构数据链接到书目信息、序列数据库和NCBI的Taxonomy中,运用3D结构浏览器和Cn3D,可以从Entrez获得分子间相互作用的图像 |
PDB http://www.rcsb.org/ | 生物大分子(如蛋白质和核酸)数据库,包括由全世界生物学家和生物化学家上传的蛋白质或核酸的X射线晶体衍射或者NMR核磁共振结构数据。从PDB的网站上,可以通过蛋白质的编号查找到相应的3D结构,并通过PyMol、RasMol、Chimera、VMD、Swiss-PdbViewer等软件查看、编辑 |
InterPro http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/ | 整合了CATH、CDD、PRINTS、Pfam等多个数据库,并去掉冗余数据,对蛋白质家族预测、结构域和结合位点预测进行注释 |
Brenda https://www.brenda-enzymes.org/ | 包括酶促反应、特异性、动力学参数、结构和稳定性等蛋白质功能数据及基因组序列信息 |
BKMS-react http://bkm-react.tu-bs.de/ | 包括酶促反应、动力学参数、实验条件和代谢途径等信息 |
EzCatDb http://ezcatdb.cbrc.jp/EzCatDB/ | 包括酶促反应、辅因子、中间代谢产物、催化活性结构域和结构等信息 |
M-CSAb https://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/m-csa/browse/ | 对催化残基、辅助因子和反应机理的注释 |
FireProt https://loschmidt.chemi.muni.cz/fireprotdb/ | 包括序列突变后导致的热稳定性变化数据 |
ProTherm https://www.iitm.ac.in/bioinfo/ProTherm/ | 包括序列突变后导致的热稳定性变化数据 |
eSOL http://tanpaku.org/tp-esol/index.php?lang=en | 基于蛋白质翻译和离心条件推测蛋白质溶解度 |
SoluProtMut https://loschmidt.chemi.muni.cz/soluprotmutdb/ | 包括序列突变后导致的溶解性变化数据 |
TargetTrack http://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.821654 | 蛋白质溶解性数据库 |
ProtaBank https://protabank.org/ | 包括各种突变后的蛋白质序列信息 |
hPDB http://hackage.haskell.org/package/hPDB | 可动态展示生物大分子立体结构 |
KEGG https://www.kegg.jp/ | 整合基因组、化学和系统功能信息的数据库。把从已经完整测序的基因组中得到的基因目录与更高级别的细胞、物种和生态系统水平的系统功能关联起来 |
PMD http://www.proteinmicroarray.cn/ | 蛋白质突变数据库 |
Pfam http://pfam.xfam.org/ | 蛋白质家族数据库,蛋白质家族以多序列比对和隐马尔科夫模型的形式表示 |
FIGFAMs http://blog.theseed.org/servers | 基于人工注释的来源于不同细菌,古菌等生物的蛋白质序列构成,同功能蛋白质组合为相应的集合 |
PRINTS http://bioinf.man.ac.uk/dbbrowser/PRINTS | 蛋白质Motif数据库 |
CATH http://cathdb.info/ | 以蛋白质结构域层次组织的包含类型(C)、架构(A)、拓扑学(T)和同源超家族的数据库 |
SCOP http://scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/ | 蛋白质结构分类 |
CCDC https://ccdc.cam.ac.uk/ | 剑桥晶体中心数据库 |
SWISS-3DIMAGE http://us.expasy.org/sw3d/ | 蛋白质及其他生物分子的三维图像 |
BioMagResBank http://www.bmrb.wisc.edu/ | 蛋白质、氨基酸和核苷酸的核磁共振数据库 |
SWISS-MODEL Repository http://swissmodel.expasy.org/repository/ | 自动产生蛋白质模型的数据库 |
PROTOMAP https://www.scripps.edu/cravatt/protomap/ | Swiss-Prot蛋白质自动分类系统 |
iProClass http://pir.georgetown.edu/iproclass/ | 蛋白质分类数据库 |
TIGRFAM http://www.tigr.org/TIGRFAMs/ | 蛋白质家族数据库 |
OWL http://www.bioinf.man.ac.uk/dbbrowser/OWL/ | 非冗余蛋白序列数据库,由SWISS-PROT、PIR、GenBank(由其编码序列翻译而成的氨基酸序列)和NRL-3D一级序列数据库集合而成 |
3DID http://3did.irbbarcelona.org | 包括3D结构已知的蛋白质的互作信息 |
DOMINE http://manticore.niehs.nih.gov/cgi-bin/Domine | 蛋白质结构域互作数据库 |
PiSite http://pisite.hgc.jp | 以PDB为基础,可在蛋白序列中搜寻互作位点 |
Binding MOAD http://www.BindingMOAD.org | 提供蛋白质-配体晶体结构数据信息 |
Phospho.ELM http://phospho.elm.eu.org | 蛋白质磷酸化位点数据库 |
STITCH http://stitch.embl.de/ | 蛋白质-化合物作用网数据库 |
Reactome http://www.reactome.org | 人体生命活动路径与过程数据库,提供生化过程网络图,并对参与其中的蛋白质分子有详细注解,与其他数据库如UniPort、KEGG、OMIM等建立了广泛的交叉应用 |
UniHI http://www.unihi.org | 人体蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用数据库 |
Bionemo http://bionemo.bioinfo.cnio.es | 包括与生物降解代谢相关的蛋白质、基因数据,包括蛋白序列、结构域、结构;基因序列、调控元件、转录单元等信息。除此之外还包括生物降解的代谢路径图、相关生化反应等 |
CAZy http://www.cazy.org/ | 碳水化合物活性酶数据库,包括能够合成或者分解复杂碳水化合物的酶类 |
LED http://www.led.uni-stuttgart.de/ | 脂肪酶工程数据库,整合了脂肪酶的结构域序列信息 |
MEROPS https://www.ebi.ac.uk/merops/ | 肽酶数据库,同时也包括一些蛋白质类肽酶抑制剂的信息 |
PLANT-PIs http://plantpis.ba.itb.cnr.it/ | 植物蛋白酶抑制剂及相关基因信息 |
PROSPER https://prosper.erc.monash.edu.au | 基于序列预测24个不同蛋白酶家族的催化底物和切割位点 |
CPDB 140.113.15.73/~lab/deprecated/cpdb-2009/ | 利什曼原虫中半胱氨酸蛋白酶注释数据库 |
SABIO-RK http://sabio.h-its.org/ | 包括生化反应动力学参数的数据库 |
| 分类 | 原理 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| 限制性内切酶克隆系统 | 限制性内切酶使基因片段和载体产生黏性末端, 通过T4连接酶组装 | 1.普通的双限制性内切酶克隆操作简单,但需考虑目的基因序列中酶切位点序列,适合单基因克隆; 2.稀有限制性内切酶SgfⅠ和PmeⅠ使其具备高通量操作的可行性; 3.Golden Gate可同时实现多片段酶切与模块化组装,但也需要移除目的序列中的BsaⅠ及BsmBⅠ等识别位点; 4.MASTER只能识别甲基化的4bp位点,无需考虑目的基因序列是否含有MspJⅠ识别位点序列 |
BioBrick BglBck ePath Brick Flexi cloning Golden Gate system MASTER | ||
| 同源重组克隆系统 | 基于基因片段与载体两端的同源序列进行克隆 组装 | 1.操作简单、效率高、快速、稳定,适合单基因或多基因组装; 2.无限制性内切酶和连接酶的参与; 3.无需考虑目的基因序列内部的酶切位点; 4.存在重复序列时难以组装 |
Gibson assembly OE-PCR CPEC SLIC NE-SLIC USER Gateway cloning Echo cloning Creator 酵母胞内DNA组装 枯草芽孢杆菌胞内DNA组装 大肠杆菌胞内DNA组装 | ||
| 基于寡核苷酸的架桥法克隆系统 | 基于热稳定的连接酶和寡核苷酸进行DNA组装 | 在相似的反应条件下(12个DNA片段的组装),连接反应的保真性与酵母胞内DNA组装方法相近,并高于CPEC和Gibson等方法 |
| LCR | ||
| 基于CRISPR的克隆系统 | 基于Ⅱ类type Ⅴ CRISPR系统和Taq DNA连 接酶开发的DNA无缝拼接方法 | 仅需Cpf1一种内切酶进行切割,经过条件优化或蛋白改造,连接效率可达到70%以上,并可实现21kbp长度的DNA组装 |
CCTL iCOPE |
表 2 基因高通量克隆、组装方法
Tab. 2 Methods for high-throughput gene cloning and assembly
| 分类 | 原理 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| 限制性内切酶克隆系统 | 限制性内切酶使基因片段和载体产生黏性末端, 通过T4连接酶组装 | 1.普通的双限制性内切酶克隆操作简单,但需考虑目的基因序列中酶切位点序列,适合单基因克隆; 2.稀有限制性内切酶SgfⅠ和PmeⅠ使其具备高通量操作的可行性; 3.Golden Gate可同时实现多片段酶切与模块化组装,但也需要移除目的序列中的BsaⅠ及BsmBⅠ等识别位点; 4.MASTER只能识别甲基化的4bp位点,无需考虑目的基因序列是否含有MspJⅠ识别位点序列 |
BioBrick BglBck ePath Brick Flexi cloning Golden Gate system MASTER | ||
| 同源重组克隆系统 | 基于基因片段与载体两端的同源序列进行克隆 组装 | 1.操作简单、效率高、快速、稳定,适合单基因或多基因组装; 2.无限制性内切酶和连接酶的参与; 3.无需考虑目的基因序列内部的酶切位点; 4.存在重复序列时难以组装 |
Gibson assembly OE-PCR CPEC SLIC NE-SLIC USER Gateway cloning Echo cloning Creator 酵母胞内DNA组装 枯草芽孢杆菌胞内DNA组装 大肠杆菌胞内DNA组装 | ||
| 基于寡核苷酸的架桥法克隆系统 | 基于热稳定的连接酶和寡核苷酸进行DNA组装 | 在相似的反应条件下(12个DNA片段的组装),连接反应的保真性与酵母胞内DNA组装方法相近,并高于CPEC和Gibson等方法 |
| LCR | ||
| 基于CRISPR的克隆系统 | 基于Ⅱ类type Ⅴ CRISPR系统和Taq DNA连 接酶开发的DNA无缝拼接方法 | 仅需Cpf1一种内切酶进行切割,经过条件优化或蛋白改造,连接效率可达到70%以上,并可实现21kbp长度的DNA组装 |
CCTL iCOPE |
| 1 | Zaparucha A, de Berardinis V, Vaxelaire-Vergne C. Genome mining for enzyme discovery [M]//Modern biocatalysis: advances towards synthetic biological systems. The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2018: 1-27. |
| 2 | Wang L, Dash S, Ng C Y, et al. A review of computational tools for design and reconstruction of metabolic pathways[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2017, 2(4): 243-252. |
| 3 | Hatzimanikatis V, Li CH, Ionita J A, et al. Exploring the diversity of complex metabolic networks [J]. Bioinformatics, 2005, 21(8): 1603-1609. |
| 4 | Kumar A, Wang L, Ng C Y, et al. Pathway design using de novo steps through uncharted biochemical spaces [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 184-201. |
| 5 | Mak W S, Tran S, Marcheschi R, et al. Integrative genomic mining for enzyme function to enable engineering of a non-natural biosynthetic pathway[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1). |
| 6 | Carter M S, Zhang X, Huang H, et al. Functional assignment of multiple catabolic pathways for D-apiose [J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(7): 696-705. |
| 7 | Mori Y, Shirai T. Designing artificial metabolic pathways, construction of target enzymes, and analysis of their function [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2018, 54: 41-44. |
| 8 | Li Y R, Li S J, Thodey K, et al. Complete biosynthesis of noscapine and halogenated alkaloids in yeast [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(17): E3922-E3931. |
| 9 | Thodey K, Galanie S, Smolke C D. A microbial biomanufacturing platform for natural and semisynthetic opioids [J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2014, 10(10): 837-844. |
| 10 | Sayers E W, Agarwala R, Bolton E E, et al. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(D1): D23-D28. |
| 11 | Tian W D, Arakaki A K, Skolnick J. EFICAz: a comprehensive approach for accurate genome-scale enzyme function inference [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32(21): 6226-6239. |
| 12 | Clark K, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman D J, et al. GenBank [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(D1): D67-D72. |
| 13 | Seffernick J L, de Souza M L, Sadowsky M J, et al. Melamine deaminase and atrazine chlorohydrolase: 98 percent identical but functionally different [J]. Journal of Bacteriol, 2001, 183(8): 2405-2410. |
| 14 | Burroughs A M, Allen K N, Dunaway-Mariano D, et al. Evolutionary genomics of the HAD superfamily: Understanding the structural adaptations and catalytic diversity in a superfamily of phosphoesterases and allied enzymes [J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2006, 361(5): 1003-1034. |
| 15 | Glasner M E, Fayazmanesh N, Chiang R, et al. Evolution of structure and function in the o-succinylbenzoate synthase family [J]. Faseb Journal, 2006, 20(5): A905-A905. |
| 16 | Peterhoff D, Beer B, Rajendran C, et al. A comprehensive analysis of the geranylgeranylglyceryl phosphate synthase enzyme family identifies novel members and reveals mechanisms of substrate specificity and quaternary structure organization [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2014, 92(4): 885-899. |
| 17 | Heins R A, Cheng X, Nath S, et al. Phylogenomically guided identification of industrially relevant GH1 beta-glucosidases through DNA synthesis and nanostructure-initiator mass spectrometry [J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2014, 9(9): 2082-2091. |
| 18 | Vanacek P, Sebestova E, Babkova P, et al. Exploration of enzyme diversity by integrating bioinformatics with expression analysis and biochemical characterization [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(3): 2402-2412. |
| 19 | Bairoch A, Apweiler R. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence data bank and its supplement TrEMBL in 1999 [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1999. 27(1): 49-54. |
| 20 | Marchler-Bauer A, Derbyshire M K, Gonzales N R, et al. CDD: NCBI's conserved domain database [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 43(D1): D222-D226. |
| 21 | Finn R D, Bateman A, Clements J, et al. Pfam: the protein families database [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(D1): D222-D230. |
| 22 | Sillitoe I, Lewis T E, Cuff A, et al. CATH: comprehensive structural and functional annotations for genome sequences [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 43(D1): D376-D381. |
| 23 | Meyer F, Overbeek R, Rodriguez A. FIGfams: yet another set of protein families [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2009, 37(20): 6643-6654. |
| 24 | Schnoes A M, Brown S D, Dodevski I, et al. Annotation error in public databases: misannotation of molecular function in enzyme superfamilies [J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2009, 5(12): e1000605. |
| 25 | Copp J N, Anderson D W, Akiva E, et al. Exploring the sequence, function, and evolutionary space of protein superfamilies using sequence similarity networks and phylogenetic reconstructions [J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2019, 620: 315-347. |
| 26 | Rodríguez Benítez A, Narayan A R H. Frontiers in biocatalysis: profiling function across sequence space [J]. ACS Central Science. 2019, 5(11): 1747-1749. |
| 27 | Atkinson H J, Morris J H, Ferrin T E, et al. Using sequence similarity networks for visualization of relationships across diverse protein superfamilies [J]. PLoS One, 2009, 4(2): e4345-e4358. |
| 28 | Berman H, Henrick K, Nakamura H, et al. The worldwide Protein Data Bank (wwPDB): ensuring a single, uniform archive of PDB data [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2007, 35: D301-D303. |
| 29 | Ashburner M, Ball C A, Blake J A, et al. Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology [J]. Nature Genetics, 2000, 25(1): 25-29. |
| 30 | Copp J N, Akiva E, Babbit P C, et al. Revealing unexplored sequence-function space using sequence similarity networks [J]. Biochemistry, 2018, 57(31): 4651-4662. |
| 31 | Barber A E, Babbitt P C. Pythoscape: a framework for generation of large protein similarity networks [J]. Bioinformatics, 2012, 28(21): 2845-2846. |
| 32 | Zallot R, Oberg N, Gerlt J A, The EFI web resource for genomic enzymology tools : leveraging protein, genome, and metagenome databases to discover novel enzymes and metabolic pathways [J]. Biochemistry, 2019, 58(41): 4169-4182. |
| 33 | Getz G, Starovolsky A, Domany E. F2CS: FSSP to CATH and SCOP prediction server [J]. Bioinformatics, 2004, 20(13): 2150-2152. |
| 34 | Sillitoe I, Furnham N. FunTree: advances in a resource for exploring and contextualising protein function evolution [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(D1): D317-323. |
| 35 | Lin G M, Warden-Rothman R, Voigt C A. Retrosynthetic design of metabolic pathways to chemicals not found in nature [J]. Current Opinion in Systems Biology, 2019, 14: 82-107. |
| 36 | Klucznik T, Mikulak-Klucznik B, McCormack M P, et al. Efficient syntheses of diverse, medicinally relevant targets planned by computer and executed in the laboratory [J]. Chemistry, 2018, 4(3): 522-532. |
| 37 | Musil M, Konegger H, Hon J, et al. Computational design of stable and soluble biocatalysts [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019. 9(2): 1033-1054. |
| 38 | Wilkinson D L, Harrison R G. Predicting the solubility of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 1991, 9(5): 443-448. |
| 39 | Kim J H, Kershner J P, Novikov Y, et al. Three serendipitous pathways in E. coli can bypass a block in pyridoxal-5'-phosphate synthesis [J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2010, 6: 436-448. |
| 40 | Jeffryes J G, Colastani R L, ELBADAWI-SIDHU M, et al. MINEs: open access databases of computationally predicted enzyme promiscuity products for untargeted metabolomics [J]. Journal of Cheminformatics, 2015, 7: 44-51. |
| 41 | Pertusi D A, Moura M E, Jeffryes J G, et al. Predicting novel substrates for enzymes with minimal experimental effort with active learning [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 44: 171-181. |
| 42 | Ekins S. Predicting undesirable drug interactions with promiscuous proteins in silico [J]. Drug Discov Today, 2004, 9(6): 276-285. |
| 43 | Ferrario V, Siragusa L, Ebert C, et al. BioGPS descriptors for rational engineering of enzyme promiscuity and structure based bioinformatic analysis [J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(10): e109354. |
| 44 | Campodonico M A, Andrews B A, Asenjo J A, et al. Generation of an atlas for commodity chemical production in Escherichia coli and a novel pathway prediction algorithm, GEM-Path [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2014, 25: 140-158. |
| 45 | Feher T, Planson A G, Carbonell P, et al. Validation of retroPath, a computer-aided design tool for metabolic pathway engineering [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2014, 9(11): 1446-1457. |
| 46 | Chao R, Yuan Y B, Zhao H M. Recent advances in DNA assembly technologies [J]. Fems Yeast Research, 2015, 15(1): 1-9. |
| 47 | Gould N, Hendy O, Papamichail D. Computational tools and algorithms for designing customized synthetic genes [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2014, 2: 41. |
| 48 | Jia B, Jeon C O. High-throughput recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: current status and future perspectives [J]. Open Biology, 2016, 6(8): 160196. |
| 49 | Nagase T, Yamakawa H, Tadokoro S, et al. Exploration of human ORFeome: high-throughput preparation of ORF clones and efficient characterization of their protein products [J]. DNA Research, 2008, 15(3): 137-149. |
| 50 | HamediRad M, Weisberg S, Chao R, et al. Highly efficient single-pot scarless golden gate assembly [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(5): 1047-1054. |
| 51 | Chao R, Liang J, Tasan I, et al. Fully automated one-step synthesis of single-transcript TALEN pairs using a biological foundry [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(4): 678-685. |
| 52 | Hillson N J, Rosengarten R D, Keasling J D. j5 DNA assembly design automation software [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2012, 1(1): 14-21. |
| 53 | Kanigowska P, Shen Y, Zheng Y J, et al. Smart DNA fabrication using sound waves: applying acoustic dispensing technologies to synthetic biology [J]. Jala-J. Lab. Autom, 2016, 21(1): 49-56. |
| 54 | Linshiz G, Stawski N, Goyal G, et al. PR-PR: cross-platform laboratory automation system [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2014, 3(8): 515-524. |
| 55 | Chen W H, Qin Z J, Wang J, et al. The MASTER (methylation-assisted tailorable ends rational) ligation method for seamless DNA assembly [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2013, 41(8): e93. |
| 56 | Shao Z Y, Zhao H, Zhao H M. DNA assembler, an in vivo genetic method for rapid construction of biochemical pathways [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2009, 37(2): e16. |
| 57 | Landenmark H K, Forgan D H, Cockell C S. An estimate of the total DNA in the biosphere [J]. PLoS Biology, 2015, 13(6): e1002168. |
| 58 | Shapland E B, Holmes V, Reeves C D, et al. Low-cost, high-throughput sequencing of DNA assemblies using a highly multiplexed nextera process [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(7): 860-866. |
| 59 | Dharmadi Y, Patel K, Shapland E, et al. High-throughput, cost-effective verification of structural DNA assembly [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(4). e22. |
| 60 | De Kok S, Stanton L H, Slaby T, et al. Rapid and reliable DNA assembly via ligase cycling reaction [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2014, 3(2): 97-106. |
| 61 | Lei C, Li S Y, Liu J K, et al. The CCTL (Cpf1-assisted cutting and taq DNA ligase-assisted ligation) method for efficient editing of large DNA constructs in vitro [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(9): e74. |
| 62 | Wang L, Wang H, Liu H, et al. Improved CRISPR-Cas12a-assisted one-pot DNA editing method enables seamless DNA editing [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengeering, 2019, 116(6): 1463-1474. |
| 63 | Demain A L, Vaishnav P. Production of recombinant proteins by microbes and higher organisms [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2009, 27(3): 297-306. |
| 64 | Schmidt S, Dörr M, Bornscheuer U T. Library growth and protein expression: optimal and reproducible microtiter plate expression of recombinant enzymes in E. coli using MTP shakers [M]//BORNSCHEUER U T, HÖHNE M. Protein engineering: methods and protocols. New York: Springer New York, 2018: 145-156. |
| 65 | Nakano H, Yamane T. Cell-free protein synthesis systems [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 1998, 16(2): 367-384. |
| 66 | Markel U, Essani K D, Besirlioglu V, et al. Advances in ultrahigh-throughput screening for directed enzyme evolution [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(1): 233-262. |
| 67 | Swartz J. Developing cell-free biology for industrial applications [J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 33(7): 476-485. |
| 68 | Rungpragayphan S, Nakano H, Yamane T. PCR-linked in vitro expression: a novel system for high-throughput construction and screening of protein libraries [J]. FEBS Letters, 2003, 540(1-3): 147-150. |
| 69 | Angenendt P, Nyarsik L, Szaflarski W, et al. Cell-free protein expression and functional assay in nanowell chip format [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2004, 76(7): 1844-1849. |
| 70 | Santos-Aberturas J, Dörr M, Bornscheuer U T. Normalized screening of protein engineering libraries by split-GFP crude cell extract quantification [M]// BORNSCHEUER U T, HÖHNE M. Protein engineering: methods and protocols. New York: Springer New York; 2018: 157-170. |
| 71 | Cabantous S, Waldo G S. In vivo and in vitro protein solubility assays using split GFP [J]. Nature Methods, 2006, 3(10): 845-854. |
| 72 | Guo C X, Hu Y L, Yang C Y, et al. Developing a colorimetric assay for Fe(Ⅱ)/2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase [J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2018, 548: 109-114. |
| 73 | Dekker L, Polizzi K M. Sense and sensitivity in bioprocessing-detecting cellular metabolites with biosensors [J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2017, 40: 31-36. |
| 74 | Chen X, Zhang D, Su N, et al. Visualizing RNA dynamics in live cells with bright and stable fluorescent RNAS [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(11): 1287-1293. |
| 75 | Lim H G, Jang S, Jang S, et al. Design and optimization of genetically encoded biosensors for high-throughput screening of chemicals [J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2018, 54: 18-25. |
| 76 | Zeng W, Guo L, Xu S, et al. High-throughput screening technology in industrial biotechnology [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2020.01.001 . |
| 77 | Aymard C, Bonaventura C, Henkens R, et al. High-throughput electrochemical screening assay for free and immobilized oxidases: electrochemiluminescence and intermittent pulse amperometry [J]. Chemelectrochem, 2017, 4(4): 957-966. |
| 78 | Majdinasab M, Mitsubayashi K, Marty J L. Optical and electrochemical sensors and biosensors for the detection of quinolones [J]. Trends in Biotechnology. 2019, 37(8): 898-915. |
| 79 | Si T, Li B, Comi T J, et al. Profiling of microbial colonies for high-throughput engineering of multistep enzymatic reactions via optically guided matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(36): 12466-12473. |
| 80 | De Rond T, Jian G, Amin Z, et al. A high-throughput mass spectrometric enzyme activity assay enabling the discovery of Cytochrome P450 biocatalysts [J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2019, 131(30): 10220-10225. |
| 81 | Holland-Moritz D A, Wismer M K, Mann B F, et al. Mass activated droplet sorting (MADS) enables high-throughput screening of enzymatic reactions at nanoliter scale [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59: 4470-4477. |
| 82 | Prosser G A, Larrouy-Maumus G, De Carvalho L P. Metabolomic strategies for the identification of new enzyme functions and metabolic pathways [J]. EMBO Reports, 2014, 15(6): 657-669. |
| 83 | Sévin D C, Fuhrer T, Zamboni N, Sauer U. Nontargeted in vitro metabolomics for high-throughput identification of novel enzymes in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Methods, 2017, 14(2): 187-194. |
| 84 | Dörr M, Fibinger M P C, Last D, et al. Fully automatized high-throughput enzyme library screening using a robotic platform [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2016, 113(7): 1421-1432. |
| 85 | Longwell C K, Labanieh L, Cochran J R. High-throughput screening technologies for enzyme engineering [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2017, 48: 196-202. |
| 86 | Chen I, Dorr B M, Liu D R. A general strategy for the evolution of bond-forming enzymes using yeast display [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(28): 11399-11404. |
| 87 | Qin Y L, Wu L, Wang J G, et al. A fluorescence-activated single-droplet dispenser for high accuracy single-droplet and single-cell sorting and dispensing [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(10): 6815-6819. |
| 88 | Zhu P A, Wang L Q. Passive and active droplet generation with microfluidics: a review [J]. Lab On A Chip, 2017, 17(1): 34-75. |
| 89 | Colin P Y, Kintses B, Gielen F, et al. Ultrahigh-throughput discovery of promiscuous enzymes by picodroplet functional metagenomics [J]. Nature Communication, 2015, 6: 10008. |
| 90 | Lobb B, Doxey A C. Novel function discovery through sequence and structural data mining [J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2016, 38: 53-61. |
| 91 | Davidson R, Baas B J, Akiva E, et al. A global view of structure-function relationships in the tautomerase superfamily[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2018, 293(7): 2342-2357. |
| 92 | Mashiyama S T, Malabanan M M, Akiva E, et al. Large-scale determination of sequence, structure, and function relationships in cytosolic glutathione transferases across the biosphere [J]. PLoS Biology, 2014, 12(4): e1001843. |
| 93 | Li W, Godzik A. Cd-hit: a fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences [J]. Bioinformatics, 2006, 22(13): 1658-1659. |
| 94 | Kobe B, Guss M, Huber T, Structural proteomics: high-throughput methods [M].//Totowa N J. Methods in molecular biology. London: Humana; Springer distributor. xxvi, 2008: 601 p. |
| 95 | Voss H, Heck C A, Schallmey M, et al. Database mining for novel bacterial beta-etherases, glutathione-dependent lignin-degrading enzymes [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2020, 86(2): e02026-19. |
| 96 | Hillson N, Caddick M, Cai Y Z, et al. Building a global alliance of biofoundries [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 2040-2043. |
| 97 | Chao R, Mishra S, Si T, et al. Engineering biological systems using automated biofoundries [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 42: 98-108. |
| 98 | Si T, Chao R, Min Y H, et al. Automated multiplex genome-scale engineering in yeast [J]. Nature Communications, 2017. 8: 15187. |
| 99 | Xue P, Si T, Mishra S, et al. A mass spectrometry-based high-throughput screening method for engineering fatty acid synthases with improved production of medium-chain fatty acids [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2020, 117(7): 2131-2138. |
| 100 | Wang Y, Liu Y, Liu J, et al. MACBETH: Multiplex automated Corynebacterium glutamicum base editing method [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47:200-210. |
| 101 | Zlokarnik G, Grootenhuis P D, Watson J B. High throughput P450 inhibition screens in early drug discovery [J]. Drug Discov Today, 2005, 10(21): 1443-1450. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 刘宽庆, 张以恒. 木质素的生物降解和生物利用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1264-1278. |
| [7] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | 雷航彬, 何宁, 李斐煊, 董玲玲, 王世珍. 氢化酶固定化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1485-1497. |
| [11] | 王子渊, 杨立荣, 吴坚平, 郑文隆. 酶促合成手性氨基酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1319-1349. |
| [12] | 董玲玲, 李斐煊, 雷航彬, 宋启迪, 王世珍. 仿生分区室固定化多酶体系[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1518-1529. |
| [13] | 李庚, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 王佳, 袁其朋. 过氧化物酶的重组表达和应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1498-1517. |
| [14] | 程峰, 邹树平, 徐建妙, 汤恒, 薛亚平, 郑裕国. 生物高纯精草:高光学纯L-草铵膦生物制造的创新与发展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1404-1418. |
| [15] | 张阿磊, 魏国光, 张弛, 陈磊, 周奚, 刘伟, 陈可泉. 几丁质资源生物降解和高值转化的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1279-1299. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||