Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (4): 629-650.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-073
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Advances and applications of evolutionary analysis and big-data guided bioinformatics in natural product research
ZHANG Fanzhong1,2, XIANG Changjun1,2,3, ZHANG Lihan1,2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Precise Synthesis of Functional Molecules of Zhejiang Province,Department of Chemistry,School of Science,Westlake University,Hangzhou 310030,Zhejiang,China
2.Institute of Natural Sciences,Westlake Institute for Advanced Study,Hangzhou 310024,Zhejiang,China
3.Department of Chemistry,Fudan University,Shanghai 200243,China
-
Received:2022-12-08Revised:2023-02-21Online:2023-09-14Published:2023-08-31 -
Contact:ZHANG Lihan
进化与大数据导向生物信息学在天然产物研究中的发展及应用
张凡忠1,2, 相长君1,2,3, 张骊駻1,2
- 1.西湖大学理学院化学系,浙江省功能分子精准合成重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310030
2.浙江西湖高等研究院,理学研究所,浙江 杭州 310024
3.复旦大学化学系,上海 200243
-
通讯作者:张骊駻 -
作者简介:张凡忠 (1991—),女,博士后。研究方向为微生物天然产物分离鉴定,细菌中PKS和NRPS的进化导向基因挖掘。E-mail:zhangfanzhong@westlake.edu.cn张骊駻 (1989—),男,特聘研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为天然产物分子多样性与生物合成进化,以及进化导向生物合成改造等。E-mail:zhanglihan@westlake.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(22177092);浙江省领军型创新创业团队(2020R01004);杭州市科技发展计划(20201203B122)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Fanzhong, XIANG Changjun, ZHANG Lihan. Advances and applications of evolutionary analysis and big-data guided bioinformatics in natural product research[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): 629-650.
张凡忠, 相长君, 张骊駻. 进化与大数据导向生物信息学在天然产物研究中的发展及应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(4): 629-650.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2022-073
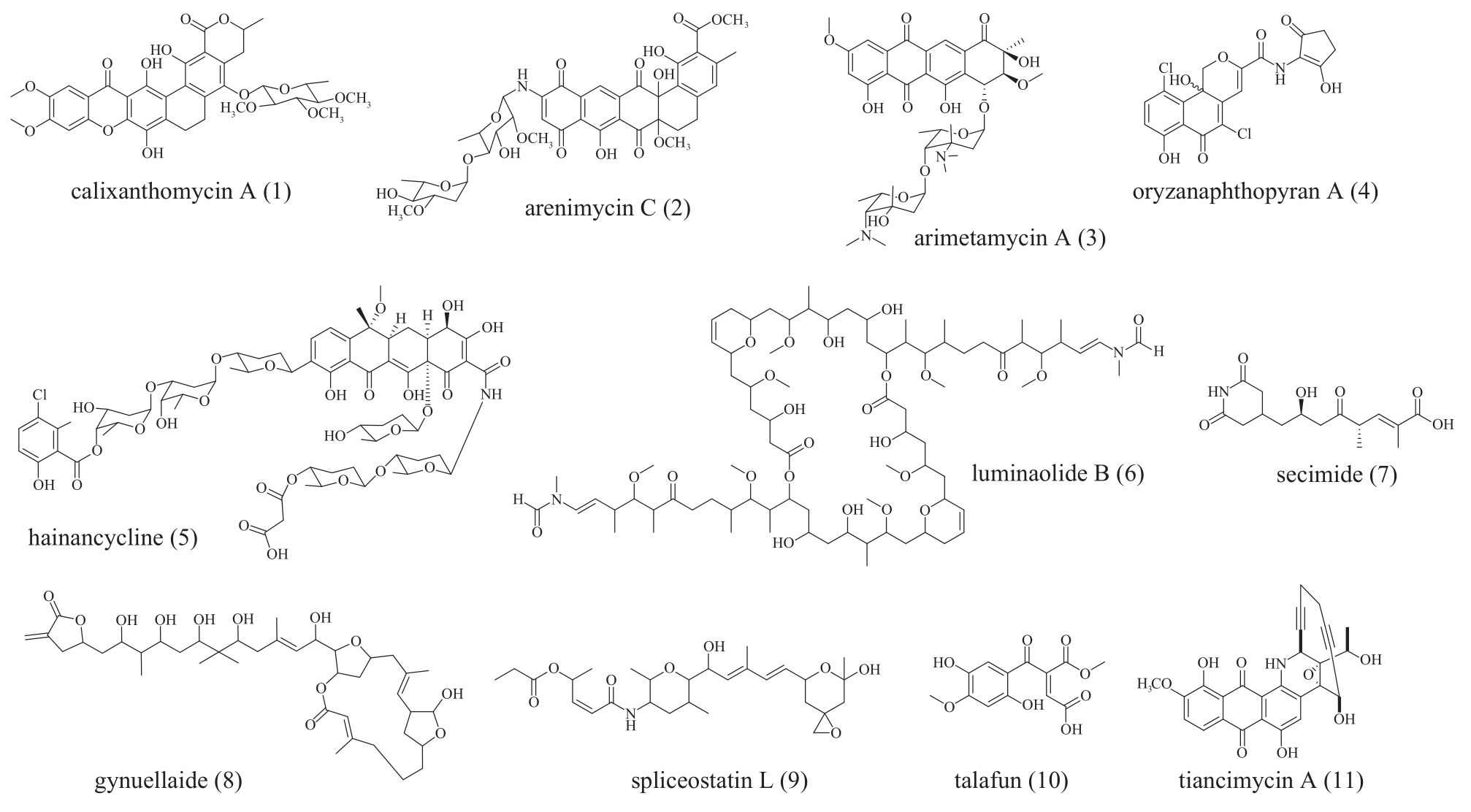
Fig. 5 The structure of polyketides molecules 1 to 10 obtained by phylogeny-guided genome miningCompounds 1 to 5 were aromatic polyketides discovered by genome mining of type Ⅱ PKS. Compounds 6 to 9 were discovered by genome mining of trans-AT PKS. Compound 10 was discovered by genome mining of fungal type Ⅰ PKS. Compounds 11 were enediynes

Fig. 9 The structure of peptide molecules 12~17 obtained by phylogeny-guided genome mining(Compounds 12 was calcium-dependent antibiotic discovered by genome mining of A domain; compounds 13~16 belonged to glycopeptide family of antibiotics discovered by genome mining of C domain;compound 17 was lipopeptide antibiotic discovered by NRPS prediction)
| 1 | CHEVRETTE M G, GAVRILIDOU A, MANTRI S, et al. The confluence of big data and evolutionary genome mining for the discovery of natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2021, 38(11): 2024-2040. |
| 2 | CHEVRETTE M G, GUTIÉRREZ-GARCÍA K, SELEM-MOJICA N, et al. Evolutionary dynamics of natural product biosynthesis in bacteria[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2020, 37(4): 566-599. |
| 3 | JENSEN P R. Natural products and the gene cluster revolution[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2016, 24(12): 968-977. |
| 4 | GAVRIILIDOU A, KAUTSAR S A, ZABURANNYI N, et al. Compendium of specialized metabolite biosynthetic diversity encoded in bacterial genomes[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2022, 7(5): 726-735. |
| 5 | CHEN S C, ZHANG C, ZHANG L H. Investigation of the molecular landscape of bacterial aromatic polyketides by global analysis of typeⅡpolyketide synthases[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edtion, 2022, 61(24): e202202286. |
| 6 | ADAMEK M, ALANJARY M, ZIEMERT N. Applied evolution: phylogeny-based approaches in natural products research[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2019, 36(9): 1295-1312. |
| 7 | PANDE S, KOST C. Bacterial unculturability and the formation of intercellular metabolic networks[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2017, 25(5): 349-361. |
| 8 | ZIEMERT N, ALANJARY M, WEBER T. The evolution of genome mining in microbes - a review[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2016, 33(8): 988-1005. |
| 9 | WALKER J M. Engineering natural products biosynthesis[M]. New York: Humana Imprint, 2022. |
| 10 | 杨谦, 程伯涛, 汤志军, 等. 基因组挖掘在天然产物发现中的应用和前景[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(5): 697-715. |
| YANG Q, CHENG B T, TANG Z J, et al. Applications and prospects of genome mining in the discovery of natural products[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(5): 697-715. | |
| 11 | ZERIKLY M, CHALLIS G L. Strategies for the discovery of new natural products by genome mining[J]. ChemBioChem, 2009, 10(4): 625-633. |
| 12 | SCHERLACH K, HERTWECK C. Mining and unearthing hidden biosynthetic potential[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 3864. |
| 13 | BAUMAN K D, BUTLER K S, MOORE B S, et al. Genome mining methods to discover bioactive natural products [J]. Natural Product Reports, 2021, 38(11): 2100-2129. |
| 14 | CRUZ-MORALES P, KOPP J F, MARTÍNEZ-GUERRERO C, et al. Phylogenomic analysis of natural products biosynthetic gene clusters allows discovery of arseno-organic metabolites in model Streptomycetes [J]. Genome Biology and Evolution, 2016, 8(6): 1906-1916. |
| 15 | KANG H S. Phylogeny-guided (meta)genome mining approach for the targeted discovery of new microbial natural products[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2017, 44(2): 285-293. |
| 16 | ALANJARY M, KRONMILLER B, ADAMEK M, et al. The antibiotic resistant target seeker (ARTS), an exploration engine for antibiotic cluster prioritization and novel drug target discovery[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(W1): W42-W48. |
| 17 | DIRENÇ MUNGAN M, ALANJARY M, BLIN K, et al. ARTS 2.0: feature updates and expansion of the antibiotic resistant target seeker for comparative genome mining[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(W1): W546-W552. |
| 18 | ZIEMERT N, PODELL S, PENN K, et al. The natural product domain seeker NaPDoS: a phylogeny based bioinformatic tool to classify secondary metabolite gene diversity[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(3): e34064. |
| 19 | KLAU L J, PODELL S, CREAMER K E, et al. The Natural Product Domain Seeker version 2 (NaPDoS2) webtool relates ketosynthase phylogeny to biosynthetic function[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2022, 298(10): 102480. |
| 20 | SÉLEM-MOJICA N, AGUILAR C, GUTIÉRREZ-GARCÍA K, et al. EvoMining reveals the origin and fate of natural product biosynthetic enzymes[J]. Microbial Genomics, 2019, 5(12): e000260. |
| 21 | NAVARRO-MUÑOZ J C, SELEM-MOJICA N, MULLOWNEY M W, et al. A computational framework to explore large-scale biosynthetic diversity[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2020, 16(1): 60-68. |
| 22 | MEDEMA M H, KOTTMANN R, YILMAZ P, et al. Minimum information about a biosynthetic gene cluster[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(9): 625-631. |
| 23 | KAUTSAR S A, BLIN K, SHAW S, et al. MIBiG 2.0: a repository for biosynthetic gene clusters of known function[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(D1): D454-D458. |
| 24 | BLIN K, SHAW S, KAUTSAR S A, et al. The antiSMASH database version 3: increased taxonomic coverage and new query features for modular enzymes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(D1): D639-D643. |
| 25 | RAWLINGS B J. Type I polyketide biosynthesis in bacteria (part A—erythromycin biosynthesis)[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2001, 18(2): 190-227. |
| 26 | HERTWECK C, LUZHETSKYY A, REBETS Y, et al. TypeⅡpolyketide synthases: gaining a deeper insight into enzymatic teamwork[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2007, 24(1): 162-190. |
| 27 | ABE I, MORITA H. Structure and function of the chalcone synthase superfamily of plant typeⅢpolyketide synthases[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2010, 27(6): 809-838. |
| 28 | YU D Y, XU F C, ZENG J, et al. TypeⅢpolyketide synthases in natural product biosynthesis[J]. IUBMB Life, 2012, 64(4): 285-295. |
| 29 | NIVINA A, YUET K P, HSU J, et al. Evolution and diversity of assembly-line polyketide synthases[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(24): 12524-12547. |
| 30 | JENKE-KODAMA H, DITTMANN E. Evolution of metabolic diversity: insights from microbial polyketide synthases[J]. Phytochemistry, 2009, 70(15-16): 1858-1866. |
| 31 | NIVINA A, HERRERA PAREDES S, FRASER H B, et al. GRINS: genetic elements that recode assembly-line polyketide synthases and accelerate their diversification[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(26): e2100751118. |
| 32 | JENKE-KODAMA H, SANDMANN A, MÜLLER R, et al. Evolutionary implications of bacterial polyketide synthases[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2005, 22(10): 2027-2039. |
| 33 | NGUYEN T, ISHIDA K, JENKE-KODAMA H, et al. Exploiting the mosaic structure of trans-acyltransferase polyketide synthases for natural product discovery and pathway dissection[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2008, 26(2): 225-233. |
| 34 | LOPEZ J V. Naturally mosaic operons for secondary metabolite biosynthesis: variability and putative horizontal transfer of discrete catalytic domains of the epothilone polyketide synthase locus[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2004, 270(5): 420-431. |
| 35 | ZHANG L H, HASHIMOTO T, QIN B, et al. Characterization of giant modular PKSs provides insight into genetic mechanism for structural diversification of aminopolyol polyketides[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edtion, 2017, 56(7): 1740-1745. |
| 36 | KEATINGE-CLAY A T. Polyketide synthase modules redefined[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edtion, 2017, 56(17): 4658-4660. |
| 37 | VANDER WOOD D A, KEATINGE-CLAY A T. The modules of trans-acyltransferase assembly lines redefined with a central acyl carrier protein[J]. Proteins, 2018, 86(6): 664-675. |
| 38 | CAFFREY P. Conserved amino acid residues correlating with ketoreductase stereospecificity in modular polyketide synthases[J]. Chembiochem, 2003, 4(7): 654-657. |
| 39 | VANDER WOOD D A, KEATINGE-CLAY A T. The modules of trans-acyltransferase assembly lines redefined with a central acyl carrier protein[J]. Proteins, 2018, 86(6): 664-675. |
| 40 | MEDEMA M H, CIMERMANCIC P, SALI A, et al. A systematic computational analysis of biosynthetic gene cluster evolution: lessons for engineering biosynthesis[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2014, 10(12): e1004016. |
| 41 | RIDLEY C P, LEE H Y, KHOSLA C. Evolution of polyketide synthases in bacteria[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(12): 4595-4600. |
| 42 | HILLENMEYER M E, VANDOVA G A, BERLEW E E, et al. Evolution of chemical diversity by coordinated gene swaps in typeⅡpolyketide gene clusters[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(45): 13952-13957. |
| 43 | GABALDÓN T, KOONIN E V. Functional and evolutionary implications of gene orthology[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2013, 14(5): 360-366. |
| 44 | FRITZSCHE K, ISHIDA K, HERTWECK C. Orchestration of discoid polyketide cyclization in the resistomycin pathway[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(26): 8307-8316. |
| 45 | FRALEY A E, DIETERICH C L, MABESOONE M F J, et al. Structure of a promiscuous thioesterase domain responsible for branching acylation in polyketide biosynthesis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edtion, 2022, 61(39): e202206385. |
| 46 | SCHWECKE T, APARICIO J F, MOLNÁR I, et al. The biosynthetic gene cluster for the polyketide immunosuppressant rapamycin[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1995, 92(17): 7839-7843. |
| 47 | HAYDOCK S F, APARICIO J F, MOLNÁR I, et al. Divergent sequence motifs correlated with the substrate specificity of (methyl) malonyl-CoA: acyl carrier protein transacylase domains in modular polyketide synthases[J]. FEBS Letters, 1995, 374(2): 246-248. |
| 48 | APARICIO J F, MOLNÁR I, SCHWECKE T., et al. Organization of the biosynthetic gene cluster for rapamycin in Streptomyces hygroscopicus: analysis of the enzymatic domains in the modular polyketide synthase[J]. Gene, 1996, 169(1): 9-16. |
| 49 | KAKAVAS S J, KATZ L, STASSI D. Identification and characterization of the niddamycin polyketide synthase genes from Streptomyces caelestis [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1997, 179(23): 7515-7522. |
| 50 | KANG H S, BRADY S F. Mining soil metagenomes to better understand the evolution of natural product structural diversity: pentangular polyphenols as a case study[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(52): 18111-18119. |
| 51 | KANG H S, BRADY S F. Arimetamycin A: improving clinically relevant families of natural products through sequence-guided screening of soil metagenomes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edtion, 2013, 52(42): 11063-11067. |
| 52 | LI L Y, HU Y L, SUN J L, et al. Resistance and phylogeny guided discovery reveals structural novelty of tetracycline antibiotics[J]. Chemical Science, 2022, 13(43): 12892-12898. |
| 53 | ZIEMERT N, JENSEN P R. Phylogenetic approaches to natural product structure prediction[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2012, 517: 161-182. |
| 54 | UEOKA R, URIA A R, REITER S, et al. Metabolic and evolutionary origin of actin-binding polyketides from diverse organisms[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(9): 705-712. |
| 55 | HELFRICH E J N, UEOKA R, DOLEV A, et al. Automated structure prediction of trans-acyltransferase polyketide synthase products[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(8): 813-821. |
| 56 | HELFRICH E J N, UEOKA R, CHEVRETTE M G, et al. Evolution of combinatorial diversity in trans-acyltransferase polyketide synthase assembly lines across bacteria[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1422. |
| 57 | GUO J, RAN H M, ZENG J, et al. Tafuketide, a phylogeny-guided discovery of a new polyketide from Talaromyces funiculosus Salicorn 58[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(12): 5323-5338. |
| 58 | SHEN B, HINDRA, YAN X H, et al. Enediynes: exploration of microbial genomics to discover new anticancer drug leads[J]. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2015, 25(1): 9-15 |
| 59 | YAN X H, GE H M, HUANG T T, et al. Strain prioritization and genome mining for enediyne natural products[J]. mBio, 2016, 7(6): e02104-e02116. |
| 60 | WEISSMAN K J. Genetic engineering of modular PKSs: from combinatorial biosynthesis to synthetic biology[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2016, 33(2): 203-230. |
| 61 | 曹晨凯, 李佳隆, 张科春. 人工代谢途径合成有机醇有机酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 902-919. |
| CAO C K, LI J L, ZHANG K C. Progress in artificial metabolic pathways for biosynthesis of organic alcohols & acids[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 902-919. | |
| 62 | BOOTH T J, BOZHÜYÜK K A J, LISTON J D, et al. Bifurcation drives the evolution of assembly-line biosynthesis[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 3498. |
| 63 | HIRSCH M, FITZGERALD B J, KEATINGE-CLAY A T. How cis-acyltransferase assembly-line ketosynthases gatekeep for processed polyketide intermediates[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2021, 16(11): 2515-2526. |
| 64 | MIYAZAWA T, HIRSCH M, ZHANG Z C, et al. An in vitro platform for engineering and harnessing modular polyketide synthases[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 80. |
| 65 | MIYAZAWA T, FITZGERALD B J, KEATINGE-CLAY A T. Preparative production of an enantiomeric pair by engineered polyketide synthases[J]. Chemical Communications, 2021, 57(70): 8762-8765. |
| 66 | PENG H Y, ISHIDA K, SUGIMOTO Y, et al. Emulating evolutionary processes to morph aureothin-type modular polyketide synthases and associated oxygenases[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 3918. |
| 67 | YUZAWA S, DENG K, WANG G, et al. Comprehensive in vitro analysis of acyltransferase domain exchanges in modular polyketide synthases and its application for short-chain ketone production[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(1): 139-147. |
| 68 | YUZAWA S, MIRSIAGHI M, JOCIC R, et al. Short-chain ketone production by engineered polyketide synthases in streptomyces albus[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 4569. |
| 69 | ZARGAR A, VALENCIA L, WANG J, et al. A bimodular PKS platform that expands the biological design space[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 61: 389-396. |
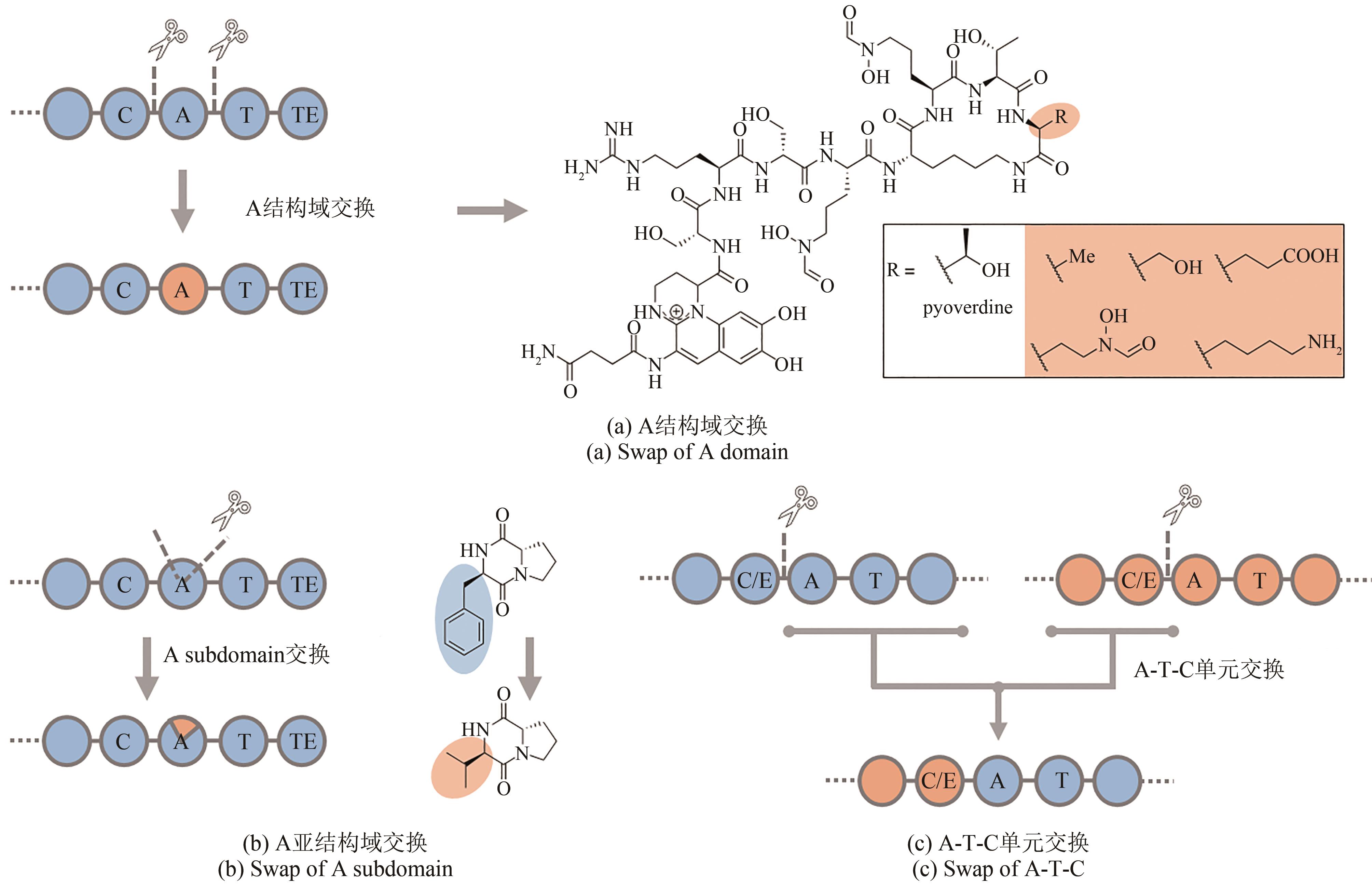
| 70 | ENG C H, YUZAWA S, WANG G, et al. Alteration of polyketide stereochemistry from anti to syn by a ketoreductase domain exchange in a typeⅠmodular polyketide synthase subunit[J]. Biochemistry, 2016, 55(12): 1677-1680. |
| 71 | HAGEN A, POUST S, DE ROND T, et al. Engineering a polyketide synthase for in vitro production of adipic acid[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(1): 21-27. |
| 72 | ZARGAR A, LAL R, VALENCIA L, et al. Chemoinformatic-guided engineering of polyketide synthases[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(22): 9896-9901. |
| 73 | MUSIOL-KROLL E M, WOHLLEBEN W. Acyltransferases as tools for polyketide synthase engineering[J]. Antibiotics, 2018, 7(3): 62. |
| 74 | KWAN D H, TOSIN M, SCHLÄGER N, et al. Insights into the stereospecificity of ketoreduction in a modular polyketide synthase[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2011, 9(7): 2053-2056. |
| 75 | BAGDE S R, MATHEWS I I, FROMME J C, et al. Modular polyketide synthase contains two reaction chambers that operate asynchronously[J]. Science, 2021, 374(6568): 723-729. |
| 76 | COGAN D P, ZHANG K M, LI X Y, et al. Mapping the catalytic conformations of an assembly-line polyketide synthase module[J]. Science, 2021, 374(6568): 729-734. |
| 77 | HERBST D A, JAKOB R P, ZÄHRINGER F, et al. Mycocerosic acid synthase exemplifies the architecture of reducing polyketide synthases[J]. Nature, 2016, 531(7595): 533-537 |
| 78 | ZHENG J T, GAY D C, DEMELER B, et al. Divergence of multimodular polyketide synthases revealed by a didomain structure[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2012, 8(7): 615-621. |
| 79 | GAY D, YOU Y O, KEATINGE-CLAY A, et al. Structure and stereospecificity of the dehydratase domain from the terminal module of the rifamycin polyketide synthase[J]. Biochemistry, 2013, 52(49): 8916-8928. |
| 80 | DUTTA S, WHICHER J R, HANSEN D A, et al. Structure of a modular polyketide synthase[J]. Nature, 2014, 510(7506): 512-517. |
| 81 | WHICHER J R, DUTTA S, HANSEN D A, et al. Structural rearrangements of a polyketide synthase module during its catalytic cycle[J]. Nature, 2014, 510(7506): 560-564. |
| 82 | FELNAGLE E A, JACKSON E E, CHAN Y A, et al. Nonribosomal peptide synthetases involved in the production of medically relevant natural products[J]. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 2008, 5(2): 191-211. |
| 83 | SIEBER S A, MARAHIEL M A. Molecular mechanisms underlying nonribosomal peptide synthesis: approaches to new antibiotics[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2005, 105(2): 715-738. |
| 84 | SÜSSMUTH R D, MAINZ A. Nonribosomal peptide synthesis-principles and prospects[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edtion, 2017, 56(14): 3770-3821. |
| 85 | JAREMKO M J, DAVIS T D, CORPUZ J C, et al. TypeⅡnon-ribosomal peptide synthetase proteins: structure, mechanism, and protein-protein interactions[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2020, 37(3): 355-379. |
| 86 | CALCOTT M J, OWEN J G, ACKERLEY D F. Efficient rational modification of non-ribosomal peptides by adenylation domain substitution[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 4554. |
| 87 | BAUNACH M, CHOWDHURY S, STALLFORTH P, et al. The landscape of recombination events that create nonribosomal peptide diversity[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2021, 38(5): 2116-2130. |
| 88 | RAUSCH C, HOOF I, WEBER T, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of condensation domains in NRPS sheds light on their functional evolution[J]. BMC Ecology and Evolution, 2007, 7: 78. |
| 89 | WHEADON M J, TOWNSEND C A. Evolutionary and functional analysis of an NRPS condensation domain integrates β-lactam, ᴅ-amino acid, and dehydroamino acid synthesis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(17): e2026017118. |
| 90 | STACHELHAUS T, MOOTZ H D, MARAHIEL M A. The specificity-conferring code of adenylation domains in nonribosomal peptide synthetases[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 1999, 6(8): 493-505. |
| 91 | RÖTTIG M, MEDEMA M H, BLIN K, et al. NRPSpredictor2—a web server for predicting NRPS adenylation domain specificity[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, 39(): W362-W367. |
| 92 | CHEVRETTE M G, AICHELER F, KOHLBACHER O, et al. SANDPUMA: ensemble predictions of nonribosomal peptide chemistry reveal biosynthetic diversity across Actinobacteria[J]. Bioinformatics, 2017, 33(20): 3202-3210. |
| 93 | ZIEMERT N, LECHNER A, WIETZ M, et al. Diversity and evolution of secondary metabolism in the marine actinomycete genus Salinispora [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(12): E1130-E1139. |
| 94 | PATTESON J B, FORTINEZ C M, PUTZ A T, et al. Structure and function of a dehydrating condensation domain in nonribosomal peptide biosynthesis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2022, 144(31): 14057-14070. |
| 95 | HOVER B M, KIM S H, KATZ M, et al. Culture-independent discovery of the malacidins as calcium-dependent antibiotics with activity against multidrug-resistant Gram-positive pathogens[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2018, 3(4): 415-422. |
| 96 | CULP E J, WAGLECHNER N, WANG W L, et al. Evolution-guided discovery of antibiotics that inhibit peptidoglycan remodelling[J]. Nature, 2020, 578(7796): 582-587. |
| 97 | XU M, WANG W L, WAGLECHNER N, et al. Phylogeny-informed synthetic biology reveals unprecedented structural novelty in type Ⅴ glycopeptide antibiotics[J]. ACS Central Science, 2022, 8(5): 615-626. |
| 98 | WANG Z Q, KOIRALA B, HERNANDEZ Y, et al. Bioinformatic prospecting and synthesis of a bifunctional lipopeptide antibiotic that evades resistance[J]. Science, 2022, 376(6596): 991-996. |
| 99 | CALCOTT M J, OWEN J G, LAMONT I L, et al. Biosynthesis of novel Pyoverdines by domain substitution in a nonribosomal peptide synthetase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 80(18): 5723-5731. |
| 100 | THIRLWAY J, LEWIS R, NUNNS L, et al. Introduction of a non-natural amino acid into a nonribosomal peptide antibiotic by modification of adenylation domain specificity[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(29): 7181-7184. |
| 101 | KRIES H, WACHTEL R, PABST A, et al. Reprogramming nonribosomal peptide synthetases for clickable amino acids[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(38): 10105-10108. |
| 102 | NGUYEN K T, RITZ D, GU J Q, et al. Combinatorial biosynthesis of novel antibiotics related to daptomycin[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(46): 17462-17467. |
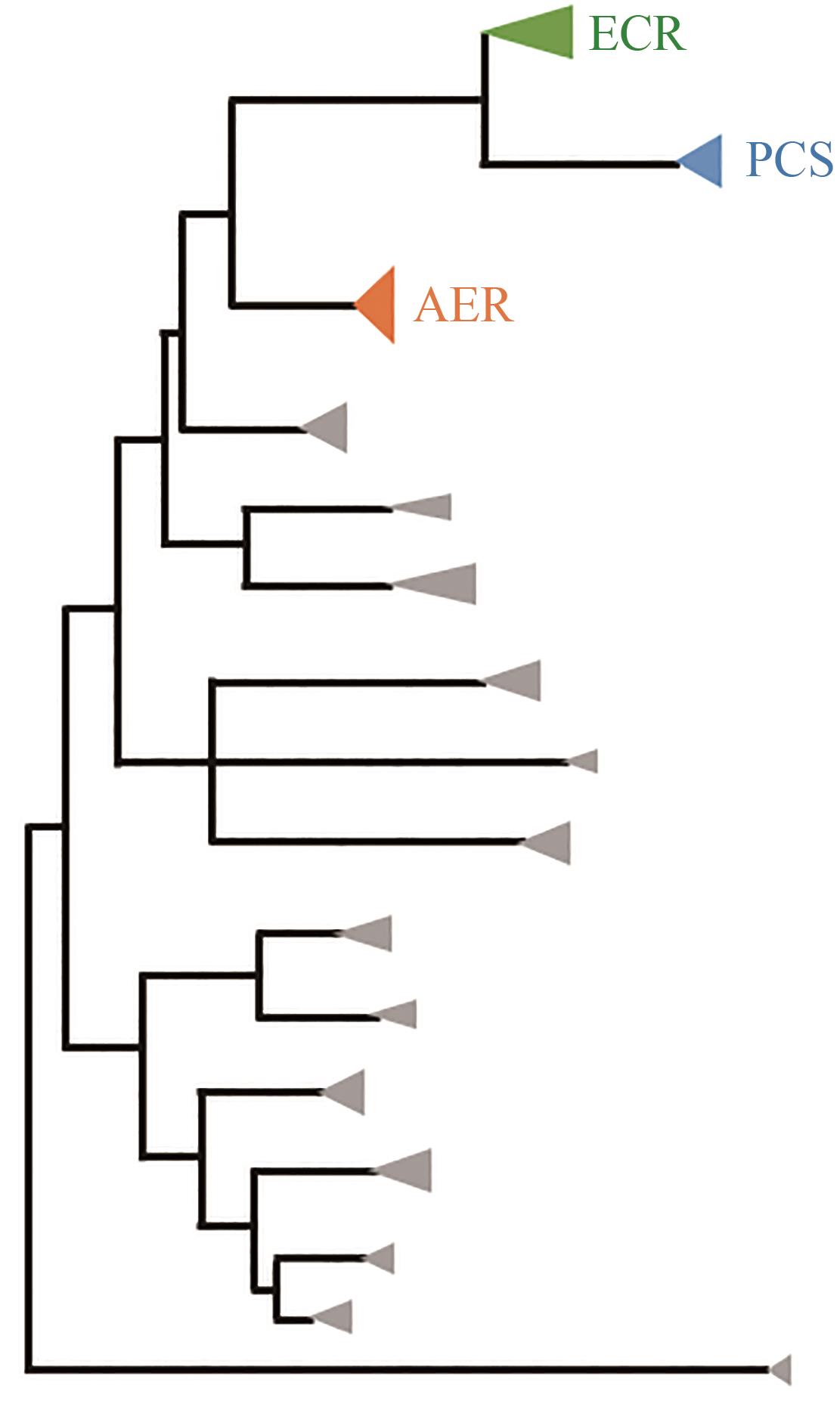
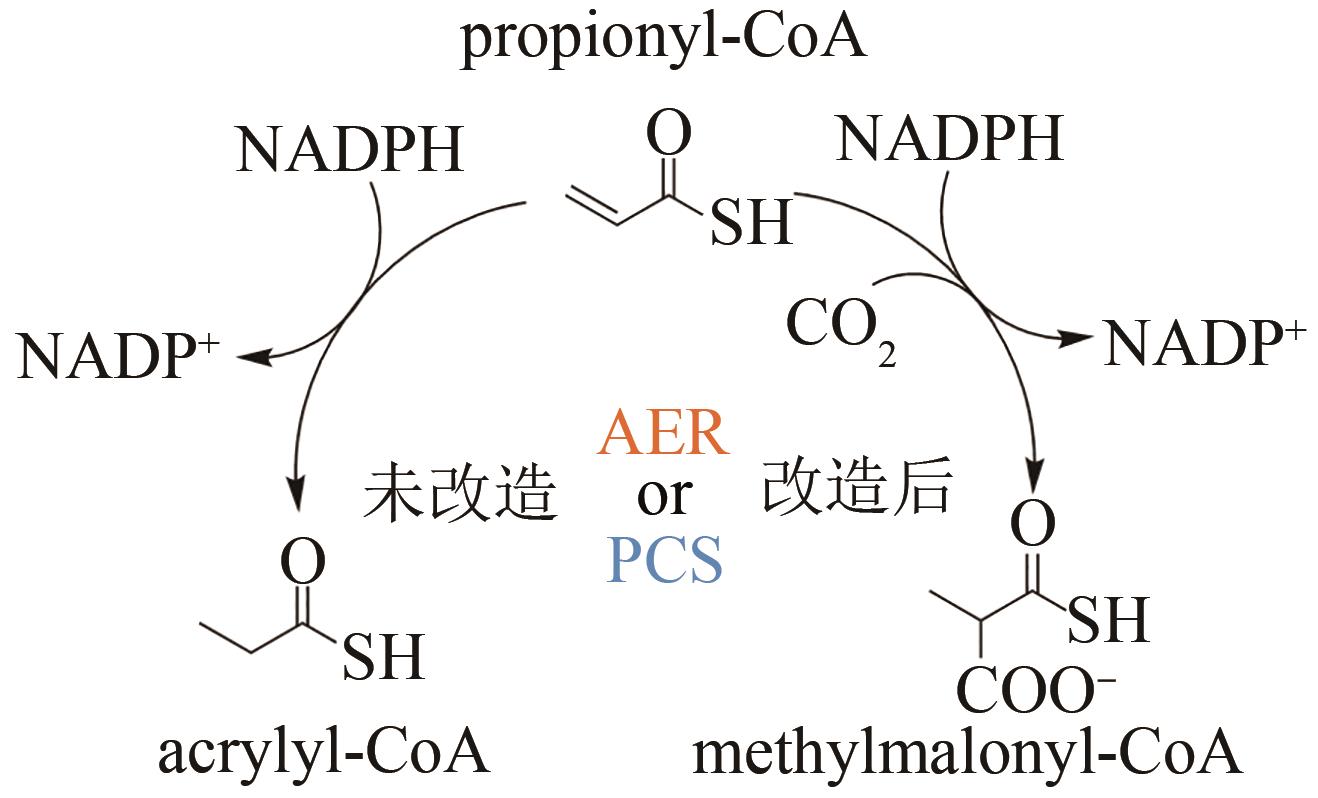
| 103 | CRÜSEMANN M, KOHLHAAS C, PIEL J. Evolution-guided engineering of nonribosomal peptide synthetase adenylation domains[J]. Chemical Science, 2013, 4(3): 1041-1045. |
| 104 | KRIES H, NIQUILLE D L, HILVERT D. A subdomain swap strategy for reengineering nonribosomal peptides[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2015, 22(5): 640-648. |
| 105 | BOZHÜYÜK K A J, LINCK A, TIETZE A, et al. Modification and de novo design of non-ribosomal peptide synthetases using specific assembly points within condensation domains[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2019, 11(7): 653-661. |
| 106 | BOZHÜYÜK K A J, WATZEL J, ABBOOD N, et al. Synthetic zippers as an enabling tool for engineering of non-ribosomal peptide synthetases[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edtion, 2021, 60(32): 17531-17538. |
| 107 | KRANZ J, WENSKI S L, DICHTER A A, et al. Influence of condensation domains on activity and specificity of adenylation domains[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2021, DOI: 10.1101/2021.08.23.457306[2023-02-01]. . |
| 108 | BOZHÜYÜK K A J, FLEISCHHACKER F, LINCK A, et al. De novo design and engineering of non-ribosomal peptide synthetases[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2018, 10(3): 275-281. |
| 109 | MINAMI A, UGAI T, OZAKI T, et al. Predicting the chemical space of fungal polyketides by phylogeny-based bioinformatics analysis of polyketide synthase-nonribosomal peptide synthetase and its modification enzymes[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 13556. |
| 110 | AWAKAWA T, FUJIOKA T, ZHANG L H, et al. Reprogramming of the antimycin NRPS-PKS assembly lines inspired by gene evolution[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3534. |
| 111 | SANTOS-ABERTURAS J, CHANDRA G, FRATTARUOLO L, et al. Uncovering the unexplored diversity of thioamidated ribosomal peptides in Actinobacteria using the RiPPER genome mining tool[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(9): 4624-4637. |
| 112 | 吕靖伟, 邓子新, 张琪, 等. 基于深度学习识别RiPPs前体肽及裂解位点[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(6), 1262-1276. |
| LYU J W, DENG Z X, ZHANG Q, et al. Identification of RiPPs precursor peptides and cleavage sites based on deep learning[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(6), 1262-1276. | |
| 113 | MEDEMA M H, TAKANO E, BREITLING R. Detecting sequence homology at the gene cluster level with MultiGeneBlast[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2013, 30(5): 1218-1223. |
| 114 | TIETZ J I, SCHWALEN C J, PATEL P S, et al. A new genome-mining tool redefines the lasso peptide biosynthetic landscape[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2017, 13(5): 470-478. |
| 115 | MERWIN N J, MOUSA W K, DEJONG C A, et al. DeepRiPP integrates multiomics data to automate discovery of novel ribosomally synthesized natural products[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(1): 371-380. |
| 116 | MARTÍN-SÁNCHEZ L, SINGH K S, AVALOS M, et al. Phylogenomic analyses and distribution of terpene synthases among Streptomyces [J]. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2019, 15: 1181-1193. |
| 117 | JIA Q D, CHEN X L, KÖLLNER T G, et al. Terpene synthase genes originated from bacteria through horizontal gene transfer contribute to terpenoid diversity in fungi[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 9223. |
| 118 | AVALOS M, GARBEVA P, VADER L, et al. Biosynthesis, evolution and ecology of microbial terpenoids[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2022, 39(2): 249-272. |
| 119 | YANG Y L, ZHANG S S, MA K, et al. Discovery and characterization of a new family of diterpene cyclases in bacteria and fungi[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edtion, 2017, 56(17): 4749-4752. |
| 120 | CHEN R, JIA Q D, MU X, et al. Systematic mining of fungal chimeric terpene synthases using an efficient precursor-providing yeast chassis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(29): e2023247118. |
| 121 | TAO H, LAUTERBACH L, BIAN G K, et al. Discovery of non-squalene triterpenes[J]. Nature, 2022, 606(7913): 414-419. |
| 122 | JIANG C G, KIM S Y, SUH D Y. Divergent evolution of the thiolase superfamily and chalcone synthase family[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 2008, 49(3): 691-701. |
| 123 | TAN Z G, CLOMBURG J M, CHEONG S, et al. A polyketoacyl-CoA thiolase-dependent pathway for the synthesis of polyketide backbones[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2020, 3(7): 593-603. |
| 124 | SHANKLIN J, GUY J E, MISHRA G, et al. Desaturases: emerging models for understanding functional diversification of diiron-containing enzymes[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2009, 284(28): 18559-18563. |
| 125 | ZHU X J, LIU J, ZHANG W J. De novo biosynthesis of terminal alkyne-labeled natural products[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(2): 115-120. |
| 126 | ZHU X J, SU M, MANICKAM K, et al. Bacterial genome mining of enzymatic tools for alkyne biosynthesis[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2015, 10(12): 2785-2793. |
| 127 | CHANG F Y, BRADY S F. Discovery of indolotryptoline antiproliferative agents by homology-guided metagenomic screening[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(7): 2478-2483. |
| 128 | CHANG F Y, TERNEI M A, CALLE P Y, et al. Targeted metagenomics: finding rare tryptophan dimer natural products in the environment[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(18): 6044-6052. |
| 129 | CIMERMANCIC P, MEDEMA M H, CLAESEN J., et al. Insights into secondary metabolism from a global analysis of prokaryotic biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Cell, 2014, 158(2): 412-421. |
| 130 | O'NEILL E C, SCHORN M, LARSON C B, et al. Targeted antibiotic discovery through biosynthesis-associated resistance determinants: target directed genome mining[J]. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 2019, 45(3): 255-277. |
| 131 | YAN Y, LIU N, TANG Y. Recent developments in self-resistance gene directed natural product discovery[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2020, 37(7): 879-892. |
| 132 | BERNHARDSGRÜTTER I, SCHELL K, PETER D M, et al. Awakening the sleeping carboxylase function of enzymes: engineering the natural CO2-binding potential of reductases[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(25): 9778-9782. |
| 133 | SIKOSEK T. Computational methods in protein evolution[M]// Methods in molecular biology. New York: Humana Press, 2019: 1064-3745. |
| 134 | HARMS M J, THORNTON J W. Analyzing protein structure and function using ancestral gene reconstruction[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2010, 20(3): 360-366. |
| 135 | CECH N B, MEDEMA M H, CLARDY J. Benefiting from big data in natural products: importance of preserving foundational skills and prioritizing data quality[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2021, 38(11): 1947-1953. |
| 136 | JEON J, KANG S, KIM H U. Predicting biochemical and physiological effects of natural products from molecular structures using machine learning[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2021, 38(11): 1954-1966. |
| [1] | FU Yu, ZHONG Fangrui. Recent advances in chemically driven enantioselective photobiocatalysis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1021-1049. |
| [2] | XIE Xiangqian, GUO Wen, WANG Huan, LI Jin. Biosynthesis and chemical synthesis of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides containing aminovinyl cysteine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 981-996. |
| [3] | TANG Zhijun, HU Youcai, LIU Wen. Enzymatic (4+2)- and (2+2)-cycloaddition reactions: fundamentals and applications of regio- and stereoselectivity [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 401-407. |
| [4] | ZHANG Jun, JIN Shixue, YUN Qian, QU Xudong. Biosynthesis of the unnatural extender units with polyketides and their structural modifications for applications in medicines [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 561-570. |
| [5] | YU Xuchang, WU Hui, LI Lei. Library construction and targeted BGC screening for more efficient discovery of microbial natural products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 492-506. |
| [6] | FENG Jin, PAN Haixue, TANG Gongli. Research advances in biosynthesis of natural product drugs within the past decade [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 408-446. |
| [7] | XI Mengyu, HU Yiling, GU Yucheng, GE Huiming. Genome mining-directed discovery for natural medicinal products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 447-473. |
| [8] | LEI Ru, TAO Hui, LIU Tiangang. Deep genome mining boosts the discovery of microbial terpenoids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 507-526. |
| [9] | SHI Xinjie, DU Yiling. Research advances in the biosynthesis of nonribosomal peptides within the bisintercalator family as anticancer drugs [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 593-611. |
| [10] | ZHANG Rui, JIN Wenzheng, CHEN Yijun. Bacterial inter-PKS hybrids and the biosynthetic algorithm of polyketides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 548-560. |
| [11] | SONG Yongxiang, ZHANG Xiufeng, LI Yanqin, XIAO Hua, YAN Yan. Resistance-gene directed discovery of bioactive natural products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 474-491. |
| [12] | HUI Zhen, TANG Xiaoyu. Applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 editing system in the study of microbial natural products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| [13] | SUN Mengchu, LU Liangyu, SHEN Xiaolin, SUN Xinxiao, WANG Jia, YUAN Qipeng. Fluorescence detection-based high-throughput screening systems and devices facilitate cell factories construction [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 947-965. |
| [14] | HU Zhehui, XU Juan, BIAN Guangkai. Application of automated high-throughput technology in natural product biosynthesis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 932-946. |
| [15] | Yang MING, Bin CHEN, Xiaoqiang HUANG. Recent advances in photoenzymatic synthesis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(4): 651-675. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||