Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (4): 638-657.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-032
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Biosynthesis of high-performance protein materials and their applications
LI Jingjing1, MA Chao2, WANG Fan1, ZHANG Hongjie1,2, LIU Kai1,2
- 1.The Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry (CIAC),Chinese Academy of Sciences,Changchun 130022,Jilin,China
2.The Department of Chemistry,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
-
Received:2022-06-01Revised:2022-07-18Online:2022-09-08Published:2022-08-31 -
Contact:LIU Kai
生物合成高性能蛋白及材料应用
李敬敬1, 马超2, 王帆1, 张洪杰1,2, 刘凯1,2
- 1.中国科学院长春应用化学研究所,吉林 长春 130022
2.清华大学化学系,北京 100084
-
通讯作者:刘凯 -
作者简介:李敬敬 (1990—),女,博士,副研究员,主要研究方向为蛋白分子的定向改造、蛋白材料的构建与应用。E-mail:jjingli@ciac.ac.cn刘凯 (1983—),男,博士,研究员/教授,主要研究方向为高性能生物大分子(核酸、蛋白)材料、生物-稀土杂化材料的合成与应用。E-mail:kailiu@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(22125701)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Jingjing, MA Chao, WANG Fan, ZHANG Hongjie, LIU Kai. Biosynthesis of high-performance protein materials and their applications[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(4): 638-657.
李敬敬, 马超, 王帆, 张洪杰, 刘凯. 生物合成高性能蛋白及材料应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(4): 638-657.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2022-032

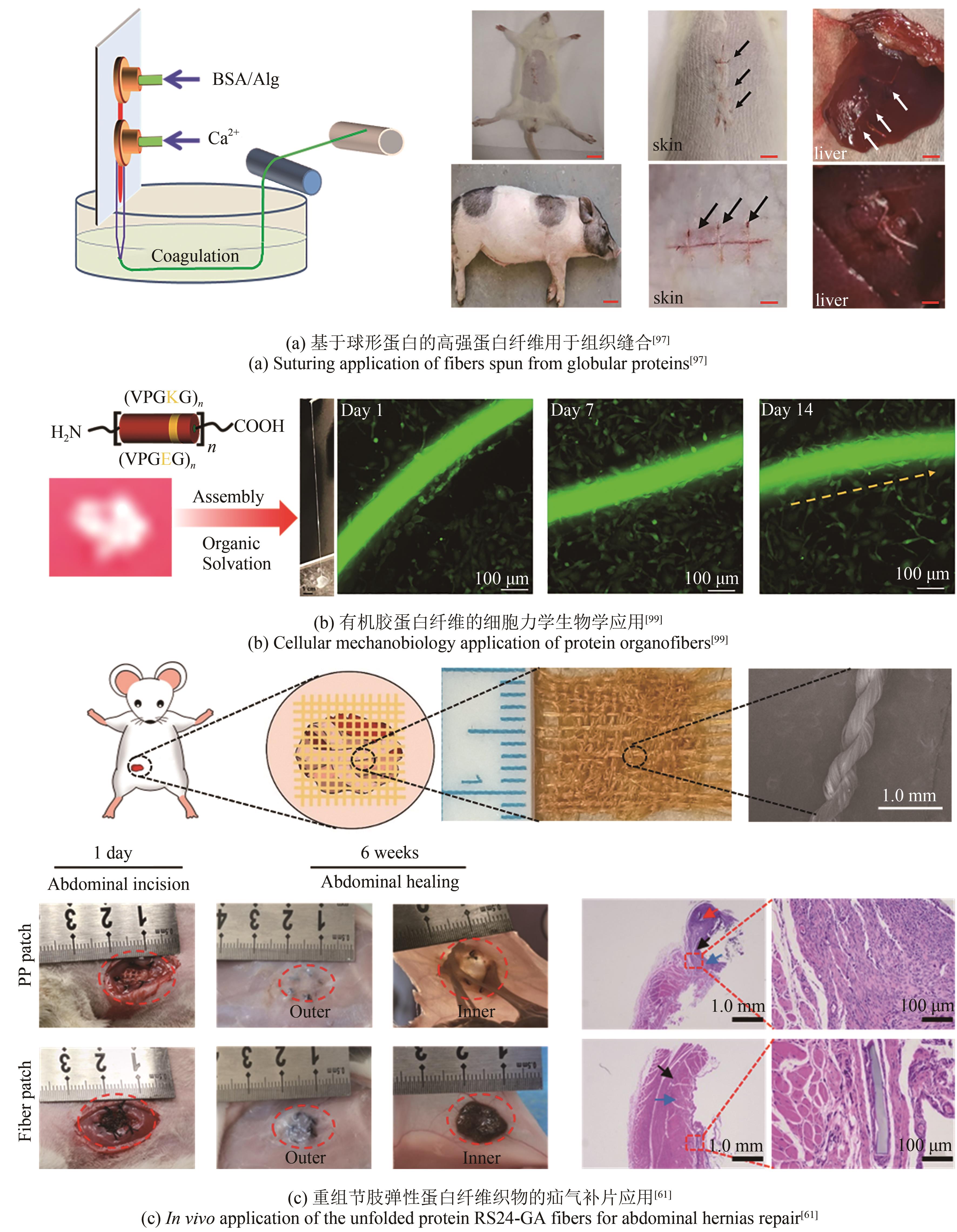
Fig. 3 Non-covalent interactions-mediated assembly of the recombinant structural proteins(a) Protein self-assembly induced by both C-terminal domain and internal actions among secondary structural elements[71]; (b) Composite assembly of recombinant structural proteins and DNA molecules[61]; (c~d) Composite assembly of supercharged recombinant structural proteins and surfactant molecules[72-73]
| 序号 | 蛋白 | 氨基酸序列 | 修饰方法 | 材料性能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 蓑衣虫丝蛋白 | (A) n -(GA) n -Linker-(GAGAGS) n | 天然蛋白 | 拉伸强度2.0 GPa,韧性364 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 2 | 重组鱿鱼环齿蛋白 | (PAATAVSHTTHHAP) [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 不同折叠结构的基序重组 | 拉伸强度650 MPa,韧性120 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 3 | 重组蛛丝蛋白 | [(GGX) n FGAILSS]128 | 不同折叠结构的基序重组与多聚化 | 拉伸强度0.98 GPa,韧性161 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 4 | 重组蛛丝蛋白 | [An(GGX) n ]192 | 蛋白共价组装 | 拉伸强度1.03 GPa,韧性114 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 5 | 重组节肢弹性蛋白 | (VGSGGRPSDSYGAPGGGNP) [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 蛋白-海藻酸盐复合 | 拉伸强度768 MPa,模量24 MPa, 韧性52 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 重组鱿鱼环齿蛋白 | (PAATAVSHTTHHAP) [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 拉伸强度606 MPa,韧性69 MJ/m3 | |||
| 6 | 重组蛛丝蛋白 | NTD-[A n (GGX) n ]-CTD | 蛋白非共价组装 | 拉伸强度834 MPa,韧性143 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 7 | 重组节肢弹性蛋白 | (VGSGGRPSDSYGAPGGGNP) [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 蛋白-DNA复合 | 韧性250 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 8 | 重组类弹性蛋白 | [(VPGVG)20pAzF]4 | 非天然氨基酸定点修饰 | 光交联反应活性 | [ |
| 9 | 重组贻贝足丝蛋白 | Mfp5-CsgA | 不同生物功能的基序进行重组 | 水下黏合性能20.9 mJ/m2 | [ |
| 10 | 重组类弹性蛋白 | [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 蛋白-表面活性剂复合 | 黏合性能16.5 MPa | [ |
| 11 | 重组类弹性蛋白 | [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 蛋白-表面活性剂-金属离子复合 | 黏合性能16 MPa | [ |
| 12 | 重组类弹性蛋白 | [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 蛋白-表面活性剂-Au复合 | 黏合性能20 MPa | [ |
Tab. 1 Properties of high-performance protein fibers and adhesives
| 序号 | 蛋白 | 氨基酸序列 | 修饰方法 | 材料性能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 蓑衣虫丝蛋白 | (A) n -(GA) n -Linker-(GAGAGS) n | 天然蛋白 | 拉伸强度2.0 GPa,韧性364 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 2 | 重组鱿鱼环齿蛋白 | (PAATAVSHTTHHAP) [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 不同折叠结构的基序重组 | 拉伸强度650 MPa,韧性120 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 3 | 重组蛛丝蛋白 | [(GGX) n FGAILSS]128 | 不同折叠结构的基序重组与多聚化 | 拉伸强度0.98 GPa,韧性161 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 4 | 重组蛛丝蛋白 | [An(GGX) n ]192 | 蛋白共价组装 | 拉伸强度1.03 GPa,韧性114 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 5 | 重组节肢弹性蛋白 | (VGSGGRPSDSYGAPGGGNP) [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 蛋白-海藻酸盐复合 | 拉伸强度768 MPa,模量24 MPa, 韧性52 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 重组鱿鱼环齿蛋白 | (PAATAVSHTTHHAP) [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 拉伸强度606 MPa,韧性69 MJ/m3 | |||
| 6 | 重组蛛丝蛋白 | NTD-[A n (GGX) n ]-CTD | 蛋白非共价组装 | 拉伸强度834 MPa,韧性143 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 7 | 重组节肢弹性蛋白 | (VGSGGRPSDSYGAPGGGNP) [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 蛋白-DNA复合 | 韧性250 MJ/m3 | [ |
| 8 | 重组类弹性蛋白 | [(VPGVG)20pAzF]4 | 非天然氨基酸定点修饰 | 光交联反应活性 | [ |
| 9 | 重组贻贝足丝蛋白 | Mfp5-CsgA | 不同生物功能的基序进行重组 | 水下黏合性能20.9 mJ/m2 | [ |
| 10 | 重组类弹性蛋白 | [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 蛋白-表面活性剂复合 | 黏合性能16.5 MPa | [ |
| 11 | 重组类弹性蛋白 | [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 蛋白-表面活性剂-金属离子复合 | 黏合性能16 MPa | [ |
| 12 | 重组类弹性蛋白 | [VPGVG(VPGKG) n ] | 蛋白-表面活性剂-Au复合 | 黏合性能20 MPa | [ |
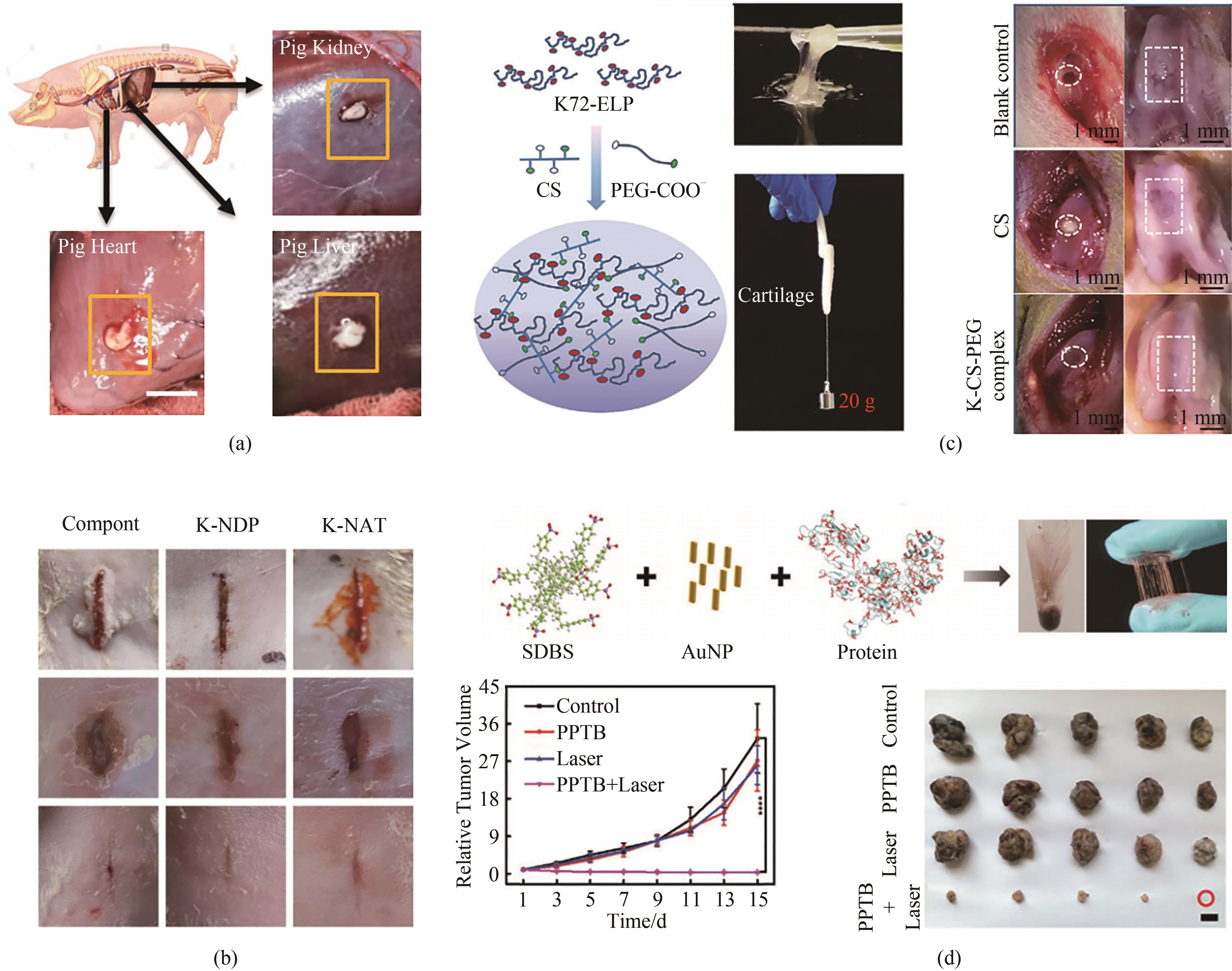
Fig. 6 Applications of high-performance protein adhesives in vivo(a~b) Supercharged ELPs-based adhesive and the applications in hemostasis and wound repair[72-73]; (c) Fabrication of the engineered protein adhesive as a conjoined network and applications in cartilage repair[115]; (d) Fabrication of protein photothermal bioplaster (protein-SDBS-GNRs) and non-invasive skin tumor therapy[88]
| 1 | WEI J J, XU L J, WU W H, et al. Genetically engineered materials: proteins and beyond[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2022, 65(3): 486-496. |
| 2 | HEIM M, KEERL D, SCHEIBEL T. Spider silk: from soluble protein to extraordinary fiber[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(20): 3584-3596. |
| 3 | MARELLI B, PATEL N, DUGGAN T, et al. Programming function into mechanical forms by directed assembly of silk bulk materials[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(3): 451-456. |
| 4 | SUN J, SU J J, MA C, et al. Fabrication and mechanical properties of engineered protein-based adhesives and fibers[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(6): e1906360. |
| 5 | 杨兆颖, 张帆, 郭建文, 等. 类弹性蛋白多肽的生物合成及其药物递送应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(4): 728-747. |
| YANG Zhaoying, ZHANG Fan, GUO Jianwen, et al. Biosynthesis of elastin-like polypeptides and their applications in drug delivery[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(4): 728-747. | |
| 6 | 王宇翔, 吴夏泠, 张文彬. 生物活体功能材料研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(4): 621-625. |
| WANG Yuxiang, WU Xialing, ZHANG Wenbin. Current advance in engineered living materials[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(4): 621-625. | |
| 7 | QIAN Z G, PAN F, XIA X X. Synthetic biology for protein-based materials[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 65: 197-204. |
| 8 | HUANG W W, LING S J, LI C M, et al. Silkworm silk-based materials and devices generated using bio-nanotechnology[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(17): 6486-6504. |
| 9 | SIONKOWSKA A. Collagen blended with natural polymers: recent advances and trends[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2021, 122: 101452. |
| 10 | BESSA P C, BALMAYOR E R, HARTINGER J, et al. Silk fibroin microparticles as carriers for delivery of human recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-2: in vitro and in vivo bioactivity[J]. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods, 2010, 16(5): 937-945. |
| 11 | MACEWAN S R, CHILKOTI A. Elastin-like polypeptides: biomedical applications of tunable biopolymers[J]. Biopolymers, 2010, 94(1): 60-77. |
| 12 | CHANG R, ZOU Q L, XING R R, et al. Peptide-based supramolecular nanodrugs as a new generation of therapeutic toolboxes against cancer[J]. Advanced Therapeutics, 2019, 2(8): 1900048. |
| 13 | LÜ S S, DUDEK D M, CAO Y, et al. Designed biomaterials to mimic the mechanical properties of muscles[J]. Nature, 2010, 465(7294): 69-73. |
| 14 | ZHANG J S, WONG S H D, WU X, et al. Engineering photoresponsive ligand tethers for mechanical regulation of stem cells[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(48): 2105765. |
| 15 | SUN H C, ZHANG X Y, MIAO L, et al. Micelle-induced self-assembling protein nanowires: versatile supramolecular scaffolds for designing the light-harvesting system[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(1): 421-428. |
| 16 | EDLUND A M, JONES J, LEWIS R, et al. Economic feasibility and environmental impact of synthetic spider silk production from Escherichia coli [J]. New Biotechnology, 2018, 42: 12-18. |
| 17 | PREIS I, ABRAMSON M, SHOSEYOV O. The modification of cell wall properties by expression of recombinant resilin in transgenic plants[J]. Molecular Biotechnology, 2018, 60(4): 310-318. |
| 18 | WHITTALL D R, BAKER K V, BREITLING R, et al. Host systems for the production of recombinant spider silk[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2021, 39(6): 560-573. |
| 19 | ZHANG J S, LEI H, QIN M, et al. Quantifying cation-π interactions in marine adhesive proteins using single-molecule force spectroscopy[J]. Supramolecular Materials, 2022, 1: 100005. |
| 20 | GUERETTE P A, HOON S, SEOW Y, et al. Accelerating the design of biomimetic materials by integrating RNA-seq with proteomics and materials science[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(10): 908-915. |
| 21 | KONO N, NAKAMURA H, OHTOSHI R, et al. The bagworm genome reveals a unique fibroin gene that provides high tensile strength[J]. Communications Biology, 2019, 2: 148. |
| 22 | AGNARSSON I, KUNTNER M, BLACKLEDGE T A. Bioprospecting finds the toughest biological material: extraordinary silk from a giant riverine orb spider[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(9): e11234. |
| 23 | YOSHIOKA T, TSUBOTA T, TASHIRO K, et al. A study of the extraordinarily strong and tough silk produced by bagworms[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1469. |
| 24 | KONO N, NAKAMURA H, TATEISHI A, et al. The balance of crystalline and amorphous regions in the fibroin structure underpins the tensile strength of bagworm silk[J]. Zoological Letters, 2021, 7(1): 11. |
| 25 | KONO N, NAKAMURA H, MORI M, et al. Multicomponent nature underlies the extraordinary mechanical properties of spider dragline silk[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(31): e2107065118. |
| 26 | AMIRAM M, HAIMOVICH A D, FAN C G, et al. Evolution of translation machinery in recoded bacteria enables multi-site incorporation of nonstandard amino acids[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(12): 1272-1279. |
| 27 | COSTA S A, SIMON J R, AMIRAM M, et al. Photo-crosslinkable unnatural amino acids enable facile synthesis of thermoresponsive nano- to microgels of intrinsically disordered polypeptides[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(5): 1704878. |
| 28 | YANG B, AYYADURAI N, YUN H, et al. In vivo residue-specific DOPA-incorporated engineered mussel bioglue with enhanced adhesion and water resistance[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(49): 13360-13364. |
| 29 | LIN S C, RYU S, TOKAREVA O, et al. Predictive modelling-based design and experiments for synthesis and spinning of bioinspired silk fibres[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 6892. |
| 30 | HEIDEBRECHT A, EISOLDT L, DIEHL J, et al. Biomimetic fibers made of recombinant spidroins with the same toughness as natural spider silk[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(13): 2189-2194. |
| 31 | ZHONG C, GURRY T, CHENG A A, et al. Strong underwater adhesives made by self-assembling multi-protein nanofibres[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2014, 9(10): 858-866. |
| 32 | CUI M K, WANG X Y, AN B L, et al. Exploiting mammalian low-complexity domains for liquid-liquid phase separation-driven underwater adhesive coatings[J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(8): eaax3155. |
| 33 | MA C, DONG J J, VIVIANI M, et al. De novo rational design of a freestanding, supercharged polypeptide, proton-conducting membrane[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(29): eabc0810. |
| 34 | LI Yuanxin, LI Jingjing, SUN Jing, et al. Bioinspired and mechanically strong fibers based on engineered non-spider chimeric proteins[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(21): 8148-8152. |
| 35 | LI J Y, ZHU Y G, YU H, et al. Microbially synthesized polymeric amyloid fiber promotes β-nanocrystal formation and displays gigapascal tensile strength[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(7): 11843-11853. |
| 36 | HUANG P S, BOYKEN S E, BAKER D. The coming of age of de novo protein design[J]. Nature, 2016, 537(7620): 320-327. |
| 37 | KING N P, SHEFFLER W, SAWAYA M R, et al. Computational design of self-assembling protein nanomaterials with atomic level accuracy[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6085): 1171-1174. |
| 38 | KING N P, BALE J B, SHEFFLER W, et al. Accurate design of co-assembling multi-component protein nanomaterials[J]. Nature, 2014, 510(7503): 103-108. |
| 39 | HSIA Y, BALE J B, GONEN S,et al. Design of a hyperstable 60-subunit protein icosahedron[J]. Nature, 2016, 535: 136-139. |
| 40 | BALE J B, GONEN S, LIU Y X, et al. Accurate design of megadalton-scale two-component icosahedral protein complexes[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6297): 389-394. |
| 41 | DOU J Y, VOROBIEVA A A, SHEFFLER W, et al. De novo design of a fluorescence-activating β-barrel[J]. Nature, 2018, 561(7724): 485-491. |
| 42 | SILVA D A, YU S, ULGE U Y, et al. De novo design of potent and selective mimics of IL-2 and IL-15[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7738): 186-191. |
| 43 | SHEN H, FALLAS J A, LYNCH E, et al. De novo design of self-assembling helical protein filaments[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6415): 705-709. |
| 44 | JUMPER J, EVANS R, PRITZEL A, et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold[J]. Nature, 2021, 596(7873): 583-589. |
| 45 | TUNYASUVUNAKOOL K, ADLER J, WU Z, et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction for the human proteome[J]. Nature, 2021, 596(7873): 590-596. |
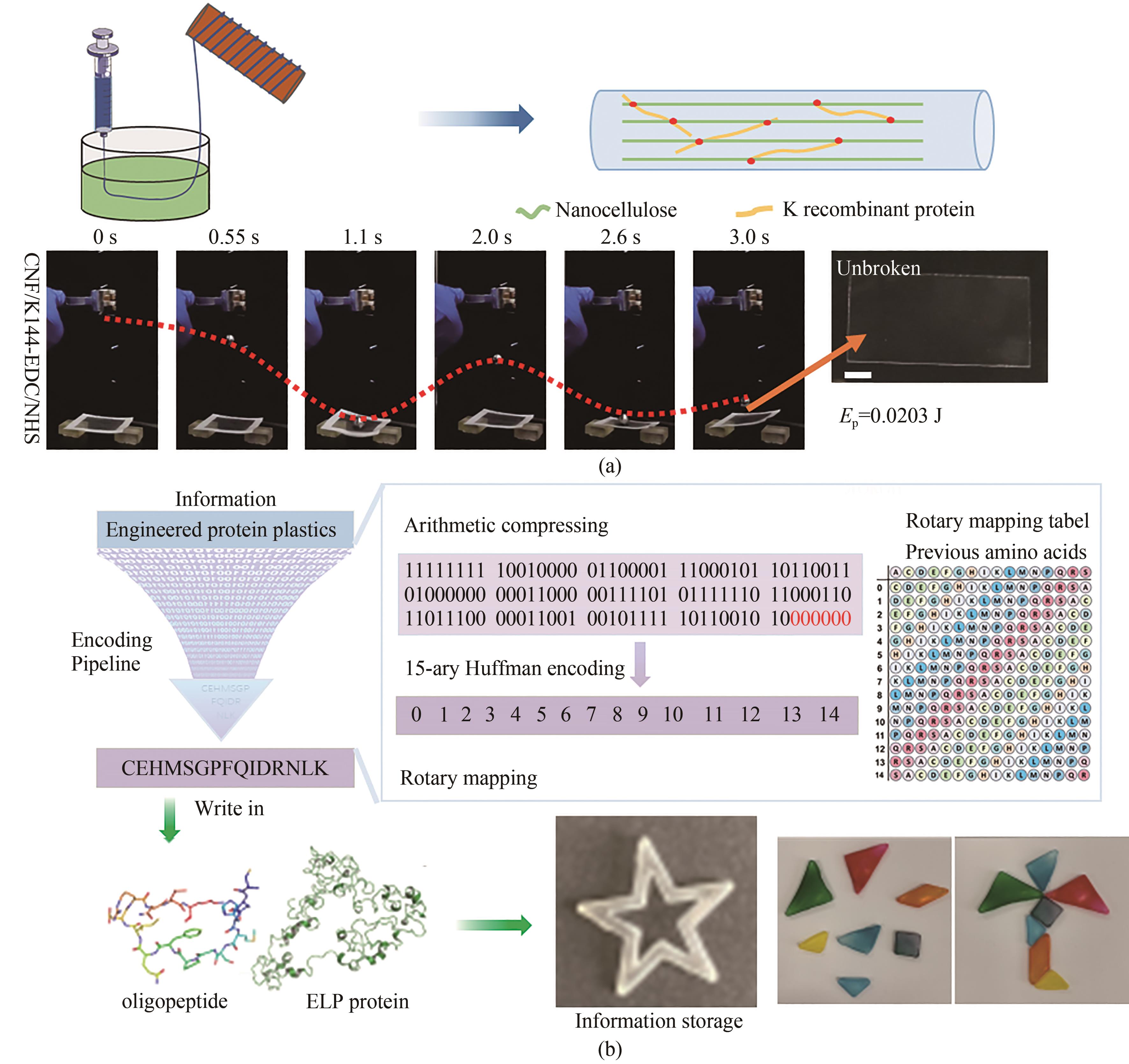
| 46 | SU J J, ZHAO K L, REN Y B, et al. Biosynthetic structural proteins with super plasticity, extraordinary mechanical performance, biodegradability, biocompatibility and information storage ability[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(12): e202117538. |
| 47 | XIA X X, QIAN Z G, KI C S, et al. Native-sized recombinant spider silk protein produced in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli results in a strong fiber[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(32): 14059-14063. |
| 48 | JIN Q, PAN F, HU C F, et al. Secretory production of spider silk proteins in metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum for spinning into tough fibers[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2022, 70: 102-114. |
| 49 | WANG T M, GUAN C G, GUO J H, et al. Pooled CRISPR interference screening enables genome-scale functional genomics study in bacteria with superior performance[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 2475. |
| 50 | LI Lei, WEI Keke, ZHENG Guosong, et al. CRISPR-Cpf1-assisted multiplex genome editing and transcriptional repression in Streptomyces [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(18): e00827. |
| 51 | BRYSON D I, FAN C G, GUO L T, et al. Continuous directed evolution of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2017, 13(12): 1253-1260. |
| 52 | WANG T N, BADRAN A H, HUANG T P, et al. Continuous directed evolution of proteins with improved soluble expression[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(10): 972-980. |
| 53 | THURONYI B W, KOBLAN L W, LEVY J M, et al. Continuous evolution of base editors with expanded target compatibility and improved activity[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(9): 1070-1079. |
| 54 | JOHNSTON C W, BADRAN A H, COLLINS J J. Continuous bioactivity-dependent evolution of an antibiotic biosynthetic pathway[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 4202. |
| 55 | MORRISON M S, WANG T N, RAGURAM A, et al. Disulfide-compatible phage-assisted continuous evolution in the periplasmic space[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 5959. |
| 56 | KOLBER N S, FATTAL R, BRATULIC S, et al. Orthogonal translation enables heterologous ribosome engineering in E. coli [J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 599. |
| 57 | ZHANG J T, ZHOU K, WANG Q B. Tailoring the self-assembly behaviors of recombinant tobacco mosaic virus by rationally introducing covalent bonding at the protein-protein interface[J]. Small, 2016, 12(36): 4955-4959. |
| 58 | ZHOU K, ZHOU Y H, YANG H C, et al. Interfacially bridging covalent network yields hyperstable and ultralong virus-based fibers for engineering functional materials[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(41): 18249-18255. |
| 59 | BOWEN C H, DAI B, SARGENT C J, et al. Recombinant spidroins fully replicate primary mechanical properties of natural spider silk[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2018, 19(9): 3853-3860. |
| 60 | BOWEN C H, SARGENT C J, WANG A, et al. Microbial production of megadalton titin yields fibers with advantageous mechanical properties[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 5182. |
| 61 | SU J J, LIU B M, HE H N, et al. Engineering high strength and super-toughness of unfolded structural proteins and their extraordinary anti-adhesion performance for abdominal hernia repair[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(19): 2200842. |
| 62 | ZHAO Lai, LI Jingjing, ZHANG Lili, et al. Biosynthetic protein and nanocellulose composite fibers with extraordinary mechanical performance[J]. Nanotoday, 2022, 44: 101485. |
| 63 | WAN S K, CHENG W H, LI J J, et al. Biological composite fibers with extraordinary mechanical strength and toughness mediated by multiple intermolecular interacting networks[J/OL]. Nano Research, 2022. . |
| 64 | HE H N, YANG C J, WANG F, et al. Mechanically strong globular-protein-based fibers obtained using a microfluidic spinning technique[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(11): 4344-4348. |
| 65 | MOZHDEHI D, LUGINBUHL K M, SIMON J R, et al. Genetically encoded lipid-polypeptide hybrid biomaterials that exhibit temperature-triggered hierarchical self-assembly[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2018, 10(5): 496-505. |
| 66 | LUGINBUHL K M, MOZHDEHI D, DZURICKY M, et al. Recombinant synthesis of hybrid lipid-peptide polymer fusions that self-assemble and encapsulate hydrophobic drugs[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(45): 13979-13984. |
| 67 | ZAKERI B, FIERER J O, CELIK E, et al. Peptide tag forming a rapid covalent bond to a protein, through engineering a bacterial adhesin[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(12): E690-E697. |
| 68 | WANG R, YANG Z G, LUO J R, et al. B12-dependent photoresponsive protein hydrogels for controlled stem cell/protein release[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(23): 5912-5917. |
| 69 | 易琪昆, 孙晨博, 杨中光, 等. 可基因编码点击化学在材料合成生物学中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(4): 690-708. |
| YI Q K, SUN C B, YANG Z G, et al. Genetically encoded click chemistry, an enabling tool for materials synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(4): 690-708. | |
| 70 | LI L L, QIAO S L, LIU W J, et al. Intracellular construction of topology-controlled polypeptide nanostructures with diverse biological functions[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 1276. |
| 71 | SARIC M, EISOLDT L, DÖRING V, et al. Interplay of different major ampullate spidroins during assembly and implications for fiber mechanics[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(9): 2006499. |
| 72 | MA Chao, SUN Jing, LI Bo, et al. Ultra-strong bio-glue from genetically engineered polypeptides[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 3613. |
| 73 | SUN Jing, XIAO Lingling, LI Bo, et al. Genetically engineered polypeptide adhesive coacervates for surgical applications[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(44): 23687-23694. |
| 74 | YAN X H, ZHU P L, FEI J B, et al. Self-assembly of peptide-inorganic hybrid spheres for adaptive encapsulation of guests[J]. Advanced Materials, 2010, 22(11): 1283-1287. |
| 75 | LIU Y N, JIN J Y, DENG H P, et al. Protein-framed multi-porphyrin micelles for a hybrid natural-artificial light-harvesting nanosystem[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(28): 7952-7957. |
| 76 | YANG G, ZHANG X, KOCHOVSKI Z, et al. Precise and reversible protein-microtubule-like structure with helicity driven by dual supramolecular interactions[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(6): 1932-1937. |
| 77 | ZHANG Lei, MA Chao, SUN Jing, et al. Genetically engineered supercharged polypeptide fluids: fast and persistent self-ordering induced by touch[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(23): 6878-6882. |
| 78 | LIU K, PESCE D, MA C, et al. Solvent-free liquid crystals and liquids based on genetically engineered supercharged polypeptides with high elasticity[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(15): 2459-2465. |
| 79 | MA C, SU J J, LI B, et al. Solvent-free plasticity and programmable mechanical behaviors of engineered proteins[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(10): 1907697. |
| 80 | SUN J, LI B, WANG F, et al. Proteinaceous fibers with outstanding mechanical properties manipulated by supramolecular interactions[J]. CCS Chemistry, 2021, 3(6): 1669-1677. |
| 81 | LI Jingjing, LI Bo, SUN Jing, et al. Engineered near-infrared fluorescent protein assemblies for robust bioimaging and therapeutic applications[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(17): 2000964. |
| 82 | ZHANG J R, SUN Y, QU Q, et al. Engineering non-covalently assembled protein nanoparticles for long-acting gouty arthritis therapy[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2021, 9(48): 9923-9931. |
| 83 | SU J J, LU S, JIANG S J, et al. Engineered protein photo-thermal hydrogels for outstanding in situ tongue cancer therapy[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(21): 2100619. |
| 84 | WANG Shidong, LI Bo, ZHANG Hongliang, et al. Improving bioavailability of hydrophobic prodrugs through supramolecular nanocarriers based on recombinant proteins for osteosarcoma treatment[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(20): 11252-11256. |
| 85 | MA Chao, LI Bo, ZHANG Jinrui, et al. Significantly improving the bioefficacy for rheumatoid arthritis with supramolecular nanoformulations[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(16): 2100098. |
| 86 | LI J L, XING R R, BAI S, et al. Recent advances of self-assembling peptide-based hydrogels for biomedical applications[J]. Soft Matter, 2019, 15(8): 1704-1715. |
| 87 | LIU J W, GE X D, LIU L, et al. Challenges and opportunities of silk protein hydrogels in biomedical applications[J]. Materials Advances, 2022, 3(5): 2291-2308. |
| 88 | WEI Z, SUN J, LU S, et al. An engineered protein – Au bioplaster for efficient skin tumor therapy[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(16): 2110062. |
| 89 | RISING A, JOHANSSON J. Toward spinning artificial spider silk[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(5): 309-315. |
| 90 | LING S J, QIN Z, LI C M, et al. Polymorphic regenerated silk fibers assembled through bioinspired spinning[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 1387. |
| 91 | FRANCO A R, PALMA KIMMERLING E, SILVA C, et al. Silk-based antimicrobial polymers as a new platform to design drug-free materials to impede microbial infections[J]. Macromolecular Bioscience, 2018, 18(12): 1800262. |
| 92 | SCHACHT K, JÜNGST T, SCHWEINLIN M, et al. Biofabrication of cell-loaded 3D spider silk constructs[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(9): 2816-2820. |
| 93 | TOMKO J A, PENA-FRANCESCH A, JUNG H, et al. Tunable thermal transport and reversible thermal conductivity switching in topologically networked bio-inspired materials[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2018, 13(10): 959-964. |
| 94 | GADDES D, JUNG H, PENA-FRANCESCH A, et al. Self-healing textile: enzyme encapsulated layer-by-layer structural proteins[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(31): 20371-20378. |
| 95 | FU J, GUERETTE P A, PAVESI A, et al. Artificial hagfish protein fibers with ultra-high and tunable stiffness[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(35): 12908-12915. |
| 96 | ANDERSSON M, JIA Q P, ABELLA A, et al. Biomimetic spinning of artificial spider silk from a chimeric minispidroin[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2017, 13(3): 262-264. |
| 97 | ZHANG J R, SUN J, LI B, et al. Robust biological fibers based on widely available proteins: facile fabrication and suturing application[J]. Small, 2020, 16(8): 1907598. |
| 98 | MOHAMMADI P, ARANKO A S, LANDOWSKI C P, et al. Biomimetic composites with enhanced toughening using silk-inspired triblock proteins and aligned nanocellulose reinforcements[J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(9): eaaw2541. |
| 99 | MA C, LI B, SHAO B Q, et al. Anisotropic protein organofibers encoded with extraordinary mechanical behavior for cellular mechanobiology applications[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(48): 21481-21487. |
| 100 | SUN J, MA C, MAITY S, et al. Reversibly photo-modulating mechanical stiffness and toughness of bioengineered protein fibers[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(6): 3222-3228. |
| 101 | LUTZ T M, KIMNA C, CASINI A, et al. Bio-based and bio-inspired adhesives from animals and plants for biomedical applications[J]. Materials Today Bio, 2022, 13: 100203. |
| 102 | SUN J, HAN J Y, WANG F, et al. Bioengineered protein-based adhesives for biomedical applications[J]. Chemistry - A European Journal, 2022, 28(1): e202102902. |
| 103 | ROBERTS A D, FINNIGAN W, KELLY P P, et al. Non-covalent protein-based adhesives for transparent substrates-bovine serum albumin vs. recombinant spider silk[J]. Materials Today Bio, 2020, 7: 100068. |
| 104 | BRENNAN M J, KILBRIDE B F, WILKER J J, et al. A bioinspired elastin-based protein for a cytocompatible underwater adhesive[J]. Biomaterials, 2017, 124: 116-125. |
| 105 | WANG R, LI J Z, CHEN W, et al. A biomimetic mussel-inspired ε-poly-L-lysine hydrogel with robust tissue-anchor and anti-infection capacity[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(8): 1604894. |
| 106 | GONZALEZ M A, SIMON J R, GHOORCHIAN A, et al. Strong, tough, stretchable, and self-adhesive hydrogels from intrinsically unstructured proteins[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(10): 1604743. |
| 107 | J-P BUFFET, CORRE E, DUVERNOIS-BERTHET E, et al. Adhesive gland transcriptomics uncovers a diversity of genes involved in glue formation in marine tube-building polychaetes[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2018, 72: 316-328. |
| 108 | BECKER P T, LAMBERT A, LEJEUNE A, et al. Identification, characterization, and expression levels of putative adhesive proteins from the tube-dwelling polychaete Sabellaria alveolata [J]. The Biological Bulletin, 2012, 223(2): 217-225. |
| 109 | SHAO H, BACHUS K N, STEWART R J. A water-borne adhesive modeled after the sandcastle glue of P. californica [J]. Macromolecular Bioscience, 2009, 9(5): 464-471. |
| 110 | DICKINSON G H, VEGA I E, WAHL K J, et al. Barnacle cement: a polymerization model based on evolutionary concepts[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 2009, 212(21): 3499-3510. |
| 111 | KEI K. Mini-review: barnacle adhesives and adhesion[J]. Biofouling, 2013, 29(6): 735-749. |
| 112 | STEWART R J. Protein-based underwater adhesives and the prospects for their biotechnological production[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2011, 89(1): 27-33. |
| 113 | PRESTI M LO, RIZZO G, FARINOLA G M, et al. Bioinspired biomaterial composite for all-water-based high-performance adhesives[J]. Advanced Science, 2021, 8(16): 2004786. |
| 114 | XIAO L L, WANG Z L, SUN Y, et al. An artificial phase-transitional underwater bioglue with robust and switchable adhesion performance[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(21): 12082-12089. |
| 115 | ZHANG J R, LI B, ZUO J L, et al. An engineered protein adhesive with properties of tissue integration and controlled release for efficient cartilage repair[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2021, 10(12): 2100109. |
| [1] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | DONG Ying, MA Mengdan, HUANG Weiren. Progress in the miniaturization of CRISPR-Cas systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 105-117. |
| [3] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | WEN Yanhua, LIU Hedong, CAO Chunlai, WU Ruibo. Applications of protein engineering in pharmaceutical industry [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 65-86. |
| [8] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [9] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [10] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [11] | WANG Ziyuan, YANG Lirong, WU Jianping, ZHENG Wenlong. A review on enzyme-catalyzed synthesis of chiral amino acids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1319-1349. |
| [12] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [13] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [14] | CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [15] | LI Shikai, ZENG Dong′ao, DU Fangzhou, ZHANG Jingzhong, YU Shuang. The construction approaches and biomaterials for vascularized organoids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 851-866. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||