Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (3): 444-463.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-003
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Rational design for functional topology and its applications in synthetic biology
SUN Zhi1, YANG Ning1, LOU Chunbo2, TANG Chao1, YANG Xiaojing1
- 1.Center for Quantitative Biology,Peking-Tsinghua Center for Life Sciences,Academy for Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies,Peking University,Beijing 100871,China
2.Cell and Gene Circuit Design Center,Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518000,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2023-01-02Revised:2023-02-09Online:2023-07-05Published:2023-06-30 -
Contact:TANG Chao, YANG Xiaojing
功能拓扑的理性设计及其在合成生物学中的应用
孙智1, 杨宁1, 娄春波2, 汤超1, 杨晓静1
- 1.北京大学定量生物学中心,北京大学-清华大学生命科学联合中心,北京大学前沿学科交叉研究院,北京大学,北京 100871
2.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,细胞与基因线路设计中心,广东 深圳 518000
-
通讯作者:汤超,杨晓静 -
作者简介:孙智 (1994—),男,博士后。研究方向为定量合成生物学,人工生命系统的理性设计。 E-mail:sunz@pku.edu.cn杨宁 (1995—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为复杂系统、定量生物学。 E-mail:yn_biophy@pku.edu.cn汤超 (1958—),男,中国科学院院士,讲席教授,博士生导师。研究方向为物理生物学,系统生物学,统计物理和复杂系统。 E-mail:tangc@pku.edu.cn杨晓静 (1978—),女,副研究员。研究方向为系统生物学,定量生物学,合成生物学。 E-mail:xiaojing_yang@pku.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0900700);北京大学-清华大学生命科学联合中心博士后基金
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SUN Zhi, YANG Ning, LOU Chunbo, TANG Chao, YANG Xiaojing. Rational design for functional topology and its applications in synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(3): 444-463.
孙智, 杨宁, 娄春波, 汤超, 杨晓静. 功能拓扑的理性设计及其在合成生物学中的应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(3): 444-463.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2023-003
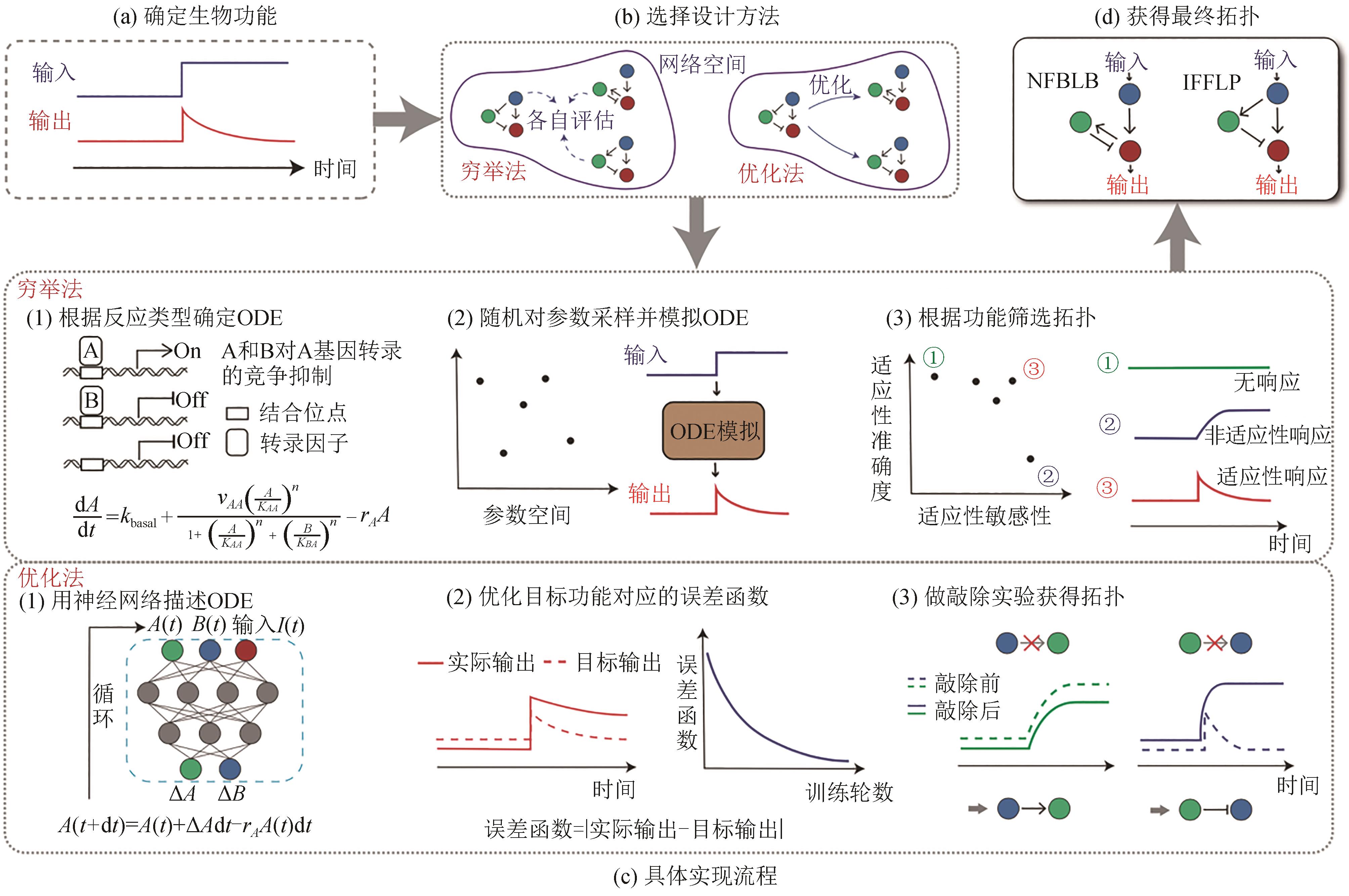
Fig. 1 Rational design for biological networks(a) Identification of biological functions. (b) Two typical design methods: enumeration and optimization. (c) Workflow for these methods. Enumeration method: determining ODE (ordinary differential equation) according to reaction types, randomly sampling parameters to simulate ODE, and finally filtering topological networks with their functions as criteria. Optimization method: describing ODE by neural network to optimize the error function, and finally obtaining the topological networks by knockout experiments. (d) Determination of the final topological networks
| 功能 | 表型 | 拓扑 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 适应性 | 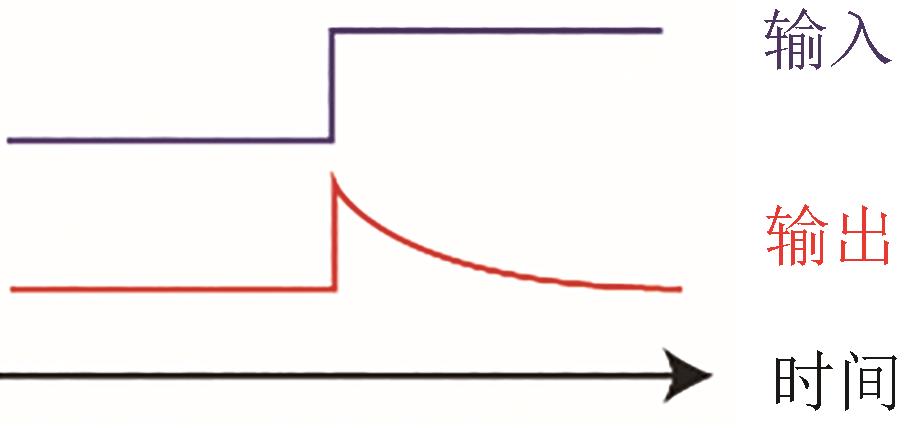 | 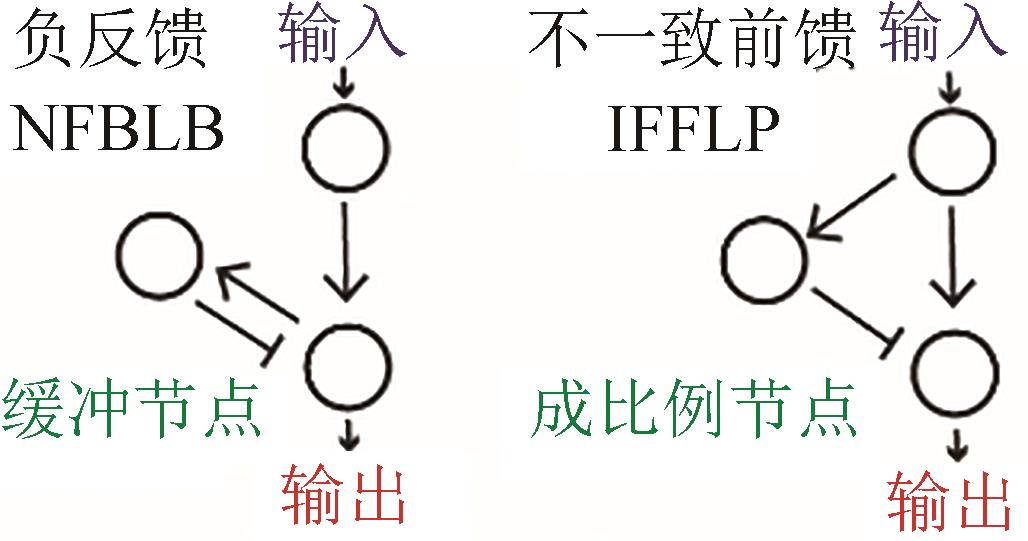 | 酶促反应网络 Me, et al., 2009[ |
| 振荡 | 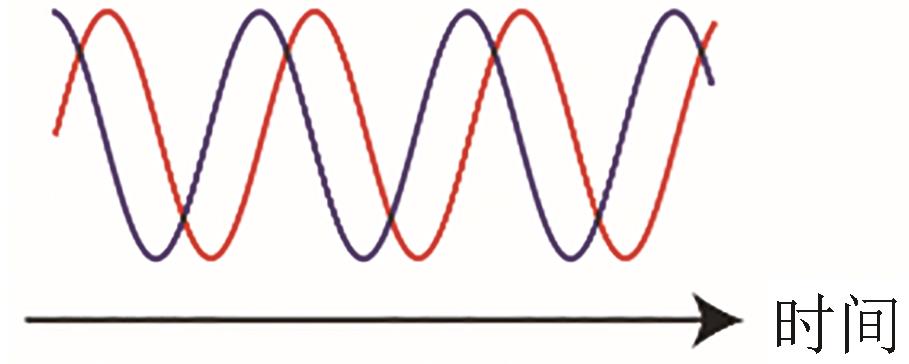 |  | Wagner, 2005[ Elowitz and Leibler, 2000[ |
| 双稳态 | 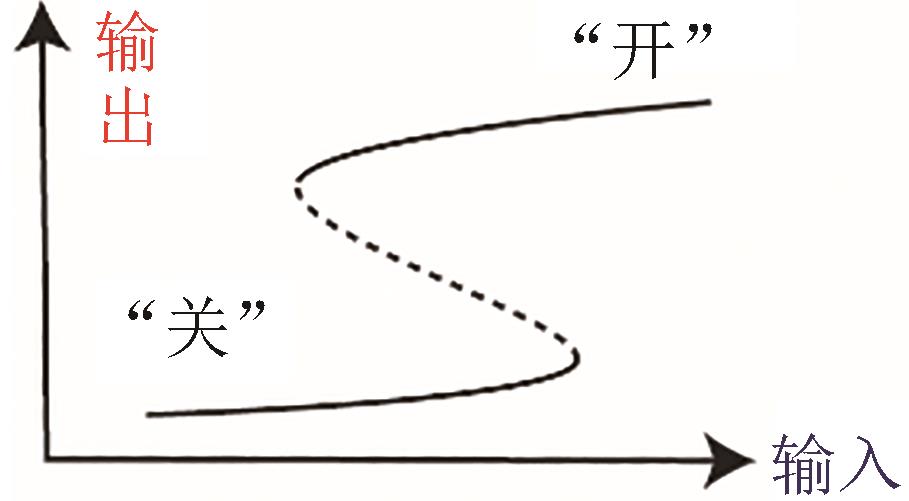 | 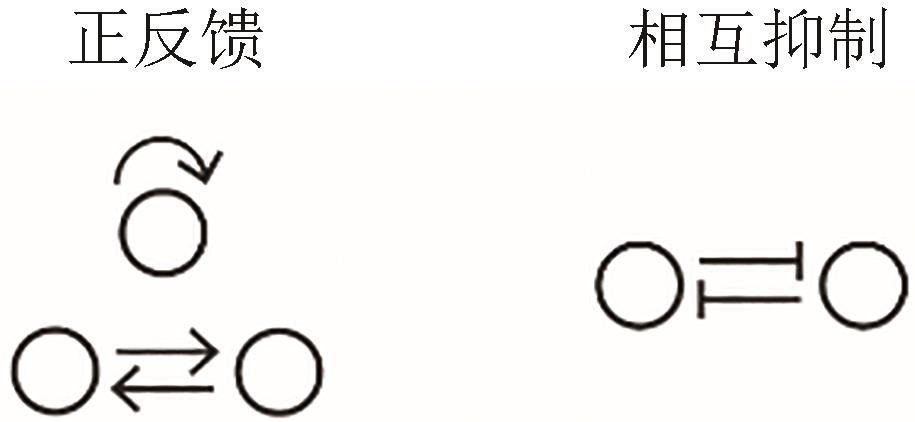 | Shah and Sarkar, 2011[ |
| 持续性检测 | 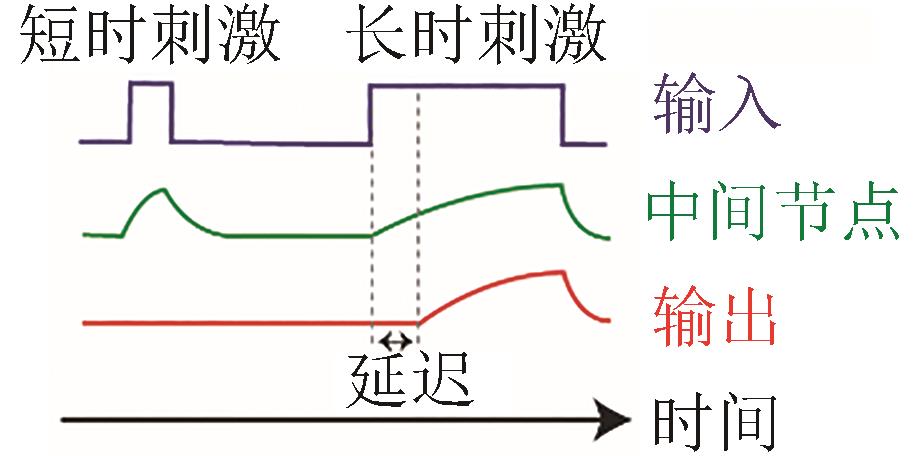 | 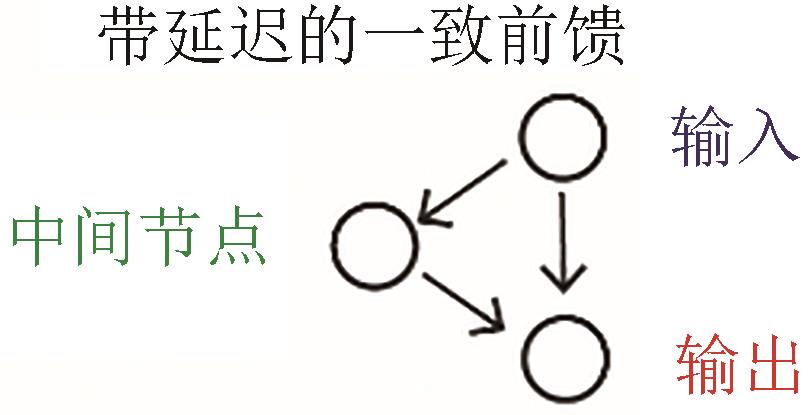 | Alon, 2007[ |
| 抗噪 | 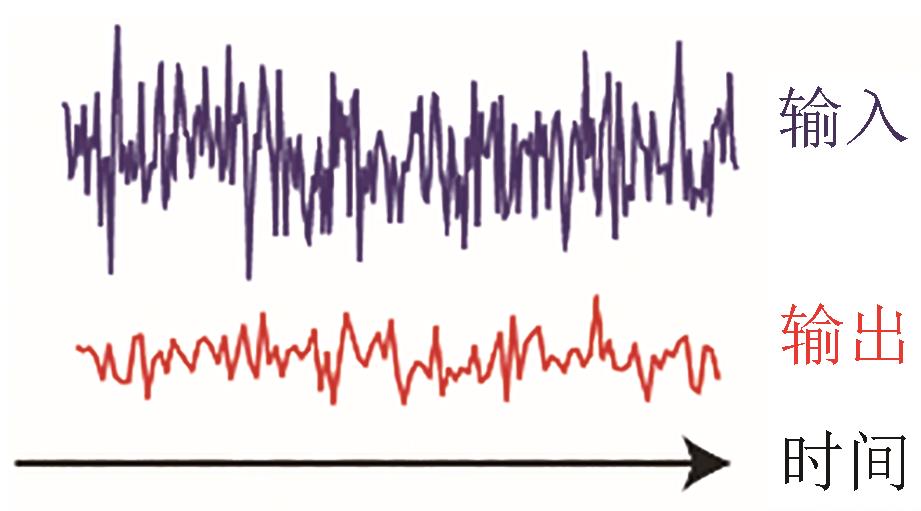 | 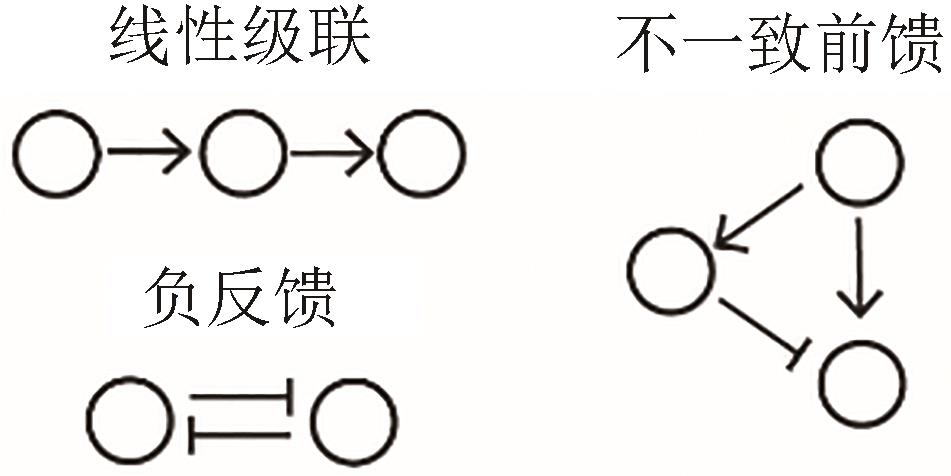 | Nie, et al., 2020[ |
| 体节发育 |  | 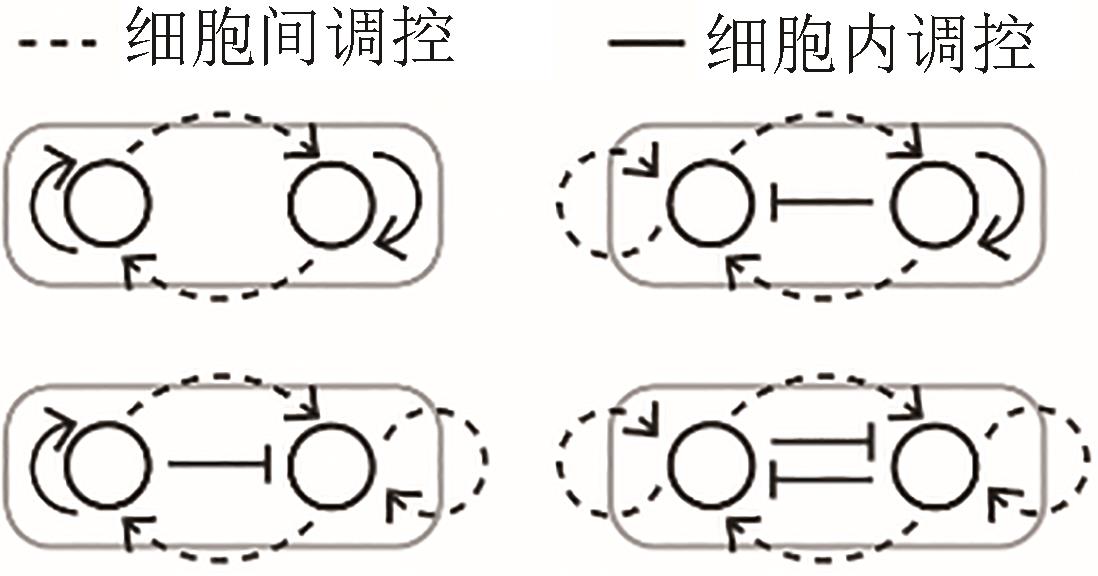 | Ma, et al., 2006[ |
| 细胞极化 | 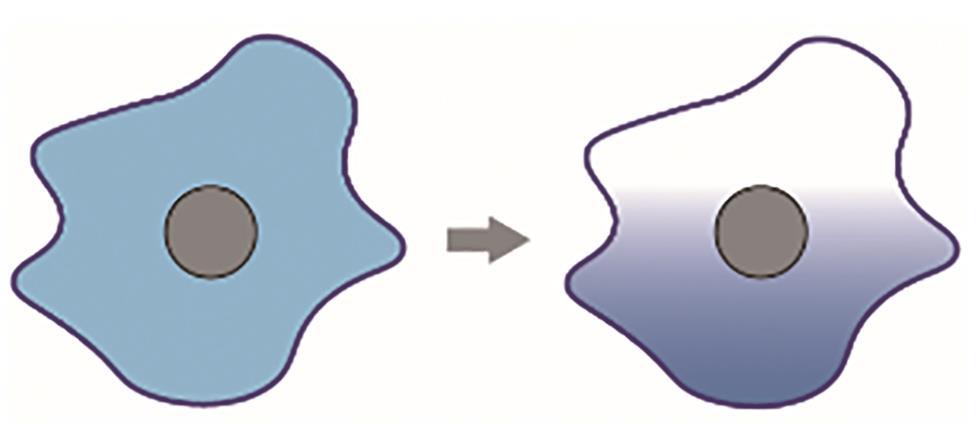 | 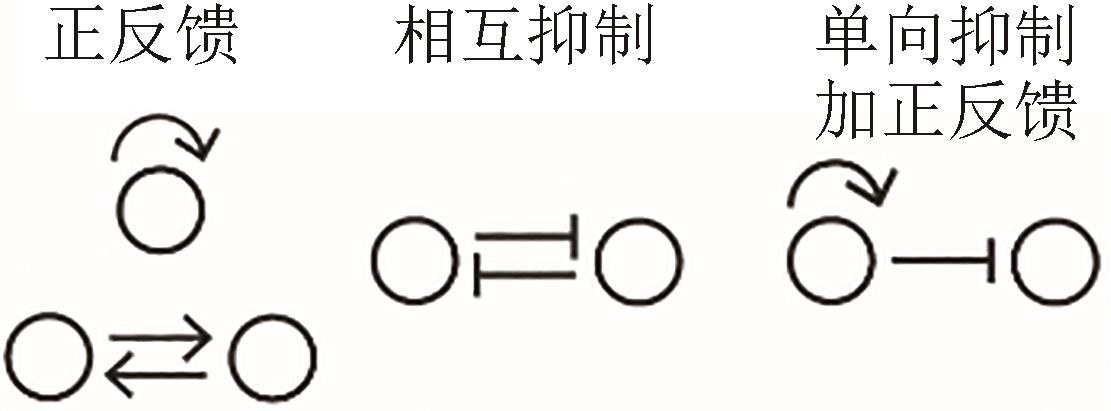 | Chau,et al., 2012[ |
| 适应性/振荡双功能 | 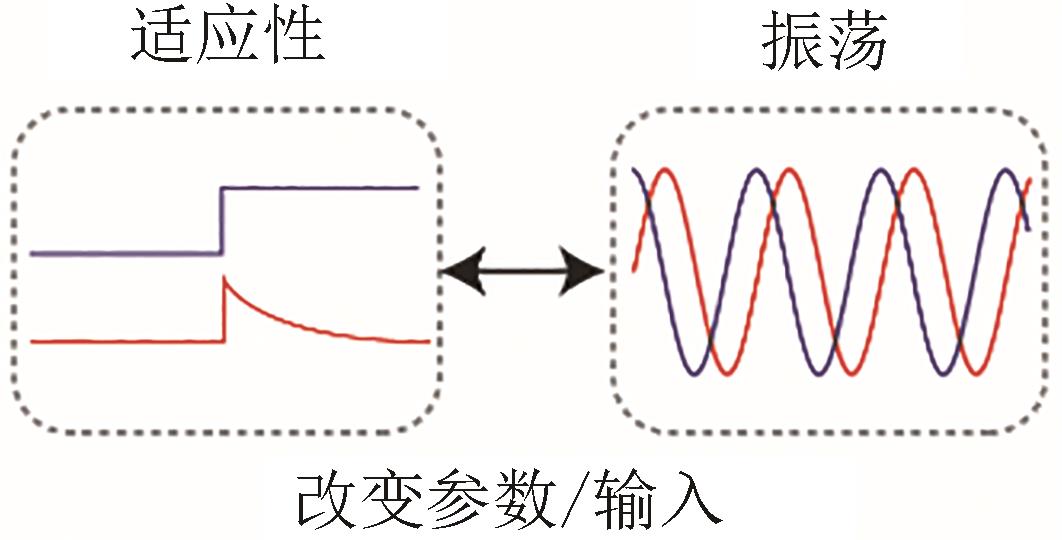 | 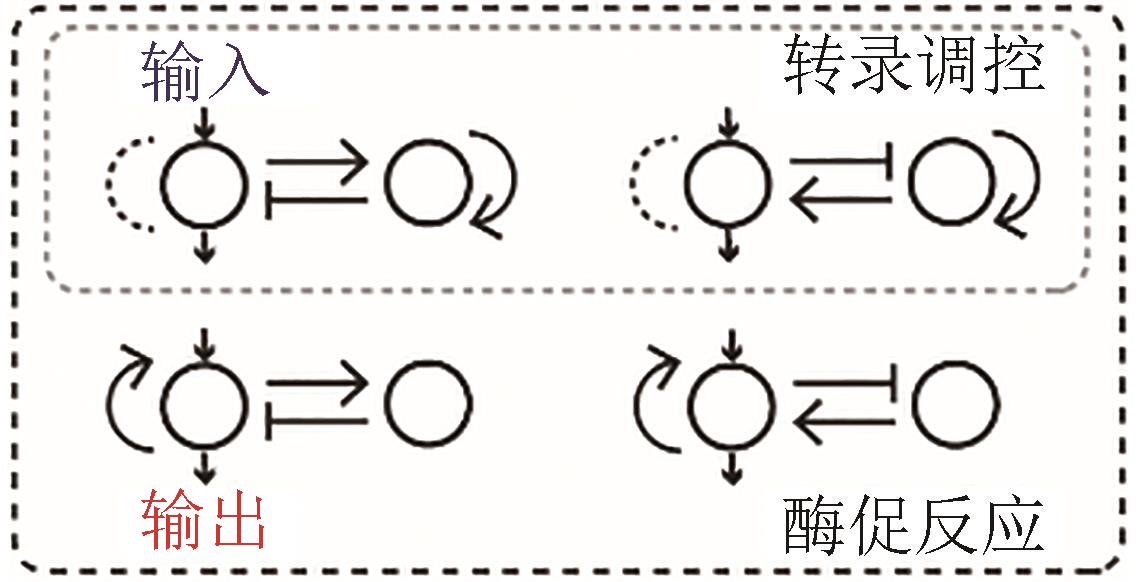 | Zhang, et al., 2019[ |
| 调频/调幅响应 | 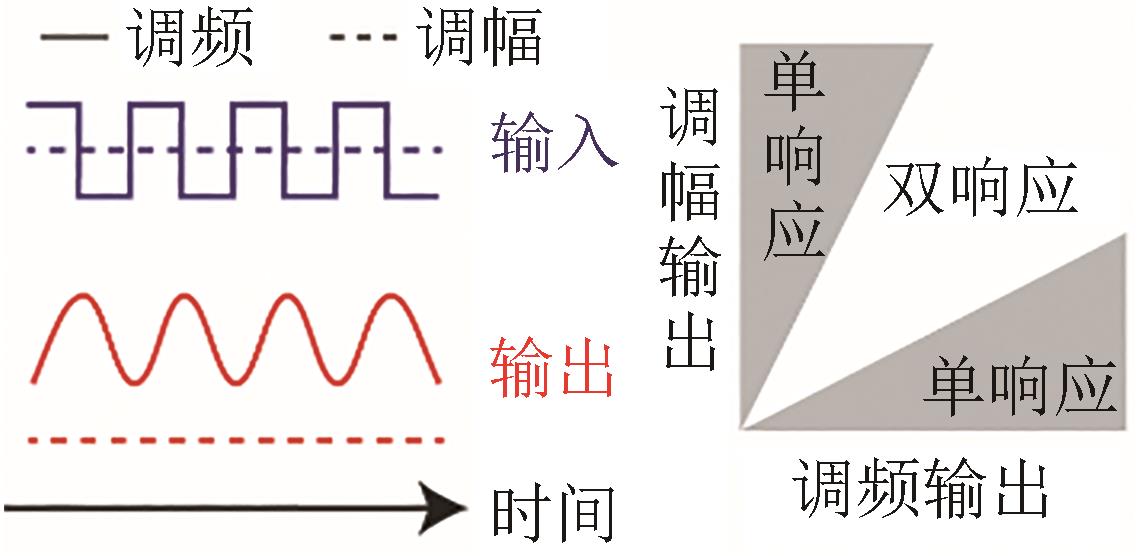 | 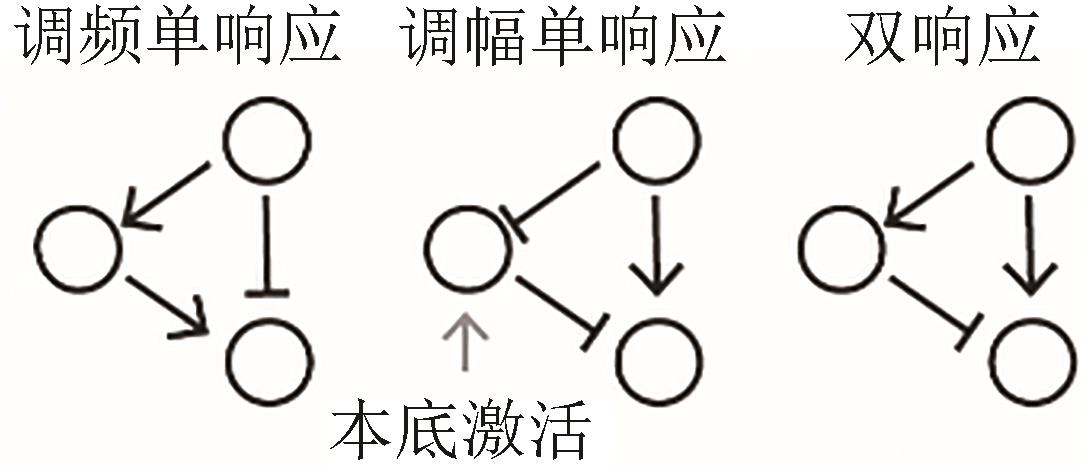 | 转录调控网络 Gao, et al., 2018[ |
Table 1 Typical functional topology developed theoretically
| 功能 | 表型 | 拓扑 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 适应性 |  |  | 酶促反应网络 Me, et al., 2009[ |
| 振荡 |  |  | Wagner, 2005[ Elowitz and Leibler, 2000[ |
| 双稳态 |  |  | Shah and Sarkar, 2011[ |
| 持续性检测 |  |  | Alon, 2007[ |
| 抗噪 |  |  | Nie, et al., 2020[ |
| 体节发育 |  |  | Ma, et al., 2006[ |
| 细胞极化 |  |  | Chau,et al., 2012[ |
| 适应性/振荡双功能 |  |  | Zhang, et al., 2019[ |
| 调频/调幅响应 |  |  | 转录调控网络 Gao, et al., 2018[ |
| 线路类型 | 节点数/设计层次 | 拓扑结构/线路特点 | 可执行功能 | 主要基因元件或模块 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基本转录调控线路 | 单节点 | 自抑制 | 降低表达噪声; 加速响应完成时间; 剂量响应线性化 | TetR自抑制;aTc剂量效应[ TetR自抑制结合光感元件LOV2响应光强度剂量[ |
| 自激活 | 双稳态自维持; “双模态”切换动力学; 参数分岔的“磁滞现象” | DBD-VP64自激活,pGal-DBD-VP64记忆瞬时乳糖浓度[ ZF-VP64自激活,响应多种瞬时刺激[ rtTA自激活线路,测试切换动力学[ tTA-VP16自激活,红霉素响应元件E-KRAB调控[ σ因子SigW自激活,利用RsiW调谐“磁滞区间”[ | ||
| 双节点 | “互抑制”型正反馈 | 双稳态自维持; “双模态”切换动力学; 参数分岔的“磁滞现象” | LacⅠ与CI构建toggle switch拨动开关[ RecA裂解CI控制双稳态切换,控制TraA表达诱发生物膜[ 利用mfLon蛋白酶控制拨动开关[ 利用UAS与pGal设计主开关,控制toggle switch开启[ PIP/E-KRAB构建toggle switch[ TALE元件设计toggle switch,耦联TALE自激活线路[ 正交TALE元件库,shRNA控制拨动开关,细胞分类器[ 定量RBS折叠自由能可预测设计toggle switch二态比例[ | |
| “激活-抑制”型负反馈 | 内源性自主振荡; 受迫振荡; “锁相”行为; 适应性响应 | LacⅠ-AraC,节点间负反馈结合自调控,设计自主振荡[ 温敏LacⅠ,补偿LacⅠ-AraC振荡线路的温度变化影响[ LacⅠ-AraC,周期性外源Arabinose驱动下的“锁相”振荡[ sense/anti-sense mRNA或siRNA设计负反馈振荡[ T7 RNAP与CRISPRi/dCpf1设计正负反馈耦合,实现RPA[ | ||
| 多节点 | 负反馈环路 | 三节点互抑制振荡 | TetR-LacⅠ-λCI的三节点互抑制负反馈环[ TetR-LacⅠ-λCI的三节点负反馈环简化,实现超稳定振荡[ 微流与光阱捕获技术,线路建库,筛选稳定振荡菌株[ | |
| 前馈线路 | 脉冲发生器(iFFL); 带通滤波器(iFFL); 信号加速器(cFFL) | 天然系统中的前馈实现信号加速与延迟的理论分析[ AHL扩散,LuxR-CI-GFP构建iFFL实现pulse generator[ LuxR-CI-GFP iFFL的空间动力学行为[ 光感pompC-LuxI-CI控制下游pLux-λ构建iFFL,边界探测[ tTA-Pip-E-KRAB构建iFFL,响应aTc剂量的band-pass filter[ 转录元件精确定量表征,构建iFFL的定量可预测设计[ | ||
| 组合逻辑线路 | 各类逻辑门线路 | 利用TetR-LacⅠ-λCI元件设计一系列逻辑门线路[ 双启动子控制阻遏蛋白的NOR Gate基本框架[ TetR family的正交NOT Gate阻遏蛋白挖掘[ | ||
| 时序逻辑线路 | 触点开关; 条件记忆学习线路; 锁存器线路 | LexA-LacⅠ NOR Gate,CI-CI434双稳态,组合构建触点开关[ tag-supD AND Gate、CI-CI434双稳态,巴甫洛夫样学习线路[ 双稳态与NOR Gate组合锁存结构,时序切换控制[ | ||
| 集成基因线路 | 多节点 | 组合前馈逻辑线路 | 逻辑门线路自动化设计; 逻辑切换动力学预测; 个性化线路设计 | Cello实现基因线路三输入逻辑真值表自动化CAD设计[ 四输入自动化设计,动力学过程表征与预测[ 基因组上Landing Pad超稳定低负载基因线路CAD设计[ 非模式菌的基础元件表征与线路CAD设计[ S. cerevisiae的基础元件设计表征与线路CAD设计[ |
| 多层次调控线路 | DNA层次 | 重组酶线路 | 带通滤波器; 表达顺序控制线路 | Bxb1、φC31、TP901重组酶受H2O2浓度调控,构建iFFL[ Cre、Flp、φC31受GIB、ABA诱导二聚化的自移除设计[ |
| RNA层次 | RNA元件 | RNA结合蛋白; RNA Replicon系统 | L7Ae、MS2结合蛋白的互抑制设计,RNA Replicon双稳态[ 使用TMP-DHFR可诱导降解标签调控L7Ae结合蛋白浓度[ | |
| CRISPR Circuit | CRISPR/Cas元件设计; Cas主蛋白中枢型线路 | TetR-CI-CRISPR/dCas9构建repressilator[ CRISPR/dCas9的转录抑制调控元件设计与表征[ dCas9*-PhlF融合构建减毒CRISPR调控系统[ 以dCas9、dCas12a为中枢蛋白设计的sgRNA调控线路等[ | ||
| 蛋白质层次 | 蛋白酶线路 | 降解肽切割调控; 分裂蛋白多聚化调控 | TEV/TVMV/SuMMV Protease移除/暴露降解肽标签调控设计[ Split TEV/TVMV/HCV Protease调控结合leucine zipper二聚化调控,设计logic gate、iFFL、protease toggle等功能[ | |
| 转录因子互作 | 多稳态基因调控线路 | GCN4、FKBP等结构域调控ZF结合蛋白二聚化多稳态线路[ | ||
| 翻译后修饰 | 超快速响应切换线路 | CRE1/STAT5设计磷酸化OR Gate,PTP-pHOG1对HOT1-pJH1去磷酸化NOT Gate,组合设计信号转导toggle switch[ | ||
| 鲁棒性控制线路 | 模块间“追溯活性” | 线路问题检查 | 负载表达动力学干扰; 元件模块化组装干扰 | pLac与lacO负载位点对LacⅠ的竞争,干扰表达动力学[ LuxR-NahR-GFP顺序组装后系统行为偏离预期[ |
| 功能修复线路 | 转录因子磷酸化线路; 激酶/磷酸酶元件开发; 减弱资源竞争模块设计; 公共资源自调节线路 | NRII(L16R)-NRII(H139N),STAT5-HKRR/ EnvZ激酶/磷酸酶活性改造,对OmpR-VP64调控活性控制,磷酸化水平负反馈线路控制表达[ ECF32 σ因子表达sRNA-mRNA负反馈;CasE切割mRNA 5′-UTR、miR-FF4设计iFFL线路等,减弱资源竞争效应[ 设计sgRNA靶向dCas9的自负反馈,公共中枢蛋白资源表达自调节,减弱下游模块间竞争[ | ||
| “线路-底盘”互作 | 线路问题检查 | 拓扑对生长的敏感性; 资源占用导致生长停滞 | AraC自激活与TetR-LacI互抑制对生长速率的不同敏感性[ pT7-T7 RNAP的自激活线路产生显著的表达量-生长异质性[ | |
| 功能修复线路 | 低拷贝基因线路设计; 表达负担负反馈线路; 毒性转录因子自负反馈; 生长速率补偿调控 | 基因组单拷贝整合的TetR-LacⅠ toggle switch[ 负担敏感phtpG1控制CRISPR/dCas9抑制的负反馈控制[ 转录因子CymR的自抑制诱导系统设计,减弱生长抑制毒性[ SpoTH元件降低ppGpp含量,维持生长速率恒定[ | ||
| 扰动噪声屏蔽 | 目的基因表达控制 | 稳定基因拷贝数变异; 组合iFFL/负反馈线路 | TALE设计线性抑制功能,稳定启动子表达受拷贝数影响[ rtTA-LacI/miR-FF3设计iFFL,排除转染量影响[ tTA-miR-FF4的iFFL与负反馈,组合控制[ | |
| 积分反馈控制线路 | σ/anti-σ; sense/anti-sense mRNA | SigW-RsiW的σ/anti-σ互作设计积分反馈控制[ tTA sense/anti-sense mRNA互作设计反馈控制[ | ||
| 鲁棒性功能拓扑发掘 | 基于拓扑约束的线路构建与扰动测试 | 基于拓扑穷举理论计算结果,T7 RNAP与CRISPR/dCpf1设计负反馈耦合线性弱自激活的基因线路,在输入信号改变、拓扑参数变异及底盘生理条件等进行系统扰动下均可实现RPA功能[ |
Table 2 Functional topology that has been constructed and used in synthetic biology
| 线路类型 | 节点数/设计层次 | 拓扑结构/线路特点 | 可执行功能 | 主要基因元件或模块 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基本转录调控线路 | 单节点 | 自抑制 | 降低表达噪声; 加速响应完成时间; 剂量响应线性化 | TetR自抑制;aTc剂量效应[ TetR自抑制结合光感元件LOV2响应光强度剂量[ |
| 自激活 | 双稳态自维持; “双模态”切换动力学; 参数分岔的“磁滞现象” | DBD-VP64自激活,pGal-DBD-VP64记忆瞬时乳糖浓度[ ZF-VP64自激活,响应多种瞬时刺激[ rtTA自激活线路,测试切换动力学[ tTA-VP16自激活,红霉素响应元件E-KRAB调控[ σ因子SigW自激活,利用RsiW调谐“磁滞区间”[ | ||
| 双节点 | “互抑制”型正反馈 | 双稳态自维持; “双模态”切换动力学; 参数分岔的“磁滞现象” | LacⅠ与CI构建toggle switch拨动开关[ RecA裂解CI控制双稳态切换,控制TraA表达诱发生物膜[ 利用mfLon蛋白酶控制拨动开关[ 利用UAS与pGal设计主开关,控制toggle switch开启[ PIP/E-KRAB构建toggle switch[ TALE元件设计toggle switch,耦联TALE自激活线路[ 正交TALE元件库,shRNA控制拨动开关,细胞分类器[ 定量RBS折叠自由能可预测设计toggle switch二态比例[ | |
| “激活-抑制”型负反馈 | 内源性自主振荡; 受迫振荡; “锁相”行为; 适应性响应 | LacⅠ-AraC,节点间负反馈结合自调控,设计自主振荡[ 温敏LacⅠ,补偿LacⅠ-AraC振荡线路的温度变化影响[ LacⅠ-AraC,周期性外源Arabinose驱动下的“锁相”振荡[ sense/anti-sense mRNA或siRNA设计负反馈振荡[ T7 RNAP与CRISPRi/dCpf1设计正负反馈耦合,实现RPA[ | ||
| 多节点 | 负反馈环路 | 三节点互抑制振荡 | TetR-LacⅠ-λCI的三节点互抑制负反馈环[ TetR-LacⅠ-λCI的三节点负反馈环简化,实现超稳定振荡[ 微流与光阱捕获技术,线路建库,筛选稳定振荡菌株[ | |
| 前馈线路 | 脉冲发生器(iFFL); 带通滤波器(iFFL); 信号加速器(cFFL) | 天然系统中的前馈实现信号加速与延迟的理论分析[ AHL扩散,LuxR-CI-GFP构建iFFL实现pulse generator[ LuxR-CI-GFP iFFL的空间动力学行为[ 光感pompC-LuxI-CI控制下游pLux-λ构建iFFL,边界探测[ tTA-Pip-E-KRAB构建iFFL,响应aTc剂量的band-pass filter[ 转录元件精确定量表征,构建iFFL的定量可预测设计[ | ||
| 组合逻辑线路 | 各类逻辑门线路 | 利用TetR-LacⅠ-λCI元件设计一系列逻辑门线路[ 双启动子控制阻遏蛋白的NOR Gate基本框架[ TetR family的正交NOT Gate阻遏蛋白挖掘[ | ||
| 时序逻辑线路 | 触点开关; 条件记忆学习线路; 锁存器线路 | LexA-LacⅠ NOR Gate,CI-CI434双稳态,组合构建触点开关[ tag-supD AND Gate、CI-CI434双稳态,巴甫洛夫样学习线路[ 双稳态与NOR Gate组合锁存结构,时序切换控制[ | ||
| 集成基因线路 | 多节点 | 组合前馈逻辑线路 | 逻辑门线路自动化设计; 逻辑切换动力学预测; 个性化线路设计 | Cello实现基因线路三输入逻辑真值表自动化CAD设计[ 四输入自动化设计,动力学过程表征与预测[ 基因组上Landing Pad超稳定低负载基因线路CAD设计[ 非模式菌的基础元件表征与线路CAD设计[ S. cerevisiae的基础元件设计表征与线路CAD设计[ |
| 多层次调控线路 | DNA层次 | 重组酶线路 | 带通滤波器; 表达顺序控制线路 | Bxb1、φC31、TP901重组酶受H2O2浓度调控,构建iFFL[ Cre、Flp、φC31受GIB、ABA诱导二聚化的自移除设计[ |
| RNA层次 | RNA元件 | RNA结合蛋白; RNA Replicon系统 | L7Ae、MS2结合蛋白的互抑制设计,RNA Replicon双稳态[ 使用TMP-DHFR可诱导降解标签调控L7Ae结合蛋白浓度[ | |
| CRISPR Circuit | CRISPR/Cas元件设计; Cas主蛋白中枢型线路 | TetR-CI-CRISPR/dCas9构建repressilator[ CRISPR/dCas9的转录抑制调控元件设计与表征[ dCas9*-PhlF融合构建减毒CRISPR调控系统[ 以dCas9、dCas12a为中枢蛋白设计的sgRNA调控线路等[ | ||
| 蛋白质层次 | 蛋白酶线路 | 降解肽切割调控; 分裂蛋白多聚化调控 | TEV/TVMV/SuMMV Protease移除/暴露降解肽标签调控设计[ Split TEV/TVMV/HCV Protease调控结合leucine zipper二聚化调控,设计logic gate、iFFL、protease toggle等功能[ | |
| 转录因子互作 | 多稳态基因调控线路 | GCN4、FKBP等结构域调控ZF结合蛋白二聚化多稳态线路[ | ||
| 翻译后修饰 | 超快速响应切换线路 | CRE1/STAT5设计磷酸化OR Gate,PTP-pHOG1对HOT1-pJH1去磷酸化NOT Gate,组合设计信号转导toggle switch[ | ||
| 鲁棒性控制线路 | 模块间“追溯活性” | 线路问题检查 | 负载表达动力学干扰; 元件模块化组装干扰 | pLac与lacO负载位点对LacⅠ的竞争,干扰表达动力学[ LuxR-NahR-GFP顺序组装后系统行为偏离预期[ |
| 功能修复线路 | 转录因子磷酸化线路; 激酶/磷酸酶元件开发; 减弱资源竞争模块设计; 公共资源自调节线路 | NRII(L16R)-NRII(H139N),STAT5-HKRR/ EnvZ激酶/磷酸酶活性改造,对OmpR-VP64调控活性控制,磷酸化水平负反馈线路控制表达[ ECF32 σ因子表达sRNA-mRNA负反馈;CasE切割mRNA 5′-UTR、miR-FF4设计iFFL线路等,减弱资源竞争效应[ 设计sgRNA靶向dCas9的自负反馈,公共中枢蛋白资源表达自调节,减弱下游模块间竞争[ | ||
| “线路-底盘”互作 | 线路问题检查 | 拓扑对生长的敏感性; 资源占用导致生长停滞 | AraC自激活与TetR-LacI互抑制对生长速率的不同敏感性[ pT7-T7 RNAP的自激活线路产生显著的表达量-生长异质性[ | |
| 功能修复线路 | 低拷贝基因线路设计; 表达负担负反馈线路; 毒性转录因子自负反馈; 生长速率补偿调控 | 基因组单拷贝整合的TetR-LacⅠ toggle switch[ 负担敏感phtpG1控制CRISPR/dCas9抑制的负反馈控制[ 转录因子CymR的自抑制诱导系统设计,减弱生长抑制毒性[ SpoTH元件降低ppGpp含量,维持生长速率恒定[ | ||
| 扰动噪声屏蔽 | 目的基因表达控制 | 稳定基因拷贝数变异; 组合iFFL/负反馈线路 | TALE设计线性抑制功能,稳定启动子表达受拷贝数影响[ rtTA-LacI/miR-FF3设计iFFL,排除转染量影响[ tTA-miR-FF4的iFFL与负反馈,组合控制[ | |
| 积分反馈控制线路 | σ/anti-σ; sense/anti-sense mRNA | SigW-RsiW的σ/anti-σ互作设计积分反馈控制[ tTA sense/anti-sense mRNA互作设计反馈控制[ | ||
| 鲁棒性功能拓扑发掘 | 基于拓扑约束的线路构建与扰动测试 | 基于拓扑穷举理论计算结果,T7 RNAP与CRISPR/dCpf1设计负反馈耦合线性弱自激活的基因线路,在输入信号改变、拓扑参数变异及底盘生理条件等进行系统扰动下均可实现RPA功能[ |
| 1 | MILO R, SHEN-ORR S, ITZKOVITZ S, et al. Network motifs: simple building blocks of complex networks[J]. Science, 2002, 298(5594): 824-827. |
| 2 | JEONG H, TOMBOR B, ALBERT R, et al. The large-scale organization of metabolic networks[J]. Nature, 2000, 407(6804): 651-654. |
| 3 | SHEN-ORR S S, MILO R, MANGAN S, et al. Network motifs in the transcriptional regulation network of Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Genetics, 2002, 31(1): 64-68. |
| 4 | LIM W A, LEE C M, TANG C. Design principles of regulatory networks: searching for the molecular algorithms of the cell[J]. Molecular Cell, 2013, 49(2): 202-212. |
| 5 | ROSENFELD N, ELOWITZ M B, ALON U. Negative autoregulation speeds the response times of transcription networks[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2002, 323(5): 785-793. |
| 6 | ISAACS F J, HASTY J, CANTOR C R, et al. Prediction and measurement of an autoregulatory genetic module[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2003, 100(13): 7714-7719. |
| 7 | GUAN Y, CHEN X M, SHAO B, et al. Mitigating host burden of genetic circuits by engineering autonegatively regulated parts and improving functional prediction[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(7): 2361-2371. |
| 8 | ALON U. Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2007, 8(6): 450-461. |
| 9 | SNEPPEN K, KRISHNA S, SEMSEY S. Simplified models of biological networks[J]. Annual Review of Biophysics, 2010, 39: 43-59. |
| 10 | OPPENHEIM A B, KOBILER O, STAVANS J, et al. Switches in bacteriophage lambda development[J]. Annual Review of Genetics, 2005, 39: 409-429. |
| 11 | BECSKEI A, SERRANO L. Engineering stability in gene networks by autoregulation[J]. Nature, 2000, 405(6786): 590-593. |
| 12 | HSU C, SCHERRER S, BUETTI-DINH A, et al. Stochastic signalling rewires the interaction map of a multiple feedback network during yeast evolution[J]. Nature Communications, 2012, 3: 682. |
| 13 | NIE Q, QIAO L X, QIU Y C, et al. Noise control and utility: from regulatory network to spatial patterning[J]. Science China Mathematics, 2020, 63(3): 425-440. |
| 14 | BOURKE ARNVIG K, PEDERSEN S, SNEPPEN K. Thermodynamics of heat-shock response[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2000, 84(13): 3005-3008. |
| 15 | KRISHNA S, JENSEN M H, SNEPPEN K. Minimal model of spiky oscillations in NF-κB signaling[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(29): 10840-10845. |
| 16 | HOELLER O, GONG D, WEINER O D. How to understand and outwit adaptation[J]. Developmental Cell, 2014, 28(6): 607-616. |
| 17 | MA W Z, LAI L H, OUYANG Q, et al. Robustness and modular design of the Drosophila segment polarity network[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2006, 2: 70. |
| 18 | MA W Z, TRUSINA A, EL-SAMAD H, et al. Defining network topologies that can achieve biochemical adaptation[J]. Cell, 2009, 138(4): 760-773. |
| 19 | BARKAI N, LEIBLER S. Robustness in simple biochemical networks[J]. Nature, 1997, 387(6636): 913-917. |
| 20 | STELLING J, GILLES E D, DOYLE F J. Robustness properties of circadian clock architectures[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(36): 13210-13215. |
| 21 | SHAH N A, SARKAR C A. Robust network topologies for generating switch-like cellular responses[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2011, 7(6): e1002085. |
| 22 | WAGNER A. Circuit topology and the evolution of robustness in two-gene circadian oscillators[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2005, 102(33): 11775-11780. |
| 23 | CHAU A H, WALTER J M, GERARDIN J, et al. Designing synthetic regulatory networks capable of self-organizing cell polarization[J]. Cell, 2012, 151(2): 320-332. |
| 24 | ZHANG M Y, TANG C. Bi-functional biochemical networks[J]. Physical Biology, 2018, 16(1): 016001. |
| 25 | GAO Z M, CHEN S H, QIN S S, et al. Network motifs capable of decoding transcription factor dynamics[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 3594. |
| 26 | QIAO L X, ZHAO W, TANG C, et al. Network topologies that can achieve dual function of adaptation and noise attenuation[J]. Cell Systems, 2019, 9(3): 271-285.e7. |
| 27 | QIAO L X, ZHANG Z B, ZHAO W, et al. Network design principle for robust oscillatory behaviors with respect to biological noise[J]. eLife, 2022, 11: e76188. |
| 28 | ELOWITZ M B, LEIBLER S. A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators[J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 335-338. |
| 29 | FRANÇOIS P, HAKIM V. Design of genetic networks with specified functions by evolution in silico [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(2): 580-585. |
| 30 | FRANÇOIS P, SIGGIA E D. A case study of evolutionary computation of biochemical adaptation[J]. Physical Biology, 2008, 5(2): 026009. |
| 31 | FRANÇOIS P, SIGGIA E D. Predicting embryonic patterning using mutual entropy fitness and in silico evolution[J]. Development, 2010, 137(14): 2385-2395. |
| 32 | LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-444. |
| 33 | SHEN J X, LIU F, TU Y H, et al. Finding gene network topologies for given biological function with recurrent neural network[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 3125. |
| 34 | CHEN F, LI C H. Inferring structural and dynamical properties of gene networks from data with deep learning[J]. NAR Genomics and Bioinformatics, 2022, 4(3): lqac068. |
| 35 | NEVOZHAY D, ADAMS R M, MURPHY K F, et al. Negative autoregulation linearizes the dose-response and suppresses the heterogeneity of gene expression[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(13): 5123-5128. |
| 36 | NEVOZHAY D, ZAL T, BALÁZSI G. Transferring a synthetic gene circuit from yeast to mammalian cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 1451. |
| 37 | GUINN M T, BALÁZSI G. Noise-reducing optogenetic negative-feedback gene circuits in human cells[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(14): 7703-7714. |
| 38 | AJO-FRANKLIN C M, DRUBIN D A, ESKIN J A, et al. Rational design of memory in eukaryotic cells[J]. Genes & Development, 2007, 21(18): 2271-2276. |
| 39 | BURRILL D R, INNISS M C, BOYLE P M, et al. Synthetic memory circuits for tracking human cell fate[J]. Genes & Development, 2012, 26(13): 1486-1497. |
| 40 | LONGO D M, HOFFMANN A, TSIMRING L S, et al. Coherent activation of a synthetic mammalian gene network[J]. Systems and Synthetic Biology, 2010, 4(1): 15-23. |
| 41 | KRAMER B P, FUSSENEGGER M. Hysteresis in a synthetic mammalian gene network[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2005, 102(27): 9517-9522. |
| 42 | CHEN D, ARKIN A P. Sequestration-based bistability enables tuning of the switching boundaries and design of a latch[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2012, 8(1): 620. |
| 43 | GARDNER T S, CANTOR C R, COLLINS J J. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 339-342. |
| 44 | KOBAYASHI H, KAERN M, ARAKI M, et al. Programmable cells: interfacing natural and engineered gene networks[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(22): 8414-8419. |
| 45 | CAMERON D E, COLLINS J J. Tunable protein degradation in bacteria[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2014, 32(12): 1276-1281. |
| 46 | WU M, SU R Q, LI X H, et al. Engineering of regulated stochastic cell fate determination[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(26): 10610-10615. |
| 47 | KRAMER B P, VIRETTA A U, DAOUD-EL BABA M, et al. An engineered epigenetic transgene switch in mammalian cells[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2004, 22(7): 867-870. |
| 48 | LEBAR T, BEZELJAK U, GOLOB A, et al. A bistable genetic switch based on designable DNA-binding domains[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 5007. |
| 49 | LI Y Q, JIANG Y, CHEN H, et al. Modular construction of mammalian gene circuits using TALE transcriptional repressors[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(3): 207-213. |
| 50 | CHEN S B, ZHANG H Q, SHI H D, et al. Automated design of genetic toggle switches with predetermined bistability[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2012, 1(7): 284-290. |
| 51 | STRICKER J, COOKSON S, BENNETT M R, et al. A fast, robust and tunable synthetic gene oscillator[J]. Nature, 2008, 456(7221): 516-519. |
| 52 | HUSSAIN F, GUPTA C, HIRNING A J, et al. Engineered temperature compensation in a synthetic genetic clock[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(3): 972-977. |
| 53 | MONDRAGÓN-PALOMINO O, DANINO T, SELIMKHANOV J, et al. Entrainment of a population of synthetic genetic oscillators[J]. Science, 2011, 333(6047): 1315-1319. |
| 54 | TIGGES M, MARQUEZ-LAGO T T, STELLING J, et al. A tunable synthetic mammalian oscillator[J]. Nature, 2009, 457(7227): 309-312. |
| 55 | TIGGES M, DÉNERVAUD N, GREBER D, et al. A synthetic low-frequency mammalian oscillator[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 38(8): 2702-2711. |
| 56 | SUN Z, WEI W J, ZHANG M Y, et al. Synthetic robust perfect adaptation achieved by negative feedback coupling with linear weak positive feedback[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022, 50(4): 2377-2386. |
| 57 | POTVIN-TROTTIER L, LORD N D, VINNICOMBE G, et al. Synchronous long-term oscillations in a synthetic gene circuit[J]. Nature, 2016, 538(7626): 514-517. |
| 58 | LURO S, POTVIN-TROTTIER L, OKUMUS B, et al. Isolating live cells after high-throughput, long-term, time-lapse microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2020, 17(1): 93-100. |
| 59 | MANGAN S, ALON U. Structure and function of the feed-forward loop network motif[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2003, 100(21): 11980-11985. |
| 60 | MANGAN S, ZASLAVER A, ALON U. The coherent feedforward loop serves as a sign-sensitive delay element in transcription networks[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2003, 334(2): 197-204. |
| 61 | KALIR S, MANGAN S, ALON U. A coherent feed-forward loop with a SUM input function prolongs flagella expression in Escherichia coli [J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2005, 1: 2005.0006. |
| 62 | MANGAN S, ITZKOVITZ S, ZASLAVER A, et al. The incoherent feed-forward loop accelerates the response-time of the gal system of Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2006, 356(5): 1073-1081. |
| 63 | KAPLAN S, BREN A, DEKEL E, et al. The incoherent feed-forward loop can generate non-monotonic input functions for genes[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2008, 4: 203. |
| 64 | GOENTORO L, SHOVAL O, KIRSCHNER M W, et al. The incoherent feedforward loop can provide fold-change detection in gene regulation[J]. Molecular Cell, 2009, 36(5): 894-899. |
| 65 | BASU S, MEHREJA R, THIBERGE S, et al. Spatiotemporal control of gene expression with pulse-generating networks[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(17): 6355-6360. |
| 66 | BASU S, GERCHMAN Y, COLLINS C H, et al. A synthetic multicellular system for programmed pattern formation[J]. Nature, 2005, 434(7037): 1130-1134. |
| 67 | TABOR J J, SALIS H M, SIMPSON Z B, et al. A synthetic genetic edge detection program[J]. Cell, 2009, 137(7): 1272-1281. |
| 68 | GREBER D, FUSSENEGGER M. An engineered mammalian band-pass network[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 38(18): e174. |
| 69 | ZONG Y Q, ZHANG H M, LYU C, et al. Insulated transcriptional elements enable precise design of genetic circuits[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 52. |
| 70 | GUET C C, ELOWITZ M B, HSING W, et al. Combinatorial synthesis of genetic networks[J]. Science, 2002, 296(5572): 1466-1470. |
| 71 | TAMSIR A, TABOR J J, VOIGT C A. Robust multicellular computing using genetically encoded NOR gates and chemical 'wires'[J]. Nature, 2011, 469(7329): 212-215. |
| 72 | STANTON B C, NIELSEN A A K, TAMSIR A, et al. Genomic mining of prokaryotic repressors for orthogonal logic gates[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2014, 10(2): 99-105. |
| 73 | LOU C B, LIU X L, NI M, et al. Synthesizing a novel genetic sequential logic circuit: a push-on push-off switch[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2010, 6: 350. |
| 74 | ZHANG H Q, LIN M, SHI H D, et al. Programming a Pavlovian-like conditioning circuit in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 3102. |
| 75 | ANDREWS L B, NIELSEN A A K, VOIGT C A. Cellular checkpoint control using programmable sequential logic[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6408): eaap8987. |
| 76 | NIELSEN A A K, DER B S, SHIN J, et al. Genetic circuit design automation[J]. Science, 2016, 352(6281): aac7341. |
| 77 | SHIN J, ZHANG S Y, DER B S, et al. Programming Escherichia coli to function as a digital display[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2020, 16(3): e9401. |
| 78 | PARK Y, ESPAH BORUJENI A, GOROCHOWSKI T E, et al. Precision design of stable genetic circuits carried in highly-insulated E. coli genomic landing pads[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2020, 16(8): e9584. |
| 79 | TAKETANI M, ZHANG J B, ZHANG S Y, et al. Genetic circuit design automation for the gut resident species Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(8): 962-969. |
| 80 | CHEN Y, ZHANG S Y, YOUNG E M, et al. Genetic circuit design automation for yeast[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2020, 5(11): 1349-1360. |
| 81 | RUBENS J R, SELVAGGIO G, LU T K. Synthetic mixed-signal computation in living cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 11658. |
| 82 | KIM T, WEINBERG B, WONG W, et al. Scalable recombinase-based gene expression cascades[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 2711. |
| 83 | WROBLEWSKA L, KITADA T, ENDO K, et al. Mammalian synthetic circuits with RNA binding proteins for RNA-only delivery[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(8): 839-841. |
| 84 | WAGNER T E, BECRAFT J R, BODNER K, et al. Small-molecule-based regulation of RNA-delivered circuits in mammalian cells[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(11): 1043-1050. |
| 85 | HENNINGSEN J, SCHWARZ-SCHILLING M, LEIBL A, et al. Single cell characterization of a synthetic bacterial clock with a hybrid feedback loop containing dCas9-sgRNA[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(12): 3377-3387. |
| 86 | NIELSEN A A K, VOIGT C A. Multi-input CRISPR/Cas genetic circuits that interface host regulatory networks[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2014, 10(11): 763. |
| 87 | ANDERSON D A, VOIGT C A. Competitive dCas9 binding as a mechanism for transcriptional control[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2021, 17(11): e10512. |
| 88 | ZHANG S Y, VOIGT C A. Engineered dCas9 with reduced toxicity in bacteria: implications for genetic circuit design[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(20): 11115-11125. |
| 89 | KUO J, YUAN R S, SÁNCHEZ C, et al. Toward a translationally independent RNA-based synthetic oscillator using deactivated CRISPR-Cas[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(14): 8165-8177. |
| 90 | SANTOS-MORENO J, TASIUDI E, STELLING J, et al. Multistable and dynamic CRISPRi-based synthetic circuits[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 2746. |
| 91 | FERNANDEZ-RODRIGUEZ J, VOIGT C A. Post-translational control of genetic circuits using Potyvirus proteases[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(13): 6493-6502. |
| 92 | GAO X J, CHONG L S, KIM M S, et al. Programmable protein circuits in living cells[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6408): 1252-1258. |
| 93 | CHEN Z B, LINTON J M, ZHU R H, et al. A synthetic protein-level neural network in mammalian cells[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2022[2022-12-31]. . |
| 94 | ZHU R H, DEL RIO-SALGADO J M, GARCIA-OJALVO J, et al. Synthetic multistability in mammalian cells[J]. Science, 2022, 375(6578): eabg9765. |
| 95 | MISHRA D, BEPLER T, TEAGUE B, et al. An engineered protein-phosphorylation toggle network with implications for endogenous network discovery[J]. Science, 2021, 373(6550): eaav0780. |
| 96 | JAYANTHI S, NILGIRIWALA K S, DEL VECCHIO D. Retroactivity controls the temporal dynamics of gene transcription[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2013, 2(8): 431-441. |
| 97 | QIAN Y L, HUANG H H, JIMÉNEZ J I, et al. Resource competition shapes the response of genetic circuits[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(7): 1263-1272. |
| 98 | NILGIRIWALA K S, JIMÉNEZ J, RIVERA P M, et al. Synthetic tunable amplifying buffer circuit in E. coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2015, 4(5): 577-584. |
| 99 | MISHRA D, RIVERA P M, LIN A, et al. A load driver device for engineering modularity in biological networks[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2014, 32(12): 1268-1275. |
| 100 | JONES R D, QIAN Y L, ILIA K, et al. Robust and tunable signal processing in mammalian cells via engineered covalent modification cycles[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 1720. |
| 101 | HUANG H H, QIAN Y L, DEL VECCHIO D. A quasi-integral controller for adaptation of genetic modules to variable ribosome demand[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 5415. |
| 102 | JONES R D, QIAN Y L, SICILIANO V, et al. An endoribonuclease-based feedforward controller for decoupling resource-limited genetic modules in mammalian cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5690. |
| 103 | FREI T, CELLA F, TEDESCHI F, et al. Characterization and mitigation of gene expression burden in mammalian cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 4641. |
| 104 | HUANG H H, BELLATO M, QIAN Y L, et al. dCas9 regulator to neutralize competition in CRISPRi circuits[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 1692. |
| 105 | ZHANG R, LI J, MELENDEZ-ALVAREZ J, et al. Topology-dependent interference of synthetic gene circuit function by growth feedback[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2020, 16(6): 695-701. |
| 106 | TAN C, MARGUET P, YOU L C. Emergent bistability by a growth-modulating positive feedback circuit[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2009, 5(11): 842-848. |
| 107 | LEE J W, GYORGY A, CAMERON D E, et al. Creating single-copy genetic circuits[J]. Molecular Cell, 2016, 63(2): 329-336. |
| 108 | CERONI F, BOO A, FURINI S, et al. Burden-driven feedback control of gene expression[J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(5): 387-393. |
| 109 | BARAJAS C, HUANG H H, GIBSON J, et al. Feedforward growth rate control mitigates gene activation burden[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 7054. |
| 110 | SEGALL-SHAPIRO T H, SONTAG E D, VOIGT C A. Engineered promoters enable constant gene expression at any copy number in bacteria[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(4): 352-358. |
| 111 | BLERIS L, XIE Z, GLASS D, et al. Synthetic incoherent feedforward circuits show adaptation to the amount of their genetic template[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2011, 7: 519. |
| 112 | LILLACCI G, BENENSON Y, KHAMMASH M. Synthetic control systems for high performance gene expression in mammalian cells[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(18): 9855-9863. |
| 113 | AOKI S K, LILLACCI G, GUPTA A, et al. A universal biomolecular integral feedback controller for robust perfect adaptation[J]. Nature, 2019, 570(7762): 533-537. |
| 114 | FREI T, CHANG C H, FILO M, et al. A genetic mammalian proportional-integral feedback control circuit for robust and precise gene regulation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2022, 119(24): e2122132119. |
| 115 | ROSENFELD N, YOUNG J W, ALON U, et al. Accurate prediction of gene feedback circuit behavior from component properties[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2007, 3: 143. |
| 116 | ROSENFELD N, YOUNG J W, ALON U, et al. Gene regulation at the single-cell level[J]. Science, 2005, 307(5717): 1962-1965. |
| 117 | SHOPERA T, HENSON W R, NG A, et al. Robust, tunable genetic memory from protein sequestration combined with positive feedback[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 43(18): 9086-9094. |
| 118 | WU F Q, SU R Q, LAI Y C, et al. Engineering of a synthetic quadrastable gene network to approach Waddington landscape and cell fate determination[J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e23702. |
| 119 | SALIS H M, MIRSKY E A, VOIGT C A. Automated design of synthetic ribosome binding sites to control protein expression[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2009, 27(10): 946-950. |
| 120 | SHI W J, MA W Z, XIONG L Y, et al. Adaptation with transcriptional regulation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 42648. |
| 121 | ALON U. An introduction to systems biology: design principles of biological circuits[M]. Boca Raton, FL: Chapman & Hall/CRC, 2007. |
| 122 | ZHANG H M, CHEN S B, SHI H D, et al. Measurements of gene expression at steady state improve the predictability of part assembly[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(3): 269-273. |
| 123 | GREEN A A, KIM J, MA D, et al. Complex cellular logic computation using ribocomputing devices[J]. Nature, 2017, 548(7665): 117-121. |
| 124 | KIM J, ZHOU Y, CARLSON P D, et al. De novo-designed translation-repressing riboregulators for multi-input cellular logic[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(12): 1173-1182. |
| 125 | CHEN Y J, LIU P, NIELSEN A A K, et al. Characterization of 582 natural and synthetic terminators and quantification of their design constraints[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(7): 659-664. |
| 126 | MEYER A J, SEGALL-SHAPIRO T H, GLASSEY E, et al. Escherichia coli "Marionette" strains with 12 highly optimized small-molecule sensors[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2019, 15(2): 196-204. |
| 127 | HOSSAIN A, LOPEZ E, HALPER S M, et al. Automated design of thousands of nonrepetitive parts for engineering stable genetic systems[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(12): 1466-1475. |
| 128 | LOU C B, STANTON B, CHEN Y J, et al. Ribozyme-based insulator parts buffer synthetic circuits from genetic context[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2012, 30(11): 1137-1142. |
| 129 | GOROCHOWSKI T E, ESPAH BORUJENI A, PARK Y, et al. Genetic circuit characterization and debugging using RNA-seq[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2017, 13(11): 952. |
| 130 | ESPAH BORUJENI A, ZHANG J, DOOSTHOSSEINI H, et al. Genetic circuit characterization by inferring RNA polymerase movement and ribosome usage[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5001. |
| 131 | FONTANARROSA P, DOOSTHOSSEINI H, BORUJENI A E, et al. Genetic circuit dynamics: hazard and glitch analysis[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(9): 2324-2338. |
| 132 | JONES T S, OLIVEIRA S M D, MYERS C J, et al. Genetic circuit design automation with Cello 2.0[J]. Nature Protocols, 2022, 17(4): 1097-1113. |
| 133 | DEL VECCHIO D, NINFA A J, SONTAG E D. Modular cell biology: retroactivity and insulation[J]. Molecular Systems Biology, 2008, 4: 161. |
| [1] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [12] | CAI Bingyu, TAN Xiangtian, LI Wei. Advances in synthetic biology for engineering stem cell [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [13] | XIE Huang, ZHENG Yilei, SU Yiting, RUAN Jingyi, LI Yongquan. An overview on reconstructing the biosynthetic system of actinomycetes for polyketides production [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [14] | ZHA Wenlong, BU Lan, ZI Jiachen. Advances in synthetic biology for producing potent pharmaceutical ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| [15] | HUI Zhen, TANG Xiaoyu. Applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 editing system in the study of microbial natural products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||