合成生物学 ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (5): 528-539.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-004
微生物环氧水解酶催化机制及应用研究进展
- 1.浙江大学药物生物技术研究所,浙江 杭州 310058
2.浙江省微生物生化与代谢工程重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310058
-
收稿日期:2020-02-27修回日期:2020-08-07出版日期:2020-10-31发布日期:2020-12-03 -
通讯作者:李永泉,毛旭明 -
作者简介:作者简介:曹菲(1995—),男,博士研究生,研究方向为微生物药物生物合成、微生物天然产物生物合成的酶学机制和化学机制研究、基于合成生物学的微生物药物开发。E-mail:feecao@zju.edu.cn
李永泉(1962—),男,博士,浙江大学求是特聘教授。研究方向为微生物合成生物学、微生物次级代谢调控和微生物制药。E-mail:lyq@zju.edu.cn
毛旭明(1978—),男,博士,教授,研究方向为基于合成生物学的微生物药物开发、微生物药物生物合成的调控机制研究、基于多组学的新活性和新结构微生物天然产物挖掘、微生物天然产物生物合成的酶学机制和化学机制研究。E-mail:xmmao@zju.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2019YFA0905400)
Recent development in catalytic mechanisms and applications of microbial epoxide hydrolases
CAO Fei1,2(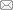 ), LI Yongquan1,2, MAO Xuming1,2
), LI Yongquan1,2, MAO Xuming1,2
- 1.Institute of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310058,Zhejiang,China
2.Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory for Microbial Biochemistry and Metabolic Engineering,Hangzhou 310058,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2020-02-27Revised:2020-08-07Online:2020-10-31Published:2020-12-03 -
Contact:LI Yongquan, MAO Xuming
摘要:
微生物来源的环氧水解酶(epoxide hydrolases,EHs,EC 3.3.2.3)能不对称水解外消旋环氧化物生成手性环氧化物和邻二醇,催化效率高且区域、立体选择性强,有利于合成高纯度的手性化合物。因此,微生物EHs成为了手性药物合成的一种非常重要的生物催化剂,也是一种强有力的生物合成元件。近10年来,随着基因组学、分子生物学、化学生物学、结构生物学等技术的快速发展,研究者又从多种微生物体内发现了多种具有潜在应用价值的EHs。与此同时,研究者也对微生物来源的EHs的酶学特性、生物大分子结构与催化机理进行了深入的研究。本文介绍了几种目前研究比较透彻的EHs催化机制,并综述了近10年来最新发现的微生物来源EHs,这些EHs具备潜在的应用价值。此外,本文总结了EHs的应用进展,重点介绍了EHs在合成生物学领域的应用。利用酶的定向进化等技术提高EHs催化性能和串联多个合成元件高效合成手性产物,是当前主要的研究趋势。
中图分类号:
引用本文
曹菲, 李永泉, 毛旭明. 微生物环氧水解酶催化机制及应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(5): 528-539.
CAO Fei, LI Yongquan, MAO Xuming. Recent development in catalytic mechanisms and applications of microbial epoxide hydrolases[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(5): 528-539.
| 编号 | 环氧水 解酶① | 菌株 | 底物 | 产物 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4R9L | Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14 | 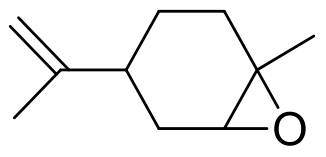 | 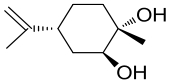 | [ |
| 2 | 4NZZ | Bacillus megaterium |  | 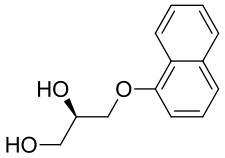 | [ |
| 3 | 5JPU | Rhodococcus erythropolis | 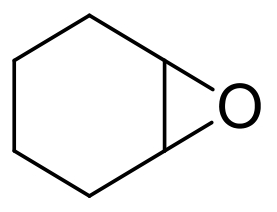 | 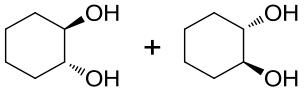 | [ |
| 4 | 6IX4 | Aspergillus usamii E001 | 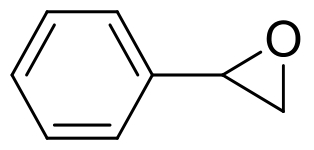 | 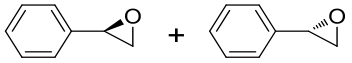 | [ |
| 5 | 未报道 | Dentipellis sp. KUC8613 | 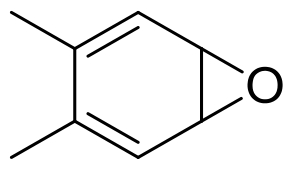 | 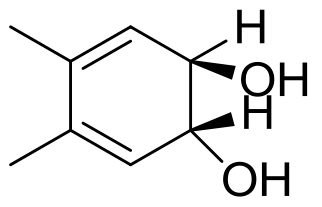 | [ |
| 6 | vEH-Am | Agromyces mediolanus | 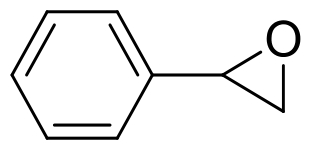 | 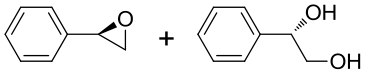 | [ |
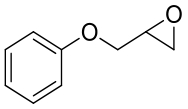 | 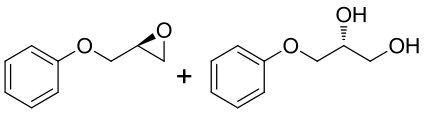 | ||||
| 7 | 未报道 | Aspergillus tubingensis TF1 |  |  | [ |
| 8 | 未报道 | Aspergillus niger ZJUTZQ208 |  |  | [ |
| 9 | 未报道 | Rhodobacterales bacterium HTCC2654 |  | 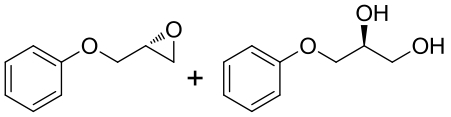 | [ |
| 10 | McEH | Caulobacter crescentus | 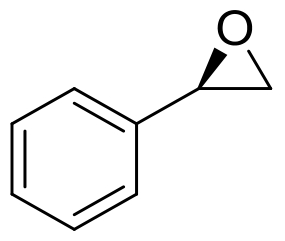 | 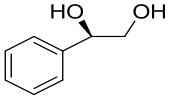 | [ |
| 11 | SpoF | Salinospora tropica CNB-440 | 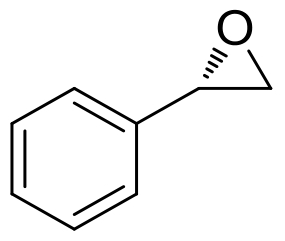 | 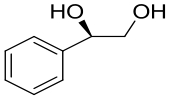 | [ |
| 12 | SgrF | Streptomyces griseus IFO | |||
| 13 | BMEH | B. megateriumQMB 1551 | 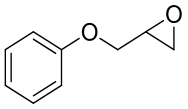 | 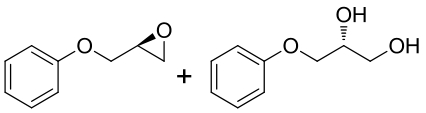 | [ |
| 14 | CMEH | Cupriavidus metallidurans-CH34 | 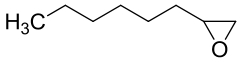 | 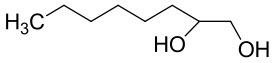 | [ |
| 15 | AmEH | Agromyces mediolanus ZJB120203 | 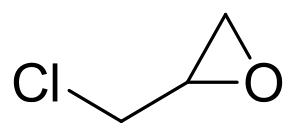 | 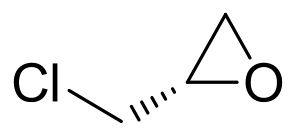 | [ |
| 16 | TpEH1 | Tsukamurella paurometabola |  | 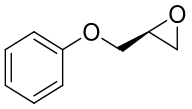 | [ |
| 17 | 未报道 | Galactomyces geotrichum ZJUTZQ200 | 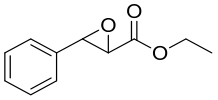 | 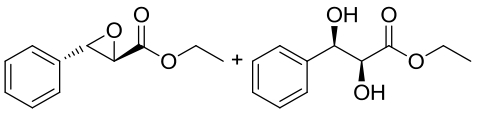 | [ |
| 18 | AbEH | Aspergillus brasiliensis CCT 1435 | 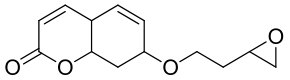 | 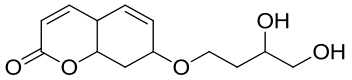 | [ |
| 19 | EphD | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | 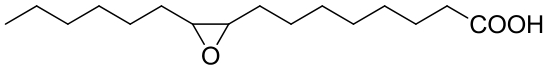 | 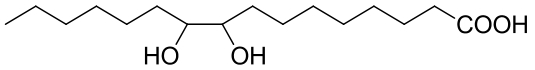 | [ |
| 20 | 3RGA | Streptomyces lasaliensis | 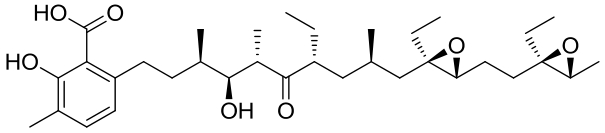 | 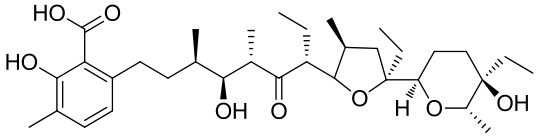 | [ |
| 21 | 5CXO | Streptomyces albus ATCC 21838 | 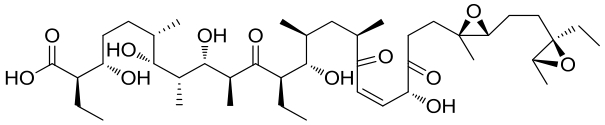 | 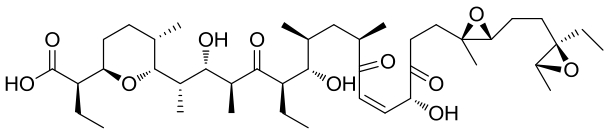 | [ |
| 22 | 6FXD | Pseudomonas fluorescens | 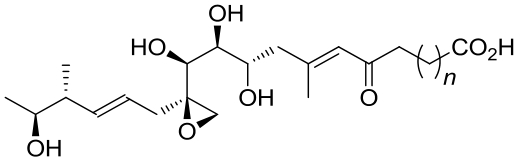 | 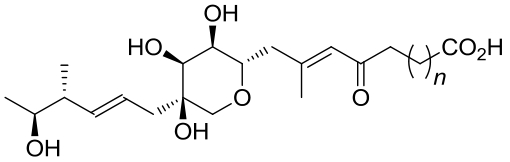 | [ |
| 23 | AurD | Calcarisporium arbuscula | 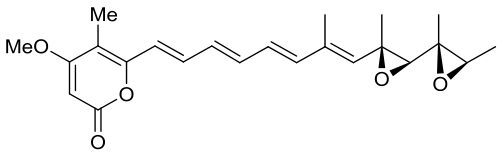 | 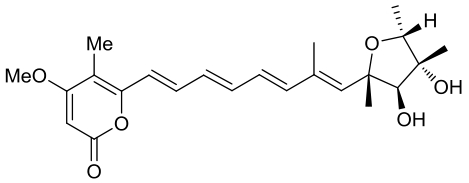 | [ |
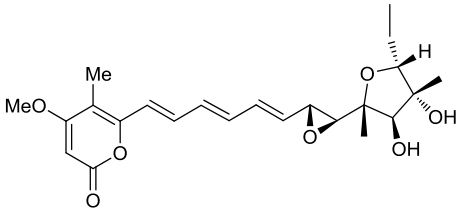 | 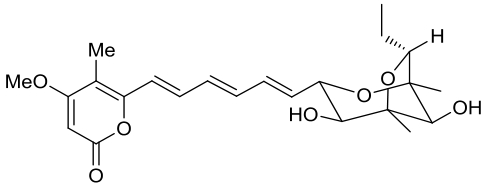 | ||||
| 24 | CtvD | Aspergillus terreus var. aureus | 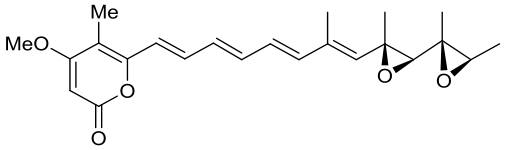 | 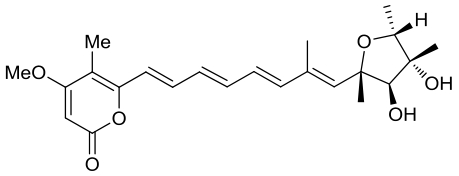 | [ |
| 25 | NcsF2 | Streptomyces carzinostaticus ATCC 15944 | 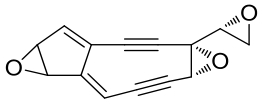 | 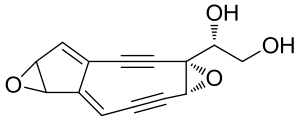 | [ |
| 26 | PenJ | Penicillium sp. | 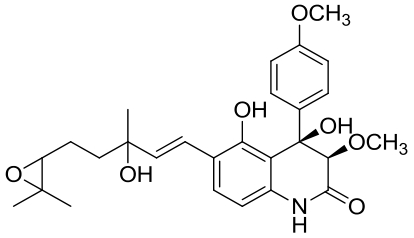 | 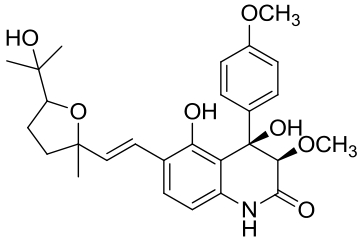 | [ |
| 27 | AsqB | Aspergillus nidulans | |||
| 28 | MonBⅠ/Ⅱ | Streptomyces cinnamonesis | 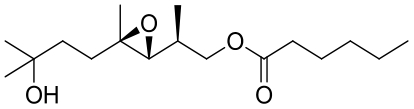 | 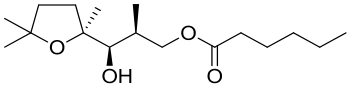 | [ |
| 29 | SalBⅠ/Ⅱ/Ⅲ | Streptomyces albus DSM 41398 | 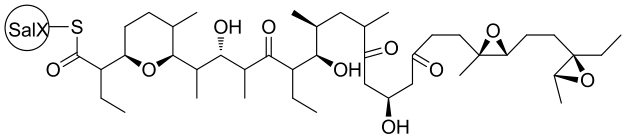 | 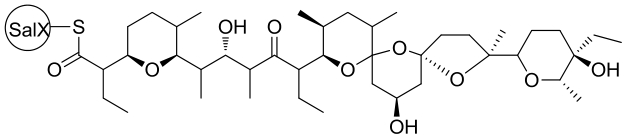 | [ |
| 30 | AuaⅠ | Stigmatella aurantiaca Sg a15 | 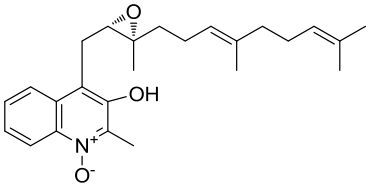 | 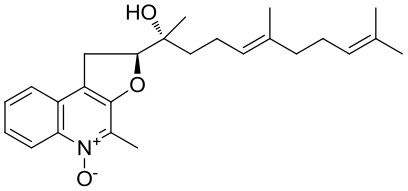 | [ |
| 31 | NsnG | Nocardiopsis sp. CMB-M0232 | 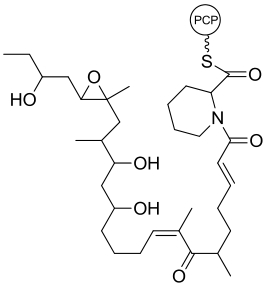 | 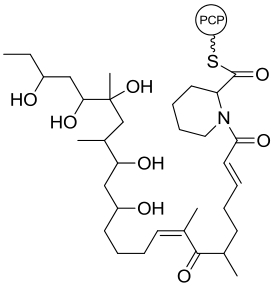 | [ |
32 33 | Alp1U Lom6 | Streptomyces ambofaciens Salinispora pacifica | 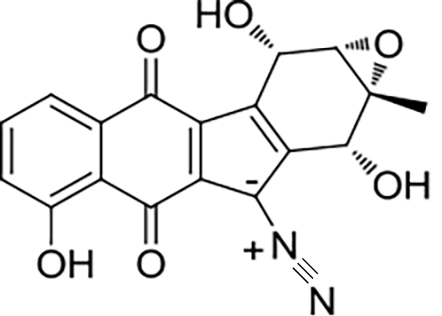 | 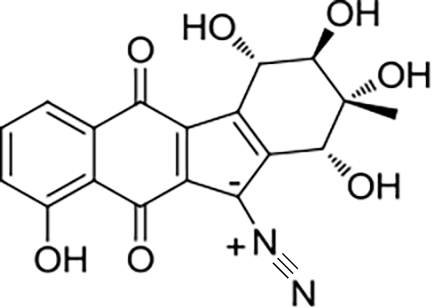 | [ |
| 34 | TsrI | Streptomyces laurentii | 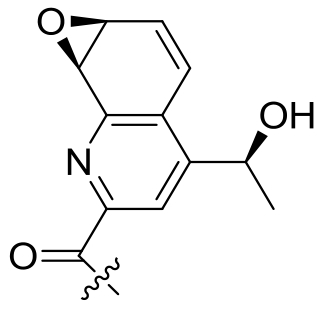 | 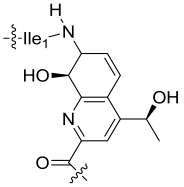 | [ |
表1 2010—2019年微生物中新发现的EHs
Tab. 1 Newly discovered microbial EHs in 2010—2019
| 编号 | 环氧水 解酶① | 菌株 | 底物 | 产物 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4R9L | Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14 |  |  | [ |
| 2 | 4NZZ | Bacillus megaterium |  |  | [ |
| 3 | 5JPU | Rhodococcus erythropolis |  |  | [ |
| 4 | 6IX4 | Aspergillus usamii E001 |  | 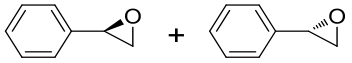 | [ |
| 5 | 未报道 | Dentipellis sp. KUC8613 |  |  | [ |
| 6 | vEH-Am | Agromyces mediolanus |  |  | [ |
 |  | ||||
| 7 | 未报道 | Aspergillus tubingensis TF1 |  |  | [ |
| 8 | 未报道 | Aspergillus niger ZJUTZQ208 |  |  | [ |
| 9 | 未报道 | Rhodobacterales bacterium HTCC2654 |  |  | [ |
| 10 | McEH | Caulobacter crescentus |  |  | [ |
| 11 | SpoF | Salinospora tropica CNB-440 |  |  | [ |
| 12 | SgrF | Streptomyces griseus IFO | |||
| 13 | BMEH | B. megateriumQMB 1551 |  |  | [ |
| 14 | CMEH | Cupriavidus metallidurans-CH34 |  |  | [ |
| 15 | AmEH | Agromyces mediolanus ZJB120203 |  |  | [ |
| 16 | TpEH1 | Tsukamurella paurometabola |  |  | [ |
| 17 | 未报道 | Galactomyces geotrichum ZJUTZQ200 |  |  | [ |
| 18 | AbEH | Aspergillus brasiliensis CCT 1435 |  |  | [ |
| 19 | EphD | Mycobacterium tuberculosis |  |  | [ |
| 20 | 3RGA | Streptomyces lasaliensis |  |  | [ |
| 21 | 5CXO | Streptomyces albus ATCC 21838 |  |  | [ |
| 22 | 6FXD | Pseudomonas fluorescens |  |  | [ |
| 23 | AurD | Calcarisporium arbuscula |  |  | [ |
 |  | ||||
| 24 | CtvD | Aspergillus terreus var. aureus |  |  | [ |
| 25 | NcsF2 | Streptomyces carzinostaticus ATCC 15944 |  |  | [ |
| 26 | PenJ | Penicillium sp. |  |  | [ |
| 27 | AsqB | Aspergillus nidulans | |||
| 28 | MonBⅠ/Ⅱ | Streptomyces cinnamonesis |  |  | [ |
| 29 | SalBⅠ/Ⅱ/Ⅲ | Streptomyces albus DSM 41398 |  |  | [ |
| 30 | AuaⅠ | Stigmatella aurantiaca Sg a15 |  |  | [ |
| 31 | NsnG | Nocardiopsis sp. CMB-M0232 |  |  | [ |
32 33 | Alp1U Lom6 | Streptomyces ambofaciens Salinispora pacifica |  |  | [ |
| 34 | TsrI | Streptomyces laurentii |  |  | [ |
| 1 | CHEN Yijun, CHEN Chen, WU Xuri. Dicarbonyl reduction by single enzyme for the preparation of chiral diols [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(5): 1742-1753. |
| 2 | STEINREIBER A, FABER K. Microbial epoxide hydrolases for preparative biotransformations [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2001, 12(6): 552-558. |
| 3 | ZOCHER F, ENZELBERGER M M, BORNSCHEUER U T, et al. Epoxide hydrolase activity of Streptomyces strains [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2000, 77(2/3): 287-292. |
| 4 | MORISSEAU C, HAMMOCK B D. Epoxide hydrolases: mechanisms, inhibitor designs, and biological roles [J]. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 2005, 45: 311-333. |
| 5 | MANOJ K, ARCHELAS A, BARATTI J, et al. Microbiological transformations. Part 45: A green chemistry preparative scale synthesis of enantiopure building blocks of Eliprodil: elaboration of a high substrate concentration epoxide hydrolase-catalyzed hydrolytic kinetic resolution process [J]. Tetrahedron, 2001, 57(4): 695-701. |
| 6 | ORRU R V, FABER K. Stereoselectivities of microbial epoxide hydrolases [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 1999, 3(1): 16-21. |
| 7 | NESTL B M, HAMMER S C, NEBEL B A, et al. New generation of biocatalysts for organic synthesis [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(12): 3070-3095. |
| 8 | 潘海峰. 新颖水解酶CESH的催化机制及其高效催化工艺研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2011. |
| PAN Haifeng. Study on the catalytic mechanism of a novel hydrolase CESH and its catalytic process with a high efficiency [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2011. | |
| 9 | 壮晓健, 金火喜, 胡忠策, 等. 微生物环氧化物水解酶的研究进展[J]. 生物技术, 2010, 20(1): 91-94. |
| ZHUANG Xiaojian, JIN Huoxi, HU Zhongce, et al. Research progress of microbial epoxide hydrolase [J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2010, 20(1): 91-94. | |
| 10 | CHOI Won Jae, CHOI Cha Yong. Production of chiral epoxides: epoxide hydrolase-catalyzed enantioselective hydrolysis [J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2005, 10(3): 167. |
| 11 | FLOOR R J, WIJMA H J, JEKEL P A, et al. X-ray crystallographic validation of structure predictions used in computational design for protein stabilization [J]. Proteins, 2015, 83(5): 940-951. |
| 12 | KONG Xudong, YUAN Shuguang, LI Lin, et al. Engineering of an epoxide hydrolase for efficient bioresolution of bulky pharmaco substrates [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of The United States Of America, 2014, 111(44): 15717-15722. |
| 13 | LI Guangyue, ZHANG Hui, SUN Zhoutong, et al. Multiparameter optimization in directed evolution: engineering thermostability, enantioselectivity, and activity of an epoxide hydrolase [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(6): 3679-3687. |
| 14 | HU Die, TANG Cunduo, YANG Biao, et al. Expression of a novel epoxide hydrolase of Aspergillus usamii E001 in Escherichia coli and its performance in resolution of racemic styrene oxide [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2015, 42(5): 671-680. |
| 15 | PARK Hongjae, MIN Byoungnam, JANG Yeongseon, et al. Comprehensive genomic and transcriptomic analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation by a mycoremediation fungus, Dentipellis sp. KUC8613 [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(19): 8145-8155. |
| 16 | JIN Huoxi, LI Yan, ZHANG Qianwei, et al. Enantioselective hydrolysis of styrene oxide and benzyl glycidyl ether by a variant of epoxide hydrolase from Agromyces mediolanus [J]. Marine Drugs, 2019, 17(6): 367. |
| 17 | DUARAH A, GOSWAMI A, BORA T C, et al. Enantioconvergent biohydrolysis of racemic styrene oxide to R-phenyl-1,2-ethanediol by a newly isolated filamentous fungus Aspergillus tubingensis TF1 [J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2013, 170(8): 1965-1973. |
| 18 | CHEN Lin, SHEN ChenHonglei, WEI Chun, et al. Bioresolution of (R)-glycidyl azide by Aspergillus niger ZJUTZQ208: a new and concise synthon for chiral vicinal amino alcohols [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2013, 97(6): 2609-2616. |
| 19 | Jung-Hee WOO, KANG Ji-Hyun, HWANG Young-Ok, et al. Biocatalytic resolution of glycidyl phenyl ether using a novel epoxide hydrolase from a marine bacterium, Rhodobacterales bacterium HTCC2654 [J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2010, 110(4): 509-509. |
| 20 | MIN Ji Young, Eun Yeol LEE. Biosynthesis of (R)-1,2-phenylethanediol and (R)-4-chloro-1,2-phenylethanediol by using two recombinant cells expressing enantiocomplementary epoxide hydrolases [J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2012, 18(1): 160-164. |
| 21 | HORSMAN G P, LECHNER A, OHNISHI Y, et al. Predictive model for epoxide hydrolase-generated stereochemistry in the biosynthesis of nine-membered enediyne antitumor antibiotics [J]. Biochemistry, 2013, 52(31): 5217-5224. |
| 22 | ZHAO Jing, CHU Yanyan, LI Aitao, et al. An unusual (R)-selective epoxide hydrolase with high activity for facile preparation of enantiopure glycidyl ethers [J]. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 2011, 353(9): 1510-1518. |
| 23 | KUMAR R, WANI S I, CHAUHAN N S, et al. Cloning and characterization of an epoxide hydrolase from Cupriavidus metallidurans-CH34 [J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2011, 79(1): 49-59. |
| 24 | XUE Feng, LIU Zhiqiang, ZOU Shuping, et al. A novel enantioselective epoxide hydrolase from Agromyces mediolanus ZJB120203: cloning, characterization and application [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2014, 49(3): 409-417. |
| 25 | WU Kai, WANG Hualei, SUN Huihui, et al. Efficient kinetic resolution of phenyl glycidyl ether by a novel epoxide hydrolase from Tsukamurella paurometabola [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(22): 9511-9521. |
| 26 | WEI Chun, LING Jinlong, SHEN Honglei, et al. Bioresolution production of (2R, 3S)-ethyl-3-phenylglycidate for chemoenzymatic synthesis of the taxol C-13 side chain by Galactomyces geotrichum ZJUTZQ200, a new epoxide-hydrolase-producing strain [J]. Molecules, 2014, 19(6): 8067-8079. |
| 27 | BELOTI L L, COSTA B Z, TOLEDO M A, et al. A novel and enantioselective epoxide hydrolase from Aspergillus brasiliensis CCT 1435: purification and characterization [J]. Protein Expression and Purification, 2013, 91(2): 175-183. |
| 28 | MADACKI J, LAVAL F, GRZEGORZEWICZ A, et al. Impact of the epoxide hydrolase EphD on the metabolism of mycolic acids in mycobacteria [J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2018, 293(14): 5172-5184. |
| 29 | HOTTA K, CHEN Xi, PATON R S, et al. Enzymatic catalysis of anti-Baldwin ring closure in polyether biosynthesis [J]. Nature, 2012, 483(7389): 355-U154. |
| 30 | LUHAVAYA H, DIAS M V, WILLIAMS S R, et al. Enzymology of pyran ring A formation in salinomycin biosynthesis [J]. Angewandte Chemie (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2015, 127(46): 13826-13829. |
| 31 | WANG Luoyi, PARNELL A, WILLIAMS C, et al. A Rieske oxygenase/epoxide hydrolase-catalysed reaction cascade creates oxygen heterocycles in mupirocin biosynthesis [J]. Nature Catalysis, 2018, 1(12): 968-976. |
| 32 | MAO Xuming, ZHAN Zhajun, GRAYSON M N, et al. Efficient biosynthesis of fungal polyketides containing the dioxabicyclo-octane ring system [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(37): 11904-11907. |
| 33 | LIN Tzu-Shyang, CHIANG Yi-Ming, WANG C C. Biosynthetic pathway of the reduced polyketide product citreoviridin in Aspergillus terreus var. aureus revealed by heterologous expression in Aspergillus nidulans [J]. Organic Letters, 2016, 18(6): 1366-1369. |
| 34 | LIN Shuangjun, HORSMAN G P, SHEN Ben. Characterization of the epoxide hydrolase NcsF2 from the neocarzinostatin biosynthetic gene cluster [J]. Organic Letters, 2010, 12(17): 3816-3819. |
| 35 | ZOU Yi, GARCIA-BORRAS M, TANG Mancheng, et al. Enzyme-catalyzed cationic epoxide rearrangements in quinolone alkaloid biosynthesis [J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2017, 13(3): 325-332. |
| 36 | SATO K, MINAMI A, OSE T, et al. Remarkable synergistic effect between MonBI and MonBII on epoxide opening reaction in ionophore polyether monensin biosynthesis [J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2011, 52(41): 5277-5280. |
| 37 | YURKOVICH M E, TYRAKIS P A, HONG H, et al. A late-stage intermediate in salinomycin biosynthesis is revealed by specific mutation in the biosynthetic gene cluster [J]. ChemBioChem, 2012, 13(1): 66-71. |
| 38 | PISTORIUS D, LI Yanyan, SANDMANN A, et al. Completing the puzzle of aurachin biosynthesis in Stigmatella aurantiaca Sg a15 [J]. Molecular BioSystems, 2011, 7(12): 3308-3315. |
| 39 | BIS D M, BAN Y H, JAMES E D, et al. Characterization of the nocardiopsin biosynthetic gene cluster reveals similarities to and differences from the rapamycin and fk-506 pathways [J]. ChemBioChem, 2015, 16(6): 990-997. |
| 40 | WANG Bin, GUO Fang, REN Jinwei, et al. Identification of Alp1U and Lom6 as epoxy hydrolases and implications for kinamycin and lomaiviticin biosynthesis [J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1): 7674. |
| 41 | ZHENG Qingfei, WANG Shoufeng, DUAN Panpan, et al. An α/β-hydrolase fold protein in the biosynthesis of thiostrepton exhibits a dual activity for endopeptidyl hydrolysis and epoxide ring opening/macrocyclization [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of The United States Of America, 2016, 113(50): 14318-14323. |
| 42 | WANG F, TAN K, BIGELOW L, et al. The crystal structure of an epoxide hydrolase from Streptomyces carzinostaticus subsp. neocarzinostaticus [DB/OL]. 2014. Protein Data Bank: . |
| 43 | WANG F, TAN K, BIGELOW L, et al. Ensemble refinement of an epoxide hydrolase from Streptomyces carzinostaticus subsp. neocarzinostaticus [DB/OL]. 2014. Protein Data Bank: . |
| 44 | TAN K, BIGELOW L, CLANCY S, et al. The crystal structure of an epoxide hydrolase from Streptomyces carzinostaticus subsp. neocarzinostaticus [DB/OL]. 2012. Protein Data Bank: . |
| 45 | SCHULZ E C, WILMANNS M, HENDERSON S, et al. The crystal structure of Mycobacterial epoxide hydrolase A [DB/OL]. 2016. Protein Data Bank: . |
| 46 | MOYNIE L, SCHNELL R, MCMAHON S A, et al. The AEROPATH project targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa: crystallographic studies for assessment of potential targets in early-stage drug discovery [J]. Acta Crystallographica Section F, 2013, 69: 25-34. |
| 47 | DE OLIVEIRA G S, ADRIANI P P, RIBEIRO J A, et al. The molecular structure of an epoxide hydrolase from Trichoderma reesei in complex with urea or amide-based inhibitors [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 129: 653-658. |
| 48 | WILSON C, DE OLIVEIRA G S, ADRIANI P P, et al. Structure of a soluble epoxide hydrolase identified in Trichoderma reesei [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Proteins and Proteomics, 2017, 1865(8): 1039-1045. |
| 49 | BAHL C D, HVORECNY K L, BRIDGES A A, et al. Signature motifs identify an acinetobacter Cif virulence factor with epoxide hydrolase activity [J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2014, 289(11): 7460-7469. |
| 50 | SUN Zaibao, ZHANG Zhijun, LI Fulong, et al. One pot asymmetric synthesis of (R)-phenylglycinol from racemic styrene oxide via cascade biocatalysis [J]. ChemCatChem, 2019, 11(16): 3802-3807. |
| 51 | YUAN Jifeng, LUKITO B R, LI Zhi. De novo biosynthesis of (S)- and (R)-phenylethanediol in yeast via artificial enzyme cascades [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(8): 1801-1808. |
| 52 | RINK R, FENNEMA M, SMIDS M, et al. Primary structure and catalytic mechanism of the epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 [J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1997, 272(23): 14650-14657. |
| 53 | 孔旭东, 郁惠蕾, 周佳海, 等. 环氧水解酶的结构基础及新酶开发[J]. 生物加工过程, 2013, 11(1): 77-86. |
| KONG Xudong, YU Huilei, ZHOU Jiahai, et al. Structure basis of EHs and development of novel EHs as biocatalyst [J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2013, 11(1): 77-86. | |
| 54 | ZOU Jinyu, HALLBERG B M, BERGFORS T, et al. Structure of Aspergillus niger epoxide hydrolase at 1.8 Å resolution: implications for the structure and function of the mammalian microsomal class of epoxide hydrolases [J]. Structure, 2000, 8(2): 111-122. |
| 55 | NARDINI M, RINK R, JANSSEN D B, et al. Structure and mechanism of the epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 [J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 2001, 11(4/5/6): 1035-1042. |
| 56 | HOPMANN K H, HALLBERG B M, HIMO F. Catalytic mechanism of limonene epoxide hydrolase, a theoretical study [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127(41): 14339-14347. |
| 57 | ARAND M, HALLBERG B M, ZOU Jinyu, et al. Structure of Rhodococcus erythropolis limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase reveals a novel active site [J]. The EMBO Journal, 2003, 22(11): 2583-2592. |
| 58 | 李昆, 杨国强, 刘媛媛, 等. 手性双金属催化剂及其在不对称催化反应中的应用[J]. 有机化学, 2013, 33(4): 749-759. |
| LI Kun, YANG Guoqiang, LIU Yuanyuan, et al. Chiral polymetallic catalysts and their applications in asymmetric catalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2013, 33(4): 749-759. | |
| 59 | 曹靖. 大基团取代的末端手性环氧化物的制备及其聚合物的合成[D]. 湘潭: 湘潭大学, 2007. |
| CAO Jing. The synthesis and polymerization of chiral terminal epoxides with bulky group [D]. Xiangtan: Xiangtan University, 2007. | |
| 60 | 张晓健, 郑裕国. 甘油原料转化生产手性环氧氯丙烷关键酶的开发[J]. 生物产业技术, 2017(6): 65-72. |
| ZHANG Xiaojian, ZHENG Yuguo. Research and development on key enzymes for biosynthesis of chiral epichlorohydrin using glycerol [J]. Biotechnology&Business, 2017(6): 65-72. | |
| 61 | 赵剑伟. 转氨酶MVTA的克隆表达及其应用于级联催化合成手性β-氨基醇和邻二醇的研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2019. |
| ZHAO Jianwei. Cloningand expression of ω-transaminase mvta applying in synthsis of chiral β-amino alcohols and vicinal diols via cascade catalysis [D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2019. | |
| 62 | 吴群, 邹树平, 郑裕国. 环氧化物水解酶在手性药物中间体合成中的应用[J]. 精细与专用化学品, 2015, 23(6): 23-29. |
| WU Qun, ZOU Shuping, ZHENG Yuguo. Applications of epoxide hydrolase in the synthesis of chiral drug intermediates [J]. Fine and Special Chemicals, 2015, 23(6): 23-29. | |
| 63 | 吴群. 环氧化物水解酶分子改造及其催化拆分环氧氯丙烷的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2015. |
| WU Qun. Molecular modification to epoxide hydrolase and its application in the resolution of epichlorohydrin [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2015. | |
| 64 | JIANG Chengjun, HONG Huabin. A new practical synthesis of ethyl (R)-(-)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutyrate from (S)-3-chloro-1,2-propanediol [J]. Letters in Organic Chemistry, 2012, 9(7): 520-521. |
| 65 | LIANG Youxiang, JIAO Song, WANG Miaomiao, et al. Overexpression of epoxide hydrolase in Rhodococcus ruber with high robustness for the synthesis of chiral epichlorohydrin [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2019, 79: 49-56. |
| 66 | ZOU Shuping, WANG Zhicai, QIN Chao, et al. Covalent immobilization of Agrobacterium radiobacter epoxide hydrolase on ethylenediamine functionalised epoxy supports for biocatalytical synthesis of (R)-epichlorohydrin [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2016, 38(9): 1579-1585. |
| 67 | JIA Xin, XU Yi, LI Zhi. Regio-and stereoselective concurrent oxidations with whole cell biocatalyst: simple and green syntheses of enantiopure 1,2-diols via oxidative kinetic resolution [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2011, 1(6): 591-596. |
| 68 | LI Keqiang, VIG S, UCKUN F M. Stereocontrolled synthesis of the tetrahydrofuran unit of annonaceous acetogenins [J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 1998, 39(15): 2063-2066. |
| 69 | HU Die, ZONG Xuncheng, XUE Feng, et al. Manipulating regioselectivity of an epoxide hydrolase for single enzymatic synthesis of (R)-1,2-diols from racemic epoxides [J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(18): 2799-2802. |
| 70 | SAINI P, KUMAR N, WANI S I, et al. Bioresolution of racemic phenyl glycidyl ether by a putative recombinant epoxide hydrolase from Streptomyces griseus NBRC 13350 [J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 33(5): 82. |
| 71 | VAN LOO B, SPELBERG J H L, KINGMA J, et al. Directed evolution of epoxide hydrolase from A. radiobacter toward higher enantioselectivity by error-prone PCR and DNA shuffling [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2004, 11(7): 981-990. |
| 72 | Myung Soo KO, LOVE J J. Step-wise directed evolution of an epoxide hydrolase against progressively larger non-natural substrates [J]. The FASEB Journal, 2017, 31(s1): 922.1-922.1. |
| 73 | ZOU Shuping, ZHENG Yuguo, WU Qun, et al. Enhanced catalytic efficiency and enantioselectivity of epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 by iterative saturation mutagenesis for (R)-epichlorohydrin synthesis [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(2): 733-742. |
| 74 | SUN Zhoutong, LONSDALE R, WU Lian, et al. Structure-guided triple-code saturation mutagenesis: efficient tuning of the stereoselectivity of an epoxide hydrolase [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(3): 1590-1597. |
| 75 | ZHENG Huabao, REETZ M T. Manipulating the stereoselectivity of limonene epoxide hydrolase by directed evolution based on iterative saturation mutagenesis [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(44): 15744-15751. |
| 76 | ZONG Xuncheng, LI Chuang, XU Yaohui, et al. Substantially improving the enantioconvergence of Pv EH1, a Phaseolus vulgaris epoxide hydrolase, towards m-chlorostyrene oxide by laboratory evolution [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18(1): 1-8. |
| 77 | LI Fulong, KONG Xudong, CHEN Qi, et al. Regioselectivity engineering of epoxide hydrolase: near-perfect enantioconvergence through a single site mutation [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(9): 8314-8317. |
| 78 | JIN Huoxi, OUYANG Xiaokun, HU Zhongce. Enhancement of epoxide hydrolase production by 60Co gamma and UV irradiation mutagenesis of Aspergillus niger ZJB-09103 [J]. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 2017, 64(3): 392-399. |
| 79 | LIANG Bo, HUANG Xuenian, TENG Yun, et al. Enhanced single-step bioproduction of the simvastatin precursor monacolin J in an industrial strain of Aspergillus terreus by employing the evolved lovastatin hydrolase [J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2018, 13(6): 1800094. |
| 80 | YU Da, WANG Jianbo, REETZ M T. Exploiting designed oxidase-peroxygenase mutual benefit system for asymmetric cascade reactions [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(14): 5655-5658. |
| 81 | NIU Guoqing, ZHENG Jiazhen, TAN Huarong. Biosynthesis and combinatorial biosynthesis of antifungal nucleoside antibiotics [J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2017, 60(9): 939-947. |
| 82 | MOSS N A, SEILER G, LEÃO T F, et al. Nature's combinatorial biosynthesis produces Vatiamides A-F [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(27): 9027-9031. |
| 83 | LIU Song, ZHANG Xian, LIU Fei, et al. Designing of a cofactor self-sufficient whole-cell biocatalyst system for production of 1,2-amino alcohols from epoxides [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(4): 734-743. |
| [1] | 郭姝媛, 张倩楠, 姑丽克孜·买买提热夏提, 杨一群, 于涛. 液体生物燃料合成与炼制的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 18-44. |
| [2] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [3] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [11] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [12] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [13] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [14] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [15] | 虞旭昶, 吴辉, 李雷. 文库构建与基因簇靶向筛选驱动的微生物天然产物高效发现[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 492-506. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
