合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (2): 369-384.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-060
合成生物学与荧光成像技术
武伟红1, 李炜2, 张先恩3, 崔宗强2
- 1.中国科学技术大学生命科学与医学部,安徽 合肥 230026
2.中国科学院武汉病毒研究所,病毒学国家重点实验室,湖北 武汉 430071
3.中国科学院生物物理研究所,生物大分子国家重点实验室,北京 100101
-
收稿日期:2021-05-13修回日期:2021-09-06出版日期:2022-04-30发布日期:2022-05-11 -
通讯作者:崔宗强 -
作者简介:武伟红 (1998—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为病毒与合成生物学。 E-mail:wuweihong@mail.ustc.edu.cn崔宗强 (1977—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为病毒学研究新技术如单病毒示踪、纳米疫苗等。创建了多种荧光纳米标记及单病毒示踪新技术,实时示踪了单个艾滋病毒、单个流感病毒脱壳过程,并实现了单拷贝艾滋病毒基因原位成像、多蛋白复合体超高分辨成像等。 E-mail:czq@wh.iov.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(31925025)
Synthetic biology for fluorescent bioimaging
WU Weihong1, LI Wei2, ZHANG Xian’en3, CUI Zongqiang2
- 1.Division of Life Sciences and Medicine,University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230026,Anhui,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Virology,Wuhan Institute of Virology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Wuhan 430071,Hubei,China
3.National Key Laboratory of Biomacromolecules,Institute of Biophysics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100101,China
-
Received:2021-05-13Revised:2021-09-06Online:2022-04-30Published:2022-05-11 -
Contact:CUI Zongqiang
摘要:
合成生物学的迅速发展为分子荧光标记与生物成像技术提供了新的机遇。基于合成生物学原理,可以建立材料生物合成新方法,开发性能优异的荧光纳米材料和探针,发展新的荧光成像技术。合成生物学应用于生物荧光成像,多涉及荧光材料与探针的设计合成、对生物靶标分子进行定点改造和修饰、荧光探针和靶标分子的可控时空耦合等以实现生物分子的精准特异性标记。这些荧光纳米材料和生物分子标记技术可应用于细胞内分子的荧光标记、成像和动态示踪,可视化解析相关的关键分子事件,从而深入揭示细胞内分子运动机制和病原致病机理等。本文主要综述了近年来合成生物学技术在生物荧光成像方面的应用,包括利用合成生物学技术合成量子点等荧光纳米材料与探针、对蛋白质和核酸分子的精准标记及其用于病毒荧光成像和示踪。最后,也对该领域面临的问题如荧光杂合生物材料可控合成、分子原位多重标记等进行了探讨和展望。合成生物学与荧光成像技术的交叉融合,将推动荧光成像技术发展和进步,并拓展合成生物学的研究领域。
中图分类号:
引用本文
武伟红, 李炜, 张先恩, 崔宗强. 合成生物学与荧光成像技术[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(2): 369-384.
WU Weihong, LI Wei, ZHANG Xian’en, CUI Zongqiang. Synthetic biology for fluorescent bioimaging[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(2): 369-384.
| 荧光材料 | 大小 | 荧光强度 | 荧光量子效率 | 荧光寿命 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 量子点 | 2~20 nm | +++++ | 0.1~0.85 | 20 min |
| 荧光蛋白 | 4 nm | + | 0.79 | 100 ms |
| 荧光RNA | 40 bp | +++ | 0.30~0.70 | > 15 min |
表1 不同荧光材料性能参数[74-76]
Tab. 1 Properties of different fluorescent materials [74-76]
| 荧光材料 | 大小 | 荧光强度 | 荧光量子效率 | 荧光寿命 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 量子点 | 2~20 nm | +++++ | 0.1~0.85 | 20 min |
| 荧光蛋白 | 4 nm | + | 0.79 | 100 ms |
| 荧光RNA | 40 bp | +++ | 0.30~0.70 | > 15 min |
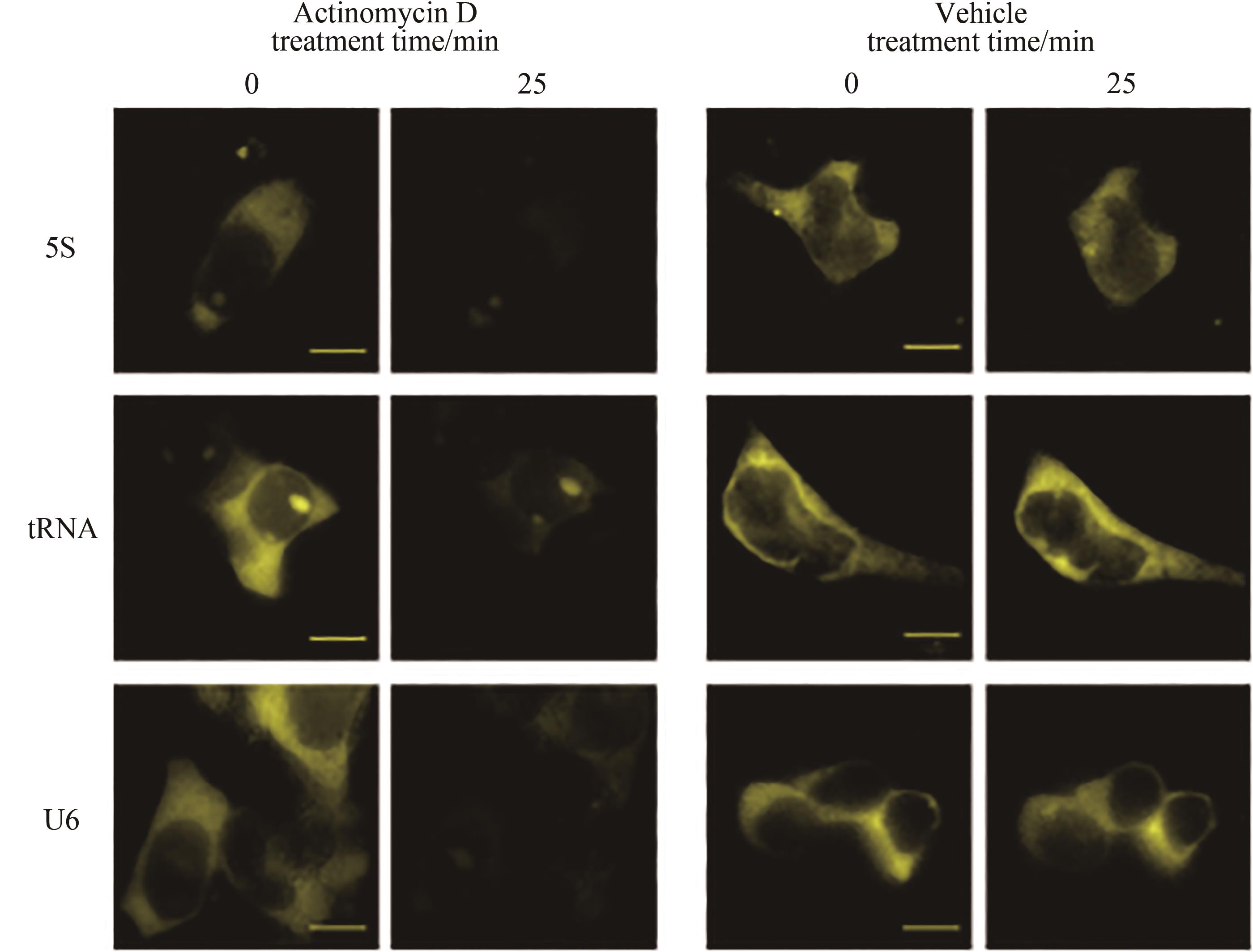
图5 核酸适配子Corn荧光基团成像单细胞中聚合酶活性示意图[87](转入报告质粒的HEK293T细胞加入荧光团DFHO可产生黄色荧光,加入RNA聚合酶抑制剂放线菌素D后荧光消失)
Fig. 5 Schematic diagram for imaging polymerase activity in single cells through aptamer corn fluorophore[87](HEK293T cells transformed with the reporter plasmid could produce yellow fluorescence by adding fluorophore DFHO, but the fluorescence disappears after adding the RNA polymerase inhibitor actinomycin D.)
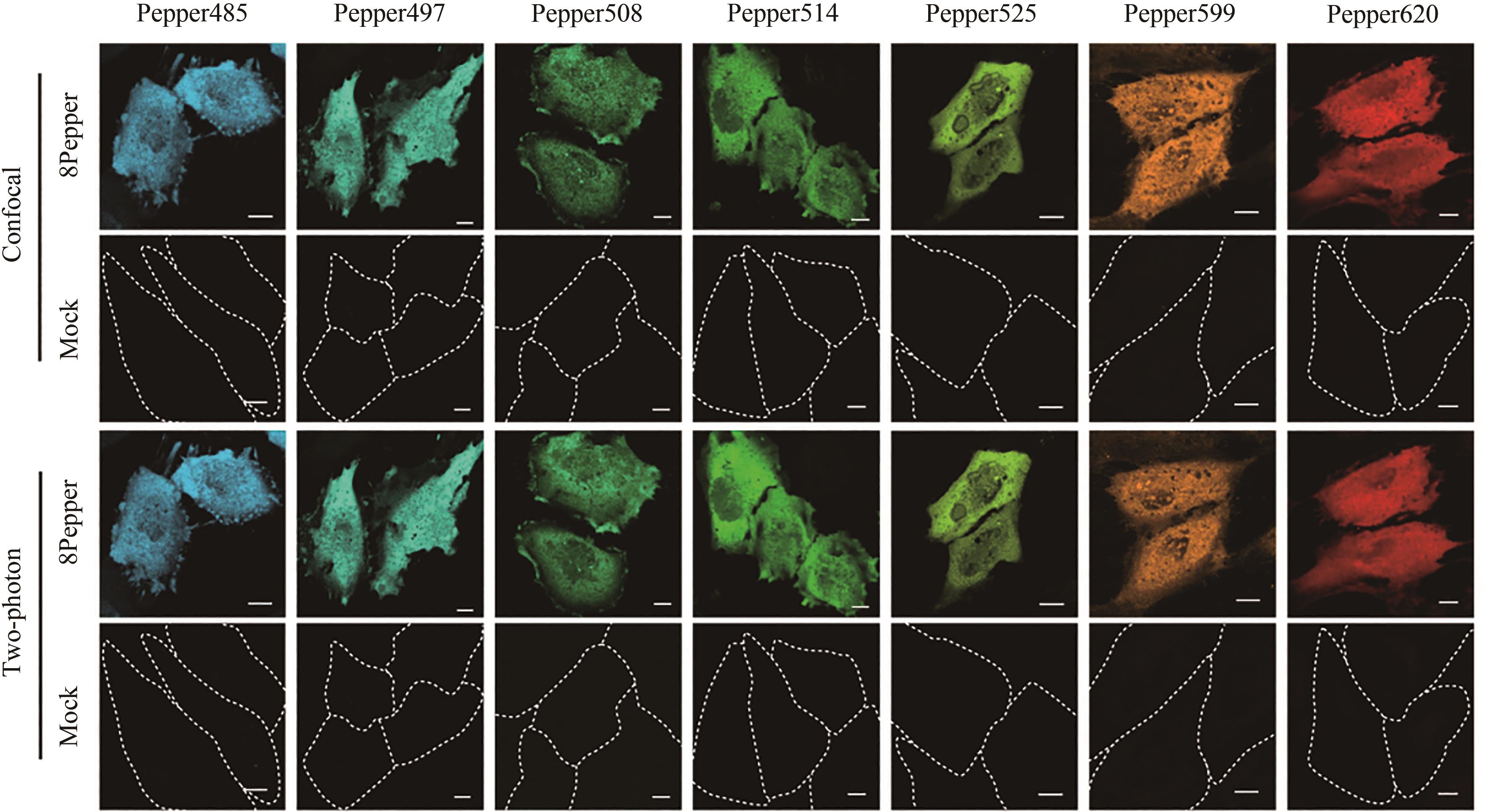
图7 荧光RNA复合体在HeLa细胞成像[76](合成染料HBC的一系列类似物与Pepper结合可发出不同颜色荧光,HBC类似物与Pepper结合物在HeLa细胞中进行成像,用空载细胞做对比,在共聚焦显微镜和双光子显微镜下进行成像观察)
Fig. 7 Schematic diagram for imaging of the fluorescent RNA complex in HeLa cells[76](A series of analogues of synthetic dye HBC combined with Pepper can emit fluorescence with different colors. HBC analogues were combined with Pepper in HeLa cells and are compared with mock cells. Imaging observation is carried out with confocal microscope and two-photon microscope.)
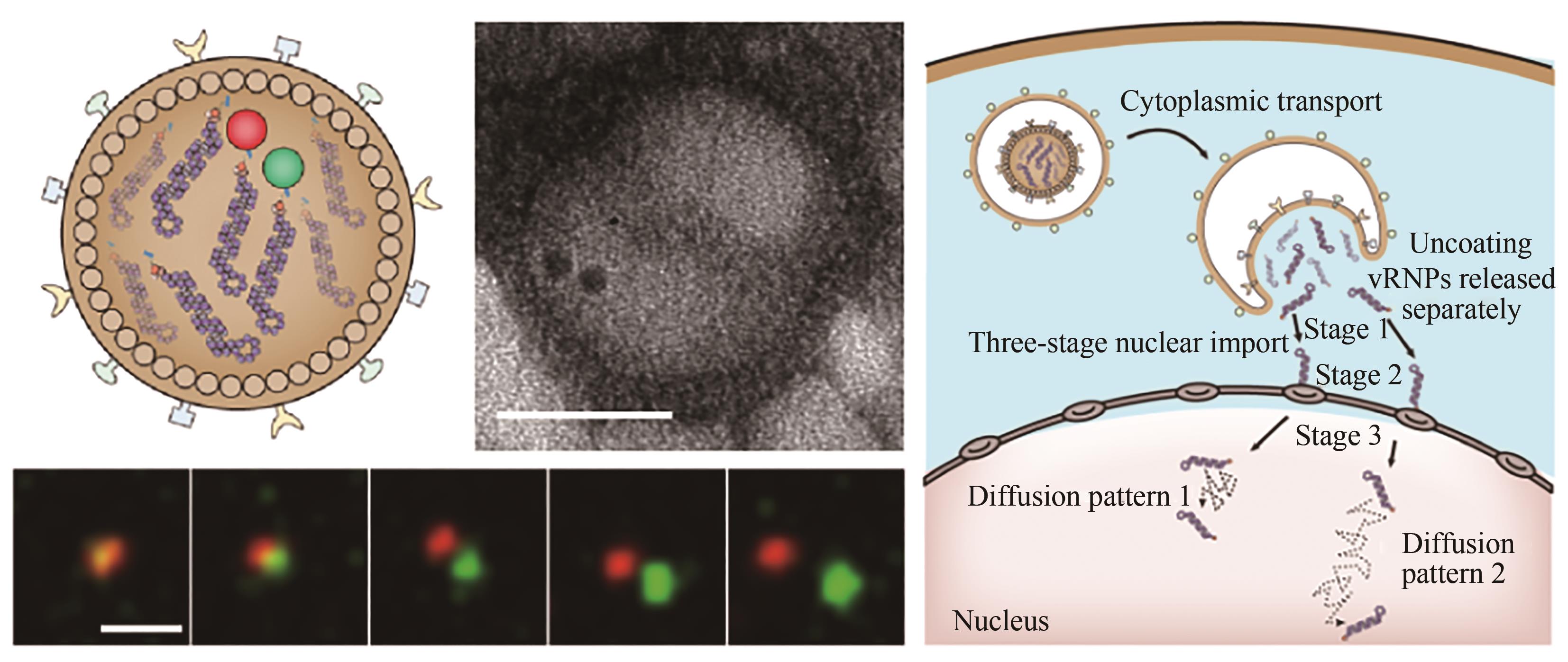
图9 流感病毒脱壳过程实时动态示踪[75][QD625在电镜下又黑又圆,而QD705为三角形。用QD625(红色)和QD705(绿色)分别标记vRNP,结果显示在脱壳过程中QD625和QD705分别释放。IAV释放的vRNPs经过三阶段的主动运输到达细胞核,在细胞核经历两种扩散模式]
Fig. 9 Real-time dynamic tracking of the influenza virus unpacking process[75][Under electron microscope, QD625 is black and round, while QD705 is triangular. vRNP is labeled with QD625 (red) and QD705 (green) respectively, and the results showed that QD625 and QD705 are released during the hulling process, respectively. IAV-released vRNPs released from IAV reach the nucleus through a three-stage active transport, where they undergo two diffusion modes.]

图11 SV40-QD VLPs用于靶向小鼠动脉粥样硬化斑块成像[100](SV40 VLPs 含有动脉粥样硬化靶向单元,凝血酶抑制剂并可以封装QD800。FH-QDs可靶向集中在小鼠体内动脉粥样硬化形成区)
Fig. 11 SV40-QD VLPs for imaging atherosclerotic plaques in targeted mice[100](SV40 VLPs contain atherosclerotic targeting units, thrombin inhibitors, which can encapsulate as QD800. FH-QDS can target atherosclerotic areas in mice.)
| 1 | BENNER S A, SISMOUR A M. Synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2005, 6(7): 533-543. |
| 2 | PATOLSKY F, ZHENG G F, LIEBER C M.Nanowire sensors for medicine and the life sciences[J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2006, 1(1):51-65. |
| 3 | CELLO J, PAUL A V, WIMMER E. Chemical synthesis of poliovirus cDNA: generation of infectious virus in the absence of natural template[J]. Science, 2002, 297(5583): 1016-1018. |
| 4 | ANNALURU N, MULLER H, MITCHELL L A, et al. Total synthesis of a functional designer eukaryotic chromosome[J]. Science, 2014, 344(6179): 55-58. |
| 5 | MERCY G, MOZZICONACCI J, SCOLARI V F, et al. 3D organization of synthetic and scrambled chromosomes[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6329): eaaf4597. |
| 6 | GIBSON D G, GLASS J I, LARTIGUE C, et al. Creation of a bacterial cell controlled by a chemically synthesized genome[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5987): 52-56. |
| 7 | FREDENS J, WANG K, DE LA TORRE D, et al. Total synthesis of Escherichia coli with a recoded genome[J]. Nature, 2019, 569(7757): 514-518. |
| 8 | SAKO Y, MINOGHCHI S, YANAGIDA T. Single-molecule imaging of EGFR signalling on the surface of living cells[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2000, 2(3): 168-172. |
| 9 | IINO R, KOYAMA I, KUSUMI A. Single molecule imaging of green fluorescent proteins in living cells: E-cadherin forms oligomers on the free cell surface[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2001, 80(6): 2667-2677. |
| 10 | HAJIPOUR F, ASAD S, AMOOZEGAR M A, et al. Developing a fluorescent hybrid nanobiosensor based on quantum dots and azoreductase enzyme for methyl red monitoring[J]. Iranian Biomedical Journal, 2021, 25(1): 8-20. |
| 11 | DERFUS A M, CHAN W C W, BHATIA S N. Probing the cytotoxicity of semiconductor quantum dots[J]. Nano Letters, 2004, 4(1): 11-18. |
| 12 | GREEN M, O'BRIEN P. Recent advances in the preparation of semiconductors as isolated nanometric particles: new routes to quantum dots[J]. Chemical Communications, 1999(22): 2235-2241. |
| 13 | MICHALET X, PINAUD F F, BENTOLILA L A, et al. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics[J]. Science, 2005, 307(5709): 538-544. |
| 14 | SCHMIDT T, SCHÜTZ G J, BAUMGARTNER W, et al. Imaging of single molecule diffusion[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1996, 93(7): 2926-2929. |
| 15 | DAHAN M, LÉVI S, LUCCARDINI C, et al. Diffusion dynamics of glycine receptors revealed by single-quantum dot tracking[J]. Science, 2003, 302(5644): 442-445. |
| 16 | ALIVISATOS A P, GU W W, LARABELL C. Quantum dots as cellular probes[J]. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 2005, 7: 55-76. |
| 17 | LIU W H, HOWARTH M, GREYTAK A B, et al. Compact biocompatible quantum dots functionalized for cellular imaging[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(4): 1274-1284. |
| 18 | CHEN G, ZHU J Y, ZHANG Z L, et al. Transformation of cell-derived microparticles into quantum-dot-labeled nanovectors for antitumor siRNA delivery[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(3): 1036-1040. |
| 19 | GIEPMANS B N G, ADAMS S R, ELLISMAN M H, et al. The fluorescent toolbox for assessing protein location and function[J]. Science, 2006, 312(5771): 217-224. |
| 20 | NAM K T, KIM D W, YOO P J, et al. Virus-enabled synthesis and assembly of nanowires for lithium ion battery electrodes[J]. Science, 2006, 312(5775): 885-888. |
| 21 | MANZO C, GARCIA-PARAJO M F. A review of progress in single particle tracking: from methods to biophysical insights[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2015, 78(12): 124601. |
| 22 | GAO X, CUI Y, LEVENSON R M, et al. In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2004, 22(8): 969-976. |
| 23 | RHYNER M N, SMITH A M, GAO X,et al. Quantum dots and multifunctional nanoparticles: new contrast agents for tumor imaging[J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2006, 1(2): 209-217. |
| 24 | ZHANG W J, CHEN G J, WANG J, et al. Design and synthesis of highly luminescent near-infrared-emitting water-soluble CdTe/CdSe/ZnS core/shell/shell quantum dots[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2009, 48(20): 9723-9731. |
| 25 | THOMPSON M A, CASOLARI J M, BADIEIROSTAMI M, et al. Three-dimensional tracking of single mRNA particles in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a double-helix point spread function[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(42): 17864-17871. |
| 26 | PINAUD F, MICHALET X, BENTOLILA L A, et al. Advances in fluorescence imaging with quantum dot bio-probes[J]. Biomaterials, 2006, 27(9): 1679-1687. |
| 27 | PARAK W J, PELLEGRINO T, PLANK C. Labelling of cells with quantum dots[J]. Nanotechnology, 2005, 16(2): R9-R25. |
| 28 | JIN D Y, XI P, WANG B M, et al. Nanoparticles for super-resolution microscopy and single-molecule tracking[J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(6): 415-423. |
| 29 | LIU M M, LI Q, LIANG L, et al. Real-time visualization of clustering and intracellular transport of gold nanoparticles by correlative imaging[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15646. |
| 30 | SMITH A M, DAVE S, NIE S M, et al. Multicolor quantum dots for molecular diagnostics of cancer[J]. Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics, 2006, 6(2): 231-244. |
| 31 | SMITH A M, GAO X H, NIE S M. Quantum dot nanocrystals for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging[J]. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 2004, 80(3): 377-385. |
| 32 | LEE S K, YUN D S, BELCHER A M. Cobalt ion mediated self-assembly of genetically engineered bacteriophage for biomimetic Co-Pt hybrid material[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2006, 7(1): 14-17. |
| 33 | SU Y Y, HU M, FAN C H, et al. The cytotoxicity of CdTe quantum dots and the relative contributions from released cadmium ions and nanoparticle properties[J]. Biomaterials, 2010, 31(18): 4829-4834. |
| 34 | CUI R J, PAN H C, ZHU J J, et al. Versatile immunosensor using CdTe quantum dots as electrochemical and fluorescent labels[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2007, 79(22): 8494-8501. |
| 35 | PROBST C E, ZRAZHEVSKIY P, BAGALKOT V, et al. Quantum dots as a platform for nanoparticle drug delivery vehicle design[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2013, 65(5): 703-718. |
| 36 | FRANKEL R B, BLAKEMORE R P, WOLFE R S. Magnetite in freshwater magnetotactic bacteria[J]. Science, 1979, 203(4387): 1355-1356. |
| 37 | FRANKEL R B, BAZYLINSKI D A. Magnetotaxis and magnetic particles in bacteria[J]. Hyperfine Interactions, 1994, 90(1): 135-142. |
| 38 | FRANKEL R B, PAPAEFTHYMIOU G C, BLAKEMORE R P, et al. Fe3O4 precipitation in magnetotactic bacteria[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1983, 763(2): 147-159. |
| 39 | DAHAN M, LÉVI S, LUCCARDINI C, et al. Diffusion dynamics of glycine receptors revealed by single-quantum dot tracking[J]. Science, 2003, 302(5644): 442-445. |
| 40 | BRUCHEZ M JR, MORONNE M, GIN P, et al. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels[J]. Science, 1998, 281(5385): 2013-2016. |
| 41 | RHYNER M N, SMITH A M, GAO X, et al. Quantum dots and targeted nanoparticle probes for in vivo tumor imaging[M]// Nanoparticles in biomedical imaging, Springer, 2008: 413-425. |
| 42 | DERFUS A M, CHAN W C W, BHATIA S N. Probing the cytotoxicity of semiconductor quantum dots[J]. Nano Letters, 2004, 4(1): 11-18. |
| 43 | PRADHAN N, REIFSNYDER D, XIE R G, et al. Surface ligand dynamics in growth of nanocrystals[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(30): 9500-9509. |
| 44 | ALDANA J, WANG Y A, PENG X G. Photochemical instability of CdSe nanocrystals coated by hydrophilic thiols[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2001, 123(36): 8844-8850. |
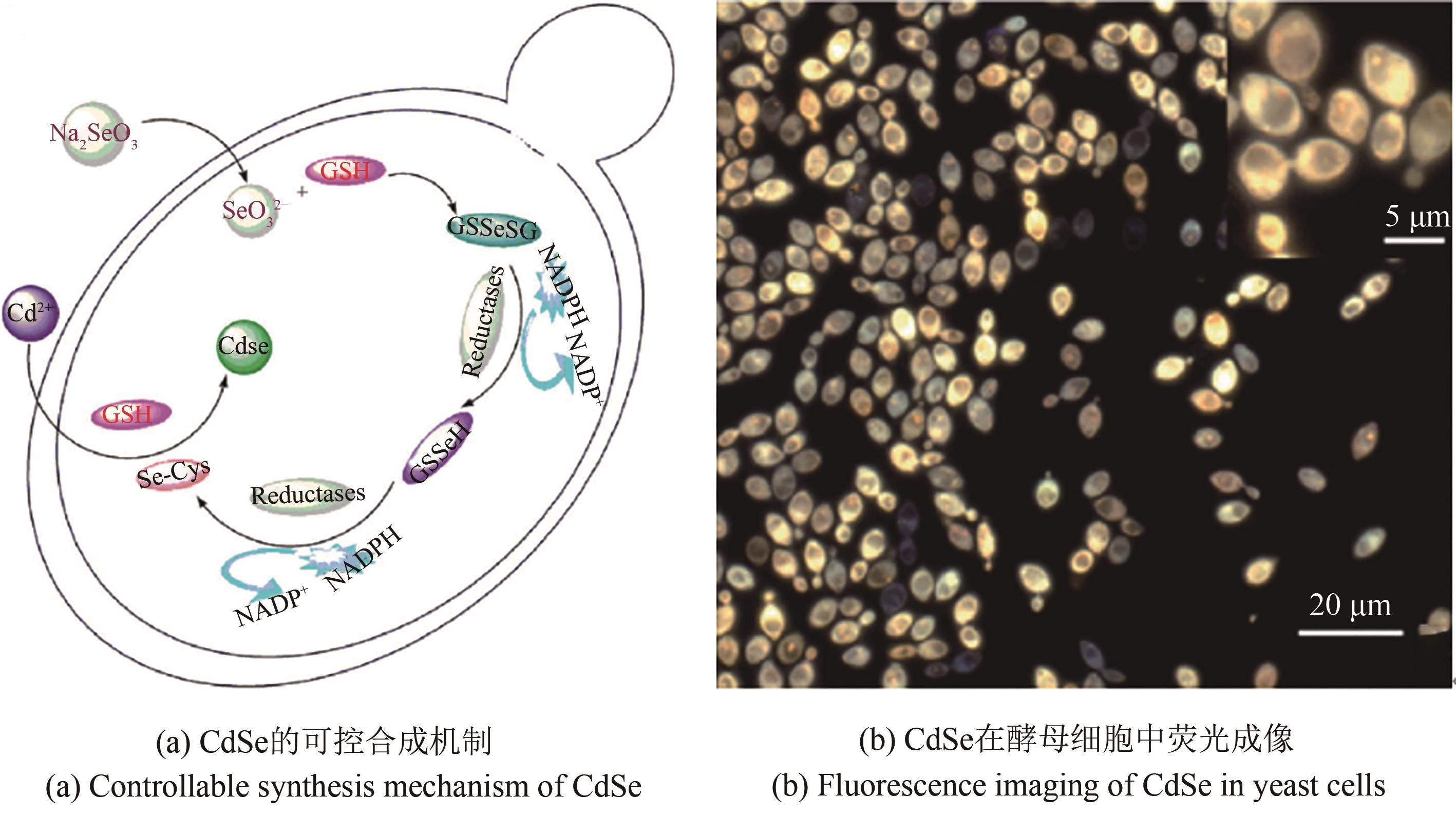
| 45 | CUI R, LIU H H, XIE H Y, et al. Living yeast cells as a controllable biosynthesizer for fluorescent quantum dots[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2009, 19(15): 2359-2364. |
| 46 | GU Y P, CUI R, ZHANG Z L, et al. Ultrasmall near-infrared Ag2Se quantum dots with tunable fluorescence for in vivo imaging[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(1): 79-82. |
| 47 | ISENBERG S L, CARTER M D, CROW B S, et al. Quantification of hydrazine in human urine by HPLC-MS-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Toxicology, 2016, 40(4): 248-254. |
| 48 | MCDONALD W H, OHI R, MIYAMOTO D T, et al. Comparison of three directly coupled HPLC MS/MS strategies for identification of proteins from complex mixtures: single-dimension LC-MS/MS, 2-phase MudPIT, and 3-phase MudPIT[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2002, 219(1): 245-251. |
| 49 | VOGESER M, SEGER C. A decade of HPLC-MS/MS in the routine clinical laboratory-goals for further developments[J]. Clinical Biochemistry, 2008, 41(9): 649-662. |
| 50 | STÜRZENBAUM S R, HÖCKNER M, PANNEERSELVAM A, et al. Biosynthesis of luminescent quantum dots in an earthworm[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2013, 8(1): 57-60. |
| 51 | SWEENEY R Y, MAO C B, GAO X X, et al. Bacterial biosynthesis of cadmium sulfide nanocrystals[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2004, 11(11): 1553-1559. |
| 52 | BAO H F, LU Z S, CUI X Q, et al. Extracellular microbial synthesis of biocompatible CdTe quantum dots[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2010, 6(9): 3534-3541. |
| 53 | HARRELL S M, MCBRIDE J R, ROSENTHAL S J. Synthesis of ultrasmall and magic-sized CdSe nanocrystals[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2013, 25(8): 1199-1210. |
| 54 | CHEN X B, SAMIA A C S, LOU Y B, et al. Investigation of the crystallization process in 2 nm CdSe quantum dots[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127(12): 4372-4375. |
| 55 | TALAPIN D V, MEKIS I, GÖTZINGER S, et al. CdSe/CdS/ZnS and CdSe/ZnSe/ZnS core-shell-shell nanocrystals[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2004, 108(49): 18826-18831. |
| 56 | DUKES A D III, MCBRIDE J R, ROSENTHAL S J. Synthesis of magic-sized CdSe and CdTe nanocrystals with diisooctylphosphinic acid[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22(23): 6402-6408. |
| 57 | TSCHIRNER N, LANGE H, SCHLIWA A, et al. Interfacial alloying in CdSe/CdS heteronanocrystals: a Raman spectroscopy analysis[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2012, 24(2): 311-318. |
| 58 | ZHAO J Y, CHEN G, GU Y P, et al. Ultrasmall magnetically engineered Ag2Se quantum dots for instant efficient labeling and whole-body high-resolution multimodal real-time tracking of cell-derived microvesicles[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(6): 1893-1903. |
| 59 | LIU H L, HONG G S, LUO Z T, et al. Atomic-precision gold clusters for NIR-II imaging[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(46): 1901015. |
| 60 | HONG G, ANTARIS A L, DAI H. Near-infrared fluorophores for biomedical imaging[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 1: 10. |
| 61 | WELSHER K, LIU Z, SHERLOCK S P, et al. A route to brightly fluorescent carbon nanotubes for near-infrared imaging in mice[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2009, 4(11): 773-780. |
| 62 | ZHANG Y, HONG G S, ZHANG Y J, et al. Ag2S quantum dot: A bright and biocompatible fluorescent nanoprobe in the second near-infrared window[J]. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(5): 3695-3702. |
| 63 | HONG G S, ROBINSON J T, ZHANG Y J, et al. In vivo fluorescence imaging with Ag2S quantum dots in the second near-infrared region[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 124(39): 9956-9959. |
| 64 | LI C Y, WANG Q B. Challenges and opportunities for intravital near-infrared fluorescence imaging technology in the second transparency window[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(10): 9654-9659. |
| 65 | YANG H C, LI R F, ZHANG Y J, et al. Colloidal alloyed quantum dots with enhanced photoluminescence quantum yield in the NIR-II window[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(6): 2601-2607. |
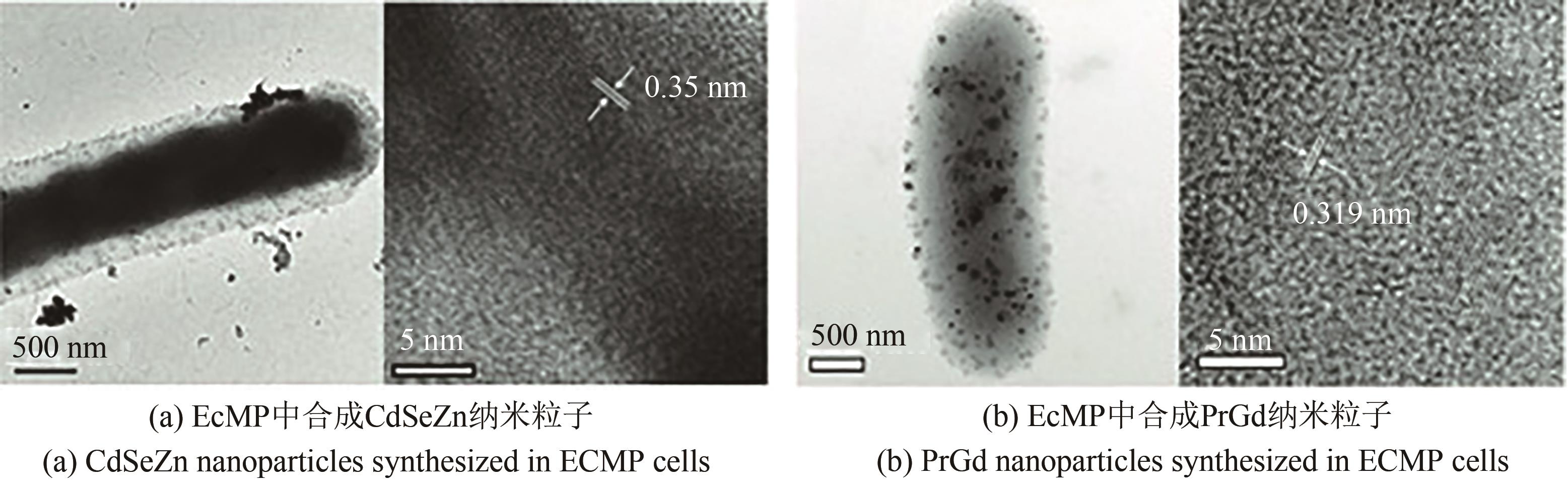
| 66 | PARK T J, LEE S Y, HEO N S, et al. In vivo synthesis of diverse metal nanoparticles by recombinant Escherichia coli [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(39): 7019-7024. |
| 67 | LIU J, CUI Z Q. Fluorescent labeling of proteins of interest in live cells: Beyond fluorescent proteins[J]. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2020, 31(6): 1587-1595. |
| 68 | KEPPLER A, GENDREIZIG S, GRONEMEYER T, et al. A general method for the covalent labeling of fusion proteins with small molecules in vivo [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2003, 21(1): 86-89. |
| 69 | ADAMS S R, CAMPBELL R E, GROSS L A, et al. New biarsenical ligands and tetracysteine motifs for protein labeling in vitro and in vivo: synthesis and biological applications[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(21): 6063-6076. |
| 70 | TANENBAUM M E, GILBERT L A, QI L S, et al. A protein-tagging system for signal amplification in gene expression and fluorescence imaging[J]. Cell, 2014, 159(3): 635-646. |
| 71 | SUMMERER D, CHEN S, WU N, et al. A genetically encoded fluorescent amino acid[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(26): 9785-9789. |
| 72 | LI Q, LI W, YIN W, et al. Single-particle tracking of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 productive entry into human primary macrophages[J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(4): 3890-3903. |
| 73 | LI Q, YIN W, LI W, et al. Encapsulating quantum dots within HIV-1 virions through site-specific decoration of the matrix protein enables single virus tracking in live primary macrophages[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 18(12): 7457-7468. |
| 74 | ALCOR D, GOUZER G, TRILLER A. Single-particle tracking methods for the study of membrane receptors dynamics[J]. European Journal of Neuroscience, 2009, 30(6): 987-997. |
| 75 | KANDI D, MANSINGH S, BEHERA A, et al. Calculation of relative fluorescence quantum yield and Urbach energy of colloidal CdS QDs in various easily accessible solvents[J]. Journal of Luminescence, 2021, 231: 117792. |
| 76 | CHEN X J, ZHANG D S, SU N, et al. Visualizing RNA dynamics in live cells with bright and stable fluorescent RNAs[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(11): 1287-1293. |
| 77 | QIN C, LI W, LI Q, et al. Real-time dissection of dynamic uncoating of individual influenza viruses[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(7): 2577-2582. |
| 78 | GHOSH I, HAMILTON A D, REGAN L. Antiparallel leucine zipper-directed protein reassembly: application to the green fluorescent protein[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2000, 122(23): 5658-5659. |
| 79 | PFLEGER K D G, SEEBER R M, EIDNE K A. Bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) for the real-time detection of protein-protein interactions[J]. Nature Protocols, 2006, 1(1): 337-345. |
| 80 | ZHANG X E, CUI Z Q, WANG D B. Sensing of biomolecular interactions using fluorescence complementing systems in living cells[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2016, 76: 243-250. |
| 81 | OUTEIRO T F, PUTCHA P, TETZLAFF J E, et al. Formation of toxic oligomeric α-synuclein species in living cells[J]. PLoS One, 2008, 3(4): e1867. |
| 82 | CHEN M H, LI W, ZHANG Z P, et al. Novel near-infrared BiFC systems from a bacterial phytochrome for imaging protein interactions and drug evaluation under physiological conditions[J]. Biomaterials, 2015, 48: 97-107. |
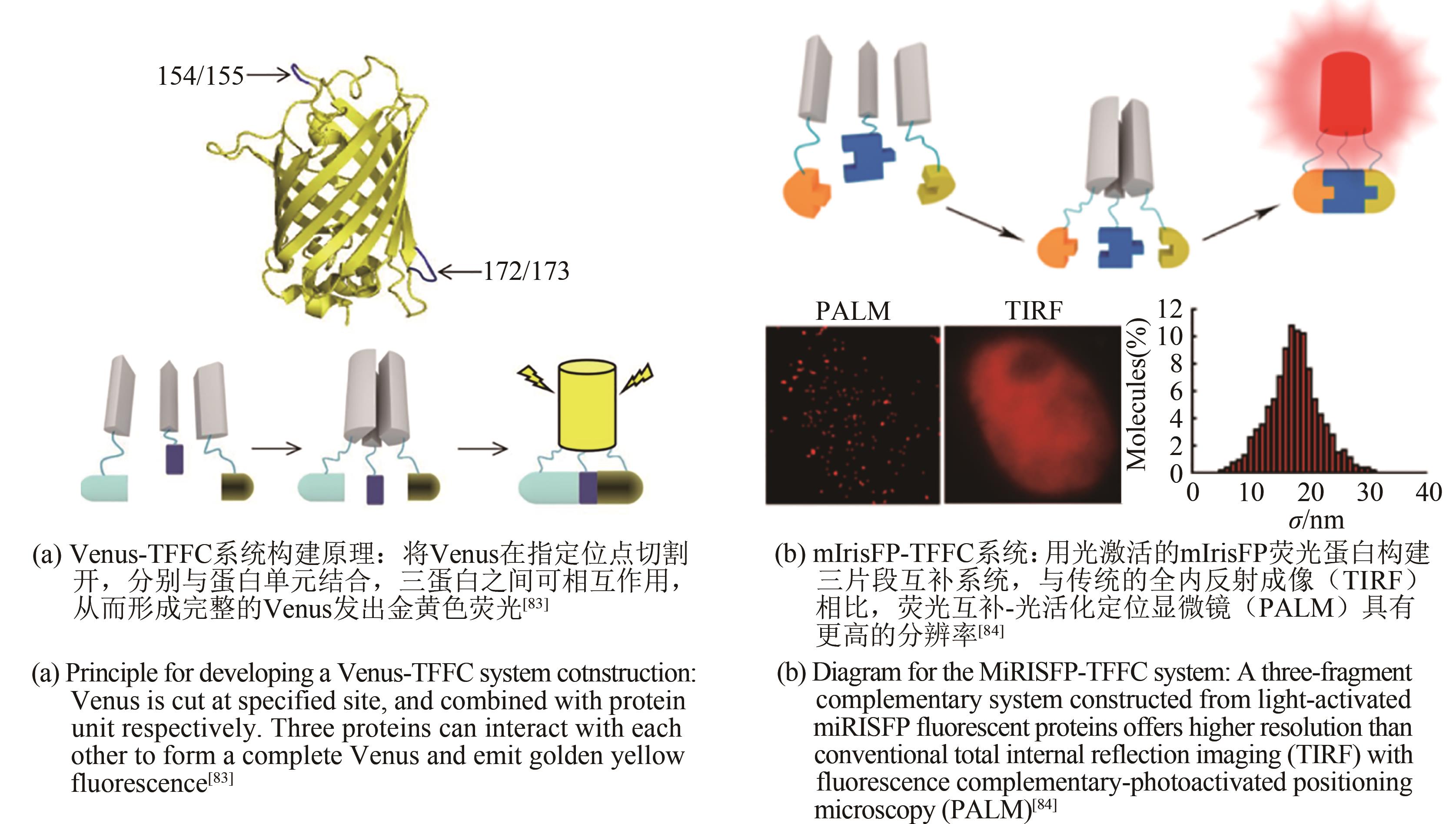
| 83 | CHEN M H, LI W, ZHANG Z P, et al. Three-fragment fluorescence complementation for imaging of ternary complexes under physiological conditions[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(22): 13299-13305. |
| 84 | CHEN M H, LIU S Y, LI W, et al. Three-fragment fluorescence complementation coupled with photoactivated localization microscopy for nanoscale imaging of ternary complexes[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(9): 8482-8490. |
| 85 | PAIGE J S, NGUYEN-DUC T, SONG W J, et al. Fluorescence imaging of cellular metabolites with RNA[J]. Science, 2012, 335(6073): 1194. |
| 86 | SONG W J, STRACK R L, JAFFREY S R. Imaging bacterial protein expression using genetically encoded RNA sensors[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(9): 873-875. |
| 87 | SONG W J, FILONOV G S, KIM H, et al. Imaging RNA polymerase III transcription using a photostable RNA-fluorophore complex[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2017, 13(11): 1187-1194. |
| 88 | FILONOV G S, MOON J D, SVENSEN N, et al. Broccoli: rapid selection of an RNA mimic of green fluorescent protein by fluorescence-based selection and directed evolution[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(46): 16299-16308. |
| 89 | BRASELMANN E, PALMER A E. A multicolor riboswitch-based platform for imaging of RNA in live mammalian cells[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2020, 641: 343-372. |
| 90 | World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): report of WHO Scientific Group[R]. Geneva: WHO, 2021 |
| 91 | LIU S L, WANG Z G, XIE H Y, et al. Single-virus tracking: from imaging methodologies to virological applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(3): 1936-1979. |
| 92 | MIYAUCHI K, KIM Y, LATINOVIC O, et al. HIV enters cells via endocytosis and dynamin-dependent fusion with endosomes[J]. Cell, 2009, 137(3): 433-444. |
| 93 | MA Y X, HE Z K, TAN T W, et al. Real-time imaging of single HIV-1 disassembly with multicolor viral particles[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(6): 6273-6282. |
| 94 | YIN W, LI W, LI Q, et al. Real-time imaging of individual virion-triggered cortical actin dynamics for human immunodeficiency virus entry into resting CD4 T cells[J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(1): 115-129. |
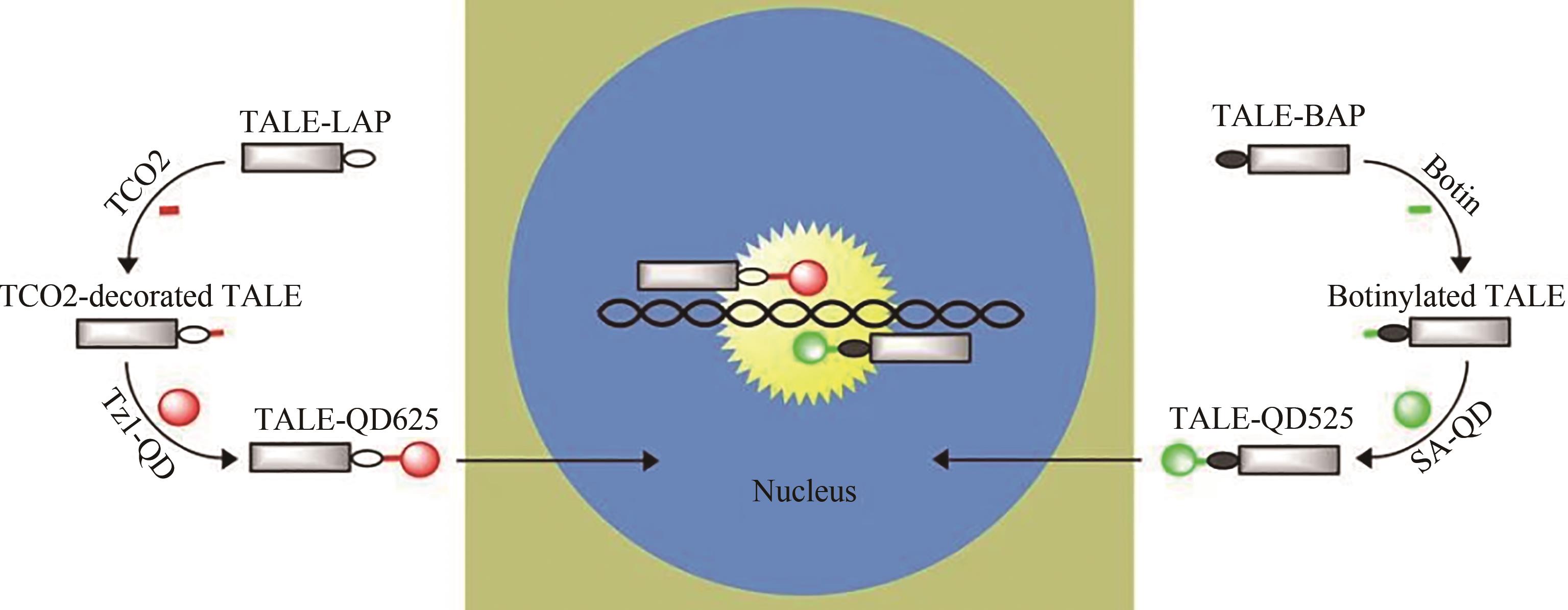
| 95 | MA Y X, WANG M X, LI W, et al. Live cell imaging of single genomic loci with quantum dot-labeled TALEs[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15318. |
| 96 | MA Y X, WANG M X, LI W, et al. Live visualization of HIV-1 proviral DNA using a dual-color-labeled CRISPR system[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(23): 12896-12901. |
| 97 | MA Y X, MAO G B, HUANG W R, et al. Quantum dot nanobeacons for single RNA labeling and imaging[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(34): 13454-13458. |
| 98 | WANG T, LI P H, ZHANG Y, et al. In vivo imaging of Zika virus reveals dynamics of viral invasion in immune-sheltered tissues and vertical propagation during pregnancy[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(14): 6430-6447. |
| 99 | LI C Y, LI F, ZHANG Y J, et al. Real-time monitoring surface chemistry-dependent in vivo behaviors of protein nanocages via encapsulating an NIR-II Ag2S quantum dot[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(12): 12255-12263. |
| 100 | SUN X X, LI W, ZHANG X W, et al. In vivo targeting and imaging of atherosclerosis using multifunctional virus-like particles of simian virus 40[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(10): 6164-6171. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [12] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [13] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [14] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [15] | 查文龙, 卜兰, 訾佳辰. 中药药效成分群的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||