|
||
|
Advances in synthetic biology for producing potent pharmaceutical ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine
Synthetic Biology Journal
2024, 5 (3):
631-657.
DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-082
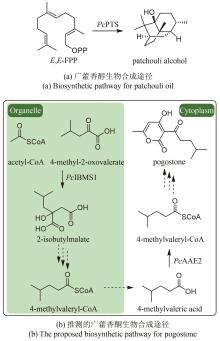
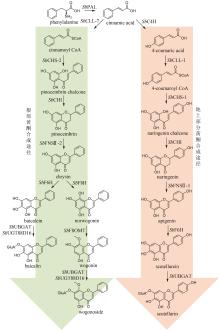
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is a treasure of Chinese civilization and also a good mine for drug development in China. Many TCM components come from rare biological species including plants, animals, and insects, making the preparation of these TCM pharmaceutical substances at large scales a bottleneck that substantially impedes TCM-based drug development. However, the rapid development of synthetic biology has provided a strategy for addressing this challenge. At present, significant progress has been made in the bio-production of individual TCM components, but the efficacy of TCM is mainly due to the synergistic effect of those ingredients, which are termed as pharmaceutical ingredient groups. Reports on constructing the bio-production platform of pharmaceutical ingredient groups are limited. Herein, we summarize research progress in the biogenic mechanism of important TCM pharmaceutical ingredient groups, such as volatile oils, saponins, flavonoids, lignans and alkaloids. Some individual components of pharmaceutical ingredient groups (e.g. ginsenosides) are synthesized by multiple branching pathways, which can be produced and formatted thereafter. On the other hand, some pharmaceutical ingredients such as sandalwood oil can be synthesized through single pathways/enzymatic reactions by engineering the key enzymes to optimize their ratio. We comment the strategy of combining enzyme engineering and metabolic engineering to optimize both the production of pharmaceutical ingredient groups and their ratio. At the end, we outline the prospect of synthetic biology research for producing pharmaceutical ingredient groups, including: (1) complete clarification of the biogenic mechanism of more complex pharmaceutical ingredient groups, (2) development of novel metabolic engineering approaches for breaking through homogenization of methodology, and (3) optimization of the catalytic characteristics of key synthetic enzymes by combining rational design and directed evolution.
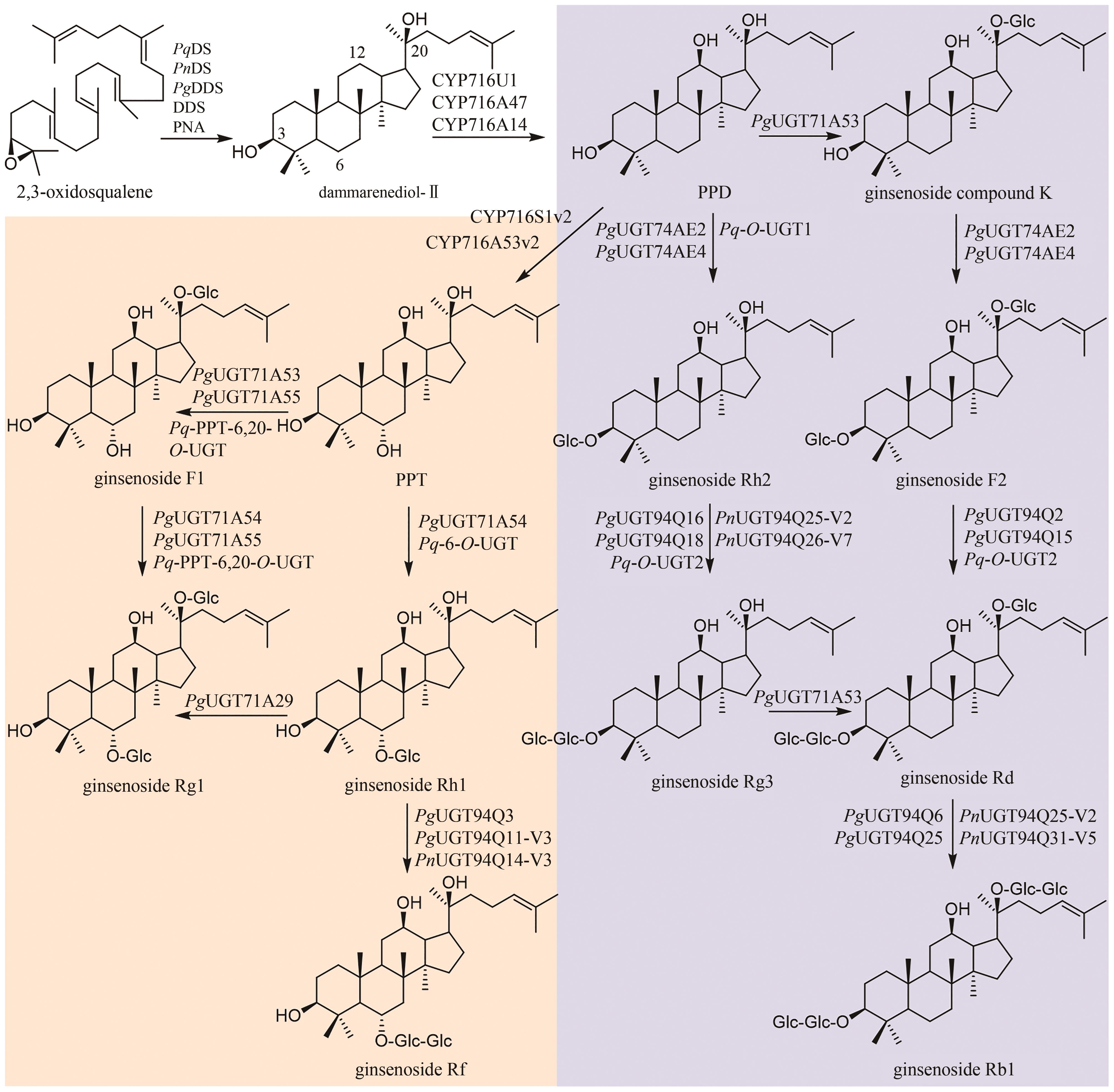
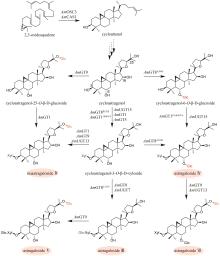
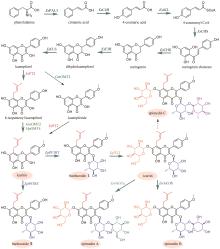
Fig. 3
Biosynthetic pathway for ginsenosides
Extracts from the Article
国内外学者对人参皂苷的生物合成进行了深入的研究(图3)。首先,达玛烯二醇-Ⅱ合酶(DS)环化2,3-环氧鲨烯,生成达玛烯二醇(dammarenediol-Ⅱ)。目前,已鉴定多个DS酶,如:人参(Panax ginseng C. A. Mey.)中的PNA[58]、DDS[59]和PgDDS[60]以及三七[Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F. H. Chen]中的PnDS[61]和西洋参(Panax quinquefolium L.)中的PqDS[62]。人参中的三个CYP酶CYP716U1、CYP716A47和CYP716A14负责催化达玛烯二醇C12位的羟基化,生成PPD;然后,CYP716S1v2和CYP716A53v2催化C6位羟基化,生成PPT(图3)[63-65]。
人参皂苷生物合成的糖基化过程十分复杂,同一步骤往往可被数种甚至几十种糖基转移酶催化,而一种糖基转移酶也常常可以接受多个底物或者催化不同位点的糖基化。因此,对于每步糖基化反应,这里仅列举催化效率较高的糖基转移酶。PPD通过两条途径生成人参皂苷Rd(图3)。在第一条途径中,PPD可在PgUGT71A53和PgUGT74AE2/PgUGT74AE4的连续催化下,发生C20位和C3位羟基的糖基化,生成人参皂苷F2;之后,在PgUGT94Q2/PgUGT94Q15/Pq-O-UGT2的催化下,C3位糖链被进一步延长,得到人参皂苷Rd[66-68]。在第二条途径中,PgUGT74AE2/PgUGT74AE4/Pq-O-UGT1催化PPD的C3位羟基的糖基化,生成人参皂苷Rh2[66,68-70];进一步在PgUGT94Q16/PgUGT94Q18/PnUGT94Q25-V2/PnUGT94Q26-V7/Pq-O-UGT2的催化下,延长C3位糖链,生成人参皂苷Rg3[66-69];最后,PgUGT71A53糖基化人参皂苷Rg3的C20位羟基,生成人参皂苷Rd[71]。人参皂苷Rd在PgUGT94Q6/PgUGT94Q25/PnUGT94Q25-V2/PnUGT94Q31-V5的催化下,延长C20位糖链,得到人参皂苷Rb1[71]。
从PPT到人参皂苷Rg1的转化也有两条途径(图3)。在第一条途径中,PgUGT71A53/PgUGT71A55/Pq-PPT-6,20-O-UGT催化PPT的C20位羟基糖基化,生成人参皂苷F1[71-73];随后,PgUGT71A54/PgUGT71A55/Pq-PPT-6,20-O-UGT糖基化人参皂苷F1的C6位羟基,得到人参皂苷Rg1[72]。在第二条途径中,PgUGT71A54/Pq-6-O-UGT催化PPT的C6位羟基糖基化,生成人参皂苷Rh1;进一步在PgUGT71A29的催化下,发生C20位羟基糖基化,生成人参皂苷Rg1[74]。此外,人参皂苷Rh1还可在PgUGT94Q3/PgUGT94Q11-V3/PnUGT94Q14-V3的催化下,发生C6位糖基化,生成人参皂苷Rf[68](图3)。
Other Images/Table from this Article
|