合成生物学 ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (6): 964-981.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-042
大肠杆菌生产饲用氨基酸的研究进展
郭亮1,2, 高聪1,2, 柳亚迪1,2, 陈修来1,2, 刘立明1,2
- 1.江南大学食品科学与技术国家重点实验室,江苏 无锡 214122
2.江南大学国际食品安全联合实验室,江苏 无锡 214122
-
收稿日期:2021-04-09修回日期:2021-05-21出版日期:2021-12-31发布日期:2022-01-21 -
通讯作者:刘立明 -
作者简介:郭亮 (1989—),男,博士,助理研究员。研究方向为合成生物学。E-mail:gliang1573@163.com刘立明 (1976—),男,博士,教授。研究方向为微生物生理功能解析与调控。E-mail:mingll@jiangnan.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金创新研究群体科学基金项目(32021005);国家自然科学基金青年项目(32000037);江苏省自然科学基金青年项目(BK20210478)
Advances in bioproduction of feed amino acid by Escherichia coli
GUO Liang1,2, GAO Cong1,2, LIU Yadi1,2, CHEN Xiulai1,2, LIU Liming1,2
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,Jiangsu,China
2.International Joint Laboratory on Food Safety,Wuxi 214122,Jiangsu,China
-
Received:2021-04-09Revised:2021-05-21Online:2021-12-31Published:2022-01-21 -
Contact:LIU Liming
摘要:
随着畜牧业的快速发展,人们对畜牧饲料蛋白的需求日益剧增。由于人们对食品安全意识的增强,迫切需要开发安全、高效、可持续动物饲料蛋白的供应途径。由于氨基酸是组成蛋白质的基本单元,所以在饲料中添加氨基酸可以替代饲料中的蛋白质,为动物细胞生长发育提供足够的营养。因此,饲用氨基酸作为动物饲料食品添加剂被广泛应用,具有广阔的市场应用前景。利用合成生物学技术,工程化改造大肠杆菌,构建的细胞工厂,以生物质为原料可绿色高效合成饲用氨基酸,而且其具有原料可再生、成本低廉、反应条件温和、环境污染小等优点,为解决动植物提取和化学炼制引起的环境污染问题提供了一种有效解决方案。本文针对饲用氨基酸(赖氨酸、甲硫氨酸、色氨酸、苏氨酸、缬氨酸和精氨酸)的生物合成途径,介绍了大肠杆菌合成饲用氨基酸的生产瓶颈,并从饲用氨基酸大肠杆菌细胞工厂的构建与优化,综述了利用合成生物学技术改造大肠杆菌细胞工厂合成饲用氨基酸的研究现状。提升饲用氨基酸的生产技术水平、提高大肠杆菌细胞的鲁棒性和增强大肠杆菌细胞对不利环境的耐受能力,可以提升饲用氨基酸发酵性能,简化发酵过程控制,降低饲用氨基酸的生产成本,是未来饲用氨基酸生产菌株工程化改造的方向。
中图分类号:
引用本文
郭亮, 高聪, 柳亚迪, 陈修来, 刘立明. 大肠杆菌生产饲用氨基酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(6): 964-981.
GUO Liang, GAO Cong, LIU Yadi, CHEN Xiulai, LIU Liming. Advances in bioproduction of feed amino acid by Escherichia coli[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(6): 964-981.
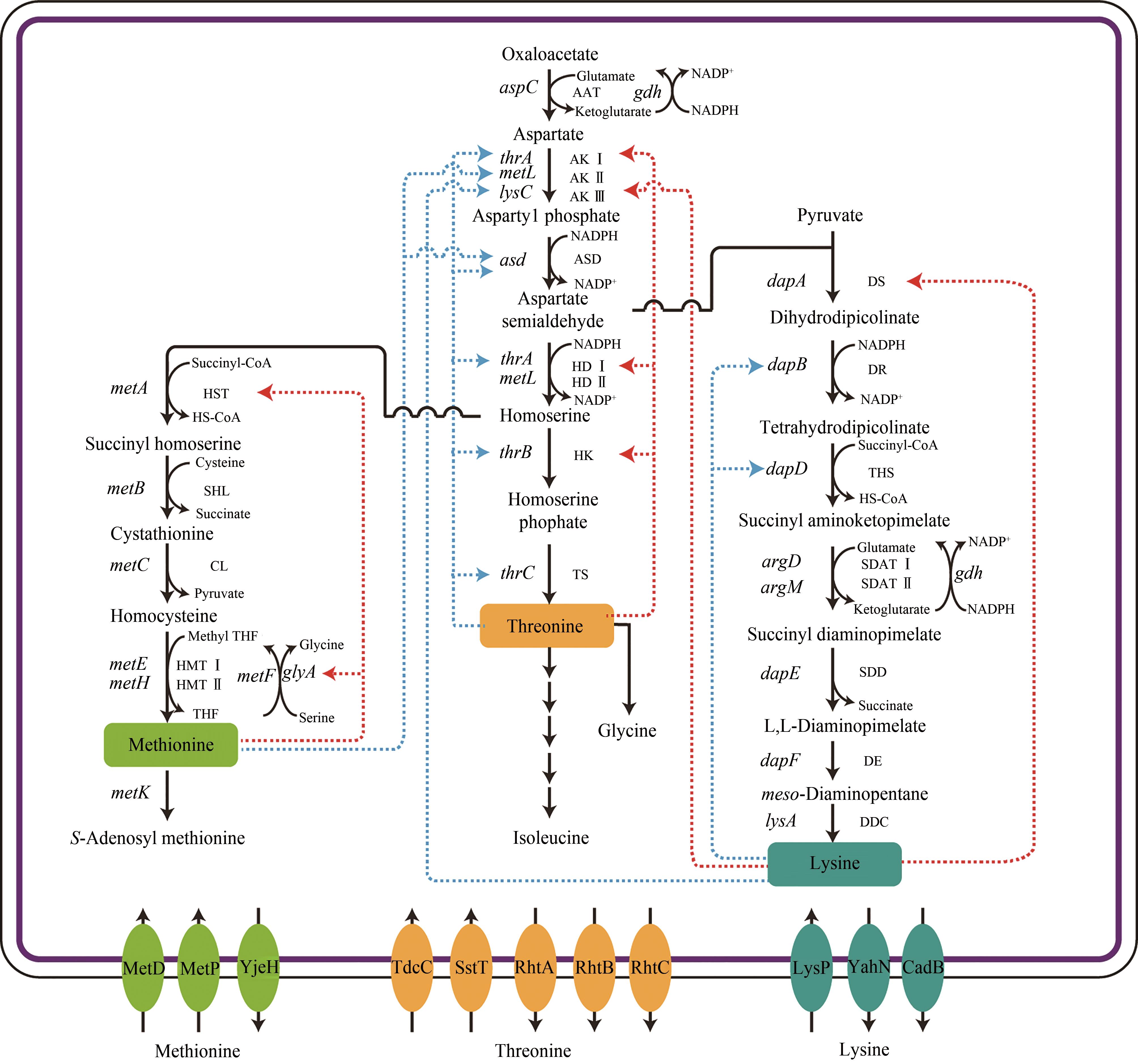
图1 大肠杆菌天冬氨酸族氨基酸的合成路径及其反馈调节示意图(红色虚线箭头表示反馈抑制、蓝色虚线箭头表示反馈阻遏、实线箭头表示一步代谢路径)途径涉及的关键酶:AAT—天冬氨酸氨基转移酶;AK Ⅰ,AK Ⅱ,AK Ⅲ—天冬氨酸激酶;ASD—天冬氨酸半醛脱氢酶;HD Ⅰ,HD Ⅱ—高丝氨酸脱氢酶;HK—高丝氨酸激酶;TS—苏氨酸合酶; DS—二氢吡啶二羧酸合酶;DR—二氢吡啶二羧酸还原酶;THS—四氢二吡啶琥珀酰酶;SDAT Ⅰ,SDAT Ⅱ—N-琥珀酰二氨基庚二酸氨基转移酶;SDD—N-琥珀酰二氨基庚二酸脱琥珀酰酶;DE—二氨基庚二酸差向异构酶;DDC—二氨基庚二酸脱羧酶;HST—O-琥珀酰高丝氨酸转琥珀酰酶;SHL—琥珀酰高丝氨酸裂解酶;CL—胱硫醚β-合成酶;HMT Ⅰ,HMT Ⅱ—半胱氨酸甲基转移酶.途径涉及的关键基因:aspC—天冬氨酸转氨酶编码基因;thrA—天冬氨酸激酶Ⅰ编码基因;metL—天冬氨酸激酶Ⅱ编码基因;lysC—天冬氨酸激酶Ⅲ编码基因;asd—天冬氨酸半醛脱氢酶编码基因;thrA—高丝氨酸脱氢酶Ⅰ编码基因;thrB—高丝氨酸激酶编码基因;thrC—苏氨酸合酶编码基因;dapA—二氢吡啶二羧酸合酶编码基因;dapB—二氢吡啶二羧酸还原酶编码基因;dapD—四氢二吡啶琥珀酰酶编码基因;argD—N-琥珀酰二氨基庚二酸氨基转移酶Ⅰ编码基因;argM—N-琥珀酰二氨基庚二酸氨基转移酶II编码基因;dapE—N-琥珀酰二氨基庚二酸脱琥珀酰酶编码基因;dapF—二氨基庚二酸差向异构酶编码基因;lysA—二氨基庚二酸脱羧酶编码基因;metA—O-琥珀酰高丝氨酸转琥珀酰酶编码基因;metB—琥珀酰高丝氨酸裂解酶编码基因;metC—胱硫醚β-合成酶编码基因;metE—半胱氨酸甲基转移酶编码基因;metH—半胱氨酸甲基转移酶编码基因;metK—蛋氨酸腺苷转移酶编码基因;gdh—谷氨酸脱氢酶编码基因;glyA—丝氨酸羟甲基转移酶编码基因;metF—亚甲基四氢叶酸还原酶编码基因
Fig. 1 Metabolic pathways of aspartate family amino acids and feedback regulations involved in E. coli(Blue dotted lines indicate feedback repression, red dotted lines indicate feedback inhibition, and solid arrows indicate one-step metabolic pathways)Key enzymes in metabolic pathway: AAT—aspartate aminotransferase; AK Ⅰ, AK Ⅱ, AK Ⅲ—aspartate kinase; ASD—aspartate semialdehyde dehydrogenase; HD Ⅰ, HD Ⅱ—homoserine dehydrogenase; HK—homoserine kinase; TS—threonine synthase; DS—dihydrodipicolinate synthase; DR—dihydrodipicolinate reductase; THS—tetrahydrodipicolinate succinyltransferase; SDAT Ⅰ, SDAT Ⅱ—succinyl diaminopimelate (DAP) aminotransferase; SDD—succinyl DAP desuccinylase; DE—L,L-DAP epimerase; DDC—meso-DAP decarboxylase; HST—homoserine succinyltransferase; SHL—succinyl homoserine lyase; CL—cystathionine lyase; HMT Ⅰ, HMT Ⅱ—homocysteine methyltransferase.Key genes in metabolic pathway: aspC—aspartate aminotransferase-encoding gene; thrA—aspartate kinase Ⅰ-encoding gene; metL—aspartate kinase Ⅱ-encoding gene; lysC—aspartate kinase Ⅲ-encoding gene; asd—aspartate semialdehyde dehydrogenase-encoding gene; thrA—homoserine dehydrogenase Ⅰ-encoding gene; thrB—homoserine kinase-encoding gene; thrC—threonine synthase-encoding gene; dapA—dihydrodipicolinate synthase-encoding gene; dapB—dihydrodipicolinate reductase-encoding gene; dapD—tetrahydrodipicolinate succinyltransferase-encoding gene; argD—succinyl diaminopimelate (DAP) aminotransferase Ⅰ-encoding gene; argM—succinyl diaminopimelate (DAP) aminotransferase Ⅱ-encoding gene; dapE—succinyl DAP desuccinylase-encoding gene; dapF—L,L-DAP epimerase; lysA—meso-DAP decarboxylase-encoding gene; metA—homoserine succinyltransferase-encoding gene; metB—succinyl homoserine lyase-encoding gene; metC—cystathionine lyase-encoding gene; metE—homocysteine methyltransferase Ⅰ-encoding gene; metH—homocysteine methyltransferase Ⅱ-encoding gene; metK—methionine adenosyltransferase-encoding gene; gdh—glutamate dehydrogenase-encoding gene; glyA—serine hydroxymethyltransferase-encoding gene; metF—methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase-encoding gene)
| 产品 | 菌株 | 性状 | 发酵 方式 | 产量 /(g/L) | 生产强度 /[g/(L·h)] | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 赖氨酸 | E. coli NT1003 | E. coli Δmet Δthr ↑ppc ↑pntB ↑aspA | 发酵罐 | 134.9 | 1.87 | [ |
| E. coli LATR11/pWG-DCSMASMBHc.gLP | E. coli LATR11 ↑lysCT344M ↑asd ↑dapAH56K ↑dapB ↑lysA ↑ppc ↑ddh | 发酵罐 | 125.6 | 3.14 | [ | |
| E. coli DL2 | E. coli MG1655 ↑lysCT253R ↑dapAE84T | 摇瓶 | 9.5 | — | [ | |
| E. coli RS3 | E. coli DL2 ↑lysCD340P ↑dapAE84TspeBA302VatpBS165NsecYM145V | 发酵罐 | 155 | 3.69 | [ | |
| E. coli Lc(H)‐Fe(M) | E. coli CCTCC M2019435 ↑lysC ↑fre | 发酵罐 | 193.6 | 4.03 | [ | |
| 苏氨酸 | E. coli TWF006/pFW01-thrA*BC-asd | E. coli TWF006 ↑thrBC ↑asd ↑thrAS345A | 摇瓶 | 15.85 | 0.44 | [ |
| E. coli W3110 pWYE134 | E. coli W3110 ↑thrL ↑thrBC ↑thrAS345A | 发酵罐 | 9.22 | 0.19 | [ | |
| E. coli THPZ | E. coli THRD ↑zwf | 发酵罐 | 126.1 | 5.25 | [ | |
| E. coli TWF106/pFT24rp | E. coli TWF001 ΔpoxB ΔpflB ΔldhA ΔadhE ΔtdcC ↑rhtC ↑pycmt | 发酵罐 | 80 | 2.22 | [ | |
| E. coli THPE5 | E. coli THRD ↑pycA ↑pckA ↑fdh ↑aspC↑gdhA ↑udhA ↑citA | 发酵罐 | 70.8 | 1.77 | [ | |
| 甲硫 氨酸 | E. coli W3110 ΔmetJ/pTrcA*H | E. coli W3110 ΔmetJ ΔmetA ΔlysA ↑yjeH | 发酵罐 | 9.75 | 0.20 | [ |
| E. coli M3/PAmZ | E. coli W3110 IJAHFEBC ↑metAfbr ↑yjeH↑serAfbr ↑metZ | 摇瓶 | 3.96 | 0.083 | [ | |
| E. coli Me05 (pETMAFbr-B-Y/pKKmetH) | E. coli W3110 ΔmetJ ΔthrC Δ lysA ↓metKpG ↑metAFbr ↑metB ↑metH | 发酵罐 | 5.62 | 0.12 | [ | |
| E. coli W3110 IJAHFEBC/pAm | E. coli W3110 IJAHFEBC ↑metAFbr ↑yjeH↑serAfbr | 发酵罐 | 16.86 | 0.35 | [ | |
| 色氨酸 | E. coli w3110 trpAE1 trpR tnaA | E. coli W3110 ΔtrpR ΔtnaA ↑trpEDCBA | 发酵罐 | 54.5 | 0.70 | [ |
| E. coli FB-04/pSV03E. coli W3110 ΔtrpRΔtnaA ΔpheA ΔtyrA ↑aroFfbr ↑trpES40FD | 发酵罐 | 13.3 | 0.029 | [ | ||
| E. coli Tna (pSC101 trp·I15) | — | 发酵罐 | 6.2 | 0.23 | [ | |
| E. coli KW023 | E. coli KW ΔtrpR ΔpykF ΔptsH ↑trpEDCBA↑aroGfbr ↓pta ↑galP ↑glk | 发酵罐 | 39.7 | 1.6 | [ | |
| E. coli T16 | E. coli TRTH Δppc ↑acs ↑aceB ↑mdh ↑pck | 发酵罐 | 54.6 | 1.52 | [ | |
| 缬氨酸 | E. coli Val (pKBRilvBNCED, pTrc184ygaZHlrp | E. coli Val ↑ilvBNCED ↑ygaZH ↑lrp | 摇瓶 | 7.55 | 0.16 | [ |
| E. coli VAMF (pKBRilvBNmutCED, pTrc184ygaZHlrp) | E. coli VAMF ↑ygaZH ↑lrp ↑ilv ↑ilvBNmutCED | 发酵罐 | 32.3 | 0.58 | [ | |
| E. coli V1 cat-PL-ilvE5.7 | E. coli K12 ΔilvIH ΔilvBN ΔlvGME ↑ilvE ↑ilvBNN17KDA | 摇瓶 | 9.8 | 0.20 | [ | |
| E. coli VHY18 | W3110 ΔlacI ΔycdN ΔycgH ΔydeU ΔyjiT Δyee ΔyjiV ΔpflB ΔldhA ΔadhE↑alsS ↑bcd ↑ilvD↑ilvCM ↑brnFE ↑spoT[R290E, K292D] | 发酵罐 | 84 | 2.33 | [ | |
| 精氨酸 | E. coli JM109-9039 | E. coli JM109 ΔargR ↑argCJBDFRGH | 摇瓶 | 0.040 | — | [ |
| E. coli SJB009 | E. coli C600+ ΔspeC ΔspeF ΔadiA ΔargR ΔargA ↑argA215 ↑argO | 发酵罐 | 11.64 | 0.24 | [ | |
| E. coli KO | E. coli MG1655 ↑argO ↑argAH15A ΔargR | 摇瓶 | 1.03 | — | [ |
表1 大肠杆菌细胞工厂生产饲用氨基酸进展比较
Tab. 1 Comparison of feed amino acid production by E. coli cell factories
| 产品 | 菌株 | 性状 | 发酵 方式 | 产量 /(g/L) | 生产强度 /[g/(L·h)] | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 赖氨酸 | E. coli NT1003 | E. coli Δmet Δthr ↑ppc ↑pntB ↑aspA | 发酵罐 | 134.9 | 1.87 | [ |
| E. coli LATR11/pWG-DCSMASMBHc.gLP | E. coli LATR11 ↑lysCT344M ↑asd ↑dapAH56K ↑dapB ↑lysA ↑ppc ↑ddh | 发酵罐 | 125.6 | 3.14 | [ | |
| E. coli DL2 | E. coli MG1655 ↑lysCT253R ↑dapAE84T | 摇瓶 | 9.5 | — | [ | |
| E. coli RS3 | E. coli DL2 ↑lysCD340P ↑dapAE84TspeBA302VatpBS165NsecYM145V | 发酵罐 | 155 | 3.69 | [ | |
| E. coli Lc(H)‐Fe(M) | E. coli CCTCC M2019435 ↑lysC ↑fre | 发酵罐 | 193.6 | 4.03 | [ | |
| 苏氨酸 | E. coli TWF006/pFW01-thrA*BC-asd | E. coli TWF006 ↑thrBC ↑asd ↑thrAS345A | 摇瓶 | 15.85 | 0.44 | [ |
| E. coli W3110 pWYE134 | E. coli W3110 ↑thrL ↑thrBC ↑thrAS345A | 发酵罐 | 9.22 | 0.19 | [ | |
| E. coli THPZ | E. coli THRD ↑zwf | 发酵罐 | 126.1 | 5.25 | [ | |
| E. coli TWF106/pFT24rp | E. coli TWF001 ΔpoxB ΔpflB ΔldhA ΔadhE ΔtdcC ↑rhtC ↑pycmt | 发酵罐 | 80 | 2.22 | [ | |
| E. coli THPE5 | E. coli THRD ↑pycA ↑pckA ↑fdh ↑aspC↑gdhA ↑udhA ↑citA | 发酵罐 | 70.8 | 1.77 | [ | |
| 甲硫 氨酸 | E. coli W3110 ΔmetJ/pTrcA*H | E. coli W3110 ΔmetJ ΔmetA ΔlysA ↑yjeH | 发酵罐 | 9.75 | 0.20 | [ |
| E. coli M3/PAmZ | E. coli W3110 IJAHFEBC ↑metAfbr ↑yjeH↑serAfbr ↑metZ | 摇瓶 | 3.96 | 0.083 | [ | |
| E. coli Me05 (pETMAFbr-B-Y/pKKmetH) | E. coli W3110 ΔmetJ ΔthrC Δ lysA ↓metKpG ↑metAFbr ↑metB ↑metH | 发酵罐 | 5.62 | 0.12 | [ | |
| E. coli W3110 IJAHFEBC/pAm | E. coli W3110 IJAHFEBC ↑metAFbr ↑yjeH↑serAfbr | 发酵罐 | 16.86 | 0.35 | [ | |
| 色氨酸 | E. coli w3110 trpAE1 trpR tnaA | E. coli W3110 ΔtrpR ΔtnaA ↑trpEDCBA | 发酵罐 | 54.5 | 0.70 | [ |
| E. coli FB-04/pSV03E. coli W3110 ΔtrpRΔtnaA ΔpheA ΔtyrA ↑aroFfbr ↑trpES40FD | 发酵罐 | 13.3 | 0.029 | [ | ||
| E. coli Tna (pSC101 trp·I15) | — | 发酵罐 | 6.2 | 0.23 | [ | |
| E. coli KW023 | E. coli KW ΔtrpR ΔpykF ΔptsH ↑trpEDCBA↑aroGfbr ↓pta ↑galP ↑glk | 发酵罐 | 39.7 | 1.6 | [ | |
| E. coli T16 | E. coli TRTH Δppc ↑acs ↑aceB ↑mdh ↑pck | 发酵罐 | 54.6 | 1.52 | [ | |
| 缬氨酸 | E. coli Val (pKBRilvBNCED, pTrc184ygaZHlrp | E. coli Val ↑ilvBNCED ↑ygaZH ↑lrp | 摇瓶 | 7.55 | 0.16 | [ |
| E. coli VAMF (pKBRilvBNmutCED, pTrc184ygaZHlrp) | E. coli VAMF ↑ygaZH ↑lrp ↑ilv ↑ilvBNmutCED | 发酵罐 | 32.3 | 0.58 | [ | |
| E. coli V1 cat-PL-ilvE5.7 | E. coli K12 ΔilvIH ΔilvBN ΔlvGME ↑ilvE ↑ilvBNN17KDA | 摇瓶 | 9.8 | 0.20 | [ | |
| E. coli VHY18 | W3110 ΔlacI ΔycdN ΔycgH ΔydeU ΔyjiT Δyee ΔyjiV ΔpflB ΔldhA ΔadhE↑alsS ↑bcd ↑ilvD↑ilvCM ↑brnFE ↑spoT[R290E, K292D] | 发酵罐 | 84 | 2.33 | [ | |
| 精氨酸 | E. coli JM109-9039 | E. coli JM109 ΔargR ↑argCJBDFRGH | 摇瓶 | 0.040 | — | [ |
| E. coli SJB009 | E. coli C600+ ΔspeC ΔspeF ΔadiA ΔargR ΔargA ↑argA215 ↑argO | 发酵罐 | 11.64 | 0.24 | [ | |
| E. coli KO | E. coli MG1655 ↑argO ↑argAH15A ΔargR | 摇瓶 | 1.03 | — | [ |
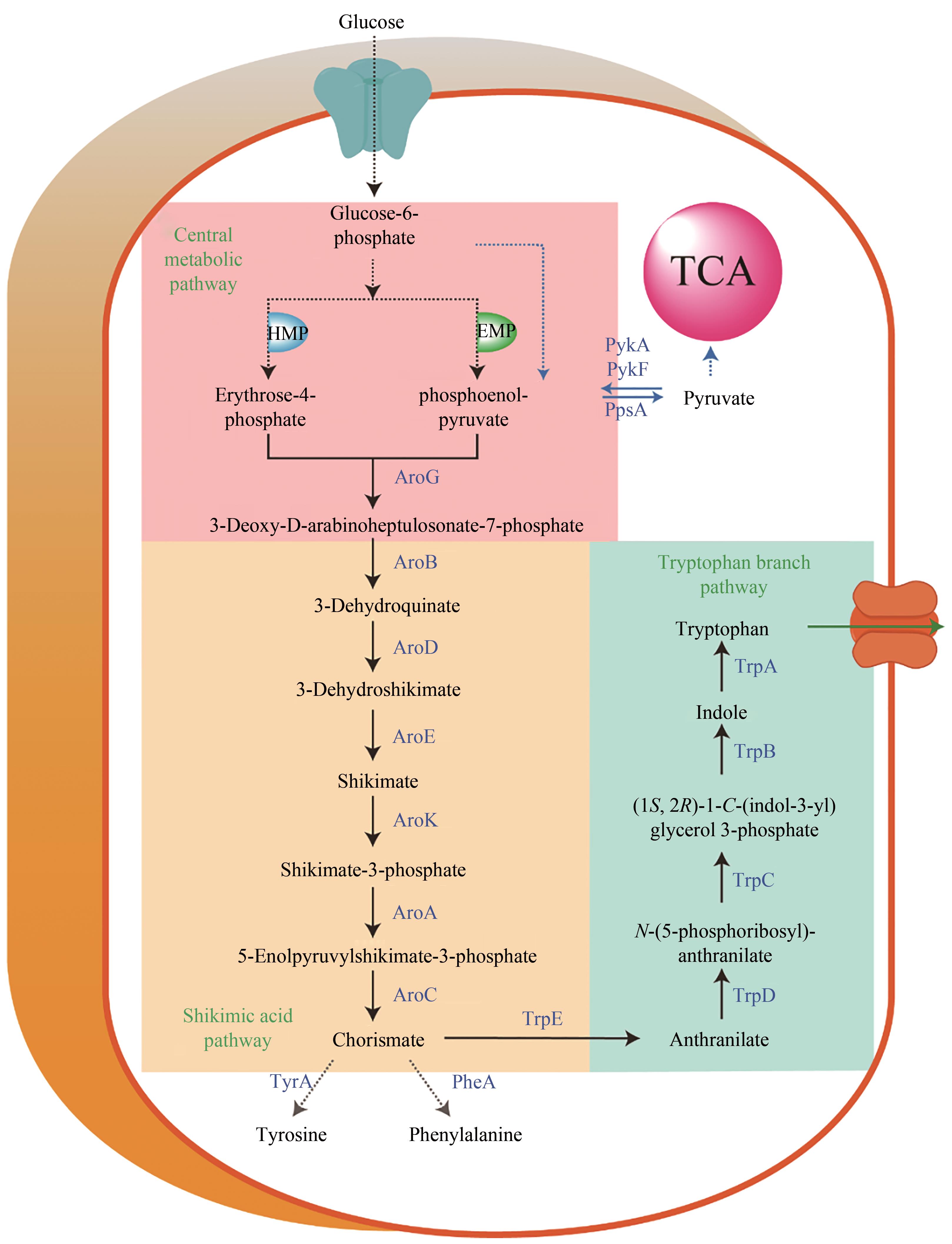
图2 大肠杆菌色氨酸合成代谢路径途径涉及的关键酶:PykF,PykA—丙酮酸激酶;PpsA—磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸合酶;AroG—3-脱氧-D-阿拉伯庚酮糖-7-磷酸合酶;AroB—3-脱氢奎宁酸合酶; AroD—3-脱氢奎宁酸脱水酶; AroE—莽草酸脱氢还原酶; AroK—莽草酸激酶;AroA—5-烯醇式丙酮酰胺莽草酸合酶; AroC—分支酸合酶; TrpE—邻氨基苯甲酸合酶; TrpD—邻氨基苯甲酸焦磷酸转移酶;TrpC—邻氨基苯甲酸异构酶;TrpB—色氨酸合酶;TrpA—吲哚甘油3-磷酸酶; TyrA—预苯酸脱氢酶; PheA—预苯酸脱水酶
Fig. 2 Schematic of the tryptophan biosynthetic pathway in E. coliKey enzymes in metabolic pathway: PykF, PykA—pyruvate kinase; PpsA—phosphoenolpyruvate synthase; AroG—3-deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate-7-phosphate (DHAP) synthase; AroB—3-dehydroquinate synthase; AroD—3-dehydroshikimate dehydratase; AroE—shikimate 5-dehydrogenase; AroK—shikimate kinase; AroA—EPSP synthase; AroC—chorismate synthase; TrpE—anthranilate synthase I; TrpD—anthranilate synthase II; TrpC—(1S,2R)-1-C-(indol-3-yl)glycerol 3-phosphate isomerase; TrpB—tryptophan synthase B; TrpA—tryptophan synthase A; TyrA—chorismate dehydrogenase; PheA—chorismate dehydratase
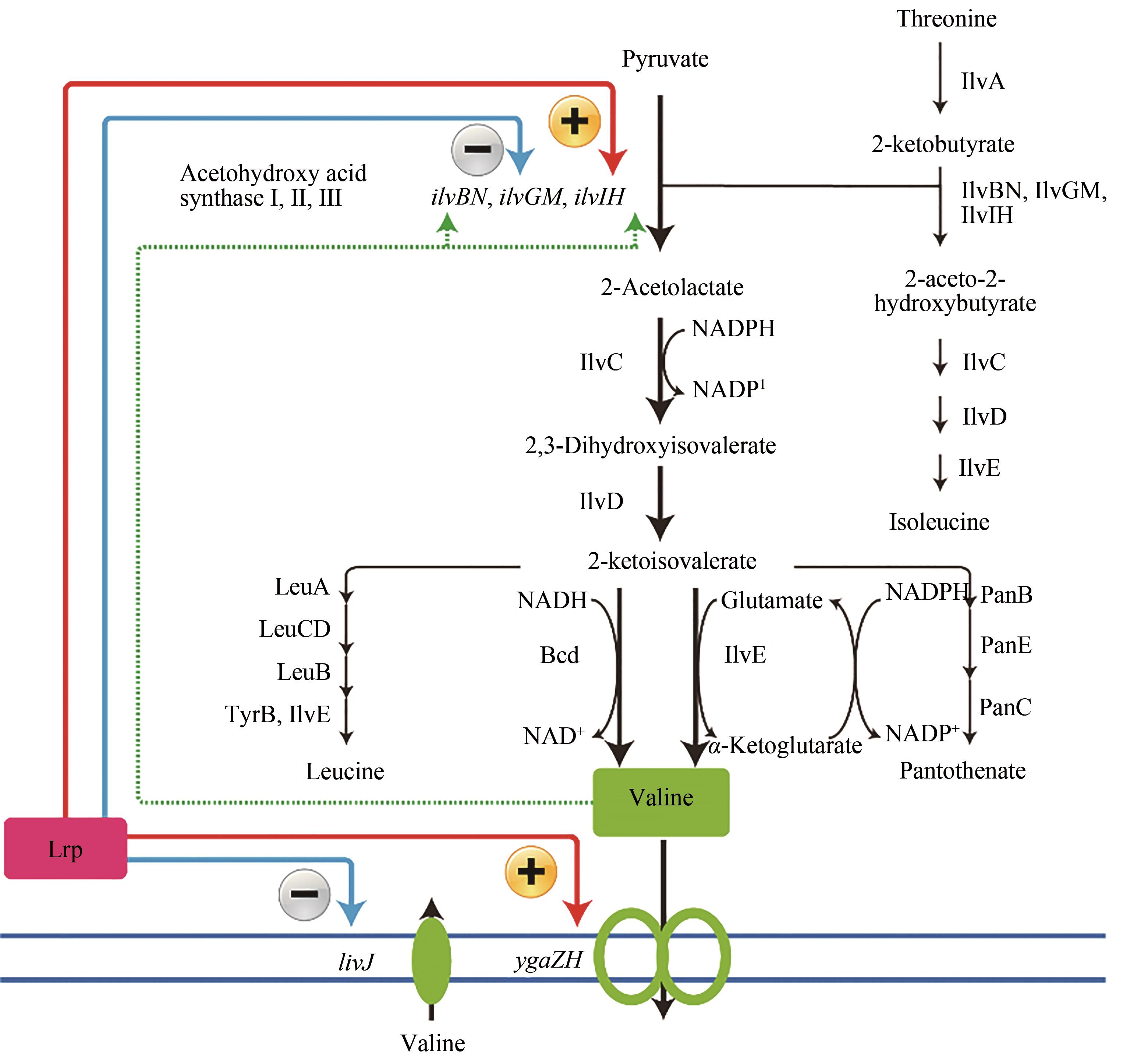
图3 大肠杆菌缬氨酸合成代谢路径(绿色虚线箭头表示缬氨酸的反馈抑制,蓝色箭头表示Lrp反馈阻遏,红色箭头表示Lrp反馈激活)途径涉及的关键酶:IlvC—乙酰羟酸还原异构酶;IlvD—二羟酸脱水酶;Bcd—亮氨酸脱氢酶;LeuA—异丙基苹果酸合酶;LeuCD—异丙基苹果酸异构酶;LeuB—3-异丙基苹果酸脱氢酶;ThrB,IlvE—芳香族氨基酸转移酶;PanB—3-甲基-2-氧代丁酸羟甲基转移酶;PanE—2-脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶;PanC—泛酸-β-丙氨酸连接酶途径涉及的关键基因:livJ—缬氨酸转运蛋白编码基因;ygaZH—缬氨酸外排蛋白编码基因;ilvBN—乙酰羟酸合酶I编码基因;ilvGM—乙酰羟酸合酶II编码基因;ilvIH—乙酰羟酸合酶Ⅲ编码基因
Fig. 3 Schematic of valine biosynthetic pathway in E. coli (Green dotted arrows indicate feedback inhibition by valine, blue dotted arrows indicate feedback repression, red arrows indicate activation of gene expression, and black arrows indicate one-step metabolic pathways)Key enzymes in metabolic pathway: IlvC—acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase; IlvD—dihydroxy acid dehydratease; Bcd—leucine dehydrogenase; LeuA—isopropylmalate synthase; LeuCD—isopropylmalate isomerase; LeuB—3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase; ThrB, IlvE—aromatic amino acid transaminase; PanB—3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate hydroxymethyltransferase; PanE—2-dehydropantoate reductase; PanC—pantoate-β-alanine ligase Key genes in metabolic pathway: livJ—valine transporter-encoding gene; ygaZH—valine exporter-encoding gene; ilvBN—acetohydroxy acid synthase I-encoding gene; ilvGM—acetohydroxy acid synthase II-encoding gene; ilvIH—acetohydroxy acid synthase Ⅲ-encoding gene

图4 微生物体内精氨酸合成代谢路径途径涉及的关键酶:ArgA—N-乙酰谷氨酸合酶;ArgJ—乙酰鸟氨酸转移酶;ArgB—乙酰谷氨酸激酶;ArgC—N-乙酰谷氨酸半醛脱氢酶;ArgD—乙酰鸟氨酸转氨酶;ArgE—乙酰鸟氨酸酶;ArgF—鸟氨酸转氨甲酰酶;ArgF′—乙酰鸟氨酸氨甲酰转移酶;ArgG—精胺琥珀酸合酶;ArgH—精氨琥珀酸酶
Fig. 4 Schematic of arginine biosynthetic pathway inmicroorganismsKey enzymes in metabolic pathway:ArgA—acetylglutamate synthase; ArgJ—ornithine acetyltransferase; ArgB—acetylglutamate kinase;ArgC—acetylglutamate semialdehyde dehydrogenase; ArgD—acetylornithine transaminase; ArgE—acetylornithine deacetylase; ArgF—ornithine transcarbamylase; ArgF′—acetylornithine carbamoyltransferase; ArgG—argininosuccinate synthase; ArgH—arginosuccinase
| 1 | 刘华阳, 李祥明. 我国疯牛病传染因子研究进展[J]. 饲料工业, 2020, 41(15): 60-64. |
| LIU H Y, LI X M. Research progress of infectious factor of BSE in China[J]. Feed Industry, 2020, 41(15): 60-64. | |
| 2 | KIDD M T, MAYNARD C W, MULLENIX G J. Progress of amino acid nutrition for diet protein reduction in poultry[J]. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology, 2021, 12(1): 45-45. |
| 3 | CARMO FELIX F K DO, JUNIOR LETTI L A, DE MELO PEREIRA G V, et al. L-lysine production improvement: a review of the state of the art and patent landscape focusing on strain development and fermentation technologies[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2019, 39(8): 1031-1055. |
| 4 | KARAU A, GRAYSON I. Amino acids in human and animal nutrition[M]// ZORN H, CZERMAK P. Biotechnology of food and feed additives, 2014: 189-228. |
| 5 | 赵静. 几种主要饲用氨基酸的营养研究进展[J]. 中国饲料添加剂, 2016(1): 10-13. |
| ZHAO J. Research advance on nutritional effects of several major feeding amino acid[J]. China Feed Additive, 2016(1): 10-13. | |
| 6 | ZHANG Y N, WANG S, DENG Y Z, et al. The application of reduced dietary crude protein levels supplemented with additional amino acids in laying ducks[J]. Poultry Science, 2021, 100(4): 1-7. |
| 7 | YANG Z Y, HTOO J K, LIAO S F. Methionine nutrition in swine and related monogastric animals: beyond protein biosynthesis[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2020, 268: 114608. |
| 8 | YOHAN P, JU-HWAN P, SURYEON P, et al. Enhanced cellular uptake and pharmacokinetic characteristics of doxorubicin-valine amide prodrug[J]. Molecules, 2016, 21(10): 1-9. |
| 9 | 谭伟杰. 2016年中国饲用氨基酸产业透视[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2016, 52(8): 12-16. |
| TAN W J. The perspective of China feed amino acid industry in 2016[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2016, 52(8): 12-16. | |
| 10 | 董德宽. 合成的饲用氨基酸[J]. 国外畜牧科技, 1983(6): 11-12. |
| DONG D K. Synthetic feed amino acids[J]. Animal Science Abroad, 1983(6): 11-12. | |
| 11 | LIU Y N, LI Q, ZHENG P, et al. Developing a high-throughput screening method for threonine overproduction based on an artificial promoter[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 1-11. |
| 12 | 董迅衍, 王小元. 微生物生产L-苏氨酸的代谢工程研究进展[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2016(12): 1233-1240. |
| DONG X Y, WANG X Y. Advances in microbial metabolic engineering to increase L-threonine production[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2016, 35(12): 1233-1240. | |
| 13 | 鲁佩玉, 孙青华. 发酵法生产氨基酸工艺研究[J]. 中国调味品, 2019, 44(1): 176-178. |
| LU P Y, SUN Q H. Study on the production process of amino acids by fermentation method[J]. China Condiment, 2019, 44(1): 176-178. | |
| 14 | LIU L, BILAL M, LUO H, et al. Metabolic engineering and fermentation process strategies for L-tryptophan production by Escherichia coli[J]. Processes, 2019, 7(4): 1-17. |
| 15 | YANG D, PARK S Y, PARK Y S, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for natural product biosynthesis[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 745-765. |
| 16 | WEI J, WANG Z, YU H, et al. Construction and fermentation of L-threonine-producing recombinant Escherichia coli [J]. Microbiology China, 2019, 46(4): 695-706. |
| 17 | HUCCETOGULLARI D, LUO Z W, LEE S Y. Metabolic engineering of microorganisms for production of aromatic compounds[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18(1): 1-29. |
| 18 | CHEN X, GAO C, GUO L, et al. DCEO biotechnology: tools to design, construct, evaluate, and optimize the metabolic pathway for biosynthesis of chemicals[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 118(1): 4-72. |
| 19 | D'ESTE M, ALVARADO-MORALES M, ANGELIDAKI I. Amino acids production focusing on fermentation technologies-A review[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2018, 36(1): 14-25. |
| 20 | WENDISCH V F. Metabolic engineering advances and prospects for amino acid production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 58: 17-34. |
| 21 | 马倩, 夏利, 谭淼, 等. 氨基酸生产的代谢工程研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 生物工程学报, 2020, 37(5): 1-20. |
| MA Q, XIA L, TAN M, et al. Advances and prospects in metabolic engineering for the production of amino acids[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37(5): 1-20. | |
| 22 | 赵嫚, 彭莉, 成浩, 等. 微生物甲硫氨酸合成调控的综合研究进展与展望[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2020, 46(24): 257-264. |
| ZHAO M, PENG L, CHENG H, et al. Advances on the biosynthesis and regulation of methionine[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(24): 257-264. | |
| 23 | BECKER J, WITTMANN C. A field of dreams: lignin valorization into chemicals, materials, fuels, and health-care products[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(6): 107360. |
| 24 | CHEN Z, LIU D. Toward glycerol biorefinery: metabolic engineering for the production of biofuels and chemicals from glycerol[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2016, 9(1): 205. |
| 25 | 王昕, 王静, 陈可泉, 等. 合成生物技术制备脂肪族二元胺的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(1): 71-83. |
| WANG X, WANG J, CHEN K Q, et al. Research progress in bioproduction of aliphatic diamines by synthetic biotechnology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(1): 71-83. | |
| 26 | TROENDLE J, SCHOPPEL K, BLEIDT A, et al. Metabolic control analysis of L-tryptophan production with Escherichia coli based on data from short-term perturbation experiments[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2020, 307: 15-28. |
| 27 | DAS A, TYAGI N, VERMA A, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli W3110 strain by incorporating genome-level modifications and synthetic plasmid modules to enhance L-Dopa production from glycerol[J]. Preparative Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2018, 48(8): 671-682. |
| 28 | PONTRELLI S, T-Y CHIU, LAN E I, et al. Escherichia coli as a host for metabolic engineering[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 50: 16-46. |
| 29 | LEE J-H, WENDISCH V F. Production of amino acids - Genetic and metabolic engineering approaches[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245: 1575-1587. |
| 30 | LEE S Y, KIM H U, CHAE T U, et al. A comprehensive metabolic map for production of bio-based chemicals[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2(1): 18-33. |
| 31 | YANG Z Y, HASAN M S, HTOO J K, et al. Effects of dietary supplementation of L-methionine vs. DL-methionine on performance, plasma concentrations of free amino acids and other metabolites, and myogenesis gene expression in young growing pigs[J]. Translational Animal Science, 2019, 3(1): 329-339. |
| 32 | WANG Y-Y, XU J-Z, ZHANG W-G. Metabolic engineering of L-leucine production in Escherichia coli and Corynebacterium glutamicum: a review[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2019, 39(5): 633-647. |
| 33 | MA Q, ZHANG Q, XU Q, et al. Systems metabolic engineering strategies for the production of amino acids[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2017, 2(2): 87-96. |
| 34 | 张震, 熊海波, 徐庆阳. 大肠杆菌高密度培养发酵L-色氨酸[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2019, 45(23): 15-20. |
| ZHANG Z, XIONG H B, XU Q Y. L-tryptophan fermentation by high cell density culture of Escherichia coli [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(23): 15-20. | |
| 35 | LI Y, WEI H, WANG T, et al. Current status on metabolic engineering for the production of L-aspartate family amino acids and derivatives[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245: 1588-1602. |
| 36 | FANG Y, WANG J, MA W, et al. Rebalancing microbial carbon distribution for L-threonine maximization using a thermal switch system[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 61: 33-46. |
| 37 | YANG D, YOO S M, GU C, et al. Expanded synthetic small regulatory RNA expression platforms for rapid and multiplex gene expression knockdown[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 54: 180-190. |
| 38 | HUANG J F, LIU Z Q, JIN L Q, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for microbial production of L-methionine[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2017, 114(4): 843-851. |
| 39 | HUANG J-F, SHEN Z-Y, MAO Q-L, et al. Systematic analysis of bottlenecks in a multibranched and multilevel regulated pathway: the molecular fundamentals of L-methionine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(11): 2577-2589. |
| 40 | TELEKI A, RAHNERT M, BUNGART O, et al. Robust identification of metabolic control for microbial L-methionine production following an easy-to-use puristic approach[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 41: 159-172. |
| 41 | ZHAO H, FANG Y, WANG X, et al. Increasing L-threonine production in Escherichia coli by engineering the glyoxylate shunt and the L-threonine biosynthesis pathway[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(13): 5505-5518. |
| 42 | XU J-Z, YANG H-K, ZHANG W-G. NADPH metabolism: a survey of its theoretical characteristics and manipulation strategies in amino acid biosynthesis[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2018, 38(7): 1061-1076. |
| 43 | 高虎涛, 申晓林, 孙新晓, 等. 代谢工程调控策略在生物合成氨基酸及其衍生物中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(9): 4058-4070. |
| GAO H T, SHEN X L, SUN X X, et al. Metabolic engineering strategies in biosynthesis of amino acids and their derivatives[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(9): 4058-4070. | |
| 44 | 李华, 董伟, 李由然, 等. 大肠杆菌MetD运输系统缺失对蛋氨酸积累的影响[J]. 微生物学通报, 2017, 44(6): 1416-1426. |
| LI H, DONG W, LI Y R, et al. Effect of inactivating MetD transporter system of Escherichia coli W3110 on L-methionine production[J]. Microbiology China, 2017, 44(6): 1416-1426. | |
| 45 | LIU Q, LIANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. YjeH Is a novel exporter of L-methionine and branched-chain amino acids in Escherichia coli [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(22): 7753-7766. |
| 46 | 杨冬美, 李华, 李由然, 等. 大肠杆菌TdcC、SstT和LIV-1系统缺失对胞外L-苏氨酸积累的影响[J]. 微生物学通报, 2017, 44(1): 20-29. |
| YANG D M, LI H, LI Y R, et al. Effects of TdcC、SstT and LIV-1 systems deletion of Escherichia coli on extracellular L-threonine accumulation[J]. Microbiology China, 2017, 44(1): 20-29. | |
| 47 | YING H X, HE X, LI Y, et al. Optimization of culture conditions for enhanced lysine production using engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2014, 172(8): 3835-3843. |
| 48 | XU J, HAN M, REN X, et al. Modification of aspartokinase Ⅲ and dihydrodipicolinate synthetase increases the production of L-lysine in Escherichia coli [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 114: 79-86. |
| 49 | GENG F, CHEN Z, ZHENG P, et al. Exploring the allosteric mechanism of dihydrodipicolinate synthase by reverse engineering of the allosteric inhibitor binding sites and its application for lysine production[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2013, 97(5): 1963-1971. |
| 50 | WANG X, LI Q, SUN C, et al. GREACE-assisted adaptive laboratory evolution in endpoint fermentation broth enhances lysine production by Escherichia coli [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18: 1-13. |
| 51 | PIAO X, WANG L, LIN B, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for production of L-aspartate and its derivative beta-alanine with high stoichiometric yield[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 54: 244-254. |
| 52 | WANG S, HOU Y, CHEN X, et al. Kick-starting evolution efficiency with an autonomous evolution mutation system[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 54: 127-136. |
| 53 | YE C, LUO Q, GUO L, et al. Improving lysine production through construction of an Escherichia coli enzyme-constrained model[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2020, 117(11): 3533-3544. |
| 54 | ZHANG X, YAN J A, YU L, et al. Construction of recombinant plasmids containing threonine operon and their effects on L-threonine accumulation[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2009, 49(5): 591-596. |
| 55 | LI Y J, ZHANG D Z, CAI N Y, et al. Betaine supplementation improved L-threonine fermentation of Escherichia coli THRD by upregulating zwf (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) expression[J]. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 2019, 39: 67-73. |
| 56 | LIU J, LI H, XIONG H, et al. Two-stage carbon distribution and cofactor generation for improving L-threonine production of Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2019, 116(1): 110-120. |
| 57 | TANG X-L, DU X-Y, CHEN L-J, et al. Enhanced production of L-methionine in engineered Escherichia coli with efficient supply of one carbon unit[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2020, 42(3): 429-436. |
| 58 | LI H, WANG B S, LI Y R, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli W3110 for the production of L-methionine[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 44(1): 75-88. |
| 59 | AZUMA S, TSUNEKAWA H, OKABE M, et al. Hyper-production of L-trytophan via fermentation with crystallization[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1993, 39: 471-476. |
| 60 | ZHAO Z-J, ZOU C, ZHU Y-X, et al. Development of L-tryptophan production strains by defined genetic modification in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2011, 38(12): 1921-1929. |
| 61 | AIBA S, TSUNEKAWA H, IMANAKA T. New approach to tryptophan production by Escherichia coli: genetic manipulation of composite plasmids in vitro [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1982, 43(2): 289-297. |
| 62 | CHEN Y, LIU Y, DING D, et al. Rational design and analysis of an Escherichia coli strain for high-efficiency tryptophan production[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 45(5): 357-367. |
| 63 | DU L, ZHANG Z, XU Q, et al. New strategy for removing acetic acid as a by-product during L-tryptophan production[J]. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, 2019, 33(1): 1471-1480. |
| 64 | PARK J H, LEE K H, KIM T Y, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of L-valine based on transcriptome analysis and in silico gene knockout simulation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(19): 7797-7802. |
| 65 | PARK J H, KIM T Y, LEE K H, et al. Fed-batch culture of Escherichia coli for L-valine production based on in silico flux response analysis[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2011, 108(4): 934-946. |
| 66 | SAVRASOVA E A, STOYNOVA N V. Application of leucine dehydrogenase Bcd from Bacillus subtilis for L-valine synthesis in Escherichia coli under microaerobic conditions[J]. Heliyon, 2019, 5(4): e01406. |
| 67 | HAO Y, MA Q, LIU X, et al. High-yield production of L-valine in engineered Escherichia coli by a novel two-stage fermentation[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 62: 198-206. |
| 68 | XU M, RAO Z, YANG J, et al. Heterologous and homologous expression of the arginine biosynthetic argC similar to H cluster from Corynebacterium crenatum for improvement of L-arginine production[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 39(3): 495-502. |
| 69 | GINESY M, BELOTSERKOVSKY J, ENMAN J, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for enhanced arginine biosynthesis[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 1-11. |
| 70 | SANDER T, WANG C Y, GLATTER T, et al. CRISPRi-based downregulation of transcriptional feedback improves growth and metabolism of arginine overproducing E. coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(9): 1983-1990. |
| 71 | LEE K H, PARK J H, KIM T Y, et al. Systems metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for L-threonine production[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2007, 3:149. |
| 72 | CHEN L, CHEN M, MA C, et al. Discovery of feed-forward regulation in L-tryptophan biosynthesis and its use in metabolic engineering of E. coli for efficient tryptophan bioproduction[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47: 434-444. |
| 73 | LI M, LIU C, YANG J, et al. Common problems associated with the microbial productions of aromatic compounds and corresponding metabolic engineering strategies[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2020, 41: 107548. |
| 74 | JIANG J, LIU T, LIN S. Research progress on the biosynthesis of aromatic compounds by microorganisms[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2019, 31(5): 430-448. |
| 75 | LI Z, WANG H, DING D, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for production of chemicals derived from the shikimate pathway[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 47(6-7): 525-535. |
| 76 | CHEN L, ZENG A-P. Rational design and metabolic analysis of Escherichia coli for effective production of L-tryptophan at high concentration[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(2): 559-568. |
| 77 | TROENDLE J, TRACHTMANN N, SPRENGER G A, et al. Fed-batch production of L-tryptophan from glycerol using recombinant Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2018, 115(12): 2881-2892. |
| 78 | NIU H, LI R, LIANG Q, et al. Metabolic engineering for improving L-tryptophan production in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 46(1): 55-65. |
| 79 | XIONG B, ZHU Y, TIAN D, et al. Flux redistribution of central carbon metabolism for efficient production of L-tryptophan in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2021, 118(3): 1393-1404. |
| 80 | LEE J, KIM J, SONG J E, et al. Production of Tyrian purple indigoid dye from tryptophan in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2020: 1-9. |
| 81 | WYNANDS B, LENZEN C, OTTO M, et al. Metabolic engineering of Pseudomonas taiwanensis VLB120 with minimal genomic modifications for high-yield phenol production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47: 121-133. |
| 82 | DING R, LIU L, CHEN X, et al. Introduction of two mutations into AroG increases phenylalanine production in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2014, 36(10): 2103-2108. |
| 83 | NODA S, KONDO A. Recent advances in microbial production of aromatic chemicals and derivatives[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2017, 35(8): 785-796. |
| 84 | WANG J, ZHANG R, ZHANG Y, et al. Developing a pyruvate-driven metabolic scenario for growth-coupled microbial production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 55: 191-200. |
| 85 | GUO L, ZHANG F, ZHANG C, et al. Enhancement of malate production through engineering of the periplasmic rTCA pathway in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2018, 115(6): 1571-1580. |
| 86 | LIU L, CHEN S, WU J. Phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system modification increases the conversion rate during L-tryptophan production in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 44(10): 1385-1395. |
| 87 | AL-BASSAM M M, KIM J N, ZARAMELA L S, et al. Optimization of carbon and energy utilization through differential translational efficiency[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-13. |
| 88 | KOENDJBIHARIE J G, KRANENBURG R VAN, KENGEN S W M. The PEP-pyruvate-oxaloacetate node: variation at the heart of metabolism[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2020: 1-19. |
| 89 | DIAO J, SONG X, ZHANG L, et al. Tailoring cyanobacteria as a new platform for highly efficient synthesis of astaxanthin[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 61: 275-287. |
| 90 | NGUYEN A D, KIM D, LEE E Y. Unlocking the biosynthesis of sesquiterpenoids from methane via the methylerythritol phosphate pathway in methanotrophic bacteria, using alpha-humulene as a model compound[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020, 61: 69-78. |
| 91 | 王均成, 王可, 张春宇. L-缬氨酸的应用和育种研究进展[J]. 发酵科技通讯, 2012, 41(01): 30-34. |
| WANG J C, WANG K, ZHANG C Y. Advances in bioproduction of L-valine[J]. Bulletin of Fermentation Science and Technology, 2012, 41(1): 30-34. | |
| 92 | JONES C M, LOZADA N J H, PFLEGER B F. Efflux systems in bacteria and their metabolic engineering applications[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(22): 9381-9393. |
| 93 | CHARLIER D, BERVOETS I. Regulation of arginine biosynthesis, catabolism and transport in Escherichia coli [J]. Amino Acids, 2019, 51(8): 1103-1127. |
| 94 | 程功, 徐建中, 张伟国. L-精氨酸生物合成机制及其代谢工程育种研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2016, 43(6): 1379-1387. |
| CHENG G, XU J Z, ZHANG W G. Progress in biosynthesis and metabolic engineering of L-arginine producer[J]. Microbiology China, 2016, 43(6): 1379-1387. | |
| 95 | LU C D. Pathways and regulation of bacterial arginine metabolism and perspectives for obtaining arginine overproducing strains[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 70(3): 261-272. |
| 96 | CHARLIER D, ROOVERS M, VLIET F VAN, et al. Arginine regulon of Escherichia coli K-12: a study of repressor-operator interactions and of in vitro binding affinities versus in vivo repression[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1992, 226(2): 367-386. |
| 97 | NANDINENI M R, GOWRISHANKAR J. Evidence for an arginine exporter encoded by yggA (argO) that is regulated by the LysR-type transcriptional regulator ArgP in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2004, 186(11): 3539-3546. |
| 98 | RAJAGOPAL B S, DEPONTE J, TUCHMAN M, et al. Use of inducible feedback-resistant N-acetylglutamate synthetase (argA) genes for enhanced arginine biosynthesis by genetically engineered Escherichia coli K-12 strains[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1998, 64(5): 1805-1811. |
| 99 | GINESY M, RUSANOVA-NAYDENOVA D, ROVA U. Tuning of the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio for the production of L-arginine by Escherichia coli [J]. Fermentation, 2017, 3(4): 1-11. |
| [1] | 郭姝媛, 张倩楠, 姑丽克孜·买买提热夏提, 杨一群, 于涛. 液体生物燃料合成与炼制的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 18-44. |
| [2] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [3] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | 赵亮, 李振帅, 付丽平, 吕明, 王士安, 张全, 刘立成, 李福利, 刘自勇. 生物转化一碳化合物原料产油脂与单细胞蛋白研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [11] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [12] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [13] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [14] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [15] | 禹伟, 高教琪, 周雍进. 一碳生物转化合成有机酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1169-1188. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
