合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (1): 16-37.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-067
合成生物学表型测试生物反应器及其装备化研究进展
郭肖杰1,2, 剪兴金1,2, 王立言3, 张翀1,2,4, 邢新会1,2,4,5
- 1.清华大学化学工程系,生物化工研究所,北京 100084
2.工业生物催化教育部重点实验室,北京 100084
3.清华大学无锡应用技术研究院生物育种中心,无锡 214000
4.清华大学合成与系统生物学中心,北京 100084
5.清华大学深圳国际研究生院生物医药与健康工程研究院,深圳 518055
-
收稿日期:2023-09-19修回日期:2023-11-02出版日期:2024-02-29发布日期:2024-03-20 -
通讯作者:邢新会 -
作者简介:郭肖杰 (1990—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为液滴微流控及其在微生物领域的装备化应用。 E-mail:gxj20@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn邢新会 (1965—),男,教授。研究方向为生物化工、生物育种技术及装备等。 E-mail:xhxing@tsinghua.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0901500);国家自然科学基金重大仪器专项(21627812);深圳市可持续发展专项(KCXFZ20201221173207022)
Progress in bioreactors and instruments for phenotype testing with synthetic biology research
GUO Xiaojie1,2, JIAN Xingjin1,2, WANG Liyan3, ZHANG Chong1,2,4, XING Xinhui1,2,4,5
- 1.Institute of Biochemical Engineering,Department of Chemical Engineering,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
2.Key Laboratory for Industrial Biocatalysis of the Ministry of Education,Beijing 100084,China
3.Biobreeding Center,Wuxi Research Institute of Applied Technologies,Tsinghua University,Wuxi 214072,Jiangsu,China
4.Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
5.Institute of Biopharmaceutical and Health Engineering,Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2023-09-19Revised:2023-11-02Online:2024-02-29Published:2024-03-20 -
Contact:XING Xinhui
摘要:
合成生物学经过多年的发展,形成了典型的细胞工厂创制“设计-构建-测试-学习”(design-build-test-learn, DBTL)循环,成为支撑面向加速生物制造发展的智慧生物育种的重要方法。其中,测试环节是对前期所设计与构建的生物体系进行表型测试,以提供大量数据用于后续的学习和迭代升级。测试阶段的通量主要依赖于细胞自身或其培养测试所使用的生物反应器及其装备,是整个DBTL流程的限速步骤。本文系统综述了合成生物学表型测试所开发的面向不同通量的生物反应器及装备,从单细胞检测和筛选及不同尺度生物反应器包括皮纳升级生物反应器、微升级生物反应器、毫升级生物反应器和升级生物反应器等,系统地介绍了各自的特点和应用场景。同时,指出了现有生物反应器及其装备的应用潜力、面临的挑战与发展趋势,为合成生物学表型测试技术研究提供重要参考。
中图分类号:
引用本文
郭肖杰, 剪兴金, 王立言, 张翀, 邢新会. 合成生物学表型测试生物反应器及其装备化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 16-37.
GUO Xiaojie, JIAN Xingjin, WANG Liyan, ZHANG Chong, XING Xinhui. Progress in bioreactors and instruments for phenotype testing with synthetic biology research[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 16-37.
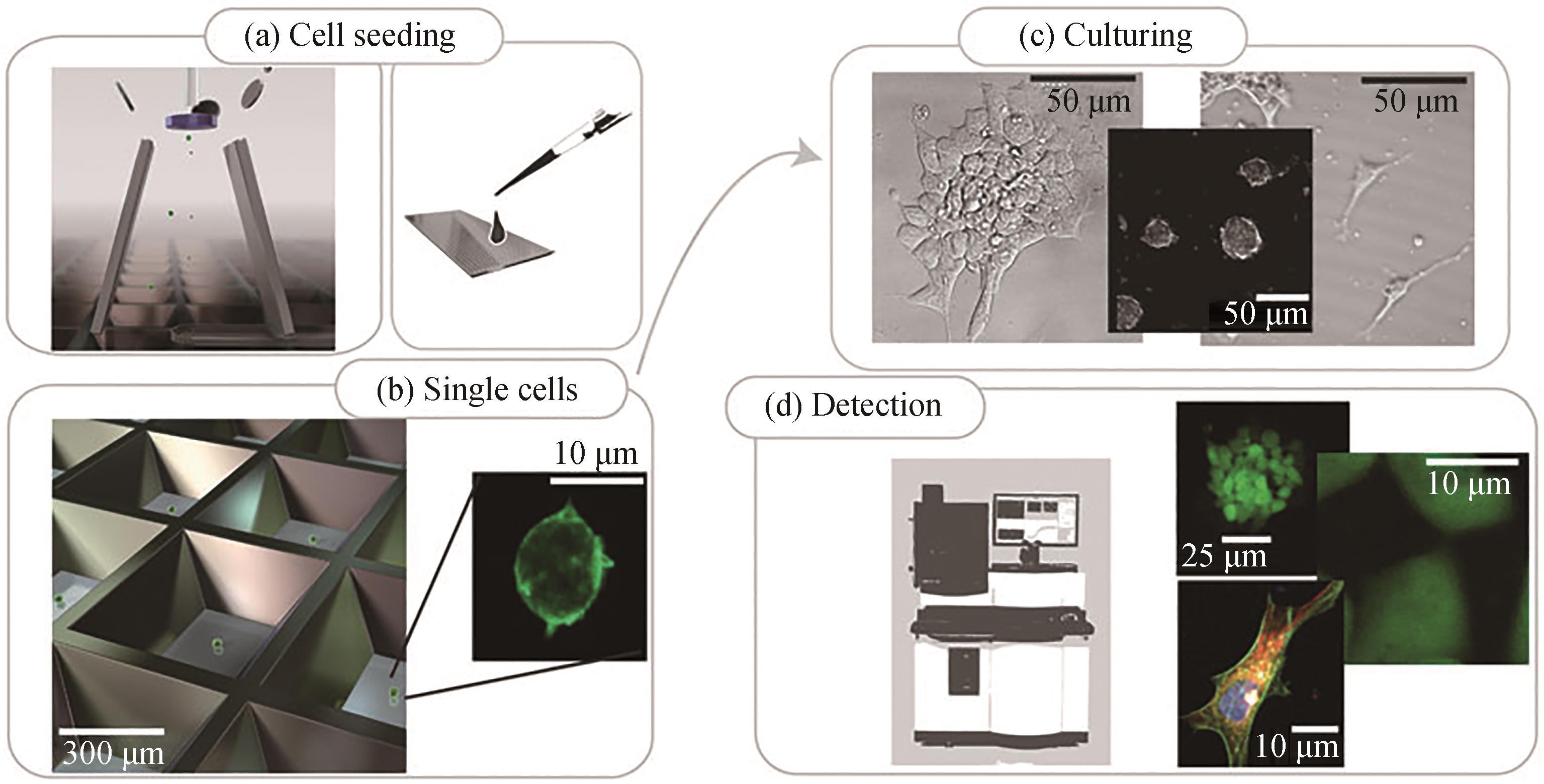
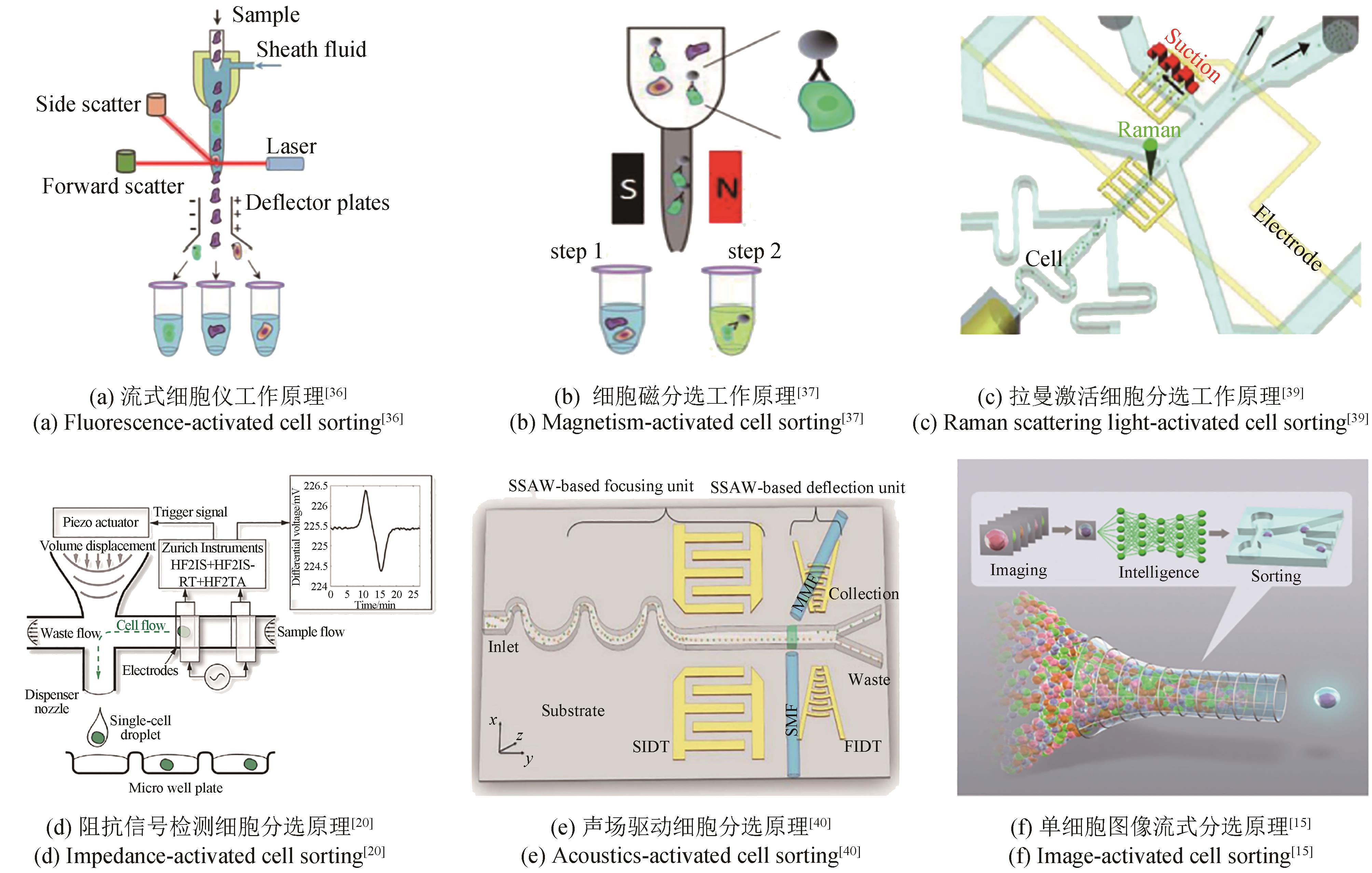
图2 基于微孔阵列的单细胞分选策略[48](a)和(b)单细胞接种(c)细胞在微孔板中培养(d)细胞检测
Fig. 2 Workflow for single cell screening based with microwells[48](a) and (b) single cell seeding, (c) cell culturing in microwells, (d) cell detection using automated imaging system
| 类型 | 典型装备 | 特点 | 主要不足 | 相关重要文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单细胞 | 细胞自体 | FACS、RACS、Namo cell、Single-cell printer | 通量高,装备成熟且种类多 | 无法对细胞进行培养,细胞裂解物或外泌物无法作为检测指标 | Sun et al.[ Gross et al.[ Zhang et al.[ |
| 皮纳 升级 | 微孔阵列 | 单细胞光导系统 | 通量高,装备类型多,可检测细胞裂解物和外泌物 | 芯片工艺复杂,操作烦琐 | Lindstrom et al.[ Weibel et al.[ |
| 微液滴 | FADS、RADS、IADS | 存在液滴融合、内容物泄漏等风险 | Jiang et al.[ Sanchez er al.[ Fu et al.[ | ||
| 微升级 | 微液滴 | MMC、MISS cell、Millidrop | 细胞培养性能好,相关装备自动化和微型化 | 液滴稳定性易受影响,脂溶性物质易逃逸出液滴 | Baraban et al.[ Jian et al.[ Jakiela et al.[ |
| 96孔板 | 酶标仪、Bioscreen生长曲线测定仪 | 使用方便,适用性广 | 蒸发问题、边缘效应、孔距离小易交叉污染、溶氧受限 | Mansoury et al.[ Duetz et al.[ | |
| 毫升级 | 深孔板 | Biolector、酶标仪 | 使用方便,适用性广 | 孔间距较小易交叉污染 | Klockner et al.[ Betts et al.[ Running et al.[ |
| 试管、摇瓶 | Micro-24 bioreactor | 相关自动化装备缺乏 | |||
搅拌釜 生物反应器 | Ambr@15 | 使用范围广,过程参数易精确控制,利于后期放大 | 操作烦琐 | Karimi et al.[ 丁宁,等[ Warr et al.[ | |
| 微型管式 生物反应器 | EVOL cell | 无气泡渗透供氧,内部流体剪切力低,易集成装备化开发 | 黏度大或含有颗粒的培养基以及易形成生物膜的菌株不适用 | Yang et al.[ Li et al.[ Jian et al.[ | |
| 升级 | 搅拌釜 生物反应器 | 多联罐、平行反应器以及其配套线检测装备(如BODS) | 使用范围广,过程参数易精确控制,利于后期工艺放大 | 体积增大、搅拌釜反应器内部的物质混合和传递难度增加 | Garcia-ochoa et al.[ Marques et al.[ Betts et al.[ |
表1 不同用途细胞工厂表型测试装备特点总结
Table 1 Characteristics of different instruments for the phenotype testing of cell factories
| 类型 | 典型装备 | 特点 | 主要不足 | 相关重要文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单细胞 | 细胞自体 | FACS、RACS、Namo cell、Single-cell printer | 通量高,装备成熟且种类多 | 无法对细胞进行培养,细胞裂解物或外泌物无法作为检测指标 | Sun et al.[ Gross et al.[ Zhang et al.[ |
| 皮纳 升级 | 微孔阵列 | 单细胞光导系统 | 通量高,装备类型多,可检测细胞裂解物和外泌物 | 芯片工艺复杂,操作烦琐 | Lindstrom et al.[ Weibel et al.[ |
| 微液滴 | FADS、RADS、IADS | 存在液滴融合、内容物泄漏等风险 | Jiang et al.[ Sanchez er al.[ Fu et al.[ | ||
| 微升级 | 微液滴 | MMC、MISS cell、Millidrop | 细胞培养性能好,相关装备自动化和微型化 | 液滴稳定性易受影响,脂溶性物质易逃逸出液滴 | Baraban et al.[ Jian et al.[ Jakiela et al.[ |
| 96孔板 | 酶标仪、Bioscreen生长曲线测定仪 | 使用方便,适用性广 | 蒸发问题、边缘效应、孔距离小易交叉污染、溶氧受限 | Mansoury et al.[ Duetz et al.[ | |
| 毫升级 | 深孔板 | Biolector、酶标仪 | 使用方便,适用性广 | 孔间距较小易交叉污染 | Klockner et al.[ Betts et al.[ Running et al.[ |
| 试管、摇瓶 | Micro-24 bioreactor | 相关自动化装备缺乏 | |||
搅拌釜 生物反应器 | Ambr@15 | 使用范围广,过程参数易精确控制,利于后期放大 | 操作烦琐 | Karimi et al.[ 丁宁,等[ Warr et al.[ | |
| 微型管式 生物反应器 | EVOL cell | 无气泡渗透供氧,内部流体剪切力低,易集成装备化开发 | 黏度大或含有颗粒的培养基以及易形成生物膜的菌株不适用 | Yang et al.[ Li et al.[ Jian et al.[ | |
| 升级 | 搅拌釜 生物反应器 | 多联罐、平行反应器以及其配套线检测装备(如BODS) | 使用范围广,过程参数易精确控制,利于后期工艺放大 | 体积增大、搅拌釜反应器内部的物质混合和传递难度增加 | Garcia-ochoa et al.[ Marques et al.[ Betts et al.[ |
| 1 | CAMERON D E, BASHOR C J, COLLINS J J. A brief history of synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2014, 12(5): 381-390. |
| 2 | 史硕博, 张翀, 成喜雨, 等. 挑战造物主:合成生物学使能工具[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 1-4. |
| SHI S B, ZHANG C, CHENG X Y, et al. Challenging the creator: an enabling tool for synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 1-4. | |
| 3 | LAWSON C E, HARCOMBE W R, HATZENPICHLER R, et al. Common principles and best practices for engineering microbiomes[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2019, 17(12): 725-741. |
| 4 | GURDO N, VOLKE D C, MCCLOSKEY D, et al. Automating the design-build-test-learn cycle towards next-generation bacterial cell factories[J]. New Biotechnology, 2023, 74: 1-15. |
| 5 | 孙梦楚, 陆亮宇, 申晓林, 等. 基于荧光检测的高通量筛选技术和装备助力细胞工厂构建[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 947-965. |
| SUN M C, LU L Y, SHEN X L, et al. Fluorescence detection-based high-throughput screening systems and devices facilitate cell factories construction[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 947-965. | |
| 6 | SANDLE T. History and development of microbiological culture media[J/OL]. The Journal (Instituteof Science and Technology), 2011: 10-14[2023-09-01]. . |
| 7 | MCKINNON K M. Flow cytometry: an overview[J]. Current Protocols in Immunology, 2018, 120(1): 5.1.1-5.1.11. |
| 8 | JAKOBSSON O, GRENVALL C, NORDIN M, et al. Acoustic actuated fluorescence activated sorting of microparticles[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2014, 14(11): 1943-1950. |
| 9 | KINNUNEN M, KARMENYAN A. Overview of single-cell elastic light scattering techniques[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2015, 20(5): 051040. |
| 10 | SU X T, SINGH K, ROZMUS W, et al. Light scattering characterization of mitochondrial aggregation in single cells[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(16): 13381-13388. |
| 11 | HUANG W E, WARD A D, WHITELEY A S. Raman tweezers sorting of single microbial cells[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2009, 1(1): 44-49. |
| 12 | MCILVENNA D, HUANG W E, DAVISON P, et al. Continuous cell sorting in a flow based on single cell resonance Raman spectra[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16(8): 1420-1429. |
| 13 | SONG Y Z, KASTER A K, VOLLMERS J, et al. Single-cell genomics based on Raman sorting reveals novel carotenoid-containing bacteria in the Red Sea[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2017, 10(1): 125-137. |
| 14 | GROSS A, SCHÖNDUBE J, NIEKRAWITZ S, et al. Single-cell printer: automated, on demand, and label free[J]. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 2013, 18(6): 504-518. |
| 15 | NITTA N, SUGIMURA T, ISOZAKI A, et al. Intelligent image-activated cell sorting[J]. Cell, 2018, 175(1): 266-276.e13. |
| 16 | KOVAC J R, VOLDMAN J. Intuitive, image-based cell sorting using optofluidic cell sorting[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2007, 79(24): 9321-9330. |
| 17 | KIM U, SOH H T. Simultaneous sorting of multiple bacterial targets using integrated dielectrophoretic-magnetic activated cell sorter[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9(16): 2313-2318. |
| 18 | ADAMS J D, KIM U, SOH H T. Multitarget magnetic activated cell sorter[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(47): 18165-18170. |
| 19 | SEMPLE J W, ALLEN D, CHANG W, et al. Rapid separation of CD4+ and CD19+ lymphocyte populations from human peripheral blood by a magnetic activated cell sorter (MACS)[J]. Cytometry, 1993, 14(8): 955-960. |
| 20 | FAENZA A, BOCCHI M, PECORARI N, et al. Impedance measurement technique for high-sensitivity cell detection in microstructures with non-uniform conductivity distribution[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2012, 12(11): 2046-2052. |
| 21 | SCHOENDUBE J, WRIGHT D, ZENGERLE R, et al. Single-cell printing based on impedance detection[J]. Biomicrofluidics, 2015, 9(1): 014117. |
| 22 | TANG D Z, JIANG L, TANG W L, et al. Cost-effective portable microfluidic impedance cytometer for broadband impedance cell analysis based on viscoelastic focusing[J]. Talanta, 2022, 242: 123274. |
| 23 | PRASHER D C. Using GFP to see the light[J]. Trends in Genetics, 1995, 11(8): 320-323. |
| 24 | POLLOK B A, HEIM R. Using GFP in FRET-based applications[J]. Trends in Cell Biology, 1999, 9(2): 57-60. |
| 25 | TAJIK M, BAHARFAR M, DONALD W A. Single-cell mass spectrometry[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40(11): 1374-1392. |
| 26 | SLAVOV N. Single-cell protein analysis by mass spectrometry[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2021, 60: 1-9. |
| 27 | SPITZER M H, NOLAN G P. Mass cytometry: single cells, many features[J]. Cell, 2016, 165(4): 780-791. |
| 28 | DE WAGENAAR B, DEKKER S, DE BOER H L, et al. Towards microfluidic sperm refinement: impedance-based analysis and sorting of sperm cells[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16(8): 1514-1522. |
| 29 | ZBOROWSKI M, CHALMERS J J. Magnetic cell sorting[M/OL]//Immunochemical protocols. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 2005: 291-300 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 30 | GROVER S C, SKIRTACH A G, GAUTHIER R C, et al. Automated single-cell sorting system based on optical trapping[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2001, 6(1): 14-22. |
| 31 | WANG M M, TU E, RAYMOND D E, et al. Microfluidic sorting of mammalian cells by optical force switching[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2005, 23(1): 83-87. |
| 32 | JOHANSSON L, NIKOLAJEFF F, JOHANSSON S, et al. On-chip fluorescence-activated cell sorting by an integrated miniaturized ultrasonic transducer[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 81(13): 5188-5196. |
| 33 | NITTA N, IINO T, ISOZAKI A, et al. Raman image-activated cell sorting[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 3452. |
| 34 | CHEN P, FENG X J, HU R, et al. Hydrodynamic gating valve for microfluidic fluorescence-activated cell sorting[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2010, 663(1): 1-6. |
| 35 | JIAN X J, GUO X J, CAI Z S, et al. Single-cell microliter-droplet screening system (MISS Cell): an integrated platform for automated high-throughput microbial monoclonal cultivation and picking[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2023, 120(3): 778-792. |
| 36 | GROSS A, SCHOENDUBE J, ZIMMERMANN S, et al. Technologies for single-cell isolation[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2015, 16(8): 16897-16919. |
| 47 | WELZEL G, SEITZ D, SCHUSTER S. Magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS) can be used as a large-scale method for establishing zebrafish neuronal cell cultures[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 7959. |
| 38 | UOSAKI H, FUKUSHIMA H, TAKEUCHI A, et al. Efficient and scalable purification of cardiomyocytes from human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells by VCAM1 surface expression[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(8): e23657. |
| 39 | ZHANG P R, REN L H, ZHANG X, et al. Raman-activated cell sorting based on dielectrophoretic single-cell trap and release[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(4): 2282-2289. |
| 40 | REN L Q, YANG S J, ZHANG P R, et al. Fluorescence-activated cell sorters: standing surface acoustic wave (SSAW)-based fluorescence-activated cell sorter[J]. Small, 2018, 14(40): 1801996. |
| 41 | BEEBE D J, MOORE J S, YU Q, et al. Microfluidic tectonics: a comprehensive construction platform for microfluidic systems[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2000, 97(25): 13488-13493. |
| 42 | HUANG L R, COX E C, AUSTIN R H, et al. Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement[J]. Science, 2004, 304(5673): 987-990. |
| 43 | LOUTHERBACK K, D'SILVA J, LIU L Y, et al. Deterministic separation of cancer cells from blood at 10 mL/min[J]. AIP Advances, 2012, 2(4): 042107. |
| 44 | AMINI H, LEE W, DI CARLO D. Inertial microfluidic physics[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2014, 14(15): 2739-2761. |
| 45 | DI CARLO D. Inertial microfluidic physics[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9(21): 3038-3046. |
| 46 | LINDSTRÖM S, ANDERSSON-SVAHN H. Overview of single-cell analyses: microdevices and applications[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2010, 10(24): 3363-3372. |
| 47 | LINDSTRÖM S, ANDERSSON-SVAHN H. Miniaturization of biological assays—overview on microwell devices for single-cell analyses[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 2011, 1810(3): 308-316. |
| 48 | LINDSTRÖM S, ANDERSSON-SVAHN H. Single-cell culture in microwells[M/OL]// Single-cell analysis. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 2012: 41-52 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 49 | ZENG S J, LIU X, XIE H A, et al. Basic technologies for droplet microfluidics[M/OL]//Microfluidics. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011: 69-90 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 50 | KHORSHIDI M ALI, RAJESWARI P K P, WÄHLBY C, et al. Automated analysis of dynamic behavior of single cells in picoliter droplets[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2014, 14(5): 931-937. |
| 51 | BOEDICKER J Q, VINCENT M E, ISMAGILOV R F. Microfluidic confinement of single cells of bacteria in small volumes initiates high-density behavior of quorum sensing and growth and reveals its variability[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(32): 5908-5911. |
| 52 | VINCENT M E, LIU W S, HANEY E B, et al. Microfluidic stochastic confinement enhances analysis of rare cells by isolating cells and creating high density environments for control of diffusible signals[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(3): 974-984. |
| 53 | ZAGNONI M, COOPER J M. Droplet microfluidics for high-throughput analysis of cells and particles[M/OL]//Methods in cell biology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2011, 102: 23-48 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 54 | HENGOJU S, TOVAR M, MAN D K W, et al. Droplet microfluidics for microbial biotechnology[M/OL]//Microfluidics in biotechnology. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020: 129-157 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 55 | TU R, LI L P, YUAN H L, et al. Biosensor-enabled droplet microfluidic system for the rapid screening of 3-dehydroshikimic acid produced in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2020, 47(12): 1155-1160. |
| 56 | LI L P, TU R, SONG G T, et al. Development of a synthetic 3-dehydroshikimate biosensor in Escherichia coli for metabolite monitoring and genetic screening[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(2): 297-306. |
| 57 | TERRY S C, JERMAN J H, ANGELL J B. A gas chromatographic air analyzer fabricated on a silicon wafer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 1979, 26(12): 1880-1886. |
| 58 | WEIBEL D B, DILUZIO W R, WHITESIDES G M. Microfabrication meets microbiology[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2007, 5(3): 209-218. |
| 59 | XIA Y N, WHITESIDES G M. Soft lithography[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 1998, 37(5): 550-575. |
| 60 | WHITESIDES G M, OSTUNI E, TAKAYAMA S, et al. Soft lithography in biology and biochemistry[J]. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 2001, 3: 335-373. |
| 61 | VAN DEN BERG A, LAMMERINK T S J. Micro total analysis systems: microfluidic aspects, integration concept and applications[M/OL]//Topics in current chemistry: microsystem technology in chemistry and life science. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1998: 21-49 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 62 | FRISAN T, LEVITSKY V, MASUCCI M. Limiting dilution assay[M/OL]//Epstein-Barr virus protocols. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 2003: 213-216 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 63 | SÁNCHEZ BAREA J, LEE J, KANG D K. Recent advances in droplet-based microfluidic technologies for biochemistry and molecular biology[J]. Micromachines, 2019, 10(6): 412. |
| 64 | KAMINSKI T S, GARSTECKI P. Controlled droplet microfluidic systems for multistep chemical and biological assays[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(20): 6210-6226. |
| 65 | JOENSSON H N, ANDERSSON SVAHN H. Droplet microfluidics—a tool for single-cell analysis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(49): 12176-12192. |
| 66 | VOLLENBROEK J C, NIEUWELINK A E, BOMER J G, et al. Droplet microreactor for high-throughput fluorescence-based measurements of single catalyst particle acidity[J]. Microsystems & Nanoengineering, 2023, 9: 39. |
| 67 | KAMINSKI T S, SCHELER O, GARSTECKI P. Droplet microfluidics for microbiology: techniques, applications and challenges[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16(12): 2168-2187. |
| 68 | ZHU P G, WANG L Q. Passive and active droplet generation with microfluidics: a review[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2017, 17(1): 34-75. |
| 69 | VÁŇOVÁ B, MALICHEROVÁ B, BURJANIVOVÁ T, et al. Droplet digital PCR as a novel diagnostic tool[J/OL]. Klinicka Onkologie, 2021, 34(1): 33-39[2023-09-01]. . |
| 70 | LI H Y, BAI R L, ZHAO Z Y, et al. Application of droplet digital PCR to detect the pathogens of infectious diseases[J]. Bioscience Reports, 2018, 38(6): BSR20181170. |
| 71 | SHEMBEKAR N, CHAIPAN C, UTHARALA R, et al. Droplet-based microfluidics in drug discovery, transcriptomics and high-throughput molecular genetics[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16(8): 1314-1331. |
| 72 | WANG X X, XIN Y, REN L H, et al. Positive dielectrophoresis-based Raman-activated droplet sorting for culture-free and label-free screening of enzyme function in vivo [J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(32): eabb3521. |
| 73 | YANG L, JENSEN K F. Mass transport and reactions in the tube-in-tube reactor[J]. Organic Process Research & Development, 2013, 17(6): 927-933. |
| 74 | MARTIN K, HENKEL T, BAIER V, et al. Generation of larger numbers of separated microbial populations by cultivation in segmented-flow microdevices[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2003, 3(3): 202-207. |
| 75 | LI R R, GUO X J, XIONG K, et al. Microbial micro-tube culture system: a miniature bioreactor for controllable bubble-free oxygen supply based on high gas-permeability Teflon tube[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 191: 108789. |
| 76 | MAHLER L, TOVAR M, WEBER T, et al. Enhanced and homogeneous oxygen availability during incubation of microfluidic droplets[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(123): 101871-101878. |
| 77 | BARET J C, MILLER O J, TALY V, et al. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting (FADS): efficient microfluidic cell sorting based on enzymatic activity[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9(13): 1850-1858. |
| 78 | OTA Y, SAITO K, TAKAGI T, et al. Fluorescent nucleic acid probe in droplets for bacterial sorting (FNAP-sort) as a high-throughput screening method for environmental bacteria with various growth rates[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(4): e0214533. |
| 79 | WANG X X, REN L H, SU Y T, et al. Raman-activated droplet sorting (RADS) for label-free high-throughput screening of microalgal single-cells[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(22): 12569-12577. |
| 80 | SAFIR F, VU N, TADESSE L F, et al. Combining acoustic bioprinting with AI-assisted Raman spectroscopy for high-throughput identification of bacteria in blood[J]. Nano Letters, 2023, 23(6): 2065-2073. |
| 81 | ZANG E, BRANDES S, TOVAR M, et al. Real-time image processing for label-free enrichment of Actinobacteria cultivated in picolitre droplets[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2013, 13(18): 3707-3713. |
| 82 | WATTERSON W J, TANYERI M, WATSON A R, et al. Droplet-based high-throughput cultivation for accurate screening of antibiotic resistant gut microbes[J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e56998. |
| 83 | GIRAULT M, KIM H, ARAKAWA H, et al. An on-chip imaging droplet-sorting system: a real-time shape recognition method to screen target cells in droplets with single cell resolution[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 40072. |
| 84 | LIU X, PAINTER R E, ENESA K, et al. High-throughput screening of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in picodroplets[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16(9): 1636-1643. |
| 85 | FAN W H, CHEN X, GE Y Q, et al. Single-cell impedance analysis of osteogenic differentiation by droplet-based microfluidics[J]. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2019, 145: 111730. |
| 86 | VAN MEERTEN S G J, VAN BENTUM P J M, KENTGENS A P M. Shim-on-chip design for microfluidic NMR detectors[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(17): 10134-10138. |
| 87 | DAVOODI H, NORDIN N, BORDONALI L, et al. An NMR-compatible microfluidic platform enabling in situ electrochemistry[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2020, 20(17): 3202-3212. |
| 88 | GOTO H, KANAI Y, YOTSUI A, et al. Microfluidic screening system based on boron-doped diamond electrodes and dielectrophoretic sorting for directed evolution of NAD(P)-dependent oxidoreductases[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2020, 20(4): 852-861. |
| 89 | PAN C W, HORVATH D G, BRAZA S, et al. Sorting by interfacial tension (SIFT): label-free selection of live cells based on single-cell metabolism[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2019, 19(8): 1344-1351. |
| 90 | SUN S W, KENNEDY R T. Droplet electrospray ionization mass spectrometry for high throughput screening for enzyme inhibitors[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(18): 9309-9314. |
| 91 | HOLLAND-MORITZ D A, WISMER M K, MANN B F, et al. Mass activated droplet sorting (MADS) enables high-throughput screening of enzymatic reactions at nanoliter scale[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(11): 4470-4477. |
| 92 | GIELEN F, HOURS R, EMOND S, et al. Ultrahigh-throughput–directed enzyme evolution by absorbance-activated droplet sorting (AADS)[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(47): E7383-E7389. |
| 93 | DUNCOMBE T A, PONTI A, SEEBECK F P, et al. UV–vis spectra-activated droplet sorting for label-free chemical identification and collection of droplets[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(38): 13008-13013. |
| 94 | HASAN S, GEISSLER D, WINK K, et al. Fluorescence lifetime-activated droplet sorting in microfluidic chip systems[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2019, 19(3): 403-409. |
| 95 | FERRARO D, CHAMP J, TESTE B, et al. Droplet microfluidic and magnetic particles platform for cancer typing[M/OL]// Methods in molecular biology: microchip diagnostics. New York: Humana Press, 2017, 1547: 113-121 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 96 | ZHU G P, WANG Q Y, MA Z K, et al. Droplet manipulation under a magnetic field: a review[J]. Biosensors, 2022, 12(3): 156. |
| 97 | SHAH G J, OHTA A T, CHIOU E P Y, et al. EWOD-driven droplet microfluidic device integrated with optoelectronic tweezers as an automated platform for cellular isolation and analysis[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9(12): 1732-1739. |
| 98 | SCHMID L, WEITZ D A, FRANKE T. Sorting drops and cells with acoustics: acoustic microfluidic fluorescence-activated cell sorter[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2014, 14(19): 3710-3718. |
| 99 | SCIAMBI A, ABATE A R. Accurate microfluidic sorting of droplets at 30 kHz[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2015, 15(1): 47-51. |
| 100 | QIN Y L, WU L, WANG J G, et al. A fluorescence-activated single-droplet dispenser for high accuracy single-droplet and single-cell sorting and dispensing[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(10): 6815-6819. |
| 101 | KIM H S, HSU S C, HAN S I, et al. High-throughput droplet microfluidics screening platform for selecting fast-growing and high lipid-producing microalgae from a mutant library[J]. Plant Direct, 2017, 1(3): e00011. |
| 102 | FU X Z, ZHANG Y Y, XU Q A, et al. Recent advances on sorting methods of high-throughput droplet-based microfluidics in enzyme directed evolution[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2021, 9: 666867. |
| 103 | 秦伟彤, 杨广宇. 微液滴高通量筛选方法的研究与应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 966-979. |
| QIN W T, YANG G Y. Research and application progress of microdroplets high throughput screening methods[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 966-979. | |
| 104 | CHIU F W Y, STAVRAKIS S. High-throughput droplet-based microfluidics for directed evolution of enzymes[J]. Electrophoresis, 2019, 40(21): 2860-2872. |
| 105 | BROWER K K, CARSWELL-CRUMPTON C, KLEMM S, et al. Double emulsion flow cytometry with high-throughput single droplet isolation and nucleic acid recovery[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2020, 20(12): 2062-2074. |
| 106 | BROWER K K, KHARITON M, SUZUKI P H, et al. Double emulsion picoreactors for high-throughput single-cell encapsulation and phenotyping via FACS[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(19): 13262-13270. |
| 107 | COWELL T, HAN H S. Double emulsion flow cytometry for rapid single genome detection[M/OL]// Methods in molecular biology: single-cell assays. New York: Humana, 2023, 2689: 155-167 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 108 | SCHAERLI Y. Bacterial microcolonies in gel beads for high-throughput screening[J/OL]. Bio-protocol, 2018, 8(13): e2911[2023-09-01]. . |
| 109 | BARET J C. Surfactants in droplet-based microfluidics[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2012, 12(3): 422-433. |
| 110 | RIECHERS B, MAES F, AKOURY E, et al. Surfactant adsorption kinetics in microfluidics[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(41): 11465-11470. |
| 111 | ETIENNE G, VIAN A, BIOČANIN M, et al. Cross-talk between emulsion drops: how are hydrophilic reagents transported across oil phases?[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(24): 3903-3912. |
| 112 | CHOWDHURY M S, ZHENG W S, KUMARI S, et al. Dendronized fluorosurfactant for highly stable water-in-fluorinated oil emulsions with minimal inter-droplet transfer of small molecules[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 4546. |
| 113 | COURTOIS F, OLGUIN L F, WHYTE G, et al. Controlling the retention of small molecules in emulsion microdroplets for use in cell-based assays[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 81(8): 3008-3016. |
| 114 | GRUNER P, RIECHERS B, SEMIN B, et al. Controlling molecular transport in minimal emulsions[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 10392. |
| 115 | MAZUTIS L, BARET J C, TREACY P, et al. Multi-step microfluidic droplet processing: kinetic analysis of an in vitro translated enzyme[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9(20): 2902-2908. |
| 116 | SKHIRI Y, GRUNER P, SEMIN B, et al. Dynamics of molecular transport by surfactants in emulsions[J]. Soft Matter, 2012, 8(41): 10618-10627. |
| 117 | PAN M, ROSENFELD L, KIM M, et al. Fluorinated pickering emulsions impede interfacial transport and form rigid interface for the growth of anchorage-dependent cells[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(23): 21446-21453. |
| 118 | SANDOZ P A, CHUNG A J, WEAVER W M, et al. Sugar additives improve signal fidelity for implementing two-phase resorufin-based enzyme immunoassays[J]. Langmuir, 2014, 30(23): 6637-6643. |
| 119 | MAYR L M, BOJANIC D. Novel trends in high-throughput screening[J]. Current Opinion in Pharmacology, 2009, 9(5): 580-588. |
| 120 | JAKIELA S, KAMINSKI T S, CYBULSKI O, et al. Bacterial growth and adaptation in microdroplet chemostats[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(34): 8908-8911. |
| 121 | GRODRIAN A, METZE J, HENKEL T, et al. Segmented flow generation by chip reactors for highly parallelized cell cultivation[J]. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2004, 19(11): 1421-1428. |
| 122 | DUETZ W A, CHASE M, BILLS G. Miniaturization of fermentations[M/OL]//Manual of industrial microbiology and biotechnology. Washington, DC, USA: ASM Press, 2010: 99-116 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 123 | SARNAIK A, LIU A, NIELSEN D, et al. High-throughput screening for efficient microbial biotechnology[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 64: 141-150. |
| 124 | HERMANN R, LEHMANN M, BÜCHS J. Characterization of gas-liquid mass transfer phenomena in microtiter plates[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2003, 81(2): 178-186. |
| 125 | ELIAS C B, DESAI R B, PATOLE M S, et al. Turbulent shear stress—effect on mammalian cell culture and measurement using laser Doppler anemometer[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1995, 50(15): 2431-2440. |
| 126 | AULD D S, COASSIN P A, COUSSENS N P, et al. Microplate selection and recommended practices in high-throughput screening and quantitative biology[M/OL]. Assay guidance manual [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, 2004. . |
| 127 | HUBER R, RITTER D, HERING T, et al. Robo-Lector-a novel platform for automated high-throughput cultivations in microtiter plates with high information content[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2009, 8(1): 42. |
| 128 | PILAREK M, GLAZYRINA J, NEUBAUER P. Enhanced growth and recombinant protein production of Escherichia coli by a perfluorinated oxygen carrier in miniaturized fed-batch cultures[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2011, 10: 50. |
| 129 | PILAREK M, BRAND E, HILLIG F, et al. Enhanced plasmid production in miniaturized high-cell-density cultures of Escherichia coli supported with perfluorinated oxygen carrier[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2013, 36(8): 1079-1086. |
| 130 | MEYER A, CONDON R G G, KEIL G, et al. Fluorinert, an oxygen carrier, improves cell culture performance in deep square 96-well plates by facilitating oxygen transfer[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2012, 28(1): 171-178. |
| 131 | MANSOURY M, HAMED M, KARMUSTAJI R, et al. The edge effect: a global problem. The trouble with culturing cells in 96-well plates[J]. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 2021, 26: 100987. |
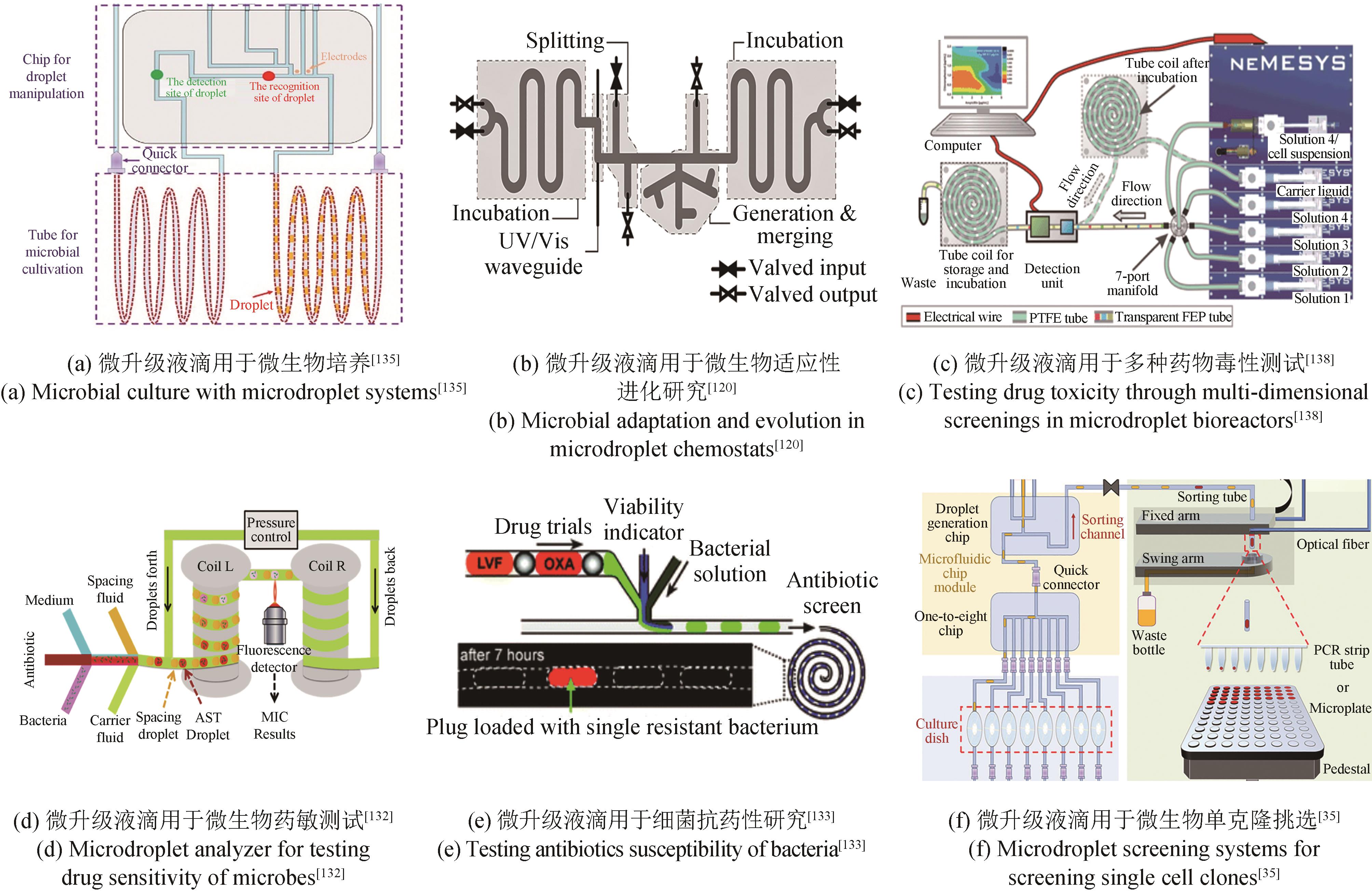
| 132 | BARABAN L, BERTHOLLE F, SALVERDA M L M, et al. Millifluidic droplet analyser for microbiology[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2011, 11(23): 4057-4062. |
| 133 | BOEDICKER J Q, LI L, KLINE T R, et al. Detecting bacteria and determining their susceptibility to antibiotics by stochastic confinement in nanoliter droplets using plug-based microfluidics[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2008, 8(8): 1265-1272. |
| 134 | BOITARD L, COTTINET D, BREMOND N, et al. Growing microbes in millifluidic droplets[J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2015, 15(3): 318-326. |
| 135 | JIAN X J, GUO X J, WANG J, et al. Microbial microdroplet culture system (MMC): an integrated platform for automated, high-throughput microbial cultivation and adaptive evolution[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2020, 117(6): 1724-1737. |
| 136 | DONG L B, CHEN D W, LIU S J, et al. Automated chemotactic sorting and single-cell cultivation of microbes using droplet microfluidics[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 24192. |
| 137 | AOI Y, EPSTEIN S. New devices for cultivation[M/OL]//Manual of environmental microbiology. 4th Edition. Washington, DC, USA: ASM Press, 2015: 2.1.3[2023-09-01]. . |
| 138 | CAO J L, KÜRSTEN D, SCHNEIDER S, et al. Uncovering toxicological complexity by multi-dimensional screenings in microsegmented flow: modulation of antibiotic interference by nanoparticles[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2012, 12(3): 474-484. |
| 139 | CHEN D L, LI L, REYES S, et al. Using three-phase flow of immiscible liquids to prevent coalescence of droplets in microfluidic channels: criteria to identify the third liquid and validation with protein crystallization[J]. Langmuir: the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids, 2007, 23(4): 2255-2260. |
| 140 | CHEN D L, ISMAGILOV R F. Microfluidic cartridges preloaded with nanoliter plugs of reagents: an alternative to 96-well plates for screening[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2006, 10(3): 226-231. |
| 141 | SHUI L L, EIJKEL J C T, VAN DEN BERG A. Multiphase flow in microfluidic systems-control and applications of droplets and interfaces[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2007, 133(1): 35-49. |
| 142 | BETTS J I, BAGANZ F. Miniature bioreactors: current practices and future opportunities[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2006, 5: 21. |
| 143 | GARCIA-OCHOA F, GOMEZ E. Bioreactor scale-up and oxygen transfer rate in microbial processes: an overview[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2009, 27(2): 153-176. |
| 144 | DUETZ W A. Microtiter plates as mini-bioreactors: miniaturization of fermentation methods[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2007, 15(10): 469-475. |
| 145 | ZIMMERMANN H F, JOHN G T, TRAUTHWEIN H, et al. Rapid evaluation of oxygen and water permeation through microplate sealing tapes[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2003, 19(3): 1061-1063. |
| 146 | DUETZ W A, RÜEDI L, HERMANN R, et al. Methods for intense aeration, growth, storage, and replication of bacterial strains in microtiter plates[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 66(6): 2641-2646. |
| 147 | MARQUES M P C, CABRAL J M S, FERNANDES P. Bioprocess scale-up: quest for the parameters to be used as criterion to move from microreactors to lab-scale[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2010, 85(9): 1184-1198. |
| 148 | WEWETZER S J, KUNZE M, LADNER T, et al. Parallel use of shake flask and microtiter plate online measuring devices (RAMOS and BioLector) reduces the number of experiments in laboratory-scale stirred tank bioreactors[J]. Journal of Biological Engineering, 2015, 9: 9. |
| 149 | FUNKE M, DIEDERICHS S, KENSY F, et al. The baffled microtiter plate: increased oxygen transfer and improved online monitoring in small scale fermentations[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2009, 103(6): 1118-1128. |
| 150 | KLÖCKNER W, BÜCHS J. Advances in shaking technologies[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2012, 30(6): 307-314. |
| 151 | KUMAR S, WITTMANN C, HEINZLE E. Review: minibioreactors[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2004, 26(1): 1-10. |
| 152 | BÜCHS J. Introduction to advantages and problems of shaken cultures[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2001, 7(2): 91-98. |
| 153 | WITTMANN C, KIM H M, JOHN G, et al. Characterization and application of an optical sensor for quantification of dissolved O2 in shake-flasks[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2003, 25(5): 377-380. |
| 154 | TAKAHASHI M, AOYAGI H. Practices of shake-flask culture and advances in monitoring CO2 and O2 [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(10): 4279-4289. |
| 155 | WARR S R C. Microbioreactors and scale-down models: growth of CHO cells using the pall micro24 microreactor system[M/OL]// Methods in molecular biology: animal cell biotechnology. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 2014, 1104: 149-165 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 156 | RAMIREZ-VARGAS R, VITAL-JACOME M, CAMACHO-PEREZ E, et al. Characterization of oxygen transfer in a 24-well microbioreactor system and potential respirometric applications[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2014, 186: 58-65. |
| 157 | BETTS J I, DOIG S D, BAGANZ F. Characterization and application of a miniature 10 mL stirred-tank bioreactor, showing scale-down equivalence with a conventional 7 L reactor[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2006, 22(3): 681-688. |
| 158 | HORTSCH R, STRATMANN A, WEUSTER-BOTZ D. New milliliter-scale stirred tank bioreactors for the cultivation of mycelium forming microorganisms[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2010, 106(3): 443-451. |
| 159 | KARIMI A, GOLBABAEI F, MEHRNIA M R, et al. Oxygen mass transfer in a stirred tank bioreactor using different impeller configurations for environmental purposes[J]. Iranian Journal of Environmental Health Science & Engineering, 2013, 10(1): 6. |
| 160 | AMER M, FENG Y, RAMSEY J D. Using CFD simulations and statistical analysis to correlate oxygen mass transfer coefficient to both geometrical parameters and operating conditions in a stirred-tank bioreactor[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2019, 35(3): e2785. |
| 161 | 丁宁, 李超, 白力, 等. 机械搅拌式动物细胞反应器不同桨型组合的CFD数值模拟与优化[J]. 生物工程学报, 2020, 36(6): 1209-1215. |
| DING N, LI C, BAI L, et al. Numerical simulation and optimization of impeller combination used in stirred bioreactor[J]. Chinese journal of biotechnology, 2020, 36(6): 1209-1215. | |
| 162 | LATTERMANN C, BÜCHS J. Microscale and miniscale fermentation and screening[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2015, 35: 1-6. |
| 163 | RIEDLBERGER P, WEUSTER-BOTZ D. New miniature stirred-tank bioreactors for parallel study of enzymatic biomass hydrolysis[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 106: 138-146. |
| 164 | WARR S. Ambr®15 microbioreactors for CHO cell cultivation[M/OL]// Methods in molecular biology: animal cell biotechnology. New York: Humana Press, 2020, 2095: 43-67 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 165 | ZHOU C J, XIE B Q, LI S W, et al. Rapid measurement of gas diffusivity in liquids using a tube-in-tube reactor with an unsteady-state strategy[J]. AIChE Journal, 2020, 66(11): e17015. |
| 166 | ZWEIGERDT R, ANDRÉE B, KROPP C, et al. Bioreactors for expansion of pluripotent stem cells and their differentiation to cardiac cells[M/OL]//Bioreactors: design, operation and novel applications. New York:John Wiley & Sons, 2016: 175-200 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 167 | ASK M, STOCKS S M. Aerobic bioreactors: condensers, evaporation rates, scale-up and scale-down[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2022, 44(7): 813-822. |
| 168 | NEUBAUER P, JUNNE S. Scale-up and scale-down methodologies for bioreactors[M/OL]// Bioreactors: design, operation and novel applications, New York:John Wiley & Sons, 2016: 323-354 [2023-09-01]. . |
| 169 | HEYMAN B, TULKE H, PUTRI S P, et al. Online monitoring of the respiratory quotient reveals metabolic phases during microaerobic 2,3-butanediol production with Bacillus licheniformis [J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2020, 20(3/4): 133-144. |
| 170 | LI X Y, YU C, YAO J M, et al. An online respiratory quotient-feedback strategy of feeding yeast extract for efficient arachidonic acid production by Mortierella alpina [J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2018, 5: 83. |
| 171 | 庄英萍, 田锡炜, 张嗣良. 基于多尺度参数相关分析的细胞培养过程优化与放大[J]. 生物产业技术, 2018(1): 49-55. |
| ZHUANG Y P, TIAN X W, ZHANG S L. Cell culture process optimization and scale-up based on multi-scale parameter related analysis[J]. Biotechnology & Business, 2018(1): 49-55. | |
| 172 | 储炬, 杭海峰, 庄英萍. 工业微生物发酵过程放大策略[J]. 生物产业技术, 2009(4): 68-72. |
| CHU J, HANG H F, ZHUANG Y P. Scale-up strategy of industrial microbial fermentation process[J]. Biotechnology & Business, 2009(4): 68-72. | |
| 173 | KUNERT R, REINHART D. Advances in recombinant antibody manufacturing[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(8): 3451-3461. |
| 174 | SCARFF M, ARNOLD S A, HARVEY L M, et al. Near infrared spectroscopy for bioprocess monitoring and control: current status and future trends[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2006, 26(1): 17-39. |
| 175 | BUCKLEY K, RYDER A G. Applications of Raman spectroscopy in biopharmaceutical manufacturing: a short review[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2017, 71(6): 1085-1116. |
| 176 | DE BEER T R M, BODSON C, DEJAEGHER B, et al. Raman spectroscopy as a process analytical technology (PAT) tool for the in-line monitoring and understanding of a powder blending process[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2008, 48(3): 772-779. |
| 177 | DE BEER T, BURGGRAEVE A, FONTEYNE M, et al. Near infrared and Raman spectroscopy for the in-process monitoring of pharmaceutical production processes[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2011, 417(1/2): 32-47. |
| 178 | JIANG J J, YANG G Y, MA F Q. Fluorescence coupling strategies in fluorescence-activated droplet sorting (FADS) for ultrahigh-throughput screening of enzymes, metabolites, and antibodies[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2023, 66: 108173. |
| 179 | RUNNING J A, BANSAL K. Oxygen transfer rates in shaken culture vessels from Fernbach flasks to microtiter plates[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2016, 113(8): 1729-1735. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [12] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [13] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [14] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [15] | 查文龙, 卜兰, 訾佳辰. 中药药效成分群的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||