Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (2): 302-319.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-063
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
DNA nanotechnology and synthetic biology
SHI Qian, WU Yuanyuan, YANG yang
- Institute of Molecular Medicine,Renji Hospital,School of Medicine,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 200127,China
-
Received:2021-06-04Revised:2021-10-24Online:2022-05-11Published:2022-04-30 -
Contact:YANG yang
DNA纳米技术与合成生物学
施茜, 吴园园, 杨洋
- 上海交通大学医学院附属仁济医院,分子医学研究院,上海 200127
-
通讯作者:杨洋 -
作者简介:施茜 (1988—),女,博士后。研究方向为基于核酸纳米结构的药物递送。 E-mail:sshiqian@hotmail.com杨洋 (1983—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为核酸纳米自组装与磷脂膜工程,核酸信息存储与计算。 E-mail:yang.yang.nano@sjtu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0902600);国家自然科学基金(NSF21977069)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SHI Qian, WU Yuanyuan, YANG yang. DNA nanotechnology and synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(2): 302-319.
施茜, 吴园园, 杨洋. DNA纳米技术与合成生物学[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(2): 302-319.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2021-063
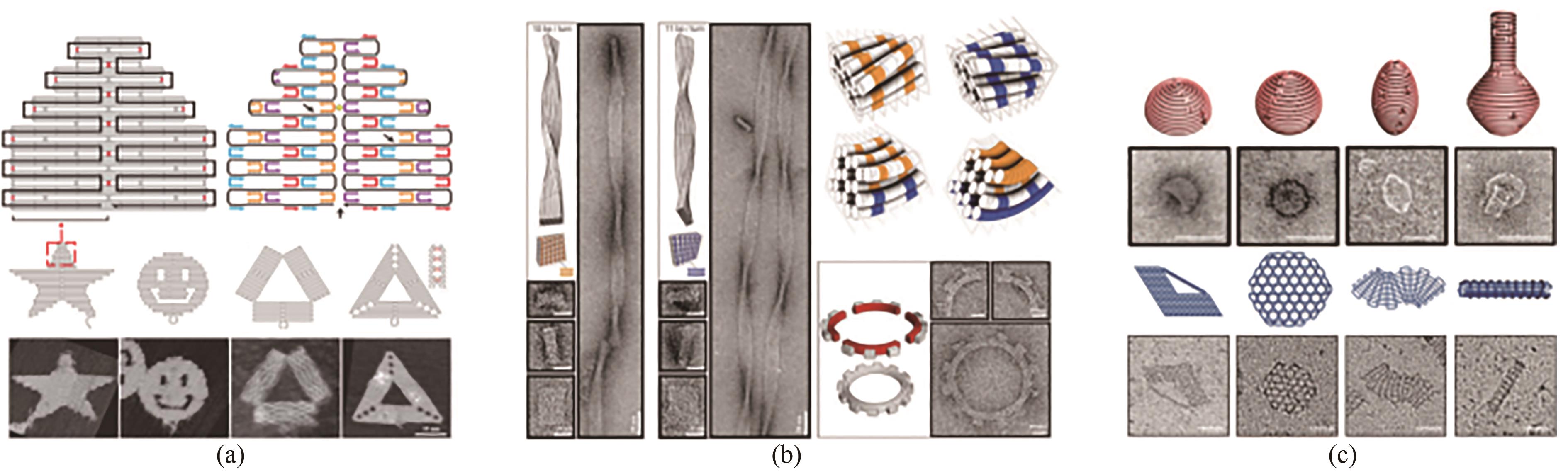
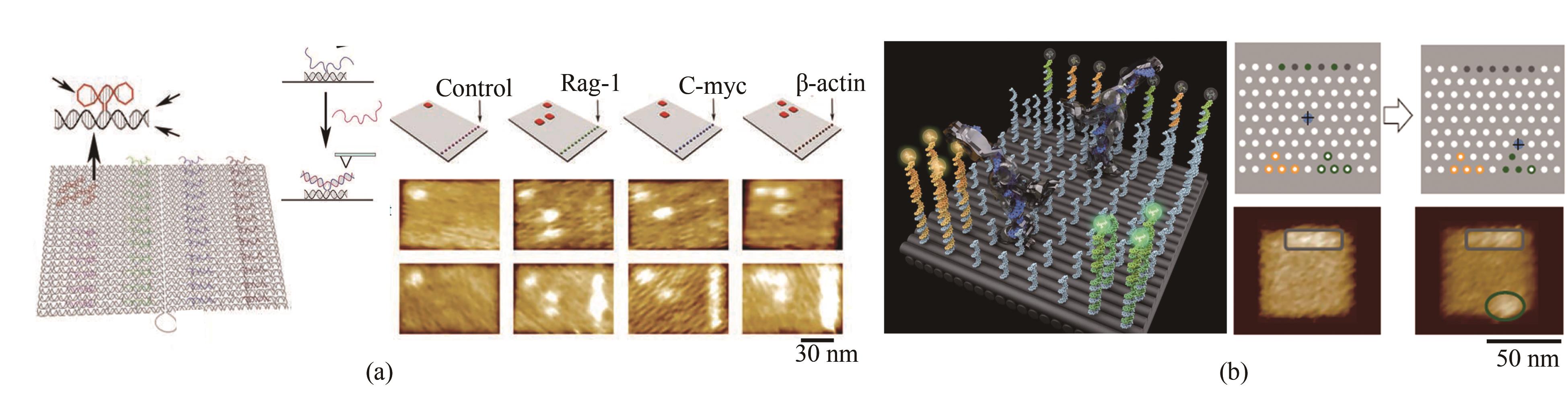
Fig. 2 Basic principle of DNA origami and its development (Scale bar: 50 nm)(a) Principle for the 2D assembly of DNA origami[9]; (b) 3D structure assembly with the bending control[11]; (c) Design for curved surface and DNA gridiron[12-13]
| 根据结合方式分类 | DNA修饰 | 蛋白修饰 | 优点 | 缺点 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非共价偶联 | 生物素-链亲和素[ | 生物素 | 链亲和素 | ①具有可逆性; | 结合不稳定 |
| Ni-NTA-Histag[ | NTA | Histag | ②可进行定点定位修饰 | ||
| 抗体-抗原[ | 抗原 | 抗体 | |||
| 核酸适配体-蛋白[ | 核酸适配体 | — | |||
| DNA结合蛋白[ | 特异的dsDNA | 锌指蛋白 | |||
| RNA-病毒蛋白[ | RNA | 病毒蛋白 | |||
| DNA-衣壳蛋白[ | — | 衣壳蛋白 | |||
| 共价偶联 | √非特异性 | ①结合较稳定; | 结合位点不易控制 | ||
| SPDP[ | 氨基 | 半胱氨酸残基 | ②反应温和,步骤简单 | ||
| Sulfo-SMCC[ | 氨基 | 半胱氨酸残基 | |||
| √特异性 | |||||
| SNAP-tag[ | O6-烷基鸟嘌呤 | SNAP-tag | ①结合较稳定; | 需要进行蛋白质工程 | |
| Halo-tag[ | 5-氯已烷 | Halo-tag | ②可控制结合位点 | 操作较复杂 |
Tab. 1 Classification of protein assembly
| 根据结合方式分类 | DNA修饰 | 蛋白修饰 | 优点 | 缺点 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非共价偶联 | 生物素-链亲和素[ | 生物素 | 链亲和素 | ①具有可逆性; | 结合不稳定 |
| Ni-NTA-Histag[ | NTA | Histag | ②可进行定点定位修饰 | ||
| 抗体-抗原[ | 抗原 | 抗体 | |||
| 核酸适配体-蛋白[ | 核酸适配体 | — | |||
| DNA结合蛋白[ | 特异的dsDNA | 锌指蛋白 | |||
| RNA-病毒蛋白[ | RNA | 病毒蛋白 | |||
| DNA-衣壳蛋白[ | — | 衣壳蛋白 | |||
| 共价偶联 | √非特异性 | ①结合较稳定; | 结合位点不易控制 | ||
| SPDP[ | 氨基 | 半胱氨酸残基 | ②反应温和,步骤简单 | ||
| Sulfo-SMCC[ | 氨基 | 半胱氨酸残基 | |||
| √特异性 | |||||
| SNAP-tag[ | O6-烷基鸟嘌呤 | SNAP-tag | ①结合较稳定; | 需要进行蛋白质工程 | |
| Halo-tag[ | 5-氯已烷 | Halo-tag | ②可控制结合位点 | 操作较复杂 |
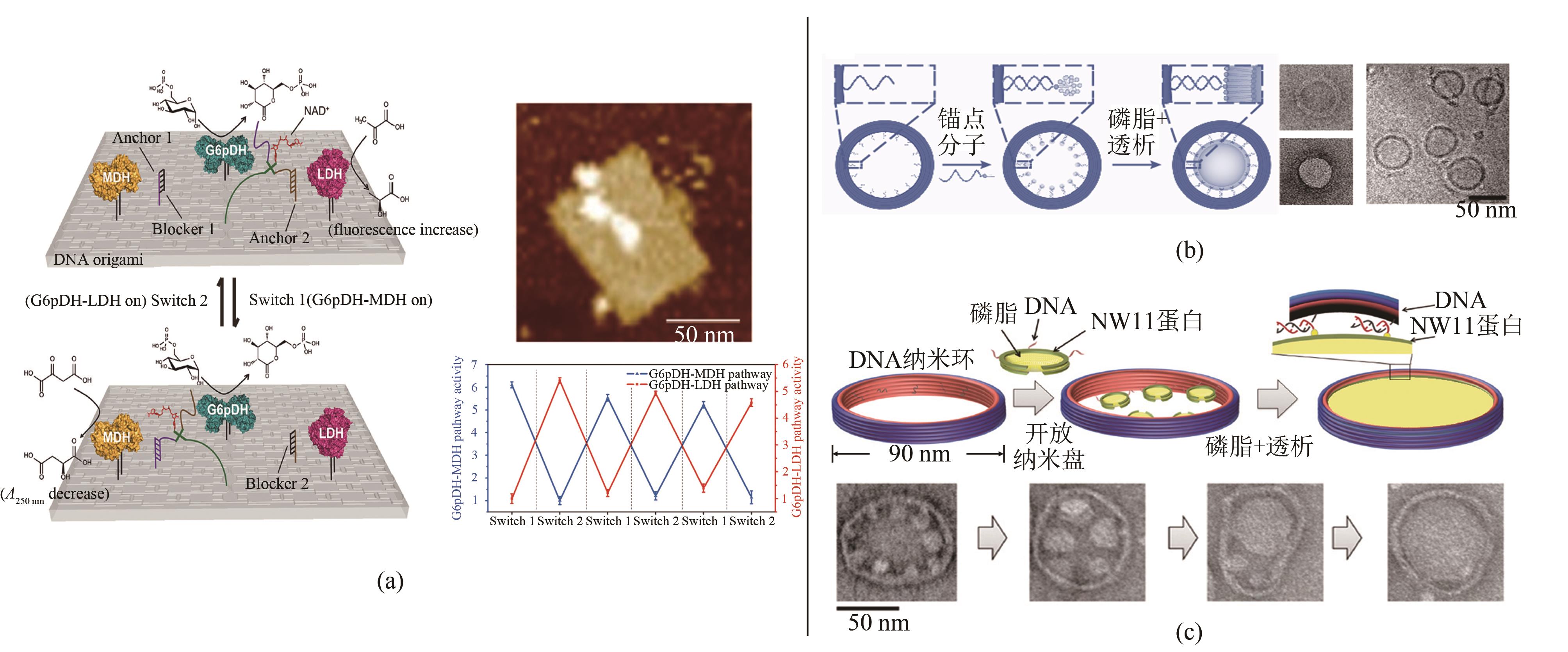
Fig. 4 DNA nanoframe-directed assembly of proteins and phospholipids(a) DNA swing arm and regulation on cascade enzymatic reactions[61]; (b) Vesicles with controllable sizes [62]; (c) Two-dimensional lipid bilayer assembly[64]

Fig. 5 Mimic and construction of cell elements(a) Simulation of the nuclear pore complex [55]; (b) Simulation of cytoskeleton protein and network [70]

Fig. 6 Mimic king biological reactions and biochemical systems(a) Simulation of SNAREs protein-induced membrane fusion[71]; (b) Mimicking BAR protein-induced membrane tubulation [74]; (c) Producing RNA in a nanofactory[75]; (d) Assembly TMV capsid protein on the DNA template [52]; (e) Autonomous regulation of the thrombin dependent coagulation [77]; (f) Simulation of the G-actin movement [78]

Fig. 7 Applications in biomedicines(a) Logic-gate controlled DNA nanorobot[81]; (b) Viral capsid protein modified DNA nanostructure[104]; (c) Virus-inspired membrane-coated DNA nanostructure[105]
| 1 | JACOB F, MONOD J. On the regulation of gene activity[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology, 1961, 26: 193-211. |
| 2 | ELOWITZ M B, LEIBLER S. A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators[J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 335-338. |
| 3 | GARDNER T S, CANTOR C R, COLLINS J J. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 339-342. |
| 4 | FREDENS J, WANG K, DE LA TORRE D, et al. Total synthesis of Escherichia coli with a recoded genome[J]. Nature, 2019, 569(7757): 514-518. |
| 5 | 合成生物学全球初创公司图谱,万亿美金市场现状梳理[R/OL]. CB Insights, 2020. . |
| 6 | GROUP B F, BAKER D, CHURCH G, et al. Engineering life: Building a FAB for biology[J]. Scientific American, 2006, 294(6): 44-51. |
| 7 | SEEMAN N C. Nucleic acid junctions and lattices[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 1982, 99(2): 237-247. |
| 8 | SEEMAN N C, SLEIMAN H F. DNA nanotechnology[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2018, 3: 17068. |
| 9 | ROTHEMUND P W K. Folding DNA to create nanoscale shapes and patterns[J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7082): 297-302. |
| 10 | SANDERSON K. Bioengineering: what to make with DNA origami[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7286): 158-159. |
| 11 | DIETZ H, DOUGLAS S M, SHIH W M. Folding DNA into twisted and curved nanoscale shapes[J]. Science, 2009, 325(5941): 725-730. |
| 12 | HAN D R, PAL S, NANGREAVE J, et al. DNA origami with complex curvatures in three-dimensional space[J]. Science, 2011, 332(6027): 342-346. |
| 13 | HAN D R, PAL S, YANG Y, et al. DNA gridiron nanostructures based on four-arm junctions[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6126): 1412-1415. |
| 14 | Tikhomirov G, Petersen P, Qian L. Fractal assembly of micrometre-scale DNA origami arrays with arbitrary patterns[J]. Nature, 2017, 552(7683): 67. |
| 15 | WAGENBAUER K F, SIGL C, DIETZ H. Gigadalton-scale shape-programmable DNA assemblies[J]. Nature, 2017, 552(7683): 78-83. |
| 16 | YAN H, PARK S H, FINKELSTEIN G, et al. DNA-templated self-assembly of protein arrays and highly conductive nanowires[J]. Science, 2003, 301(5641): 1882-1884. |
| 17 | LIU W Y, ZHONG H, WANG R S, et al. Crystalline two-dimensional DNA-origami arrays[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 123(1): 278-281. |
| 18 | DOUGLAS S M, DIETZ H, LIEDL T, et al. Self-assembly of DNA into nanoscale three-dimensional shapes[J]. Nature, 2009, 459(7245): 414-418. |
| 19 | PRAETORIUS F, DIETZ H. Self-assembly of genetically encoded DNA-protein hybrid nanoscale shapes[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6331): eaam5488. |
| 20 | ZHANG J P, LIU Y, KE Y G, et al. Periodic square-like gold nanoparticle arrays templated by self-assembled 2D DNA Nanogrids on a surface[J]. Nano Letters, 2006, 6(2): 248-251. |
| 21 | LUND K, LIU Y, LINDSAY S, et al. Self-assembling a molecular pegboard[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127(50): 17606-17607. |
| 22 | DONG Y C, YANG Y R, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Cuboid vesicles formed by frame-guided assembly on DNA origami scaffolds[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(6): 1586-1589. |
| 23 | KE Y G, ONG L L, SHIH W M, et al. Three-dimensional structures self-assembled from DNA bricks[J]. Science, 2012, 338(6111): 1177-1183. |
| 24 | ONG L L, HANIKEL N, YAGHI O K, et al. Programmable self-assembly of three-dimensional nanostructures from 10, 000 unique components[J]. Nature, 2017, 552(7683): 72-77. |
| 25 | YAO G, ZHANG F, WANG F, et al. Meta-DNA structures[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2020, 12(11): 1067-1075. |
| 26 | CHANDRAN H, GOPALKRISHNAN N, YURKE B, et al. Meta-DNA: synthetic biology via DNA nanostructures and hybridization reactions[J]. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface, 2012, 9(72): 1637-1653. |
| 27 | YANG Y, ZHANG R, FAN C H. Shaping functional materials with DNA frameworks[J]. Trends in Chemistry, 2020, 2(2): 137-147. |
| 28 | ZHANG Y Y, MAO X H, LI F, et al. Nanoparticle-assisted alignment of carbon nanotubes on DNA origami[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(12): 4892-4896. |
| 29 | PEI H, SHA R J, WANG X W, et al. Organizing end-site-specific SWCNTs in specific loci using DNA[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(30): 11923-11928. |
| 30 | SUN W, SHEN J, ZHAO Z, et al. Precise pitch-scaling of carbon nanotube arrays within three-dimensional DNA nanotrenches[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6493): 874-877. |
| 31 | ATSUMI H, BELCHER A M. DNA origami and G-quadruplex hybrid complexes induce size control of single-walled carbon nanotubes via biological activation[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(8): 7986-7995. |
| 32 | KNUDSEN J B, LIU L, BANK KODAL A L, et al. Routing of individual polymers in designed patterns[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(10): 892-898. |
| 33 | TOKURA Y, HARVEY S, CHEN C J, et al. Fabrication of defined polydopamine nanostructures by DNA origami-templated polymerization[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(6): 1587-1591. |
| 34 | KE Y G, LINDSAY S, CHANG Y, et al. Self-assembled water-soluble nucleic acid probe tiles for label-free RNA hybridization assays[J]. Science, 2008, 319(5860): 180-183. |
| 35 | LIN C, JUNGMANN R, LEIFER A M, et al. Submicrometre geometrically encoded fluorescent barcodes self-assembled from DNA[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2012, 4(10): 832-839. |
| 36 | SEELIG G, SOLOVEICHIK D, ZHANG D Y, et al. Enzyme-free nucleic acid logic circuits[J]. Science, 2006, 314(5805): 1585-1588. |
| 37 | QIAN L L, WINFREE E. Scaling up digital circuit computation with DNA strand displacement cascades[J]. Science, 2011, 332(6034): 1196-1201. |
| 38 | TIKHOMIROV G, PETERSEN P, QIAN L. Programmable disorder in random DNA tilings[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2017, 12(3): 251-259. |
| 39 | PETERSEN P, TIKHOMIROV G, QIAN L. Information-based autonomous reconfiguration in systems of interacting DNA nanostructures[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 5362. |
| 40 | CHERRY K M, QIAN L. Scaling up molecular pattern recognition with DNA-based winner-take-all neural networks[J]. Nature, 2018, 559(7714): 370-376. |
| 41 | WOODS D, DOTY D, MYHRVOLD C, et al. Diverse and robust molecular algorithms using reprogrammable DNA self-assembly[J]. Nature, 2019, 567(7748): 366-372. |
| 42 | SHERMAN W B, SEEMAN N C. A precisely controlled DNA biped walking device[J]. Nano Letters, 2004, 4(7): 1203-1207. |
| 43 | GU H, CHAO J, XIAO S J, et al. A proximity-based programmable DNA nanoscale assembly line[J]. Nature, 2010, 465(7295): 202-205. |
| 44 | TIAN Y, HE Y, CHEN Y, et al. A DNAzyme that walks processively and autonomously along a one-dimensional track[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2005, 44(28): 4355-4358. |
| 45 | LUND K, MANZO A J, DABBY N, et al. Molecular robots guided by prescriptive landscapes[J]. Nature, 2010, 465(7295): 206-210. |
| 46 | THUBAGERE A J, LI W, JOHNSON R F, et al. A cargo-sorting DNA robot[J]. Science, 2017, 357(6356): 1112. |
| 47 | MALLIK L, DHAKAL S, NICHOLS J, et al. Electron microscopic visualization of protein assemblies on flattened DNA origami[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(7): 7133-7141. |
| 48 | SHEN W Q, ZHONG H, NEFF D, et al. NTA directed protein nanopatterning on DNA origami nanoconstructs[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(19): 6660-6661. |
| 49 | YAMAZAKI T, HEDDLE J G, KUZUYA A, et al. Orthogonal enzyme arrays on a DNA origami scaffold bearing size-tunable wells[J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(15): 9122-9126. |
| 50 | CHHABRA R, SHARMA J, KE Y G, et al. Spatially addressable multiprotein nanoarrays templated by aptamer-tagged DNA nanoarchitectures[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(34): 10304-10305. |
| 51 | NGO T A, NAKATA E, SAIMURA M, et al. Spatially organized enzymes drive cofactor-coupled cascade reactions[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(9): 3012-3021. |
| 52 | ZHOU K, KE Y G, WANG Q B. Selective in situ assembly of viral protein onto DNA origami[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(26): 8074-8077. |
| 53 | KOPATZ I, ZALK R, LEVI-KALISMAN Y, et al. Packaging of DNA origami in viral capsids[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(21): 10160-10166. |
| 54 | FU J L, LIU M H, LIU Y, et al. Interenzyme substrate diffusion for an enzyme cascade organized on spatially addressable DNA nanostructures[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(12): 5516-5519. |
| 55 | FISHER P, SHEN Q, AKPINAR B, et al. A programmable DNA origami platform for organizing intrinsically disordered nucleoporins within nanopore confinement[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(2): 1508-1518. |
| 56 | NAKATA E, DINH H, NGO T A, et al. A modular zinc finger adaptor accelerates the covalent linkage of proteins at specific locations on DNA nanoscaffolds[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(6): 1016-1019. |
| 57 | KOßMANN K J, ZIEGLER C, ANGELIN A, et al. A rationally designed connector for assembly of protein-functionalized DNA nanostructures[J]. ChemBioChem, 2016, 17(12): 1102-1106. |
| 58 | VOIGT N V, TØRRING T, ROTARU A, et al. Single-molecule chemical reactions on DNA origami[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2010, 5(3): 200-203. |
| 59 | RINKER S, KE Y G, LIU Y, et al. Self-assembled DNA nanostructures for distance-dependent multivalent ligand-protein binding[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2008, 3(7): 418-422. |
| 60 | FU J, YANG Y R, JOHNSON-BUCK A, et al. Multi-enzyme complexes on DNA scaffolds capable of substrate channelling with an artificial swinging arm[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2014, 9(7): 531-536. |
| 61 | KE G L, LIU M H, JIANG S X, et al. Directional regulation of enzyme pathways through the control of substrate channeling on a DNA origami scaffold[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 128(26): 7609-7612. |
| 62 | YANG Y, WANG J, SHIGEMATSU H, et al. Self-assembly of size-controlled liposomes on DNA nanotemplates[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2016, 8(5): 476-483. |
| 63 | ZHANG Z, YANG Y, PINCET F, et al. Placing and shaping liposomes with reconfigurable DNA nanocages[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2017, 9(7): 653-659. |
| 64 | ZHAO Z, ZHANG M, HOGLE J M, et al. DNA-corralled nanodiscs for the structural and functional characterization of membrane proteins and viral entry[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(34): 10639-10643. |
| 65 | KETTERER P, ANANTH A N, LAMAN TRIP D S, et al. DNA origami scaffold for studying intrinsically disordered proteins of the nuclear pore complex[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 902. |
| 66 | LANGECKER M, ARNAUT V, MARTIN T G, et al. Synthetic lipid membrane channels formed by designed DNA nanostructures[J]. Science, 2012, 338(6109): 932-936. |
| 67 | LÜ C, GU X Y, LI H W, et al. Molecular transport through a biomimetic DNA channel on live cell membranes[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(11): 14616-14626. |
| 68 | LANPHERE C, OFFENBARTL-STIEGERT D, DOREY A, et al. Design, assembly, and characterization of membrane-spanning DNA nanopores[J]. Nature Protocols, 2021, 16(1): 86-130. |
| 69 | DOHERTY G J, MCMAHON H T. Mechanisms of endocytosis[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2009, 78: 857-902. |
| 70 | JOURNOT C M A, RAMAKRISHNA V, WALLACE M I, et al. Modifying membrane morphology and interactions with DNA origami clathrin-mimic networks[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(9): 9973-9979. |
| 71 | XU W M, NATHWANI B, LIN C X, et al. A programmable DNA origami platform to organize SNAREs for membrane fusion[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(13): 4439-4447. |
| 72 | BIAN X, ZHANG Z, XIONG Q C, et al. A programmable DNA-origami platform for studying lipid transfer between bilayers[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(8): 830-837 |
| 73 | FROST A, UNGER V M, DE CAMILLI P. The BAR domain superfamily: membrane-molding macromolecules[J]. Cell, 2009, 137(2): 191-196. |
| 74 | GROME M W, ZHANG Z, PINCET F, et al. Vesicle tubulation with self-assembling DNA nanosprings[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(19): 5330-5334. |
| 75 | HAHN J, CHOU L Y T, SØRENSEN R S, et al. Extrusion of RNA from a DNA-origami-based nanofactory[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(2): 1550-1559. |
| 76 | ZHOU K, ZHOU Y H, PAN V, et al. Programming dynamic assembly of viral proteins with DNA origami[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(13): 5929-5932. |
| 77 | YANG L L, ZHAO Y M, XU X M, et al. An intelligent DNA nanorobot for autonomous anticoagulation[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(40): 17697-17704. |
| 78 | FUJITA K, OHMACHI M, IKEZAKI K, et al. Direct visualization of human myosin II force generation using DNA origami-based thick filaments[J]. Communications Biology, 2019, 2: 437. |
| 79 | ANGELL C, XIE S B, ZHANG L F, et al. DNA nanotechnology for precise control over drug delivery and gene therapy[J]. Small, 2016, 12(9): 1117-1132. |
| 80 | HU Q Q, LI H, WANG L H, et al. DNA nanotechnology-enabled drug delivery systems[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(10): 6459-6506. |
| 81 | DOUGLAS S M, BACHELET I, CHURCH G M. A logic-gated nanorobot for targeted transport of molecular payloads[J]. Science, 2012, 335(6070): 831-834. |
| 82 | AGUDELO D, BOURASSA P, BÉRUBÉ G, et al. Intercalation of antitumor drug doxorubicin and its analogue by DNA duplex: Structural features and biological implications[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2014, 66: 144-150. |
| 83 | KIM K R, KIM D R, LEE T, et al. Drug delivery by a self-assembled DNA tetrahedron for overcoming drug resistance in breast cancer cells[J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(20): 2010. |
| 84 | NAITO Y, UI-TEI K. siRNA design software for a target gene-specific RNA interference[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2012, 3: 102. |
| 85 | GUO P X, COBAN O, SNEAD N M, et al. Engineering RNA for targeted siRNA delivery and medical application[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2010, 62(6): 650-666. |
| 86 | LEE H, LYTTON-JEAN A K R, CHEN Y, et al. Molecularly self-assembled nucleic acid nanoparticles for targeted in vivo siRNA delivery[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2012, 7(6): 389-393. |
| 87 | RAHMAN M A, WANG P F, ZHAO Z X, et al. Systemic delivery of Bc12-targeting siRNA by DNA nanoparticles suppresses cancer cell growth[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(50): 16023-16027. |
| 88 | LIU J B, SONG L L, LIU S L, et al. A DNA-based nanocarrier for efficient gene delivery and combined cancer therapy[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 18(6): 3328-3334. |
| 89 | JIANG Q, SHI Y F, ZHANG Q, et al. A self-assembled DNA origami-gold nanorod complex for cancer theranostics[J]. Small, 2015, 11(38): 5134-5141. |
| 90 | WANG P F, RAHMAN M A, ZHAO Z X, et al. Visualization of the cellular uptake and trafficking of DNA origami nanostructures in cancer cells[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(7): 2478-2484. |
| 91 | GE Z L, GUO L J, WU G Q, et al. DNA origami-enabled engineering of ligand-drug conjugates for targeted drug delivery[J]. Small, 2020, 16(16): 1904857. |
| 92 | RANIOLO S, VINDIGNI G, OTTAVIANI A, et al. Selective targeting and degradation of doxorubicin-loaded folate-functionalized DNA nanocages[J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2018, 14(4): 1181-1190. |
| 93 | VINDIGNI G, RANIOLO S, OTTAVIANI A, et al. Receptor-mediated entry of pristine octahedral DNA nanocages in mammalian cells[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(6): 5971-5979. |
| 94 | LIANG L, LI J, LI Q, et al. Single-particle tracking and modulation of cell entry pathways of a tetrahedral DNA nanostructure in live cells[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(30): 7745-7750. |
| 95 | KEUM J W, AHN J H, Design BERMUDEZ H., assembly, and activity of antisense DNA nanostructures[J]. Small, 2011, 7(24): 3529-3535. |
| 96 | BURNS J R, LAMARRE B, PYNE A L B, et al. DNA origami inside-out viruses[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(3): 767-773. |
| 97 | LIU K, XU C, LIU J Y. Regulation of cell binding and entry by DNA origami mediated spatial distribution of aptamers[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2020, 8(31): 6802-6809. |
| 98 | BHATIA D, ARUMUGAM S, NASILOWSKI M, et al. Quantum dot-loaded monofunctionalized DNA icosahedra for single-particle tracking of endocytic pathways[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2016, 11(12): 1112-1119. |
| 99 | XIA K, KONG H T, CUI Y Z, et al. Systematic study in mammalian cells showing no adverse response to tetrahedral DNA nanostructure[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(18): 15442-15448. |
| 100 | BASTINGS M M C, ANASTASSACOS F M, PONNUSWAMY N, et al. Modulation of the cellular uptake of DNA origami through control over mass and shape[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 18(6): 3557-3564. |
| 101 | ZENG Y, LIU J J, YANG S, et al. Time-lapse live cell imaging to monitor doxorubicin release from DNA origami nanostructures[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2018, 6(11): 1605-1612. |
| 102 | KIM K R, LEE T, KIM B S, et al. Correction: Utilizing the bioorthogonal base-pairing system of l-DNA to design ideal DNA nanocarriers for enhanced delivery of nucleic acid cargos[J]. Chemical Science, 2015, 6(3): 2122. |
| 103 | LI Q S, ZHAO D, SHAO X R, et al. Aptamer-modified tetrahedral DNA nanostructure for tumor-targeted drug delivery[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(42): 36695-36701. |
| 104 | MIKKILÄ J, ESKELINEN A P, NIEMELÄ E H, et al. Virus-encapsulated DNA origami nanostructures for cellular delivery[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(4): 2196-2200. |
| 105 | PERRAULT S D, SHIH W M. Virus-inspired membrane encapsulation of DNA nanostructures to achieve in vivo stability[J]. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(5): 5132-5140. |
| 106 | MA W J, ZHAN Y X, ZHANG Y X, et al. An intelligent DNA nanorobot with in vitro enhanced protein lysosomal degradation of HER2[J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(7): 4505-4517. |
| 107 | LI S P, JIANG Q, LIU S L, et al. A DNA nanorobot functions as a cancer therapeutic in response to a molecular trigger in vivo [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(3): 258-264. |
| 108 | LIU S L, JIANG Q, ZHAO X, et al. A DNA nanodevice-based vaccine for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Nature Materials, 2021, 20(3): 421-430. |
| [1] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | ZHANG Xuanliang, LI Qingting, WANG Fei. Data writing in DNA storage systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1125-1141. |
| [12] | CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [13] | CAI Bingyu, TAN Xiangtian, LI Wei. Advances in synthetic biology for engineering stem cell [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [14] | XIE Huang, ZHENG Yilei, SU Yiting, RUAN Jingyi, LI Yongquan. An overview on reconstructing the biosynthetic system of actinomycetes for polyketides production [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [15] | ZHA Wenlong, BU Lan, ZI Jiachen. Advances in synthetic biology for producing potent pharmaceutical ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||