|
||
|
Advances in synthetic biology for producing potent pharmaceutical ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine
Synthetic Biology Journal
2024, 5 (3):
631-657.
DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-082
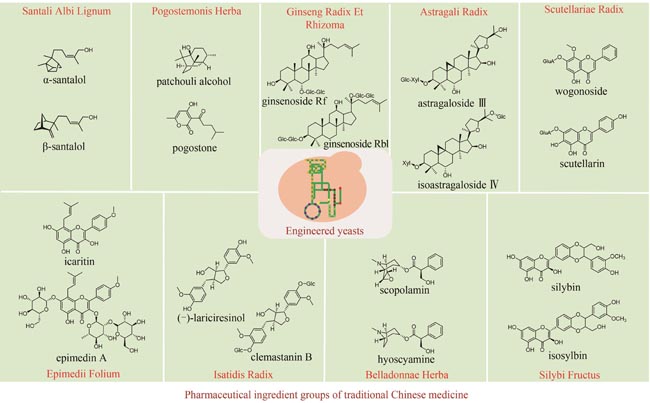
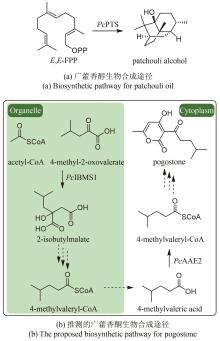
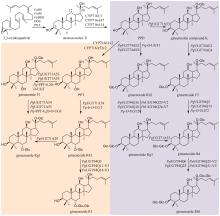
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is a treasure of Chinese civilization and also a good mine for drug development in China. Many TCM components come from rare biological species including plants, animals, and insects, making the preparation of these TCM pharmaceutical substances at large scales a bottleneck that substantially impedes TCM-based drug development. However, the rapid development of synthetic biology has provided a strategy for addressing this challenge. At present, significant progress has been made in the bio-production of individual TCM components, but the efficacy of TCM is mainly due to the synergistic effect of those ingredients, which are termed as pharmaceutical ingredient groups. Reports on constructing the bio-production platform of pharmaceutical ingredient groups are limited. Herein, we summarize research progress in the biogenic mechanism of important TCM pharmaceutical ingredient groups, such as volatile oils, saponins, flavonoids, lignans and alkaloids. Some individual components of pharmaceutical ingredient groups (e.g. ginsenosides) are synthesized by multiple branching pathways, which can be produced and formatted thereafter. On the other hand, some pharmaceutical ingredients such as sandalwood oil can be synthesized through single pathways/enzymatic reactions by engineering the key enzymes to optimize their ratio. We comment the strategy of combining enzyme engineering and metabolic engineering to optimize both the production of pharmaceutical ingredient groups and their ratio. At the end, we outline the prospect of synthetic biology research for producing pharmaceutical ingredient groups, including: (1) complete clarification of the biogenic mechanism of more complex pharmaceutical ingredient groups, (2) development of novel metabolic engineering approaches for breaking through homogenization of methodology, and (3) optimization of the catalytic characteristics of key synthetic enzymes by combining rational design and directed evolution.
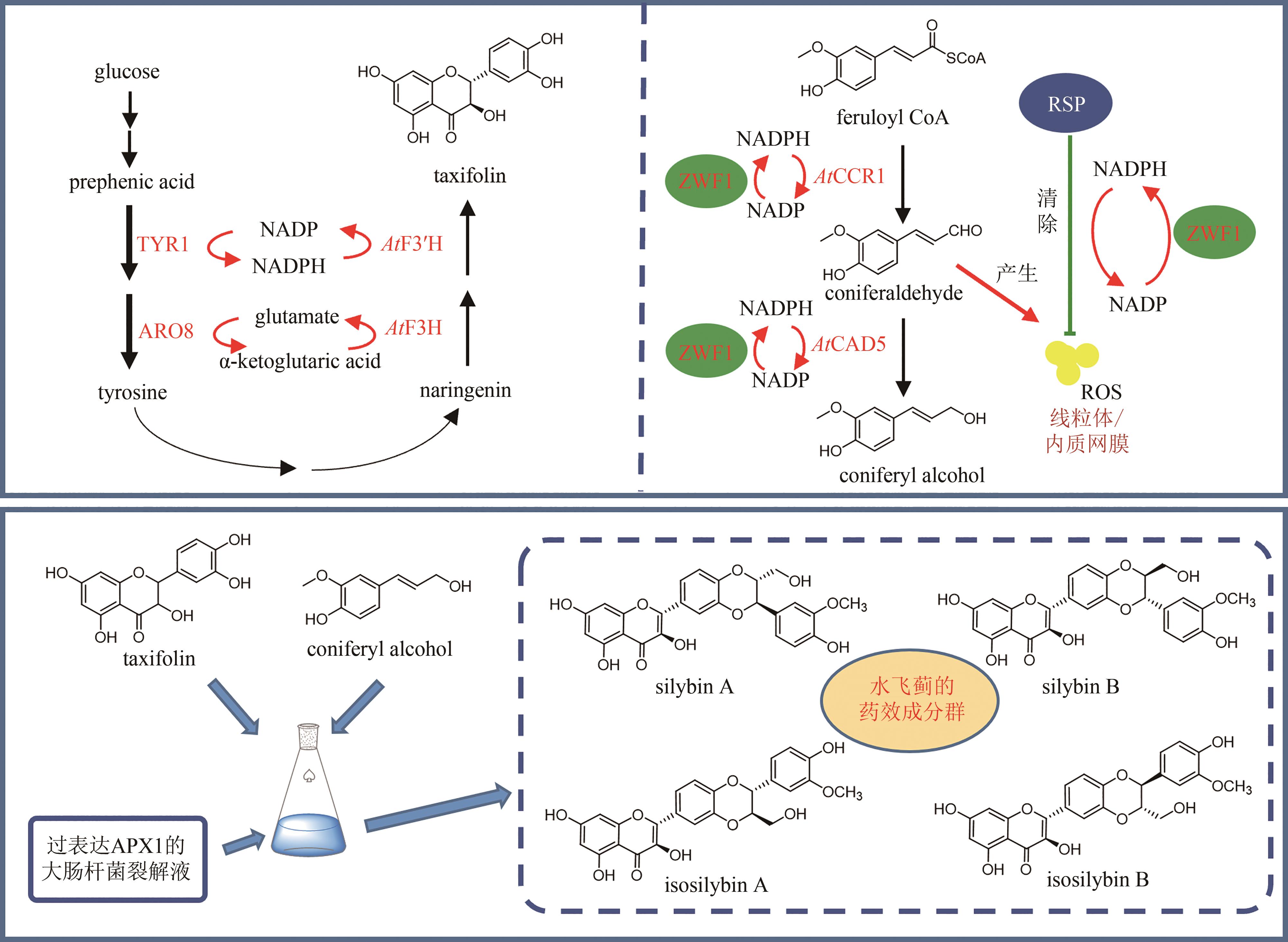
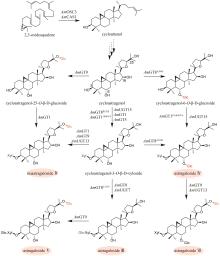
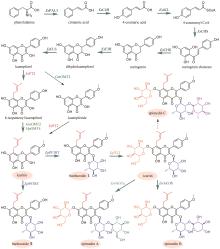
Fig. 11
Production of silybin constituent groups through synthetic biology approach
Extracts from the Article
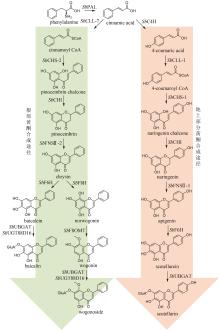
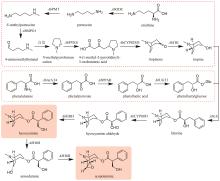
《中国药典》收录的药材水飞蓟为菊科植物水飞蓟Silybum marianum(L.)Gaertn的干燥成熟果实,具有清热解毒、疏肝利胆的功效。水飞蓟宾类成分是水飞蓟的药效物质,对肝炎等多种肝脏疾病具有显著疗效,其中主要药效成分为水飞蓟宾(silybin)A、水飞蓟宾B以及异水飞蓟宾(isosilybin)A、异水飞蓟宾B。除这四种药效成分外,水飞蓟还含有其他19种结构类似的化合物,致使四种药效成分的定向富集十分困难[12]。水飞蓟宾类化合物的两个生物合成前体紫杉叶素(taxifolin)和松柏醇(coniferyl alcohol)分别属于黄酮和苯丙素。因此,水飞蓟宾类化合物属于黄酮与苯丙素的杂合化合物,其生物合成途径包含了典型的黄酮和苯丙素途径(图11)。水飞蓟中的过氧化物酶(APX1)负责催化紫杉叶素和松柏醇偶联,生成水飞蓟宾A、水飞蓟宾B以及异水飞蓟宾A、异水飞蓟宾B(图11)[124]。因此,APX1是实现水飞蓟宾A、水飞蓟宾B以及异水飞蓟宾A、异水飞蓟宾B四种药效成分定向合成的关键酶。
在水飞蓟宾类成分的生物合成途径中,从酪氨酸到最终产物需要多达15个生物合成酶,并且涉及多种辅因子和毒性中间体。本课题组采用细胞工厂结合体外酶法的策略实现了水飞蓟宾类成分的“从头”合成[120]。首先建立了紫杉叶素和松柏醇的细胞工厂。通过表达莽草酸/芳香氨基酸合成途径中两个关键酶的突变体ScARO4K229L和ScARO7G229S,解除酪氨酸对ScARO4和ScARO7的负反馈抑制作用。重点选择与前体供给、辅因子再生以及细胞耐受等多种因素关联的关键蛋白,开展优化,简化调控环节,从而减轻细胞负荷。例如:通过过表达TYR1和ARO8,既加速了前体化合物酪氨酸的合成,又促进了NADPH和α-酮戊二酸两种辅因子的再生循环;通过过表达ZWF1,既加快了NADPH循环,又显著降低了中间体松柏醛对酵母细胞的毒性(图11)。最终,组合表达6种酵母内源基因以及14种来自于不同植物和细菌的异源基因,构建了紫杉叶素和松柏醇的细胞工厂。最后,采用大肠杆菌表达APX1t,通过体外酶法合成水飞蓟宾类化合物,经大孔吸附树脂纯化后,产率达301 mg/L,并且水飞蓟宾A、水飞蓟宾B以及异水飞蓟宾A、异水飞蓟宾B含量超过90%[120]。从而实现了水飞蓟宾类药效成分的高度富集。
Other Images/Table from this Article
|