Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (2): 279-301.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-008
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Integration of synthetic biology and nanobiotechnology for biomedical applications
ZHENG Hanqi1, WU Qing1, LI Hongjun1,2, GU Zhen1,2,3,4
- 1.Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory for Advanced Drug Delivery Systems,College of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310058,Zhejiang,China
2.Zhejiang Laboratory of Systems & Precision Medicine,Liangzhu Laboratory,Zhejiang University Medical Center,Hangzhou 311121,Zhejiang,China
3.Department of General Surgery,Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital,School of Medicine,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310016,Zhejiang,China
4.MOE Key Laboratory of Macromolecular Synthesis and Functionalization,Department of Polymer Science and Engineering,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310027,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2022-01-27Revised:2022-02-21Online:2022-05-11Published:2022-04-30 -
Contact:LI Hongjun, GU Zhen
合成生物学与纳米生物学的交叉融合及其在生物医药领域的应用
郑涵奇1, 吴晴1, 李洪军1,2, 顾臻1,2,3,4
- 1.浙江省先进递药系统重点实验室,浙江大学药学院,浙江 杭州 310058
2.浙江省系统与精准医学实验室,良渚实验室,浙江大学医学中心,浙江 杭州 311121
3.浙江大学医学院附属邵逸夫医院,普外科,浙江 杭州 310016
4.高分子合成与功能化教育部重点实验室,浙江大学高分子科学与工程系,浙江 杭州 310027
-
通讯作者:李洪军,顾臻 -
作者简介:郑涵奇 (2000—),男,硕士研究生。研究方向为新型工程化免疫细胞及其在肿瘤免疫治疗中的应用。 E-mail:zhenghanqi@zju.edu.cn李洪军 (1989—),男,浙江大学特聘研究员,博士生导师。研究方向包括新型工程化免疫细胞用于肿瘤免疫治疗的开发、智能型药物递送系统/器件的开发等。 E-mail:hongjun@zju.edu.cn顾臻 (1980—),男,浙江大学求是讲席教授、药学院院长,教育部“长江学者”讲席教授,浙江省先进递药系统重点实验室主任,国家重点研发计划项目首席科学家,博士生导师。研究方向包括蛋白质/核酸递药系统、生理响应材料、免疫治疗制剂、细胞治疗策略等。 E-mail:guzhen@zju.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFA0909900);国家自然科学基金(52173142);浙江大学科研启动经费
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHENG Hanqi, WU Qing, LI Hongjun, GU Zhen. Integration of synthetic biology and nanobiotechnology for biomedical applications[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(2): 279-301.
郑涵奇, 吴晴, 李洪军, 顾臻. 合成生物学与纳米生物学的交叉融合及其在生物医药领域的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(2): 279-301.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2022-008
| 载体类型 | 载体材料 | 递送目标类别 | 特征 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机纳米载体 | 两性离子氨基脂质纳米颗粒 | 长RNA(含Cas9 mRNA、sgRNA) | 可以将多个长RNA打包递送,有望提供DNA修复模板来介导HDR(同源介导的双链DNA修复)基因校正 | [ |
| 基于卵磷脂的纳米脂质体 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 高生物相容性、低细胞毒性和高溶液稳定性 | [ | |
| 基于可电离脂质的脂质纳米颗粒 | Cas9-sgRNA质粒 | 促进膜融合、膜破裂和内涵体逃逸 | [ | |
| 可生物还原的脂质纳米颗粒 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP, Cas9 mRNA/sgRNA | 响应还原性细胞内环境,更有效释放RNA和蛋白质 | [ | |
| 转铁蛋白修饰的脂质体 | DNA | 将功能蛋白的肿瘤靶向潜力和优异的基因递送性能相结合 | [ | |
| 超支化阳离子聚(β-氨基酯) | Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 能以不同表面电荷实现分子量在一定范围内的蛋白质的胞质递送 | [ | |
| 氟化酸不稳定支链富羟基聚阳离子 | Cas9-sgRNA质粒 | 良好的pH响应降解性、生物相容性 | [ | |
| 乳糖衍生的支链阳离子生物聚合物 | Cas9-sgRNA质粒 | 优异的降解性、生物相容性、基因转染性能和肝癌细胞靶向能力 | [ | |
| 聚(二硫化物) | DNA、mRNA和RNP三种形式的CRISPR-Cas9 | 极大限度地减少了不可降解聚合物载体常见的细胞毒性 | [ | |
| 阳离子α-螺旋多肽 | Cas9质粒/sgRNA | 具有作为高效基因载体和细胞膜穿透剂的双重功能 | [ | |
| 无机纳米载体 | 金纳米粒 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP,DNA, Cas9-sgRNA质粒 | 具有独特的光学和结构特性,可以作为基因递送的多功能平台 | [ |
| 镧系元素掺杂的上转换纳米粒子 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 作为纳米传感器,可以通过光来远程控制基因编辑工具的释放 | [ | |
| 纳米级沸石咪唑骨架 | 质粒DNA,Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 在内涵体pH下质子化,促进内涵体逃逸,增强了向细胞核的递送 | [ | |
| 功能化的介孔二氧化硅颗粒 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 具有高表面积和可调节的孔径,可以和修饰硼酸基团的蛋白质形成配位和静电相互作用,提高向细胞内递送的效率 | [ | |
| 生物仿生 纳米载体 | 细胞膜衍生纳米囊泡 | 质粒cDNA | MSC纳米囊泡具有生物相容性,并保留了MSC对各种肿瘤细胞的表面相关靶向能力 | [ |
| 细胞外囊泡 | CRISPR/Cas9质粒,Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 可以被修饰改造以实现靶向递送 | [ | |
| DNA纳米线球 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP | DNA纳米线球和sgRNA引导序列之间部分互补时能实现更高效率的基因编辑 | [ | |
| 病毒样颗粒 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 实现瞬时快速递送,并降低脱靶率 | [ |
Tab. 1 Representative carriers used for delivering gene circuits/genome editing systems
| 载体类型 | 载体材料 | 递送目标类别 | 特征 | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机纳米载体 | 两性离子氨基脂质纳米颗粒 | 长RNA(含Cas9 mRNA、sgRNA) | 可以将多个长RNA打包递送,有望提供DNA修复模板来介导HDR(同源介导的双链DNA修复)基因校正 | [ |
| 基于卵磷脂的纳米脂质体 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 高生物相容性、低细胞毒性和高溶液稳定性 | [ | |
| 基于可电离脂质的脂质纳米颗粒 | Cas9-sgRNA质粒 | 促进膜融合、膜破裂和内涵体逃逸 | [ | |
| 可生物还原的脂质纳米颗粒 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP, Cas9 mRNA/sgRNA | 响应还原性细胞内环境,更有效释放RNA和蛋白质 | [ | |
| 转铁蛋白修饰的脂质体 | DNA | 将功能蛋白的肿瘤靶向潜力和优异的基因递送性能相结合 | [ | |
| 超支化阳离子聚(β-氨基酯) | Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 能以不同表面电荷实现分子量在一定范围内的蛋白质的胞质递送 | [ | |
| 氟化酸不稳定支链富羟基聚阳离子 | Cas9-sgRNA质粒 | 良好的pH响应降解性、生物相容性 | [ | |
| 乳糖衍生的支链阳离子生物聚合物 | Cas9-sgRNA质粒 | 优异的降解性、生物相容性、基因转染性能和肝癌细胞靶向能力 | [ | |
| 聚(二硫化物) | DNA、mRNA和RNP三种形式的CRISPR-Cas9 | 极大限度地减少了不可降解聚合物载体常见的细胞毒性 | [ | |
| 阳离子α-螺旋多肽 | Cas9质粒/sgRNA | 具有作为高效基因载体和细胞膜穿透剂的双重功能 | [ | |
| 无机纳米载体 | 金纳米粒 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP,DNA, Cas9-sgRNA质粒 | 具有独特的光学和结构特性,可以作为基因递送的多功能平台 | [ |
| 镧系元素掺杂的上转换纳米粒子 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 作为纳米传感器,可以通过光来远程控制基因编辑工具的释放 | [ | |
| 纳米级沸石咪唑骨架 | 质粒DNA,Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 在内涵体pH下质子化,促进内涵体逃逸,增强了向细胞核的递送 | [ | |
| 功能化的介孔二氧化硅颗粒 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 具有高表面积和可调节的孔径,可以和修饰硼酸基团的蛋白质形成配位和静电相互作用,提高向细胞内递送的效率 | [ | |
| 生物仿生 纳米载体 | 细胞膜衍生纳米囊泡 | 质粒cDNA | MSC纳米囊泡具有生物相容性,并保留了MSC对各种肿瘤细胞的表面相关靶向能力 | [ |
| 细胞外囊泡 | CRISPR/Cas9质粒,Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 可以被修饰改造以实现靶向递送 | [ | |
| DNA纳米线球 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP | DNA纳米线球和sgRNA引导序列之间部分互补时能实现更高效率的基因编辑 | [ | |
| 病毒样颗粒 | Cas9/sgRNA RNP | 实现瞬时快速递送,并降低脱靶率 | [ |
| 细菌 | 细菌改造 | 修饰纳米材料 | 效能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetococcus marinus MC-1 | 包含一串磁性氧化铁纳米晶体 | 含药物纳米脂质体 | 磁引导细菌将含药纳米脂质体运输到SCID Beige小鼠HCT116异种移植结直肠肿瘤的缺氧区 | [ |
| S. typhimurium VNP20009 | 兼性厌氧,减毒营养缺陷型突变体 | PLGA纳米粒 | 将纳米颗粒在BALB/c小鼠的4T1乳腺癌原位模型中的保留和分布提高100倍 | [ |
| S. typhimurium ELH1301, E. coli Nissle 1917 | 具有编码气体囊泡的工程基因簇 | 蛋白质外壳的纳米气体囊泡 | 超声波报告基因工程,用于超声成像 | [ |
| E. coli MG1655 | 过表达呼吸链酶Ⅱ(NDH-Ⅱ) | 磁性Fe3O4纳米粒子 | 在BALB/c小鼠的CT 26结肠癌部位原位催化产生H2O2,诱导肿瘤细胞死亡 | [ |
| E. coli MG1655 | 表达硝酸盐/亚硝酸盐还原酶 | 碳点掺杂氮化碳 | 光控细菌代谢物疗法,光照射下生成NO抑制BALB/c小鼠4T1肿瘤生长 | [ |
| E. coli | 过表达过氧化氢酶 | 含Ce6涂层的聚多巴胺纳米粒 | NIR光照射下实现光热疗法和光动力疗法,在荷瘤BALB/c裸鼠中抑制肿瘤生长 | [ |
| S. typhimurium YB1 | 缺氧靶向 | 载有吲哚菁绿(ICG)的纳米颗粒 | 在NIR激光照射下,产生光热杀伤能力,根除C57 BL/6小鼠的MB49实体瘤 | [ |
| Magnetococcus marinus AMB-1 | 趋磁性和缺氧靶向 | 光触发的吲哚菁绿纳米粒子 | 磁驱动富集到肿瘤部位,光热疗法消除MCF-7荷瘤BALB/c裸鼠中的肿瘤 | [ |
Tab. 2 Representative hybrid systems of engineered bacteria and nanocomponents
| 细菌 | 细菌改造 | 修饰纳米材料 | 效能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetococcus marinus MC-1 | 包含一串磁性氧化铁纳米晶体 | 含药物纳米脂质体 | 磁引导细菌将含药纳米脂质体运输到SCID Beige小鼠HCT116异种移植结直肠肿瘤的缺氧区 | [ |
| S. typhimurium VNP20009 | 兼性厌氧,减毒营养缺陷型突变体 | PLGA纳米粒 | 将纳米颗粒在BALB/c小鼠的4T1乳腺癌原位模型中的保留和分布提高100倍 | [ |
| S. typhimurium ELH1301, E. coli Nissle 1917 | 具有编码气体囊泡的工程基因簇 | 蛋白质外壳的纳米气体囊泡 | 超声波报告基因工程,用于超声成像 | [ |
| E. coli MG1655 | 过表达呼吸链酶Ⅱ(NDH-Ⅱ) | 磁性Fe3O4纳米粒子 | 在BALB/c小鼠的CT 26结肠癌部位原位催化产生H2O2,诱导肿瘤细胞死亡 | [ |
| E. coli MG1655 | 表达硝酸盐/亚硝酸盐还原酶 | 碳点掺杂氮化碳 | 光控细菌代谢物疗法,光照射下生成NO抑制BALB/c小鼠4T1肿瘤生长 | [ |
| E. coli | 过表达过氧化氢酶 | 含Ce6涂层的聚多巴胺纳米粒 | NIR光照射下实现光热疗法和光动力疗法,在荷瘤BALB/c裸鼠中抑制肿瘤生长 | [ |
| S. typhimurium YB1 | 缺氧靶向 | 载有吲哚菁绿(ICG)的纳米颗粒 | 在NIR激光照射下,产生光热杀伤能力,根除C57 BL/6小鼠的MB49实体瘤 | [ |
| Magnetococcus marinus AMB-1 | 趋磁性和缺氧靶向 | 光触发的吲哚菁绿纳米粒子 | 磁驱动富集到肿瘤部位,光热疗法消除MCF-7荷瘤BALB/c裸鼠中的肿瘤 | [ |
| 1 | BENNER S A, SISMOUR A M. Synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2005, 6(7): 533-543. |
| 2 | OMIDVAR R, AYALA Y A, BRANDEL A, et al. Quantification of nanoscale forces in lectin-mediated bacterial attachment and uptake into giant liposomes[J]. Nanoscale, 2021, 13(7): 4016-4028. |
| 3 | ENDY D. Foundations for engineering biology[J]. Nature, 2005, 438(7067): 449-453. |
| 4 | XIE M, FUSSENEGGER M. Designing cell function: assembly of synthetic gene circuits for cell biology applications[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2018, 19(8): 507-525. |
| 5 | JUSIAK B, CLETO S, PEREZ-PIÑERA P, et al. Engineering synthetic gene circuits in living cells with CRISPR technology[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2016, 34(7): 535-547. |
| 6 | CHURCH G M, ELOWITZ M B, SMOLKE C D, et al. Realizing the potential of synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2014, 15(4): 289-294. |
| 7 | ORIVE G, GASCÓN A R, HERNÁNDEZ R M, et al. Techniques: new approaches to the delivery of biopharmaceuticals[J]. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 2004, 25(7): 382-387. |
| 8 | RAZZACKI S Z, THWAR P K, YANG M, et al. Integrated microsystems for controlled drug delivery[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2004, 56(2): 185-198. |
| 9 | JAHANGIRIAN H, LEMRASKI E G, WEBSTER T J, et al. A review of drug delivery systems based on nanotechnology and green chemistry: Green nanomedicine[J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2017, 12: 2957-2978. |
| 10 | PATRA J K, DAS G, FRACETO L F, et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2018, 16(1): 71. |
| 11 | CHOI Y, PARK T J, LEE D C, et al. Recombinant Escherichia coli as a biofactory for various single- and multi-element nanomaterials[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(23): 5944-5949. |
| 12 | IRAVANI S, VARMA R S. Biofactories: engineered nanoparticles via genetically engineered organisms[J]. Green Chemistry, 2019, 21(17): 4583-4603. |
| 13 | JAHROMI L P, FUHRMANN G. Bacterial extracellular vesicles: understanding biology promotes applications as nanopharmaceuticals[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2021, 173: 125-140. |
| 14 | 冯晴晴, 张天鲛, 赵潇, 等. 合成纳米生物学——合成生物学与纳米生物学的交叉前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2022,3(2): 260-278. |
| FENG Qingqing, ZHANG Tianjiao, ZHAO Xiao, et al. Synthetic nanobiology——fusion of synthetic biology and nanobiology. Synthetic Biology Journal[J], 2022,3(2): 260-278. | |
| 15 | CHANNON K, BROMLEY E H, WOOLFSON D N. Synthetic biology through biomolecular design and engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2008, 18(4): 491-498. |
| 16 | KIM J K, YANG S Y, LEE Y, et al. Functional nanomaterials based on block copolymer self-assembly[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2010, 35(11): 1325-1349. |
| 17 | GAUR D, DUBEY N C, TRIPATHI B P. Biocatalytic self-assembled synthetic vesicles and coacervates: from single compartment to artificial cells[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 299: 102566. |
| 18 | TABEBORDBAR M, ZHU K X, CHENG J K W, et al. In vivo gene editing in dystrophic mouse muscle and muscle stem cells[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6271): 407-411. |
| 19 | LONG C Z, AMOASII L, MIREAULT A A, et al. Postnatal genome editing partially restores dystrophin expression in a mouse model of muscular dystrophy[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6271): 400-403. |
| 20 | NELSON C E, HAKIM C H, OUSTEROUT D G, et al. In vivo genome editing improves muscle function in a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6271): 403-407. |
| 21 | WANG D, ZHANG F, GAO G P. CRISPR-based therapeutic genome editing: strategies and in vivo delivery by AAV vectors[J]. Cell, 2020, 181(1): 136-150. |
| 22 | WANG H X, LI M Q, LEE C M, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing for disease modeling and therapy: challenges and opportunities for nonviral delivery[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(15): 9874-9906. |
| 23 | LATTANZI A, MENEGHINI V, PAVANI G, et al. Optimization of CRISPR/Cas9 delivery to human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells for therapeutic genomic rearrangements[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2019, 27(1): 137-150. |
| 24 | WILBIE D, WALTHER J, MASTROBATTISTA E. Delivery aspects of CRISPR/cas for in vivo genome editing[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2019, 52(6): 1555-1564. |
| 25 | RAN F A, HSU P D, WRIGHT J, et al. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system[J]. Nature Protocols, 2013, 8(11): 2281-2308. |
| 26 | NIU Y Y, SHEN B, CUI Y Q, et al. Generation of gene-modified cynomolgus monkey via Cas9/RNA-mediated gene targeting in one-cell embryos[J]. Cell, 2014, 156(4): 836-843. |
| 27 | ZURIS J A, THOMPSON D B, SHU Y L, et al. Cationic lipid-mediated delivery of proteins enables efficient protein-based genome editing in vitro and in vivo [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(1): 73-80. |
| 28 | SUN W J, JI W Y, HALL J M, et al. Efficient delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome editing via self-assembled DNA nanoclews[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(41): 12029-33. |
| 29 | SUN W J, WANG J Q, HU Q Y, et al. CRISPR-Cas12a delivery by DNA-mediated bioresponsive editing for cholesterol regulation[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(21): eaba2983. |
| 30 | SHIN M D, SHUKLA S, CHUNG Y H, et al. COVID-19 vaccine development and a potential nanomaterial path forward[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2020, 15(8): 646-655. |
| 31 | PATEL S, ASHWANIKUMAR N, ROBINSON E, et al. Boosting intracellular delivery of lipid nanoparticle-encapsulated mRNA[J]. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(9): 5711-5718. |
| 32 | TANG Q, LIU J, JIANG Y, et al. Cell-selective messenger RNA delivery and CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing by modulating the interface of phenylboronic acid-derived lipid nanoparticles and cellular surface sialic acid[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(50): 46585-46590. |
| 33 | ZHANG S, SHEN J T, LI D L, et al. Strategies in the delivery of Cas9 ribonucleoprotein for CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(2): 614-648. |
| 34 | GAO X, TAO Y, LAMAS V, et al. Treatment of autosomal dominant hearing loss by in vivo delivery of genome editing agents[J]. Nature, 2018, 553(7687): 217-221. |
| 35 | CHO E Y, RYU J Y, LEE H, et al. Lecithin nano-liposomal particle as a CRISPR/Cas9 complex delivery system for treating type 2 diabetes[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2019, 17(1): 19. |
| 36 | MILLER J B, ZHANG S Y, KOS P, et al. Non-viral CRISPR/cas gene editing in vitro and in vivo enabled by synthetic nanoparticle co-delivery of Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(4): 1059-1063. |
| 37 | LI C H, YANG T R, WENG Y H, et al. Ionizable lipid-assisted efficient hepatic delivery of gene editing elements for oncotherapy[J]. Bioactive Materials, 2022, 9: 590-601. |
| 38 | FINN J D, SMITH A R, PATEL M C, et al. A single administration of CRISPR/Cas9 lipid nanoparticles achieves robust and persistent in vivo genome editing[J]. Cell Reports, 2018, 22(9): 2227-2235. |
| 39 | FU A L, TANG R, HARDIE J, et al. Promises and pitfalls of intracellular delivery of proteins[J]. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2014, 25(9): 1602-1608. |
| 40 | LIU J, CHANG J, JIANG Y, et al. Fast and efficient CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in vivo enabled by bioreducible lipid and messenger RNA nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla), 2019, 31(33): e1902575. |
| 41 | WANG M, ZURIS J A, MENG F T, et al. Efficient delivery of genome-editing proteins using bioreducible lipid nanoparticles[J]. PNAS, 2016, 113(11): 2868-2873. |
| 42 | WANG K, SHANG F S, CHEN D G, et al. Protein liposomes-mediated targeted acetylcholinesterase gene delivery for effective liver cancer therapy[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2021, 19(1): 31. |
| 43 | CHENG Q, WEI T, FARBIAK L, et al. Selective organ targeting (SORT) nanoparticles for tissue-specific mRNA delivery and CRISPR-Cas gene editing[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2020, 15(4): 313-320. |
| 44 | WANG W W, BALK M, DENG Z J, et al. Engineering biodegradable micelles of polyethylenimine-based amphiphilic block copolymers for efficient DNA and siRNA delivery[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2016, 242: 71-79. |
| 45 | SHEN J, LU Z G, WANG J Z, et al. Traceable nano-biohybrid complexes by one-step synthesis as CRISPR-chem vectors for neurodegenerative diseases synergistic treatment[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(27): 2101993. |
| 46 | FANG H P, CHEN J, LIN L, et al. A strategy of killing three birds with one stone for cancer therapy through regulating the tumor microenvironment by H2O2-responsive gene delivery system[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(51): 47785-47797. |
| 47 | SHARMA R, ZHANG I, SHIAO T C, et al. Low generation polyamine dendrimers bearing flexible tetraethylene glycol as nanocarriers for plasmids and siRNA[J]. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(9): 5106-5119. |
| 48 | RUI Y, WILSON D R, CHOI J, et al. Carboxylated branched poly (β-amino ester) nanoparticles enable robust cytosolic protein delivery and CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing[J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(12): eaay3255. |
| 49 | XU X D, WU J, LIU Y L, et al. Ultra-pH-responsive and tumor-penetrating nanoplatform for targeted siRNA delivery with robust anti-cancer efficacy[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 128(25): 7207-7210. |
| 50 | LAO Y H, LI M Q, GAO M A, et al. HPV oncogene manipulation using nonvirally delivered CRISPR/Cas9 or natronobacterium gregoryi argonaute[J]. Advanced Science, 2018, 5(7): 1700540. |
| 51 | QI Y, SONG H Q, XIAO H H, et al. Fluorinated acid-labile branched hydroxyl-rich nanosystems for flexible and robust delivery of plasmids[J]. Small, 2018, 14(42): 1803061. |
| 52 | QI Y, LIU Y L, YU B R, et al. A lactose-derived CRISPR/Cas9 delivery system for efficient genome editing in vivo to treat orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(17): 2001424. |
| 53 | WANG H X, SONG Z Y, LAO Y H, et al. Nonviral gene editing via CRISPR/Cas9 delivery by membrane-disruptive and endosomolytic helical polypeptide[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(19): 4903-4908. |
| 54 | GUO J J, WAN T, LI B W, et al. Rational design of poly(disulfide) s as a universal platform for delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 machineries toward therapeutic genome editing[J]. ACS Central Science, 2021, 7(6): 990-1000. |
| 55 | WANG F, GAO J Y, XIAO J G, et al. Dually gated polymersomes for gene delivery[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 18(9): 5562-5568. |
| 56 | VEIMAN K L, KÜNNAPUU K, LEHTO T, et al. PEG shielded MMP sensitive CPPs for efficient and tumor specific gene delivery in vivo [J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2015, 209: 238-247. |
| 57 | LIU C, WANG N, LUO R, et al. A programmable hierarchical-responsive nanoCRISPR elicits robust activation of endogenous target to treat cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(20): 9833-9846. |
| 58 | WANG H X, YANG X Z, SUN C Y, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 2-responsive micelle for siRNA delivery[J]. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(26): 7622-7634. |
| 59 | CHEN Z M, LIU F Y, CHEN Y K, et al. Targeted delivery of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated cancer gene therapy via liposome-templated hydrogel nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(46): 1703036. |
| 60 | LI L, SONG L J, LIU X W, et al. Artificial virus delivers CRISPR-Cas9 system for genome editing of cells in mice[J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(1): 95-111. |
| 61 | WILLIFORD J M, WU J, REN Y, et al. Recent advances in nanoparticle-mediated siRNA delivery[J]. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 2014, 16: 347-370. |
| 62 | ANSELMO A C, MITRAGOTRI S. Nanoparticles in the clinic[J]. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine, 2016, 1(1): 10-29. |
| 63 | LEE Y W, LUTHER D C, KRETZMANN J A, et al. Protein delivery into the cell cytosol using non-viral nanocarriers[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(11): 3280-3292. |
| 64 | WANG P, ZHANG L M, XIE Y, et al. Genome editing for cancer therapy: delivery of Cas9 protein/sgRNA plasmid via a gold nanocluster/lipid core-shell nanocarrier[J]. Advanced Science, 2017, 4(11): 1700175. |
| 65 | MOUT R, RAY M, YESILBAG TONGA G, et al. Direct cytosolic delivery of CRISPR/Cas9-ribonucleoprotein for efficient gene editing[J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(3): 2452-2458. |
| 66 | LEE K, CONBOY M, PARK H M, et al. Nanoparticle delivery of Cas9 ribonucleoprotein and donor DNA in vivo induces homology-directed DNA repair[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 1(11): 889-901. |
| 67 | LEE B, LEE K, PANDA S, et al. Nanoparticle delivery of CRISPR into the brain rescues a mouse model of fragile X syndrome from exaggerated repetitive behaviours[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 2(7): 497-507. |
| 68 | YANG Y M, HAN Y, SUN Q Y, et al. Au-siRNA@ aptamer nanocages as a high-efficiency drug and gene delivery system for targeted lung cancer therapy[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2021, 19(1): 54. |
| 69 | SHAHBAZI R, SGHIA-HUGHES G, REID J L, et al. Targeted homology-directed repair in blood stem and progenitor cells with CRISPR nanoformulations[J]. Nature Materials, 2019, 18(10): 1124-1132. |
| 70 | WANG P, ZHANG L M, ZHENG W F, et al. Thermo-triggered release of CRISPR-Cas9 system by lipid-encapsulated gold nanoparticles for tumor therapy[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 130(6): 1507-1512. |
| 71 | PAN Y C, YANG J J, LUAN X W, et al. Near-infrared upconversion-activated CRISPR-Cas9 system: a remote-controlled gene editing platform[J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(4): eaav7199. |
| 72 | PODDAR A, CONESA J J, LIANG K, et al. Encapsulation, visualization and expression of genes with biomimetically mineralized zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8)[J]. Small, 2019, 15(36): 1902268. |
| 73 | ALYAMI M Z, ALSAIARI S K, LI Y Y, et al. Cell-type-specific CRISPR/Cas9 delivery by biomimetic metal organic frameworks[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(4): 1715-1720. |
| 74 | ALSAIARI S K, PATIL S, ALYAMI M, et al. Endosomal escape and delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing machinery enabled by nanoscale zeolitic imidazolate framework[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(1): 143-146. |
| 75 | WANG Y Y, SHAHI P K, XIE R S, et al. A pH-responsive silica-metal-organic framework hybrid nanoparticle for the delivery of hydrophilic drugs, nucleic acids, and CRISPR-Cas9 genome-editing machineries[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2020, 324: 194-203. |
| 76 | YANG X T, TANG Q, JIANG Y, et al. Nanoscale ATP-responsive zeolitic imidazole framework-90 as a general platform for cytosolic protein delivery and genome editing[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(9): 3782-3786. |
| 77 | YUE H H, ZHOU X M, CHENG M, et al. Graphene oxide-mediated Cas9/sgRNA delivery for efficient genome editing[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(3): 1063-1071. |
| 78 | SALEKDEH P R, MA'MANI L, TAVAKKOLY-BAZZAZ J, et al. Bi-functionalized aminoguanidine-PEGylated periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles: a promising nanocarrier for delivery of Cas9-sgRNA ribonucleoproteine[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2021, 19(1): 95. |
| 79 | LIU B, EJAZ W, GONG S, et al. Engineered interactions with mesoporous silica facilitate intracellular delivery of proteins and gene editing[J]. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(5): 4014-4021. |
| 80 | ZHOU W H, CUI H D, YING L M, et al. Enhanced cytosolic delivery and release of CRISPR/Cas9 by black phosphorus nanosheets for genome editing[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 130(32): 10425-10429. |
| 81 | LI S J, SONG Z Y, LIU C Y, et al. Biomimetic mineralization-based CRISPR/Cas9 ribonucleoprotein nanoparticles for gene editing[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(51): 47762-47770. |
| 82 | HAN X, XU X, WU Z H, et al. Synchronous conjugation of i-motif DNA and therapeutic siRNA on the vertexes of tetrahedral DNA nanocages for efficient gene silence[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2021, 11(10): 3286-3296. |
| 83 | MITCHELL M J, BILLINGSLEY M M, HALEY R M, et al. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2021, 20(2): 101-124. |
| 84 | KANETI L, BRONSHTEIN T, MALKAH DAYAN N, et al. Nanoghosts as a novel natural nonviral gene delivery platform safely targeting multiple cancers[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(3): 1574-1582. |
| 85 | LIN Y, WU J H, GU W H, et al. Exosome-liposome hybrid nanoparticles deliver CRISPR/Cas9 system in MSCs[J]. Advanced Science, 2018, 5(4): 1700611. |
| 86 | LU M, ZHAO X Y, XING H N, et al. Cell-free synthesis of connexin 43-integrated exosome-mimetic nanoparticles for siRNA delivery[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2019, 96: 517-536. |
| 87 | LÜ P, JAVIDI-PARSIJANI P, ATALA A, et al. Delivering Cas9/sgRNA ribonucleoprotein (RNP) by lentiviral capsid-based bionanoparticles for efficient 'hit-and-Run' genome editing[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(17): e99. |
| 88 | MANGEOT P E, RISSON V, FUSIL F, et al. Genome editing in primary cells and in vivo using viral-derived Nanoblades loaded with Cas9-sgRNA ribonucleoproteins[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 45. |
| 89 | KAMERKAR S, LEBLEU V S, SUGIMOTO H, et al. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer[J]. Nature, 2017, 546(7659): 498-503. |
| 90 | XU Q, ZHANG Z, ZHAO L, et al. Tropism-facilitated delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 system with chimeric antigen receptor-extracellular vesicles against B-cell malignancies[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2020, 326: 455-467. |
| 91 | WANG Q Y, YU J J, KADUNGURE T, et al. ARMMs as a versatile platform for intracellular delivery of macromolecules[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 960. |
| 92 | GEE P, LUNG M S Y, OKUZAKI Y, et al. Extracellular nanovesicles for packaging of CRISPR-Cas9 protein and sgRNA to induce therapeutic exon skipping[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 1334. |
| 93 | ZHUANG J L, TAN J Z, WU C L, et al. Extracellular vesicles engineered with valency-controlled DNA nanostructures deliver CRISPR/Cas9 system for gene therapy[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(16): 8870-8882. |
| 94 | REN K, LIU Y, WU J, et al. A DNA dual lock-and-key strategy for cell-subtype-specific siRNA delivery[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 13580. |
| 95 | HERRMANN I K, WOOD M J A, FUHRMANN G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2021, 16(7): 748-759. |
| 96 | CULLY M. Exosome-based candidates move into the clinic[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2021, 20(1): 6-7. |
| 97 | AUSLÄNDER S, FUSSENEGGER M. Engineering gene circuits for mammalian cell-based applications[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2016, 8(7): a023895. |
| 98 | ARATBONI H A, RAFIEI N, KHORASHAD L K, et al. LED control of gene expression in a nanobiosystem composed of metallic nanoparticles and a genetically modified E. coli strain[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2021, 19(1): 190. |
| 99 | HASTY J, PRADINES J, DOLNIK M, et al. Noise-based switches and amplifiers for gene expression[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2000, 97(5): 2075-2080. |
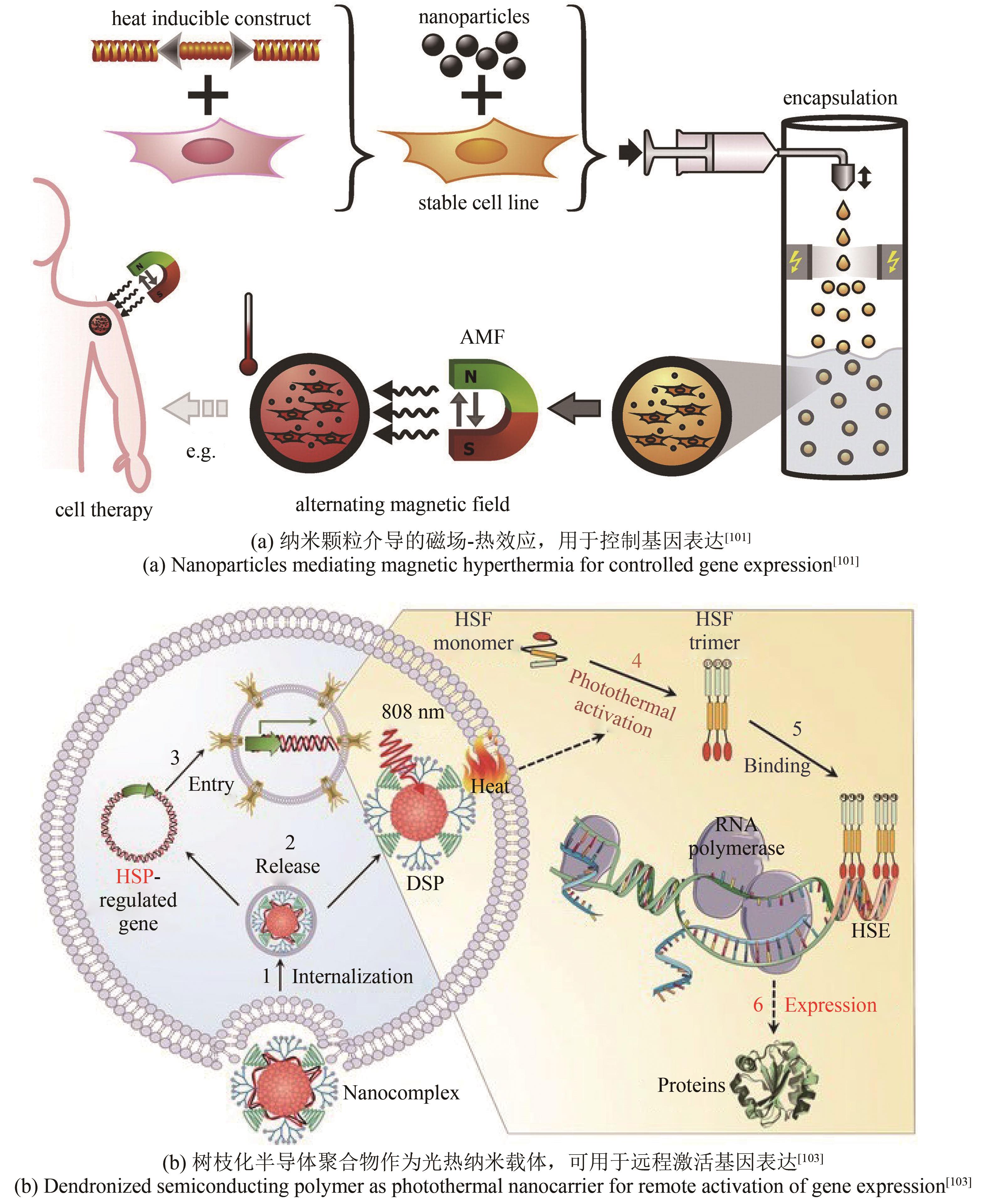
| 100 | TANG Q S, ZHANG D S, CONG X M, et al. Using thermal energy produced by irradiation of Mn-Zn ferrite magnetic nanoparticles (MZF-NPs) for heat-inducible gene expression[J]. Biomaterials, 2008, 29(17): 2673-2679. |
| 101 | ORTNER V, KASPAR C, HALTER C, et al. Magnetic field-controlled gene expression in encapsulated cells[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2012, 158(3): 424-432. |
| 102 | YAMAGUCHI M, ITO A, ONO A, et al. Heat-inducible gene expression system by applying alternating magnetic field to magnetic nanoparticles[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2014, 3(5): 273-279. |
| 103 | LÜ Y, CUI D, SUN H, et al. Dendronized semiconducting polymer as photothermal nanocarrier for remote activation of gene expression[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(31): 9155-9159. |
| 104 | WANG Y X, LI S L, ZHANG P B, et al. Photothermal-responsive conjugated polymer nanoparticles for remote control of gene expression in living cells[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(8): 1705418. |
| 105 | BAKHTIARI A, HSIAO D, JIN G X, et al. An efficient method based on the photothermal effect for the release of molecules from metal nanoparticle surfaces[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(23): 4166-4169. |
| 106 | TAN S W, WU T T, ZHANG D, et al. Cell or cell membrane-based drug delivery systems[J]. Theranostics, 2015, 5(8): 863-881. |
| 107 | REN E, LIU C, LV P, et al. Genetically engineered cellular membrane vesicles as tailorable shells for therapeutics[J]. Advanced Science, 2021, 8(21): 2100460. |
| 108 | NIEL G VAN, D'ANGELO G, RAPOSO G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2018, 19(4): 213-228. |
| 109 | SHI X J, CHENG Q Q, HOU T L, et al. Genetically engineered cell-derived nanoparticles for targeted breast cancer immunotherapy[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2020, 28(2): 536-547. |
| 110 | SU D D, TSAI H I, XU Z X, et al. Exosomal PD-L1 functions as an immunosuppressant to promote wound healing[J]. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 2020, 9(1): 1709262. |
| 111 | SHELLER-MILLER S, RADNAA E, YOO J K, et al. Exosomal delivery of NF-κB inhibitor delays LPS-induced preterm birth and modulates fetal immune cell profile in mouse models[J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(4): eabd3865. |
| 112 | KOJIMA R, BOJAR D, RIZZI G, et al. Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson's disease treatment[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1305. |
| 113 | MORISHITA M, TAKAHASHI Y, MATSUMOTO A, et al. Exosome-based tumor antigens-adjuvant co-delivery utilizing genetically engineered tumor cell-derived exosomes with immunostimulatory CpG DNA[J]. Biomaterials, 2016, 111: 55-65. |
| 114 | ZHANG P F, LIU G, CHEN X Y. Nanobiotechnology: Cell membrane-based delivery systems[J]. Nano Today, 2017, 13: 7-9. |
| 115 | ZHANG P F, CHEN Y X, ZENG Y, et al. Virus-mimetic nanovesicles as a versatile antigen-delivery system[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(45): E6129-E6138. |
| 116 | LIU X, YUAN L Z, ZHANG L, et al. Bioinspired artificial nanodecoys for Hepatitis B virus[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(38): 12499-12503. |
| 117 | ZHANG X J, XU Q B, ZI Z K, et al. Programmable extracellular vesicles for macromolecule delivery and genome modifications[J]. Developmental Cell, 2020, 55(6): 784-801.e9. |
| 118 | LÜ P, LIU X, CHEN X M, et al. Genetically engineered cell membrane nanovesicles for oncolytic adenovirus delivery: a versatile platform for cancer virotherapy[J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(5): 2993-3001. |
| 119 | RICHTER M, VADER P, FUHRMANN G. Approaches to surface engineering of extracellular vesicles[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2021, 173: 416-426. |
| 120 | CHEN L X, VALENTINE J L, HUANG C J, et al. Outer membrane vesicles displaying engineered glycotopes elicit protective antibodies[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(26): E3609-E3618. |
| 121 | GUJRATI V, KIM S, KIM S H, et al. Bioengineered bacterial outer membrane vesicles as cell-specific drug-delivery vehicles for cancer therapy[J]. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(2): 1525-1537. |
| 122 | LI Y, ZHAO R, CHENG K, et al. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles presenting programmed death 1 for improved cancer immunotherapy via immune activation and checkpoint inhibition[J]. ACS Nano, 2020: 2020Nov24. |
| 123 | WEI X L, ZHANG G, RAN D N, et al. T-cell-mimicking nanoparticles can neutralize HIV infectivity[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(45): 1802233. |
| 124 | WANG C, WANG S B, CHEN Y, et al. Membrane nanoparticles derived from ACE2-rich cells block SARS-CoV-2 infection[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(4): 6340-6351. |
| 125 | MENG Q F, ZHAO Y Y, DONG C B, et al. Genetically programmable fusion cellular vesicles for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(50): 26320-26326. |
| 126 | XU Z X, TSAI H I, XIAO Y M, et al. Engineering programmed death ligand-1/cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 dual-targeting nanovesicles for immunosuppressive therapy in transplantation[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(7): 7959-7969. |
| 127 | LI L Y, MIAO Q W, MENG F Q, et al. Genetic engineering cellular vesicles expressing CD64 as checkpoint antibody carrier for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(12): 6033-6043. |
| 128 | ZHANG X D, WANG C, WANG J Q, et al. PD-1 blockade cellular vesicles for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(22): 1707112. |
| 129 | PANG X, LIU X, CHENG Y, et al. Sono-immunotherapeutic nanocapturer to combat multidrug-resistant bacterial infections[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(35): 1902530. |
| 130 | CHEN Z W, WANG Z J, GU Z. Bioinspired and biomimetic nanomedicines[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2019, 52(5): 1255-1264. |
| 131 | ZHANG X D, WANG J Q, CHEN Z W, et al. Engineering PD-1-presenting platelets for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 18(9): 5716-5725. |
| 132 | MAUSE S F, HUNDELSHAUSEN P VON, ZERNECKE A, et al. Platelet microparticles: a transcellular delivery system for RANTES promoting monocyte recruitment on endothelium[J]. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 2005, 25(7): 1512-1518. |
| 133 | WANG C, SUN W J, YE Y Q, et al. In situ activation of platelets with checkpoint inhibitors for post-surgical cancer immunotherapy[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 1: 11. |
| 134 | HU Q Y, SUN W J, WANG J Q, et al. Conjugation of haematopoietic stem cells and platelets decorated with anti-PD-1 antibodies augments anti-leukaemia efficacy[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 2(11): 831-840. |
| 135 | ZHANG X D, KANG Y, WANG J Q, et al. Engineered PD-L1-expressing platelets reverse new-onset type 1 diabetes[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(26): 1907692. |
| 136 | EDMUNDSON M C, CAPENESS M, HORSFALL L. Exploring the potential of metallic nanoparticles within synthetic biology[J]. New Biotechnology, 2014, 31(6): 572-578. |
| 137 | PRINDLE A, SAMAYOA P, RAZINKOV I, et al. A sensing array of radically coupled genetic 'biopixels'[J]. Nature, 2012, 481(7379): 39-44. |
| 138 | JEWETT M C, PATOLSKY F. Nanobiotechnology: synthetic biology meets materials science[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2013, 24(4): 551-554. |
| 139 | WANG J, LI Y Y, NIE G J. Multifunctional biomolecule nanostructures for cancer therapy[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2021, 6(9): 766-783. |
| 140 | WANG Z G, DING B Q. Engineering DNA self-assemblies as templates for functional nanostructures[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2014, 47(6): 1654-1662. |
| 141 | DEY S, FAN C H, GOTHELF K V, et al. DNA origami[J]. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 2021, 1: 13. |
| 142 | KE Y G, ONG L L, SHIH W M, et al. Three-dimensional structures self-assembled from DNA bricks[J]. Science, 2012, 338(6111): 1177-1183. |
| 143 | SEEMAN N C, SLEIMAN H F. DNA nanotechnology[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2018, 3: 17068. |
| 144 | 施茜, 吴园园, 杨洋. DNA 纳米技术与合成生物学[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(2): 302-319. |
| SHI Qian, WU Yuanyuan, YANG yang. DNA nanotechnology and synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(2): 302-319. | |
| 145 | LI S P, JIANG Q, LIU S L, et al. A DNA nanorobot functions as a cancer therapeutic in response to a molecular trigger in vivo [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(3): 258-264. |
| 146 | LIU S L, JIANG Q, ZHAO X, et al. A DNA nanodevice-based vaccine for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Nature Materials, 2021, 20(3): 421-430. |
| 147 | KE G L, LIU M H, JIANG S X, et al. Directional regulation of enzyme pathways through the control of substrate channeling on a DNA origami scaffold[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2016, 128(26): 7609-7612. |
| 148 | YAO G B, ZHANG F, WANG F, et al. Meta-DNA structures[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2020, 12(11): 1067-1075. |
| 149 | HSIA Y, BALE J B, GONEN S, et al. Design of a hyperstable 60-subunit protein icosahedron[J]. Nature, 2016, 535(7610): 136-139. |
| 150 | GU C K, ZHANG T, LÜ C Y, et al. His-mediated reversible self-assembly of ferritin nanocages through two different switches for encapsulation of cargo molecules[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(12): 17080-17090. |
| 151 | HARTZELL E J, LIESER R M, SULLIVAN M O, et al. Modular hepatitis B virus-like particle platform for biosensing and drug delivery[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(10): 12642-12651. |
| 152 | KIM E Y, TULLMAN-ERCEK D. Engineering nanoscale protein compartments for synthetic organelles[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2013, 24(4): 627-632. |
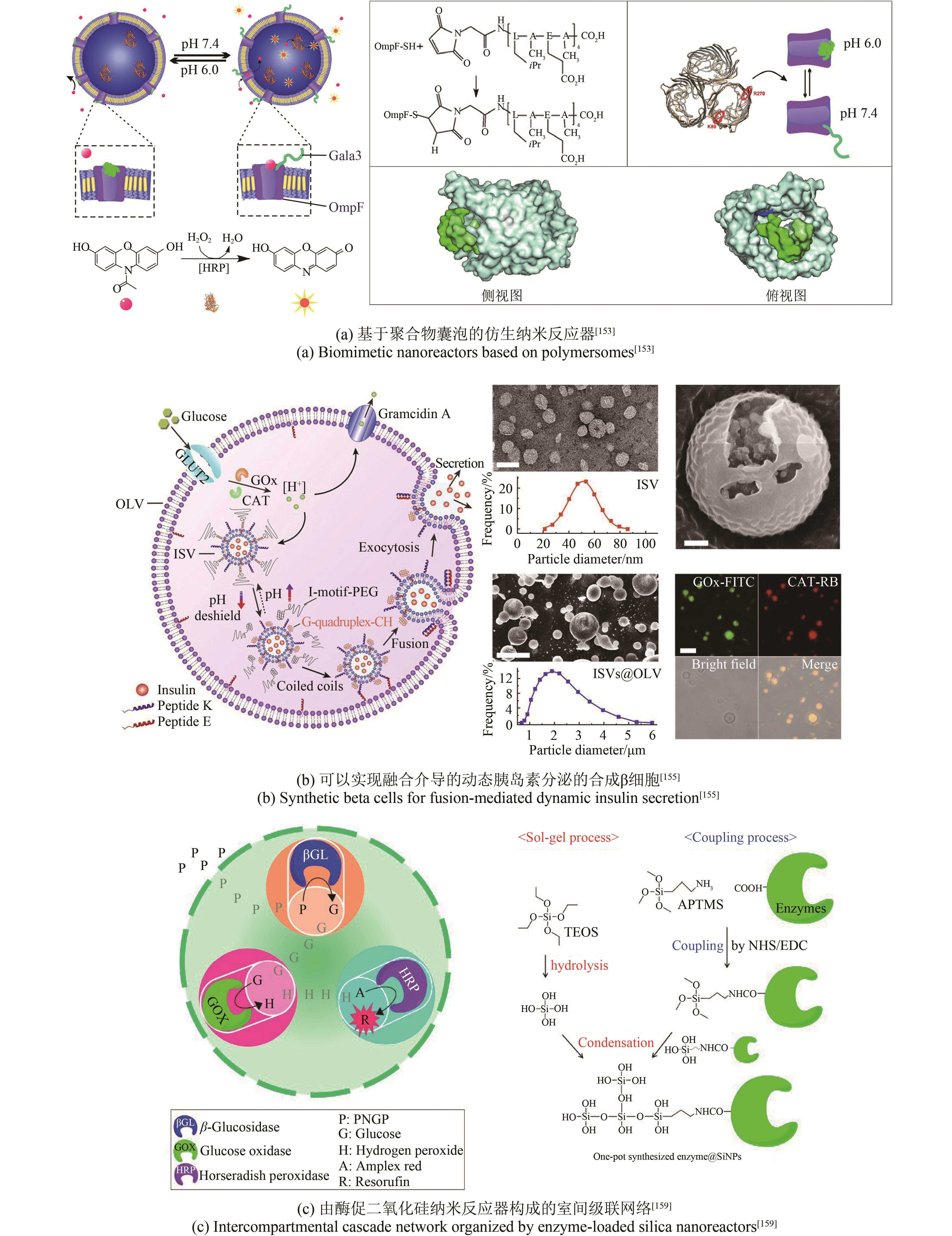
| 153 | EDLINGER C, EINFALT T, SPULBER M, et al. Biomimetic strategy to reversibly trigger functionality of catalytic nanocompartments by the insertion of pH-responsive biovalves[J]. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(9): 5790-5798. |
| 154 | YU J C, QIAN C G, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Hypoxia and H2O2 dual-sensitive vesicles for enhanced glucose-responsive insulin delivery[J]. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(2): 733-739. |
| 155 | CHEN Z W, WANG J Q, SUN W J, et al. Synthetic beta cells for fusion-mediated dynamic insulin secretion[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(1): 86-93. |
| 156 | PETERS R J R W, MARGUET M, MARAIS S, et al. Cascade reactions in multicompartmentalized polymersomes[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2014, 126(1): 150-154. |
| 157 | XU C, HU S, CHEN X Y. Artificial cells: from basic science to applications[J]. Materials Today, 2016, 19(9): 516-532. |
| 158 | KÜCHLER A, YOSHIMOTO M, LUGINBÜHL S, et al. Enzymatic reactions in confined environments[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2016, 11(5): 409-420. |
| 159 | JO S M, WURM F R, LANDFESTER K. Biomimetic cascade network between interactive multicompartments organized by enzyme-loaded silica nanoreactors[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(40): 34230-34237. |
| 160 | CHEN F M, ZANG Z S, CHEN Z, et al. Nanophotosensitizer-engineered Salmonella bacteria with hypoxia targeting and photothermal-assisted mutual bioaccumulation for solid tumor therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2019, 214: 119226. |
| 161 | ZHENG D W, CHEN Y, LI Z H, et al. Optically-controlled bacterial metabolite for cancer therapy[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1680. |
| 162 | FELFOUL O, MOHAMMADI M, TAHERKHANI S, et al. Magneto-aerotactic bacteria deliver drug-containing nanoliposomes to tumour hypoxic regions[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2016, 11(11): 941-947. |
| 163 | FORBES N S. Engineering the perfect (bacterial) cancer therapy[J]. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2010, 10(11): 785-794. |
| 164 | AKIN D, STURGIS J, RAGHEB K, et al. Bacteria-mediated delivery of nanoparticles and cargo into cells[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2007, 2(7): 441-449. |
| 165 | BOURDEAU R W, LEE-GOSSELIN A, LAKSHMANAN A, et al. Acoustic reporter genes for noninvasive imaging of microorganisms in mammalian hosts[J]. Nature, 2018, 553(7686): 86-90. |
| 166 | DENG X Y, YANG W B, SHAO Z W, et al. Genetically modified bacteria for targeted phototherapy of tumor[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 272: 120809. |
| 167 | DEWHIRST M W, SECOMB T W. Transport of drugs from blood vessels to tumour tissue[J]. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2017, 17(12): 738-750. |
| 168 | SUH S, JO A, TRAORE M A, et al. Nanoscale bacteria-enabled autonomous drug delivery system (NanoBEADS) enhances intratumoral transport of nanomedicine[J]. Advanced Science, 2019, 6(3): 1801309. |
| 169 | FAN J X, PENG M Y, WANG H, et al. Engineered bacterial bioreactor for tumor therapy via Fenton-like reaction with localized H2O2 generation[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(16): 1808278. |
| 170 | XING J H, YIN T, LI S M, et al. Sequential magneto-actuated and optics-triggered biomicrorobots for targeted cancer therapy[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(11): 2008262. |
| 171 | NEWICK K, O'BRIEN S, MOON E, et al. CAR T cell therapy for solid tumors[J]. Annual Review of Medicine, 2017, 68: 139-152. |
| 172 | MAUDE S L, LAETSCH T W, BUECHNER J, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults with B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2018, 378(5): 439-448. |
| 173 | TANG L, ZHENG Y R, MELO M B, et al. Enhancing T cell therapy through TCR-signaling-responsive nanoparticle drug delivery[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(8): 707-716. |
| 174 | NIE W D, WEI W, ZUO L P, et al. Magnetic nanoclusters armed with responsive PD-1 antibody synergistically improved adoptive T-cell therapy for solid tumors[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(2): 1469-1478. |
| 175 | HAO M X, HOU S Y, LI W S, et al. Combination of metabolic intervention and T cell therapy enhances solid tumor immunotherapy[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2020, 12(571): eaaz6667. |
| 176 | KIM G B, ARAGON-SANABRIA V, RANDOLPH L, et al. High-affinity mutant Interleukin-13 targeted CAR T cells enhance delivery of clickable biodegradable fluorescent nanoparticles to glioblastoma[J]. Bioactive Materials, 2020, 5(3): 624-635. |
| 177 | SIRIWON N, KIM Y J, SIEGLER E, et al. CAR-T cells surface-engineered with drug-encapsulated nanoparticles can ameliorate intratumoral T-cell hypofunction[J]. Cancer Immunology Research, 2018, 6(7): 812-824. |
| 178 | CHEN Q, HU Q Y, DUKHOVLINOVA E, et al. Photothermal therapy promotes tumor infiltration and antitumor activity of CAR T cells[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(23): 1900192. |
| 179 | HU Q, LI H, ARCHIBONG E, et al. Inhibition of post-surgery tumour recurrence via a hydrogel releasing CAR-T cells and anti-PDL1-conjugated platelets[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2021, 5(9): 1038-1047. |
| 180 | HARMSEN S, MEDINE E I, MOROZ M, et al. A dual-modal PET/near infrared fluorescent nanotag for long-term immune cell tracking[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 269: 120630. |
| 181 | UJÉDA L. Nanotechnology and synthetic biology: the ambiguity of the nano-bio convergence[J]. Philosophia Scientae, 2019, 23(23-1): 57-72. |
| 182 | PURNICK P E, WEISS R. The second wave of synthetic biology: from modules to systems[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2009, 10(6): 410-422. |
| [1] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | LIU Xiaoyue, WANG Pandi, WU Gang, LIU Fang. Efficient biosynthesis of glucoraphanin in Brassicaceae crops by genetic engineering [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 136-156. |
| [4] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [11] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [12] | ZHANG Xuanliang, LI Qingting, WANG Fei. Data writing in DNA storage systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1125-1141. |
| [13] | CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [14] | CAI Bingyu, TAN Xiangtian, LI Wei. Advances in synthetic biology for engineering stem cell [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [15] | XIE Huang, ZHENG Yilei, SU Yiting, RUAN Jingyi, LI Yongquan. An overview on reconstructing the biosynthetic system of actinomycetes for polyketides production [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||