Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (3): 474-491.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-099
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Resistance-gene directed discovery of bioactive natural products
SONG Yongxiang1,2,3, ZHANG Xiufeng1,2,3, LI Yanqin1,2,3, XIAO Hua1,2,3, YAN Yan1,2,3
- 1.Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology,Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica,Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering,South China Sea Institute of Oceanology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Guangzhou 510301,Guangdong,China
2.Sanya Institute of Ocean Eco-Environmental Engineering,Sanya 572000,Hainan,China
3.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
-
Received:2023-12-01Revised:2024-03-08Online:2024-07-12Published:2024-06-30 -
Contact:YAN Yan
自抗性基因导向的活性天然产物挖掘
宋永相1,2,3, 张秀凤1,2,3, 李艳芹1,2,3, 肖华1,2,3, 闫岩1,2,3
- 1.中国科学院热带海洋生物资源与生态重点实验室,广东省海洋药物重点实验室,中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院,中国科学院南海海洋研究所,广东 广州 510301
2.三亚海洋生态环境工程研究院,海南 三亚 572000
3.中国科学院大学,北京 100049
-
通讯作者:闫岩 -
作者简介:宋永相 (1980—),男,博士,副研究员。研究方向为海洋微生物活性物质的发掘与应用。E-mail:songx@scsio.ac.cn闫岩 (1986—),男,博士,研究员。研究方向为海洋活性天然产物的挖掘与合成生物学智造。E-mail:yyan@scsio.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(32000044);国家重点研发计划(2022YFC2805000);海南省科技计划三亚崖州湾科技城联合项目(2021CXLH0013)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SONG Yongxiang, ZHANG Xiufeng, LI Yanqin, XIAO Hua, YAN Yan. Resistance-gene directed discovery of bioactive natural products[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 474-491.
宋永相, 张秀凤, 李艳芹, 肖华, 闫岩. 自抗性基因导向的活性天然产物挖掘[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 474-491.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2023-099
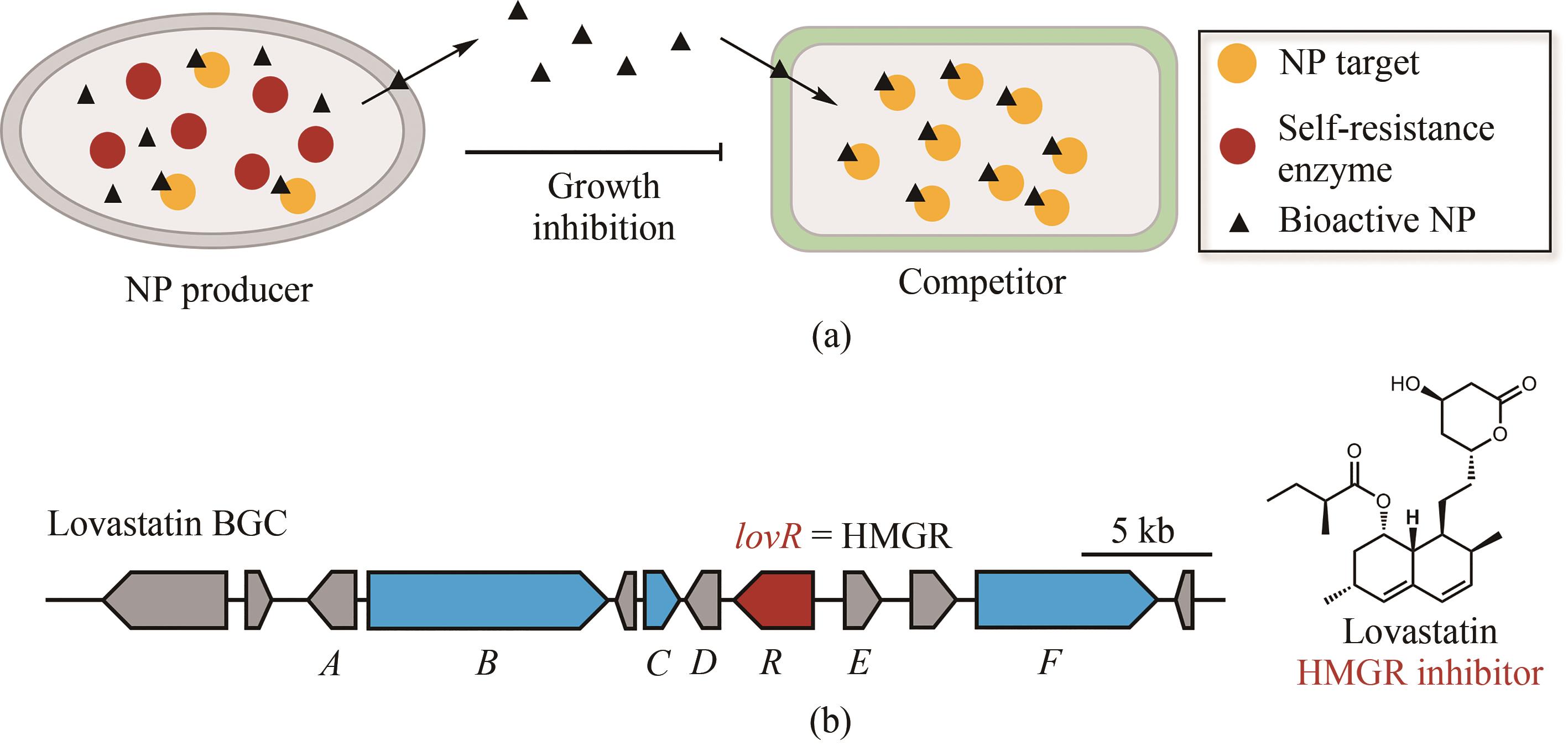
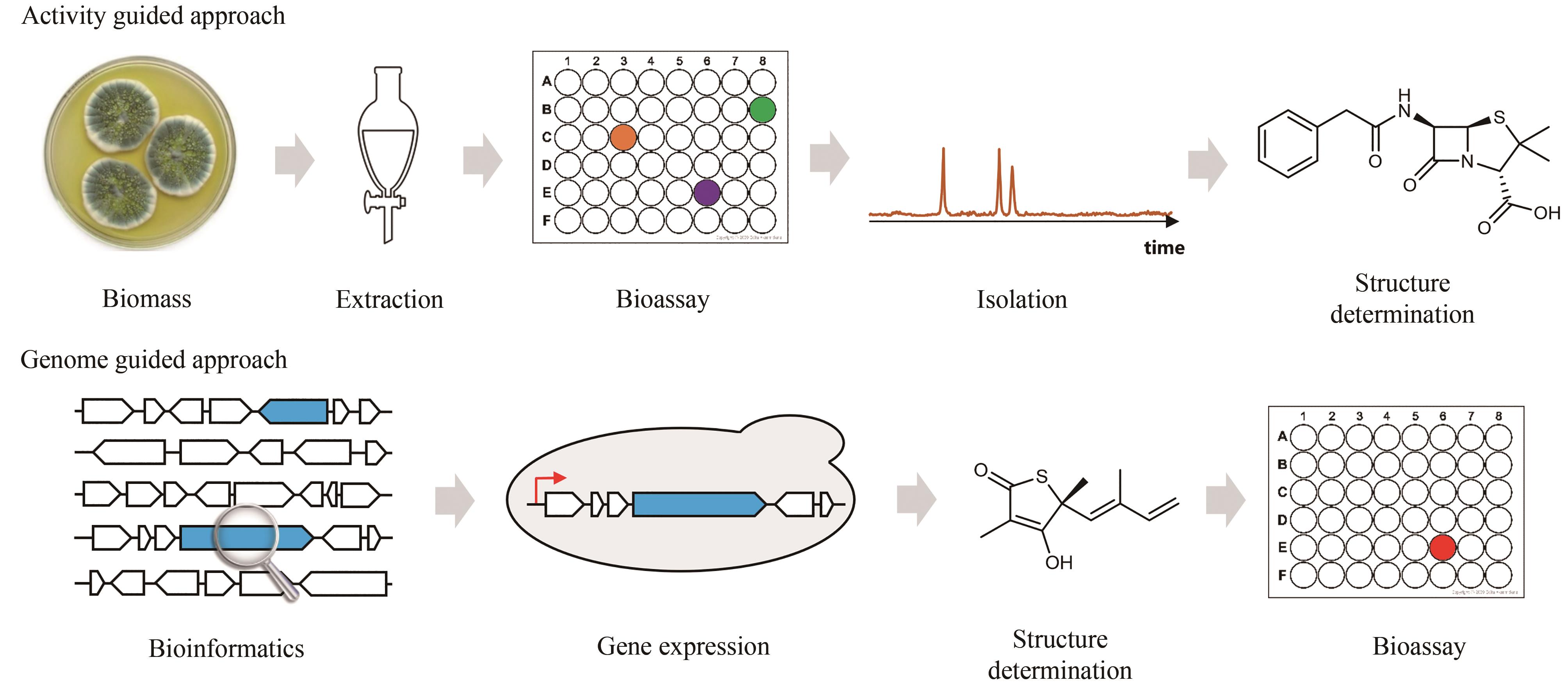
Fig. 2 Simultaneous localization of genes encoding core biosynthetic enzymes and for self-resistance(a) Microorganisms produce natural products (black triangles) as a strategy to kill competitors by inhibiting their essential metabolic enzymes (yellow balls). To ensure their own survival, these microorganisms express the self-resistance enzymes (red balls) capable of complementing the functions of those targeted metabolic enzymes; (b) Simultaneous localization of the core enzymes for lovastatin biosynthesis (blue) and the self-resistance genes encoding HMG-CoA reductase within lovastatin biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC). This gene cluster includes another copy of HMGR encoded by lovR (red).

Fig. 3 Self-resistance gene directed localization of the biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) for the production of natural products(The biosynthetic core genes, self-resistance genes and other related genes are shown in blue, red and grey, respectively.)
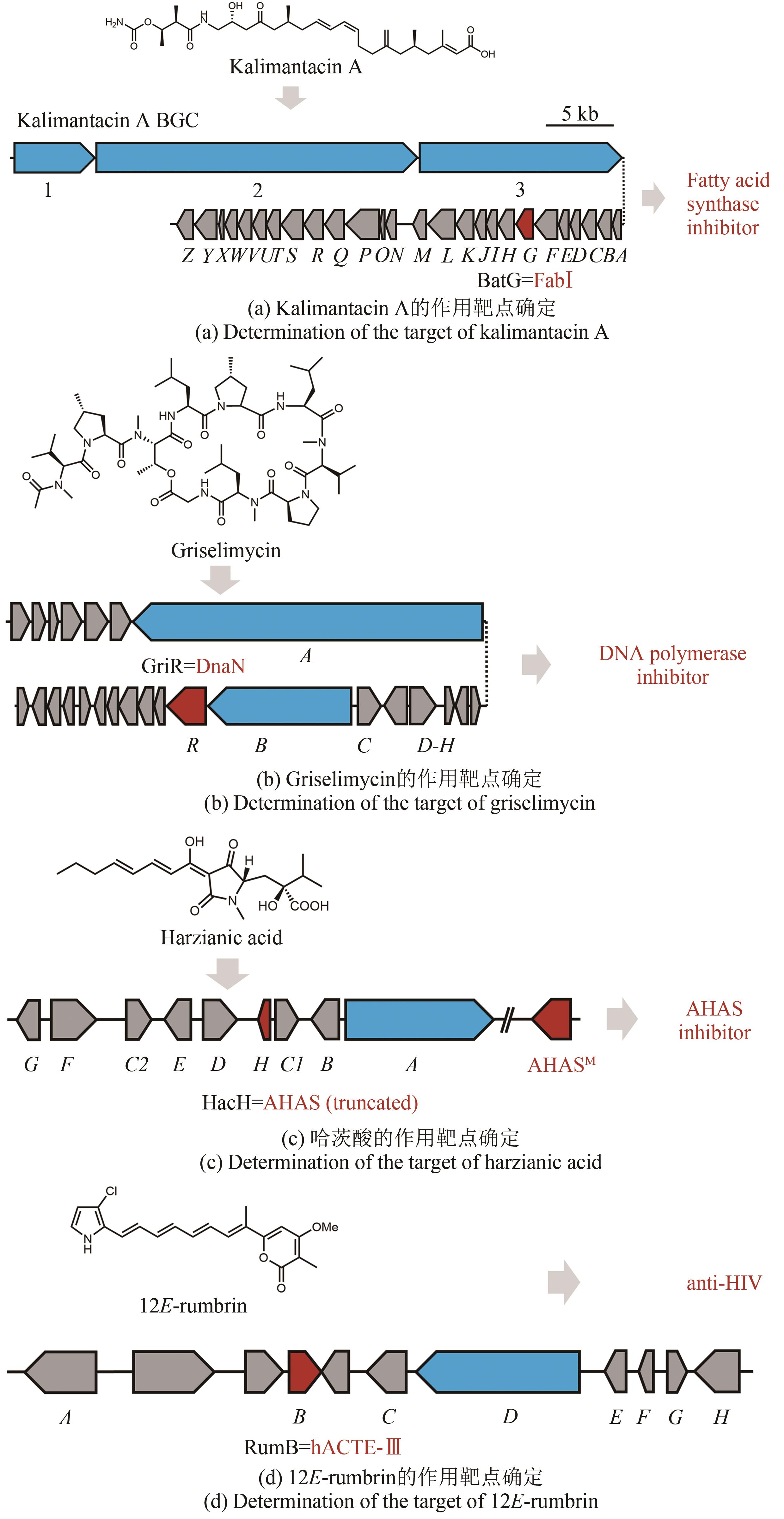
Fig. 4 Determination of the target of natural products through their resistance genes(Biosynthetic core genes, self-resistance genes and other related genes are shown in blue, red and grey, respectively.)
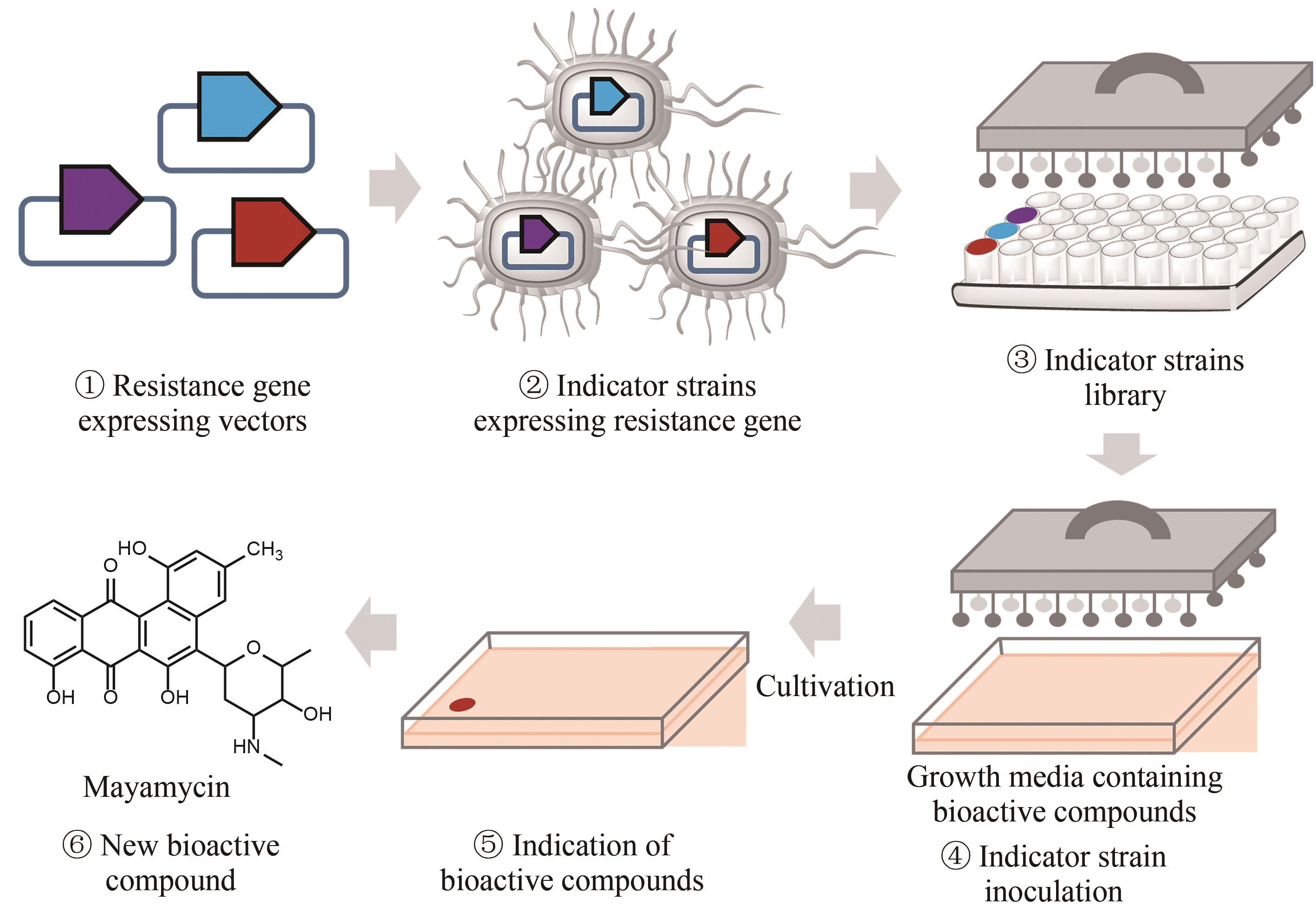
Fig. 5 Workflow of the resistance gene directed dereplication of natural products① Construction of vectors expressing a known antibiotic resistance gene; ② Construction of strains capable of indicating the presence of known bioactive compounds; ③ Construction of a library of indicator strains; ④ Inoculation of the indicator strains to media containing bioactive natural products; ⑤ Identification of natural products with new modes of action; ⑥ Isolation of natural products with new modes of action

Fig. 6 Discovery of bioactive natural products guided by their resistance genes(Biosynthetic core genes, self-resistance genes and other related genes are shown in blue, red and grey, respectively.)
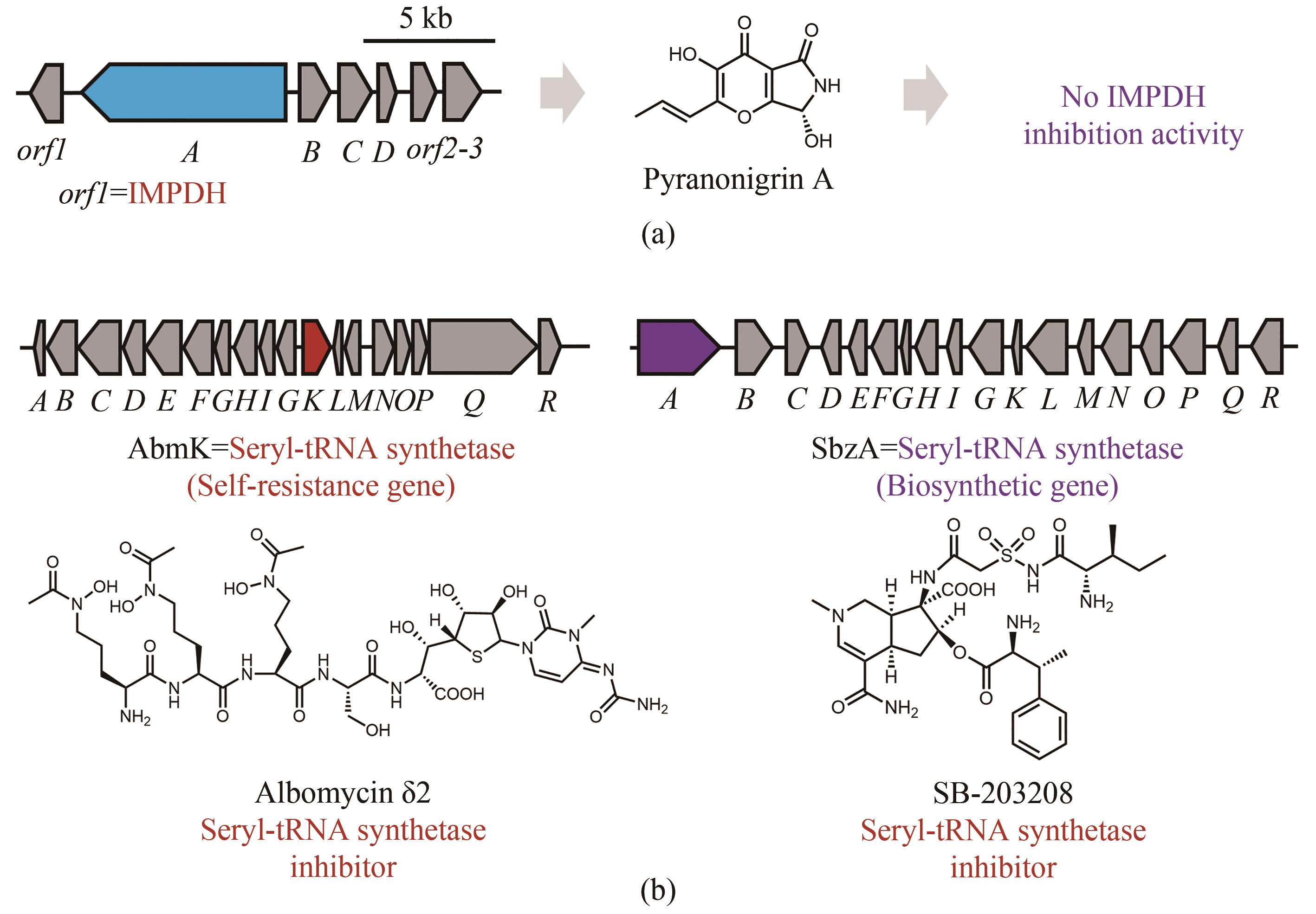
Fig. 7 “False positive” resistance genes in the biosynthetic gene clusters of natural products(Biosynthetic core genes, self-resistance genes and other related genes are shown in blue, red and grey, respectively.)(a) An IMPDH was localized with the biosynthetic genes of pyranonigrin, which exhibit no IMPDH inhibition activity (purple); (b) Albomycin δ2 is an inhibitor of seryl-tRNA synthetase (red), however the seryl-tRNA synthetase homolog is encoded in the BGC with another inhibitor of seryl-tRNA synthetase SB-203208, which functions as a core enzyme (purple) encoded by the biosynthetic gene.
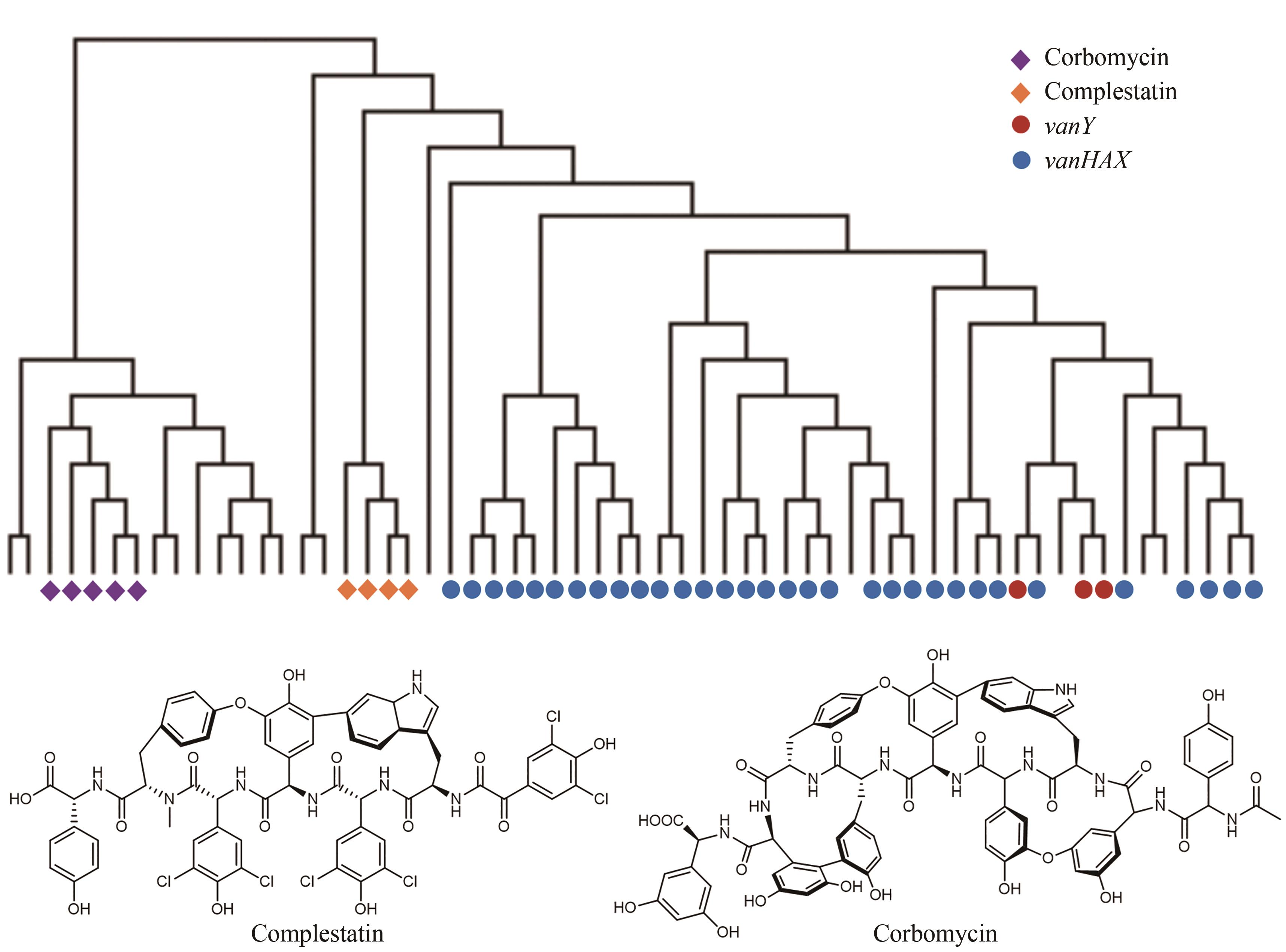
Fig. 8 Discovery of new antibiotics guided by the resistance gene phylogeny(Among 71 BGCs for the biosynthesis of glycopeptides, the self-resistance determinants of complestatin and corbomycin are different from the known determinants vanY and vanHAX in the phylogeny.)
| 1 | NEWMAN D J, CRAGG G M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2020, 83(3): 770-803. |
| 2 | ATANASOV A G, ZOTCHEV S B, DIRSCH V M, et al. Natural products in drug discovery: advances and opportunities[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2021, 20(3): 200-216. |
| 3 | CANTRELL C L, DAYAN F E, DUKE S O. Natural products as sources for new pesticides[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2012, 75(6): 1231-1242. |
| 4 | YAN Y, LIU Q K, JACOBSEN S E, et al. The impact and prospect of natural product discovery in agriculture: new technologies to explore the diversity of secondary metabolites in plants and microorganisms for applications in agriculture[J]. EMBO Reports, 2018, 19(11): e46824. |
| 5 | DAYAN F E, DUKE S O. Natural compounds as next-generation herbicides[J]. Plant Physiology, 2014, 166(3): 1090-1105. |
| 6 | DAYAN F E, OWENS D K, DUKE S O. Rationale for a natural products approach to herbicide discovery[J]. Pest Management Science, 2012, 68(4): 519-528. |
| 7 | SONG C G, YANG J, ZHANG M Z, et al. Marine natural products: the important resource of biological insecticide[J]. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 2021, 18(5): e2001020. |
| 8 | HENKE M T, KELLEHER N L. Modern mass spectrometry for synthetic biology and structure-based discovery of natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2016, 33(8): 942-950. |
| 9 | DUKE S O, ROMAGNI J G, DAYAN F E. Natural products as sources for new mechanisms of herbicidal action[J]. Crop Protection, 2000, 19(8-10): 583-589. |
| 10 | DAYAN F E, CANTRELL C L, DUKE S O. Natural products in crop protection[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2009, 17(12): 4022-4034. |
| 11 | CRAGG G M, NEWMAN D J, SNADER K M. Natural products in drug discovery and development[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 1997, 60(1): 52-60. |
| 12 | MULLOWNEY M W, DUNCAN K R, ELSAYED S S, et al. Artificial intelligence for natural product drug discovery[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2023, 22(11): 895-916. |
| 13 | CHOPRA B, DHINGRA A K. Natural products: a lead for drug discovery and development[J]. Phytotherapy Research, 2021, 35(9): 4660-4702. |
| 14 | NEWMAN D J, CRAGG G M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the 30 years from 1981 to 2010[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2012, 75(3): 311-335. |
| 15 | NEWMAN D J, CRAGG G M, SNADER K M. The influence of natural products upon drug discovery[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2000, 17(3): 215-234. |
| 16 | LOBANOVSKA M, PILLA G. Penicillin’s discovery and antibiotic resistance: lessons for the future?[J]. The Yale Journal of Biology and Medicine, 2017, 90(1): 135-145. |
| 17 | NÜTZMANN H W, SCAZZOCCHIO C, OSBOURN A. Metabolic gene clusters in eukaryotes[J]. Annual Review of Genetics, 2018, 52: 159-183. |
| 18 | FISCHBACH M A, WALSH C T. Assembly-line enzymology for polyketide and nonribosomal peptide antibiotics: logic, machinery, and mechanisms[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2006, 106(8): 3468-3496. |
| 19 | ROBBINS T, LIU Y C, CANE D E, et al. Structure and mechanism of assembly line polyketide synthases[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2016, 41: 10-18. |
| 20 | SÜSSMUTH R D, MAINZ A. Nonribosomal peptide synthesis-principles and prospects[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(14): 3770-3821. |
| 21 | CHRISTIANSON D W. Structural and chemical biology of terpenoid cyclases[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(17): 11570-11648. |
| 22 | RUDOLF J D, CHANG C Y. Terpene synthases in disguise: enzymology, structure, and opportunities of non-canonical terpene synthases[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2020, 37(3): 425-463. |
| 23 | KIM H U, BLIN K, LEE S Y, et al. Recent development of computational resources for new antibiotics discovery[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2017, 39: 113-120. |
| 24 | MEDEMA M H, FISCHBACH M A. Computational approaches to natural product discovery[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(9): 639-648. |
| 25 | RUTLEDGE P J, CHALLIS G L. Discovery of microbial natural products by activation of silent biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2015, 13(8): 509-523. |
| 26 | CIMERMANCIC P, MEDEMA M H, CLAESEN J, et al. Insights into secondary metabolism from a global analysis of prokaryotic biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Cell, 2014, 158(2): 412-421. |
| 27 | WALSH C T, FISCHBACH M A. Natural products version 2.0: connecting genes to molecules[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(8): 2469-2493. |
| 28 | HARVEY A L, EDRADA-EBEL R, QUINN R J. The re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics era[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2015, 14(2): 111-129. |
| 29 | VAN LANEN S G, SHEN B. Microbial genomics for the improvement of natural product discovery[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2006, 9(3): 252-260. |
| 30 | LAUTRU S, DEETH R J, BAILEY L M, et al. Discovery of a new peptide natural product by Streptomyces coelicolor genome mining[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2005, 1(5): 265-269. |
| 31 | CLEVENGER K D, BOK J W, YE R, et al. A scalable platform to identify fungal secondary metabolites and their gene clusters[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2017, 13(8): 895-901. |
| 32 | ZHANG J J, TANG X Y, MOORE B S. Genetic platforms for heterologous expression of microbial natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2019, 36(9): 1313-1332. |
| 33 | HOPWOOD D A. Genetic contributions to understanding polyketide synthases[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1997, 97(7): 2465-2498. |
| 34 | SCHERLACH K, HERTWECK C. Mining and unearthing hidden biosynthetic potential[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 3864. |
| 35 | BAUMAN K D, BUTLER K S, MOORE B S, et al. Genome mining methods to discover bioactive natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2021, 38(11): 2100-2129. |
| 36 | ZIEMERT N, ALANJARY M, WEBER T. The evolution of genome mining in microbes—a review[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2016, 33(8): 988-1005. |
| 37 | 杨谦, 程伯涛, 汤志军, 等. 基因组挖掘在天然产物发现中的应用和前景[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(5): 697-715. |
| YANG Q, CHENG B T, TANG Z J, et al. Applications and prospects of genome mining in the discovery of natural products[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(5): 697-715. | |
| 38 | GALM U, HAGER M H, VAN LANEN S G, et al. Antitumor antibiotics: bleomycin, enediynes, and mitomycin[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2005, 105(2): 739-758. |
| 39 | WEISBLUM B. Erythromycin resistance by ribosome modification[J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 1995, 39(3): 577-585. |
| 40 | YAN Y, LIU N, TANG Y. Recent developments in self-resistance gene directed natural product discovery[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2020, 37(7): 879-892. |
| 41 | ALMABRUK K H, DINH L K, PHILMUS B. Self-resistance of natural product producers: past, present, and future focusing on self-resistant protein variants[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2018, 13(6): 1426-1437. |
| 42 | O'NEILL E C, SCHORN M, LARSON C B, et al. Targeted antibiotic discovery through biosynthesis-associated resistance determinants: target directed genome mining[J]. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 2019, 45(3): 255-277. |
| 43 | STANCU C, SIMA A. Statins: mechanism of action and effects[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2001, 5(4): 378-387. |
| 44 | CHAMILOS G, LEWIS R E, KONTOYIANNIS D P. Lovastatin has significant activity against zygomycetes and interacts synergistically with voriconazole[J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2006, 50(1): 96-103. |
| 45 | HUTCHINSON C R, KENNEDY J, PARK C, et al. Aspects of the biosynthesis of non-aromatic fungal polyketides by iterative polyketide synthases[J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2000, 78(3-4): 287-295. |
| 46 | STEFFENSKY M, MÜHLENWEG A, WANG Z X, et al. Identification of the novobiocin biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces spheroides NCIB 11891[J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2000, 44(5): 1214-1222. |
| 47 | WANG Z X, LI S M, HEIDE L. Identification of the coumermycin A(1) biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces rishiriensis DSM 40489[J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2000, 44(11): 3040-3048. |
| 48 | BENTLEY R. Mycophenolic acid: a one hundred year odyssey from antibiotic to immunosuppressant[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2000, 100(10): 3801-3826. |
| 49 | REGUEIRA T B, KILDEGAARD K R, HANSEN B G, et al. Molecular basis for mycophenolic acid biosynthesis in Penicillium brevicompactum [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(9): 3035-3043. |
| 50 | LIN H C, CHOOI Y H, DHINGRA S, et al. The fumagillin biosynthetic gene cluster in Aspergillus fumigatus encodes a cryptic terpene cyclase involved in the formation of β-trans-bergamotene[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(12): 4616-4619. |
| 51 | BIRCH A J, HUSSAIN S F. Studies in relation to biosynthesis. Part ⅩⅩⅩⅧ. A preliminary study of fumagillin[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society C: Organic, 1969(11): 1473. |
| 52 | LIU S, WIDOM J, KEMP C W, et al. Structure of human methionine aminopeptidase-2 complexed with fumagillin[J]. Science, 1998, 282(5392): 1324-1327. |
| 53 | CAMPOY S, ADRIO J L. Antifungals[J]. Biochemical Pharmacology, 2017, 133: 86-96. |
| 54 | SILVA FERREIRA M E DA, COLOMBO A L, PAULSEN I, et al. The ergosterol biosynthesis pathway, transporter genes, and azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus [J]. Medical Mycology, 2005, 43(): S313-S319. |
| 55 | LIU N, ABRAMYAN E D, CHENG W, et al. Targeted genome mining reveals the biosynthetic gene clusters of natural product CYP51 inhibitors[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(16): 6043-6047. |
| 56 | MATTHEUS W, MASSCHELEIN J, GAO L J, et al. The kalimantacin/batumin biosynthesis operon encodes a self-resistance isoform of the FabⅠ bacterial target[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2010, 17(10): 1067-1071. |
| 57 | HEATH R J, ROCK C O. A triclosan-resistant bacterial enzyme[J]. Nature, 2000, 406(6792): 145-146. |
| 58 | TOYOHARA M. Aspects of the antituberculous activity of 27753-RP, a new semisynthetic derivative of griselimycine[J]. Annales de L’Institut Pasteur Microbiology, 1987, 138(6): 737-744. |
| 59 | HOAGLAND D T, LIU J Y, LEE R B, et al. New agents for the treatment of drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis [J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2016, 102: 55-72. |
| 60 | KLING A, LUKAT P, ALMEIDA D V, et al. Antibiotics. Targeting DnaN for tuberculosis therapy using novel griselimycins[J]. Science, 2015, 348(6239): 1106-1112. |
| 61 | VINALE F, FLEMATTI G, SIVASITHAMPARAM K, et al. Harzianic acid, an antifungal and plant growth promoting metabolite from Trichoderma harzianum [J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2009, 72(11): 2032-2035. |
| 62 | LONHIENNE T, LOW Y S, GARCIA M D, et al. Structures of fungal and plant acetohydroxyacid synthases[J]. Nature, 2020, 586(7828): 317-321. |
| 63 | XIE L N, ZANG X, CHENG W, et al. Harzianic acid from Trichoderma afroharzianum is a natural product inhibitor of acetohydroxyacid synthase[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021: , 143(25): 9575-9584. |
| 64 | MCCOURT J A, DUGGLEBY R G. Acetohydroxyacid synthase and its role in the biosynthetic pathway for branched-chain amino acids[J]. Amino Acids, 2006, 31(2): 173-210. |
| 65 | JASTRZĘBOWSKA K, GABRIEL I. Inhibitors of amino acids biosynthesis as antifungal agents[J]. Amino Acids, 2015, 47(2): 227-249. |
| 66 | ZHONG B F, WAN J, SHANG C H, et al. Biosynthesis of rumbrins and inspiration for discovery of HIV inhibitors[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2022, 12(11): 4193-4203. |
| 67 | LIU L X, MARGOTTIN F, LE GALL S, et al. Binding of HIV-1 Nef to a novel thioesterase enzyme correlates with Nef-mediated CD4 down-regulation[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1997, 272(21): 13779-13785. |
| 68 | PALMEIRA J D F, ARGAÑARAZ G A, DE OLIVEIRA G X L M, et al. Physiological relevance of ACOT8-Nef interaction in HIV infection[J]. Reviews in Medical Virology, 2019, 29(5): e2057. |
| 69 | STAUDT R P, ALVARADO J J, EMERT-SEDLAK L A, et al. Structure, function, and inhibitor targeting of HIV-1 Nef-effector kinase complexes[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2020, 295(44): 15158-15171. |
| 70 | HOBSON C, CHAN A N, WRIGHT G D. The antibiotic resistome: a guide for the discovery of natural products as antimicrobial agents[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(6): 3464-3494. |
| 71 | GAUDÊNCIO S P, PEREIRA F. Dereplication: racing to speed up the natural products discovery process[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2015, 32(6): 779-810. |
| 72 | COX G, SIERON A, KING A M, et al. A common platform for antibiotic dereplication and adjuvant discovery[J]. Cell Chemical Biology, 2017, 24(1): 98-109. |
| 73 | ZUBYK H L, COX G, WRIGHT G D. Antibiotic dereplication using the antibiotic resistance platform[J]. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 2019(152): e60536. |
| 74 | TANG M C, ZOU Y, YEE D, et al. Identification of the pyranonigrin A biosynthetic gene cluster by genome mining in Penicillium thymicola IBT 5891[J]. AIChE Journal, 2018, 64(12): 4182-4186. |
| 75 | TANG X Y, LI J, MILLÁN-AGUIÑAGA N, et al. Identification of thiotetronic acid antibiotic biosynthetic pathways by target-directed genome mining[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2015, 10(12): 2841-2849. |
| 76 | WHITE S W, ZHENG J, ZHANG Y M, et al. The structural biology of type Ⅱ fatty acid biosynthesis[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2005, 74: 791-831. |
| 77 | YAO J W, ROCK C O. How bacterial pathogens eat host lipids: implications for the development of fatty acid synthesis therapeutics[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2015, 290(10): 5940-5946. |
| 78 | SASAKI H, OISHI H, HAYASHI T, et al. Thiolactomycin, a new antibiotic. Ⅱ. Structure elucidation[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 1982, 35(4): 396-400. |
| 79 | YEH H H, AHUJA M, CHIANG Y M, et al. Resistance gene-guided genome mining: serial promoter exchanges in Aspergillus nidulans reveal the biosynthetic pathway for fellutamide B, a proteasome inhibitor[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2016, 11(8): 2275-2284. |
| 80 | RODRIGUEZ-VILARIÑO S, ARRIBAS J, ARIZTI P, et al. Proteolytic processing and assembly of the C5 subunit into the proteasome complex[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2000, 275(9): 6592-6599. |
| 81 | HINES J, GROLL M, FAHNESTOCK M, et al. Proteasome inhibition by fellutamide B induces nerve growth factor synthesis[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2008, 15(5): 501-512. |
| 82 | BAUMANN S, HERRMANN J, RAJU R, et al. Cystobactamids: myxobacterial topoisomerase inhibitors exhibiting potent antibacterial activity[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(52): 14605-14609. |
| 83 | VETTING M W, HEGDE S S, ZHANG Y, et al. Pentapeptide-repeat proteins that act as topoisomerase poison resistance factors have a common dimer interface[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section F, Structural Biology and Crystallization Communications, 2011, 67(Pt 3): 296-302. |
| 84 | PANTER F, KRUG D, BAUMANN S, et al. Self-resistance guided genome mining uncovers new topoisomerase inhibitors from myxobacteria[J]. Chemical Science, 2018, 9(21): 4898-4908. |
| 85 | YAN Y, LIU Q K, ZANG X, et al. Resistance-gene-directed discovery of a natural-product herbicide with a new mode of action[J]. Nature, 2018, 559(7714): 415-418. |
| 86 | AMORIM FRANCO T M, BLANCHARD J S. Bacterial branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis: structures, mechanisms, and drugability[J]. Biochemistry, 2017, 56(44): 5849-5865. |
| 87 | HALL C J, MACKIE E R R, GENDALL A R, et al. Review: amino acid biosynthesis as a target for herbicide development[J]. Pest Management Science, 2020, 76(12): 3896-3904. |
| 88 | FLINT D H, NUDELMAN A. Studies on the active site of dihydroxy-acid dehydratase[J]. Bioorganic Chemistry, 1993, 21(4): 367-385. |
| 89 | TSUDA Y, KANEDA M, TADA A, et al. Aspterric acid, a new sesquiterpenoid of the carotane group, a metabolite from Aspergillus terreus IFO-6123. X-Ray crystal and molecular structure of its p-bromobenzoate[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications, 1978(4): 160. |
| 90 | ALANJARY M, KRONMILLER B, ADAMEK M, et al. The Antibiotic Resistant Target Seeker (ARTS), an exploration engine for antibiotic cluster prioritization and novel drug target discovery[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(W1): W42-W48. |
| 91 | BLIN K, WOLF T, CHEVRETTE M G, et al. antiSMASH 4.0-improvements in chemistry prediction and gene cluster boundary identification[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(W1): W36-W41. |
| 92 | WEBER T, BLIN K, DUDDELA S, et al. antiSMASH 3.0-a comprehensive resource for the genome mining of biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 43(W1): W237-W243. |
| 93 | MUNGAN M D, ALANJARY M, BLIN K, et al. ARTS 2.0: feature updates and expansion of the Antibiotic Resistant Target Seeker for comparative genome mining[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(W1): W546-W552. |
| 94 | DE LOS SANTOS E L C, CHALLIS G L. clusterTools: proximity searches for functional elements to identify putative biosynthetic gene clusters[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2017, 119214. (2017-12-12)[2023-12-01]. . |
| 95 | EDDY S R. What is a hidden Markov model?[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2004, 22(10): 1315-1316. |
| 96 | BRAUN V, PRAMANIK A, GWINNER T, et al. Sideromycins: tools and antibiotics[J]. BioMetals 2009, 22(1): 3-13. |
| 97 | ZENG Y, KULKARNI A, YANG Z Y, et al. Biosynthesis of albomycin δ2 provides a template for assembling siderophore and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitor conjugates[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2012, 7(9): 1565-1575. |
| 98 | GARG R P, QIAN X L, ALEMANY L B, et al. Investigations of valanimycin biosynthesis: elucidation of the role of seryl-tRNA[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(18): 6543-6547. |
| 99 | STEFANSKA A L, CASSELS R, READY S J, et al. SB-203207 and SB-203208, two novel isoleucyl tRNA synthetase inhibitors from a Streptomyces sp. Ⅰ. Fermentation, isolation and properties[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 2000, 53(4): 357-363. |
| 100 | HU Z J, AWAKAWA T, MA Z J, et al. Aminoacyl sulfonamide assembly in SB-203208 biosynthesis[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 184. |
| 101 | THAKER M N, WANG W L, SPANOGIANNOPOULOS P, et al. Identifying producers of antibacterial compounds by screening for antibiotic resistance[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(10): 922-927. |
| 102 | CULP E J, WAGLECHNER N, WANG W L, et al. Evolution-guided discovery of antibiotics that inhibit peptidoglycan remodelling[J]. Nature, 2020, 578(7796): 582-587. |
| [1] | ZHONG Quanzhou, SHAN Yiyi, PEI Qingyun, JIN Yanyun, WANG Yihan, MENG Luyuan, WANG Xinyun, ZHANG Yuxin, LIU Kunyuan, WANG Huizhong, FENG Shangguo. Research progress in the production of α-arbutin through biosynthesis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 118-135. |
| [2] | ZHU Fanghuan, CEN Xuecong, CHEN Zhen. Research progress of diols production by microbes [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [3] | LIU Yining, PU Wei, YANG Jinxing, WANG Yu. Recent advances in the biosynthesis of ω-amino acids and lactams [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1350-1366. |
| [4] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [5] | CHENG Xiaolei, LIU Tiangang, TAO Hui. Recent research progress in non-canonical biosynthesis of terpenoids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1050-1071. |
| [6] | LIU Zijian, MU Baiyang, DUAN Zhiqiang, WANG Xuan, LU Xiaojie. Advances in the development of DNA-compatible chemistries [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1102-1124. |
| [7] | ZHANG Shouqi, WANG Tao, KONG Yao, ZOU Jiasheng, LIU Yuanning, XU Zhengren. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of natural products: evolution of synthetic methodology and strategy [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 913-940. |
| [8] | XIE Xiangqian, GUO Wen, WANG Huan, LI Jin. Biosynthesis and chemical synthesis of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides containing aminovinyl cysteine [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 981-996. |
| [9] | TANG Zhijun, HU Youcai, LIU Wen. Enzymatic (4+2)- and (2+2)-cycloaddition reactions: fundamentals and applications of regio- and stereoselectivity [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 401-407. |
| [10] | Jun ZHANG, Shixue JIN, Qian YUN, Xudong QU. Biosynthesis of the unnatural extender units with polyketides and their structural modifications for applications in medicines [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 561-570. |
| [11] | Xiwei CHEN, Huaran ZHANG, Yi ZOU. Biosynthesis and metabolic engineering of fungal non-ribosomal peptides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 571-592. |
| [12] | Xuchang YU, Hui WU, Lei LI. Library construction and targeted BGC screening for more efficient discovery of microbial natural products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 492-506. |
| [13] | FENG Jin, PAN Haixue, TANG Gongli. Research advances in biosynthesis of natural product drugs within the past decade [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 408-446. |
| [14] | XI Mengyu, HU Yiling, GU Yucheng, GE Huiming. Genome mining-directed discovery for natural medicinal products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 447-473. |
| [15] | Ru LEI, Hui TAO, Tiangang LIU. Deep genome mining boosts the discovery of microbial terpenoids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 507-526. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||