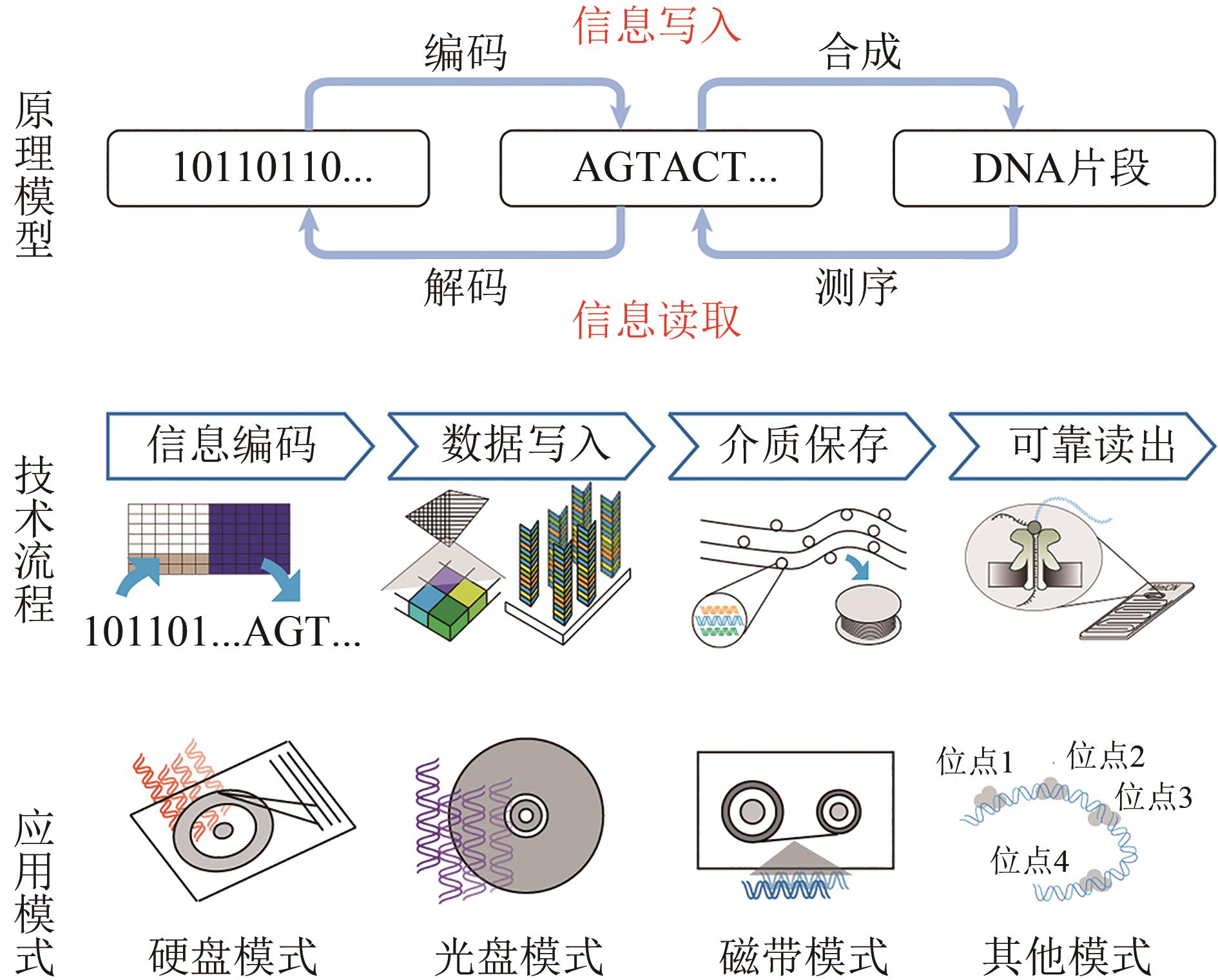
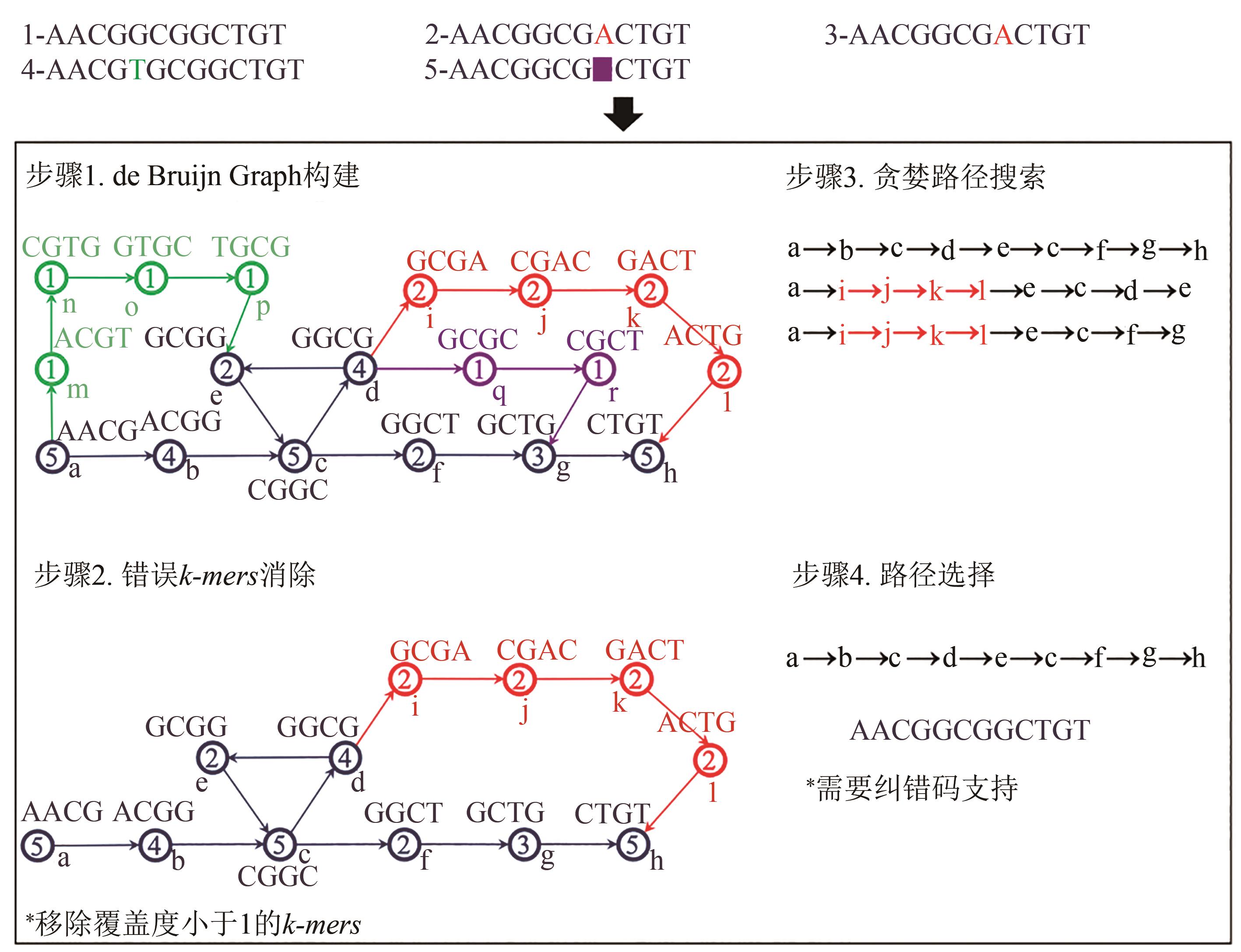
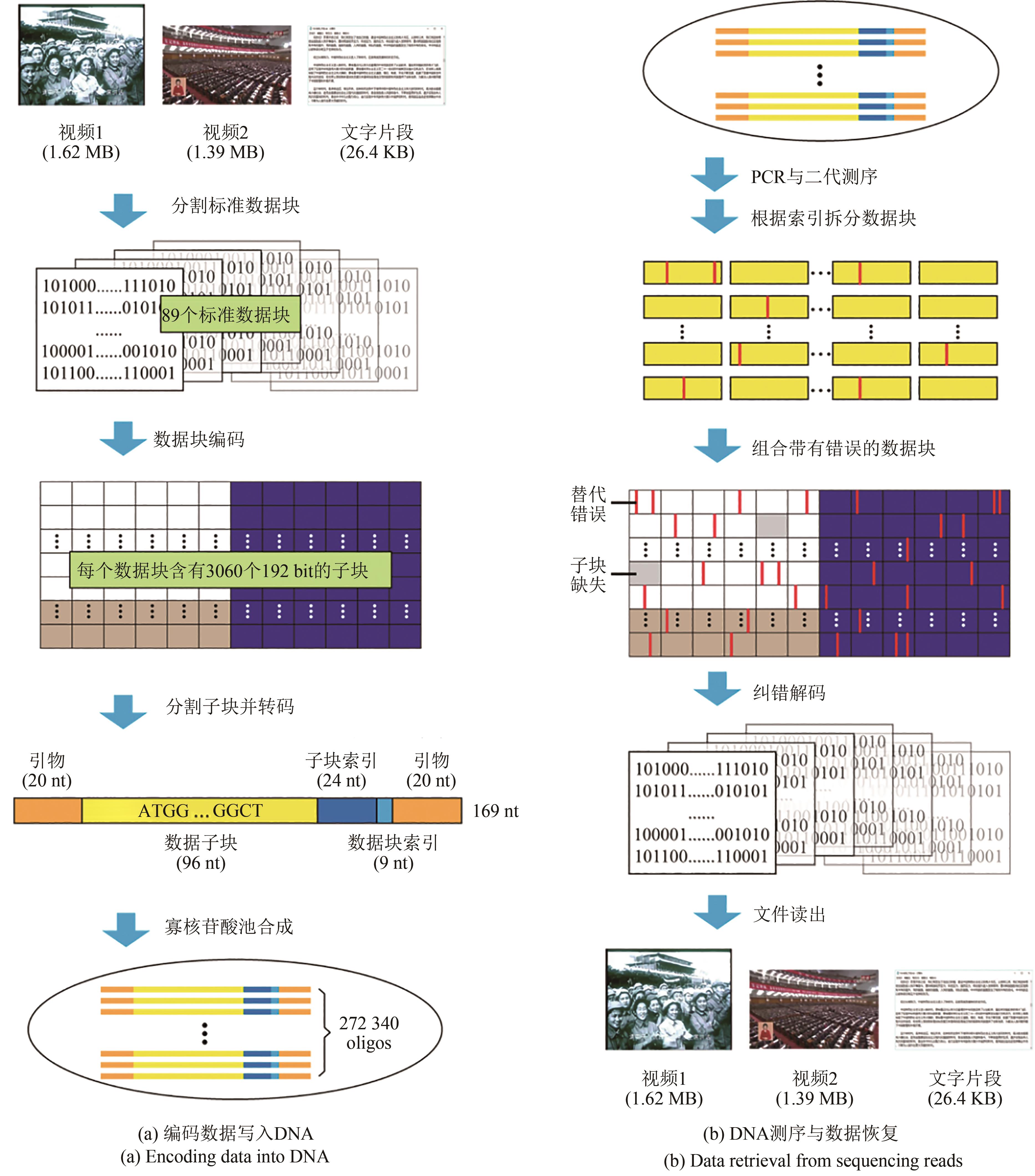
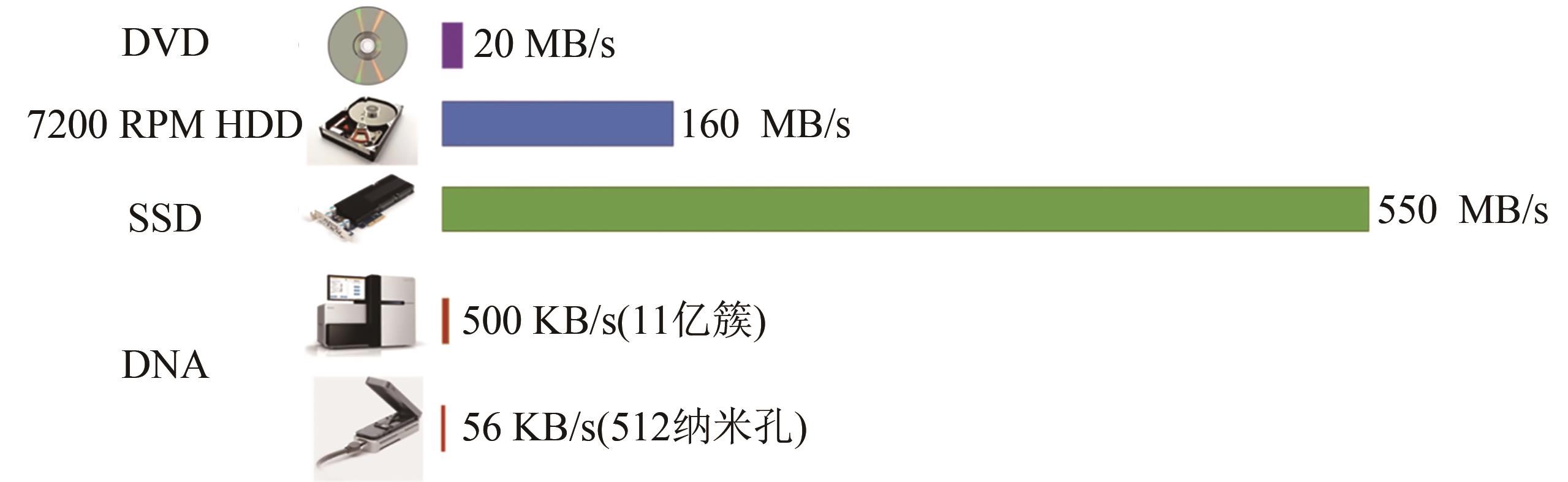
Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (3): 309-322.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-001
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
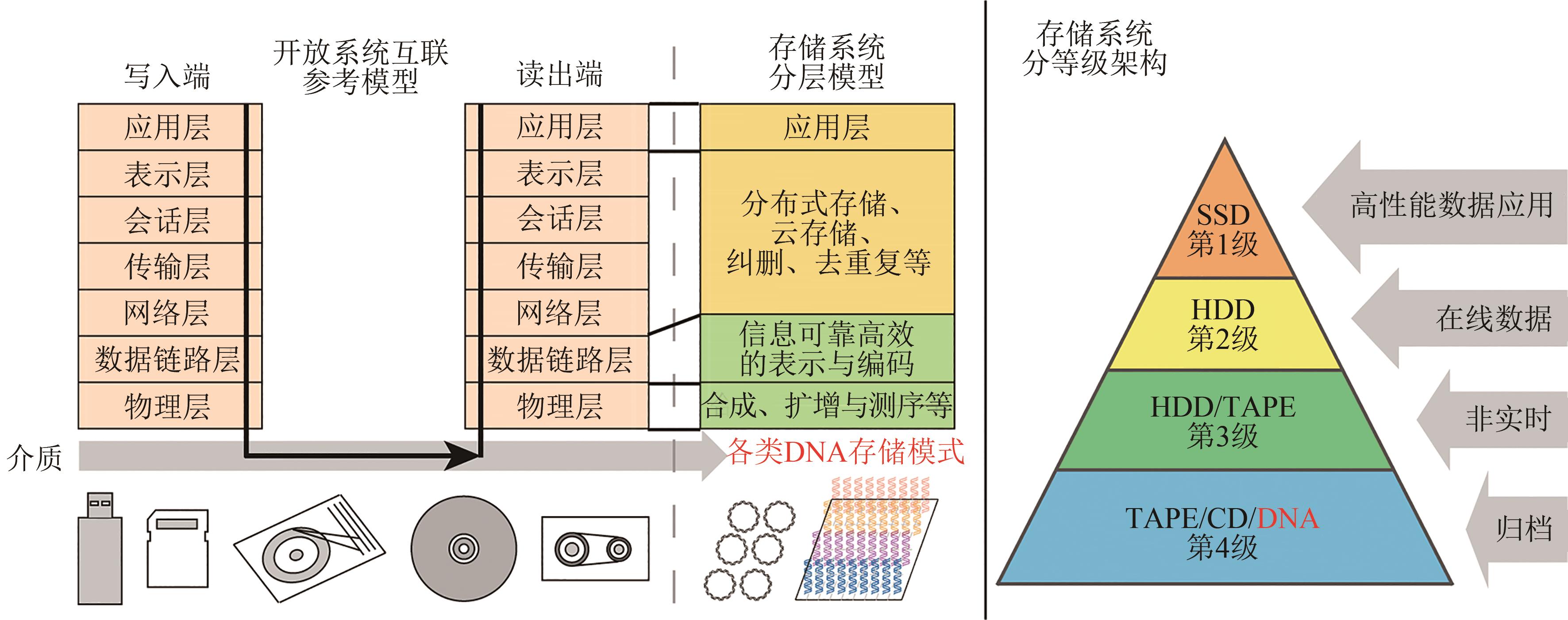
DNA information storage: bridging biological and digital world
HAN Mingzhe1,2, CHEN Weigang1,3, SONG Lifu1,2, LI Bingzhi1,2, YUAN Yingjin1,2
- 1.Frontier Science Center for Synthetic Biology and Key Laboratory of Systems Bioengineering (Ministry of Education),Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
2.School of Chemical Engineering and Technology,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
3.School of Microelectronics,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
-
Received:2021-01-04Revised:2021-03-02Online:2021-07-13Published:2021-06-30 -
Contact:YUAN Yingjin
DNA信息存储:生命系统与信息系统的桥梁
韩明哲1,2, 陈为刚1,3, 宋理富1,2, 李炳志1,2, 元英进1,2
- 1.天津大学,合成生物学前沿科学中心,系统生物工程教育部重点实验室,天津 300072
2.天津大学化工学院,天津 300072
3.天津大学微电子学院,天津 300072
-
通讯作者:元英进 -
作者简介:韩明哲 (1996—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为合成生物学及DNA信息存储。E-mail:mickeyhan@tju.edu.cn元英进 (1963—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为合成生物学及人工基因组化学合成。E-mail:yjyuan@tju.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HAN Mingzhe, CHEN Weigang, SONG Lifu, LI Bingzhi, YUAN Yingjin. DNA information storage: bridging biological and digital world[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 309-322.
韩明哲, 陈为刚, 宋理富, 李炳志, 元英进. DNA信息存储:生命系统与信息系统的桥梁[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(3): 309-322.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2021-001
| 1 | Semiconductor Industry Association. Decadal plan for semiconductors [EB/OL]. [2020-12-02]. . |
| 2 | FONTANA R E, DECAD G M, HETZLER S R. Volumetric density trends (TB/in.3) for storage components: TAPE, hard disk drives, NAND, and Blu-ray[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 117(17): 17E301. |
| 3 | ZHIRNOV V, ZADEGAN R M, SANDHU G S, et al. Nucleic acid memory[J]. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(4): 366-370. |
| 4 | KOSURI S, CHURCH G M. Large-scale de novo DNA synthesis: technologies and applications[J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(5): 499-507. |
| 5 | WU Y, LI B Z, ZHAO M, et al. Bug mapping and fitness testing of chemically synthesized chromosome X[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6329): eaaf4706. |
| 6 | XIE Z X, LI B Z, MITCHELL L A, et al. "Perfect" designer chromosome V and behavior of a ring derivative[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6329): eaaf4704. |
| 7 | 陈欣懋, 欧阳颀. 生物逆向工程设计在合成生物学中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(1): 29-43. |
| CHEN X M, OUYANG Q. The application of biological reverse engineering in synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 29-43. | |
| 8 | 彭凯, 逯晓云, 程健, 等. DNA合成、组装与纠错技术研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(6): 697-708. |
| PENG K, LU X Y, CHENG J, et al. Advances in technologies for de novo DNA synthesis, assembly and error correction[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(6): 697-708. | |
| 9 | 曹中正, 张心怡, 徐艺源, 等. 基因组编辑技术及其在合成生物学中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(4): 413-426. |
| CAO Z Z, ZHANG X Y, XU Y Y, et al. Genome editing technology and its applications in synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(4): 413-426. | |
| 10 | 王会, 戴俊彪, 罗周卿. 基因组的"读-改-写"技术[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(5): 503-515. |
| WANG H, DAI J B, LUO Z Q. Reading, editing, and writing techniques for genome research[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(5): 503-515. | |
| 11 | 丁明珠, 李炳志, 王颖, 等. 合成生物学重要研究方向进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(1): 7-28. |
| DING M Z, LI B Z, WANG Y, et al. Significant research progress in synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 7-28. | |
| 12 | Wire Business. Twist Bioscience, Illumina and Western Digital form alliance with Microsoft to advance data storage in DNA [EB/OL]. [2020-11-12]. . |
| 13 | CEZE L, NIVALA J, STRAUSS K. Molecular digital data storage using DNA[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2019, 20(8): 456-66. |
| 14 | MEISER L C, ANTKOWIAK P L, KOCH J, et al. Reading and writing digital data in DNA[J]. Nature Protocols, 2020, 15(1): 86-101. |
| 15 | DONG Y, SUN F, PING Z, et al. DNA storage: research landscape and future prospects[J]. National Science Review, 2020, 7(6): 1092-1107. |
| 16 | PING Z, MA D, HUANG X, et al. Carbon-based archiving: current progress and future prospects of DNA-based data storage[J]. GigaScience, 2019, 8(6): giz075. |
| 17 | LIM C K, NIRANTAR S, YEW W S, et al. Novel modalities in DNA data storage[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2020.12.008 . |
| 18 | 周廷尧, 罗源, 蒋兴宇. DNA数据存储:保存策略与数据加密[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(3): 371-383. |
| ZHOU T Y, LUO Y, JIANG X Y. DNA data storage: preservation approach and data encryption[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 371-383. | |
| 19 | CHURCH G M, GAO Y, KOSURI S. Next-generation digital information storage in DNA[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6102): 1628. |
| 20 | KEIGER D. DNA hard drive [EB/OL]. [2012-11-30]. . |
| 21 | 毕昆, 顾万君, 陆祖宏. DNA 存储中的编码技术[J]. 生物信息学, 2020, 18(2): 76-85. |
| BI K, GU W J, LU Z H. Coding algorithms in DNA storage[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioinformatics, 2020, 18(2): 76-85. | |
| 22 | Bioscience Twist. Product sheet of Twist oligo pools [EB/OL]. [2019-08-29]. |
| 23 | GenScript. Precise synthetic oligo pools [EB/OL]. [2021-02-01]. . |
| 24 | LIU L, LI Y, LI S, et al. Comparison of next-generation sequencing systems [J]. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology, 2012, 2012: 251364. |
| 25 | GOLDMAN N, BERTONE P, CHEN S Y, et al. Towards practical, high-capacity, low-maintenance information storage in synthesized DNA [J]. Nature, 2013, 494(7435): 77-80. |
| 26 | GRASS R N, HECKEL R, PUDDU M, et al. Robust chemical preservation of digital information on DNA in silica with error-correcting codes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(8): 2552-2555. |
| 27 | ERLICH Y, ZIELINSKI D. DNA Fountain enables a robust and efficient storage architecture[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6328): 950-953. |
| 28 | ANAVY L, VAKNIN I, ATAR O, et al. Data storage in DNA with fewer synthesis cycles using composite DNA letters[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(10): 1229-1236. |
| 29 | CHOI Y, RYU T, LEE A C, et al. High information capacity DNA-based data storage with augmented encoding characters using degenerate bases[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 6582. |
| 30 | HOSHIKA S, LEAL N A, KIM M J, et al. Hachimoji DNA and RNA: a genetic system with eight building blocks[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6429): 884-887. |
| 31 | HECKEL R, SHOMORONY I, RAMCHANDRAN K, et al. Fundamental limits of DNA storage systems[C]//2017 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT). Aachen, Germany: IEEE, 2017: 3130-3134. |
| 32 | PRESS W H, HAWKINS J A, JONES S K, et al. HEDGES error-correcting code for DNA storage corrects indels and allows sequence constraints[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(31): 18489-18496. |
| 33 | SABARY O, YUCOVICH A, SHAPIRA G, et al. Reconstruction Algorithms for DNA-Storage Systems[EB/OL]. [2021-05-25]. . |
| 34 | SONG L, GENG F, GONG Z, et al. Super-robust data storage in DNA by de Bruijn graph-based decoding[EB/OL]. [2021-05-25]. . |
| 35 | LEE H H, KALHOR R, GOELA N, et al. Terminator-free template-independent enzymatic DNA synthesis for digital information storage[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 2383. |
| 36 | LEE H, WIEGAND D J, GRISWOLD K, et al. Photon-directed multiplexed enzymatic DNA synthesis for molecular digital data storage[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5246. |
| 37 | LIN K N, VOLKEL K, TUCK J M, et al. Dynamic and scalable DNA-based information storage[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1), 2981. |
| 38 | CHOI Y, BAE H J, LEE A C, et al. DNA micro‐disks for the management of DNA‐based data storage with Index and Write‐Once-Read‐Many (WORM) memory features[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(37): 2001249. |
| 39 | GAO Y, CHEN X, QIAO H, et al. Low-bias manipulation of DNA oligo pool for robust data storage[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(12): 3344-3352. |
| 40 | ORGANICK L, ANG S D, CHEN Y J, et al. Random access in large-scale DNA data storage[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(7): 242-248. |
| 41 | TAKAHASHI C N, NGUYEN B H, STRAUSS K, et al. Demonstration of end-to-end automation of DNA data storage[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 4998. |
| 42 | NEWMAN S, STEPHENSON A P, WILLSEY M, et al. High density DNA data storage library via dehydration with digital microfluidic retrieval[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1706. |
| 43 | SHANKLAND S. Startup packs all 16GB of Wikipedia onto DNA strands to demonstrate new storage tech [EB/OL]. [2019-07-02]. . |
| 44 | 陈为刚, 黄刚, 李炳志, 等. 音视频文件的DNA信息存储[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2019, 50(1): 81-85. |
| CHEN W G, HUANG G, LI B Z, et al. DNA information storage for audio and video files[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Vitae, 2019, 50(1): 81-85. | |
| 45 | PING Z, CHEN S, ZHOU G, et al. Towards practical and robust DNA-based data archiving by codec system named 'Yin-Yang'[EB/OL]. [2021-05-25]. . |
| 46 | BORNHOLT J, LOPEZ R, CARMEAN D M, et al. Toward a DNA-based archival storage system[J]. IEEE Micro, 2017, 37(3): 98-104. |
| 47 | YAZDI S M H T, YUAN Y, MA J, et al. A rewritable, random-access DNA-based storage system[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 14138. |
| 48 | CHEN W G, HAN M Z, ZHOU J T, et al. An artificial chromosome for data storage[J]. National Science Review, 2021, 8(5): nwab028. |
| 49 | ZHU Y O, SIEGAl M L, HALL D W, et al. Precise estimates of mutation rate and spectrum in yeast[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(22): E2310-E2318. |
| 50 | LEE H, POPODI E, TANG H, et al. Rate and molecular spectrum of spontaneous mutations in the bacterium Escherichia coli as determined by whole-genome sequencing[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(41): E2774-E2783. |
| 51 | SONG L F, ZENG A P. Orthogonal information encoding in living cells with high error- tolerance, safety, and fidelity [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(3): 866-874. |
| 52 | DEAMER D, AKESON M, BRANTON D. Three decades of nanopore sequencing[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2016, 34(5): 518-524. |
| 53 | DAVIS J. Microvenus[J]. Art Journal, 1996, 55(1): 70-74. |
| 54 | BANCROFT C, BOWLER T, BLOOM B, et al. Long-term storage of information in DNA[J]. Science, 2001, 293(5536): 1763-1765. |
| 55 | WONG P C, WONG K K, FOOTE H. Organic data memory using the DNA approach[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2003, 46(1): 95-98. |
| 56 | GUSTAFSSON C. For anyone who ever said there's no such thing as a poetic gene[J]. Nature, 2009, 458(7239): 703. |
| 57 | YACHIE N, SEKIYAMA K, SUGAHARA J, et al. Alignment-based approach for durable data storage into living organisms[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2007, 23(2): 501-505. |
| 58 | AILENBERG M, ROTSTEIN O D. An improved Huffman coding method for archiving text, images, and music characters in DNA[J]. Biotechniques, 2009, 47(3): 747-751. |
| 59 | NGUYEN H H, PARK J, PARK S J, et al. Long-term stability and integrity of plasmid-based DNA data storage[J]. Polymers, 2018, 10(1): 28. |
| 60 | GIBSON D G, GLASS J I, LARTIGUE C, et al. Creation of a bacterial cell controlled by a chemically synthesized genome[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5987): 52-56. |
| 61 | SHIPMAN S L, NIVALA J, MACKLIS J D, et al. CRISPR-Cas encoding of a digital movie into the genomes of a population of living bacteria[J]. Nature, 2017, 547(7663): 345-349. |
| 62 | HAO M, QIAO H, GAO Y, et al. A mixed culture of bacterial cells enables an economic DNA storage on a large scale[J]. Communications Biology, 2020, 3(1): 416. |
| 63 | AUSLÄNDER S, FUSSENEGGER M. Dynamic genome engineering in living cells[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6211): 813-814. |
| 64 | FARZADFARD F, LU T K. Emerging applications for DNA writers and molecular recorders[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6405): 870-875. |
| 65 | FARZADFARD F, LU T K. Genomically encoded analog memory with precise in vivo DNA writing in living cell populations[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6211): . |
| 66 | SHETH R U, YIM S S, WU F L, et al. Multiplex recording of cellular events over time on CRISPR biological tape[J]. Science, 2017, 358(6369): 1457-1461. |
| 67 | TANG W, LIU D R. Rewritable multi-event analog recording in bacterial and mammalian cells[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6385): eaap8992. |
| 68 | PERLI S D, CUI C H, LU T K. Continuous genetic recording with self-targeting CRISPR-Cas in human cells[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6304): aag0511. |
| 69 | FARZADFARD F, GHARAEI N, HIGASHIKUNI Y, et al. Single-nucleotide-resolution computing and memory in living cells[J]. Molecular Cell, 2019, 75(4): 769-780. |
| 70 | YIM S S, MCBEE R M, SONG A M, et al. Robust direct digital-to-biological data storage in living cells[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2021, 17(3):246-253. |
| 71 | TABATABAEI S K, WANG B, ATHREYA N B M, et al. DNA punch cards for storing data on native DNA sequences via enzymatic nicking[J]. Nature communications, 2020, 11(1): 1742. |
| 72 | CHEN K, KONG J, ZHU J, et al. Digital data storage using DNA nanostructures and solid-state nanopores[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 19(2): 1210-1215. |
| 73 | CHEN K, ZHU J, BOSKOVIC F, et al. Nanopore-based DNA hard drives for rewritable and secure data storage[J]. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(5): 3754-3760. |
| 74 | LOPEZ R, CHEN Y J, ANG S D, et al. DNA assembly for nanopore data storage readout[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 2933. |
| 75 | ZHANG Y, WANG F, CHAO J, et al. DNA origami cryptography for secure communication[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 5469. |
| 76 | Semiconductor Research Corporation. 2018 semiconductor synthetic biology roadmap [R]. Durham, NC, USA: SRC, 2018. |
| 77 | MCCALLUM J C. Disk drive prices 1955+ [EB/OL]. [2021-05-25]. . |
| 78 | IARPA. IARPA BAA on molecular information storage [EB/OL]. [2021-05-25]. . |
| 79 | MARKOWITZ D. SRC/IARPA Workshop on DNA-based massive information storage [EB/OL]. [2021-05-25]. . |
| 80 | ANTKOWIAK P L, LIETARD J, DARESTANI M Z, et al. Low cost DNA data storage using photolithographic synthesis and advanced information reconstruction and error correction[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5345. |
| 81 | Illumina. Illumina sequencing platforms [EB/OL]. [2021-05-25]. |
| 82 | Illumina. Run time estimates for each sequencing step on the Illumina sequencing platforms. [EB/OL]. [2021-05-25]. . |
| 83 | KONO N, ARAKAWA K. Nanopore sequencing: review of potential applications in functional genomics[J]. Development, Growth & Differentiation, 2019, 61(5): 316-326. |
| 84 | YUAN Z, LIU Y, DAI M, et al. Controlling DNA translocation through solid-state nanopores[J]. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2020, 15: 80. |
| 85 | STANLEY P M, STRITTMATTER L M, VICKERS A M, et al. Decoding DNA data storage for investment[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2020, 45: 107639. |
| 86 | HECKEL R, MIKUTIS G, GRASS R N. A characterization of the DNA data storage channel[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 9663. |
| 87 | MAO W, DIGGAVI S N, KANNAN S. Models and information-theoretic bounds for nanopore sequencing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2018, 64(4): 3216-3236. |
| 88 | MERCIER H, BHARGAVA V K, TAROKH V. A survey of error-correcting codes for channels with symbol synchronization errors[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2010, 12(1): 87-96. |
| 89 | 平质, 张颢龄, 陈世宏, 等. Chamaeleo: DNA存储碱基编解码算法的可拓展集成与系统评估平台[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(3): 412-427. |
| PING Z, ZHANG H L, CHEN S H, et al. Chamaeleo: an integrated evaluation platform for DNA storage[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 412-427. | |
| 90 | Semiconductor Research Corporation. Decadal plan for semiconductors full report [R]. Durham: SRC, 2021. |
| 91 | PUZIS R, FARBIASH D, BRODT O, et al. Increased cyber-biosecurity for DNA synthesis [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(12): 1379-1381. |
| 92 | NEY P, KOSCHER K, ORGANICK L, et al. Computer security, privacy, and DNA sequencing: compromising computers with synthesized DNA, privacy leaks, and more[C]//26th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 17). Vancouver, BC, Canada: USENIX Association, 2017: 765-779. |
| 93 | KOCH J, GANTENBEIN S, MASANIA K, et al. A DNA-of-things storage architecture to create materials with embedded memory [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(1): 39-43. |
| 94 | Gartner. Gartner unveils top predictions for IT organizations and users in 2021 and beyond [EB/OL]. Gartner [2020-10-21]. . |
| [1] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | ZHANG Xuanliang, LI Qingting, WANG Fei. Data writing in DNA storage systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1125-1141. |
| [12] | CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [13] | CAI Bingyu, TAN Xiangtian, LI Wei. Advances in synthetic biology for engineering stem cell [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [14] | XIE Huang, ZHENG Yilei, SU Yiting, RUAN Jingyi, LI Yongquan. An overview on reconstructing the biosynthetic system of actinomycetes for polyketides production [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [15] | ZHA Wenlong, BU Lan, ZI Jiachen. Advances in synthetic biology for producing potent pharmaceutical ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||