Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (1): 6-21.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-092
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
An evolutionary perspective on quantitative biological principles and synthetic life design
ZHAO Xiaoyu1,2, ZHANG Hao1, LI Xuefei1, HU Zheng1
- 1.Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Science,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
2.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
-
Received:2021-09-18Revised:2021-11-08Online:2022-03-14Published:2022-02-28 -
Contact:HU Zheng
进化视角下的定量生物学规律与人工生命合成
赵晓宇1,2, 张浩1, 李雪飞1, 胡政1
- 1.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,深圳合成生物学创新研究院,广东 深圳 518055
2.中国科学院大学,北京 100049
-
通讯作者:胡政 -
作者简介:赵晓宇 (1999—),女,硕士研究生。主要研究方向为细菌与肿瘤。E-mail:xy.zhao1@siat.ac.cn胡政 (1987—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为基因组学、进化生物学和定量生物学。E-mail:zheng.hu@siat.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金青年基金(32000886);广东省自然科学基金杰出青年基金(2021B1515020042);广东省自然科学基金面上项目(2114050001502)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHAO Xiaoyu, ZHANG Hao, LI Xuefei, HU Zheng. An evolutionary perspective on quantitative biological principles and synthetic life design[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(1): 6-21.
赵晓宇, 张浩, 李雪飞, 胡政. 进化视角下的定量生物学规律与人工生命合成[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(1): 6-21.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2021-092
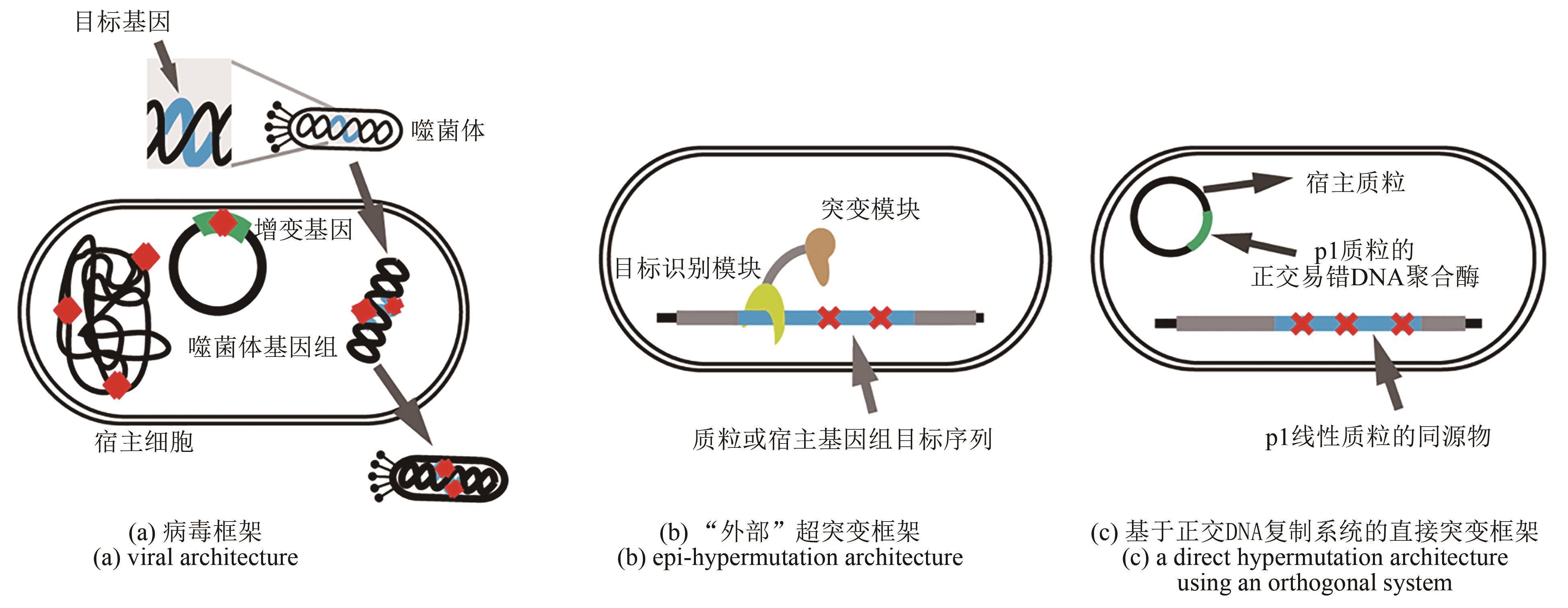
| 方法 | 框架 | 原理 | 进化对象 | 突变速率 | 实例 | 突破性与局限性 | 方法延伸 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PACE[ | 病毒框架 | 将目的蛋白与噬菌体生命周期耦联,利用宿主的致突变质粒和辅助质粒完成突变与扩增,通过自动化连续培养实现选择与连续进化 | 包含目的基因的噬菌体 | 2.3×10-3 bp/代;突变文库数量可达到109个 | 碱基编辑器[ | 优点:应用范围最广且优化速度较快,是其他进化方法的100倍 缺点:只适用于能被噬菌体感染的原核生物;只能突变引起gⅢ基因表达变化的蛋白;操作和设备复杂 | SE-PACE系统[ |
| CRISPR-X[ | “外部”突变框架 | CRISPR系统融合胞苷脱氨酶(AID),将目标基因的C脱氨并修复为T,实现碱基对直接替换 | 哺乳细胞 | 1×10-3 bp/代 | 慢性髓系白血病细胞中的耐药突变[ | 优点:适用于哺乳细胞,实现特定碱基对替换 缺点:只能实现C到T的突变,突变率较低,未实现真正的连续进化 | 胞嘧啶剪辑编辑器[ |
| OrthoRep[ | 直接突变框架 | 含有目标基因和突变的DNAP的质粒、含有所有必需基因的质粒负责靶基因的复制与突变,与基因组的复制正交 | 酵母中的正交突变质粒 | 1×10-5 bp/代;能保持超过300 代的高突变率 | 进化耐药性疟疾二氢叶酸还原酶[ | 优点:正交系统可保持细胞基因组的稳定,实现连续进化 缺点:局限于酵母;系统设计复杂;外源性基因低表达 | OrthoRep基因表达盒[ |
Table 1 Principles and methods for continuous directed-evolution
| 方法 | 框架 | 原理 | 进化对象 | 突变速率 | 实例 | 突破性与局限性 | 方法延伸 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PACE[ | 病毒框架 | 将目的蛋白与噬菌体生命周期耦联,利用宿主的致突变质粒和辅助质粒完成突变与扩增,通过自动化连续培养实现选择与连续进化 | 包含目的基因的噬菌体 | 2.3×10-3 bp/代;突变文库数量可达到109个 | 碱基编辑器[ | 优点:应用范围最广且优化速度较快,是其他进化方法的100倍 缺点:只适用于能被噬菌体感染的原核生物;只能突变引起gⅢ基因表达变化的蛋白;操作和设备复杂 | SE-PACE系统[ |
| CRISPR-X[ | “外部”突变框架 | CRISPR系统融合胞苷脱氨酶(AID),将目标基因的C脱氨并修复为T,实现碱基对直接替换 | 哺乳细胞 | 1×10-3 bp/代 | 慢性髓系白血病细胞中的耐药突变[ | 优点:适用于哺乳细胞,实现特定碱基对替换 缺点:只能实现C到T的突变,突变率较低,未实现真正的连续进化 | 胞嘧啶剪辑编辑器[ |
| OrthoRep[ | 直接突变框架 | 含有目标基因和突变的DNAP的质粒、含有所有必需基因的质粒负责靶基因的复制与突变,与基因组的复制正交 | 酵母中的正交突变质粒 | 1×10-5 bp/代;能保持超过300 代的高突变率 | 进化耐药性疟疾二氢叶酸还原酶[ | 优点:正交系统可保持细胞基因组的稳定,实现连续进化 缺点:局限于酵母;系统设计复杂;外源性基因低表达 | OrthoRep基因表达盒[ |
| 28 | MA Y Q, ZHANG J Y, YIN W J, et al. Targeted AID-mediated mutagenesis (TAM) enables efficient genomic diversification in mammalian cells[J]. Nature Methods, 2016, 13(12): 1029-1035. |
| 29 | GAUDELLI N M, KOMOR A C, REES H A, et al. Programmable base editing of A•T to G•C in genomic DNA without DNA cleavage[J]. Nature, 2017, 551(7681): 464-471. |
| 30 | ANZALONE A V, RANDOLPH P B, DAVIS J R, et al. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA[J]. Nature, 2019, 576(7785): 149-157. |
| 31 | ZHONG Z W, RAVIKUMAR A, LIU C C. Tunable expression systems for orthogonal DNA replication[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(12): 2930-2934. |
| 32 | ARZUMANYAN G A, GABRIEL K N, RAVIKUMAR A, et al. Mutually orthogonal DNA replication systems in vivo [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(7): 1722-1729. |
| 33 | JAVANPOUR A A, LIU C C. Genetic compatibility and extensibility of orthogonal replication[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(6): 1249-1256. |
| 34 | YANG K K, WU Z, ARNOLD F H. Machine-learning-guided directed evolution for protein engineering[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(8): 687-694. |
| 35 | WU Z, KAN S B J, LEWIS R D, et al. Machine learning-assisted directed protein evolution with combinatorial libraries[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(18): 8852-8858. |
| 36 | MUSDAL Y, GOVINDARAJAN S, MANNERVIK B. Exploring sequence-function space of a poplar glutathione transferase using designed information-rich gene variants[J]. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection, 2017, 30(8): 543-549. |
| 37 | ROMERO P A, KRAUSE A, ARNOLD F H. Navigating the protein fitness landscape with Gaussian processes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(3): E193-E201. |
| 38 | HAMEDIRAD M, CHAO R, WEISBERG S, et al. Towards a fully automated algorithm driven platform for biosystems design[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 5150. |
| 39 | BASHIR A, YANG Q, WANG J P, et al. Machine learning guided aptamer refinement and discovery[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 2366. |
| 40 | Knight C G, Platt M, Rowe W, et al. Array-based evolution of DNA aptamers allows modelling of an explicit sequence-fitness landscape[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2009, 37(1):e6. |
| 41 | SCHISSEL C K, MOHAPATRA S, WOLFE J M, et al. Deep learning to design nuclear-targeting abiotic miniproteins[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2021, 13(10): 992-1000. |
| 42 | BEDBROOK C N, YANG K K, RICE A J, et al. Machine learning to design integral membrane channelrhodopsins for efficient eukaryotic expression and plasma membrane localization[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2017, 13(10): e1005786. |
| 43 | BEDBROOK C N, YANG K K, ROBINSON J E, et al. Machine learning-guided channelrhodopsin engineering enables minimally invasive optogenetics[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(11): 1176-1184. |
| 44 | LIAO M J, DIN M O, TSIMRING L, et al. Rock-paper-scissors: engineered population dynamics increase genetic stability[J]. Science, 2019, 365(6457): 1045-1049. |
| 45 | SHAHAB R L, BRETHAUER S, DAVEY M P, et al. A heterogeneous microbial consortium producing short-chain fatty acids from lignocellulose[J]. Science, 2020, 369(6507): eabb1214. |
| 46 | BUSKIRK S W, PEACE R E, LANG G I. Hitchhiking and epistasis give rise to cohort dynamics in adapting populations[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(31): 8330-8335. |
| 47 | RUGBJERG P, MYLING-PETERSEN N, PORSE A, et al. Diverse genetic error modes constrain large-scale bio-based production[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 787. |
| 48 | RACKHAM O, CHIN J W. A network of orthogonal ribosome·mRNA pairs[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2005, 1(3): 159-166. |
| 49 | VECCHIO D DEL. Modularity, context-dependence, and insulation in engineered biological circuits[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2015, 33(2): 111-119. |
| 50 | ISAACS F J, DWYER D J, DING C M, et al. Engineered riboregulators enable post-transcriptional control of gene expression[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2004, 22(7): 841-847. |
| 51 | UMENHOFFER K, FEHÉR T, BALIKÓ G, et al. Reduced evolvability of Escherichia coli MDS42, an IS-less cellular chassis for molecular and synthetic biology applications[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2010, 9: 38. |
| 52 | SUÁREZ G A, RENDA B A, DASGUPTA A, et al. Reduced mutation rate and increased transformability of transposon-free acinetobacter baylyi ADP1-ISx[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2017, 83(17): e01025-e01017. |
| 53 | GENG P, LEONARD S P, MISHLER D M, et al. Synthetic genome defenses against selfish DNA elements stabilize engineered bacteria against evolutionary failure[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(3): 521-531. |
| 54 | CHAN C T Y, LEE J W, CAMERON D E, et al. 'Deadman' and 'Passcode' microbial kill switches for bacterial containment[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2016, 12(2): 82-86. |
| 55 | LIANG P X, ZHANG Y T, XU B, et al. Deletion of genomic islands in the Pseudomonas putida KT2440 genome can create an optimal chassis for synthetic biology applications[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2020, 19(1): 70. |
| 56 | KAMP A VON, KLAMT S. Growth-coupled overproduction is feasible for almost all metabolites in five major production organisms[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15956. |
| 57 | GODARA A, KAO K C. Adaptive laboratory evolution for growth coupled microbial production[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2020, 36(11): 175. |
| 58 | FONG S S, BURGARD A P, HERRING C D, et al. In silico design and adaptive evolution of Escherichia coli for production of lactic acid[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2005, 91(5): 643-648. |
| 59 | RUGBJERG P, SARUP-LYTZEN K, NAGY M, et al. Synthetic addiction extends the productive life time of engineered Escherichia coli populations[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(10): 2347-2352. |
| 60 | SON H I, WEISS A, YOU L C. Design patterns for engineering genetic stability[J]. Current Opinion in Biomedical Engineering, 2021, 19: 100297. |
| 61 | DAI Z J, LEE A J, ROBERTS S, et al. Versatile biomanufacturing through stimulus-responsive cell-material feedback[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(10): 1017-1024. |
| 62 | SEGALL-SHAPIRO T H, SONTAG E D, VOIGT C A. Engineered promoters enable constant gene expression at any copy number in bacteria[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(4): 352-358. |
| 63 | LIU Q J, SCHUMACHER J, WAN X Y, et al. Orthogonality and burdens of heterologous AND gate gene circuits in E. coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(2): 553-564. |
| 1 | 刘陈立, 汤超, 汤雷翰, 等. 定量至简, 工程至繁: 定量工程生物学[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(3): 261-263. |
| LIU C L, TANG C, TANG L H, et al. Quantifying to simplicity, engineering to complexity: quantitative engineering biology[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(3): 261-263. | |
| 2 | SLEIGHT S C, SAURO H M. Visualization of evolutionary stability dynamics and competitive fitness of Escherichia coli engineered with randomized multigene circuits[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2013, 2(9): 519-528. |
| 3 | KURLAND C G, DONG H. Bacterial growth inhibition by overproduction of protein[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 1996, 21(1): 1-4. |
| 4 | CARBONELL-BALLESTERO M, GARCIA-RAMALLO E, MONTAÑEZ R, et al. Dealing with the genetic load in bacterial synthetic biology circuits: convergences with the Ohm's law[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 44(1): 496-507. |
| 5 | QIAN Y L, HUANG H H, JIMÉNEZ J I, et al. Resource competition shapes the response of genetic circuits[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(7): 1263-1272. |
| 6 | WANG Y J, XUE P, CAO M F, et al. Directed evolution: methodologies and applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(20): 12384-12444. |
| 7 | LIU W R, CREMER J, LI D J, et al. An evolutionarily stable strategy to colonize spatially extended habitats[J]. Nature, 2019, 575(7784): 664-668. |
| 8 | ELLIS T. Predicting how evolution will beat us[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2019, 12(1): 41-43. |
| 9 | MILLS D R, PETERSON R L, SPIEGELMAN S. An extracellular Darwinian experiment with a self-duplicating nucleic acid molecule[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1967, 58(1): 217-224. |
| 10 | ESVELT K M, CARLSON J C, LIU D R. A system for the continuous directed evolution of biomolecules[J]. Nature, 2011, 472(7344): 499-503. |
| 11 | 蒋迎迎, 曲戈, 孙周通. 机器学习助力酶定向进化[J]. 生物学杂志, 2020, 37(4): 1-11. |
| 64 | CASTLE S D, GRIERSON C S, GOROCHOWSKI T E. Towards an engineering theory of evolution[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 3326. |
| 65 | JACK B R, LEONARD S P, MISHLER D M, et al. Predicting the genetic stability of engineered DNA sequences with the EFM calculator[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(8): 939-943. |
| 66 | CERONI F, ALGAR R, STAN G B, et al. Quantifying cellular capacity identifies gene expression designs with reduced burden[J]. Nature Methods, 2015, 12(5): 415-418. |
| 67 | BORKOWSKI O, BRICIO C, MURGIANO M, et al. Cell-free prediction of protein expression costs for growing cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1457. |
| 68 | BAIER F, SCHAERLI Y. Addressing evolutionary questions with synthetic biology[M]// CROMBACH A. Evolutionary Systems Biology-Advances, Questions, and Opportunities. 2nd ed. Villeurbanne, France: Springer Press, 2021:135-157. |
| 69 | FREDENS J, WANG K H, DE LA TORRE D, et al. Total synthesis of Escherichia coli with a recoded genome[J]. Nature, 2019, 569(7757): 514-518. |
| 70 | HOSHIKA S, LEAL N A, KIM M J, et al. Hachimoji DNA and RNA: a genetic system with eight building blocks[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6429): 884-887. |
| 71 | PELLETIER J F, SUN L J, WISE K S, et al. Genetic requirements for cell division in a genomically minimal cell[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(9): 2430-2440.e16. |
| 72 | HUTCHISON C A 3rd, CHUANG R Y, NOSKOV V N, et al. Design and synthesis of a minimal bacterial genome[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6280): aad6253. |
| 73 | GROSBERG R K, STRATHMANN R R. The evolution of multicellularity: a minor major transition? [J]. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 2007, 38: 621-654. |
| 74 | NIKLAS K J. The evolutionary-developmental origins of multicellularity[J]. American Journal of Botany, 2014, 101(1): 6-25. |
| 75 | KAISER D, ROBINSON M, KROOS L. Myxobacteria, polarity, and multicellular morphogenesis[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2010, 2(8): a000380. |
| 11 | JIANG Y Y, QU G, SUN Z T. Machine learning-assisted enzyme directed evolution[J]. Journal of Biology, 2020, 37(4): 1-11. |
| 12 | RIX G, LIU C C. Systems for in vivo hypermutation: a quest for scale and depth in directed evolution[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2021, 64: 20-26. |
| 13 | 陈珏, 黄佳敏, 燕天鹤, 等. 随机突变文库构建与筛选研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37(1): 163-177. |
| CHEN J, HUANG J M, YAN T H, et al. Progress in the construction and screening of random mutation library[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37(1): 163-177. | |
| 14 | 郭园, 赵仲麟. 微生物系统定向进化与合成生物学应用研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2017, 33(1): 76-82. |
| GUO Yuan, ZHAO Zhonglin. Advances on applications of synthetic biology and directed evolution in microbial systems[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2017, 33(1): 76-82. | |
| 15 | CARLSON J C, BADRAN A H, GUGGIANA-NILO D A, et al. Negative selection and stringency modulation in phage-assisted continuous evolution[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2014, 10(3): 216-222. |
| 16 | 翟昊天, 祁庆生, 侯进. 体内连续进化技术的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37(2): 486-499. |
| ZHAI H T, QI Q S, HOU J. Recent advances of continuous in vivo evolution[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37(2): 486-499. | |
| 17 | FIJALKOWSKA I J, SCHAAPER R M. Mutants in the ExoⅠ motif of Escherichia coli dnaQ: defective proofreading and inviability due to error catastrophe[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1996, 93(7): 2856-2861. |
| 18 | HESS G T, FRÉSARD L, HAN K, et al. Directed evolution using dCas9-targeted somatic hypermutation in mammalian cells[J]. Nature Methods, 2016, 13(12): 1036-1042. |
| 19 | KOMOR A C, KIM Y B, PACKER M S, et al. Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage[J]. Nature, 2016, 533(7603): 420-424. |
| 20 | COX E C, HORNER D L. Structure and coding properties of a dominant Escherichia coli mutator gene, mutD [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1983, 80(8): 2295-2299. |
| 21 | SHIMODA C, ITADANI A, SUGINO A, et al. Isolation of thermotolerant mutants by using proofreading-deficient DNA polymerase delta as an effective mutator in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Genes & Genetic Systems, 2006, 81(6): 391-397. |
| 22 | RAVIKUMAR A, ARZUMANYAN G A, OBADI M K A, et al. Scalable, continuous evolution of genes at mutation rates above genomic error thresholds[J]. Cell, 2018, 175(7): 1946-1957.e13. |
| 23 | THURONYI B W, KOBLAN L W, LEVY J M, et al. Continuous evolution of base editors with expanded target compatibility and improved activity[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(9): 1070-1079. |
| 24 | HU J H, MILLER S M, GEURTS M H, et al. Evolved Cas9 variants with broad PAM compatibility and high DNA specificity[J]. Nature, 2018, 556(7699): 57-63. |
| 25 | BLUM T R, LIU H, PACKER M S, et al. Phage-assisted evolution of botulinum neurotoxin proteases with reprogrammed specificity[J]. Science, 2021, 371(6531): 803-810. |
| 26 | WANG T N, BADRAN A H, HUANG T P, et al. Continuous directed evolution of proteins with improved soluble expression[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(10): 972-980. |
| 27 | ROTH T B, WOOLSTON B M, STEPHANOPOULOS G, et al. Phage-assisted evolution of bacillus methanolicus methanol dehydrogenase 2[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(4): 796-806. |
| 76 | BENABENTOS R, HIROSE S, SUCGANG R, et al. Polymorphic members of the lag gene family mediate kin discrimination in dictyostelium[J]. Current Biology, 2009, 19(7): 567-572. |
| 77 | RATCLIFF W C, DENISON R F, BORRELLO M, et al. Experimental evolution of multicellularity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(5): 1595-1600. |
| 78 | RATCLIFF W C, FANKHAUSER J D, ROGERS D W, et al. Origins of multicellular evolvability in snowflake yeast[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 6102. |
| 79 | LANDGE A N, JORDAN B M, DIEGO X, et al. Pattern formation mechanisms of self-organizing reaction-diffusion systems[J]. Developmental Biology, 2020, 460(1): 2-11. |
| 80 | LIU C L, FU X F, LIU L Z, et al. Sequential establishment of stripe patterns in an expanding cell population[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6053): 238-241. |
| 81 | SOLÉ R, OLLÉ-VILA A, VIDIELLA B, et al. The road to synthetic multicellularity[J]. Current Opinion in Systems Biology, 2018, 7: 60-67. |
| 82 | 肖敏凤, 张炳照, 刘陈立. 合成生物学在生命起源、进化、结构和功能相互关系研究中的作用[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2015, 45(10): 915-927. |
| XIAO M F, ZHANG B Z, LIU C L. Synthetic biology in studying the origin of life, evolution, and structure-function relation[J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2015, 45(10): 915-927. | |
| 83 | SCHAERLI Y, JIMÉNEZ A, DUARTE J M, et al. Synthetic circuits reveal how mechanisms of gene regulatory networks constrain evolution[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2018, 14(9): e8102. |
| 84 | LAGATOR M, SARIKAS S, ACAR H, et al. Regulatory network structure determines patterns of intermolecular epistasis[J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e28921. |
| 85 | HARMS M J, THORNTON J W. Evolutionary biochemistry: revealing the historical and physical causes of protein properties[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2013, 14(8): 559-571. |
| 86 | STARR T N, THORNTON J W. Epistasis in protein evolution[J]. Protein Science, 2016, 25(7): 1204-1218. |
| 87 | STARR T N, PICTON L K, THORNTON J W. Alternative evolutionary histories in the sequence space of an ancient protein[J]. Nature, 2017, 549(7672): 409-413. |
| 88 | STARR T N, FLYNN J M, MISHRA P, et al. Pervasive contingency and entrenchment in a billion years of Hsp90 evolution[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(17): 4453-4458. |
| 89 | CLIFTON B E, JACKSON C J. Ancestral protein reconstruction yields insights into adaptive evolution of binding specificity in solute-binding proteins[J]. Cell Chemical Biology, 2016, 23(2): 236-245. |
| 90 | FRAEBEL D T, MICKALIDE H, SCHNITKEY D, et al. Environment determines evolutionary trajectory in a constrained phenotypic space[J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e24669. |
| 91 | CAO Y, RYSER M D, PAYNE S, et al. Collective space-sensing coordinates pattern scaling in engineered bacteria[J]. Cell, 2016, 165(3): 620-630. |
| 92 | POELWIJK F J, DE VOS M G J, TANS S J. Tradeoffs and optimality in the evolution of gene regulation[J]. Cell, 2011, 146(3): 462-470. |
| 93 | ÇAĞATAY T, TURCOTTE M, ELOWITZ M B, et al. Architecture-dependent noise discriminates functionally analogous differentiation circuits[J]. Cell, 2009, 139(3): 512-522. |
| 94 | ERICKSON D W, SCHINK S J, PATSALO V, et al. A global resource allocation strategy governs growth transition kinetics of Escherichia coli [J]. Nature, 2017, 551(7678): 119-123. |
| 95 | MA N J, ISAACS F J. Genomic recoding broadly obstructs the propagation of horizontally transferred genetic elements[J]. Cell Systems, 2016, 3(2): 199-207. |
| 96 | BÓDI Z, FARKAS Z, NEVOZHAY D, et al. Phenotypic heterogeneity promotes adaptive evolution[J]. PLoS Biology, 2017, 15(5): e2000644. |
| 97 | NEJMAN D, LIVYATAN I, FUKS G, et al. The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor type-specific intracellular bacteria[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6494): 973-980. |
| 98 | HOFER M, LUTOLF M P. Engineering organoids[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2021, 6(5): 402-420. |
| 99 | SEPICH-POORE G D, ZITVOGEL L, STRAUSSMAN R, et al. The microbiome and human cancer[J]. Science, 2021, 371(6536): eabc4552. |
| 100 | PEISAJOVICH S G. Evolutionary synthetic biology[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2012, 1(6): 199-210. |
| 101 | TAYLOR T. Evolutionary innovations and where to find them: Routes to open-ended evolution in natural and artificial systems[J]. Artificial Life, 2019, 25(2): 207-224. |
| 102 | ROTHSCHILD L J. A powerful toolkit for synthetic biology: Over 3.8 billion years of evolution[J]. BioEssays, 2010, 32(4): 304-313. |
| 103 | LOPATKIN A J, COLLINS J J. Predictive biology: modelling, understanding and harnessing microbial complexity[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2020, 18(9): 507-520. |
| 104 | LOPATKIN A J, SYSOEVA T A, YOU L C. Dissecting the effects of antibiotics on horizontal gene transfer: Analysis suggests a critical role of selection dynamics[J]. BioEssays, 2016, 38(12): 1283-1292. |
| 105 | ENKE T N, DATTA M S, SCHWARTZMAN J, et al. Modular assembly of polysaccharide-degrading marine microbial communities[J]. Current Biology, 2019, 29(9): 1528-1535. |
| 106 | GOLDFORD J E, LU N X, BAJIĆ D, et al. Emergent simplicity in microbial community assembly[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6401): 469-474. |
| 107 | SANCHEZ A, GORE J. Feedback between population and evolutionary dynamics determines the fate of social microbial populations[J]. PLoS Biology, 2013, 11(4): e1001547. |
| 108 | HEKSTRA D R, LEIBLER S. Contingency and statistical laws in replicate microbial closed ecosystems[J]. Cell, 2012, 149(5): 1164-1173. |
| 109 | GALLUP O, MING H, ELLIS T. Ten future challenges for synthetic biology[J]. Engineering Biology, 2021, 5(3): 51-59. |
| [1] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [12] | CAI Bingyu, TAN Xiangtian, LI Wei. Advances in synthetic biology for engineering stem cell [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [13] | XIE Huang, ZHENG Yilei, SU Yiting, RUAN Jingyi, LI Yongquan. An overview on reconstructing the biosynthetic system of actinomycetes for polyketides production [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [14] | ZHA Wenlong, BU Lan, ZI Jiachen. Advances in synthetic biology for producing potent pharmaceutical ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| [15] | HUI Zhen, TANG Xiaoyu. Applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 editing system in the study of microbial natural products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||