Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (5): 870-883.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-019
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Advances in synthetic biology for photosynthetic carbon assimilation
SHENG Yangyang, XU Xiumei, ZHANG Qiaohong, ZHANG Lixin
- State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Adaptation and Improvement,School of Life Sciences,Henan University,Kaifeng 475004,Henan,China
-
Received:2022-04-02Revised:2022-06-29Online:2022-11-16Published:2022-10-31 -
Contact:ZHANG Lixin
光合作用碳同化的合成生物学研究进展
盛阳阳, 徐秀美, 张巧红, 张立新
- 河南大学生命科学学院,省部共建作物逆境适应与改良国家重点实验室,河南 开封 475004
-
通讯作者:张立新 -
作者简介:盛阳阳 (1990—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为光合作用碳同化。 E-mail:shengyangyang727@163.com张立新 (1970—),男,教授。研究方向为光合作用功能调控机理。 E-mail:zhanglixin@henu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SHENG Yangyang, XU Xiumei, ZHANG Qiaohong, ZHANG Lixin. Advances in synthetic biology for photosynthetic carbon assimilation[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 870-883.
盛阳阳, 徐秀美, 张巧红, 张立新. 光合作用碳同化的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(5): 870-883.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2022-019
| 提高Rubisco酶的羧化活性 | 研究策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 寻找其他物种中高活性的Rubisco酶 | 高羧化酶活性 | [ |
| 高亲和力 | [ | |
| 筛选Rubisco酶高活性品种 | 高羧化酶活性 | [ |
| 人工合成肽 | 无明显作用 | [ |
| 引进Rubisco生物合成依赖的辅助因子 | 折叠伴侣蛋白、组装伴侣蛋白及活化酶 | [ |
Tab. 1 Summary of Rubisco enzyme activity by synthetic biological research
| 提高Rubisco酶的羧化活性 | 研究策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 寻找其他物种中高活性的Rubisco酶 | 高羧化酶活性 | [ |
| 高亲和力 | [ | |
| 筛选Rubisco酶高活性品种 | 高羧化酶活性 | [ |
| 人工合成肽 | 无明显作用 | [ |
| 引进Rubisco生物合成依赖的辅助因子 | 折叠伴侣蛋白、组装伴侣蛋白及活化酶 | [ |
| 引进CO2浓缩机制 | 研究策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| GLK基因的引入 | 促进产量增加 | [ |
| 转运蛋白的引入 | 条件促进,可以提高光合速率和碳同化率 | [ |
| 蓝藻羧酶体的引入 | 有待进一步探索研究 | [ |
Tab. 2 Summary of CO2 enrichment mechanisms by synthetic biological research
| 引进CO2浓缩机制 | 研究策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| GLK基因的引入 | 促进产量增加 | [ |
| 转运蛋白的引入 | 条件促进,可以提高光合速率和碳同化率 | [ |
| 蓝藻羧酶体的引入 | 有待进一步探索研究 | [ |
| 降低光呼吸 | 研究策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 叶绿体甘油酸支路 | 叶绿体乙醇酸转化为甘油酸,生物量增加,无NH3的释放 | [ |
| 过氧化物酶体甘油酸支路 | 绕过了线粒体中的甘氨酸到丝氨酸的转化,同时将CO2释放的位置从线粒体转移到过氧化物酶体,无NH3的释放 | [ |
| 叶绿体乙醇酸氧化支路 | 光呼吸途径的碳全部丢失,无NH3的释放 | [ |
| 3-羟基丙酸盐支路 | 实现光呼吸期间CO2的净同化,无NH3的释放 | [ |
Tab. 3 Summary of photorespiration pathways by synthetic biological research
| 降低光呼吸 | 研究策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 叶绿体甘油酸支路 | 叶绿体乙醇酸转化为甘油酸,生物量增加,无NH3的释放 | [ |
| 过氧化物酶体甘油酸支路 | 绕过了线粒体中的甘氨酸到丝氨酸的转化,同时将CO2释放的位置从线粒体转移到过氧化物酶体,无NH3的释放 | [ |
| 叶绿体乙醇酸氧化支路 | 光呼吸途径的碳全部丢失,无NH3的释放 | [ |
| 3-羟基丙酸盐支路 | 实现光呼吸期间CO2的净同化,无NH3的释放 | [ |

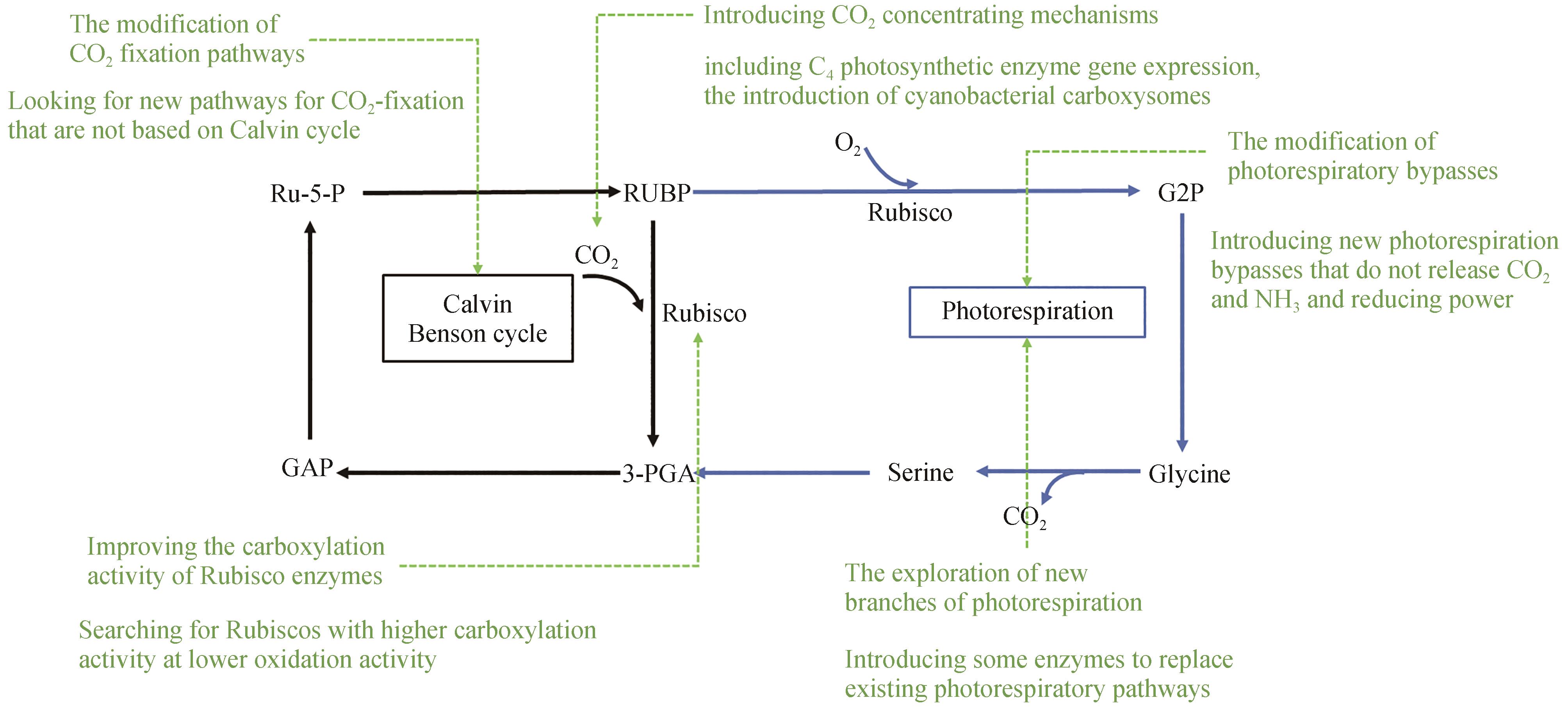
Fig. 2 Natural and synthetic photorespiratory bypassesBlack arrow, classic photorespiratory bypass; Blue arrow, chloroplastic glycerate bypass; Orange arrow, peroxisomal glycerate bypass; Green arrow, chloroplastic glycolate oxidation bypass; Purple arrow, 3-hydroxypropionate bypass; Red arrow, A new photorespiratory bypasses in riceRUBP—Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate; G2P—2-phosphoglyceric acid; 3-PGA—3-phosphoglyceric acid
| 59 | RAVEN J A, COCKELL C S, DE LA ROCHA C L. The evolution of inorganic carbon concentrating mechanisms in photosynthesis[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B, Biological Sciences, 2008, 363(1504): 2641-2650. |
| 60 | LANGDALE J A. C4 cycles: past, present, and future research on C4 photosynthesis[J]. The Plant Cell, 2011, 23(11): 3879-3892. |
| 61 | KLAVSEN S K, MADSEN T V, MABERLY S C. Crassulacean acid metabolism in the context of other carbon-concentrating mechanisms in freshwater plants: a review[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2011, 109(1/2/3): 269-279. |
| 62 | VON CAEMMERER S, QUICK W P, FURBANK R T. The development of C₄ rice: current progress and future challenges[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6089): 1671-1672. |
| 63 | LONG S P, MARSHALL-COLON A, ZHU X G. Meeting the global food demand of the future by engineering crop photosynthesis and yield potential[J]. Cell, 2015, 161(1): 56-66. |
| 64 | MIYAO M, MASUMOTO C, MIYAZAWA S I, et al. Lessons from engineering a single-cell C4 photosynthetic pathway into rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(9): 3021-3029. |
| 65 | WANG P, KHOSHRAVESH R, KARKI S, et al. Re-creation of a key step in the evolutionary switch from C3 to C4 leaf anatomy[J]. Current Biology, 2017, 27(21): 3278-3287.e6. |
| 66 | YEH S Y, LIN H H, CHANG Y M, et al. Maize Golden2-like transcription factors boost rice chloroplast development, photosynthesis, and grain yield[J]. Plant Physiology, 2021, 188(1): 442-459. |
| 67 | MCGRATH J M, LONG S P. Can the cyanobacterial carbon-concentrating mechanism increase photosynthesis in crop species? A theoretical analysis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2014, 164(4): 2247-2261. |
| 68 | YANG S M, CHANG C Y, YANAGISAWA M, et al. Transgenic rice expressing cyanobacterial bicarbonate transporter exhibited enhanced photosynthesis, growth and grain yield[J]. Photosynthesis Energy from the Sun, 2008:1247-1250. |
| 69 | HAY W T, BIHMIDINE S, MUTLU N, et al. Enhancing soybean photosynthetic CO2 assimilation using a cyanobacterial membrane protein, ictB [J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2017, 212: 58-68. |
| 70 | ROLLAND V, BADGER M R, PRICE G D. Redirecting the cyanobacterial bicarbonate transporters BicA and SbtA to the chloroplast envelope: soluble and membrane cargos need different chloroplast targeting signals in plants[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 185. |
| 71 | UEHARA S, ADACHI F, ITO-INABA Y, et al. Specific and efficient targeting of cyanobacterial bicarbonate transporters to the inner envelope membrane of chloroplasts in Arabidopsis [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 16. |
| 72 | ATKINSON N, FEIKE D, MACKINDER L C M, et al. Introducing an algal carbon-concentrating mechanism into higher plants: location and incorporation of key components[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 14(5): 1302-1315. |
| 73 | BADGER M R, HANSON D, PRICE G D. Evolution and diversity of CO2 concentrating mechanisms in cyanobacteria[J]. Functional Plant Biology: FPB, 2002, 29(3): 161-173. |
| 74 | LONG B M, RAE B D, ROLLAND V, et al. Cyanobacterial CO2-concentrating mechanism components: function and prospects for plant metabolic engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2016, 31: 1-8. |
| 75 | RAE B D, LONG B M, BADGER M R, et al. Functions, compositions, and evolution of the two types of carboxysomes: polyhedral microcompartments that facilitate CO2 fixation in cyanobacteria and some proteobacteria[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews: MMBR, 2013, 77(3): 357-379. |
| 76 | LONG B M, BADGER M R, WHITNEY S M, et al. Analysis of carboxysomes from Synechococcus PCC7942 reveals multiple Rubisco complexes with carboxysomal proteins CcmM and CcaA[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2007, 282(40): 29323-29335. |
| 77 | PRICE G D, BADGER M R, WOODGER F J, et al. Advances in understanding the cyanobacterial CO2-concentrating-mechanism (CCM): functional components, Ci transporters, diversity, genetic regulation and prospects for engineering into plants[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2007, 59(7): 1441-1461. |
| 78 | PRICE G D. Inorganic carbon transporters of the cyanobacterial CO2 concentrating mechanism[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2011, 109(1/2/3): 47-57. |
| 79 | SHIVELY J M, BALL F, BROWN D H, et al. Functional organelles in prokaryotes: polyhedral inclusions (carboxysomes) of Thiobacillus neapolitanus [J]. Scientific Reports, 1973, 182(4112): 584-586. |
| 80 | CANNON G C, HEINHORST S, KERFELD C A. Carboxysomal carbonic anhydrases: structure and role in microbial CO2 fixation[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Proteins and Proteomics, 2010, 1804(2): 382-392. |
| 81 | SO A K C, ESPIE G S, WILLIAMS E B, et al. A novel evolutionary lineage of carbonic anhydrase (ε class) is a component of the carboxysome shell[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2004, 186(3): 623-630. |
| 82 | MANGAN N M, FLAMHOLZ A, HOOD R D, et al. pH determines the energetic efficiency of the cyanobacterial CO2 concentrating mechanism[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(36): E5354-E5362. |
| 83 | GONZALEZ-ESQUER C R, SHUBITOWSKI T B, KERFELD C A. Streamlined construction of the cyanobacterial CO2-fixing organelle via protein domain fusions for use in plant synthetic biology[J]. The Plant Cell, 2015, 27(9): 2637-2644. |
| 84 | LIN M T, OCCHIALINI A, ANDRALOJC P J, et al. β-Carboxysomal proteins assemble into highly organized structures in Nicotiana chloroplasts[J]. The Plant Journal, 2014, 79(1): 1-12. |
| 85 | BONACCI W, TENG P K, AFONSO B, et al. Modularity of a carbon-fixing protein organelle[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(2): 478-483. |
| 86 | PENGELLY J J L, FÖRSTER B, VON CAEMMERER S, et al. Transplastomic integration of a cyanobacterial bicarbonate transporter into tobacco chloroplasts[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2014, 65(12): 3071-3080. |
| 87 | LONG B M, HEE W Y, SHARWOOD R E, et al. Carboxysome encapsulation of the CO2-fixing enzyme Rubisco in tobacco chloroplasts[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3570. |
| 88 | HANSON M R, LIN M T, CARMO-SILVA A E, et al. Towards engineering carboxysomes into C3 plants[J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2016, 87(1): 38-50. |
| 89 | TCHERKEZ G. The mechanism of Rubisco-catalysed oxygenation[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2016, 39(5): 983-997. |
| 90 | MAURINO V G, PETERHANSEL C. Photorespiration: current status and approaches for metabolic engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2010, 13(3): 248-255. |
| 91 | PETERHANSEL C, MAURINO V G. Photorespiration redesigned[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 155(1): 49-55. |
| 92 | FIELD C B, BEHRENFELD M J, RANDERSON J T, et al. Primary production of the biosphere: integrating terrestrial and oceanic components[J]. Science, 1998, 281(5374): 237-240. |
| 93 | GIORDANO M, BEARDALL J, RAVEN J A. CO2 concentrating mechanisms in algae: mechanisms, environmental modulation, and evolution[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2005, 56: 99-131. |
| 94 | WINGLER A, LEA P J, QUICK W P, et al. Photorespiration: metabolic pathways and their role in stress protection[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 2000, 355(1402): 1517-1529. |
| 95 | SOUTH P F, CAVANAGH A P, LIU H W, et al. Synthetic glycolate metabolism pathways stimulate crop growth and productivity in the field[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6422): eaat9077. |
| 96 | TIMM S, NUNES-NESI A, PÄRNIK T, et al. A cytosolic pathway for the conversion of hydroxypyruvate to glycerate during photorespiration in Arabidopsis [J]. The Plant Cell, 2008, 20(10): 2848-2859. |
| 1 | SILVIA M. Agriculture has to increase production by 70%: FAO chief[EB/OL]. [2009-10-14]. . |
| 2 | TILMAN D, CASSMAN K G, MATSON P A, et al. Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices[J]. Nature, 2002, 418(6898): 671-677. |
| 3 | MAURINO V G, WEBER A P M. Engineering photosynthesis in plants and synthetic microorganisms[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 64(3): 743-751. |
| 4 | WHITNEY S M, HOUTZ R L, ALONSO H. Advancing our understanding and capacity to engineer nature's CO2-sequestering enzyme, Rubisco[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 155(1): 27-35. |
| 5 | ZHU X G, LONG S P, ORT D R. Improving photosynthetic efficiency for greater yield[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010, 61: 235-261. |
| 6 | 程建峰, 沈允钢. 试析光合作用的研究动向[J]. 植物学报, 2011, 46(6): 694-704. |
| CHENG J F, SHEN Y G. On the trends of photosynthesis research[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2011, 46(6): 694-704. | |
| 7 | 朱观林, 郭龙彪, 钱前. 水稻的高光效分子育种[J]. 中国稻米, 2009, 15(5): 5-10. |
| ZHU G L, GUO L B, QIAN Q. Molecular breeding of rice with high light efficiency[J]. China Rice, 2009, 15(5): 5-10. | |
| 8 | 张立新, 卢从明, 彭连伟, 等. 利用合成生物学原理提高光合作用效率的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2017, 33(3): 486-493. |
| ZHANG L X, LU C M, PENG L W, et al. Progress in improving photosynthetic efficiency by synthetic biology[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 33(3): 486-493. | |
| 9 | 程建峰, 沈允钢. 作物高光效之管见[J]. 作物学报, 2010, 36(8): 1235-1247. |
| CHENG J F, SHEN Y G. My humble opinions on high photosynthetic efficiency of crop[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2010, 36(8): 1235-1247. | |
| 10 | 张春霆. 合成生物学: 我国急需发展的前沿科学[J]. 前沿科学, 2007, 1(3): 55. |
| ZHANG C T. Synthetic biology: frontier science in urgent need of development in China[J]. Frontier Science, 2007, 1(3): 55. | |
| 11 | DRUBIN D A, WAY J C, SILVER P A. Designing biological systems[J]. Genes & Development, 2007, 21(3): 242-254. |
| 12 | 熊燕, 陈大明, 杨琛, 等. 合成生物学发展现状与前景[J]. 生命科学, 2011, 23(9): 826-837. |
| XIONG Y, CHEN D M, YANG C, et al. Progress and perspective of synthetic biology[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2011, 23(9): 826-837. | |
| 13 | STEEN E J, KANG Y S, BOKINSKY G, et al. Microbial production of fatty-acid-derived fuels and chemicals from plant biomass[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7280):559-563. |
| 14 | DEKISHIMA Y, LAN E I, SHEN C R, et al. Extending carbon chain length of 1-butanol pathway for 1-hexanol synthesis from glucose by engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(30):11399-11401. |
| 15 | MAHISHI L H, TRIPATHI G, RAWAL S K. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) synthesis by recombinant Escherichia coli harbouring Streptomyces aureofaciens PHB biosynthesis genes: effect of various carbon and nitrogen sources[J]. Microbiological Research, 2003, 158(1): 19-27. |
| 16 | YANG T H, KIM T W, KANG H O, et al. Biosynthesis of polylactic acid and its copolymers using evolved propionate CoA transferase and PHA synthase[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2010, 105(1): 150-160. |
| 17 | AJIKUMAR P K, XIAO W H, TYO K E J, et al. Isoprenoid pathway optimization for taxol precursor overproduction in Escherichia coli [J]. Science, 2010, 330(6000): 70-74. |
| 18 | LEVSKAYA A, CHEVALIER A A, TABOR J J, et al. Engineering Escherichia coli to see light[J]. Nature, 2005, 438(7067): 441-442. |
| 97 | AHMAD R, BILAL M, JEON J H, et al. Improvement of biomass accumulation of potato plants by transformation of cyanobacterial photorespiratory glycolate catabolism pathway genes[J]. Plant Biotechnology Reports, 2016, 10(5): 269-276. |
| 98 | DE F C CARVALHO J, MADGWICK P J, POWERS S J, et al. An engineered pathway for glyoxylate metabolism in tobacco plants aimed to avoid the release of ammonia in photorespiration[J]. BMC Biotechnology, 2011, 11: 111. |
| 99 | MAIER A, FAHNENSTICH H, VON CAEMMERER S, et al. Transgenic introduction of a glycolate oxidative cycle into A. thaliana chloroplasts leads to growth improvement[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2012, 3: 38. |
| 100 | KEBEISH R, NIESSEN M, THIRUVEEDHI K, et al. Chloroplastic photorespiratory bypass increases photosynthesis and biomass production in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2007, 25(5): 593-599. |
| 101 | SHIH P M, ZARZYCKI J, NIYOGI K K, et al. Introduction of a synthetic CO2-fixing photorespiratory bypass into a Cyanobacterium[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2014, 289(14): 9493-9500. |
| 102 | ERB T J, ZARZYCKI J. Biochemical and synthetic biology approaches to improve photosynthetic CO2-fixation[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2016, 34: 72-79. |
| 103 | DALAL J, LOPEZ H, VASANI N B, et al. A photorespiratory bypass increases plant growth and seed yield in biofuel crop Camelina sativa [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2015, 8: 175. |
| 104 | NÖLKE G, HOUDELET M, KREUZALER F, et al. The expression of a recombinant glycolate dehydrogenase polyprotein in potato (Solanum tuberosum) plastids strongly enhances photosynthesis and tuber yield[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2014, 12(6): 734-742. |
| 105 | FAHNENSTICH H, SCARPECI T E, VALLE E M, et al. Generation of hydrogen peroxide in chloroplasts of Arabidopsis overexpressing glycolate oxidase as an inducible system to study oxidative stress[J]. Plant Physiology, 2008, 148(2): 719-729. |
| 106 | OLIVER D J. The effect of glyoxylate on photosynthesis and photorespiration by isolated soybean mesophyll cells[J]. Plant Physiology, 1980, 65(5): 888-892. |
| 107 | XIN C P, THOLEN D, DEVLOO V, et al. The benefits of photorespiratory bypasses: how can they work? [J]. Plant Physiology, 2014, 167(2): 574-585. |
| 108 | PETERHANSEL C, BLUME C, OFFERMANN S. Photorespiratory bypasses: how can they work? [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 64(3): 709-715. |
| 19 | TOPP S, GALLIVAN J P. Riboswitches in unexpected places - a synthetic riboswitch in a protein coding region[J]. RNA, 2008, 14(12): 2498-2503. |
| 20 | WERLEN C, JASPERS M C M, VAN DER MEER J R. Measurement of biologically available naphthalene in gas and aqueous phases by use of a Pseudomonas putida biosensor[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70(1): 43-51. |
| 21 | ATSUMI S, HANAI T, LIAO J C. Non-fermentative pathways for synthesis of branched-chain higher alcohols as biofuels[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7174): 86-89. |
| 22 | ZHANG K C, SAWAYA M R, EISENBERG D S, et al. Expanding metabolism for biosynthesis of nonnatural alcohols[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(52): 20653-20658. |
| 23 | SHEN C R, LAN E I, DEKISHIMA Y, et al. Driving forces enable high-titer anaerobic 1-butanol synthesis in Escherichia coli [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(9): 2905-2915. |
| 24 | HANANIA U, ARIEL T, TEKOAH Y, et al. Establishment of a tobacco BY2 cell line devoid of plant-specific xylose and fucose as a platform for the production of biotherapeutic proteins[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(9): 1120-1129. |
| 25 | ČERMÁK T, CURTIN S J, GIL-HUMANES J, et al. A multipurpose toolkit to enable advanced genome engineering in plants[J]. The Plant Cell, 2017, 29(6): 1196-1217. |
| 26 | PARRY M A J, KEYS A J, MADGWICK P J, et al. Rubisco regulation: a role for inhibitors[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2008, 59(7): 1569-1580. |
| 27 | ANDERSSON I, BACKLUND A. Structure and function of Rubisco[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2008, 46(3): 275-291. |
| 28 | ANDERSSON I. Catalysis and regulation in Rubisco[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2008, 59(7): 1555-1568. |
| 29 | WHITNEY S M, BALDET P, HUDSON G S, et al. Form I Rubiscos from non-green algae are expressed abundantly but not assembled in tobacco chloroplasts[J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2001, 26(5): 535-547. |
| 30 | LIN M T, OCCHIALINI A, ANDRALOJC P J, et al. A faster Rubisco with potential to increase photosynthesis in crops[J]. Nature, 2014, 513(7519): 547-550. |
| 31 | ZHU X G, PORTIS A R, LONG S P. Would transformation of C3 crop plants with foreign Rubisco increase productivity? A computational analysis extrapolating from kinetic properties to canopy photosynthesis[J]. Plant, Cell and Environment, 2004, 27(2): 155-165. |
| 32 | MATSUMURA H, SHIOMI K, YAMAMOTO A, et al. Hybrid Rubisco with complete replacement of rice Rubisco small subunits by sorghum counterparts confers C4 plant-like high catalytic activity[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(11): 1570-1581. |
| 33 | PRINS A, ORR D J, ANDRALOJC P J, et al. Rubisco catalytic properties of wild and domesticated relatives provide scope for improving wheat photosynthesis[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(6): 1827-1838. |
| 34 | WHITNEY S M, KANE H J, HOUTZ R L, et al. Rubisco oligomers composed of linked small and large subunits assemble in tobacco plastids and have higher affinities for CO2 and O2 [J]. Plant Physiology, 2009, 149(4): 1887-1895. |
| 35 | DURÃO P, AIGNER H, NAGY P, et al. Opposing effects of folding and assembly chaperones on evolvability of Rubisco[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(2): 148-155. |
| 46 | GUTTERIDGE S, GATENBY A A. Rubisco synthesis, assembly, mechanism, and regulation[J]. The Plant Cell, 1995, 7(7): 809-819. |
| 37 | QU Y C, SAKODA K, FUKAYAMA H, et al. Overexpression of both Rubisco and Rubisco activase rescues rice photosynthesis and biomass under heat stress[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2021, 44(7): 2308-2320. |
| 38 | KANEVSKI I, MALIGA P, RHOADES D F, et al. Plastome engineering of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in tobacco to form a sunflower large subunit and tobacco small subunit hybrid[J]. Plant Physiology, 1999, 119(1): 133-142. |
| 39 | WHITNEY S M, ANDREWS T J. Plastome-encoded bacterial ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RubisCO) supports photosynthesis and growth in tobacco[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2001, 98(25): 14738-14743. |
| 40 | ISHIKAWA C, HATANAKA T, MISOO S, et al. Functional incorporation of sorghum small subunit increases the catalytic turnover rate of Rubisco in transgenic rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(3): 1603-1611. |
| 41 | MARTIN-AVILA E, LIM Y L, BIRCH R, et al. Modifying plant photosynthesis and growth via simultaneous chloroplast transformation of Rubisco large and small subunits[J]. The Plant Cell, 2020, 32(9): 2898-2916. |
| 42 | PARRY M A J, ANDRALOJC P J, MITCHELL R A C, et al. Manipulation of Rubisco: the amount, activity, function and regulation[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2003, 54(386): 1321-1333. |
| 43 | SPREITZER R J, SALVUCCI M E. Rubisco: structure, regulatory interactions, and possibilities for a better enzyme[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2002, 53: 449-475. |
| 44 | PORTIS A R JR. Rubisco activase-rubisco's catalytic chaperone[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2003, 75(1): 11-27. |
| 45 | 张国, 王玮, 邹琦. Rubisco活化酶的分子生物学[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2004, 40(5): 633-637. |
| ZHANG G, WANG W, ZOU Q. Molecular biology of rubisco activase[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2004, 40(5): 633-637. | |
| 46 | REITH M, CATTOLICO R A. Inverted repeat of Olisthodiscus luteus chloroplast DNA contains genes for both subunits of ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase and the 32,000-dalton QB protein: phylogenetic implications[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1986, 83(22): 8599-8603. |
| 47 | DELWICHE C F, PALMER J D. Rampant horizontal transfer and duplication of Rubisco genes in eubacteria and plastids[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 1996, 13(6): 873-882. |
| 48 | TABITA F R. Microbial ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase: a different perspective[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 1999, 60(1):1-28. |
| 49 | JOSHI J, MUELLER-CAJAR O, TSAI Y C C, et al. Role of small subunit in mediating assembly of red-type form I Rubisco[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2015, 290(2): 1066-1074. |
| 50 | GUNN L H, MARTIN AVILA E, BIRCH R, et al. The dependency of red Rubisco on its cognate activase for enhancing plant photosynthesis and growth[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(41): 25890-25896. |
| 51 | SALESSE-SMITH C E, SHARWOOD R E, BUSCH F A, et al. Overexpression of Rubisco subunits with RAF1 increases Rubisco content in maize[J]. Nature Plants, 2018, 4(10): 802-810. |
| 52 | WHITNEY S M, BIRCH R, KELSO C, et al. Improving recombinant Rubisco biogenesis, plant photosynthesis and growth by coexpressing its ancillary RAF1 chaperone[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(11): 3564-3569. |
| 53 | FLECKEN M, WANG H P, POPILKA L, et al. Dual functions of a Rubisco activase in metabolic repair and recruitment to carboxysomes[J]. Cell, 2020, 183(2): 457-473.e20. |
| 54 | SASCHENBRECKER S, BRACHER A, RAO K V, et al. Structure and function of RbcX, an assembly chaperone for hexadecameric rubisco[J]. Cell, 2007, 129(6): 1189-1200. |
| 55 | XIA L Y, JIANG Y L, KONG W W, et al. Molecular basis for the assembly of RuBisCO assisted by the chaperone Raf1[J]. Nature Plants, 2020, 6(6): 708-717. |
| 56 | HUANG F, KONG W W, SUN Y Q, et al. Rubisco accumulation factor 1 (Raf1) plays essential roles in mediating Rubisco assembly and carboxysome biogenesis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(29): 17418-17428. |
| 57 | PARRY M A J, ANDRALOJC P J, SCALES J C, et al. Rubisco activity and regulation as targets for crop improvement[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 64(3): 717-730. |
| 58 | CAI Z, LIU G X, ZHANG J L, et al. Development of an activity-directed selection system enabled significant improvement of the carboxylation efficiency of Rubisco[J]. Protein & Cell, 2014, 5(7): 552-562. |
| 109 | BETTI M, BAUWE H, BUSCH F A, et al. Manipulating photorespiration to increase plant productivity: recent advances and perspectives for crop improvement[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(10): 2977-2988. |
| 110 | SAGE T L, SAGE R F. The functional anatomy of rice leaves: implications for refixation of photorespiratory CO2 and efforts to engineer C4 photosynthesis into rice[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2009, 50(4): 756-772. |
| 111 | BUSCH F A, SAGE T L, COUSINS A B, et al. C3 plants enhance rates of photosynthesis by reassimilating photorespired and respired CO2 [J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2013, 36(1): 200-212. |
| 112 | BRAUN H P, ZABALETA E. Carbonic anhydrase subunits of the mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase complex (complex I) in plants[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2007, 129(1): 114-122. |
| 113 | KHURSHID G, ABBASSI A Z, KHALID M F, et al. A cyanobacterial photorespiratory bypass model to enhance photosynthesis by rerouting photorespiratory pathway in C3 plants[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 20879. |
| 114 | SHEN B R, WANG L M, LIN X L, et al. Engineering a new chloroplastic photorespiratory bypass to increase photosynthetic efficiency and productivity in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(2): 199-214. |
| 115 | Online computer library center: future agriculture project[EB/OL]. http: . |
| [1] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [12] | CAI Bingyu, TAN Xiangtian, LI Wei. Advances in synthetic biology for engineering stem cell [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [13] | XIE Huang, ZHENG Yilei, SU Yiting, RUAN Jingyi, LI Yongquan. An overview on reconstructing the biosynthetic system of actinomycetes for polyketides production [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [14] | ZHA Wenlong, BU Lan, ZI Jiachen. Advances in synthetic biology for producing potent pharmaceutical ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| [15] | HUI Zhen, TANG Xiaoyu. Applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 editing system in the study of microbial natural products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||