Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (5): 915-931.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-031
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Optimization and upgradation of microalgal photosynthesis for carbon peak and carbon neutrality goals
WANG Song1, WU Sha1,2, JIANG Yanan1, HU Zhangli1,3
- 1.Guangdong Technology Research Center for Marine Algal Bioengineering,College of Life Sciences and Oceanography,Shenzhen University,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
2.College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering,Shenzhen University,Shenzhen 518060,Guangdong,China
3.Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou),Guangzhou 511458,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2022-05-26Revised:2022-08-25Online:2022-11-16Published:2022-10-31 -
Contact:HU Zhangli
微藻光合作用的优化升级助力“双碳”目标
王松1, 吴莎1,2, 江亚男1, 胡章立1,3
- 1.深圳大学生命与海洋科学学院,广东省海洋藻类工程技术研究中心,广东 深圳 518055
2.深圳大学物理与光电工程学院,广东 深圳 518060
3.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州),广东 广州 511458
-
通讯作者:胡章立 -
作者简介:王松 (1989—),男,博士,副研究员。研究方向为微藻生物技术、微藻规模化养殖。 E-mail:wangsong@szu.edu.cn胡章立 (1964—),男,博士,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为藻类分子生物学、合成生物学。 E-mail:huzl@szu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2019YFA0902500);深圳市可持续发展专项(KCXFZ20211020164013021)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Song, WU Sha, JIANG Yanan, HU Zhangli. Optimization and upgradation of microalgal photosynthesis for carbon peak and carbon neutrality goals[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 915-931.
王松, 吴莎, 江亚男, 胡章立. 微藻光合作用的优化升级助力“双碳”目标[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(5): 915-931.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2022-031
| 1 | MOREIRA D, PIRES J C M. Atmospheric CO2 capture by algae: negative carbon dioxide emission path[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 215: 371-379. |
| 2 | FALKOWSKI P. Ocean science: the power of plankton[J]. Nature, 2012, 483(7387): S17-S20. |
| 3 | TRÉGUER P, BOWLER C, MORICEAU B, et al. Influence of diatom diversity on the ocean biological carbon pump[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2018, 11(1): 27-37. |
| 4 | FIELD C B, BEHRENFELD M J, RANDERSON J T, et al. Primary production of the biosphere: integrating terrestrial and oceanic components[J]. Science, 1998, 281(5374): 237-240. |
| 5 | MANDOTRA S K, SHARMA C, SRIVASTAVA N, et al. Current prospects and future developments in algal bio-hydrogen production: a review[J]. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 2021: 1-18. |
| 6 | KOTHARI R, AHMAD S, PATHAK V V, et al. Algal-based biofuel generation through flue gas and wastewater utilization: a sustainable prospective approach[J]. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 2021, 11(4): 1419-1442. |
| 7 | CHISTI Y. Biodiesel from microalgae[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2007, 25(3): 294-306. |
| 8 | CHEW K W, YAP J Y, SHOW P L, et al. Microalgae biorefinery: high value products perspectives[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 229: 53-62. |
| 9 | LEVASSEUR W, PERRÉ P, POZZOBON V. A review of high value-added molecules production by microalgae in light of the classification[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2020, 41: 107545. |
| 10 | MILANO J, ONG H C, MASJUKI H H, et al. Microalgae biofuels as an alternative to fossil fuel for power generation[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 58: 180-197. |
| 11 | WANG Y W, TIBBETTS S M, MCGINN P J. Microalgae as sources of high-quality protein for human food and protein supplements[J]. Foods (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 10(12): 3002. |
| 12 | DINESHBABU G, GOSWAMI G, KUMAR R, et al. Microalgae-nutritious, sustainable aqua- and animal feed source[J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 2019, 62: 103545. |
| 13 | KHAN M I, SHIN J H, KIM J D. The promising future of microalgae: current status, challenges, and optimization of a sustainable and renewable industry for biofuels, feed, and other products[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17(1): 36. |
| 14 | VALVERDE F, ROMERO-CAMPERO F J, LEÓN R, et al. New challenges in microalgae biotechnology[J]. European Journal of Protistology, 2016, 55: 95-101. |
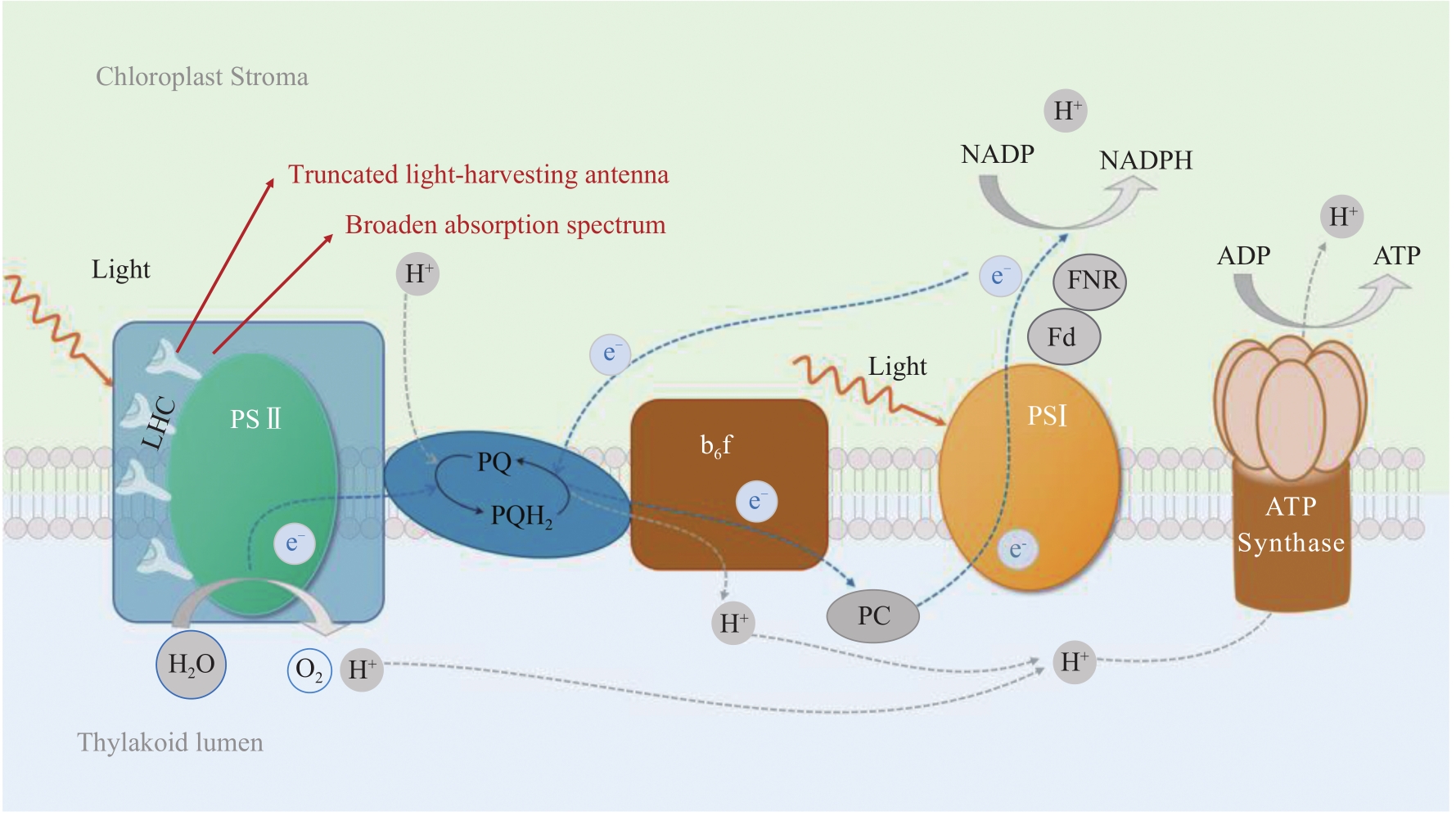
| 15 | MELIS A. Solar energy conversion efficiencies in photosynthesis: minimizing the chlorophyll antennae to maximize efficiency[J]. Plant Science, 2009, 177(4): 272-280. |
| 16 | HAMBOURGER M, MOORE G F, KRAMER D M, et al. Biology and technology for photochemical fuel production[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2009, 38(1): 25-35. |
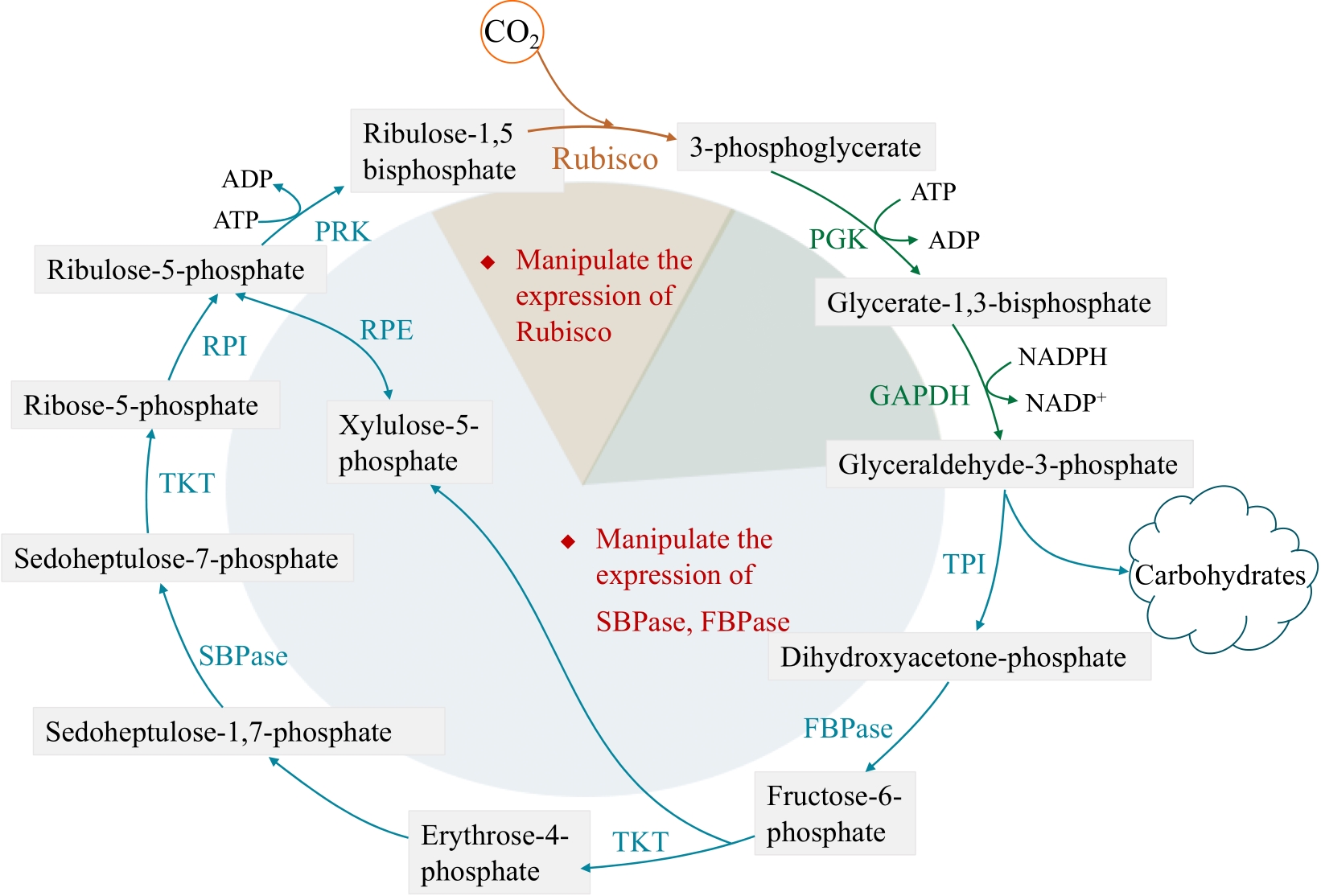
| 17 | ZHU X G, LONG S P, ORT D R. Improving photosynthetic efficiency for greater yield[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010, 61: 235-261. |
| 18 | MINAGAWA J, TOKUTSU R. Dynamic regulation of photosynthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii [J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2015, 82(3): 413-428. |
| 19 | KOSSALBAYEV B D, TOMO T, ZAYADAN B K, et al. Determination of the potential of cyanobacterial strains for hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(4): 2627-2639. |
| 20 | SCHENK P M, THOMAS-HALL S R, STEPHENS E, et al. Second generation biofuels: high-efficiency microalgae for biodiesel production[J]. BioEnergy Research, 2008, 1(1): 20-43. |
| 21 | NEGI S, PERRINE Z, FRIEDLAND N, et al. Light regulation of light-harvesting antenna size substantially enhances photosynthetic efficiency and biomass yield in green algae [J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2020, 103(2): 584-603. |
| 22 | WITT H T. Coupling of quanta, electrons, fields, ions and phosphrylation in the functional membrane of photosynthesis. Results by pulse spectroscopic methods[J]. Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics, 1971, 4(4): 365-477. |
| 23 | WHITMARSH J, GOVINDJEE. Photosynthesis[M]// TRIGG G L. Encyclopedia of applied physics. New York: VCH Publishers, Inc., 1995(13): 513-532. |
| 24 | MELIS A, NEIDHARDT J, BENEMANN J R. Dunaliella salina (Chlorophyta) with small chlorophyll antenna sizes exhibit higher photosynthetic productivities and photon use efficiencies than normally pigmented cells [J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 1998, 10(6): 515-525. |
| 25 | KIRK J T O. Light and photosynthesis in aquatic ecosystems[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1994. |
| 26 | NATALI A, ROY L M, CROCE R. In vitro reconstitution of light-harvesting complexes of plants and green algae[J]. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE, 2014(92): e51852. |
| 27 | WANG W D, YU L J, XU C Z, et al. Structural basis for blue-green light harvesting and energy dissipation in diatoms[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6427): eaav0365. |
| 28 | MUSSGNUG J H, THOMAS-HALL S, RUPPRECHT J, et al. Engineering photosynthetic light capture: impacts on improved solar energy to biomass conversion[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2007, 5(6): 802-814. |
| 29 | CROCE R, VAN GRONDELLE R, VAN AMERONGEN H, et al. Light harvesting in cyanobacteria: the phycobilisomes[M]// Light harvesting in photosynthesis. CRC Press, 2018: 77-93. |
| 30 | POLLE J E W, KANAKAGIRI S D, MELIS A. tla1, a DNA insertional transformant of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a truncated light-harvesting chlorophyll antenna size[J]. Planta, 2003, 217(1): 49-59. |
| 31 | VON WETTSTEIN D, GOUGH S, KANNANGARA C G. Chlorophyll biosynthesis[J]. The Plant Cell, 1995, 7(7): 1039-1057. |
| 32 | TANAKA A, ITO H, TANAKA R, et al. Chlorophyll a oxygenase (CAO) is involved in chlorophyll b formation from chlorophyll A[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1998, 95(21): 12719-12723. |
| 33 | PERRINE Z, NEGI S, SAYRE R T. Optimization of photosynthetic light energy utilization by microalgae[J]. Algal Research, 2012, 1(2): 134-142. |
| 34 | KUMAR V, SHARMA N, JAISWAL K K, et al. Microalgae with a truncated light-harvesting antenna to maximize photosynthetic efficiency and biomass productivity: recent advances and current challenges[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2021, 104: 83-91. |
| 35 | WOBBE L, REMACLE C. Improving the sunlight-to-biomass conversion efficiency in microalgal biofactories[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2015, 201: 28-42. |
| 36 | LIU J Y, SONG Y M, QIU W. Oleaginous microalgae Nannochloropsis as a new model for biofuel production: review & analysis[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 72: 154-162. |
| 37 | BASSO S, SIMIONATO D, GEROTTO C, et al. Characterization of the photosynthetic apparatus of the Eustigmatophycean Nannochloropsis gaditana: evidence of convergent evolution in the supramolecular organization of photosystemⅠ[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 2014, 1837(2): 306-314. |
| 38 | KOH H G, KANG N K, JEON S, et al. Heterologous synthesis of chlorophyll b in Nannochloropsis salina enhances growth and lipid production by increasing photosynthetic efficiency[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2019, 12: 122. |
| 39 | FU W Q, CHAIBOONCHOE A, KHRAIWESH B, et al. Intracellular spectral recompositioning of light enhances algal photosynthetic efficiency[J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(9): e1603096. |
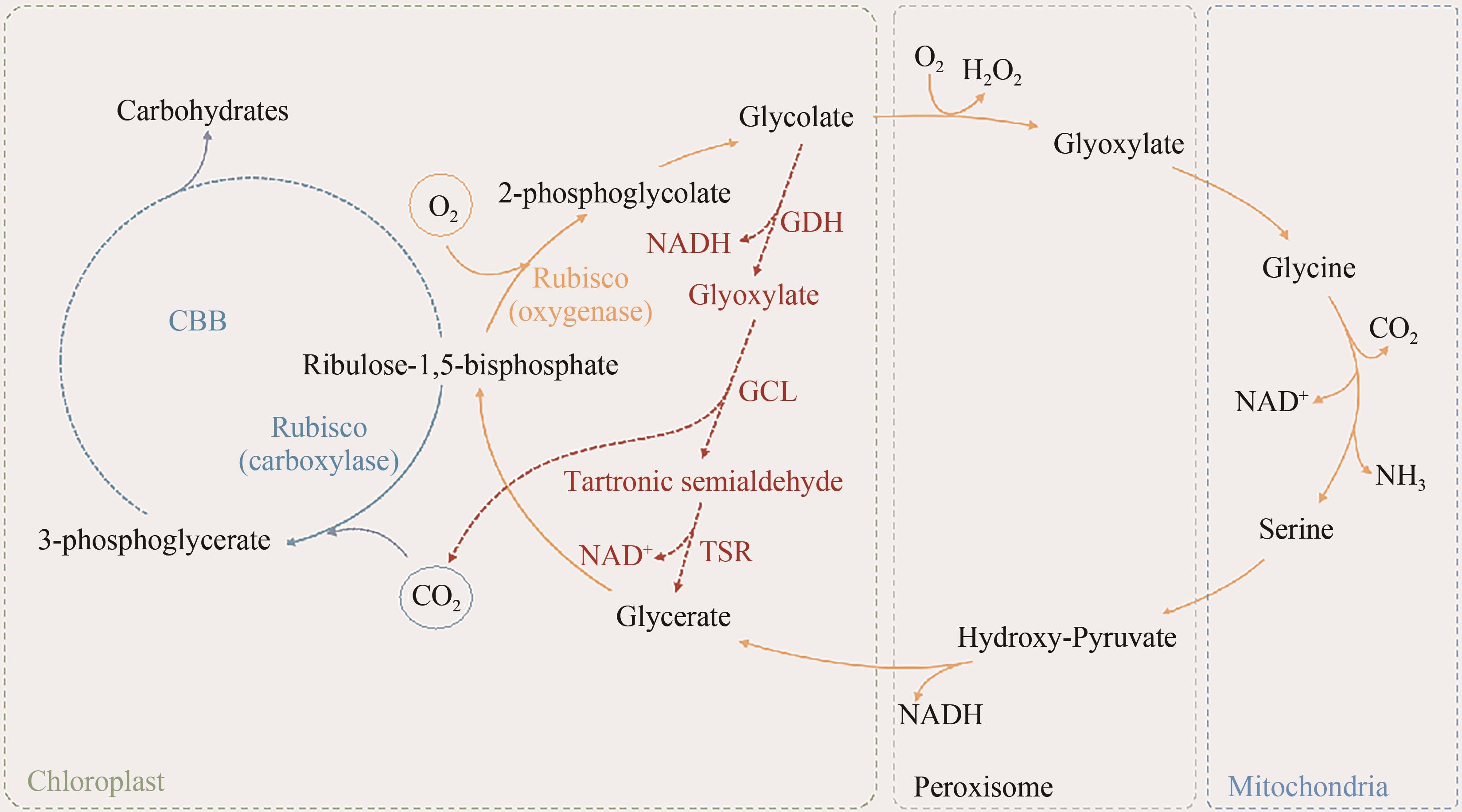
| 40 | WANG S, WU S, YANG G P, et al. A review on the progress, challenges and prospects in commercializing microalgal fucoxanthin[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2021, 53: 107865. |
| 41 | GIMPEL J A, NOUR-ELDIN H H, SCRANTON M A, et al. Refactoring the six-gene photosystem Ⅱ core in the chloroplast of the green algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2016, 5(7): 589-596. |
| 42 | RAINES C A, LLOYD J C, DYER T A. New insights into the structure and function of sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase; an important but neglected Calvin cycle enzyme[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 1999, 50(330): 1-8. |
| 43 | ABEBE T, WISE R P, SKADSEN R W. Comparative transcriptional profiling established the awn as the major photosynthetic organ of the barley spike while the lemma and the palea primarily protect the seed[J]. The Plant Genome, 2009, 2(3). |
| 44 | ANDERSSON I, BACKLUND A. Structure and function of Rubisco[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2008, 46(3): 275-291. |
| 45 | LIN M T, OCCHIALINI A, ANDRALOJC P J, et al. A faster Rubisco with potential to increase photosynthesis in crops[J]. Nature, 2014, 513(7519): 547-550. |
| 46 | ERB T J, ZARZYCKI J. A short history of RubisCO: the rise and fall (?) of Nature's predominant CO2 fixing enzyme[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2018, 49: 100-107. |
| 47 | MCNEVIN D, VON CAEMMERER S, FARQUHAR G. Determining RuBisCO activation kinetics and other rate and equilibrium constants by simultaneous multiple non-linear regression of a kinetic model[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2006, 57(14): 3883-3900. |
| 48 | VECCHI V, BARERA S, BASSI R, et al. Potential and challenges of improving photosynthesis in algae[J]. Plants, 2020, 9(1): 67. |
| 49 | LIN M T, HANSON M R. Red algal Rubisco fails to accumulate in transplastomic tobacco expressing Griffithsia monilis RbcL and RbcS genes[J]. Plant Direct, 2018, 2(2): e00045. |
| 50 | OLIVER A, PODELL S, PINOWSKA A, et al. Diploid genomic architecture of Nitzschia inconspicua, an elite biomass production diatom[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11: 15592. |
| 51 | WHITNEY S M, BALDET P, HUDSON G S, et al. Form I Rubiscos from non-green algae are expressed abundantly but not assembled in tobacco chloroplasts[J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2001, 26(5): 535-547. |
| 52 | ORR D J, WORRALL D, LIN M T, et al. Hybrid cyanobacterial-tobacco rubisco supports autotrophic growth and procarboxysomal aggregation[J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 182(2): 807-818. |
| 53 | CARMO-SILVA E, SCALES J C, MADGWICK P J, et al. Optimizing Rubisco and its regulation for greater resource use efficiency[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2015, 38(9): 1817-1832. |
| 54 | WEI L, WANG Q T, XIN Y, et al. Enhancing photosynthetic biomass productivity of industrial oleaginous microalgae by overexpression of RuBisCO activase[J]. Algal Research, 2017, 27: 366-375. |
| 55 | DORON L, SEGAL N, GIBORI H, et al. The BSD2 ortholog in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is a polysome-associated chaperone that co-migrates on sucrose gradients with the rbcL transcript encoding the Rubisco large subunit[J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2014, 80(2): 345-355. |
| 56 | SHARWOOD R E. Engineering chloroplasts to improve Rubisco catalysis: prospects for translating improvements into food and fiber crops[J]. The New Phytologist, 2017, 213(2): 494-510. |
| 57 | TCHERKEZ G G B, FARQUHAR G D, ANDREWS T J. Despite slow catalysis and confused substrate specificity, all ribulose bisphosphate carboxylases may be nearly perfectly optimized[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(19): 7246-7251. |
| 58 | FANG L, LIN H X, LOW C S, et al. Expression of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase in Dunaliella bardawil leads to enhanced photosynthesis and increased glycerol production[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2012, 10(9): 1129-1135. |
| 59 | HAMMEL A, SOMMER F, ZIMMER D, et al. Overexpression of sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase enhances photosynthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and has no effect on the abundance of other Calvin-Benson cycle enzymes[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 868. |
| 60 | OGAWA T, TAMOI M, KIMURA A, et al. Enhancement of photosynthetic capacity in Euglena gracilis by expression of cyanobacterial fructose-1,6-/ sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase leads to increases in biomass and wax ester production[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2015, 8: 80. |
| 61 | YANG B, LIU J, MA X N, et al. Genetic engineering of the Calvin cycle toward enhanced photosynthetic CO2 fixation in microalgae[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2017, 10: 229. |
| 62 | DE PORCELLINIS A J, NØRGAARD H, BREY L M F, et al. Overexpression of bifunctional fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase/sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase leads to enhanced photosynthesis and global reprogramming of carbon metabolism in Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 47: 170-183. |
| 63 | DEJTISAKDI W, MILLER S M. Overexpression of Calvin cycle enzyme fructose 1, 6-bisphosphatase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii has a detrimental effect on growth[J]. Algal Research, 2016, 14: 116-126. |
| 64 | SALVUCCI M E, DERIDDER B P, PORTIS A R JR. Effect of activase level and isoform on the thermotolerance of photosynthesis in Arabidopsis [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2006, 57(14): 3793-3799. |
| 65 | DALAL J, LOPEZ H, VASANI N B, et al. A photorespiratory bypass increases plant growth and seed yield in biofuel crop Camelina sativa [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2015, 8: 175. |
| 66 | SOMERVILLE C R. An early Arabidopsis demonstration. resolving a few issues concerning photorespiration[J]. Plant Physiology, 2001, 125(1): 20-24. |
| 67 | BAUWE H, HAGEMANN M, FERNIE A R. Photorespiration: players, partners and origin[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2010, 15(6): 330-336. |
| 68 | KEBEISH R, NIESSEN M, THIRUVEEDHI K, et al. Chloroplastic photorespiratory bypass increases photosynthesis and biomass production in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2007, 25(5): 593-599. |
| 69 | RADEMACHER N, KERN R, FUJIWARA T, et al. Photorespiratory glycolate oxidase is essential for the survival of the red alga Cyanidioschyzon merolae under ambient CO2 conditions[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(10): 3165-3175. |
| 70 | SHIH P M, ZARZYCKI J, NIYOGI K K, et al. Introduction of a synthetic CO2-fixing photorespiratory bypass into a cyanobacterium[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2014, 289(14): 9493-9500. |
| 71 | THOMS S, PAHLOW M, WOLF-GLADROW D A. Model of the carbon concentrating mechanism in chloroplasts of eukaryotic algae[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2001, 208(3): 295-313. |
| 72 | SPALDING M H. Microalgal carbon-dioxide-concentrating mechanisms: Chlamydomonas inorganic carbon transporters[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2007, 59(7): 1463-1473. |
| 73 | BADGER M R, PRICE G D. CO2 concentrating mechanisms in cyanobacteria: molecular components, their diversity and evolution[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2003, 54(383): 609-622. |
| 74 | WANG Y J, STESSMAN D J, SPALDING M H. The CO2 concentrating mechanism and photosynthetic carbon assimilation in limiting CO2: how Chlamydomonas works against the gradient[J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2015, 82(3): 429-448. |
| 75 | SOLOVCHENKO A, KHOZIN-GOLDBERG I. High-CO2 tolerance in microalgae: possible mechanisms and implications for biotechnology and bioremediation[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2013, 35(11): 1745-1752. |
| 76 | HUANG Y, CHENG J, LU H X, et al. Transcriptome and key genes expression related to carbon fixation pathways in Chlorella PY-ZU1 cells and their growth under high concentrations of CO2 [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2017, 10: 181. |
| 77 | WEI L, SHEN C, HAJJAMI M EL, et al. Knockdown of carbonate anhydrase elevates Nannochloropsis productivity at high CO2 level[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 54: 96-108. |
| 78 | KAMENNAYA N A, AHN S, PARK H, et al. Installing extra bicarbonate transporters in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 enhances biomass production[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2015, 29: 76-85. |
| 79 | LIN W R, LAI Y C, SUNG P K, et al. Enhancing carbon capture and lipid accumulation by genetic carbonic anhydrase in microalgae[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2018, 93: 131-141. |
| 80 | MOHR R, VOß B, SCHLIEP M, et al. A new chlorophyll d-containing cyanobacterium: evidence for niche adaptation in the genus Acaryochloris [J]. The ISME Journal, 2010, 4(11): 1456-1469. |
| 81 | NÜRNBERG D J, MORTON J, SANTABARBARA S, et al. Photochemistry beyond the red limit in chlorophyll f-containing photosystems[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6394): 1210-1213. |
| 82 | CHEN M. Chlorophyll modifications and their spectral extension in oxygenic photosynthesis[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2014, 83: 317-340. |
| 83 | HO M Y, SHEN G Z, CANNIFFE D P, et al. Light-dependent chlorophyll f synthase is a highly divergent paralog of PsbA of photosystem II[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6302): aaf9178. |
| 84 | SHEN G Z, CANNIFFE D P, HO M Y, et al. Characterization of chlorophyll f synthase heterologously produced in Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2019, 140(1): 77-92. |
| 85 | SIMKIN A J, MCAUSLAND L, LAWSON T, et al. Overexpression of the RieskeFeS protein increases electron transport rates and biomass yield[J]. Plant Physiology, 2017, 175(1): 134-145. |
| 86 | WEIGEL M, VAROTTO C, PESARESI P, et al. Plastocyanin is indispensable for photosynthetic electron flow in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2003, 278(33): 31286-31289. |
| 87 | ZHOU X T, WANG F, MA Y P, et al. Ectopic expression of SsPETE2, a plastocyanin from Suaeda salsa, improves plant tolerance to oxidative stress[J]. Plant Science, 2018, 268: 1-10. |
| 88 | LEVIN G, KULIKOVSKY S, LIVEANU V, et al. The desert green algae Chlorella ohadii thrives at excessively high light intensities by exceptionally enhancing the mechanisms that protect photosynthesis from photoinhibition[J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2021, 106(5): 1260-1277. |
| 89 | LA ROCCA N, SCIUTO K, MENEGHESSO A, et al. Photosynthesis in extreme environments: responses to different light regimes in the Antarctic alga Koliella antarctica [J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2015, 153(4): 654-667. |
| 90 | KROMDIJK J, GŁOWACKA K, LEONELLI L, et al. Improving photosynthesis and crop productivity by accelerating recovery from photoprotection[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6314): 857-861. |
| 91 | MURCHIE E H, NIYOGI K K. Manipulation of photoprotection to improve plant photosynthesis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 155(1): 86-92. |
| 92 | GIOVAGNETTI V, JAUBERT M, SHUKLA M K, et al. Biochemical and molecular properties of LHCX1, the essential regulator of dynamic photoprotection in diatoms[J]. Plant Physiology, 2021, 188(1): 509-525. |
| 93 | KAŇA R, KOTABOVÁ E, SOBOTKA R, et al. Non-photochemical quenching in cryptophyte alga Rhodomonas salina is located in chlorophyll a/c antennae[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(1): e29700. |
| 94 | PEERS G, TRUONG T B, OSTENDORF E, et al. An ancient light-harvesting protein is critical for the regulation of algal photosynthesis[J]. Nature, 2009, 462(7272): 518-521. |
| 95 | LEONELLI L, ERICKSON E, LYSKA D, et al. Transient expression in Nicotiana benthamiana for rapid functional analysis of genes involved in non-photochemical quenching and carotenoid biosynthesis[J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2016, 88(3): 375-386. |
| 96 | UEMURA K, ANWARUZZAMAN, MIYACHI S, et al. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from thermophilic red algae with a strong specificity for CO2 fixation[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 1997, 233(2): 568-571. |
| 97 | HASLAM R P, KEYS A J, ANDRALOJC P J, et al. Specificity of diatom rubisco[M]// OMASA K, NOUCHI I, DE KOK L J. Plant Responses to Air Pollution and Global Change. Tokyo: Springer Japan, 2005: 157-164. |
| 98 | READ B A, TABITA F R. High substrate specificity factor ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from eukaryotic marine algae and properties of recombinant cyanobacterial rubisco containing “algal” residue modifications[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 1994, 312(1): 210-218. |
| 99 | PARRY M A J, KEYS A J, MADGWICK P J, et al. Rubisco regulation: a role for inhibitors[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2008, 59(7): 1569-1580. |
| 100 | LOGANATHAN N, TSAI Y C C, MUELLER-CAJAR O. Characterization of the heterooligomeric red-type Rubisco activase from red algae[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(49): 14019-14024. |
| 101 | ZHANG J L, LIU G X, CARVAJAL A I, et al. Discovery of a readily heterologously expressed Rubisco from the deep sea with potential for CO2 capture[J]. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 2021, 8: 86. |
| 102 | TABITA F R, SATAGOPAN S, HANSON T E, et al. Distinct form Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, and Ⅳ Rubisco proteins from the three kingdoms of life provide clues about Rubisco evolution and structure/function relationships[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2008, 59(7): 1515-1524. |
| 103 | SAIBO N J M, LOURENÇO T, OLIVEIRA M M. Transcription factors and regulation of photosynthetic and related metabolism under environmental stresses[J]. Annals of Botany, 2008, 103(4): 609-623. |
| 104 | ZHOU C G, LI C H. A novel R2R3-MYB transcription factor BpMYB106 of birch (Betula platyphylla) confers increased photosynthesis and growth rate through up-regulating photosynthetic gene expression[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 315. |
| 105 | YU X B, ZHENG G Y, SHAN L L, et al. Reconstruction of gene regulatory network related to photosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2014, 5: 273. |
| 106 | PERVEEN S, QU M N, CHEN F M, et al. Overexpression of maize transcription factor mEmBP-1 increases photosynthesis, biomass, and yield in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2020, 71(16): 4944-4957. |
| 107 | LI X, WANG P, LI J, et al. Maize GOLDEN2-LIKE genes enhance biomass and grain yields in rice by improving photosynthesis and reducing photoinhibition[J]. Communications Biology, 2020, 3: 151. |
| 108 | CHEN F M, ZHENG G Y, QU M N, et al. Knocking out negative regulator of photosynthesis 1 increases rice leaf photosynthesis and biomass production in the field[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2021, 72(5): 1836-1849. |
| 109 | TOKUTSU R, FUJIMURA-KAMADA K, MATSUO T, et al. The CONSTANS flowering complex controls the protective response of photosynthesis in the green alga Chlamydomonas [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 4099. |
| 110 | ROGERS K, CHEN X M. Biogenesis, turnover, and mode of action of plant microRNAs[J]. The Plant Cell, 2013, 25(7): 2383-2399. |
| 111 | ZHANG J P, YU Y, FENG Y Z, et al. MiR408 regulates grain yield and photosynthesis via a phytocyanin protein[J]. Plant Physiology, 2017, 175(3): 1175-1185. |
| 112 | PAN J W, HUANG D H, GUO Z L, et al. Overexpression of microRNA408 enhances photosynthesis, growth, and seed yield in diverse plants[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2018, 60(4): 323-340. |
| 113 | FUCHS G. Alternative pathways of carbon dioxide fixation: insights into the early evolution of life? [J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2011, 65: 631-658. |
| 114 | DUCAT D C, SILVER P A. Improving carbon fixation pathways[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2012, 16(3/4): 337-344. |
| 115 | BAR-EVEN A, NOOR E, LEWIS N E, et al. Design and analysis of synthetic carbon fixation pathways[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(19): 8889-8894. |
| 116 | DURALL C, RUKMINASARI N, LINDBLAD P. Enhanced growth at low light intensity in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC 6803 by overexpressing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase[J]. Algal Research, 2016, 16: 275-281. |
| 117 | ZARZYCKI J, BRECHT V, MÜLLER M, et al. Identifying the missing steps of the autotrophic 3-hydroxypropionate CO2 fixation cycle in Chloroflexus aurantiacus [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(50): 21317-21322. |
| 118 | SHEN B R, WANG L M, LIN X L, et al. Engineering a new chloroplastic photorespiratory bypass to increase photosynthetic efficiency and productivity in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(2): 199-214. |
| 119 | PAUL M J, FOYER C H. Sink regulation of photosynthesis[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2001, 52(360): 1383-1400. |
| 120 | PAUL M J, PELLNY T K. Carbon metabolite feedback regulation of leaf photosynthesis and development[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2003, 54(382): 539-547. |
| 121 | ABRAMSON B W, KACHEL B, KRAMER D M, et al. Increased photochemical efficiency in cyanobacteria via an engineered sucrose sink[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2016, 57(12): 2451-2460. |
| [1] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [12] | CAI Bingyu, TAN Xiangtian, LI Wei. Advances in synthetic biology for engineering stem cell [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [13] | XIE Huang, ZHENG Yilei, SU Yiting, RUAN Jingyi, LI Yongquan. An overview on reconstructing the biosynthetic system of actinomycetes for polyketides production [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [14] | ZHA Wenlong, BU Lan, ZI Jiachen. Advances in synthetic biology for producing potent pharmaceutical ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| [15] | HUI Zhen, TANG Xiaoyu. Applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 editing system in the study of microbial natural products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 658-671. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||