合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (1): 191-201.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-021
肿瘤类器官及其在合成生物学中的研究进展
孟倩1, 尹聪1, 黄卫人1,2
- 1.深圳大学第一附属医院泌尿外科,国家地方联合医学合成生物学临床应用关键技术工程实验室,广东 深圳 518036
2.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院合成生物学研究所,广东 深圳 518000
-
收稿日期:2023-03-07修回日期:2023-07-11出版日期:2024-02-29发布日期:2024-03-20 -
通讯作者:黄卫人 -
作者简介:孟倩 (1999—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为泌尿系统肿瘤发生机制及精准治疗研究。 E-mail:mengqian0722@163.com黄卫人 (1980—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为:(1)肿瘤合成生物学研究;(2)肿瘤类器官培养及精准医学研究。 E-mail:pony8980@163.com -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2019YFA0906000);深圳市医疗卫生三名工程(SZSM202011017)
Tumor organoids and their research progress in synthetic biology
MENG Qian1, YIN Cong1, HUANG Weiren1,2
- 1.Department of Urology,The First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University,National and Local Joint Medical Synthetic Biology Clinical Application Key Technology Engineering Laboratory,Shenzhen 518036,Guangdong,China
2.Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518000,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2023-03-07Revised:2023-07-11Online:2024-02-29Published:2024-03-20 -
Contact:HUANG Weiren
摘要:
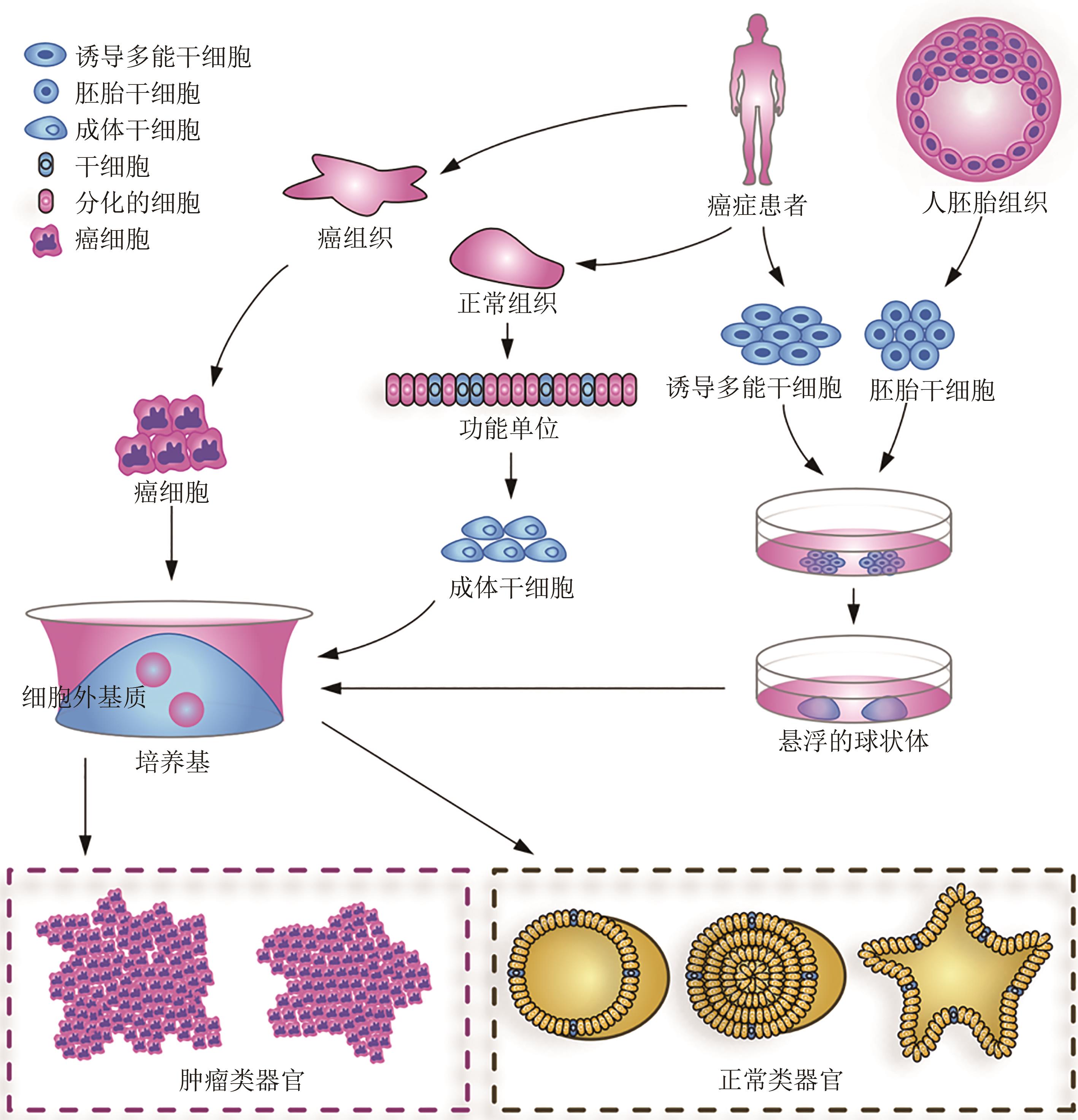
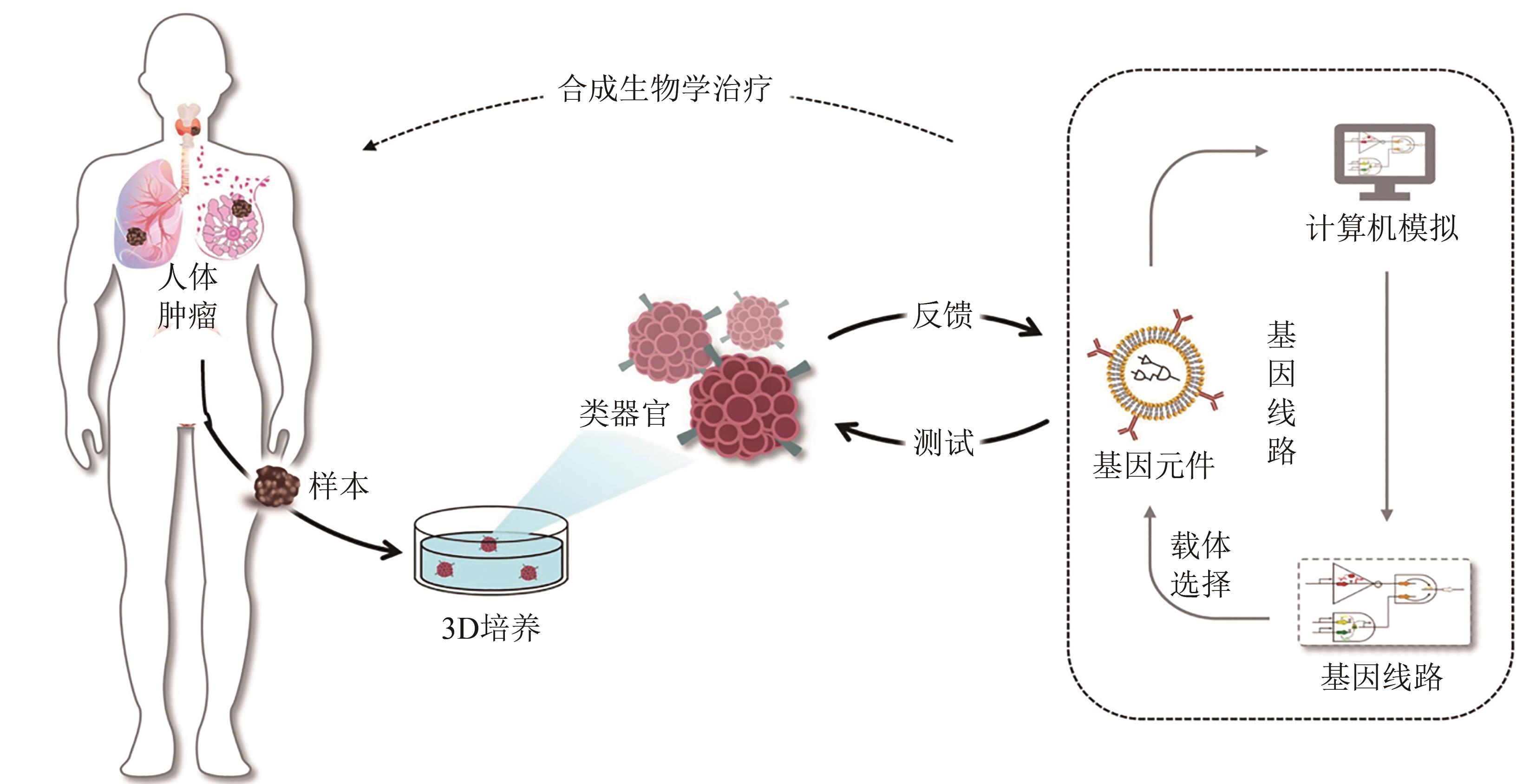
类器官技术的发展为更接近机体细胞组成和病理生理特征的癌症模型开辟了新途径。患者来源的肿瘤类器官在多次传代后仍能维持原有肿瘤的组织病理学及遗传表型特征,不仅可作为测试新型抗癌药物的优良模型,也可通过其药物敏感性测试预测患者的临床反应,为肿瘤患者的个体化精准治疗提供可靠的依据。合成生物学是以工程学思想为指导,提供独特工具来重建空间和动态信号,调控细胞间通信。合成生物学的快速发展,为肿瘤类器官在肿瘤的发生发展及肿瘤治疗等方面提供了一系列崭新的思路和方法,包括如何工程化重建类器官空间与动态信号、细胞稳态维持、细胞间通信调控等。本文概述了肿瘤类器官的构建过程及其在合成生物学中的应用,讨论了肿瘤类器官当前在构建效率、标准化、自动化、精确度等方面的局限性,最后展望了合成生物学在推动肿瘤类器官结构和功能复杂化方面的前景。
中图分类号:
引用本文
孟倩, 尹聪, 黄卫人. 肿瘤类器官及其在合成生物学中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(1): 191-201.
MENG Qian, YIN Cong, HUANG Weiren. Tumor organoids and their research progress in synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(1): 191-201.
| 1 | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| 2 | WU C C, LI M N, MENG H B, et al. Analysis of status and countermeasures of cancer incidence and mortality in China[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2019, 62(5): 640-647. |
| 3 | SU M, XIAO Y H, MA J L, et al. Circular RNAs in cancer: emerging functions in hallmarks, stemness, resistance and roles as potential biomarkers[J]. Molecular Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 90. |
| 4 | BALANI S, NGUYEN L V, EAVES C J. Modeling the process of human tumorigenesis[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15422. |
| 5 | GILLET J P, VARMA S, GOTTESMAN M M. The clinical relevance of cancer cell lines[J]. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 2013, 105(7): 452-458. |
| 6 | ZHOU J J, SU J, FU X T, et al. Microfluidic device for primary tumor spheroid isolation[J].Experimental Hematology & Oncology, 2017, 6(1): 22. |
| 7 | BEN-DAVID U, HA G, TSENG Y Y, et al. Patient-derived xenografts undergo mouse-specific tumor evolution[J]. Nature Genetics, 2017, 49(11): 1567-1575. |
| 8 | BYRNE A T, ALFÉREZ D G, AMANT F, et al. Interrogating open issues in cancer medicine with patient-derived xenografts[J]. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2017, 17:632. |
| 9 | GAO H, KORN J M, FERRETTI S, et al. High-throughput screening using patient-derived tumor xenografts to predict clinical trial drug response[J]. Nature Medicine, 2015, 21(11): 1318-1325. |
| 10 | ROSENBLUTH J M, SCHACKMANN R C J, GRAY G K, et al. Organoid cultures from normal and cancer-prone human breast tissues preserve complex epithelial lineages[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 1711. |
| 11 | DUTTA D, HEO I, CLEVERS H. Disease modeling in stem cell-derived 3D organoid systems[J]. Trends in Molecular Medicine, 2017, 23(5): 393-410. |
| 12 | QIAN X Y, SONG H J, MING G L. Brain organoids: advances, applications and challenges[J]. Development, 2019, 146(8): dev166074. |
| 13 | TANG X Y, WU S S, WANG D, et al. Human organoids in basic research and clinical applications[J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2022, 7: 168. |
| 14 | SHINOZAWA T, KIMURA M, CAI Y Q, et al. High-fidelity drug-induced liver injury screen using human pluripotent stem cell-derived organoids[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 160(3): 831-846.e10. |
| 15 | COWAN C S, RENNER M, DE GENNARO M, et al. Cell types of the human retina and its organoids at single-cell resolution[J]. Cell, 2020, 182(6): 1623-1640.e34. |
| 16 | ZHAO J, FU Y, YAMAZAKI Y, et al. APOE4 exacerbates synapse loss and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease patient iPSC-derived cerebral organoids[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5540. |
| 17 | SABATE-SOLER S, NICKELS S L, SARAIVA C, et al. Microglia integration into human midbrain organoids leads to increased neuronal maturation and functionality[J]. Glia, 2022, 70(7): 1267-1288. |
| 18 | HUANG W K, WONG S Z H, PATHER S R, et al. Generation of hypothalamic arcuate organoids from human induced pluripotent stem cells[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2021, 28(9): 1657-1670.e10. |
| 19 | UNGRICHT R, GUIBBAL L, LASBENNES M C, et al. Genome-wide screening in human kidney organoids identifies developmental and disease-related aspects of nephrogenesis[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2022, 29(1): 160-175.e7. |
| 20 | MAIER C F, ZHU L, NANDURI L K, et al. Patient-derived organoids of cholangiocarcinoma[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(16): 8675. |
| 21 | HENDRIKS D, ARTEGIANI B, HU H L, et al. Establishment of human fetal hepatocyte organoids and CRISPR-Cas9-based gene knockin and knockout in organoid cultures from human liver[J]. Nature Protocols, 2021, 16(1): 182-217. |
| 22 | BETGE J, RINDTORFF N, SAUER J, et al. The drug-induced phenotypic landscape of colorectal cancer organoids[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 3135. |
| 23 | QIANG Y L, YAO N, ZUO F, et al. Tumor organoid model and its pharmacological applications in tumorigenesis prevention[J]. Current Molecular Pharmacology, 2023, 14(4): 435-447. |
| 24 | LI M H, GONG J, GAO L X, et al. Advanced human developmental toxicity and teratogenicity assessment using human organoid models[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022, 235: 113429. |
| 25 | MAHAPATRA C, LEE R D, PAUL M K. Emerging role and promise of nanomaterials in organoid research[J]. Drug Discovery Today, 2022, 27(3): 890-899. |
| 26 | PRIOR N, INACIO P, HUCH M. Liver organoids: from basic research to therapeutic applications[J]. Gut, 2019, 68(12): 2228-2237. |
| 27 | STEIN M C, BRAUN F, KREBS C F, et al. Kidney organoid systems for studies of immune-mediated kidney diseases: challenges and opportunities[J]. Cell and Tissue Research, 2021, 385(2): 457-473. |
| 28 | LU Z L, NIE B N, ZHAI W W, et al. Delineating the longitudinal tumor evolution using organoid models[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2021, 48(7): 560-570. |
| 29 | XU H X, LYU X D, YI M, et al. Organoid technology and applications in cancer research[J]. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 2018, 11(1): 116. |
| 30 | ELBADAWY M, ABUGOMAA A, YAMAWAKI H, et al. Development of prostate cancer organoid culture models in basic medicine and translational research[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(4): 777. |
| 31 | BAO Y L, WANG L, PAN H T, et al. Animal and organoid models of liver fibrosis[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2021, 12: 666138. |
| 32 | CHEN H D, ZHUO Q F, YE Z, et al. Organoid model: a new hope for pancreatic cancer treatment?[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Reviews on Cancer, 2021, 1875(1): 188466. |
| 33 | REN X X, CHEN W K, YANG Q X, et al. Patient-derived cancer organoids for drug screening: basic technology and clinical application[J]. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2022, 37(8): 1446-1454. |
| 34 | CHOI H, KIM H J, YANG J, et al. Acetylation changes tau interactome to degrade tau in Alzheimer's disease animal and organoid models[J]. Aging Cell, 2020, 19(1): e13081. |
| 35 | WILSON H V. On some phenomena of coalescence and regeneration in sponges[J]. Journal of Experimental Zoology, 1907, 5(2): 245-258. |
| 36 | BRÜMMER F, NICKEL M. Sustainable use of marine resources: cultivation of sponges[M/OL]//Progress in molecular and subcellular biology: sponges (porifera). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2003, 37: 143-162 [2023-02-01]. . |
| 37 | EVANS G S, FLINT N, SOMERS A S, et al. The development of a method for the preparation of rat intestinal epithelial cell primary cultures[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 1992, 101(1): 219-231. |
| 38 | WHITEHEAD R H, DEMMLER K, ROCKMAN S P, et al. Clonogenic growth of epithelial cells from normal colonic mucosa from both mice and humans[J]. Gastroenterology, 1999, 117(4): 858-865. |
| 39 | FUKAMACHI H. Proliferation and differentiation of fetal rat intestinal epithelial cells in primary serum-free culture[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 1992, 103(2): 511-519. |
| 40 | PERREAULT N, BEAULIEU J F. Use of the dissociating enzyme thermolysin to generate viable human normal intestinal epithelial cell cultures[J]. Experimental Cell Research, 1996, 224(2): 354-364. |
| 41 | SATO T, VRIES R G, SNIPPERT H J, et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche[J]. Nature, 2009, 459(7244): 262-265. |
| 42 | GAO D, VELA I, SBONER A, et al. Organoid cultures derived from patients with advanced prostate cancer[J]. Cell, 2014, 159(1): 176-187. |
| 43 | VAN DE WETERING M, FRANCIES H E, FRANCIS J M, et al. Prospective derivation of a living organoid biobank of colorectal cancer patients[J]. Cell, 2015, 161(4): 933-945. |
| 44 | BOJ S F, HWANG C I, BAKER L A, et al. Organoid models of human and mouse ductal pancreatic cancer[J]. Cell, 2015, 160(1/2): 324-338. |
| 45 | SACHS N, DE LIGT J, KOPPER O, et al. A living biobank of breast cancer organoids captures disease heterogeneity[J]. Cell, 2018, 172(1/2): 373-386.e10. |
| 46 | YAN H H N, SIU H C, LAW S, et al. A comprehensive human gastric cancer organoid biobank captures tumor subtype heterogeneity and enables therapeutic screening[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2018, 23(6): 882-897.e11. |
| 47 | LIU H, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived organoid retinoblastoma reveals a cancerous origin[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(52): 33628-33638. |
| 48 | NORRIE J L, NITYANANDAM A, LAI K R, et al. Retinoblastoma from human stem cell-derived retinal organoids[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 4535. |
| 49 | MO S B, TANG P Y, LUO W Q, et al. Patient-derived organoids from colorectal cancer with paired liver metastasis reveal tumor heterogeneity and predict response to chemotherapy[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(31): 2204097. |
| 50 | DING S L, HSU C, WANG Z H, et al. Patient-derived micro-organospheres enable clinical precision oncology[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2022, 29(6): 905-917.e6. |
| 51 | BHATIA S, KRAMER M, RUSSO S, et al. Patient-derived triple-negative breast cancer organoids provide robust model systems that recapitulate tumor intrinsic characteristics[J]. Cancer Research, 2022, 82(7): 1174-1192. |
| 52 | DRIEHUIS E, KRETZSCHMAR K, CLEVERS H. Establishment of patient-derived cancer organoids for drug-screening applications[J]. Nature Protocols, 2020, 15(10): 3380-3409. |
| 53 | DIJKSTRA K K, CATTANEO C M, WEEBER F, et al. Generation of tumor-reactive T cells by co-culture of peripheral blood lymphocytes and tumor organoids[J]. Cell, 2018, 174(6): 1586-1598.e12. |
| 54 | ZHAO H, CHENG Y L, KALRA A, et al. Generation and multiomic profiling of a TP53/CDKN2A double-knockout gastroesophageal junction organoid model[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2022, 14(673): eabq6146. |
| 55 | NUCIFORO S, FOFANA I, MATTER M S, et al. Organoid models of human liver cancers derived from tumor needle biopsies[J]. Cell Reports, 2018, 24(5): 1363-1376. |
| 56 | TIRIAC H, BELLEAU P, ENGLE D D, et al. Organoid profiling identifies common responders to chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Discovery, 2018, 8(9): 1112-1129. |
| 57 | CHEN P, ZHANG X, DING R B, et al. Patient-derived organoids can guide personalized-therapies for patients with advanced breast cancer[J]. Advanced Science, 2021, 8(22): 2101176. |
| 58 | LEE S H, HU W H, MATULAY J T, et al. Tumor evolution and drug response in patient-derived organoid models of bladder cancer[J]. Cell, 2018, 173(2): 515-528.e17. |
| 59 | 类器官药物敏感性检测指导肿瘤精准治疗临床应用专家共识(2022年版)编写专家组. 类器官药物敏感性检测指导肿瘤精准治疗临床应用专家共识(2022年版)[J]. 中国癌症防治杂志, 2022, 14(3): 234-239. |
| Group of expert consensus of clinical application about tumor precision therapy guided by organoid-based drug sensitivity testing (2022 edition). Expert consensus of clinical application about tumor precision therapy guided by organoid-based drug sensitivity testing (2022 edition) [J]. Chinese Journal of Oncology Prevention and Treatment, 2022, 14(3): 234-239. | |
| 60 | GAO M, HARPER M M, LIN M, et al. Development of a single-cell technique to increase yield and use of gastrointestinal cancer organoids for personalized medicine application[J]. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 2021, 232(4): 504-514. |
| 61 | CAMERON D E, BASHOR C J, COLLINS J J. A brief history of synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2014, 12(5): 381-390. |
| 62 | JIANG K Y, KOOB J, DAWN CHEN X, et al. Programmable eukaryotic protein synthesis with RNA sensors by harnessing ADAR[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2023, 41(5): 698-707. |
| 63 | KHALIL A S, COLLINS J J. Synthetic biology: applications come of age[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2010, 11(5): 367-379. |
| 64 | SCHMIDT F, ZIMMERMANN J, TANNA T, et al. Noninvasive assessment of gut function using transcriptional recording sentinel cells[J]. Science, 2022, 376(6594): eabm6038. |
| 65 | 吴晓昊, 廖荣东, 李飞云, 等. 合成生物学在疾病诊疗中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(2): 244-262. |
| WU X H, LIAO R D, LI F Y, et al. Applications of synthetic biology in disease diagnosis and treatment[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(2): 244-262. | |
| 66 | GUO W X, LI L, HE J, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics identifies a distinct luminal progenitor cell type in distal prostate invagination tips[J]. Nature Genetics, 2020, 52(9): 908-918. |
| 67 | OGAWA J, PAO G M, SHOKHIREV M N, et al. Glioblastoma model using human cerebral organoids[J]. Cell Reports, 2018, 23(4): 1220-1229. |
| 68 | BIAN S, REPIC M, GUO Z M, et al. Genetically engineered cerebral organoids model brain tumor formation[J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(8): 631-639. |
| 69 | DEKKERS J F, WHITTLE J R, VAILLANT F, et al. Modeling breast cancer using CRISPR-Cas9-mediated engineering of human breast organoids[J]. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 2020, 112(5): 540-544. |
| 70 | JACOB F, SALINAS R D, ZHANG D Y, et al. A patient-derived glioblastoma organoid model and biobank recapitulates inter- and intra-tumoral heterogeneity[J]. Cell, 2020, 180(1): 188-204.e22. |
| 71 | SCHNALZGER T E, DE GROOT M H, ZHANG C C, et al. 3D model for CAR-mediated cytotoxicity using patient-derived colorectal cancer organoids[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2019, 38(12): e100928. |
| 72 | YU L, LI Z C, MEI H B, et al. Patient-derived organoids of bladder cancer recapitulate antigen expression profiles and serve as a personal evaluation model for CAR-T cells in vitro [J]. Clinical & Translational Immunology, 2021, 10(2): e1248. |
| 73 | SAKO K, PRADHAN S J, BARONE V, et al. Optogenetic control of nodal signaling reveals a temporal pattern of nodal signaling regulating cell fate specification during gastrulation[J]. Cell Reports, 2016, 16(3): 866-877. |
| 74 | ČAPEK D, SMUTNY M, TICHY A M, et al. Light-activated Frizzled7 reveals a permissive role of non-canonical Wnt signaling in mesendoderm cell migration[J]. eLife, 2019, 8: 42093. |
| 75 | REPINA N A, BAO X P, ZIMMERMANN J A, et al. Optogenetic control of Wnt signaling for modeling early embryogenic patterning with human pluripotent stem cells[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2019[2023-02-01]. . |
| 76 | LEGNINI I, EMMENEGGER L, ZAPPULO A, et al. Spatio-temporal, optogenetic control of gene expression in organoids[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 461850[2023-02-10]. . |
| 77 | KARTHAUS W R, IAQUINTA P J, DROST J, et al. Identification of multipotent luminal progenitor cells in human prostate organoid cultures[J]. Cell, 2014, 159(1): 163-175. |
| 78 | NEAL J T, LI X N, ZHU J J, et al. Organoid modeling of the tumor immune microenvironment[J]. Cell, 2018, 175(7): 1972-1988.e16. |
| 79 | HU Y W, SUI X Z, SONG F, et al. Lung cancer organoids analyzed on microwell arrays predict drug responses of patients within a week[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 2581. |
| 80 | LEE K K, MCCAULEY H A, BRODA T R, et al. Human stomach-on-a-chip with luminal flow and peristaltic-like motility[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(20): 3079-3085. |
| 81 | PARK S E, GEORGESCU A, HUH D. Organoids-on-a-chip[J]. Science, 2019, 364(6444): 960-965. |
| 82 | SACKMANN E K, FULTON A L, BEEBE D J. The present and future role of microfluidics in biomedical research[J]. Nature, 2014, 507(7491): 181-189. |
| 83 | SCHUSTER B, JUNKIN M, KASHAF S S, et al. Automated microfluidic platform for dynamic and combinatorial drug screening of tumor organoids[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5271. |
| 84 | BIAN X S, LI G, WANG C, et al. A deep learning model for detection and tracking in high-throughput images of organoid[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2021, 134: 104490. |
| 85 | SKARDAL A, ALEMAN J, FORSYTHE S, et al. Drug compound screening in single and integrated multi-organoid body-on-a-chip systems[J]. Biofabrication, 2020, 12(2): 025017. |
| 86 | KELLER P J, LIN A F, ARENDT L M, et al. Mapping the cellular and molecular heterogeneity of normal and malignant breast tissues and cultured cell lines[J].Breast Cancer Research, 2010, 12(5): R87. |
| 87 | PRIYA R, ALLANKI S, GENTILE A, et al. Tension heterogeneity directs form and fate to pattern the myocardial wall[J]. Nature, 2020, 588(7836): 130-134. |
| 88 | BRASSARD J A, LUTOLF M P. Engineering stem cell self-organization to build better organoids[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2019, 24(6): 860-876. |
| 89 | STEVENS A J, HARRIS A R, GERDTS J, et al. Programming multicellular assembly with synthetic cell adhesion molecules[J]. Nature, 2023, 614(7946): 144-152. |
| 90 | TRENTESAUX C, YAMADA T, KLEIN O D, et al. Harnessing synthetic biology to engineer organoids and tissues[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(1): 10-19. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [12] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [13] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [14] | 洪源, 刘妍. 脑类器官在再生医学中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 754-769. |
| [15] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||