Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (3): 399-411.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-040
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
A global patent analysis: trends in DNA synthesis and information storage
CHEN Daming1, ZHANG Xuebo1, LIU Xiao1, MA Yue1,2, XIONG Yan1,2
- 1.Shanghai Information Center for Life Sciences,Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shanghai 200031,China
2.University of Chinese academy Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
-
Received:2021-04-01Revised:2021-05-06Online:2021-07-13Published:2021-06-30 -
Contact:XIONG Yan
从全球专利分析看DNA合成与信息存储技术发展趋势
陈大明1, 张学博1, 刘晓1, 马悦1,2, 熊燕1,2
- 1.中国科学院上海生命科学信息中心,中国科学院上海营养与健康研究所,上海 200031
2.中国科学院大学,北京 100049
-
通讯作者:熊燕 -
作者简介:陈大明 (1982—),男,硕士,研究员。研究方向为科技情报、专利分析等。E-mail:chendaming@sibs.ac.cn熊燕 (1967—),女,博士,研究员。研究方向为科技战略情报研究。E-mail:yxiong@sibs.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“合成生物学”重点专项(2020YFA0908600);国家自然科学基金(NFSC)-中国科学院(CAS)联合项目“合成生物学发展战略研究(2021-2035)”(XK2019SMA002)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CHEN Daming, ZHANG Xuebo, LIU Xiao, MA Yue, XIONG Yan. A global patent analysis: trends in DNA synthesis and information storage[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 399-411.
陈大明, 张学博, 刘晓, 马悦, 熊燕. 从全球专利分析看DNA合成与信息存储技术发展趋势[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(3): 399-411.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2021-040

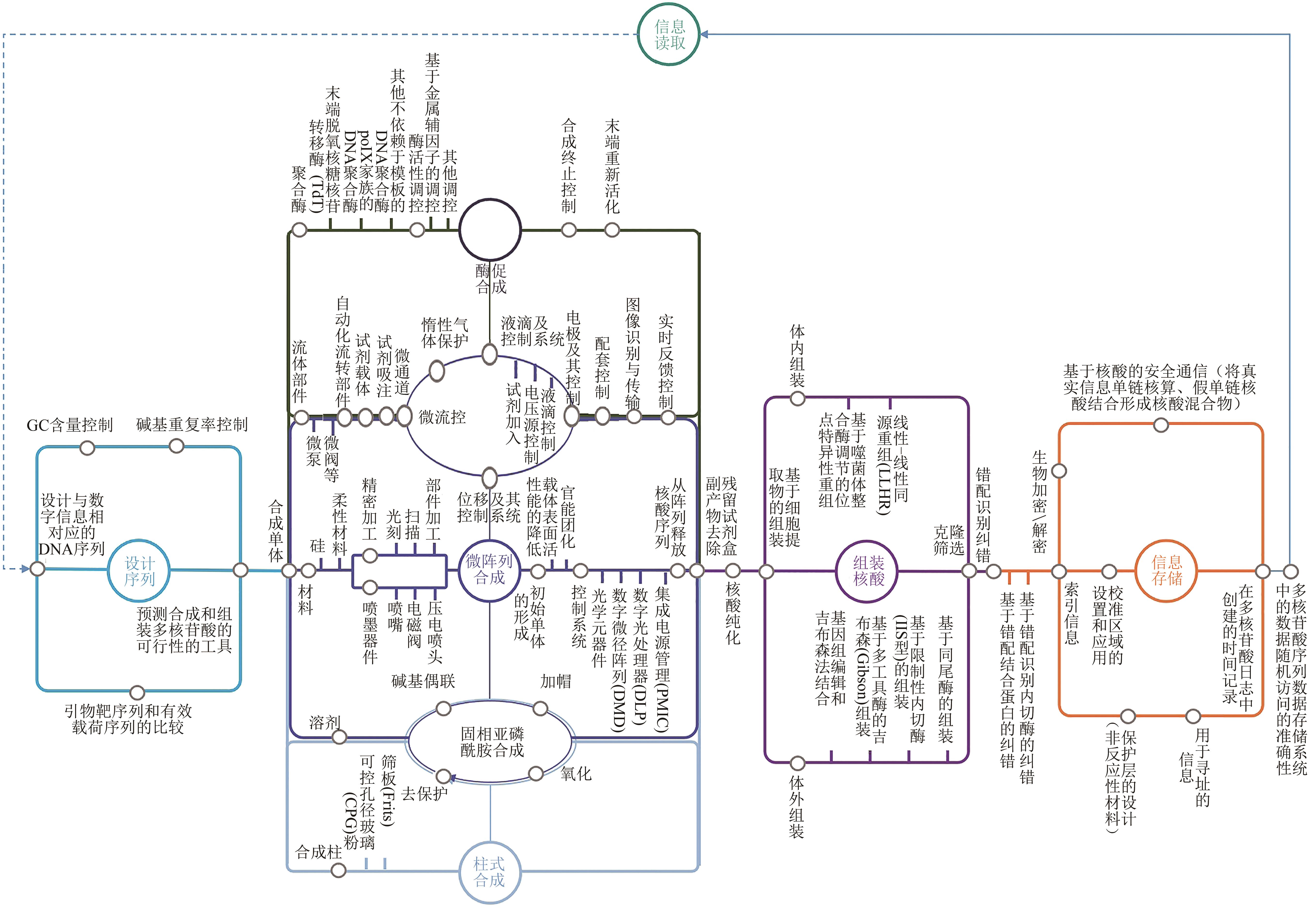
Fig. 1 Patent publication numbers and representative patentees of DNA synthesis and storage, and the cost changes for gene synthesis during 2001—2020[①The patent search date is March 1, 2021; The corresponding year in the figure is the patent publication year, and the publication amount of the country (region) shown is the amount of patents published by the corresponding Intellectual Property Office in the corresponding region; ②The enterprises (or institutional platforms) shown in the figure are represented by those who have joined the development of DNA synthesis and storage technologies at the corresponding stage]
| 代表性专利①(申请号) | 申请年 | 技术内容 | 当前申请(专利权)人 |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/779389 | 2001 | 减少合成过程中臭氧相关的降解 | 昂飞 |
| US10/355433 | 2003 | 合成期间的黏度控制 | 安捷伦 |
| US10/652063 | 2003 | 功能化载体(通过三芳基甲基连接基团与固体支持物结合) | 安捷伦、科罗拉多州立大学 |
| US10/652054 | 2003 | 利用环外胺三芳基甲基保护基的前体,促进核苷酸间键的形成 | 安捷伦、科罗拉多州立大学 |
| US10/652064 | 2003 | 多核苷酸的前体 | 安捷伦、科罗拉多州立大学 |
| US11/118599 | 2005 | 基材和合成试剂 | 安捷伦、科罗拉多州立大学 |
| EP2005251944 | 2005 | 原位合成多核苷酸的循环,包括单体附着、官能团化产生步骤 | 安捷伦 |
| US11/284495 | 2005 | 寡核苷酸阵列的切割 | 安捷伦 |
| US11/203328 | 2005 | 控制从阵列释放的寡核苷酸序列的方法(利用硅烷醇作为可切割的接头,所有释放的单链寡核苷酸的3´和5´末端都不适合作为酶促反应的底物) | 安捷伦 |
| US11/469405 | 2006 | 用于新寡核苷酸的脱三苯甲基化的装置 | 安捷伦 |
| US11/899828 | 2007 | α-效应亲核试剂的保护(避免酸诱导的脱嘌呤) | 安捷伦 |
| US11/897898 | 2007 | 硫醚取代的芳基碳酸酯保护基团 | 安捷伦、科罗拉多州立大学 |
| US13/670220 | 2012 | 用于寡核苷酸合成或纯化的试剂 | 安捷伦 |
| PCT/IL2014/050938 | 2014 | 液滴包含基因合成试剂,在容器内的位置通过电压源控制来确定,通过依次确定液滴位置来执行基因合成过程 | Yeda 研发有限公司 |
| US15/304701 | 2015 | 酶促添加核苷酸-纯化-酶促扩增的循环 | DNA Script公司 |
| EP2015807404 | 2015 | 用乙酰氧基-甲基保护非天然核苷酸,将保护的非天然核苷酸掺入固体支持物的核苷酸序列中,在非天然核苷酸中除去乙酰氧基甲基 | 安捷伦 |
| US15/742237 | 2016 | 在酶促合成核酸序列的过程中,利用受保护的核苷酸与通用模板结合使用以指导合成 | 赛默飞世尔 |
| US15/051511 | 2016 | 偶联寡核苷酸的方法:使用试剂活化第一寡核苷酸的末端,将其与第二寡核苷酸的末端缀合,以产生酰胺键连接 | 安捷伦 |
| US15/814826 | 2017 | 组合两个液滴以促进两种不同寡核苷酸之间的连接,实现高保真度的合成 | Gen-9公司 |
| CN201780061546.X | 2017 | 多核苷酸合成装置中,在固体表面增加表面积的纹理(内部区域包含多个凹陷或突起),以增加合成产量 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US16/099487 | 2017 | 在酶促合成中,使用电极来调控反应区和反应位点的pH,从而调控聚合酶的活性 | 哈佛大学 |
| SG10202009688Q | 2017 | 含有特定序列的polX家族的DNA聚合酶,能用于合成没有模板链的核酸分子 | DNA Script公司、巴斯德研究所、法国国家科学研究中心 |
| PCT/FR2017/050215 | 2017 | 用于实施酶促合成的设备,包括合成装置和计算机系统,其中合成装置由反应器、试剂供应管、温度调控装置等组成 | DNA Script公司 |
| US16/165952 | 2018 | 基板上每个结构与加热单元(包括可寻址电极)接触,通过加热电极使分布于表面的溶剂处于气相,促进多核苷酸与溶剂的缩合 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US16/479141 | 2018 | 通过掺入预定义序列的核苷酸、第二链的核苷酸,来延伸第一链(通过聚合酶的作用) | 牛津纳米孔科技公司 |
| US16/636875 | 2018 | 利用含有特定序列的DNA聚合酶,提高酶促合成的效率 | DNA Script公司 |
| CN201880095407.3 | 2018 | 用于在寡核苷酸的合成期间使核苷亚磷酰胺双重偶联的方法,核苷残基的游离羟基与受保护的核苷亚磷酰胺的第一样品偶联,随后暴露于氧化剂,再与受保护的核苷亚磷酰胺的第二样品实现第二偶联,并进一步暴露于氧化剂 | 安捷伦 |
| CN201980048339.X | 2019 | 在连接酶的作用下,利用预定序列的第一核苷酸与预定序列的第二核苷酸杂交,在裂解位点处裂解双链多核苷酸 | 牛津纳米孔科技公司 |
| CN201910834783.6 | 2019 | 在末端脱氧核糖核苷转移酶的氨基酸序列中特定位点引入突变,提高了其与3′羟基末端的核苷酸的偶合效率,从而改进酶促反应合成核酸的方法 | 中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所 |
| US16/239453 | 2019 | 装置的可寻址电极可控制多核苷酸合成(脱保护、延伸或裂解等) | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US16/726073 | 2019 | 有效洗涤此前合成步骤的残留试剂、溶剂或副产物,以降低多核苷酸合成的错误率 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| PCT/EP2019/087048 | 2019 | 利用引发剂、阻滞剂在同一反应容器中合成多种寡核苷酸的方法,并对其加以寡核苷酸的测定 | DNA Script公司 |
| US17/033017 | 2020 | 使用通用引物,在聚合酶的作用下实现与模板链互补的合成;错配的异源双链可被核酸内切酶识别并切割,从而减少合成错误 | Gen-9公司 |
| US16/925785 | 2020 | 设计具有特定的氨基酸序列的末端脱氧核糖核苷转移酶 | DNA Script公司 |
| US16/854719 | 2020 | 多核苷酸合成装置的表面结构含二氧化硅,在表面上设多个凹槽或柱,每个凹槽或柱的宽度为6.8~500 nm,间距长度约为宽度的2倍,深度约为长度的60%~125%,表面上的多个基因座直径为0.5~100 μm,每个簇包含50~500个基因座并且具有0.5~2 mm的横截面 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US16/920204 | 2020 | 利用单向错配核酸内切酶活性的分子,使核苷酸错配的多个双链核酸分子断裂,去除错配的核苷酸 | Codex DNA公司 |
| PCT/US2020/037104 | 2020 | 通过调节金属辅因子的氧化态,调节末端脱氧核苷酸转移酶(TdT)等聚合酶促进的多核苷酸合成 | 微软 |
| PCT/GB2020/050247 | 2020 | 含有特定序列的末端脱氧核糖核苷转移酶 | Nuclera Nucleics公司 |
| PCT/EP2020/053417 | 2020 | 多模板的无模板酶促合成 | DNA Script公司 |
| US16/832990 | 2020 | 使用纳米流体装置合成寡核苷酸,在多个纳米孔通道中有与多个电极接触的电解质溶液,可通过电压控制从电极处的电解质溶液产生酸 | Palogen公司 |
| US16/921712 | 2020 | 用于从头合成高度精确的核酸序列的装置,该装置具有主通道和微通道,其中微通道具有高的表面积与体积比;在微通道中可添加特异的延伸反应试剂的液滴,留出足够的时间进行延伸反应;该设备可降低合成的错误率 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| PCT/GB2020/050558 | 2020 | 固体支持物上,在2´端受控的局部脱保护基础上合成寡核苷酸 | Nuclera Nucleics公司 |
| US17/021616 | 2020 | 用于合成DNA或RNA的自动化模块化系统和方法 | Synthego公司 |
Tab. 1 Representative patents of oligonucleotide or polynucleotide synthesis
| 代表性专利①(申请号) | 申请年 | 技术内容 | 当前申请(专利权)人 |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/779389 | 2001 | 减少合成过程中臭氧相关的降解 | 昂飞 |
| US10/355433 | 2003 | 合成期间的黏度控制 | 安捷伦 |
| US10/652063 | 2003 | 功能化载体(通过三芳基甲基连接基团与固体支持物结合) | 安捷伦、科罗拉多州立大学 |
| US10/652054 | 2003 | 利用环外胺三芳基甲基保护基的前体,促进核苷酸间键的形成 | 安捷伦、科罗拉多州立大学 |
| US10/652064 | 2003 | 多核苷酸的前体 | 安捷伦、科罗拉多州立大学 |
| US11/118599 | 2005 | 基材和合成试剂 | 安捷伦、科罗拉多州立大学 |
| EP2005251944 | 2005 | 原位合成多核苷酸的循环,包括单体附着、官能团化产生步骤 | 安捷伦 |
| US11/284495 | 2005 | 寡核苷酸阵列的切割 | 安捷伦 |
| US11/203328 | 2005 | 控制从阵列释放的寡核苷酸序列的方法(利用硅烷醇作为可切割的接头,所有释放的单链寡核苷酸的3´和5´末端都不适合作为酶促反应的底物) | 安捷伦 |
| US11/469405 | 2006 | 用于新寡核苷酸的脱三苯甲基化的装置 | 安捷伦 |
| US11/899828 | 2007 | α-效应亲核试剂的保护(避免酸诱导的脱嘌呤) | 安捷伦 |
| US11/897898 | 2007 | 硫醚取代的芳基碳酸酯保护基团 | 安捷伦、科罗拉多州立大学 |
| US13/670220 | 2012 | 用于寡核苷酸合成或纯化的试剂 | 安捷伦 |
| PCT/IL2014/050938 | 2014 | 液滴包含基因合成试剂,在容器内的位置通过电压源控制来确定,通过依次确定液滴位置来执行基因合成过程 | Yeda 研发有限公司 |
| US15/304701 | 2015 | 酶促添加核苷酸-纯化-酶促扩增的循环 | DNA Script公司 |
| EP2015807404 | 2015 | 用乙酰氧基-甲基保护非天然核苷酸,将保护的非天然核苷酸掺入固体支持物的核苷酸序列中,在非天然核苷酸中除去乙酰氧基甲基 | 安捷伦 |
| US15/742237 | 2016 | 在酶促合成核酸序列的过程中,利用受保护的核苷酸与通用模板结合使用以指导合成 | 赛默飞世尔 |
| US15/051511 | 2016 | 偶联寡核苷酸的方法:使用试剂活化第一寡核苷酸的末端,将其与第二寡核苷酸的末端缀合,以产生酰胺键连接 | 安捷伦 |
| US15/814826 | 2017 | 组合两个液滴以促进两种不同寡核苷酸之间的连接,实现高保真度的合成 | Gen-9公司 |
| CN201780061546.X | 2017 | 多核苷酸合成装置中,在固体表面增加表面积的纹理(内部区域包含多个凹陷或突起),以增加合成产量 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US16/099487 | 2017 | 在酶促合成中,使用电极来调控反应区和反应位点的pH,从而调控聚合酶的活性 | 哈佛大学 |
| SG10202009688Q | 2017 | 含有特定序列的polX家族的DNA聚合酶,能用于合成没有模板链的核酸分子 | DNA Script公司、巴斯德研究所、法国国家科学研究中心 |
| PCT/FR2017/050215 | 2017 | 用于实施酶促合成的设备,包括合成装置和计算机系统,其中合成装置由反应器、试剂供应管、温度调控装置等组成 | DNA Script公司 |
| US16/165952 | 2018 | 基板上每个结构与加热单元(包括可寻址电极)接触,通过加热电极使分布于表面的溶剂处于气相,促进多核苷酸与溶剂的缩合 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US16/479141 | 2018 | 通过掺入预定义序列的核苷酸、第二链的核苷酸,来延伸第一链(通过聚合酶的作用) | 牛津纳米孔科技公司 |
| US16/636875 | 2018 | 利用含有特定序列的DNA聚合酶,提高酶促合成的效率 | DNA Script公司 |
| CN201880095407.3 | 2018 | 用于在寡核苷酸的合成期间使核苷亚磷酰胺双重偶联的方法,核苷残基的游离羟基与受保护的核苷亚磷酰胺的第一样品偶联,随后暴露于氧化剂,再与受保护的核苷亚磷酰胺的第二样品实现第二偶联,并进一步暴露于氧化剂 | 安捷伦 |
| CN201980048339.X | 2019 | 在连接酶的作用下,利用预定序列的第一核苷酸与预定序列的第二核苷酸杂交,在裂解位点处裂解双链多核苷酸 | 牛津纳米孔科技公司 |
| CN201910834783.6 | 2019 | 在末端脱氧核糖核苷转移酶的氨基酸序列中特定位点引入突变,提高了其与3′羟基末端的核苷酸的偶合效率,从而改进酶促反应合成核酸的方法 | 中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所 |
| US16/239453 | 2019 | 装置的可寻址电极可控制多核苷酸合成(脱保护、延伸或裂解等) | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US16/726073 | 2019 | 有效洗涤此前合成步骤的残留试剂、溶剂或副产物,以降低多核苷酸合成的错误率 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| PCT/EP2019/087048 | 2019 | 利用引发剂、阻滞剂在同一反应容器中合成多种寡核苷酸的方法,并对其加以寡核苷酸的测定 | DNA Script公司 |
| US17/033017 | 2020 | 使用通用引物,在聚合酶的作用下实现与模板链互补的合成;错配的异源双链可被核酸内切酶识别并切割,从而减少合成错误 | Gen-9公司 |
| US16/925785 | 2020 | 设计具有特定的氨基酸序列的末端脱氧核糖核苷转移酶 | DNA Script公司 |
| US16/854719 | 2020 | 多核苷酸合成装置的表面结构含二氧化硅,在表面上设多个凹槽或柱,每个凹槽或柱的宽度为6.8~500 nm,间距长度约为宽度的2倍,深度约为长度的60%~125%,表面上的多个基因座直径为0.5~100 μm,每个簇包含50~500个基因座并且具有0.5~2 mm的横截面 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US16/920204 | 2020 | 利用单向错配核酸内切酶活性的分子,使核苷酸错配的多个双链核酸分子断裂,去除错配的核苷酸 | Codex DNA公司 |
| PCT/US2020/037104 | 2020 | 通过调节金属辅因子的氧化态,调节末端脱氧核苷酸转移酶(TdT)等聚合酶促进的多核苷酸合成 | 微软 |
| PCT/GB2020/050247 | 2020 | 含有特定序列的末端脱氧核糖核苷转移酶 | Nuclera Nucleics公司 |
| PCT/EP2020/053417 | 2020 | 多模板的无模板酶促合成 | DNA Script公司 |
| US16/832990 | 2020 | 使用纳米流体装置合成寡核苷酸,在多个纳米孔通道中有与多个电极接触的电解质溶液,可通过电压控制从电极处的电解质溶液产生酸 | Palogen公司 |
| US16/921712 | 2020 | 用于从头合成高度精确的核酸序列的装置,该装置具有主通道和微通道,其中微通道具有高的表面积与体积比;在微通道中可添加特异的延伸反应试剂的液滴,留出足够的时间进行延伸反应;该设备可降低合成的错误率 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| PCT/GB2020/050558 | 2020 | 固体支持物上,在2´端受控的局部脱保护基础上合成寡核苷酸 | Nuclera Nucleics公司 |
| US17/021616 | 2020 | 用于合成DNA或RNA的自动化模块化系统和方法 | Synthego公司 |
代表性专利① (申请号) | 申请年 | 技术内容 | 当前申请(专利权)人 |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/897340 | 2001 | 第一硅烷用于降低表面能,第二硅烷用于分子的官能化(用于形成固相合成的初始单体) | 安捷伦 |
| US15/860445 | 2018 | 将电磁辐射(EMR)施加到表面预定区域,以移除预定区域、能够结合核苷的反应性基团,从而定义不同的寡核苷酸延伸的基因座 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US11/117884 | 2005 | 喷墨打印头溶剂、可寻址核苷酸阵列 | 安捷伦 |
| US10/932886 | 2004 | 喷射器将液滴分配至基板 | 安捷伦 |
| US15/929030 | 2018 | 用于DNA合成装置的芯片,通过芯片控制每个电极 | 英特尔公司 |
| US11/365770 | 2006 | 使用基板旋转进行阵列制备,每种核酸占据支持物的单独已知区域 | 昂飞 |
| PCT/US2018/041397 | 2018 | 合成装置中,利用光学寻址系统选择性地将光传递到孔,以介导或控制孔中的反应 | 德雷珀实验室(The Charles Stark Draper Laboratory) |
| HK19122646 | 2019 | 用于核酸延伸的柔性材料,包括尼龙、硝化纤维素、聚丙烯、聚碳酸酯、聚乙烯、聚氨酯、聚苯乙烯、缩醛、丙烯酸、丙烯腈、丁二烯苯乙烯、聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯、聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯、聚氯乙烯、透明PVC箔、苯乙烯聚合物、含氟聚合物、聚醚砜或聚酰亚胺,在预定位置的表面上沉积核苷 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| EP2004803181 | 2004 | 设有用于DNA并行合成的矩阵 | 合成基因组股份有限公司 |
Tab. 2 Representative patents of inkjet printing and microfluidics
代表性专利① (申请号) | 申请年 | 技术内容 | 当前申请(专利权)人 |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/897340 | 2001 | 第一硅烷用于降低表面能,第二硅烷用于分子的官能化(用于形成固相合成的初始单体) | 安捷伦 |
| US15/860445 | 2018 | 将电磁辐射(EMR)施加到表面预定区域,以移除预定区域、能够结合核苷的反应性基团,从而定义不同的寡核苷酸延伸的基因座 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US11/117884 | 2005 | 喷墨打印头溶剂、可寻址核苷酸阵列 | 安捷伦 |
| US10/932886 | 2004 | 喷射器将液滴分配至基板 | 安捷伦 |
| US15/929030 | 2018 | 用于DNA合成装置的芯片,通过芯片控制每个电极 | 英特尔公司 |
| US11/365770 | 2006 | 使用基板旋转进行阵列制备,每种核酸占据支持物的单独已知区域 | 昂飞 |
| PCT/US2018/041397 | 2018 | 合成装置中,利用光学寻址系统选择性地将光传递到孔,以介导或控制孔中的反应 | 德雷珀实验室(The Charles Stark Draper Laboratory) |
| HK19122646 | 2019 | 用于核酸延伸的柔性材料,包括尼龙、硝化纤维素、聚丙烯、聚碳酸酯、聚乙烯、聚氨酯、聚苯乙烯、缩醛、丙烯酸、丙烯腈、丁二烯苯乙烯、聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯、聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯、聚氯乙烯、透明PVC箔、苯乙烯聚合物、含氟聚合物、聚醚砜或聚酰亚胺,在预定位置的表面上沉积核苷 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| EP2004803181 | 2004 | 设有用于DNA并行合成的矩阵 | 合成基因组股份有限公司 |
代表性专利① (申请号) | 申请年 | 技术内容 | 当前申请 (专利权)人 |
|---|---|---|---|
| US11/804996 | 2007 | 分析靶核酸序列中是否存在可能会破坏多重寡核苷酸组装反应的预定干扰序列,再利用聚合酶来实现核苷酸的组装 | Gen-9公司 |
| US14/379005 | 2013 | 液滴中的组装 | 哈佛大学 |
| EP2015818477 | 2015 | 定点的DNA切割 | Gen-9公司 |
| US14/752773 | 2015 | 用于分析确定连续、较大的核酸序列的计算机实现过程 | 10X基因组学有限公司 |
| EP2015852140 | 2015 | 检测错误组装的核酸 | Gen-9公司 |
| EP2015747649 | 2015 | 末端具有序列互补区域的两个双链核酸片段共价连接 | 生命技术公司 |
| PCT/US2017/050164 | 2017 | 利用RNA引导的内切核酸酶,其能够靶向并切割DNA序列,产生特征DNA片段,退火后实现DNA片段的共价连接 | 麻省理工学院 |
| US16/231117 | 2018 | 在高保真度多核苷酸组装中操纵液滴 | Gen-9公司 |
| CN201811377712.X | 2018 | 利用酿酒酵母体内组装系统组装和储存长序列,同时设强纠错系统 | 天津大学 |
| US16/736258 | 2020 | 利用细胞提取物、核酸外切酶、单链结合蛋白的蛋白质组合物等来实现高效的核酸组装 | 赛默飞世尔 |
| US16/879705 | 2020 | 利用核酸内切酶、核酸外切酶、聚合酶和连接酶的组合来组装核酸 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| PCT/EP2020/060535 | 2020 | 在多个反应室中将两个或更多个预定核酸片段多重组装 | 赛默飞世尔 |
Tab. 3 Representative patents of DNA assembly
代表性专利① (申请号) | 申请年 | 技术内容 | 当前申请 (专利权)人 |
|---|---|---|---|
| US11/804996 | 2007 | 分析靶核酸序列中是否存在可能会破坏多重寡核苷酸组装反应的预定干扰序列,再利用聚合酶来实现核苷酸的组装 | Gen-9公司 |
| US14/379005 | 2013 | 液滴中的组装 | 哈佛大学 |
| EP2015818477 | 2015 | 定点的DNA切割 | Gen-9公司 |
| US14/752773 | 2015 | 用于分析确定连续、较大的核酸序列的计算机实现过程 | 10X基因组学有限公司 |
| EP2015852140 | 2015 | 检测错误组装的核酸 | Gen-9公司 |
| EP2015747649 | 2015 | 末端具有序列互补区域的两个双链核酸片段共价连接 | 生命技术公司 |
| PCT/US2017/050164 | 2017 | 利用RNA引导的内切核酸酶,其能够靶向并切割DNA序列,产生特征DNA片段,退火后实现DNA片段的共价连接 | 麻省理工学院 |
| US16/231117 | 2018 | 在高保真度多核苷酸组装中操纵液滴 | Gen-9公司 |
| CN201811377712.X | 2018 | 利用酿酒酵母体内组装系统组装和储存长序列,同时设强纠错系统 | 天津大学 |
| US16/736258 | 2020 | 利用细胞提取物、核酸外切酶、单链结合蛋白的蛋白质组合物等来实现高效的核酸组装 | 赛默飞世尔 |
| US16/879705 | 2020 | 利用核酸内切酶、核酸外切酶、聚合酶和连接酶的组合来组装核酸 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| PCT/EP2020/060535 | 2020 | 在多个反应室中将两个或更多个预定核酸片段多重组装 | 赛默飞世尔 |
代表性专利① (申请号) | 申请年 | 技术内容 | 当前申请 (专利权)人 |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/565372 | 2016 | 集核酸合成、核酸测序和计算机设备于一体的存储系统 | 华盛顿大学 |
| US15/394484 | 2016 | 利用控制器对封装有DNA数据的液滴进行控制 | 英特尔公司 |
| US15/625998 | 2017 | 在多核苷酸序列的日志中创建时间记录 | 微软 |
| US15/427808 | 2017 | 提高存储在多核苷酸序列数据存储系统中数据的随机访问的准确性 | 微软 |
| US15/431897 | 2017 | 向多核苷酸添加取代原始校准区域的序列来修饰校准区域 | 华盛顿大学、微软 |
| PCT/US2017/029751 | 2017 | 将真实信息单链核酸、假单链核酸结合形成核酸混合物,从而保障基于核酸的安全通信 | 哈佛大学 |
| US15/427344 | 2017 | 比较引物靶序列和有效载荷序列,使引物靶序列的区域、有效载荷序列的区域有大于阈值的相似性 | 微软 |
| CN201880026589.9 | 2018 | 信息的生物加密或生物解密 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US16/017714 | 2018 | 数据存储介质包括干燥产物,保护DNA免受降解 | 微软 |
| PCT/US2018/056900 | 2018 | 确定核苷酸序列,鉴定序列中核苷酸之间的转换或边界,将预定值分配给所鉴定的转变或边界,以产生对应序列中的编码值 | 哈佛大学 |
| EP2018779622 | 2018 | 编码信息的方法中,根据核酸的多态特征生成加密密钥,将加密信息编码成合成DNA | 苏黎世联邦理工学院 |
| PCT/GB2019/053669 | 2019 | 多核苷酸链移动通过纳米反应器时,对其进行选择性修饰 | 牛津纳米孔科技公司 |
| PCT/US2019/058414 | 2019 | 数据存储介质包括二维(2D)支撑结构(金属箔,玻璃或塑料),人工合成的、编码数字信息的DNA分子置于其上,而整个结构置于非反应性材料(例如二氧化硅)或金属薄层的保护层中,以保护DNA免受降解;同时,设有可寻址的特定数字信息 | 微软 |
| IL277102 | 2020 | 索引信息被添加到多个DNA片段 | 欧洲分子生物学实验室 |
| PCT/US2020/032384 | 2020 | 用优化的数据结构和功能,搜索和提取DNA中存储的数据 | Catalog公司 |
Tab. 4 Representative patents of DNA storage
代表性专利① (申请号) | 申请年 | 技术内容 | 当前申请 (专利权)人 |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/565372 | 2016 | 集核酸合成、核酸测序和计算机设备于一体的存储系统 | 华盛顿大学 |
| US15/394484 | 2016 | 利用控制器对封装有DNA数据的液滴进行控制 | 英特尔公司 |
| US15/625998 | 2017 | 在多核苷酸序列的日志中创建时间记录 | 微软 |
| US15/427808 | 2017 | 提高存储在多核苷酸序列数据存储系统中数据的随机访问的准确性 | 微软 |
| US15/431897 | 2017 | 向多核苷酸添加取代原始校准区域的序列来修饰校准区域 | 华盛顿大学、微软 |
| PCT/US2017/029751 | 2017 | 将真实信息单链核酸、假单链核酸结合形成核酸混合物,从而保障基于核酸的安全通信 | 哈佛大学 |
| US15/427344 | 2017 | 比较引物靶序列和有效载荷序列,使引物靶序列的区域、有效载荷序列的区域有大于阈值的相似性 | 微软 |
| CN201880026589.9 | 2018 | 信息的生物加密或生物解密 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US16/017714 | 2018 | 数据存储介质包括干燥产物,保护DNA免受降解 | 微软 |
| PCT/US2018/056900 | 2018 | 确定核苷酸序列,鉴定序列中核苷酸之间的转换或边界,将预定值分配给所鉴定的转变或边界,以产生对应序列中的编码值 | 哈佛大学 |
| EP2018779622 | 2018 | 编码信息的方法中,根据核酸的多态特征生成加密密钥,将加密信息编码成合成DNA | 苏黎世联邦理工学院 |
| PCT/GB2019/053669 | 2019 | 多核苷酸链移动通过纳米反应器时,对其进行选择性修饰 | 牛津纳米孔科技公司 |
| PCT/US2019/058414 | 2019 | 数据存储介质包括二维(2D)支撑结构(金属箔,玻璃或塑料),人工合成的、编码数字信息的DNA分子置于其上,而整个结构置于非反应性材料(例如二氧化硅)或金属薄层的保护层中,以保护DNA免受降解;同时,设有可寻址的特定数字信息 | 微软 |
| IL277102 | 2020 | 索引信息被添加到多个DNA片段 | 欧洲分子生物学实验室 |
| PCT/US2020/032384 | 2020 | 用优化的数据结构和功能,搜索和提取DNA中存储的数据 | Catalog公司 |
代表性专利① (申请号) | 申请年 | 技术内容 | 当前申请(专利权)人 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2016/031674 | 2016 | 在核酸扩增产物的有效除去非靶核酸序列(例如引物序列) | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US15/156134 | 2016 | 无细胞的核酸克隆 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US15/259420 | 2016 | 在DNA合成中,对恶意序列进行检测 | SAP公司 |
| US16/098471 | 2016 | 对存储中的由GC含量和DNA序列的碱基重复率的参数加以控制,使DNA序列中GC含量为45%~60%,且不超过2个连续的单碱基存在 | 华大基因 |
| US15/607364 | 2017 | 碱基检出算法用于分析原始数据,并可识别碱基在多核苷酸链上的给定位置 | 微软 |
| CN201810986270.2 | 2018 | 在将数字信息转换成核酸序列时,在保障碱基的存储密度及编码效率的前提下,控制GC含量的比例,提高存储的效率 | 华为技术有限公司 |
| US16/759282 | 2018 | 用于预测合成和组装多核苷酸的可行性的软件工具,通过分析GC含量等参数对多核苷酸进行评分 | Twist生物科学公司 |
Tab. 5 Other representative patents
代表性专利① (申请号) | 申请年 | 技术内容 | 当前申请(专利权)人 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2016/031674 | 2016 | 在核酸扩增产物的有效除去非靶核酸序列(例如引物序列) | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US15/156134 | 2016 | 无细胞的核酸克隆 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| US15/259420 | 2016 | 在DNA合成中,对恶意序列进行检测 | SAP公司 |
| US16/098471 | 2016 | 对存储中的由GC含量和DNA序列的碱基重复率的参数加以控制,使DNA序列中GC含量为45%~60%,且不超过2个连续的单碱基存在 | 华大基因 |
| US15/607364 | 2017 | 碱基检出算法用于分析原始数据,并可识别碱基在多核苷酸链上的给定位置 | 微软 |
| CN201810986270.2 | 2018 | 在将数字信息转换成核酸序列时,在保障碱基的存储密度及编码效率的前提下,控制GC含量的比例,提高存储的效率 | 华为技术有限公司 |
| US16/759282 | 2018 | 用于预测合成和组装多核苷酸的可行性的软件工具,通过分析GC含量等参数对多核苷酸进行评分 | Twist生物科学公司 |
| 1 | 陈大明, 刘晓, 范月蕾,等. 从全球专利分析看合成生物学技术发展趋势[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(3): 372-384. |
| CHEN D M, LIU X, FAN Y L, et al. A global patent analysis: trends in DNA synthesis and information storage[J]. 2020, 1(3): 372-384. | |
| 2 | MICHELSON A M, TODD A R. Nucleotides part XXXII. Synthesis of a dithymidine dinucleotide containing a 3′, 5′-internucleotidic linkage[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, 1955(8):2632-2638. |
| 3 | SCHEUERBRANDT G, DUFFIELD A M, NUSSBAUM A L. Stepwise synthesis of deoxyribo-oligonucleotides[J]. Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications, 1963, 11(2):152-155. |
| 4 | KHORANA H G, BÜCHI H, CARUTHERS M H, et al. Progress in the total synthesis of the gene for ala-tRNA[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology, 1968, 33: 35. |
| 5 | AGARWAL K L, KUMAR A, KHORANA H G. CIX. Total synthesis of the structural gene for an alanine transfer ribonucleic acid from yeast. Synthesis of a dodecadeoxynucleotide and a decadeoxynucleotide corresponding to the nucleotide sequence 46 to 65[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1972, 72(2): 351-371. |
| 6 | BÜCHI H, KHORANA H G. CV. Total synthesis of the structural gene for an alanine transfer ribonucleic acid from yeast. Chemical synthesis of an icosadeoxyribonucleotide corresponding to the nucleotide sequence 31 to 50[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1972, 72(2): 251-288. |
| 7 | BEAUCAGE S L, CARUTHERS M H. Deoxynucleoside phosphoramidites-A new class of key intermediates for deoxypolynucleotide synthesis[J]. Cheminform, 1981, 22(20): 1859-1862. |
| 8 | 赵国屏. 合成生物学——革命性的新兴交叉学科,“会聚”研究范式的典型[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2015, 45(10): 905-908. |
| ZHAO G P. Synthetic biology: a revolutionary new interdisciplinary discipline and a typical "convergence" research paradigm[J]. SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences, 2015, 45(10): 905-908. | |
| 9 | SAINI N, RAMAKRISHNAN S, ELANGO R, et al. Migrating bubble during break-induced replication drives conservative DNA synthesis.[J]. Nature, 2013, 502(7471): 389-392. |
| 10 | KOSURI S, CHURCH G M. Large-scale de novo DNA synthesis: technologies and applications[J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(5): 499-507. |
| 11 | SAAEM I, MA K S, MARCHI A N, et al. In situ synthesis of DNA microarray on functionalized cyclic olefin copolymer substrate.[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2010, 2(2): 491-497. |
| 12 | KIM C C, JOYCE E A, CHAN K, et al. Improved analytical methods for microarray-based genome-composition analysis[J]. Genome Biology, 2002, 3(11): 0065. |
| 13 | GUNDERSON K L, STEEMERS F J, LEE G, et al. A genome-wide scalable SNP genotyping assay using microarray technology.[J]. Nature Genetics, 2005, 37: 549-554. |
| 14 | PAUL S S, TRABELSI H, YASEEN Y, et al. Microbial cell factories engineering for production of biomolecules[M]. Mehsana, Gujarat, India: Academic Press, 2021. |
| 15 | LI S, ZHAO G, JIN W. Enabling technologies in synthetic biology—DNA synthesis, assembly and editing[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 33(3): 343-360. |
| 16 | MEISER L C, KOCH J, ANTKOWIAK P L, et al. DNA synthesis for true random number generation[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5869. |
| 17 | SELBERG J, MARCELLA G, ROLANDI M, et al. The potential for convergence between Synthetic Biology and Bioelectronics[J]. Cell Systems, 2018, 7(3): 231-244. |
| 18 | ZHIRNOV V V, RASIC D. 2018 semiconductor synthetic biology roadmap[R]. Durham: Semiconductor Research Corporation, 2018. |
| 19 | SONG X P, BOUILLON C, LESCRINIER E,et al. Dipeptides as leaving group in the enzyme-catalyzed DNA synthesis[J]. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 2012, 9(12): 2685-2700. |
| 20 | CHURCH G M, GAO Y, KOSURI S. Next-generation digital information storage in DNA[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6102): 1628. |
| 21 | SHIPMAN S L, NIVALA J, MACKLIS J D, et al. Molecular recordings by directed CRISPR spacer acquisition[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6298): aaf1175. |
| 22 | SHIPMAN S L, NIVALA J, MACKLIS J D, et al. CRISPR-Cas encoding of a digital movie into the genomes of a population of living bacteria[J]. Nature, 2017, 547(7663): 345-349. |
| 23 | GOLDMAN N, BERTONE P, CHEN S, et al. Towards practical, high-capacity, low-maintenance information storage in synthesized DNA[J]. Nature, 2013, 494(7435): 77-80. |
| 24 | ERLICH Y, ZIELINSKI D. DNA Fountain enables a robust and efficient storage architecture[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6328): 950-954. |
| 25 | Potomac Institute for Policy Studies. The future of DNA data storage[R]. Arlington: Potomac Institute for Policy Studies, 2018. |
| 26 | PLUMMER D, HILL J, SALLAM R, et al. Top Strategic Predictions for 2020 and Beyond[R]. Stamford: Gartner Inc, 2020. |
| [1] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xuanliang, LI Qingting, WANG Fei. Data writing in DNA storage systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1125-1141. |
| [3] | HUANG Xiaoluo, DAI Junbiao. DNA synthesis technology: foundation of DNA data storage [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 335-353. |
| [4] | YAN Han, XIAO Pengfeng, LIU Quanjun, LU Zuhong. In situ chemical synthesis of DNA microarrays [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 354-370. |
| [5] | HAN Mingzhe, CHEN Weigang, SONG Lifu, LI Bingzhi, YUAN Yingjin. DNA information storage: bridging biological and digital world [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 309-322. |
| [6] | DONG Yiming, SUN Fajia, WU Ruijun, QIAN Long. Research progress on DNA molecules for digital information storage [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 323-334. |
| [7] | GAO Yanmin, TANG Mengtong, LIU Qian, QIAO Hongyan, WANG Taoxue, QI Hao. The pivotal biochemical methods in DNA data storage [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 384-398. |
| [8] | PENG Kai, LU Xiaoyun, CHENG Jian, LIU Ying, JIANG Huifeng, GUO Xiaoxian. Advances in technologies for de novo DNA synthesis, assembly and error correction [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(6): 697-708. |
| [9] | Daming CHEN, Guangming ZHOU, Xiao LIU, Yuelei FAN, Yue WANG, Kaiyun MAO, Xuebo ZHANG, Yan XIONG. Analysis of global patents for the trend of synthetic biology inventions [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(3): 372-384. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||