Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (2): 263-282.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-067
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Applications of microbial synthetic biology in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases
GAO Xianyun, NIU Lingxue, JIAN Ni, GUAN Ningzi
- Shanghai Key Laboratory of Regulatory Biology,School of Life Sciences,East China Normal University,Shanghai 200241,China
-
Received:2022-11-24Revised:2023-01-21Online:2023-04-27Published:2023-04-30 -
Contact:GUAN Ningzi
微生物合成生物学在疾病诊疗上的应用进展
高纤云, 牛灵雪, 见妮, 管宁子
- 华东师范大学生命科学学院,上海市调控生物学重点实验室,上海 200241
-
通讯作者:管宁子 -
作者简介:高纤云 (1999—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为益生菌传感器的开发与应用。E-mail:Xianyun_gao@163.com管宁子 (1987—),女,副研究员,硕士生导师。研究方向为微生物医学合成生物学,包括智能微生物药物工厂设计构建、益生菌传感器开发、原核细胞使能技术开发、精准可控的肿瘤免疫治疗等。E-mail:nzguan@bio.ecnu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2019YFA0904500);国家自然科学基金(31901023)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
GAO Xianyun, NIU Lingxue, JIAN Ni, GUAN Ningzi. Applications of microbial synthetic biology in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(2): 263-282.
高纤云, 牛灵雪, 见妮, 管宁子. 微生物合成生物学在疾病诊疗上的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(2): 263-282.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2022-067

Fig. 2 Prevention and treatment of pathogen infection with engineered microorganisms(a) Gene circuit developed with TypeⅠquorum sensing mechanism in P. aeruginosa. The transcription factor LasR synthesized by engineered Escherichia coli can bind to acyl hyperserine lactone (AHL), a quorum sensing autoinducer secreted by P. aeruginosa, to activate the synthesis of the lysin: pseudomonectin.(b) Lactobacillus reuteri engineered with Staphylococcus aureus detection system through the Agr quorum sensing mechanism (agrQS). The expression of glucuronidase GusA is repressed by AIP-I to inhibit the enzymatic hydrolysis of 4-nitrobenzen-β-D-glucosidic acid to produce p-nitrophenol, a yellow pigment that can be detected at 405 nm. Thus, AIP-I from nanomolar to micromolar level can be detected by the change of light absorbance.(c) A closed-loop detection and killing device for Escherichia coli based on Vibrio cholerae quorum sensing. Autoinductor CAI-1 secreted by E. coli can activate the expression of YebF-Art-085 to lyse the bacteria, releasing intracellular autolysin Art-085 to kill V. cholerae.(d) Design of Lactococcus lactate hybrid receptor CqsS-NisK, which detects Vibrio cholerae by sensing inducer CAI-1 to trigger the expression of gene encode an enzyme reporter that can be easily detected in fecal samples.
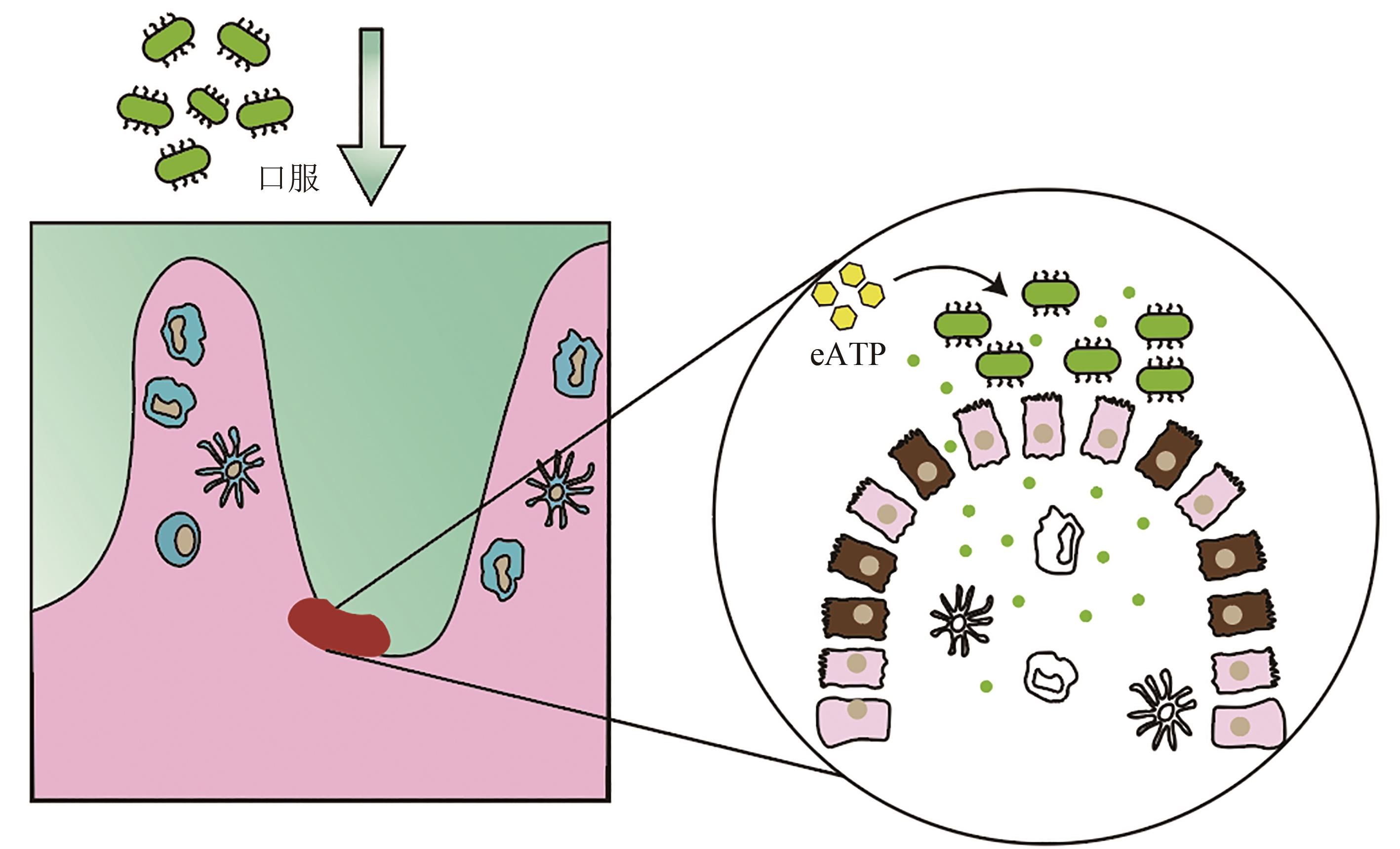
Fig. 5 Alleviation of enteritis by oral administration of engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Highly sensitive human purinergic receptor P2Y2 is expressed in S. cerevisiae, and EATP-degrading enzyme is designed to be secreted when P2Y2 receptor is activated. Engineering S. cerevisiae is constructed to sense and regulate the pro-inflammatory molecules
| 1 | CHUA K J, KWOK W C, AGGARWAL N, et al. Designer probiotics for the prevention and treatment of human diseases[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2017, 40: 8-16. |
| 2 | CHARBONNEAU M R, ISABELLA V M, LI N, et al. Developing a new class of engineered live bacterial therapeutics to treat human diseases[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1738. |
| 3 | VANDENBROUCKE K, DE HAARD H, BEIRNAERT E, et al. Orally administered L. lactis secreting an anti-TNF Nanobody demonstrate efficacy in chronic colitis[J]. Mucosal Immunology, 2010, 3(1): 49-56. |
| 4 | 韦瑶, 龚剑峰, 朱维铭, 等. 粪便菌群移植治疗溃疡性结肠炎9例临床分析[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2014, 34(10): 970-973. |
| WEI Y, GONG J F, ZHU W M, et al. Effect of fecal microbiota transplantation on uerative colitis: a study of 9 patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Surgery, 2014, 34(10): 970-973. | |
| 5 | FDA. Enforcement policy regarding investigational new drug requirements for use of fecal microbiota for transplantation to treat Clostridium difficile infection not responsive to standard therapies[EB/OL]. [2022-12-01]. . |
| 6 | GOH Y L, HE H F, MARCH J C. Engineering commensal bacteria for prophylaxis against infection[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2012, 23(6): 924-930. |
| 7 | YANG G L, JIANG Y L, YANG W T, et al. Effective treatment of hypertension by recombinant Lactobacillus plantarum expressing angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptide[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14(1): 202. |
| 8 | DUONG M T Q, QIN Y S, YOU S H, et al. Bacteria-cancer interactions: bacteria-based cancer therapy[J]. Experimental & Molecular Medicine, 2019, 51(12): 1-15. |
| 9 | GURBATRI C R, ARPAIA N, DANINO T. Engineering bacteria as interactive cancer therapies[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6622): 858-864. |
| 10 | SOUZA B M, PREISSER T M, PEREIRA V B, et al. Lactococcus lactis carrying the pValac eukaryotic expression vector coding for IL-4 reduces chemically-induced intestinal inflammation by increasing the levels of IL-10-producing regulatory cells[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15(1): 150. |
| 11 | AUSLÄNDER S, AUSLÄNDER D, FUSSENEGGER M. Synthetic biology-the synthesis of biology[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2017, 56(23): 6396-6419. |
| 12 | STEIDLER L, HANS W, SCHOTTE L, et al. Treatment of murine colitis by Lactococcus lactis secreting interleukin-10[J]. Science, 2000, 289(5483): 1352-1355. |
| 13 | TABOR J J, GROBAN E S, VOIGT C A. Performance characteristics for sensors and circuits used to program E. coli [M]//Systems biology and biotechnology of Escherichia coli. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 2009: 401-439. |
| 14 | WETTSTADT S, LLAMAS M A. Role of regulated proteolysis in the communication of bacteria with the environment[J]. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 2020, 7: 586497. |
| 15 | GAO R, STOCK A M. Biological insights from structures of two-component proteins[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2009, 63: 133-154. |
| 16 | SCHMIDL S R, EKNESS F, SOFJAN K, et al. Rewiring bacterial two-component systems by modular DNA-binding domain swapping[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(7): 690-698. |
| 17 | LAZAR J T, TABOR J J. Bacterial two-component systems as sensors for synthetic biology applications[J]. Current Opinion in Systems Biology, 2021, 28: 100398. |
| 18 | THEURETZBACHER U. Accelerating resistance, inadequate antibacterial drug pipelines and international responses[J]. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 2012, 39(4): 295-299. |
| 19 | SPELLBERG B, BARTLETT J, WUNDERINK R, et al. Novel approaches are needed to develop tomorrow's antibacterial therapies[J]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 2015, 191(2): 135-140. |
| 20 | LI L, KOIRALA B, HERNANDEZ Y, et al. Identification of structurally diverse menaquinone-binding antibiotics with in vivo activity against multidrug-resistant pathogens[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2022, 7(1): 120-131. |
| 21 | SMITH D R, TEMIME L, OPATOWSKI L. Microbiome-pathogen interactions drive epidemiological dynamics of antibiotic resistance: a modeling study applied to nosocomial pathogen control[J]. eLife, 2021, 10: e68764. |
| 22 | PALMA M L, GARCIA-BATES T M, MARTINS F S, et al. Correction to: genetically engineered probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains mature human dendritic cells and stimulate Gag-specific memory CD8+ T cells ex vivo [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(13): 5461. |
| 23 | KAMIYA S, YONEZAWA H, OSAKI T. Role of probiotics in eradication therapy for helicobacter pylori infection[J]. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 2019, 1149: 243-255. |
| 24 | VALDÉS-VARELA L, GUEIMONDE M, RUAS-MADIEDO P. Probiotics for prevention and treatment of clostridium difficile infection[J]. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 2018, 1050: 161-176. |
| 25 | ENACHE-ANGOULVANT A, HENNEQUIN C. Invasive Saccharomyces infection: a comprehensive review[J]. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 2005, 41(11): 1559-1568. |
| 26 | MUÑOZ P, BOUZA E, CUENCA-ESTRELLA M, et al. Saccharomyces cerevisiae fungemia: an emerging infectious disease[J]. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 2005, 40(11): 1625-1634. |
| 27 | BESSELINK M H, VAN SANTVOORT H C, BUSKENS E, et al. Probiotic prophylaxis in patients with predicted severe acute pancreatitis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Nederlands Tijdschrift Voor Geneeskunde, 2008, 152(12): 685-696. |
| 28 | HWANG I Y, LEE H L, HUANG J G, et al. Engineering microbes for targeted strikes against human pathogens[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2018, 75(15): 2719-2733. |
| 29 | CHANG W, SMALL D A, TOGHROL F, et al. Microarray analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa reveals induction of pyocin genes in response to hydrogen peroxide[J]. BMC Genomics, 2005, 6: 115. |
| 30 | CHANG W, SMALL D A, TOGHROL F, et al. Microarray analysis of toxicogenomic effects of peracetic acid on Pseudomonas aeruginosa [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(15): 5893-5899. |
| 31 | SAEIDI N, WONG C K, LO T M, et al. Engineering microbes to sense and eradicate Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a human pathogen[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2011, 7: 521. |
| 32 | HWANG I Y, TAN M H, KOH E, et al. Reprogramming microbes to be pathogen-seeking killers[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2014, 3(4): 228-237. |
| 33 | HWANG I Y, KOH E, WONG A, et al. Engineered probiotic Escherichia coli can eliminate and prevent Pseudomonas aeruginosa gut infection in animal models[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15028. |
| 34 | BEGLEY M, GAHAN C G M, HILL C. The interaction between bacteria and bile[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2005, 29(4): 625-651. |
| 35 | RIDLON J M, KANG D J, HYLEMON P B. Bile salt biotransformations by human intestinal bacteria[J]. Journal of Lipid Research, 2006, 47(2): 241-259. |
| 36 | ZHU D L, SORG J A, SUN X M. Clostridioides difficile biology: sporulation, germination, and corresponding therapies for C. difficile infection[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2018, 8: 29. |
| 37 | KOH E, HWANG I Y, LEE H L, et al. Engineering probiotics to inhibit Clostridioides difficile infection by dynamic regulation of intestinal metabolism[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 3834. |
| 38 | PALMER J D, PIATTELLI E, MCCORMICK B A, et al. Engineered probiotic for the inhibition of salmonella via tetrathionate-induced production of microcin H47[J]. ACS Infectious Diseases, 2018, 4(1): 39-45. |
| 39 | BLOT S, VANDEWOUDE K, COLARDYN F. Staphylococcus aureus infections[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 1998, 339(27): 2025-2026, authorreply 2026-2027. |
| 40 | LUBKOWICZ D, HO C L, HWANG I Y, et al. Reprogramming probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri as a biosensor for Staphylococcus aureus derived AIP-I detection[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(5): 1229-1237. |
| 41 | JAYARAMAN P, HOLOWKO M B, YEOH J W, et al. Repurposing a two-component system-based biosensor for the killing of vibrio cholerae[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(7): 1403-1415. |
| 42 | MAO N, CUBILLOS-RUIZ A, CAMERON D E, et al. Probiotic strains detect and suppress cholera in mice[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2018, 10(445): eaao2586. |
| 43 | BORRERO J, CHEN Y Q, DUNNY G M, et al. Modified lactic acid bacteria detect and inhibit multiresistant enterococci[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(3): 299-306. |
| 44 | GELDART K, BORRERO J, KAZNESSIS Y N. Chloride-inducible expression vector for delivery of antimicrobial peptides targeting antibiotic-resistant enterococcus faecium[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(11): 3889-3897. |
| 45 | GEBRAYEL P, NICCO C, KHODOR S AL, et al. Microbiota medicine: towards clinical revolution[J].Journal of Translational Medicine, 2022, 20(1): 1-20. |
| 46 | 刘俊希, 王舒, 魏祯, 等. 中药有效成分通过调节肠道菌群及代谢物组成影响相关疾病治疗作用概述[J]. 中医药学报, 2022, 50(2): 92-97. |
| LIU J X, WANG S, WEI Z, et al. Therapeutic effects of active components of Chinese medicinal on related diseases by regulating intestinal flora and metabolite composition[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology, 2022, 50(2): 92-97. | |
| 47 | 丁萌, 郭栋. 从脾胃论中青年高血压病的中医病机及治疗[J]. 中国中医药现代远程教育, 2022, 20(6): 63-66. |
| DING M, GUO D. Discussion on the Chinese medicine pathogenesis and treatment of hypertension in young and middle-aged people from the perspective of spleen and stomach[J]. Chinese Medicine Modern Distance Education of China, 2022, 20(6): 63-66. | |
| 48 | CHOCKALINGAM A. Impact of world hypertension day[J]. The Canadian Journal of Cardiology, 2007, 23(7): 517-519. |
| 49 | SANTISTEBAN M M, QI Y F, ZUBCEVIC J, et al. Hypertension-linked pathophysiological alterations in the gut[J]. Circulation Research, 2017, 120(2): 312-323. |
| 50 | LE CHATELIER E, NIELSEN T, QIN J J, et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers[J]. Nature, 2013, 500(7464): 541-546. |
| 51 | TORAL M, ROMERO M, RODRÍGUEZ-NOGALES A, et al. Lactobacillus fermentum improves tacrolimus-induced hypertension by restoring vascular redox state and improving eNOS coupling[J]. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 2018, 62(14): e1800033. |
| 52 | WILCK N, MATUS M G, KEARNEY S M, et al. Salt-responsive gut commensal modulates TH17 axis and disease[J]. Nature, 2017, 551(7682): 585-589. |
| 53 | ZHANG Z, ZHAO J T, TIAN C Y, et al. Targeting the gut microbiota to investigate the mechanism of lactulose in negating the effects of a high-salt diet on hypertension[J]. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 2019, 63(11): e1800941. |
| 54 | OGURTSOVA K, GUARIGUATA L, BARENGO N C, et al. IDF diabetes Atlas: global estimates of undiagnosed diabetes in adults for 2021[J]. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 2022, 183: 109118. |
| 55 | RIGLAR D T, SILVER P A. Engineering bacteria for diagnostic and therapeutic applications[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2018, 16(4): 214-225. |
| 56 | WANG K, LIAO M F, ZHOU N, et al. Parabacteroides distasonis alleviates obesity and metabolic dysfunctions via production of succinate and secondary bile acids[J]. Cell Reports, 2019, 26(1): 222-235.e5. |
| 57 | CHIMEREL C, EMERY E, SUMMERS D K, et al. Bacterial metabolite indole modulates incretin secretion from intestinal enteroendocrine L cells[J]. Cell Reports, 2014, 9(4): 1202-1208. |
| 58 | WEI P J, YANG Y, LI T Y, et al. A engineered Bifidobacterium longum secreting a bioative penetratin-Glucagon-like peptide 1 fusion protein enhances Glucagon-like peptide 1 absorption in the intestine[J/OL]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015[2022-12-01]. . |
| 59 | XU F F, WANG K Y, WANG N, et al. Modified human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) produced in E. coli has a long-acting therapeutic effect in type 2 diabetic mice[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(7): e0181939. |
| 60 | ZENG Z, YU R, ZUO F L, et al. Heterologous expression and delivery of biologically active exendin-4 by lactobacillus paracasei L14[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(10): e0165130. |
| 61 | ZHANG X Y, MA N, LING W, et al. Optogenetic operated probiotics to regulate host metabolism by mimicking enteroendocrine[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2021[2022-12-01]. . |
| 62 | ZHANG X Y, MA N, LING W, et al. A micro-nano optogenetic system based on probiotics for in situ host metabolism regulation[J]. Nano Research, 2023, 16(2): 2829-2839. |
| 63 | LINGVAY I, SUMITHRAN P, COHEN R V, et al. Obesity management as a primary treatment goal for type 2 diabetes: time to reframe the conversation[J]. Lancet, 2022, 399(10322): 394-405. |
| 64 | WANG L F, CHEN T T, WANG H, et al. Engineered bacteria of MG1363-pMG36e-GLP-1 attenuated obesity-induced by high fat diet in mice[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2021, 11: 595575. |
| 65 | CHEN Z Y, GUO L L, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Incorporation of therapeutically modified bacteria into gut microbiota inhibits obesity[J]. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2014, 124(8): 3391-3406. |
| 66 | LU J, ZHU X Y, ZHANG C, et al. Co-expression of alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase in Bacillus subtilis for alcohol detoxification[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2020, 135: 110890. |
| 67 | BAILEY R L, WEST K P, BLACK R E. The epidemiology of global micronutrient deficiencies[J]. Annals of Nutrition & Metabolism, 2015, 66(): 22-33. |
| 68 | SOMABHAI C A, RAGHUVANSHI R, NARESHKUMAR G. Genetically engineered Escherichia coli nissle 1917 synbiotics reduce metabolic effects induced by chronic consumption of dietary fructose[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(10): e0164860. |
| 69 | CHAUDHARI A S, RAGHUVANSHI R, KUMAR G N. Genetically engineered Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 synbiotic counters fructose-induced metabolic syndrome and iron deficiency[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(11): 4713-4723. |
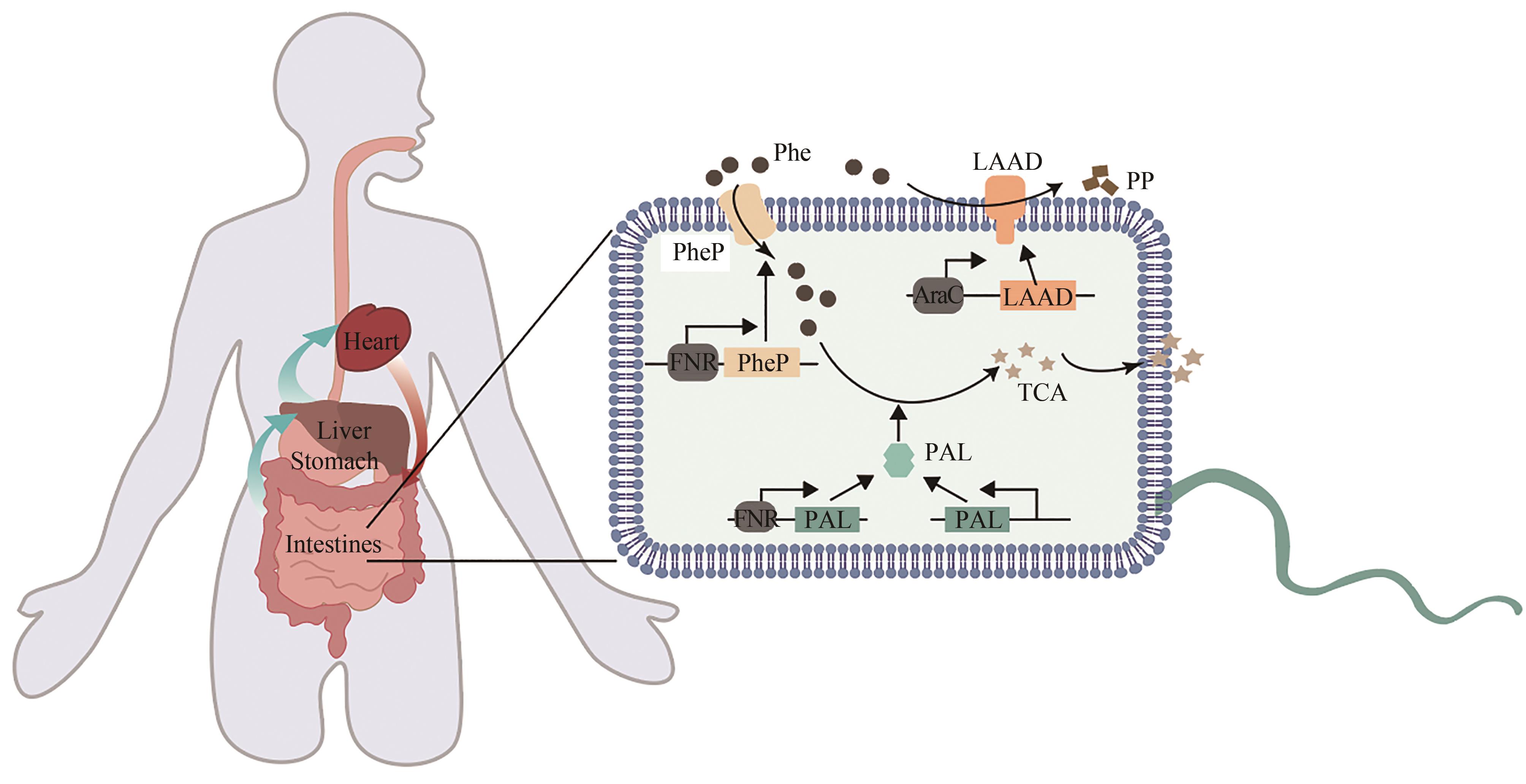
| 70 | 顾学范. 苯丙酮尿症的诊断和治疗[J]. 广东医学, 2000, 21(7): 535-536. |
| GU X F. Diagnosis and treatment of phenylketonuria[J]. Guangdong Medical Journal, 2000, 21(7): 535-536. | |
| 71 | LEVY H L, SARKISSIAN C N, SCRIVER C R. Phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL): from discovery to enzyme substitution therapy for phenylketonuria[J]. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 2018, 124(4): 223-229. |
| 72 | HAUSMANN O, DAHA M, LONGO N, et al. Pegvaliase: immunological profile and recommendations for the clinical management of hypersensitivity reactions in patients with phenylketonuria treated with this enzyme substitution therapy[J]. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 2019, 128(1/2): 84-91. |
| 73 | LIU J Z, JIA X Y, ZHANG J, et al. Study on a novel strategy to treatment of phenylketonuria[J]. Artificial Cells, Blood Substitutes, and Biotechnology, 2002, 30(4): 243-257. |
| 74 | SARKISSIAN C N, SHAO Z, BLAIN F, et al. A different approach to treatment of phenylketonuria: phenylalanine degradation with recombinant phenylalanine ammonia lyase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(5): 2339-2344. |
| 75 | KANG T S, WANG L, SARKISSIAN C N, et al. Converting an injectable protein therapeutic into an oral form: phenylalanine ammonia lyase for phenylketonuria[J]. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 2010, 99(1): 4-9. |
| 76 | DURRER K E, ALLEN M S, HUNT VON HERBING I. Genetically engineered probiotic for the treatment of phenylketonuria (PKU); assessment of a novel treatment in vitro and in the PAHenu2 mouse model of PKU[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(5): e0176286. |
| 77 | ISABELLA V M, HA B N, CASTILLO M J, et al. Development of a synthetic live bacterial therapeutic for the human metabolic disease phenylketonuria[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(9): 857-864. |
| 78 | PUURUNEN M K, VOCKLEY J, SEARLE S L, et al. Safety and pharmacodynamics of an engineered E. coli Nissle for the treatment of phenylketonuria: a first-in-human phase 1/2a study[J]. Nature Metabolism, 2021, 3(8): 1125-1132. |
| 79 | ADOLFSEN K J, CALLIHAN I, MONAHAN C E, et al. Improvement of a synthetic live bacterial therapeutic for phenylketonuria with biosensor-enabled enzyme engineering[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 6215. |
| 80 | FAN Y, PEDERSEN O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2021, 19(1): 55-71. |
| 81 | CHEN H C, HE C K, CHEN T Y, et al. New strategy for precise cancer therapy: tumor-specific delivery of mitochondria-targeting photodynamic therapy agents and in situ O2-generation in hypoxic tumors[J]. Biomaterials Science, 2020, 8(14): 3994-4002. |
| 82 | SAHU A, KWON I, TAE G Y. Improving cancer therapy through the nanomaterials-assisted alleviation of hypoxia[J]. Biomaterials, 2020, 228: 119578. |
| 83 | TANIGUCHI S I, FUJIMORI M, SASAKI T, et al. Targeting solid tumors with non-pathogenic obligate anaerobic bacteria[J]. Cancer Science, 2010, 101(9): 1925-1932. |
| 84 | HOFFMAN R M, ZHAO M. Methods for the development of tumor-targeting bacteria[J]. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery, 2014, 9(7): 741-750. |
| 85 | BADIE F, GHANDALI M, TABATABAEI S A, et al. Use of Salmonella bacteria in cancer therapy: direct, drug delivery and combination approaches[J]. Frontiers in Oncology, 2021, 11: 624759. |
| 86 | ASADOLLAHI P, GHANAVATI R, ROHANI M, et al. Anti-cancer effects of Bifidobacterium species in colon cancer cells and a mouse model of carcinogenesis[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(5): e0232930. |
| 87 | PIONTEK A, EICHNER M, ZWANZIGER D, et al. Targeting claudin-overexpressing thyroid and lung cancer by modified Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin[J]. Molecular Oncology, 2020, 14(2): 261-276. |
| 88 | VEZIANT J, VILLÉGER R, BARNICH N, et al. Gut microbiota as potential biomarker and/or therapeutic target to improve the management of cancer: focus on colibactin-producing Escherichia coli in colorectal cancer[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13(9): 2215. |
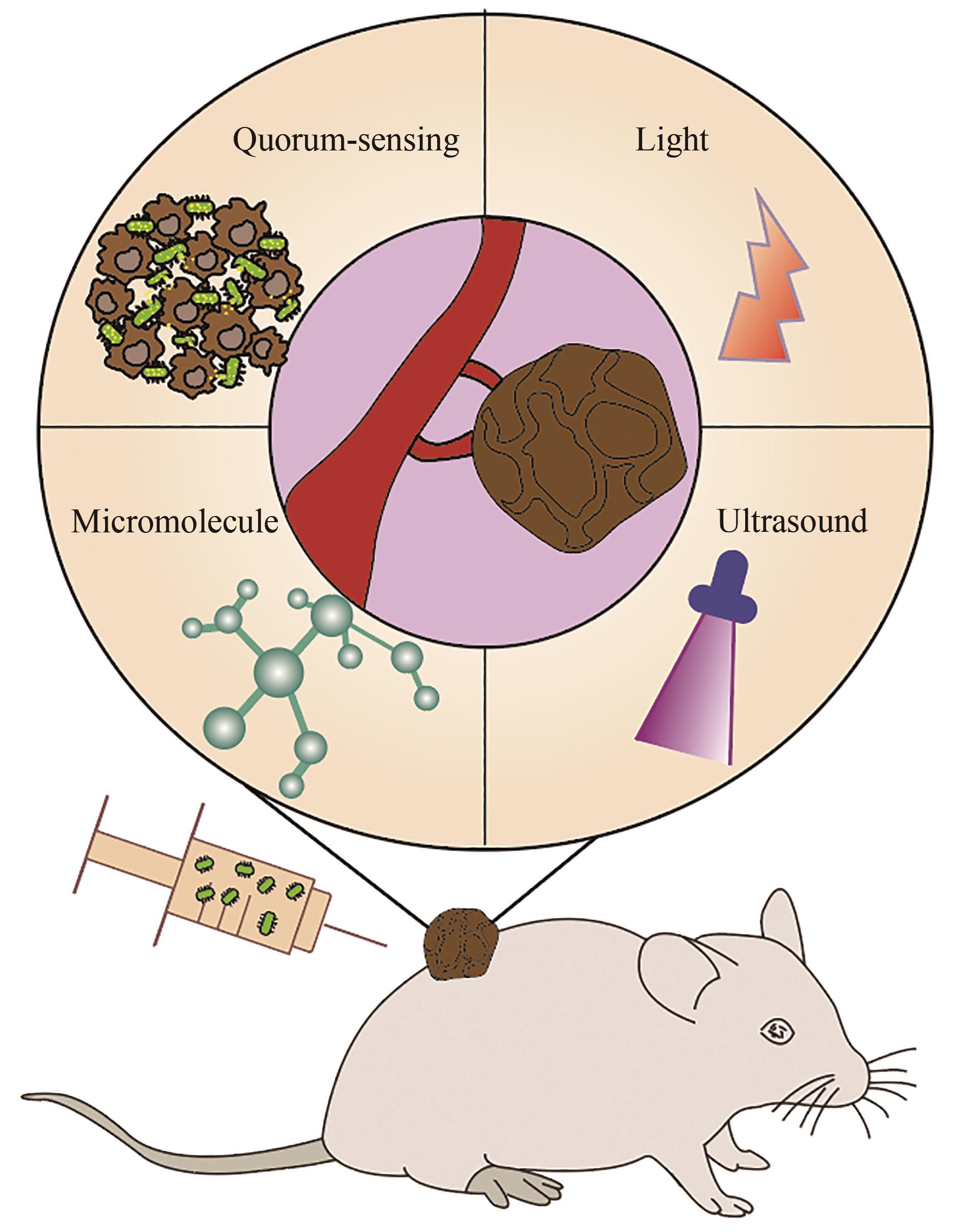
| 89 | ANDINO A, HANNING I. Salmonella enterica: survival, colonization, and virulence differences among serovars[J]. The Scientific World Journal, 2015, 2015: 520179. |
| 90 | LOW K B, ITTENSOHN M, LE T, et al. Lipid A mutant Salmonella with suppressed virulence and TNFα induction retain tumor-targeting in vivo [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 1999, 17(1): 37-41. |
| 91 | BACON G A, BURROWS T W, YATES M. The effects of biochemical mutation on the virulence of Bacterium typhosum; the loss of virulence of certain mutants[J]. British Journal of Experimental Pathology, 1951, 32(2): 85-96. |
| 92 | HOISETH S K, STOCKER B A D. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines[J]. Nature, 1981, 291(5812): 238-239. |
| 93 | LOW K B, ITTENSOHN M, LE T, et al. VNP20009, a genetically modified Salmonella typhimurium for the treatment of solid tumors[J]. Proceedings of the American Association for Cancer Research, 1999, 40: 87. |
| 94 | CLAIRMONT C, LEE K C, PIKE J, et al. Biodistribution and genetic stability of the novel antitumor agent VNP20009, a genetically modified strain of Salmonella typhimuvium [J]. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 2000, 181(6): 1996-2002. |
| 95 | TOSO J F, GILL V J, HWU P, et al. PhaseⅠstudy of the intravenous administration of attenuated Salmonella typhimurium to patients with metastatic melanoma[J]. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2002, 20(1): 142-152. |
| 96 | YANG Y W, ZHANG C M, HUANG X J, et al. Tumor-targeted delivery of a C-terminally truncated FADD (N-FADD) significantly suppresses the B16F10 melanoma via enhancing apoptosis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 34178. |
| 97 | SONG M, KIM H J, KIM E Y, et al. ppGpp-dependent stationary phase induction of genes on Salmonella pathogenicity island 1[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2004, 279(33): 34183-34190. |
| 98 | NA H S, KIM H J, LEE H C, et al. Immune response induced by Salmonella typhimurium defective in ppGpp synthesis[J]. Vaccine, 2006, 24(12): 2027-2034. |
| 99 | YI X, ZHOU H L, CHAO Y, et al. Bacteria-triggered tumor-specific thrombosis to enable potent photothermal immunotherapy of cancer[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(33): eaba3546. |
| 100 | ZHENG J H, NGUYEN V H, JIANG S N, et al. Two-step enhanced cancer immunotherapy with engineered Salmonella typhimurium secreting heterologous flagellin[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2017, 9(376): eaak9537. |
| 101 | ZHAO M, YANG M, LI X M, et al. Tumor-targeting bacterial therapy with amino acid auxotrophs of GFP-expressing Salmonella typhimurium [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2005, 102(3): 755-760. |
| 102 | HIROSHIMA Y, ZHANG Y, ZHAO M, et al. Tumor-targeting Salmonella typhimurium A1-R in combination with trastuzumab eradicates HER-2-positive cervical cancer cells in patient-derived mouse models[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(6): e0120358. |
| 103 | YOON W, PARK Y C, KIM J, et al. Application of genetically engineered Salmonella typhimurium for interferon-gamma-induced therapy against melanoma[J]. European Journal of Cancer, 2017, 70: 48-61. |
| 104 | SHI L, YU B, CAI C H, et al. Angiogenic inhibitors delivered by the typeⅢsecretion system of tumor-targeting Salmonella typhimurium safely shrink tumors in mice[J]. AMB Express, 2016, 6(1): 56. |
| 105 | SWOFFORD C A, VAN DESSEL N, FORBES N S. Quorum-sensing Salmonella selectively trigger protein expression within tumors[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(11): 3457-3462. |
| 106 | DIN M O, DANINO T, PRINDLE A, et al. Synchronized cycles of bacterial lysis for in vivo delivery[J]. Nature, 2016, 536(7614): 81-85. |
| 107 | WU M R, JUSIAK B, LU T K. Engineering advanced cancer therapies with synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2019, 19(4): 187-195. |
| 108 | CAMACHO E M, MESA-PEREIRA B, MEDINA C, et al. Engineering Salmonella as intracellular factory for effective killing of tumour cells[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 30591. |
| 109 | PANTELI J T, FORKUS B A, VAN DESSEL N, et al. Genetically modified bacteria as a tool to detect microscopic solid tumor masses with triggered release of a recombinant biomarker[J]. Integrative Biology, 2015, 7(4): 423-434. |
| 110 | CHEN J Q, ZHAN Y F, WANG W, et al. The engineered Salmonella typhimurium inhibits tumorigenesis in advanced glioma[J]. OncoTargets and Therapy, 2015, 8: 2555-2563. |
| 111 | HE L, ZHANG Y W, MA G L, et al. Near-infrared photoactivatable control of Ca2+ signaling and optogenetic immunomodulation[J]. eLife, 2015, 4: e10024. |
| 112 | DANINO T, PRINDLE A, KWONG G A, et al. Programmable probiotics for detection of cancer in urine[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2015, 7(289): 289ra84. |
| 113 | HO C L, TAN H Q, CHUA K J, et al. Engineered commensal microbes for diet-mediated colorectal-cancer chemoprevention[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 2(1): 27-37. |
| 114 | GURBATRI C R, LIA I, VINCENT R, et al. Engineered probiotics for local tumor delivery of checkpoint blockade nanobodies[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2020, 12(530): eaax0876. |
| 115 | YUE Y L, XU J Q, LI Y, et al. Antigen-bearing outer membrane vesicles as tumour vaccines produced in situ by ingested genetically engineered bacteria[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2022, 6(7): 898-909. |
| 116 | PAN H Z, LI L Y, PANG G J, et al. Engineered NIR light-responsive bacteria as anti-tumor agent for targeted and precise cancer therapy[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 426: 130842. |
| 117 | CHEN Y H, DU M, YUAN Z, et al. Spatiotemporal control of engineered bacteria to express interferon-γ by focused ultrasound for tumor immunotherapy[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 4468. |
| 118 | ARCHER E J, ROBINSON A B, SÜEL G M. Engineered E. coli that detect and respond to gut inflammation through nitric oxide sensing[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2012, 1(10): 451-457. |
| 119 | RIGLAR D T, GIESSEN T W, BAYM M, et al. Engineered bacteria can function in the mammalian gut long-term as live diagnostics of inflammation[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2017, 35(7): 653-658. |
| 120 | NEURATH M F. Targeting immune cell circuits and trafficking in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Nature Immunology, 2019, 20(8): 970-979. |
| 121 | INDA M, JIMENEZ M, LIU Q, et al. Ingestible capsule for detecting labile inflammatory biomarkers in situ [EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2022[2022-12-01]. . |
| 122 | OLSZAK T, AN D D, ZEISSIG S, et al. Microbial exposure during early life has persistent effects on natural killer T cell function[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6080): 489-493. |
| 123 | YAN X, LIU X Y, ZHANG D, et al. Construction of a sustainable 3-hydroxybutyrate-producing probiotic Escherichia coli for treatment of colitis[J]. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 2021, 18(10): 2344-2357. |
| 124 | CUI M H, PANG G J, ZHANG T, et al. Optotheranostic nanosystem with phone visual diagnosis and optogenetic microbial therapy for ulcerative colitis At-home care[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(4): 7040-7052. |
| 125 | MADDALONI M, KOCHETKOVA I, JUN S M, et al. Milk-based nutraceutical for treating autoimmune arthritis via the stimulation of IL-10- and TGF-β-producing CD39+ regulatory T cells[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(1): e0117825. |
| 126 | DEL CARMEN S, MARTÍN ROSIQUE R, SARAIVA T, et al. Protective effects of lactococci strains delivering either IL-10 protein or cDNA in a TNBS-induced chronic colitis model[J]. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, 2014, 48(): S12-S17. |
| 127 | HANSON M L, HIXON J A, LI W Q, et al. Oral delivery of IL-27 recombinant bacteria attenuates immune colitis in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 146(1): 210-221.e13. |
| 128 | AUBRY C, MICHON C, CHAIN F, et al. Protective effect of TSLP delivered at the gut mucosa level by recombinant lactic acid bacteria in DSS-induced colitis mouse model[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 176. |
| 129 | SHIGEMORI S, WATANABE T, KUDOH K, et al. Oral delivery of Lactococcus lactis that secretes bioactive heme oxygenase-1 alleviates development of acute colitis in mice[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 189. |
| 130 | WEI P J, YANG Y, LIU Z B, et al. Oral Bifidobacterium longum expressing alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone to fight experimental colitis[J]. Drug Delivery, 2016, 23(6): 2058-2064. |
| 131 | MAYER L. Immunology of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology, 1990, 6(4): 556-560. |
| 132 | SCOTT B M, GUTIÉRREZ-VÁZQUEZ C, SANMARCO L M, et al. Self-tunable engineered yeast probiotics for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Nature Medicine, 2021, 27(7): 1212-1222. |
| 133 | MUTALIK V K, GUIMARAES J C, CAMBRAY G, et al. Precise and reliable gene expression via standard transcription and translation initiation elements[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(4): 354-360. |
| 134 | ZHANG Y, ZOU Z P, CHEN S Y, et al. Design and optimization of E. coli artificial genetic circuits for detection of explosive composition 2, 4-dinitrotoluene[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2022, 207: 114205. |
| 135 | KOSURI S, GOODMAN D B, CAMBRAY G, et al. Composability of regulatory sequences controlling transcription and translation in Escherichia coli [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(34): 14024-14029. |
| 136 | 孙怡, 张腾, 吕波, 等. 胞内生物传感器提高微生物细胞工厂的精细调控[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 521-534. |
| SUN Y, ZHANG T, LYU B, et al. Improvement for fine regulation of microbial cell factory by intracellular biosensors[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(2): 521-534. |
| [1] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [12] | CAI Bingyu, TAN Xiangtian, LI Wei. Advances in synthetic biology for engineering stem cell [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [13] | XIE Huang, ZHENG Yilei, SU Yiting, RUAN Jingyi, LI Yongquan. An overview on reconstructing the biosynthetic system of actinomycetes for polyketides production [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [14] | ZHA Wenlong, BU Lan, ZI Jiachen. Advances in synthetic biology for producing potent pharmaceutical ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| [15] | HUI Zhen, TANG Xiaoyu. Applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 editing system in the study of microbial natural products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||