合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (1): 154-173.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-010
工程化细胞外囊泡的设计合成与生物医学应用
刘夺1,2, 刘培源1, 李连月1, 王雅欣1, 崔钰惠1, 薛慧敏1, 王汉杰1
- 1.天津大学生命科学学院,天津市微纳生物材料与检疗技术工程中心,天津市生物大分子结构功能与应用重点实验室,天津 300072
2.天津大学化工学院,合成生物学前沿科学中心,天津 300072
-
收稿日期:2023-02-01修回日期:2023-12-27出版日期:2024-02-29发布日期:2024-03-20 -
通讯作者:王汉杰 -
作者简介:刘夺 (1987—),男,博士,副研究员。研究方向为纳米医药合成生物学,从事细菌、酵母设计再造用于医药合成与在体递送等生命健康应用研究。 E-mail:duo_liu0@tju.edu.cn王汉杰 (1984—),男,博士,教授,天津大学生命科学学院副院长。研究方向为纳米生物学、合成生物学和生物医学工程等多学科交叉领域,从事肠道细菌的合成生物学设计再造及生命健康应用研究。 E-mail:wanghj@tju.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划项目(2019YFA0906500);国家自然科学基金优秀青年项目(32122047);国家自然科学基金面上项目(31971300)
Design and synthesis of engineered extracellular vesicles and their biomedical applications
LIU Duo1,2, LIU Peiyuan1, LI Lianyue1, WANG Yaxin1, CUI Yuhui1, XUE Huimin1, WANG Hanjie1
- 1.School of Life Sciences,Tianjin University,Tianjin Engineering Center of Micro-Nano Biomaterials and Detection-Treatment Technology,Tianjin Key Laboratory of Function and Application of Biological Macromolecules,Tianjin 300072,China
2.Frontiers Science Center for Synthetic Biology,School of Chemical Engineering and Technology,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
-
Received:2023-02-01Revised:2023-12-27Online:2024-02-29Published:2024-03-20 -
Contact:WANG Hanjie
摘要:
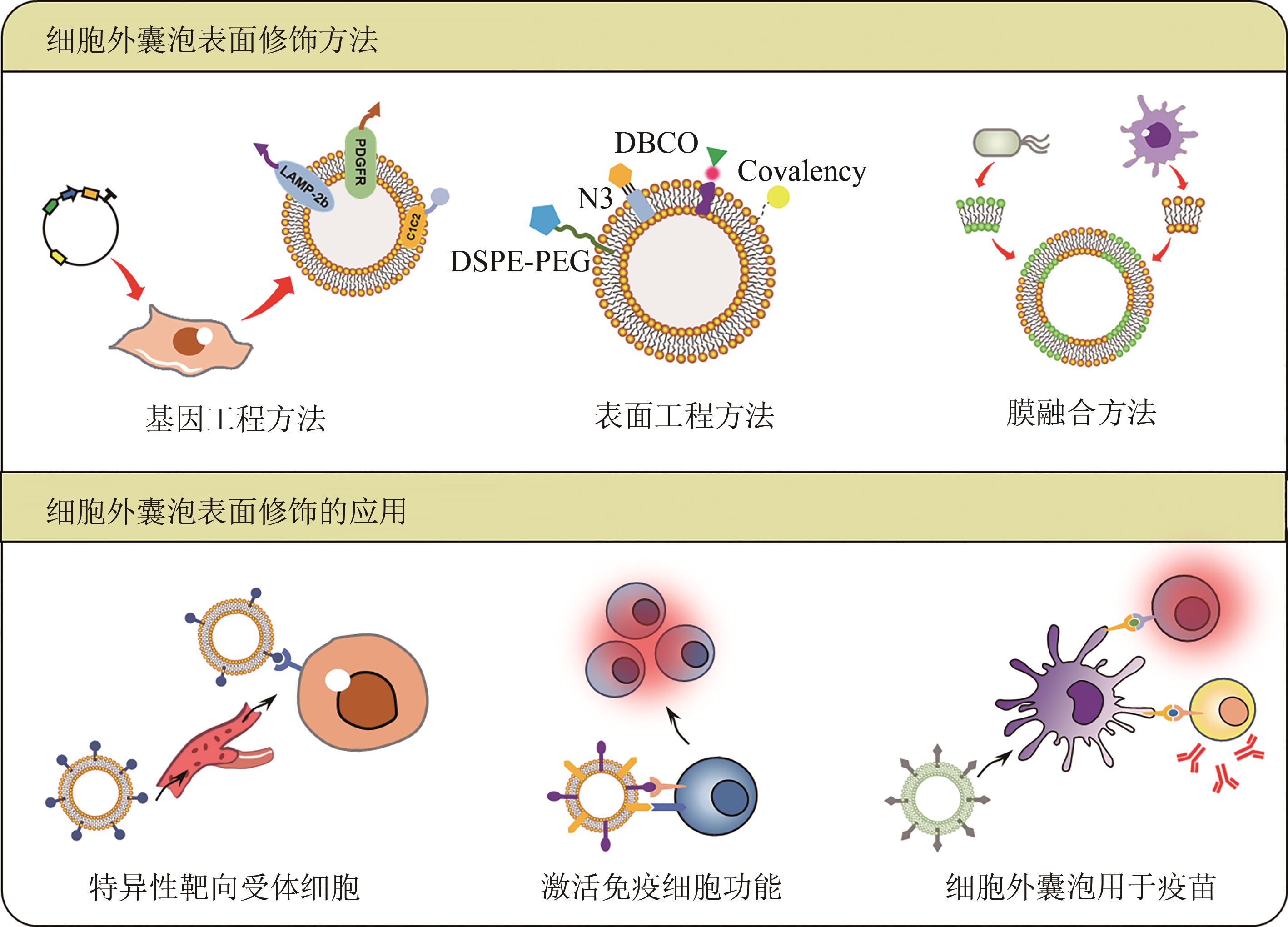
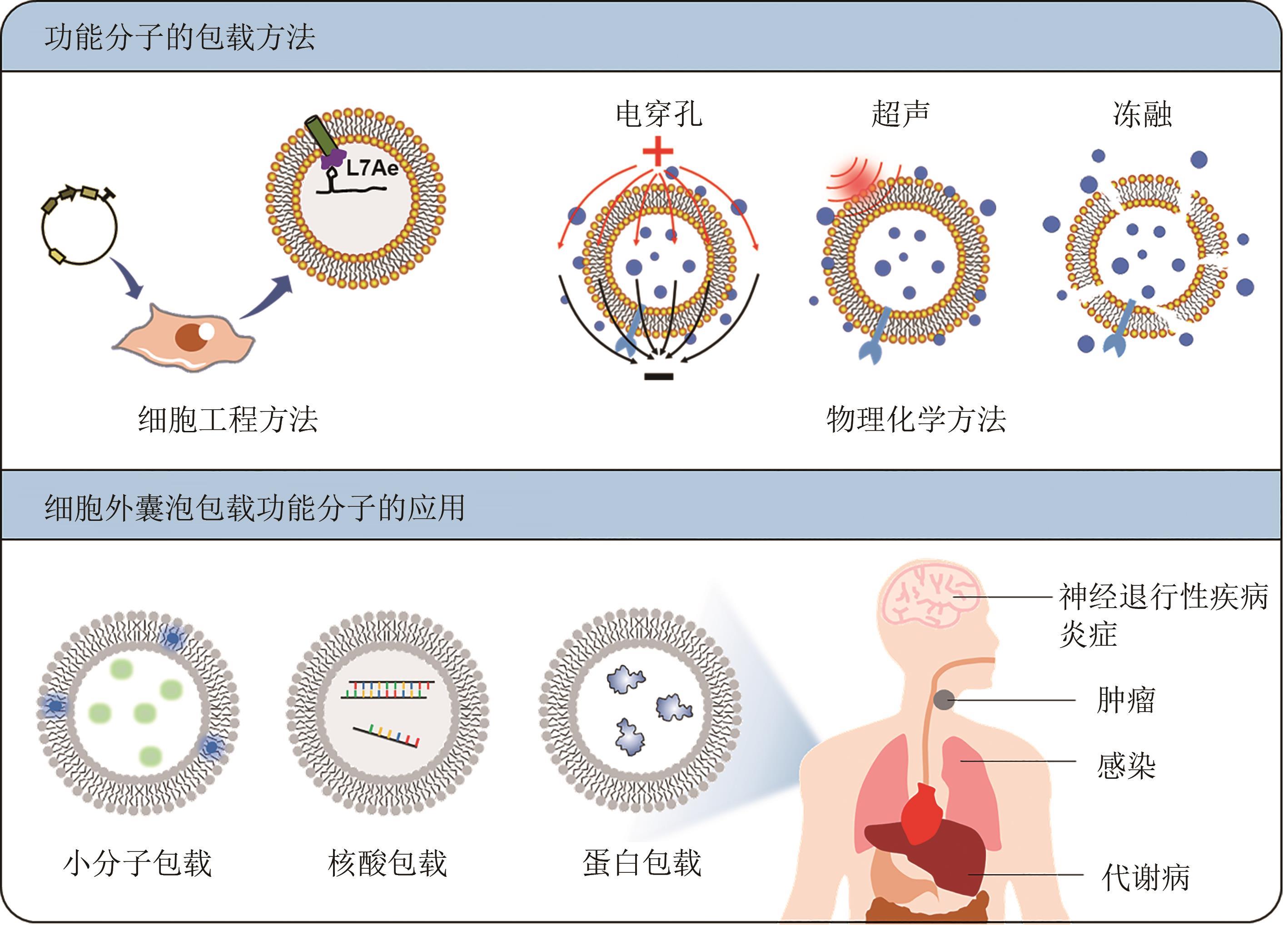
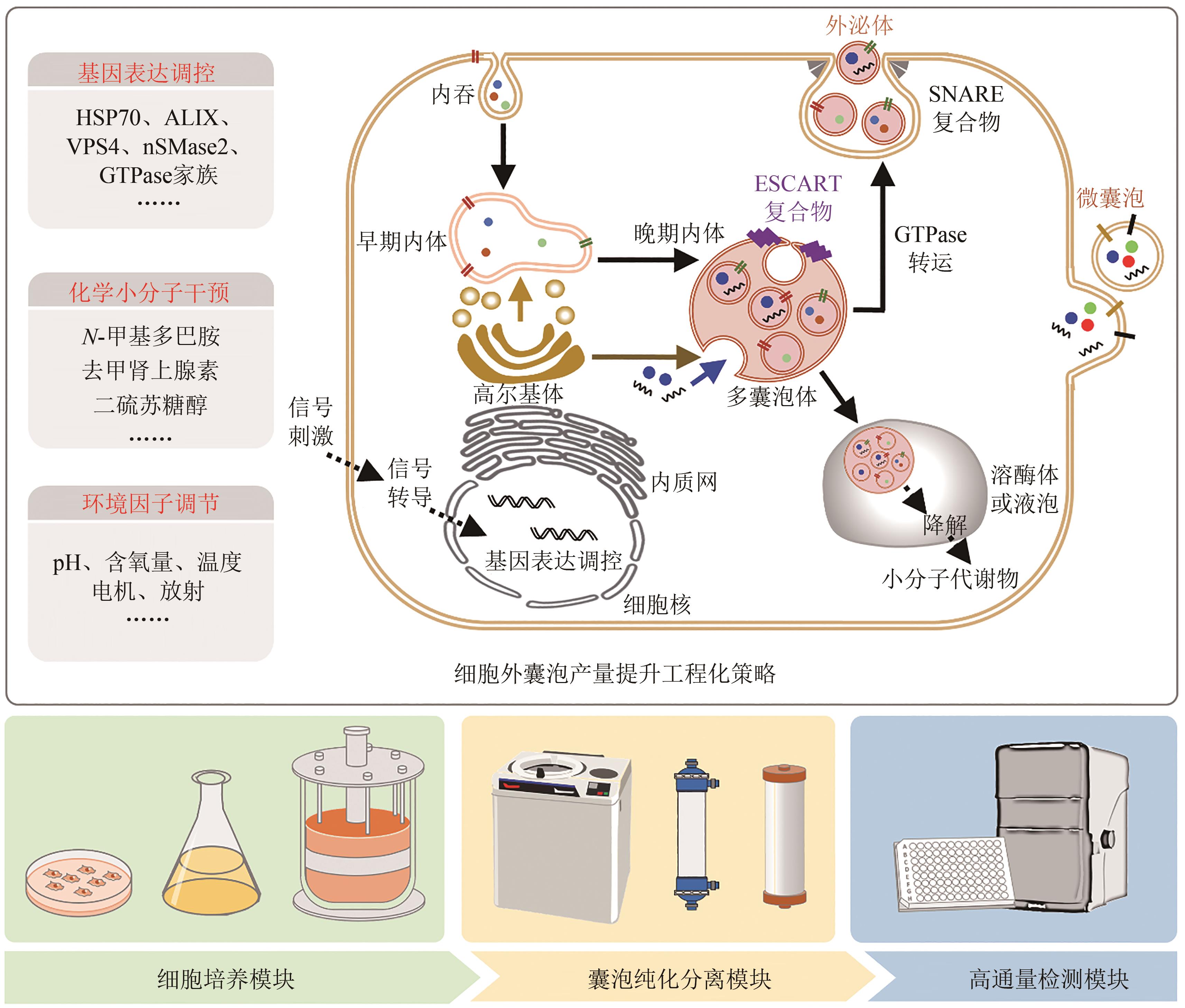
近年来,细胞外囊泡因其与疾病发生发展密切相关而受到越来越广泛的关注。随着细胞外囊泡参与生命功能调控的机制被不断解析,利用细胞外囊泡作为药物载体,用于靶向治疗的工作也相继开展。细胞外囊泡作为药物载体,与人工载体相比,具有高生物相容性、低免疫原性和良好的生物膜融合能力,同时有着参与细胞通信的归巢效应等天然优势。然而,细胞外囊泡的生物医学应用也存在表面修饰复杂、包载能力差、产量较低等问题,导致使用范围严重受限。工程化细胞外囊泡是指对天然细胞外囊泡进行人工改造,使其能够特异性靶向受体细胞或组织,实现所包载功能分子的精准递送,并支撑可放大生产的模式,从而展现出广阔的生物医学应用前景。合成生物学技术的引入,可实现底盘细胞的从头设计再造,支撑细胞外囊泡的标准化、模块化合成。本文首先概括了工程化细胞外囊泡的表面修饰、工程化细胞外囊泡的功能分子包载的方法和应用;其次总结了工程化细胞外囊泡的生产制备,如提升细胞外囊泡产量的工程化策略、细胞外囊泡的放大生产与提取纯化等;最后展望了合成生物学通过改造底盘细胞基因组、人工设计囊泡表面蛋白、调控分子包载的细胞过程等定制化合成细胞外囊泡的前景。合成生物学技术的发展与使用可推动工程化细胞外囊泡的定制化设计与合成,将进一步精细控制其属性、提升其效能、拓展其应用,争取将其早日广泛应用于人类健康事业。
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘夺, 刘培源, 李连月, 王雅欣, 崔钰惠, 薛慧敏, 王汉杰. 工程化细胞外囊泡的设计合成与生物医学应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 154-173.
LIU Duo, LIU Peiyuan, LI Lianyue, WANG Yaxin, CUI Yuhui, XUE Huimin, WANG Hanjie. Design and synthesis of engineered extracellular vesicles and their biomedical applications[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 154-173.
| 修饰分子 | 来源细胞 | 受体细胞 | 目标功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RVG肽 | HEK293T | 脑神经细胞 | 治疗阿尔兹海默病 | [ |
| Anti-CD3,Anti-EGFR | Expi293F | T细胞 | 杀伤乳腺癌细胞 | [ |
| LLO | 细菌 | DC细胞 | 实现抗原呈递 | [ |
| MERS-CoV的RBD | 细菌 | 免疫细胞 | 人工抗原 | [ |
| SPIKE的RBD | 细菌 | 免疫细胞 | 人工疫苗 | [ |
| 适配体AS1411 | 小鼠DC细胞 | 肿瘤细胞 | 杀伤癌细胞 | [ |
| c(RGDyK)肽 | MSC | 脑血管内皮细胞 | 治疗缺血脑损伤 | [ |
| 动物源配体 | 杂合膜融合 | 血管细胞 | 促血管生成 | [ |
| 动物源配体 | 杂合膜融合 | 巨噬细胞 | 杀伤癌细胞 | [ |
| c(RGDyK)肽 | MSC | 脑血管内皮细胞 | 治疗缺血脑损伤 | [ |
| α(FRα) | 动物细胞 | 脑实质 | 脑部递送 | [ |
| RVG肽 | 小鼠DC细胞 | 神经元细胞 | 治疗神经损伤 | [ |
| IMTP肽 | 骨髓MSC | 心肌组织 | 修复心肌 | [ |
| iRGD肽 | 动物细胞 | 肿瘤细胞 | 杀伤癌细胞 | [ |
| GE11肽 | HEK293T | 乳腺癌细胞 | 杀伤癌细胞 | [ |
| ICAM1 | DC细胞 | DC、T细胞 | 活化免疫功能 | [ |
| MFGE8 | 巨噬细胞 | 巨噬细胞 | 活化免疫功能 | [ |
| CIC2 | 纤维肉瘤细胞 | 抗原呈递细胞 | 活化免疫功能 | [ |
| CAR | CAR-T | 肿瘤细胞 | 杀伤癌细胞 | [ |
| PD-1 | T细胞 | 肿瘤细胞 | 阻断免疫逃逸 | [ |
| 异源抗原 | 细菌 | 免疫细胞 | 活化免疫功能 | [ |
表1 细胞外囊泡表面修饰的应用
Table 1 Applications of the surface modifications of extracellular vesicles
| 修饰分子 | 来源细胞 | 受体细胞 | 目标功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RVG肽 | HEK293T | 脑神经细胞 | 治疗阿尔兹海默病 | [ |
| Anti-CD3,Anti-EGFR | Expi293F | T细胞 | 杀伤乳腺癌细胞 | [ |
| LLO | 细菌 | DC细胞 | 实现抗原呈递 | [ |
| MERS-CoV的RBD | 细菌 | 免疫细胞 | 人工抗原 | [ |
| SPIKE的RBD | 细菌 | 免疫细胞 | 人工疫苗 | [ |
| 适配体AS1411 | 小鼠DC细胞 | 肿瘤细胞 | 杀伤癌细胞 | [ |
| c(RGDyK)肽 | MSC | 脑血管内皮细胞 | 治疗缺血脑损伤 | [ |
| 动物源配体 | 杂合膜融合 | 血管细胞 | 促血管生成 | [ |
| 动物源配体 | 杂合膜融合 | 巨噬细胞 | 杀伤癌细胞 | [ |
| c(RGDyK)肽 | MSC | 脑血管内皮细胞 | 治疗缺血脑损伤 | [ |
| α(FRα) | 动物细胞 | 脑实质 | 脑部递送 | [ |
| RVG肽 | 小鼠DC细胞 | 神经元细胞 | 治疗神经损伤 | [ |
| IMTP肽 | 骨髓MSC | 心肌组织 | 修复心肌 | [ |
| iRGD肽 | 动物细胞 | 肿瘤细胞 | 杀伤癌细胞 | [ |
| GE11肽 | HEK293T | 乳腺癌细胞 | 杀伤癌细胞 | [ |
| ICAM1 | DC细胞 | DC、T细胞 | 活化免疫功能 | [ |
| MFGE8 | 巨噬细胞 | 巨噬细胞 | 活化免疫功能 | [ |
| CIC2 | 纤维肉瘤细胞 | 抗原呈递细胞 | 活化免疫功能 | [ |
| CAR | CAR-T | 肿瘤细胞 | 杀伤癌细胞 | [ |
| PD-1 | T细胞 | 肿瘤细胞 | 阻断免疫逃逸 | [ |
| 异源抗原 | 细菌 | 免疫细胞 | 活化免疫功能 | [ |
| 1 | VAN NIEL G, D'ANGELO G, RAPOSO G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2018, 19(4): 213-228. |
| 2 | BROWN L, WOLF J M, PRADOS-ROSALES R, et al. Through the wall: extracellular vesicles in Gram-positive bacteria, mycobacteria and fungi[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2015, 13(10): 620-630. |
| 3 | LIAN M Q, CHNG W H, LIANG J, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: recent advancements and current challenges on their use for biomedical applications[J]. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 2022, 11(12): e12283. |
| 4 | KALLURI R, LEBLEU V S. The biology , function , and biomedical applications of exosomes[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6478): eaau6977. |
| 5 | DELCAYRE A, ESTELLES A, SPERINDE J, et al. Exosome display technology: applications to the development of new diagnostics and therapeutics[J]. Blood Cells, Molecules & Diseases, 2005, 35(2): 158-168. |
| 6 | CLARIDGE B, LOZANO J, POH Q H, et al. Development of extracellular vesicle therapeutics: challenges, considerations, and opportunities[J]. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 2021, 9: 734720. |
| 7 | KIM O Y, DINH N T H, PARK H T, et al. Bacterial protoplast-derived nanovesicles for tumor targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics[J]. Biomaterials, 2017, 113: 68-79. |
| 8 | LIU C, LIU X, XIANG X C, et al. A nanovaccine for antigen self-presentation and immunosuppression reversal as a personalized cancer immunotherapy strategy[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2022, 17: 531-540. |
| 9 | ALVES N J, TURNER K B, DANIELE M A, et al. Bacterial nanobioreactors—directing enzyme packaging into bacterial outer membrane vesicles[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(44): 24963-24972. |
| 10 | YOU D G, LIM G T, KWON S L, et al. Metabolically engineered stem cell-derived exosomes to regulate macrophage heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(23): eabe0083. |
| 11 | ZHANG P J, DONG B, ZENG E, et al. In vivo tracking of multiple tumor exosomes labeled by phospholipid-based bioorthogonal conjugation[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(19): 11273-11279. |
| 12 | TAKAYAMA Y, KUSAMORI K, NISHIKAWA M. Click chemistry as a tool for cell engineering and drug delivery[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(1): 172. |
| 13 | NIE W D, WU G H, ZHANG J F, et al. Responsive exosome nano-bioconjugates for synergistic cancer therapy[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(5): 2018-2022. |
| 14 | LI Q Y, SONG Y N, WANG Q Z, et al. Engineering extracellular vesicles with platelet membranes fusion enhanced targeted therapeutic angiogenesis in a mouse model of myocardial ischemia reperfusion[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(8): 3916-3931. |
| 15 | RAYAMAJHI S, NGUYEN T D T, MARASINI R, et al. Macrophage-derived exosome-mimetic hybrid vesicles for tumor targeted drug delivery[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2019, 94: 482-494. |
| 16 | WANG D D, LIU C H, YOU S Q, et al. Bacterial vesicle-cancer cell hybrid membrane-coated nanoparticles for tumor specific immune activation and photothermal therapy[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(37): 41138-41147. |
| 17 | GRAPP M, WREDE A, SCHWEIZER M, et al. Choroid plexus transcytosis and exosome shuttling deliver folate into brain parenchyma[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2123. |
| 18 | ALVAREZ-ERVITI L, SEOW Y Q, YIN H F, et al. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2011, 29: 341-345. |
| 19 | MENTKOWSKI K I, LANG J K. Exosomes engineered to express a cardiomyocyte binding peptide demonstrate improved cardiac retention in vivo [J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 10041. |
| 20 | SLACK R J, MACDONALD S J F, ROPER J A, et al. Emerging therapeutic opportunities for integrin inhibitors[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2022, 21: 60-78. |
| 21 | OHNO S I, TAKANASHI M, SUDO K, et al. Systemically injected exosomes targeted to EGFR deliver antitumor microRNA to breast cancer cells[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2013, 21(1): 185-191. |
| 22 | ZEELENBERG I S, OSTROWSKI M, KRUMEICH S, et al. Targeting tumor antigens to secreted membrane vesicles in vivo induces efficient antitumor immune responses[J]. Cancer Research, 2008, 68(4): 1228-1235. |
| 23 | KOJIMA R, BOJAR D, RIZZI G, et al. Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson's disease treatment[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1305. |
| 24 | CHENG Q Q, DAI Z F, SMBATYAN G, et al. Eliciting anti-cancer immunity by genetically engineered multifunctional exosomes[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2022, 30(9): 3066-3077. |
| 25 | GUJRATI V, KIM S H, KIM S H, et al. Bioengineered bacterial outer membrane vesicles as cell-specific drug-delivery vehicles for cancer therapy[J]. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(2): 1525-1537. |
| 26 | LI Y, MA X T, YUE Y L, et al. Rapid surface display of mRNA antigens by bacteria-derived outer membrane vesicles for a personalized tumor vaccine[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(20): e2109984. |
| 27 | VAN DEN BERG VAN SAPAROEA H B, HOUBEN D, KUIJL C, et al. Combining protein ligation systems to expand the functionality of semi-synthetic outer membrane vesicle nanoparticles[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 890. |
| 28 | SHEHATA M M, MOSTAFA A, TEUBNER L, et al. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles (OMVs)-based dual vaccine for influenza a H1N1 virus and MERS-CoV[J]. Vaccines, 2019, 7(2): 46. |
| 29 | CHENG K M, ZHAO R F, LI Y, et al. Bioengineered bacteria-derived outer membrane vesicles as a versatile antigen display platform for tumor vaccination via plug-and-display technology[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 2041. |
| 30 | YUE Y L, XU J Q, LI Y, et al. Antigen-bearing outer membrane vesicles as tumour vaccines produced in situ by ingested genetically engineered bacteria[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2022, 6(7): 898-909. |
| 31 | JIANG L L, DRIEDONKS T A P, JONG W S P, et al. A bacterial extracellular vesicle-based intranasal vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 protects against disease and elicits neutralizing antibodies to wild-type and Delta variants[J]. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 2022, 11(3): e12192. |
| 32 | WAN Y, WANG L X, ZHU C D, et al. Aptamer-conjugated extracellular nanovesicles for targeted drug delivery[J]. Cancer Research, 2018, 78(3): 798-808. |
| 33 | WAN S, ZHANG L Q, WANG S, et al. Molecular recognition-based DNA nanoassemblies on the surfaces of nanosized exosomes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(15): 5289-5292. |
| 34 | ANTES T J, MIDDLETON R C, LUTHER K M, et al. Targeting extracellular vesicles to injured tissue using membrane cloaking and surface display[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2018, 16(1): 61. |
| 35 | TIAN Y, ZHANG F, QIU Y F, et al. Reduction of choroidal neovascularization via cleavable VEGF antibodies conjugated to exosomes derived from regulatory T cells[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2021, 5: 968-982. |
| 36 | LIM G T, YOU D G, HAN H S, et al. Bioorthogonally surface-edited extracellular vesicles based on metabolic glycoengineering for CD44-mediated targeting of inflammatory diseases[J]. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 2021, 10(5): e12077. |
| 37 | ZHANG E, LIU Y W, HAN C S, et al. Visualization and identification of bioorthogonally labeled exosome proteins following systemic administration in mice[J]. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 2021, 9: 657456. |
| 38 | SMYTH T, PETROVA K, PAYTON N M, et al. Surface functionalization of exosomes using click chemistry[J]. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2014, 25(10): 1777-1784. |
| 39 | JAFARI D, SHAJARI S, JAFARI R, et al. Designer exosomes: a new platform for biotechnology therapeutics[J]. BioDrugs, 2020, 34(5): 567-586. |
| 40 | TIAN T, ZHANG H X, HE C P, et al. Surface functionalized exosomes as targeted drug delivery vehicles for cerebral ischemia therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2018, 150: 137-149. |
| 41 | JIANG Y, WANG L, ZHANG P J, et al. Chemoenzymatic labeling of extracellular vesicles for visualizing their cellular internalization in real time[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(2): 2103-2111. |
| 42 | WANG X, CHEN Y H, ZHAO Z A, et al. Engineered exosomes with ischemic myocardium-targeting peptide for targeted therapy in myocardial infarction[J]. Journal of the American Heart Association, 2018, 7(15): e008737. |
| 43 | SEGURA E, GUÉRIN C, HOGG N, et al. CD8+ dendritic cells use LFA-1 to capture MHC-peptide complexes from exosomes in vivo [J]. Journal of Immunology, 2007, 179(3): 1489-1496. |
| 44 | HANAYAMA R, TANAKA M, MIWA K, et al. Identification of a factor that links apoptotic cells to phagocytes[J]. Nature, 2002, 417(6885): 182-187. |
| 45 | HARTMAN Z C, WEI J P, GLASS O K, et al. Increasing vaccine potency through exosome antigen targeting[J]. Vaccine, 2011, 29(50): 9361-9367. |
| 46 | FU W Y, LEI C H, LIU S W, et al. CAR exosomes derived from effector CAR-T cells have potent antitumour effects and low toxicity[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 4355. |
| 47 | LI B Q, FANG T L, LI Y, et al. Engineered T cell extracellular vesicles displaying PD-1 boost anti-tumor immunity[J]. Nano Today, 2022, 46: 101606. |
| 48 | KAMERKAR S, LEBLEU V S, SUGIMOTO H, et al. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer[J]. Nature, 2017, 546: 498-503. |
| 49 | XIE J H, LI Q Q, HAESEBROUCK F, et al. The tremendous biomedical potential of bacterial extracellular vesicles[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40(10): 1173-1194. |
| 50 | IRENE C, FANTAPPIÈ L, CAPRONI E, et al. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles engineered with lipidated antigens as a platform for Staphylococcus aureus vaccine[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(43): 21780-21788. |
| 51 | ZANELLA I, KÖNIG E, TOMASI M, et al. Proteome-minimized outer membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli as a generalized vaccine platform[J]. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 2021, 10(4): e12066. |
| 52 | CHEN L X, VALENTINE J L, HUANG C J, et al. Outer membrane vesicles displaying engineered glycotopes elicit protective antibodies[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(26): E3609-E3618. |
| 53 | WANG Q Y, YU J J, KADUNGURE T, et al. ARMMs as a versatile platform for intracellular delivery of macromolecules[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 960. |
| 54 | ZHANG S Y, DONG Y, WANG Y X, et al. Selective encapsulation of therapeutic mRNA in engineered extracellular vesicles by DNA aptamer[J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(20): 8563-8570. |
| 55 | YIM N B, RYU S W, CHOI K S, et al. Exosome engineering for efficient intracellular delivery of soluble proteins using optically reversible protein-protein interaction module[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 12277. |
| 56 | CHOI H J, KIM Y E, MIRZAAGHASI A, et al. Exosome-based delivery of super-repressor IκBα relieves sepsis-associated organ damage and mortality[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(15): eaaz6980. |
| 57 | LUAN X, SANSANAPHONGPRICHA K, MYERS I, et al. Engineering exosomes as refined biological nanoplatforms for drug delivery[J]. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 2017, 38(6): 754-763. |
| 58 | KIM H J, KIM D J, NAM H S, et al. Engineered extracellular vesicles and their mimetics for clinical translation[J]. Methods, 2020, 177: 80-94. |
| 59 | OSHCHEPKOVA A, ZENKOVA M, VLASSOV V. Extracellular vesicles for therapeutic nucleic acid delivery: loading strategies and challenges[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(8): 7287. |
| 60 | YANG Z G, SHI J F, XIE J, et al. Large-scale generation of functional mRNA-encapsulating exosomes via cellular nanoporation[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 4: 69-83. |
| 61 | ZHU Q W, LING X Z, YANG Y L, et al. Embryonic stem cells-derived exosomes endowed with targeting properties as chemotherapeutics delivery vehicles for glioblastoma therapy[J]. Advanced Science, 2019, 6(6): 1801899. |
| 62 | KIM M S, HANEY M J, ZHAO Y L, et al. Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome MDR in cancer cells[J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine, 2016, 12(3): 655-664. |
| 63 | KIM M S, HANEY M J, ZHAO Y L, et al. Engineering macrophage-derived exosomes for targeted paclitaxel delivery to pulmonary metastases: in vitro and in vivo evaluations[J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine, 2018, 14(1): 195-204. |
| 64 | AGRAWAL A K, AQIL F, JEYABALAN J, et al. Milk-derived exosomes for oral delivery of paclitaxel[J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine, 2017, 13(5): 1627-1636. |
| 65 | ZHANG J H, JI C, ZHANG H B, et al. Engineered neutrophil-derived exosome-like vesicles for targeted cancer therapy[J]. Science Advances, 2022, 8(2): eabj8207. |
| 66 | WANG J, TANG W, YANG M, et al. Inflammatory tumor microenvironment responsive neutrophil exosomes-based drug delivery system for targeted glioma therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 273: 120784. |
| 67 | WANG J, CHEN P, DONG Y, et al. Designer exosomes enabling tumor targeted efficient chemo/gene/photothermal therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 276: 121056. |
| 68 | SINGLA D K, JOHNSON T A, DARGANI Z T. Exosome treatment enhances anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages and reduces inflammation-induced pyroptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(10): 1224. |
| 69 | DARGANI Z T, SINGLA D K. Embryonic stem cell-derived exosomes inhibit doxorubicin-induced TLR4-NLRP3-mediated cell death-pyroptosis[J]. American Journal of Physiology Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 2019, 317(2): H460-H471. |
| 70 | ZHANG C, SONG J, LOU L, et al. Doxorubicin-loaded nanoparticle coated with endothelial cells-derived exosomes for immunogenic chemotherapy of glioblastoma[J]. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine, 2020, 6(3): e10203. |
| 71 | WEI H X, CHEN J Y, WANG S L, et al. A nanodrug consisting of doxorubicin and exosome derived from mesenchymal stem cells for osteosarcoma treatment in vitro [J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2019, 14: 8603-8610. |
| 72 | TIAN Y H, LI S P, SONG J, et al. A doxorubicin delivery platform using engineered natural membrane vesicle exosomes for targeted tumor therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(7): 2383-2390. |
| 73 | WANG Q L, ZHUANG X Y, MU J Y, et al. Delivery of therapeutic agents by nanoparticles made of grapefruit-derived lipids[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 1867. |
| 74 | ZHANG M Z, XIAO Bo, WANG H, et al. Edible ginger-derived nano-lipids loaded with doxorubicin as a novel drug-delivery approach for colon cancer therapy[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2016, 24(10): 1783-1796. |
| 75 | POPOWSKI K D, MOATTI A, SCULL G, et al. Inhalable dry powder mRNA vaccines based on extracellular vesicles[J]. Matter, 2022, 5(9): 2960-2974. |
| 76 | YOU Y, TIAN Y, YANG Z G, et al. Intradermally delivered mRNA-encapsulating extracellular vesicles for collagen-replacement therapy[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2023, 7: 887-900. |
| 77 | JANG S C, ECONOMIDES K D, MONIZ R J, et al. ExoSTING, an extracellular vesicle loaded with STING agonists, promotes tumor immune surveillance[J]. Communications Biology, 2021, 4: 497. |
| 78 | O'BRIEN K, BREYNE K, UGHETTO S, et al. RNA delivery by extracellular vesicles in mammalian cells and its applications[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2020, 21: 585-606. |
| 79 | USMAN W M, PHAM T C, KWOK Y Y, et al. Efficient RNA drug delivery using red blood cell extracellular vesicles[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 2359. |
| 80 | POMATTO M A C, BUSSOLATI B, D'ANTICO S, et al. Improved loading of plasma-derived extracellular vesicles to encapsulate antitumor miRNAs[J]. Molecular Therapy-Methods & Clinical Development, 2019, 13: 133-144. |
| 81 | SHTAM T A, KOVALEV R A, VARFOLOMEEVA E Y, et al. Exosomes are natural carriers of exogenous siRNA to human cells in vitro [J]. Cell Communication and Signaling, 2013, 11: 88. |
| 82 | BHASKARAN V, NOWICKI M O, IDRISS M, et al. The functional synergism of microRNA clustering provides therapeutically relevant epigenetic interference in glioblastoma[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 442. |
| 83 | ZHUANG X Y, TENG Y, SAMYKUTTY A, et al. Grapefruit-derived nanovectors delivering therapeutic miR17 through an intranasal route inhibit brain tumor progression[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2016, 24(1): 96-105. |
| 84 | TENG Y, MU J Y, HU X, et al. Grapefruit-derived nanovectors deliver miR-18a for treatment of liver metastasis of colon cancer by induction of M1 macrophages[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(18): 25683-25697. |
| 85 | WANG J, CAO Z Y, WANG P P, et al. Apoptotic extracellular vesicles ameliorate multiple myeloma by restoring fas-mediated apoptosis[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(9): 14360-14372. |
| 86 | YUAN Z Q, KOLLURI K K, GOWERS K H C, et al. TRAIL delivery by MSC-derived extracellular vesicles is an effective anticancer therapy[J]. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 2017, 6(1): 1265291. |
| 87 | DAI S M, ZHOU X Y, WANG B M, et al. Enhanced induction of dendritic cell maturation and HLA-A*0201-restricted CEA-specific CD8+ CTL response by exosomes derived from IL-18 gene-modified CEA-positive tumor cells[J]. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2006, 84(12): 1067-1076. |
| 88 | YANG Y S, XIU F M, CAI Z J, et al. Increased induction of antitumor response by exosomes derived from interleukin-2 gene-modified tumor cells[J]. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 2007, 133(6): 389-399. |
| 89 | CHENG Q Q, DAI Z F, SHI X J, et al. Expanding the toolbox of exosome-based modulators of cell functions[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 277: 121129. |
| 90 | HANEY M J, KLYACHKO N L, ZHAO Y L, et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson's disease therapy[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2015, 207: 18-30. |
| 91 | HANEY M J, KLYACHKO N L, HARRISON E B, et al. TPP1 delivery to lysosomes with extracellular vesicles and their enhanced brain distribution in the animal model of batten disease[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2019, 8(11): e1801271. |
| 92 | KIM S M, YANG Y S, OH J, et al. Cancer-derived exosomes as a delivery platform of CRISPR/Cas9 confer cancer cell tropism-dependent targeting[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2017, 266: 8-16. |
| 93 | LUO L, WU Z, WANG Y, et al. Regulating the production and biological function of small extracellular vesicles: current strategies, applications and prospects[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2021, 19(1): 422. |
| 94 | ZHAO K N, BLEACKLEY M, CHISANGA D, et al. Extracellular vesicles secreted by Saccharomyces cerevisiae are involved in cell wall remodelling[J]. Communications Biology, 2019, 2: 305. |
| 95 | DATTA A, KIM H Y, MCGEE L, et al. High-throughput screening identified selective inhibitors of exosome biogenesis and secretion: a drug repurposing strategy for advanced cancer[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 8161. |
| 96 | WANG J L, BONACQUISTI E E, BROWN A D, et al. Boosting the biogenesis and secretion of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(3): 660. |
| 97 | NAKAMURA Y, KITA S, TANAKA Y, et al. Adiponectin stimulates exosome release to enhance mesenchymal stem-cell-driven therapy of heart failure in mice[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2020, 28(10): 2203-2219. |
| 98 | RUAN X F, JU C W, SHEN Y, et al. Suxiao Jiuxin pill promotes exosome secretion from mouse cardiac mesenchymal stem cells in vitro [J]. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 2018, 39(4): 569-578. |
| 99 | ORTEGA F G, ROEFS M T, DE MIGUEL PEREZ D, et al. Interfering with endolysosomal trafficking enhances release of bioactive exosomes[J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine, 2019, 20: 102014. |
| 100 | INGATO D, EDSON J A, ZAKHARIAN M, et al. Cancer cell-derived, drug-loaded nanovesicles induced by sulfhydryl-blocking for effective and safe cancer therapy[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(9): 9568-9577. |
| 101 | HANNAFON B N, CARPENTER K J, BERRY W L, et al. Exosome-mediated microRNA signaling from breast cancer cells is altered by the anti-angiogenesis agent docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)[J]. Molecular Cancer, 2015, 14: 133. |
| 102 | JACKSON E K, CHENG D M, MI Z C, et al. Guanosine regulates adenosine levels in the kidney[J]. Physiological Reports, 2014, 2(5): e12028. |
| 103 | GARCIA N A, ONTORIA-OVIEDO I, GONZÁLEZ-KING H, et al. Glucose starvation in cardiomyocytes enhances exosome secretion and promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(9): e0138849. |
| 104 | LOGOZZI M, MIZZONI D, ANGELINI D F, et al. Microenvironmental pH and exosome levels interplay in human cancer cell lines of different histotypes[J]. Cancers, 2018, 10(10): 370. |
| 105 | BAN J J, LEE M J, IM W S, et al. Low pH increases the yield of exosome isolation[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2015, 461(1): 76-79. |
| 106 | SIMKO V, IULIANO F, SEVCIKOVA A, et al. Hypoxia induces cancer-associated cAMP/PKA signalling through HIF-mediated transcriptional control of adenylyl cyclases Ⅵ and Ⅶ[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 10121. |
| 107 | HEDLUND M, NAGAEVA O, KARGL D, et al. Thermal- and oxidative stress causes enhanced release of NKG2D ligand-bearing immunosuppressive exosomes in leukemia/lymphoma T and B cells[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(2): e16899. |
| 108 | HASAN M, HAMA S, KOGURE K. Low electric treatment activates rho GTPase via heat shock protein 90 and protein kinase C for intracellular delivery of siRNA[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 4114. |
| 109 | FUKUTA T, NISHIKAWA A, KOGURE K. Low level electricity increases the secretion of extracellular vesicles from cultured cells[J]. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 2020, 21: 100713. |
| 110 | MCANDREWS K M, KALLURI R. Mechanisms associated with biogenesis of exosomes in cancer[J]. Molecular Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 52. |
| 111 | WHITFORD W, GUTERSTAM P. Exosome manufacturing status[J]. Future Medicinal Chemistry, 2019, 11(10): 1225-1236. |
| 112 | MAYELA M, KAMERKAR S, SUGIMOTO H, et al. Generation and testing of clinical-grade exosomes for pancreatic cancer[J]. JCI Insight, 2018, 3(8): e99263. |
| 113 | REINER A T, WITWER K W, VAN BALKOM B W M, et al. Concise review: developing best-practice models for the therapeutic use of extracellular vesicles[J]. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 2017, 6(8): 1730-1739. |
| 114 | NIKFARJAM S, REZAIE J, ZOLBANIN N M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell derived-exosomes: a modern approach in translational medicine[J]. Journal of Translational Medicine, 2020, 18(1): 449. |
| 115 | ANDRIOLO G, PROVASI E, CICERO V LO, et al. Exosomes from human cardiac progenitor cells for therapeutic applications: development of a GMP-grade manufacturing method[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2018, 9: 1169. |
| 116 | KOMOR A C, KIM Y B, PACKER M S, et al. Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage[J]. Nature, 2016, 533(7603): 420-424. |
| 117 | MA Y Q, ZHANG J Y, YIN W J, et al. Targeted AID-mediated mutagenesis (TAM) enables efficient genomic diversification in mammalian cells[J]. Nature Methods, 2016, 13(12): 1029-1035. |
| 118 | NISHIDA K, ARAZOE T, YACHIE N, et al. Targeted nucleotide editing using hybrid prokaryotic and vertebrate adaptive immune systems[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6305): aaf8729. |
| 119 | ZHAO D D, LI J, LI S W, et al. Glycosylase base editors enable C-to-A and C-to-G base changes[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39: 35-40. |
| 120 | ANZALONE A V, RANDOLPH P B, DAVIS J R, et al. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA[J]. Nature, 2019, 576(7785): 149-157. |
| 121 | ABUDAYYEH O O, GOOTENBERG J S, KONERMANN S, et al. C2C2 is a single-component programmable RNA-guided RNA-targeting CRISPR effector[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6299): aaf5573. |
| 122 | CAMPA C C, WEISBACH N R, SANTINHA A J, et al. Multiplexed genome engineering by Cas12a and CRISPR arrays encoded on single transcripts[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(9): 887-893. |
| 123 | ZHANG Y P, WANG J, WANG Z B, et al. A gRNA-tRNA array for CRISPR-Cas9 based rapid multiplexed genome editing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1053. |
| 124 | GIBSON D G, GLASS J I, LARTIGUE C, et al. Creation of a bacterial cell controlled by a chemically synthesized genome[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5987): 52-56. |
| 125 | FREDENS J, WANG K H, DE LA TORRE D, et al. Total synthesis of Escherichia coli with a recoded genome[J]. Nature, 2019, 569(7757): 514-518. |
| 126 | XIE Z X, LIU D, LI B Z, et al. Design and chemical synthesis of eukaryotic chromosomes[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(23): 7191-7207. |
| 127 | WANG J, XIE Z X, MA Y, et al. Ring synthetic chromosome Ⅴ SCRaMbLE[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3783. |
| 128 | JIA B, WU Y, LI B Z, et al. Precise control of SCRaMbLE in synthetic haploid and diploid yeast[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1933. |
| 129 | ZHOU S J, WU Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Dynamics of synthetic yeast chromosome evolution shaped by hierarchical chromatin organization[J]. National Science Review, 2023, 10(5): nwad073. |
| 130 | ZHENG D W, CHEN Y, LI Z H, et al. Optically-controlled bacterial metabolite for cancer therapy[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1680. |
| 131 | ZHOU J, LI M Y, CHEN Q F, et al. Programmable probiotics modulate inflammation and gut microbiota for inflammatory bowel disease treatment after effective oral delivery[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 3432. |
| 132 | CAO Z P, WANG X Y, PANG Y, et al. Biointerfacial self-assembly generates lipid membrane coated bacteria for enhanced oral delivery and treatment[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 5783. |
| 133 | CUI M H, SUN T, LI S B, et al. NIR light-responsive bacteria with live bio-glue coatings for precise colonization in the gut[J]. Cell Reports, 2021, 36(11): 109690. |
| 134 | PAN H Z, SUN T, CUI M H, et al. Light-sensitive Lactococcus lactis for microbe-gut-brain axis regulating via upconversion optogenetic micro-nano system[J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(4): 6049-6063. |
| 135 | CUI M H, LING W, ZHANG L L, et al. Smartphone bioelectronic drug with visual colorimetric sensor and bulk nanoencapsulation optogenetic bacteria for chronic kidney disease theragnostics[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 451: 138812. |
| 136 | ZHANG X Y, MA N, LING W, et al. A micro-nano optogenetic system based on probiotics for in situ host metabolism regulation[J]. Nano Research, 2023, 16(2): 2829-2839. |
| 137 | WEISKOPF K, RING A M, HO C C M, et al. Engineered SIRPα variants as immunotherapeutic adjuvants to anticancer antibodies[J]. Science, 2013, 341(6141): 88-91. |
| 138 | MAURER M F, LEWIS K E, KUIJPER J L, et al. The engineered CD80 variant fusion therapeutic davoceticept combines checkpoint antagonism with conditional CD28 costimulation for anti-tumor immunity[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 1790. |
| 139 | GAINZA P, WEHRLE S, VAN HALL-BEAUVAIS A, et al. De novo design of protein interactions with learned surface fingerprints[J]. Nature, 2023, 617(7959): 176-184. |
| 140 | DANIEL-ADRIANO S, CORREIA B E, PROCKO E. Motif-driven design of protein-protein interfaces[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2016, 1414: 285-304. |
| 141 | CHEN Y X, CHEN Q, LIU H Y. DEPACT and PACMatch: a workflow of designing de novo protein pockets to bind small molecules[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2022, 62(4): 971-985. |
| 142 | CHEN R, WANG S K, BELK J A, et al. Engineering circular RNA for enhanced protein production[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2023, 41: 262-272. |
| 143 | GERSTBERGER S, HAFNER M, ASCANO M, et al. Evolutionary conservation and expression of human RNA-binding proteins and their role in human genetic disease[J]. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 2014, 825: 1-55. |
| 144 | SORK H, CORSO G, KRJUTSKOV K, et al. Heterogeneity and interplay of the extracellular vesicle small RNA transcriptome and proteome[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 10813. |
| 145 | WU T, YE L J, ZHAO D D, et al. Membrane engineering - a novel strategy to enhance the production and accumulation of β-carotene in Escherichia coli [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 43: 85-91. |
| 146 | CHEN Y, XIAO W H, WANG Y, et al. Lycopene overproduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through combining pathway engineering with host engineering[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15(1): 113. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 董颖, 马孟丹, 黄卫人. CRISPR-Cas系统的小型化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 105-117. |
| [3] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [11] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [12] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [13] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [14] | 胡可儿, 王汉奇, 黄儒麒, 张灿阳, 邢新会, 马少华. 整合设计策略下的工程化类器官与类器官芯片技术[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 883-897. |
| [15] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||