合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (3): 527-547.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-085
紫杉醇生物合成机制研究进展
刘晓楠1,2(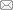 ), 李静1,2,3, 祝晓熙1,2, 徐子硕1,2,4,5, 齐健1,2, 江会锋1,2
), 李静1,2,3, 祝晓熙1,2, 徐子硕1,2,4,5, 齐健1,2, 江会锋1,2
- 1.中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所,低碳合成工程生物学重点实验室,天津 300308
2.国家合成生物技术创新中心,天津 300308
3.南开大学化学学院,天津 300071
4.东北林业大学,东北盐碱植被恢复与重建教育部重点实验室,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150040
5.东北林业大学,黑龙江省植物天然活性物质的合成与利用重点实验室,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150040
-
收稿日期:2023-11-17修回日期:2024-04-12出版日期:2024-06-30发布日期:2024-07-12 -
通讯作者:刘晓楠,江会锋 -
作者简介:刘晓楠 (1990—),女,博士,副研究员,硕士生导师。研究方向为植物天然产物合成、酵母基因组工程。E-mail:liu_xn@tib.cas.cn江会锋 (1981—),男,博士,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为新酶设计与酵母基因组工程。E-mail:jiang_hf@tib.cas.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(32371499);中国博士后科学基金(2019M661032);北京生命科技研究院有限公司重点项目(2023200CB0090)
Research advances on paclitaxel biosynthesis
LIU Xiaonan1,2( ), LI Jing1,2,3, ZHU Xiaoxi1,2, XU Zishuo1,2,4,5, QI Jian1,2, JIANG Huifeng1,2
), LI Jing1,2,3, ZHU Xiaoxi1,2, XU Zishuo1,2,4,5, QI Jian1,2, JIANG Huifeng1,2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Engineering Biology for Low-Carbon Manufacturing,Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Tianjin 300308,China
2.National Center of Technology Innovation for Synthetic Biology,Tianjin 300308,China
3.College of Chemistry,Nankai University,Tianjin 300071,China
4.Key Laboratory of Saline-Alkali Vegetation Ecology Restoration,Northeast Forestry University,Harbin 150040,Heilongjiang,China
5.Heilongjiang Key Laboratory of Plant Bioactive Substance Biosynthesis and Utilization,Northeast Forestry University,Harbin 150040,Heilongjiang,China
-
Received:2023-11-17Revised:2024-04-12Online:2024-06-30Published:2024-07-12 -
Contact:LIU Xiaonan, JIANG Huifeng
摘要:
紫杉醇是目前已发现的最具抗癌活性的天然广谱抗癌药物之一,其生产方式主要依赖于从珍稀植物红豆杉中进行分离提取以及化学半合成,因其含量稀少,生产能力受到严重的限制。随着红豆杉基因组的全解析和合成生物学的迅速发展,通过合成生物技术,构建重组工程细胞合成紫杉醇及其关键前体成为解决当前供需不平衡和资源有限的有效方法。本文针对紫杉醇生物合成途径解析、红豆杉组学分析、底盘细胞构建、关键前体合成、紫杉醇合成途径关键酶的改造及催化机理解析等相关研究进展开展系统性的综述,尤其对近期发表的关于氧杂环丁烷环形成的相关突破性研究进行了详细介绍,并基于相关进展探讨当前紫杉醇合成生物学研究面临的关键酶催化效率低下、产物杂泛性严重、具体反应顺序未知等技术挑战及生物合成紫杉醇关键中间体的未来前景。助力加强对紫杉醇合成通路和催化过程的理解,进一步实现紫杉醇的绿色、高效生物合成。
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘晓楠, 李静, 祝晓熙, 徐子硕, 齐健, 江会锋. 紫杉醇生物合成机制研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 527-547.
LIU Xiaonan, LI Jing, ZHU Xiaoxi, XU Zishuo, QI Jian, JIANG Huifeng. Research advances on paclitaxel biosynthesis[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 527-547.

图2 紫杉醇生物合成途径解析[模块1代表巴卡亭Ⅲ生物合成途径推测1(蓝色)和巴卡亭Ⅲ生物合成途径推测2(黄色)。模块2(绿色)表示β-苯丙烯醇侧链生物合成途径。模块3(紫色)代表紫杉醇生物合成途径。TS—紫杉二烯合成酶;T5αOH—紫杉二烯-5α-羟化酶;TAT—紫杉二烯-5α-醇-O-乙酰基转移酶;T10βOH—紫杉烷-10β-羟化酶;T13αOH—紫杉烷-13α-羟化酶;T2αOH—紫杉烷-2α-羟化酶;T9αOH—紫杉烷-9α-羟化酶;T7βOH—紫杉烷-7β-羟化酶;T1βOH—紫杉烷-1β-羟化酶;TBT—紫杉烷-2α-O-苯甲酰转移酶;DBAT—10-去乙酰巴卡亭Ⅲ10-O-乙酰转移酶;TOT—紫杉烷环氧化酶;BAPT—巴卡亭Ⅲ-3-氨基,13-苯丙酰转移酶;T2′αOH—紫杉烷-2′α-羟化酶;DBTNBT—3′-N-去苯甲酰-2′-脱氧紫杉醇-N-苯酰转移酶;PAM—苯丙氨酸氨基变位酶;PCL—β-苯丙氨酸辅酶A连接酶]
Fig. 2 Recently discovered pathways for paclitaxel biosynthesis[Module 1 representing speculated baccatin Ⅲ biosynthetic pathway 1 (bule) and speculated baccatin Ⅲ biosynthetic pathway 2 (yellow). Module 2 (green) representing the β-phenylalanoyl side chain pathway. Module 3 (purple) representing paclitaxel biosynthetic pathway. TS—taxadiene synthase; T5αOH—taxane 5α-hydroxylase; TAT—taxadiene-5α-ol-O-acetyl transferase; T10βOH—taxane 10β-hydroxylase; T13αOH—taxane 13α- hydroxylase; T2αOH—taxane 2α-hydroxylase; T9αOH—taxane 9α-hydroxylase; T7βOH—taxane 7β-hydroxylase; T1βOH—taxane 1β-hydroxylase; TBT—taxane 2α-O-benzoyltransferase; DBAT—10-deacetyl baccatin Ⅲ-10-O-acetyltransferase; TOT—taxane oxetanase; BAPT—baccatin Ⅲ-3-amino, 13-phenylpropanoyltransferase; T2′αOH—taxane 2′α-hydroxylase; DBTNBT—3′-N-debenzoyl-2′-deoxytaxol-N-benzoyltransferase; PAM—phenylalanine aminomutase; PCL—β-phenylalanine coenzyme A ligase.]
| 酶名称 | 简写 | 登录号 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase | GGPPS | AF081514 | [ |
| 2 | Taxadiene synthase | TS | AY364469 | [ |
| 3 | Taxadiene-5α-hydroxylase | T5αOH | AY289209 | [ |
| 4 | Taxadiene-13α-hydroxylase | T13αOH | AY056019 | [ |
| 5 | Taxadiene-5α-ol-O-acetyl transferase | TAT | AF190130 | [ |
| 6 | Taxadiene-10β-hydroxylase | T10βOH | AF318211/AY563635 | [ |
| 7 | Taxadiene-7β-hydroxylase | T7βOH | AY307951 | [ |
| 8 | Taxadiene-2α-hydroxylase | T2αOH | AY518383 | [ |
| 9 | Taxane-2α-O-benzoyl transferase | TBT | AF297618 | [ |
| 10 | 10-deacetylbaccatin Ⅲ-10-O-acetyl transferase | DBAT | AF193765 | [ |
| 11 | Phenylalanine aminomutase | PAM | AY582743 | [ |
| 12 | β-phenylalanoyl-CoA ligase | PCL | KM593667 | [ |
| 13 | Baccatin Ⅲ: 3-amino, 13-phenylpropanoyltransferase | BAPT | AY082804 | [ |
| 14 | Taxane-2′α-hydroxylase | T2′αOH | KP178208 | [ |
| 15 | N-benzoyl transferase | DBTNBT | AF466397 | [ |
| 16 | Taxadiene-14β-hydroxylase | T14βOH | AY188177 | [ |
| 17 | Cytochrome P450 reductase | TcCPR | AY571340 | [ |
| 18 | C4β-C20 epoxidase | [ | ||
| 19 | Taxane 1β-hydroxylase | T1βOH | [ | |
| 20 | Taxane 9α-hydroxylase | T9αOH | [ | |
| 21 | Taxane 9α-dioxygenase | [ | ||
| 22 | Phenylalanine-CoA ligase | PCL | [ | |
| 23 | Taxane oxetanase | TOT | [ | |
| 24 | Taxane 9α-hydroxylase | T9αH1 | [ | |
| 25 | Taxane 9α-hydroxylase | CYP725A37 | PP197199/PP197200 | [ |
| 26 | Taxane oxetanase | CYP725A55 | PP197201 | [ |
| 27 | Acyltransferase | AT5 | PP197202 | [ |
表1 已知的紫杉醇生物合成酶及参考文献
Table 1 Identified paclitaxel biosynthetic enzymes
| 酶名称 | 简写 | 登录号 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase | GGPPS | AF081514 | [ |
| 2 | Taxadiene synthase | TS | AY364469 | [ |
| 3 | Taxadiene-5α-hydroxylase | T5αOH | AY289209 | [ |
| 4 | Taxadiene-13α-hydroxylase | T13αOH | AY056019 | [ |
| 5 | Taxadiene-5α-ol-O-acetyl transferase | TAT | AF190130 | [ |
| 6 | Taxadiene-10β-hydroxylase | T10βOH | AF318211/AY563635 | [ |
| 7 | Taxadiene-7β-hydroxylase | T7βOH | AY307951 | [ |
| 8 | Taxadiene-2α-hydroxylase | T2αOH | AY518383 | [ |
| 9 | Taxane-2α-O-benzoyl transferase | TBT | AF297618 | [ |
| 10 | 10-deacetylbaccatin Ⅲ-10-O-acetyl transferase | DBAT | AF193765 | [ |
| 11 | Phenylalanine aminomutase | PAM | AY582743 | [ |
| 12 | β-phenylalanoyl-CoA ligase | PCL | KM593667 | [ |
| 13 | Baccatin Ⅲ: 3-amino, 13-phenylpropanoyltransferase | BAPT | AY082804 | [ |
| 14 | Taxane-2′α-hydroxylase | T2′αOH | KP178208 | [ |
| 15 | N-benzoyl transferase | DBTNBT | AF466397 | [ |
| 16 | Taxadiene-14β-hydroxylase | T14βOH | AY188177 | [ |
| 17 | Cytochrome P450 reductase | TcCPR | AY571340 | [ |
| 18 | C4β-C20 epoxidase | [ | ||
| 19 | Taxane 1β-hydroxylase | T1βOH | [ | |
| 20 | Taxane 9α-hydroxylase | T9αOH | [ | |
| 21 | Taxane 9α-dioxygenase | [ | ||
| 22 | Phenylalanine-CoA ligase | PCL | [ | |
| 23 | Taxane oxetanase | TOT | [ | |
| 24 | Taxane 9α-hydroxylase | T9αH1 | [ | |
| 25 | Taxane 9α-hydroxylase | CYP725A37 | PP197199/PP197200 | [ |
| 26 | Taxane oxetanase | CYP725A55 | PP197201 | [ |
| 27 | Acyltransferase | AT5 | PP197202 | [ |
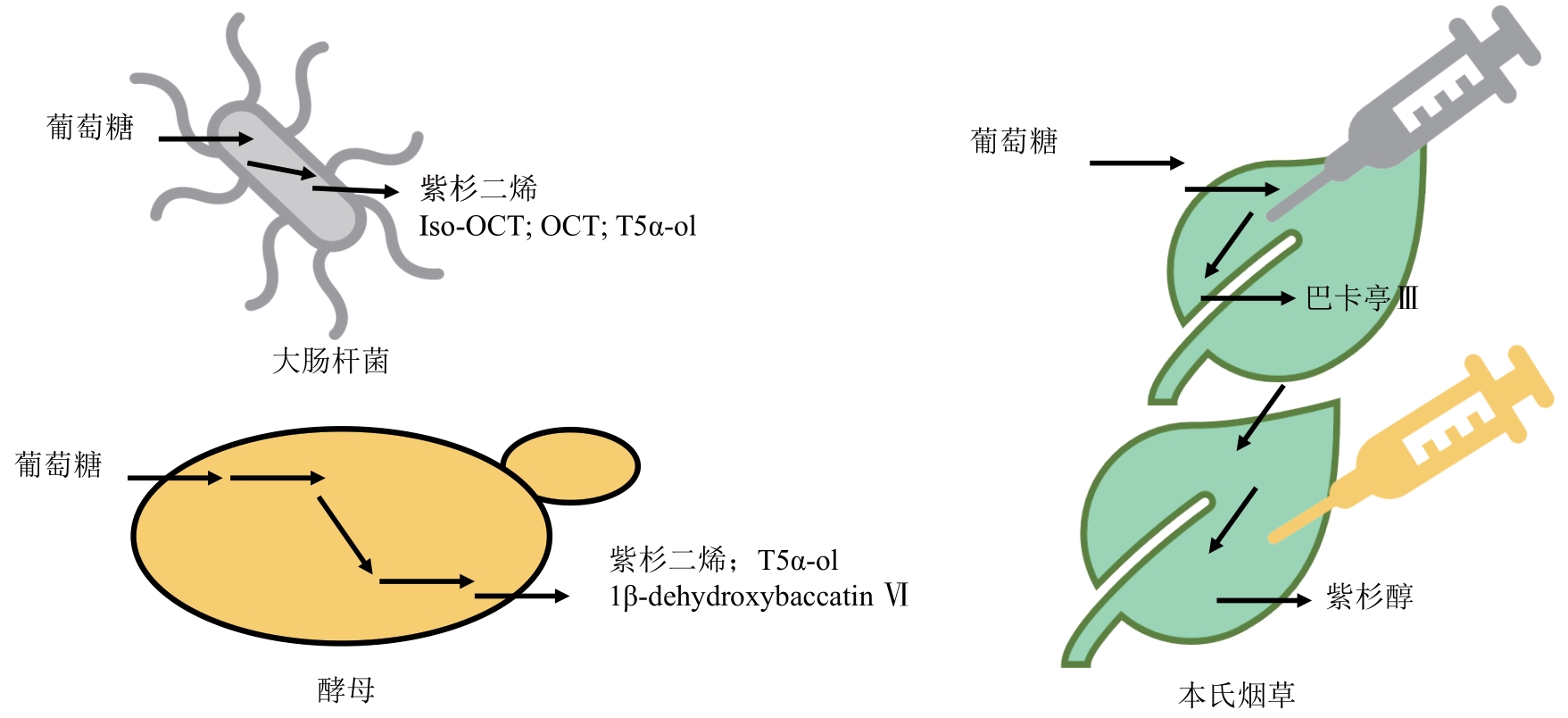
| 合成体系 | 产物 | 产量 | 研究方法 | 发表 时间 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大肠杆菌 | 紫杉二烯 | 1.3 mg/L | 过表达IDI、GGPPS、TS、DXP | 2001 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 紫杉二烯 | 1 g/L | 多变量模块化代谢工程,过表达TS和T5αOH | 2010 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | (58±3) mg/L | |||
| 大肠杆菌 | 紫杉二烯 | 4.5 mg/g DW | JM109(DE3)菌株,22 °C | 2012 | [ |
| 链格孢菌TPF6 | 紫杉二烯 | (61.9±6.3) μg/L | alcA启动子,过表达IDI、tHMGR | 2017 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 氧化紫杉烷 | 27 mg/L | TbrTS,Taxus CPR,T5αOH-GSTGS-CPR,引入异源MVA途径 | 2022 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | 7 mg/L | |||
| 大肠杆菌 | 紫杉二烯 | 93.5 mg/L | 融合表达GGPP和TS | 2022 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 氧化紫杉烷 | (570±45) mg/L | P450酶N端修饰 | 2016 | [ |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌 | 紫杉二烯 | 17.8 mg/L | 过表达MEP途径,GGPPS和TS | 2019 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯 | 8.7 mg/L | 共表达tHMGR、突变调节蛋白UPC2-1、GGPPS和TS | 2008 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯 | 72.8 mg/L | YSG50菌株,GGPPSbc | 2014 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 氧化紫杉烷 | 33 mg/L | 大肠杆菌和酿酒酵母共培养 | 2015 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯 | 129 mg/L | 增加MBP标签的多拷贝TS,20 ℃ | 2020 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | 20 mg/L | 对发酵工艺的改进,pH优化 | 2021 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-yl-乙酸酯 | 3.7 mg/L | |||
| 酿酒酵母 | 氧化紫杉烷 | 78 mg/L | |||
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | 42 mg/L | 2×YP, 统计学确定性筛选设计 | 2022 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-yl-乙酸酯 | 22 mg/L | |||
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | (38.1±8.4) mg/L | 启动子pHXT7,融合表达T5OH和CPR,中性pH条件下静息细胞测定 | 2022 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 氧化紫杉烷 | (361.4±52.4) mg/L | |||
| 解脂耶氏酵母 | 紫杉二烯 | 101.4 mg/L | 融合表达SUMO与TS,过表达tHMG1、GGS1和TS | 2023 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯 | 215 mg/L | 计算代谢工程 | 2023 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | 43.65 mg/L | |||
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-乙酸酯 | 26.2 mg/L | |||
| 酿酒酵母 | 1β-dehydroxybaccatin Ⅵ | 细胞共共表达已鉴定的12个基因并饲喂紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | 2024 | [ | |
| 拟南芥 | 紫杉二烯 | 600 ng/g DW | 糖皮质激素诱导表达TS | 2004 | [ |
| 本氏烟草 | 紫杉二烯 | 50 μg/g DW | 表达TS,MeJA诱导,沉默PSY和PDS | 2014 | [ |
| 本氏烟草 | 紫杉二烯 | (56.6±3.2) µg/g fresh weight | 区室化策略, DXS和GGPPS共表达 | 2019 | [ |
| 本氏烟草 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | (1.3±0.5) µg/g fresh weight | |||
| 红花烟草 | 紫杉二烯 | 87.8 μg/g DW | TS的N端融合叶绿体转运肽 | 2021 | [ |
| 本氏烟草 | 巴卡亭Ⅲ | 154.87 ng/g fresh weight | 瞬时表达C4β-C20环氧化酶基因、T9αOH、T1βOH和T9OX与其他9个已知基因 | 2023 | [ |
| 紫杉醇 | 64.29 ng/g fresh weight | 瞬时表达PCL与BAPT、PAM、DBTNBT、T2′OH | |||
| 本氏烟草 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | 弱组成型启动子NOS弱化T5αOH的表达 | |||
| 5α,10β-二乙酰氧基- 紫杉二烯-13α-醇 | 42 µg/g DW | (NOS)T10βOH、DBAT和(NOS)T13αOH | 2024 | [ | |
| 本氏烟草 | 巴卡亭Ⅲ | 瞬时表达TOT和T9αOH-1与其他7个已知合成基因 | 2024 | [ |
表2 紫杉醇生产的异源表达体系
Table 2 Heterologous expression systems for paclitaxel production
| 合成体系 | 产物 | 产量 | 研究方法 | 发表 时间 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大肠杆菌 | 紫杉二烯 | 1.3 mg/L | 过表达IDI、GGPPS、TS、DXP | 2001 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 紫杉二烯 | 1 g/L | 多变量模块化代谢工程,过表达TS和T5αOH | 2010 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | (58±3) mg/L | |||
| 大肠杆菌 | 紫杉二烯 | 4.5 mg/g DW | JM109(DE3)菌株,22 °C | 2012 | [ |
| 链格孢菌TPF6 | 紫杉二烯 | (61.9±6.3) μg/L | alcA启动子,过表达IDI、tHMGR | 2017 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 氧化紫杉烷 | 27 mg/L | TbrTS,Taxus CPR,T5αOH-GSTGS-CPR,引入异源MVA途径 | 2022 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | 7 mg/L | |||
| 大肠杆菌 | 紫杉二烯 | 93.5 mg/L | 融合表达GGPP和TS | 2022 | [ |
| 大肠杆菌 | 氧化紫杉烷 | (570±45) mg/L | P450酶N端修饰 | 2016 | [ |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌 | 紫杉二烯 | 17.8 mg/L | 过表达MEP途径,GGPPS和TS | 2019 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯 | 8.7 mg/L | 共表达tHMGR、突变调节蛋白UPC2-1、GGPPS和TS | 2008 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯 | 72.8 mg/L | YSG50菌株,GGPPSbc | 2014 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 氧化紫杉烷 | 33 mg/L | 大肠杆菌和酿酒酵母共培养 | 2015 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯 | 129 mg/L | 增加MBP标签的多拷贝TS,20 ℃ | 2020 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | 20 mg/L | 对发酵工艺的改进,pH优化 | 2021 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-yl-乙酸酯 | 3.7 mg/L | |||
| 酿酒酵母 | 氧化紫杉烷 | 78 mg/L | |||
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | 42 mg/L | 2×YP, 统计学确定性筛选设计 | 2022 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-yl-乙酸酯 | 22 mg/L | |||
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | (38.1±8.4) mg/L | 启动子pHXT7,融合表达T5OH和CPR,中性pH条件下静息细胞测定 | 2022 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 氧化紫杉烷 | (361.4±52.4) mg/L | |||
| 解脂耶氏酵母 | 紫杉二烯 | 101.4 mg/L | 融合表达SUMO与TS,过表达tHMG1、GGS1和TS | 2023 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯 | 215 mg/L | 计算代谢工程 | 2023 | [ |
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | 43.65 mg/L | |||
| 酿酒酵母 | 紫杉二烯-5α-乙酸酯 | 26.2 mg/L | |||
| 酿酒酵母 | 1β-dehydroxybaccatin Ⅵ | 细胞共共表达已鉴定的12个基因并饲喂紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | 2024 | [ | |
| 拟南芥 | 紫杉二烯 | 600 ng/g DW | 糖皮质激素诱导表达TS | 2004 | [ |
| 本氏烟草 | 紫杉二烯 | 50 μg/g DW | 表达TS,MeJA诱导,沉默PSY和PDS | 2014 | [ |
| 本氏烟草 | 紫杉二烯 | (56.6±3.2) µg/g fresh weight | 区室化策略, DXS和GGPPS共表达 | 2019 | [ |
| 本氏烟草 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | (1.3±0.5) µg/g fresh weight | |||
| 红花烟草 | 紫杉二烯 | 87.8 μg/g DW | TS的N端融合叶绿体转运肽 | 2021 | [ |
| 本氏烟草 | 巴卡亭Ⅲ | 154.87 ng/g fresh weight | 瞬时表达C4β-C20环氧化酶基因、T9αOH、T1βOH和T9OX与其他9个已知基因 | 2023 | [ |
| 紫杉醇 | 64.29 ng/g fresh weight | 瞬时表达PCL与BAPT、PAM、DBTNBT、T2′OH | |||
| 本氏烟草 | 紫杉二烯-5α-醇 | 弱组成型启动子NOS弱化T5αOH的表达 | |||
| 5α,10β-二乙酰氧基- 紫杉二烯-13α-醇 | 42 µg/g DW | (NOS)T10βOH、DBAT和(NOS)T13αOH | 2024 | [ | |
| 本氏烟草 | 巴卡亭Ⅲ | 瞬时表达TOT和T9αOH-1与其他7个已知合成基因 | 2024 | [ |
| 1 | WANI M C, TAYLOR H L, WALL M E, et al. Plant antitumor agents. Ⅵ. The isolation and structure of taxol, a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from Taxus brevifolia [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1971, 93(9): 2325-2327. |
| 2 | PROTA A E, BARGSTEN K, ZURWERRA D, et al. Molecular mechanism of action of microtubule-stabilizing anticancer agents[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6119): 587-590. |
| 3 | CROTEAU R, KETCHUM R E B, LONG R M, et al. Taxol biosynthesis and molecular genetics[J]. Phytochemistry Reviews, 2006, 5(1): 75-97. |
| 4 | MIN L, HAN J C, ZHANG W, et al. Strategies and lessons learned from total synthesis of taxol[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2023, 123(8): 4934-4971. |
| 5 | 邓夏萌, 曹辉, 沈海伟, 等. 紫杉醇及其衍生物的半合成概述[J]. 浙江化工, 2018, 49(5): 1-8. |
| DENG X M, CAO H, SHEN H W, et al. Semi-synthetic overview of taxol and its derivatives[J]. Zhejiang Chemical Industry, 2018, 49(5): 1-8. | |
| 6 | KANDA Y, ISHIHARA Y, WILDE N C, et al. Two-phase total synthesis of taxanes: tactics and strategies[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2020, 85(16): 10293-10320. |
| 7 | ZHANG Y J, SCOSSA F, FERNIE A R. The genomes of Taxus species unveil novel candidates in the biosynthesis of taxoids[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(11): 1773-1775. |
| 8 | BIAN G K, YUAN Y J, TAO H, et al. Production of taxadiene by engineering of mevalonate pathway in Escherichia coli and endophytic fungus Alternaria alternata TPF6[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 12(4): 1600697. |
| 9 | KÖKSAL M, JIN Y H, COATES R M, et al. Taxadiene synthase structure and evolution of modular architecture in terpene biosynthesis[J]. Nature, 2011, 469(7328): 116-120. |
| 10 | GUERRA-BUBB J, CROTEAU R, WILLIAMS R M. The early stages of taxol biosynthesis: an interim report on the synthesis and identification of early pathway metabolites[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2012, 29(6): 683-696. |
| 11 | WILLIAMS D C, WILDUNG M R, JIN A Q, et al. Heterologous expression and characterization of a “Pseudomature” form of taxadiene synthase involved in paclitaxel (Taxol) biosynthesis and evaluation of a potential intermediate and inhibitors of the multistep diterpene cyclization reaction[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2000, 379(1): 137-146. |
| 12 | ZHANG Y J, WIESE L, FANG H, et al. Synthetic biology identifies the minimal gene set required for paclitaxel biosynthesis in a plant chassis[J]. Molecular Plant, 2023, 16(12): 1951-1961. |
| 13 | JIANG B, GAO L, WANG H J, et al. Characterization and heterologous reconstitution of Taxus biosynthetic enzymes leading to baccatin Ⅲ[J]. Science, 2024, 383(6683): 622-629. |
| 14 | HEFNER J, KETCHUM R E, CROTEAU R. Cloning and functional expression of a cDNA encoding geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase from Taxus canadensis and assessment of the role of this prenyltransferase in cells induced for taxol production[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 1998, 360(1): 62-74. |
| 15 | WILDUNG M R, CROTEAU R. A cDNA clone for taxadiene synthase, the diterpene cyclase that catalyzes the committed step of taxol biosynthesis[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1996, 271(16): 9201-9204. |
| 16 | JENNEWEIN S, LONG R M, WILLIAMS R M, et al. Cytochrome P450 taxadiene 5α-hydroxylase, a mechanistically unusual monooxygenase catalyzing the first oxygenation step of taxol biosynthesis[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2004, 11(3): 379-387. |
| 17 | JENNEWEIN S, RITHNER C D, WILLIAMS R M, et al. Taxol biosynthesis: taxane 13 α-hydroxylase is a cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2001, 98(24): 13595-13600. |
| 18 | WALKER K, SCHOENDORF A, CROTEAU R. Molecular cloning of a taxa-4(20), 11(12)-dien-5α-ol-O-acetyl transferase cDNA from Taxus and functional expression in Escherichia coli [J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2000, 374(2): 371-380. |
| 19 | JENNEWEIN S, WILDUNG M R, CHAU M, et al. Random sequencing of an induced Taxus cell cDNA library for identification of clones involved in taxol biosynthesis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(24): 9149-9154. |
| 20 | SCHOENDORF A, RITHNER C D, WILLIAMS R M, et al. Molecular cloning of a cytochrome P450 taxane 10β- hydroxylase cDNA from Taxus and functional expression in yeast[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2001, 98(4): 1501-1506. |
| 21 | CHAU M, JENNEWEIN S, WALKER K, et al. Taxol biosynthesis: molecular cloning and characterization of a cytochrome P450 taxoid 7β-hydroxylase[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2004, 11(5): 663-672. |
| 22 | CHAU M, CROTEAU R. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cytochrome P450 taxoid 2α-hydroxylase involved in Taxol biosynthesis[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2004, 427(1): 48-57. |
| 23 | WALKER K, CROTEAU R. Taxol biosynthesis: molecular cloning of a benzoyl-CoA: taxane 2α-O-benzoyltransferase cDNA from taxus and functional expression in Escherichia coli [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2000, 97(25): 13591-13596. |
| 24 | WALKER K D, KLETTKE K, AKIYAMA T, et al. Cloning, heterologous expression, and characterization of a phenylalanine aminomutase involved in taxol biosynthesis[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2004, 279(52): 53947-53954. |
| 25 | RAMÍREZ-ESTRADA K, ALTABELLA T, ONRUBIA M, et al. Transcript profiling of jasmonate-elicited Taxus cells reveals a β-phenylalanine-CoA ligase[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 14(1): 85-96. |
| 26 | WALKER K, LONG R, CROTEAU R. The final acylation step in taxol biosynthesis: cloning of the taxoid C13-side-chain N-benzoyltransferase from Taxus [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(14): 9166-9171. |
| 27 | SANCHEZ-MUÑOZ R, PEREZ-MATA E, ALMAGRO L, et al. A novel hydroxylation step in the taxane biosynthetic pathway: a new approach to paclitaxel production by synthetic biology[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020, 8: 410. |
| 28 | JENNEWEIN S, RITHNER C D, WILLIAMS R M, et al. Taxoid metabolism: taxoid 14β-hydroxylase is a cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2003, 413(2): 262-270. |
| 29 | JENNEWEIN S, PARK H, DEJONG J M, et al. Coexpression in yeast of Taxus cytochrome P450 reductase with cytochrome P450 oxygenases involved in taxol biosynthesis[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2005, 89(5): 588-598. |
| 30 | YANG C S, WANG Y, SU Z, et al. Biosynthesis of the highly oxygenated tetracyclic core skeleton of taxol[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 2339. |
| 31 | EDGAR S, ZHOU K, QIAO K J, et al. Mechanistic insights into taxadiene epoxidation by taxadiene-5α-hydroxylase[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2016, 11(2): 460-469. |
| 32 | EDGAR S, LI F S, QIAO K J, et al. Engineering of taxadiene synthase for improved selectivity and yield of a key taxol biosynthetic intermediate[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(2): 201-205. |
| 33 | SAGWAN-BARKDOLL L, ANTEROLA A M. Taxadiene-5α-ol is a minor product of CYP725A4 when expressed in Escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 2018, 65(3): 294-305. |
| 34 | YADAV V G. Unraveling the multispecificity and catalytic promiscuity of taxadiene monooxygenase[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 2014, 110: 154-164. |
| 35 | ZHAO Y, LIANG F Y, XIE Y M, et al. Oxetane ring formation in taxol biosynthesis is catalyzed by a bifunctional cytochrome P450 enzyme[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(1): 801-810. |
| 36 | TONG Y R, LUO Y F, GAO W. Biosynthesis of paclitaxel using synthetic biology[J]. Phytochemistry Reviews, 2022, 21(3): 863-877. |
| 37 | WALLS L E, MALCI K, NOWROUZI B, et al. Optimizing the biosynthesis of oxygenated and acetylated taxol precursors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using advanced bioprocessing strategies[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2021, 118(1): 279-293. |
| 38 | ZHANG N, HAN Z T, SUN G L, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cytochrome P450 taxoid 9α-hydroxylase in Ginkgo biloba cells[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2014, 443(3): 938-943. |
| 39 | LIU J C T, DE LA PEÑA R, TOCOL C, et al. Reconstitution of early paclitaxel biosynthetic network[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 1419. |
| 40 | XIONG X Y, GOU J B, LIAO Q G, et al. The Taxus genome provides insights into paclitaxel biosynthesis[J]. Nature Plants, 2021, 7(8): 1026-1036. |
| 41 | CHENG J, WANG X, LIU X N, et al. Chromosome-level genome of Himalayan yew provides insights into the origin and evolution of the paclitaxel biosynthetic pathway[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(7): 1199-1209. |
| 42 | SONG C, FU F F, YANG L L, et al. Taxus yunnanensis genome offers insights into gymnosperm phylogeny and taxol production[J]. Communications Biology, 2021, 4(1): 1203. |
| 43 | 丰美静, 张恺恺, 陈段芬, 等. 多组学技术在红豆杉研究中的应用[J]. 分子植物育种, 2022, 20(3): 840-846. |
| FENG M J, ZHANG K K, CHEN D F, et al. Application of multi-omics technique in Taxus spp. research[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2022, 20(3): 840-846. | |
| 44 | LI T T, LI B B, LIAO C L, et al. Transcriptome analysis provides insights into light condition effect on paclitaxel biosynthesis in yew saplings[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2022, 22(1): 577. |
| 45 | MUBEEN S, LI Z L, HUANG Q M, et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis revealed the tissue-specific accumulations of taxanes among three experimental lines of Taxus yunnanensis [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2018, 66(40): 10410-10420. |
| 46 | WANG T, CHEN Y, ZHUANG W, et al. Transcriptome sequencing reveals regulatory mechanisms of taxol synthesis in Taxus wallichiana var. Mairei [J]. Int J Genomics, 2019, 2019: 1596895. |
| 47 | YU C N, LUO X J, ZHANG C C, et al. Tissue-specific study across the stem of Taxus media identifies a phloem-specific TmMYB3 involved in the transcriptional regulation of paclitaxel biosynthesis[J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2020, 103(1): 95-110. |
| 48 | YU C N, HOU K L, ZHANG H S, et al. Integrated mass spectrometry imaging and single-cell transcriptome atlas strategies provide novel insights into taxoid biosynthesis and transport in Taxus mairei stems[J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2023, 115(5): 1243-1260. |
| 49 | HUANG Q, ROESSNER C A, CROTEAU R, et al. Engineering Escherichia coli for the synthesis of taxadiene, a key intermediate in the biosynthesis of taxol[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2001, 9(9): 2237-2242. |
| 50 | AJIKUMAR P K, XIAO W H, TYO K E J, et al. Isoprenoid pathway optimization for taxol precursor overproduction in Escherichia coli [J]. Science, 2010, 330(6000): 70-74. |
| 51 | BOGHIGIAN B A, SALAS D, AJIKUMAR P K, et al. Analysis of heterologous taxadiene production in K- and B-derived Escherichia coli [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 93(4): 1651-1661. |
| 52 | WU Q Y, HUANG Z Y, WANG J Y, et al. Construction of an Escherichia coli cell factory to synthesize taxadien-5α-ol, the key precursor of anti-cancer drug paclitaxel[J]. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 2022, 9(1): 82. |
| 53 | WANG J Y, HUANG Z Y, WU Q Y, et al. Facile biosynthesis of taxadiene by a newly constructed Escherichia coli strain fusing enzymes taxadiene synthase and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2022, 122: 129-136. |
| 54 | BIGGS B W, LIM C G, SAGLIANI K, et al. Overcoming heterologous protein interdependency to optimize P450-mediated taxol precursor synthesis in Escherichia coli [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(12): 3209-3214. |
| 55 | ABDALLAH I I, PRAMASTYA H, VAN MERKERK R, et al. Metabolic engineering of Bacillus subtilis toward taxadiene biosynthesis as the first committed step for taxol production[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 218. |
| 56 | ENGELS B, DAHM P, JENNEWEIN S. Metabolic engineering of taxadiene biosynthesis in yeast as a first step towards taxol (paclitaxel) production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2008, 10(3-4): 201-206. |
| 57 | DING M Z, YAN H F, LI L F, et al. Biosynthesis of Taxadiene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: selection of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase directed by a computer-aided docking strategy[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(10): e109348. |
| 58 | ZHOU K, QIAO K J, EDGAR S, et al. Distributing a metabolic pathway among a microbial consortium enhances production of natural products[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(4): 377-383. |
| 59 | NOWROUZI B, LI R A, WALLS L E, et al. Enhanced production of taxadiene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2020, 19(1): 200. |
| 60 | WALLS L E, MARTINEZ J L, RIOS-SOLIS L. Enhancing Saccharomyces cerevisiae taxane biosynthesis and overcoming nutritional stress-induced pseudohyphal growth[J]. Microorganisms, 2022, 10(1): 163. |
| 61 | NOWROUZI B, LIANG L G, RIOS-SOLIS L. Exploring optimal taxol® CYP725A4 activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2022, 21(1): 197. |
| 62 | XU M, XIE W L, LUO Z, et al. Improving solubility and copy number of taxadiene synthase to enhance the titer of taxadiene in Yarrowia lipolytica [J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2023, 8(2): 331-338. |
| 63 | MALCI K, SANTIBÁÑEZ R, JONGUITUD-BORREGO N, et al. Improved production of taxol® precursors in S. cerevisiae using combinatorial in silico design and metabolic engineering[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2023, 22(1): 243. |
| 64 | BESUMBES O, SAURET-GÜETO S, PHILLIPS M A, et al. Metabolic engineering of isoprenoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis for the production of taxadiene, the first committed precursor of Taxol[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2004, 88(2): 168-175. |
| 65 | HASAN M M, KIM H S, JEON J H, et al. Metabolic engineering of Nicotiana benthamiana for the increased production of taxadiene[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2014, 33(6): 895-904. |
| 66 | LI J H, MUTANDA I, WANG K B, et al. Chloroplastic metabolic engineering coupled with isoprenoid pool enhancement for committed taxanes biosynthesis in Nicotiana benthamiana [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 4850. |
| 67 | FU J Q, XU W B, HUANG W, et al. Importation of taxadiene synthase into chloroplast improves taxadiene production in tobacco[J]. Planta, 2021, 253(5): 107. |
| 68 | BOGHIGIAN B A, ARMANDO J, SALAS D, et al. Computational identification of gene over-expression targets for metabolic engineering of taxadiene production[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 93(5): 2063-2073. |
| 69 | LONCARIC C, MERRIWEATHER E, WALKER K D. Profiling a Taxol pathway 10β-acetyltransferase: assessment of the specificity and the production of baccatin Ⅲ by in vivo acetylation in E. coli [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2006, 13(3): 309-317. |
| 70 | JULSING M K, KOULMAN A, WOERDENBAG H J, et al. Combinatorial biosynthesis of medicinal plant secondary metabolites[J]. Biomolecular Engineering, 2006, 23(6): 265-279. |
| 71 | MUTANDA I, LI J H, XU F L, et al. Recent advances in metabolic engineering, protein engineering, and transcriptome-guided insights toward synthetic production of taxol[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2021, 9: 632269. |
| 72 | DEJONG J M, LIU Y L, BOLLON A P, et al. Genetic engineering of taxol biosynthetic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2006, 93(2): 212-224. |
| 73 | JIANG Z D, KEMPINSKI C, BUSH C J, et al. Engineering triterpene and methylated triterpene production in plants provides biochemical and physiological insights into terpene metabolism[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 170(2): 702-716. |
| 74 | RONTEIN D, ONILLON S, HERBETTE G, et al. CYP725A4 from yew catalyzes complex structural rearrangement of taxa-4(5),11(12)-diene into the cyclic ether 5(12)-oxa-3(11)- cyclotaxane[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2008, 283(10): 6067-6075. |
| 75 | PEREZ-MATAS E, HIDALGO-MARTINEZ D, MOYANO E, et al. Overexpression of BAPT and DBTNBT genes in Taxus baccata in vitro cultures to enhance the biotechnological production of paclitaxel[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2024, 22(1): 233-247. |
| 76 | HE J N, PLÁCIDO J P A, PATERAKI I, et al. Hairy root induction of Taxus baccata L. by natural transformation with Rhizobium rhizogenes [J]. Horticulturae, 2022, 9(1): 4. |
| 77 | ZHOU X W, ZHU H F, LIU L, et al. A review: recent advances and future prospects of taxol-producing endophytic fungi[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 86(6): 1707-1717. |
| 78 | 赵凯, 平文祥, 周东坡. 内生真菌发酵生产紫杉醇的研究现状与展望[J]. 微生物学报, 2008, 48(3): 403-407. |
| ZHAO K, PING W X, ZHOU D P. Recent advance and prospect on taxol production by endophytic fungus fermentation—a review[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2008, 48(3): 403-407. | |
| 79 | WANG Y C, GUO B H, MIAO Z Q, et al. Transformation of taxol-producing endophytic fungi by restriction enzyme-mediated integration (REMI)[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2007, 273(2): 253-259. |
| 80 | WEI Y M, ZHOU X W, LIU L, et al. An efficient transformation system of taxol-producing endophytic fungus EFY-21 (Ozonium sp.)[J]. African Journal of Biotechnology, 2010, 9(12): 1726-1733. |
| 81 | ZHANG P, LIU T T, ZHOU P P, et al. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of a taxol-producing endophytic fungus, Cladosporium cladosporioides MD2[J]. Current Microbiology, 2011, 62(4): 1315-1320. |
| 82 | LIU L, WEI Y M, ZHOU X W, et al. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation of the taxol-producing endophytic fungus Ozonium sp EFY21[J]. Genetics and Molecular Research, 2013, 12(3): 2913-2922. |
| 83 | EL-SAYED A S A, ABDEL-GHANY S E, ALI G S. Genome editing approaches: manipulating of lovastatin and taxol synthesis of filamentous fungi by CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(10): 3953-3976. |
| 84 | VAN RIJN J P M, ESCORCIA A M, THIEL W. QM/MM study of the taxadiene synthase mechanism[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2019, 40(21): 1902-1910. |
| 85 | ANSBACHER T, FREUD Y, MAJOR D T. Slow-starter enzymes: role of active-site architecture in the catalytic control of the biosynthesis of taxadiene by taxadiene synthase[J]. Biochemistry, 2018, 57(26): 3773-3779. |
| 86 | LIU H Y, CHEN Q. Computational protein design for given backbone: recent progresses in general method-related aspects[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2016, 39: 89-95. |
| 87 | SOLIMAN S, TANG Y. Natural and engineered production of taxadiene with taxadiene synthase[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2015, 112(2): 229-235. |
| 88 | SCHREPFER P, BUETTNER A, GOERNER C, et al. Identification of amino acid networks governing catalysis in the closed complex of class Ⅰ terpene synthases[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(8): E958-E967. |
| 89 | BIGGS B W, ROUCK J E, KAMBALYAL A, et al. Orthogonal assays clarify the oxidative biochemistry of taxol P450 CYP725A4[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2016, 11(5): 1445-1451. |
| 90 | BARTON N A, MARSH B J, LEWIS W, et al. Accessing low-oxidation state taxanes: is taxadiene-4(5)-epoxide on the taxol biosynthetic pathway?[J]. Chemical Science, 2016, 7(5): 3102-3107. |
| 91 | SONG X T, WANG Q, ZHU X X, et al. Unraveling the catalytic mechanism of taxadiene-5α-hydroxylase from crystallography and computational analyses[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2024, 14(6): 3912-3925. |
| 92 | LI B J, WANG H, GONG T, et al. Improving 10-deacetylbaccatin Ⅲ-10-β-O-acetyltransferase catalytic fitness for Taxol production[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15544. |
| 93 | LIN S L, WEI T, LIN J F, et al. Bio-production of baccatin Ⅲ, an important precursor of paclitaxel by a cost-effective approach[J]. Molecular Biotechnology, 2018, 60(7): 492-505. |
| 94 | CHEN J J, LIANG X, WANG F, et al. Combinatorial mutation on the β-glycosidase specific to 7-β-xylosyltaxanes and increasing the mutated enzyme production by engineering the recombinant yeast[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2019, 9(3): 626-638. |
| 95 | 戴黄益, 何德, 刘明志. 产紫杉醇内生真菌研究的回顾、进展及趋势[J]. 西部林业科学, 2017, 46(3): 169-176, 186. |
| DAI H Y, HE D, LIU M Z. Progress and trends on researches of taxol-producing endophytic fungi[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2017, 46(3): 169-176, 186. | |
| 96 | 徐志荣, 王婷, 娄佳兰, 等. 南方红豆杉细胞悬浮培养体系优化及动力学研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 2019, 32(1): 8-14. |
| XU Z R, WANG T, LOU J L, et al. Study on optimization of cell suspension culture system and kinetics of Taxus chinensis var. mairer [J]. Forest Research, 2019, 32(1): 8-14. | |
| 97 | ZHU X X, LIU X N, LIU T, et al. Synthetic biology of plant natural products: from pathway elucidation to engineered biosynthesis in plant cells[J]. Plant Communications, 2021, 2(5): 100229. |
| 98 | 吴迎梅, 廖庆刚, 尚轶, 等. 多组学助力紫杉醇合成生物学研究[J]. 植物科学学报, 2022, 40(6): 853-866. |
| WU Y M, LIAO Q G, SHANG Y, et al. Recent progress of paclitaxel biosynthesis aided by multi-omics[J]. Plant Science Journal, 2022, 40(6): 853-866. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | 程晓雷, 刘天罡, 陶慧. 萜类化合物的非常规生物合成研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1050-1071. |
| [12] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [13] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [14] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [15] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||