合成生物学 ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (2): 234-246.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-066
细菌群体感应元件构建和工程应用
周爱林1,2, 刘奕1, 巴方1, 钟超1,3,4
- 1.上海科技大学物质科学与技术学院,上海 201210
2.上海科技大学生命科学与技术学院,上海 201210
3.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,深圳合成生物学创新研究院,中国科学院定量工程生物学重点实验室,广东 深圳 518055
4.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,深圳合成生物学创新研究院,材料合成生物学中心,广东 深圳 518055
-
收稿日期:2020-06-05修回日期:2021-02-19出版日期:2021-04-30发布日期:2021-04-30 -
通讯作者:钟超 -
作者简介:周爱林 (1999—),女,主要研究方向为合成生物学的研究。E-mail:zhoual@shanghaitech.edu.cn
钟超(1979—),男,博士,研究员。主要研究方向为利用合成生物学技术发展新材料和生物纳米技术,包括基于蛋白的水下黏合胶水和细菌生物被膜活体功能材料。E-mail:chao.zhong@siat.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(U1932204);国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0902804);上海市科学技术委员会项目(17JC1403900)
Construction and engineering application of bacterial quorum sensing elements
ZHOU Ailin1,2, LIU Yi1, BA Fang1, ZHONG Chao1,3,4
- 1.Materials and Physical Biology Division,School of Physical Science and Technology,ShanghaiTech University,Shanghai 201210,China
2.School of Life Science and Technology,ShanghaiTech University,Shanghai 201210,China
3.CAS Key Laboratory of Quantitative Engineering Biology,Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
4.Center for Materials Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2020-06-05Revised:2021-02-19Online:2021-04-30Published:2021-04-30 -
Contact:ZHONG Chao
摘要:
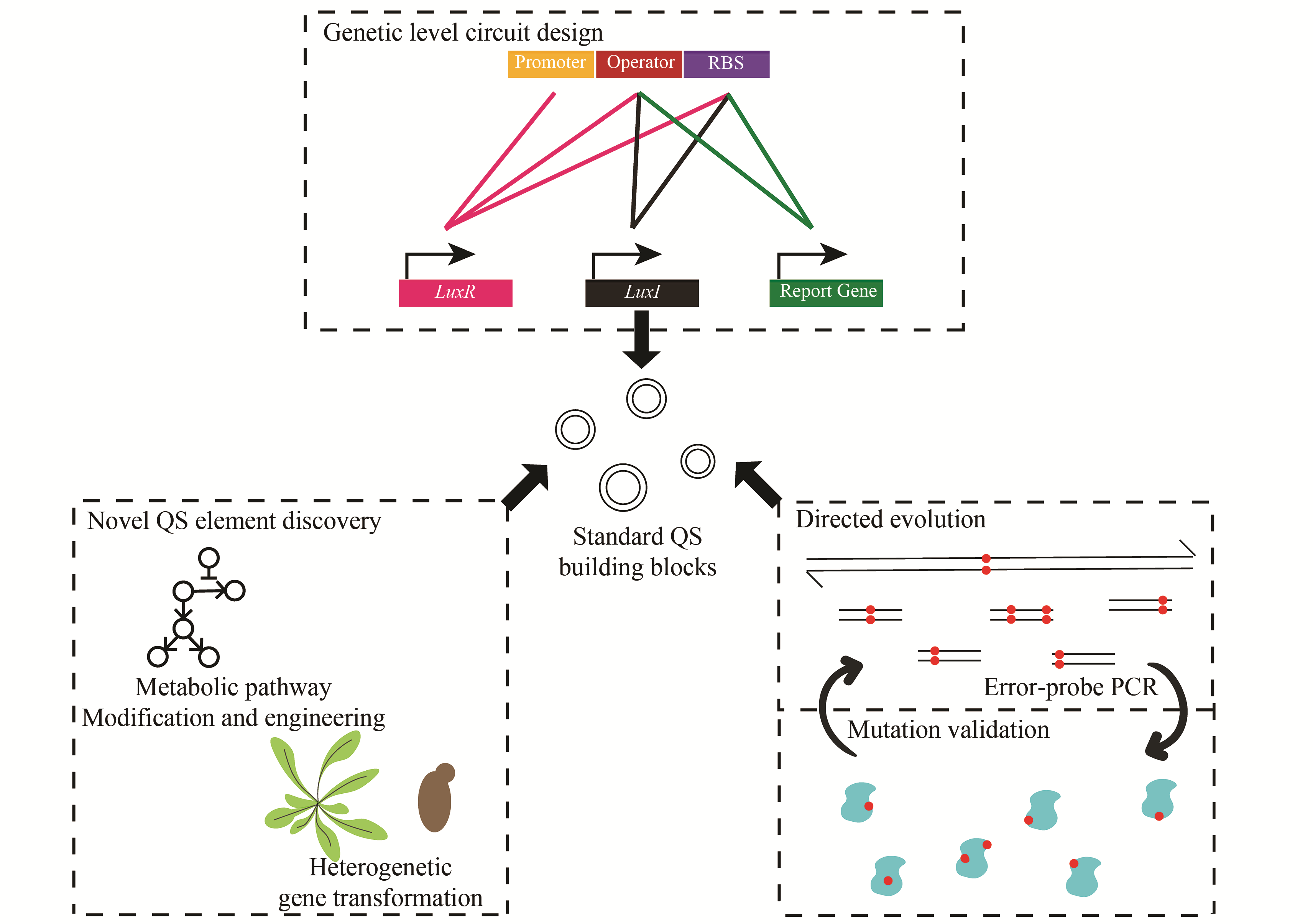
群体感应现象指的是微生物通过独特的交流方式使不同菌个体间的行为同步,从而展现群体性行为。当前在微生物群体感应系统方面的研究,除了促进或抑制天然群体感应方面的基础研究外,研究人员逐渐开始将群体感应系统引入到合成生物学的工程应用研究,并且将其广泛运用在医学、工业、环境等应用领域。本文主要总结了细菌群体感应元件在构建过程中的常用策略与方法,并探讨了基于群体感应基因元件改造的工程菌在动态代谢调节、周期性振荡呈现、异种菌种间关系的构建等方面的应用。 群体感应元件的研究主要包括新群体感应元件的开发和针对已有群体感应元件的优化。通过模拟、优化群体感应元件并将其模块化,研究人员构建了丰富的群体感应基因元件库,使群体感应能被灵活应用于不同场景。另外,通过在细菌中引入群体感应基因回路,可以将单个细菌内部的各类反馈回路较好地拓展到整个细菌群体中,而这种多细胞体系的构建,使得更多复杂的功能得以实现,如通过群体感应实现动态代谢调节从而提高发酵效率,或实现群体周期性振荡以释放肿瘤杀伤药物等。此外,环境中异种微生物的关系也可以通过外源引入群体感应来进行调控,这为微生物的共培养提供了新工具,更为复杂的合成生物学系统的建立提供了新思路。随着机器学习等计算机领域的发展,未来可以更多借助计算机来设计复杂群体感应回路,并对外源群体感应引入后的效果做出更精准的预测。
中图分类号:
引用本文
周爱林, 刘奕, 巴方, 钟超. 细菌群体感应元件构建和工程应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(2): 234-246.
ZHOU Ailin, LIU Yi, BA Fang, ZHONG Chao. Construction and engineering application of bacterial quorum sensing elements[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(2): 234-246.
| 项目 | 化学诱导剂 | 群体感应 |
|---|---|---|
| 可控性 | 较好 可以人为通过加入化学诱导剂,较为精确地控制基因表达的时间 | 较好 群体感应的基因表达开启与否本来由元件内源参数决定,除了在使用前改造元件、调整内源参数,还可以将群体感应中自体诱导物的启动子替换为外源分子调控的诱导型启动子,通过外加特定的诱导物实现对群体感应行为的控制[ |
| 动态性 | 较差 需要实时检测细胞生长状况,并在合适的时机添加诱导剂 | 较好 群体数量实时决定群体行为 |
| 可逆性 | 较差 一经添加便会一直存在于介质中,只能起到单次控制的效果[ | 较差,但可以优化 Miano等[ |
| 经济性 | 较差 现常用的化学诱导剂如IPTG等成本较高[ | 较好 只在最初基因回路构建上存在一次性成本 |
表1 化学诱导与群体感应在代谢调控中应用的对比[23-24,26,39-40]
Tab. 1 Comparison between chemical inducers and quorum sensing on their application in metabolic regulation[23-24,26,39-40]
| 项目 | 化学诱导剂 | 群体感应 |
|---|---|---|
| 可控性 | 较好 可以人为通过加入化学诱导剂,较为精确地控制基因表达的时间 | 较好 群体感应的基因表达开启与否本来由元件内源参数决定,除了在使用前改造元件、调整内源参数,还可以将群体感应中自体诱导物的启动子替换为外源分子调控的诱导型启动子,通过外加特定的诱导物实现对群体感应行为的控制[ |
| 动态性 | 较差 需要实时检测细胞生长状况,并在合适的时机添加诱导剂 | 较好 群体数量实时决定群体行为 |
| 可逆性 | 较差 一经添加便会一直存在于介质中,只能起到单次控制的效果[ | 较差,但可以优化 Miano等[ |
| 经济性 | 较差 现常用的化学诱导剂如IPTG等成本较高[ | 较好 只在最初基因回路构建上存在一次性成本 |

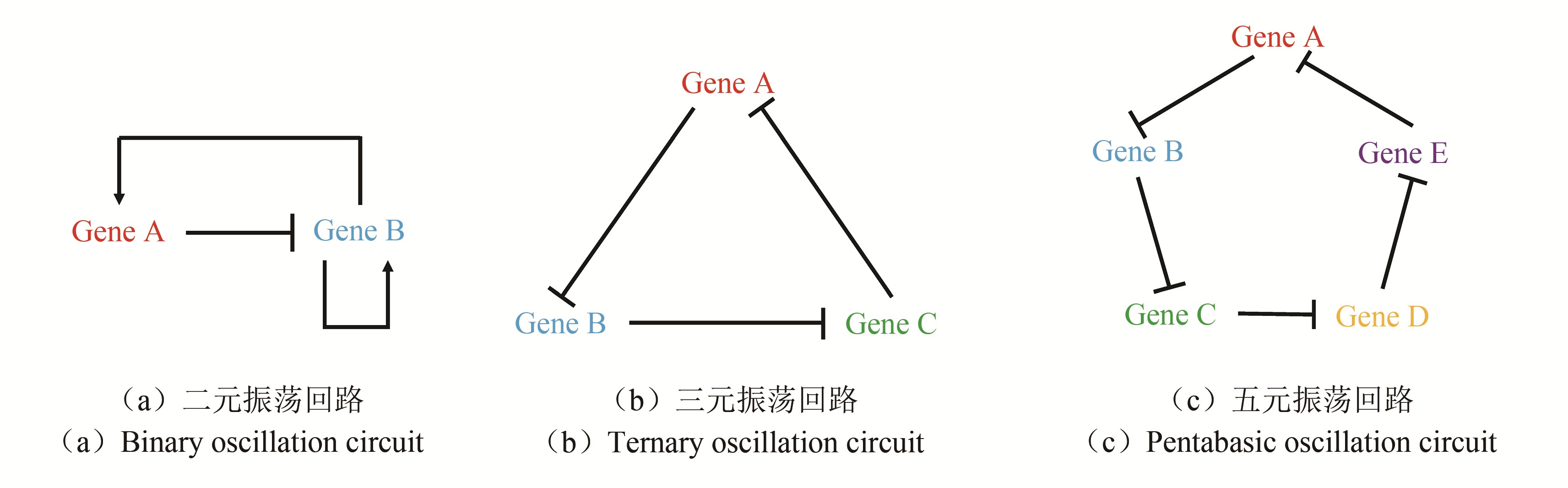
图4 三种典型思路用于构建多细胞振荡体系[30, 56-57][(a),(b),(c)分别对应三种振荡回路与群体感应结合的思路;(d)利用群体感应形成规律图案[基于思路二构建的系统,通过群体感应,自体诱导物AHL的浓度周期性到达阈值,而菌落边缘的细菌有更强的基因表达能力(表达荧光蛋白),两者构成AND逻辑门,使菌落呈现出规律的图案];(e)实现更大范围群体周期性行为的同步;(f)利用群体感应实现的震荡系统治疗癌症]
Fig. 4 Three strategies for construcling multicellular oscillation systems[30, 56-57][(a), (b) and (c) refers to each of the three strategies for combining oscillation circuit with quorum sensing.(d)Forming regular pattern using QS.By using method B, autoinducer concentration periodically reaches the threshold. Since only bacteria at the edge of the colony have higher gene expression (like the expression of fluorescent protein),an AND logic gate is constructed to make the colony show rhythmic pattern.(e)Realization of the collective oscillation in a bigger range.(f)Employment of QS oscillation system in cancer treatment]
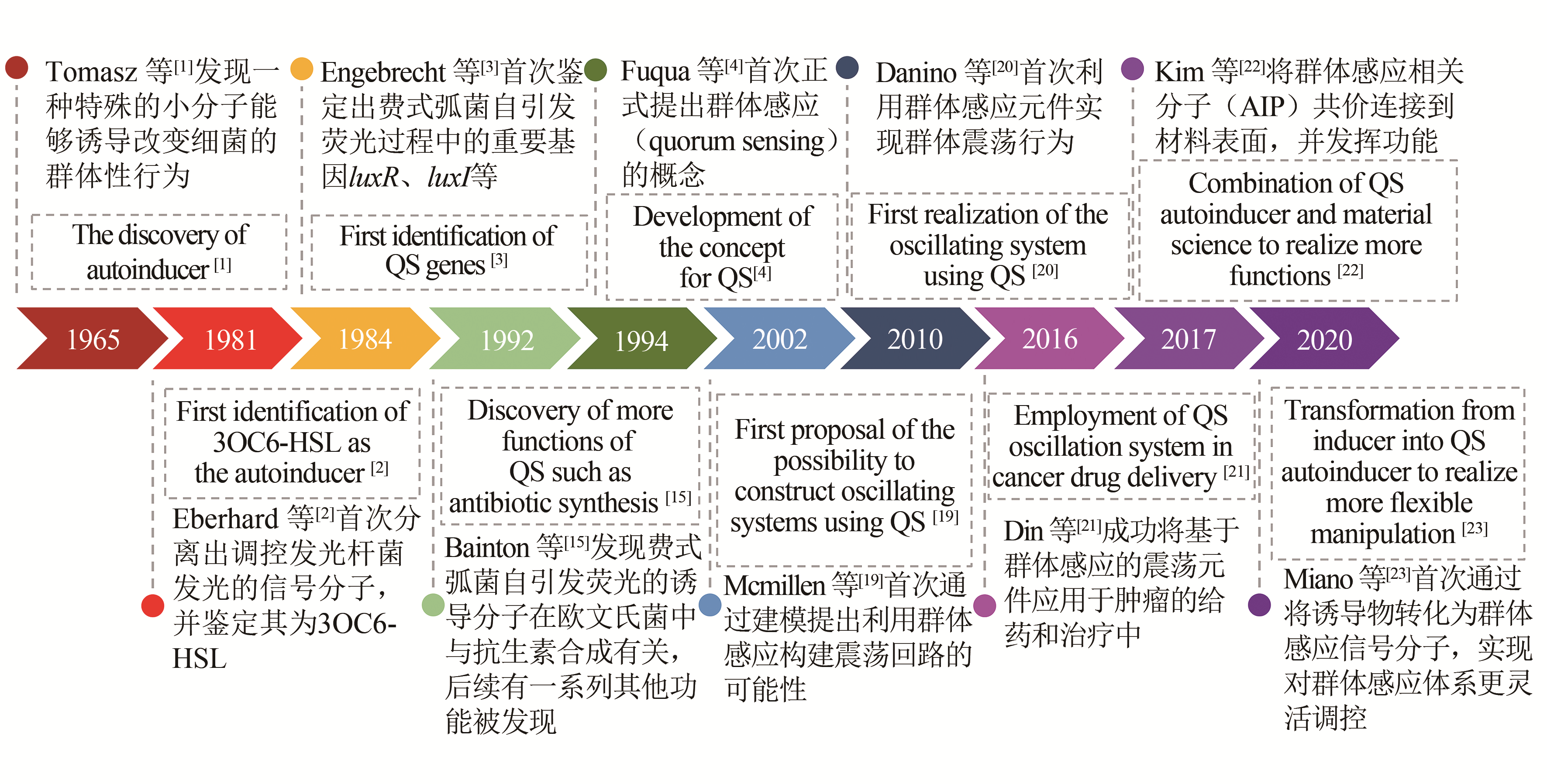
| 1 | TOMASZ A. Control of the competent state in pneumococcus by a hormone-like cell product: An example for a new type of regulatory mechanism in bacteria[J]. Nature, 1965, 208(5006): 155-159. |
| 2 | EBERHARD A, BURLINGAME A L, EBERHARD C, et al. Structural identification of autoinducer of Photobacterium fischeri luciferase[J]. Biochemistry, 1981, 20(9): 2444-2449. |
| 3 | ENGEBRECHT J, SILVERMAN M. Identification of genes and gene products necessary for bacterial bioluminescence[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1984, 81(13): 4154-4158. |
| 4 | FUQUA W C, WINANS S C, GREENBERG E P. Quorum sensing in bacteria-the luxr-luxi family of cell density-responsive transcriptional regulators[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1994, 176(2): 269-275. |
| 5 | MUKHERJEE S, BOSSIER B L. Bacterial quorum sensing in complex and dynamically changing environments[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2019, 17(6): 371-382. |
| 6 | PAPENFORT K, BASSLER B L. Quorum sensing signal-response systems in Gram-negative bacteria[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(9): 576-588. |
| 7 | POTTATHIL M, LAZAZZERA B A. The extracellular Phr peptide-rap phosphatase signaling circuit of Bacillus subtilis [J]. Frontiers in Bioscience, 2003, 8: 32-45. |
| 8 | GROSSMAN A D. Genetic networks controlling the initiation of sporulation and the development of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Annual Review of Genetics, 1995, 29: 477-508. |
| 9 | JI G Y, BEAVIS R C, NOVICK R P. Cell density control of staphylococcal virulence mediated by an octapeptide pheromone[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1995, 92(26): 12055-12059. |
| 10 | PEARSON J P, FELDMAN M, IGLEWSKI B H, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell-to-cell signaling is required for virulence in a model of acute pulmonary infection[J]. Infection and Immunity, 2000, 68(7): 4331-4334. |
| 11 | PIRHONEN M, FLEGO D, HEIKINHEIMO R, et al. A small diffusible signal molecule is responsible for the global control of virulence and exoenzyme production in the plant pathogen Erwinia carotovora [J]. Embo Journal, 1993, 12(6): 2467-2476. |
| 12 | BOUAYED N, DIETRICH N, LAFFORGUE C, et al. Process-oriented review of bacterial quorum quenching for membrane biofouling mitigation in membrane bioreactors (mbrs)[J]. Membranes, 2016, 6(4):52. |
| 13 | POLLAK S, OMER BENDORI S, ELDAR A. A complex path for domestication of B. subtilis sociality[J]. Current Genetics, 2015, 61(4): 493-496. |
| 14 | OGER P, KIM K S, SACKETT R L, et al. Octopine-type Ti plasmids code for a mannopine-inducible dominant-negative allele of traR, the quorum-sensing activator that regulates Ti plasmid conjugal transfer[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 1998, 27(2): 277-288. |
| 15 | BAINTON N J, STEAD P, CHHABRA S R, et al. N-(3-oxohexanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone regulates carbapenem antibiotic production in Erwinia carotovora [J]. Biochemical Journal, 1992, 288: 997-1004. |
| 16 | YUKSEL M, POWER J J, RIBBE J, et al. Fitness trade-offs in competence differentiation of Bacillus subtilis [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, 7:888. |
| 17 | JOHNSEN P J, DUBNAU D, LEVIN B R. Episodic selection and the maintenance of competence and natural transformation in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Genetics, 2009, 181(4): 1521-1533. |
| 18 | CONNELL J L, KIM J, SHEAR J B, et al. Real-time monitoring of quorum sensing in 3D-printed bacterial aggregates using scanning electrochemical microscopy[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(51): 18255-18260. |
| 19 | MCMILLEN D, KOPELL N, HASTY J, et al. Synchronizing genetic relaxation oscillators by intercell signaling[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(2): 679-684. |
| 20 | DANINO T, MONDRAGON-PALOMINO O, TSIMRING L, et al. A synchronized quorum of genetic clocks[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7279): 326-330. |
| 21 | DIN M O, DANINO T, PRINDLE A, et al. Synchronized cycles of bacterinl lysis for in vivo delivery[J]. Nature, 2016, 536(7614): 81-85. |
| 22 | KIM M K, ZHAO A S, WANG A, et al. Surface-attached molecules control Staphylococcus aureus quorum sensing and biofilm development[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2017, 2(8). DOI:http://doi.org/10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.80 . |
| 23 | MIANO A, LIAO M J, HASTY J. Inducible cell-to-cell signaling for tunable dynamics in microbial communities[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1193-1200. |
| 24 | LIU H W, FAN K L, LI H J, et al. Synthetic gene circuits enable Escherichia coli to use endogenous H2S as a signaling molecule for quorum sensing[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(9): 2113-2120. |
| 25 | CHEN M T, WEISS R. Artificial cell-cell communication in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae using signaling elements from Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2005, 23(12): 1551-1555. |
| 26 | WILLIAMS T C, NIELSEN L K, VICKERS C E. Engineered quorum sensing using pheromone-mediated cell-to-cell communication in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2013, 2(3): 136-149. |
| 27 | MINOGUE T D, WEHLAND-VON TREBRA M, BERNHARD F, et al. The autoregulatory role of EsaR, a quorum-sensing regulator in Pantoea stewartii ssp. stewartii: evidence for a repressor function[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2002, 44(6): 1625-1635. |
| 28 | SONG S Y, VUAI M S, ZHONG M T. The role of bacteria in cancer therapy - enemies in the past, but allies at present[J]. Infectious Agents and Cancer, 2018, 13(9). DOI: http://doi.org/10.1186/s13027-018-0180-y . |
| 29 | SHONG J, HUANG Y M, BYSTROFF C, et al. Directed evolution of the quorum-sensing regulator EsaR for increased signal sensitivity[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2013, 8(4): 789-795. |
| 30 | PRINDLE A, SAMAYOA P, RAZINKOV I, et al. A sensing array of radically coupled genetic 'biopixels'[J]. Nature, 2012, 481(7379): 39-44. |
| 31 | SHONG J, COLLINS C H. Engineering the esaR promoter for tunable quorum sensing-dependent gene expression[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2013, 2(10): 568-575. |
| 32 | SOMA Y, HANAI T. Self-induced metabolic state switching by a tunable cell density sensor for microbial isopropanol production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 30: 7-15. |
| 33 | TABOR J J, SALIS H M, SIMPSON Z B, et al. A synthetic genetic edge detection program[J]. Cell, 2009, 137(7): 1272-1281. |
| 34 | ARKIN A P, FLETCHER D A. Fast, cheap and somewhat in control[J]. Genome Biology, 2006, 7(8). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2006-7-8-114 . |
| 35 | TAMSIR A, TABOR J J, VOIGT C A. Robust multicellular computing using genetically encoded NOR gates and chemical 'wires'[J]. Nature, 2011, 469(7329): 212-215. |
| 36 | LALWANI M A, ZHAO E M, AVALOS J L. Current and future modalities of dynamic control in metabolic engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2018, 52: 56-65. |
| 37 | LEE S K, CHOU H, HAM T S, et al. Metabolic engineering of microorganisms for biofuels production: from bugs to synthetic biology to fuels[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2008, 19(6): 556-563. |
| 38 | KEASLING J D. Synthetic biology for synthetic chemistry[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2008, 3(1): 64-76. |
| 39 | KEASLING J D. Manufacturing molecules through metabolic engineering[J]. Science, 2010, 330(6009): 1355-1358. |
| 40 | TERPE K. Overview of bacterial expression systems for heterologous protein production: from molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 72(2): 211-222. |
| 41 | GUPTA A, REIZMAN I M B, REISCH C R, et al. Dynamic regulation of metabolic flux in engineered bacteria using a pathway-independent quorum-sensing circuit[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2017, 35(3): 273-279. |
| 42 | KIM E M, WOO H M, TIAN T, et al. Autonomous control of metabolic state by a quorum sensing (QS)-mediated regulator for bisabolene production in engineered E. coli [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 44: 325-336. |
| 43 | BROCKMAN I M, PRATHER K L J. Dynamic metabolic engineering: New strategies for developing responsive cell factories[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2015, 10(9): 1360-1369. |
| 44 | SHEN Y P, FONG L S, YAN Z B, et al. Combining directed evolution of pathway enzymes and dynamic pathway regulation using a quorum-sensing circuit to improve the production of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2019, 12. DOI:10.1186/s13068-019-1438-3 . |
| 45 | GU F, JIANG W, MU Y L, et al. Quorum sensing-based dual-function switch and its application in solving two key metabolic engineering problems[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(2): 209-217. |
| 46 | JIANG W, HE X, LUO Y, et al. Two completely orthogonal quorum sensing systems with self-produced autoinducers enable automatic delayed cascade control[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(9): 2588-2599. |
| 47 | DAHL R H, ZHANG F, ALONSO-GUTIERREZ J, et al. Engineering dynamic pathway regulation using stress-response promoters[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(11): 1039-1046. |
| 48 | HE X Y, CHEN Y, LIANG Q F, et al. Autoinduced and gate controls metabolic pathway dynamically in response to microbial communities and cell physiological state[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(3): 463-470. |
| 49 | STRICKER J, COOKSON S, BENNETT M R, et al. A fast, robust and tunable synthetic gene oscillator[J]. Nature, 2008, 456(7221): 516-519. |
| 50 | MATHER W, BENNETT M R, HASTY J, et al. Delay-induced degrade-and-fire oscillations in small genetic circuits[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102(6). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.068105 . |
| 51 | BARKAI N, LEIBLER S. Biological rhythms-circadian clocks limited by noise[J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 267-268. |
| 52 | ATKINSON M R, SAVAGEAU M A, MYERS J T, et al. Development of genetic circuitry exhibiting toggle switch or oscillatory behavior in Escherichia coli [J]. Cell, 2003, 113(5): 597-607. |
| 53 | HASTY J, MCMILLEN D, ISAACS F, et al. Computational studies of gene regulatory networks: in numero molecular biology[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2001, 2(4): 268-279. |
| 54 | ELOWITZ M B, LEIBLER S. A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators[J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 335-338. |
| 55 | NIEDERHOLTMEYER H, SUN Z Z, HORI Y, et al. Rapid cell-free forward engineering of novel genetic ring oscillators[J]. eLife, 2015, 4: e09771. |
| 56 | PAYNE S, LI B C, CAO Y X L, et al. Temporal control of self-organized pattern formation without morphogen gradients in bacteria[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2013, 9:697. |
| 57 | CHOWDHURY S, CASTRO S, COKER C, et al. Programmable bacteria induce durable tumor regression and systemic antitumor immunity[J]. Nature Medicine, 2019, 25(7): 1057-1063. |
| 58 | BABAN C K, CRONIN M, O'HANLON D, et al. Bacteria as vectors for gene therapy of cancer[J]. Bioengineered Bugs, 2010, 1(6): 385-394. |
| 59 | SONG S, VUAI M S, ZHONG M. The role of bacteria in cancer therapy - enemies in the past, but allies at present[J]. Infectious Agent Cancer, 2018, 13(1):1-7. |
| 60 | KIM J K, CHEN Y, HIRNING A J, et al. Long-range temporal coordination of gene expression in synthetic microbial consortia[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(11): 1102-1109. |
| 61 | HOOD L. Tackling the microbiome[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6086): 1209. |
| 62 | SCOTT S R, HASTY J. Quorum sensing communication modules for microbial consortia[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(9): 969-977. |
| 63 | CHEN Y, KIM J K, HIRNING A J, et al. Emergent genetic oscillations in a synthetic microbial consortium[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6251): 986-989. |
| 64 | BRENNER K, KARIG D K, WEISS R, et al. Engineered bidirectional communication mediates a consensus in a microbial biofilm consortium[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(44): 17300-17304. |
| 65 | DU P, ZHAO H W, ZHANG H Q, et al. De novo design of an intercellular signaling toolbox for multi-channel cell-cell communication and biological computation[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 4226: 4236. |
| 66 | SCOTT S R, DIN M O, BITTIHN P, et al. A stabilized microbial ecosystem of self-limiting bacteria using synthetic quorum-regulated lysis[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2017, 2: 17083. |
| 67 | DE ROY K, MARZORATI M, ABBEELE P VAN DEN, et al. Synthetic microbial ecosystems: an exciting tool to understand and apply microbial communities[J]. Environ Microbiol, 2014, 16(6): 1472-1481. |
| 68 | BALAGADDE F K, SONG H, OZAKI J, et al. A synthetic Escherichia coli predator-prey ecosystem[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2008, 4(1): 187-194. |
| 69 | KONG W T, MELDGIN D R, COLLINS J J, et al. Designing microbial consortia with defined social interactions[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(8): 821-829. |
| 70 | KIM S, KERNS S J, ZIESACK M, et al. Quorum sensing can be repurposed to promote information transfer between bacteria in the mammalian gut[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(9): 2270-2281. |
| 71 | TANG T C, AN B, HUANG Y, et al. Materials design by synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2020. |
| 72 | AN B L, WANG Y Y, JIANG X Y, et al. Programming living glue systems to perform autonomous mechanical repairs[J]. Matter, 2020, 3(6): 2080-2092. |
| 73 | CARDINALE S, ARKIN A P. Contextualizing context for synthetic biology-identifying causes of failure of synthetic biological systems[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2012, 7(7): 856-866. |
| 74 | MOSER F, BROERS N J, HARTMANS S, et al. Genetic circuit performance under conditions relevant for industrial bioreactors[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2012, 1(11): 555-564. |
| 75 | RENDA B A, HAMMERLING M J, BARRICK J E. Engineering reduced evolutionary potential for synthetic biology[J]. Molecular Biosystems, 2014, 10(7): 1668-1678. |
| 76 | DREES B, REIGER M, JUNG K, et al. A modular view of the diversity of cell-density-encoding schemes in bacterial quorum-sensing systems[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2014, 107(1): 266-277. |
| 77 | MENG F K, ELLIS T. The second decade of synthetic biology: 2010-2020[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5174-5177. |
| 78 | BASU S, GERCHMAN Y, COLLINS C H, et al. A synthetic multicellular system for programmed pattern formation[J]. Nature, 2005, 434(7037): 1130-1134. |
| 79 | HUANG J F, LIU S Y, ZHANG C, et al. Programmable and printable Bacillus subtilis biofilms as engineered living materials[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(1): 34-41. |
| [1] | 郭姝媛, 张倩楠, 姑丽克孜·买买提热夏提, 杨一群, 于涛. 液体生物燃料合成与炼制的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 18-44. |
| [2] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [3] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [11] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [12] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [13] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [14] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [15] | 虞旭昶, 吴辉, 李雷. 文库构建与基因簇靶向筛选驱动的微生物天然产物高效发现[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 492-506. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||