合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (2): 385-398.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-059
“时-空耦合”活细胞合成量子点
贾剑红1, 杨玲玲2, 刘安安1, 庞代文1
- 1.南开大学药物化学生物学国家重点实验室,化学学院分析科学研究中心,天津市生物传感及分子识别重点实验室,天津 300071
2.武汉大学高等研究院,化学与分子科学学院,湖北 武汉 430072
-
收稿日期:2021-05-08修回日期:2021-05-29出版日期:2022-04-30发布日期:2022-05-11 -
通讯作者:庞代文 -
作者简介:贾剑红 (1994—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为纳米材料生物合成。E-mail:1076215263@qq.com杨玲玲 (1992—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为纳米生物医学分析。E-mail:doublelengyang@163.com庞代文 (1961—),男,教授,博士生导师。研究方向为生物医学分析化学、纳米生物技术、纳米光电显示技术等。E-mail:dwpang@whu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(91859123);国家重点研发计划(2019YFA0210103);中央高校基本科研业务费专项(63201024);天津市自然科学基金(19JCQNJC02400)
Space-time-coupled live-cell synthesis of quantum dots
JIA Jianhong1, YANG Lingling2, LIU An’an1, PANG Daiwen1
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical Biology,College of Chemistry,Research Center for Analytical Science,Tianjin Key Laboratory of Biosensing and Molecular Recognition,Nankai University,Tianjin 300071,China
2.The Institute for Advanced Studies,College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences,Wuhan University,Wuhan 430072,Hubei,China
-
Received:2021-05-08Revised:2021-05-29Online:2022-04-30Published:2022-05-11 -
Contact:PANG Daiwen
摘要:
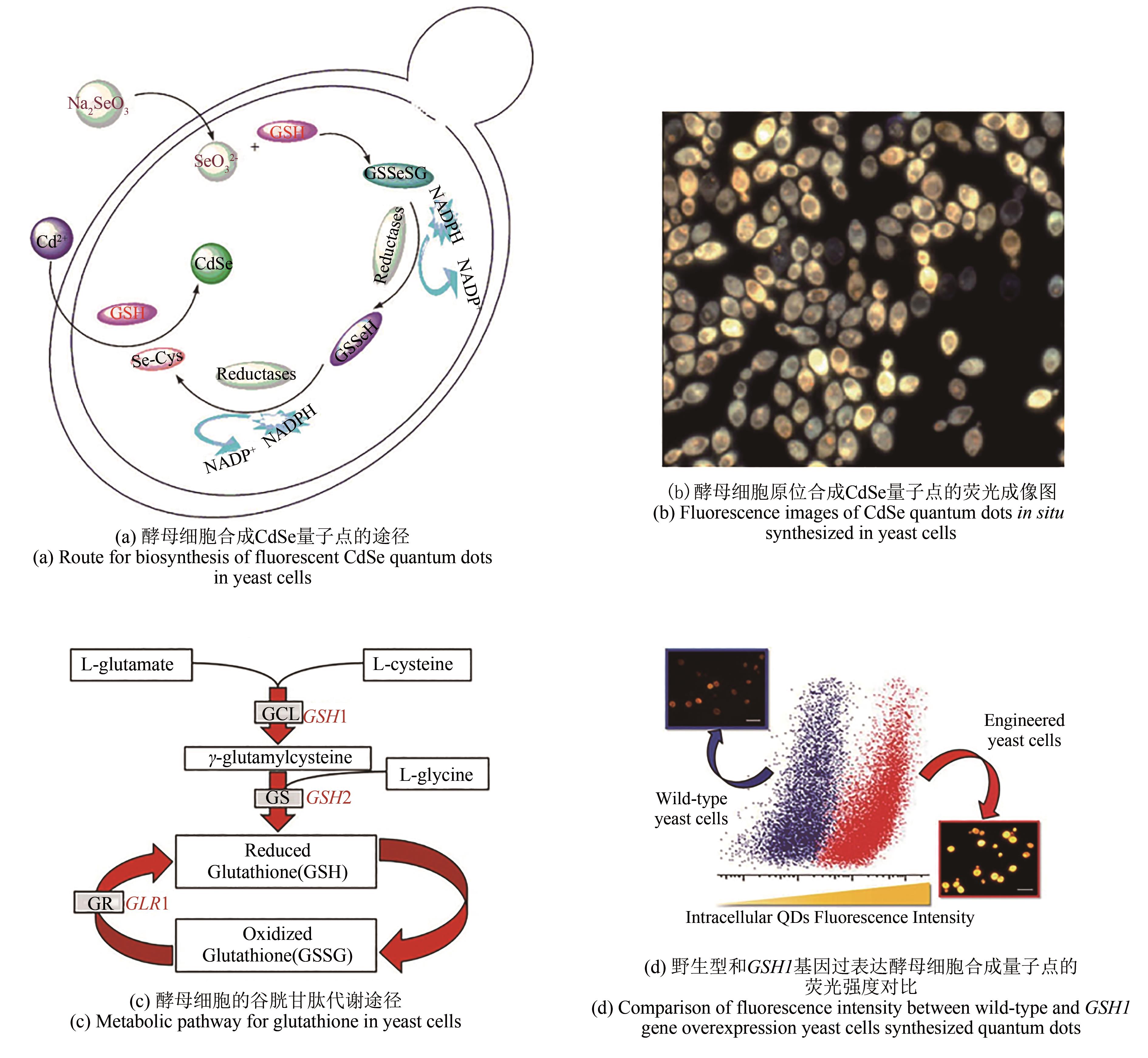
细胞是生命活动的基本单位。随着材料学、化学和生物学等多学科交叉日益加深,借助活细胞内代谢途径合成无机纳米材料的研究受到广泛关注,同时也拓展了合成生物学的研究领域。然而,活细胞合成无机纳米材料主要以胞内生物大分子为模板,且依赖单一生化反应途径,产物的尺寸、形貌和性质均难以人为调控。自2009年,本课题组通过人为设计、巧妙耦合活细胞内的硒代谢途径和重金属离子解毒途径,发展出“时-空耦合”活细胞合成策略,在真菌、细菌和哺乳动物细胞内原位合成了不同组成、尺寸和性能的无机半导体荧光纳晶(量子点)。在从物质和能量代谢的角度研究活细胞合成机理的基础上,将活细胞合成体系简化,设计构建了无细胞的准生物体系,成功合成了多种纳米材料,同时也验证了“时-空耦合”策略的正确性。本文将总结评述“时-空耦合”活细胞合成量子点的策略、机理及其在生物标记、生物成像和病原微生物与重金属离子检测等方面的应用,并简要介绍准生物体系。同时,将阐明目前活细胞合成策略面临的挑战。随着合成生物学的发展,通过“时-空耦合”活细胞合成策略可以将无机功能材料“自然地”融入生物体系,赋予生物体系超常的能力,拓展合成生物学。
中图分类号:
引用本文
贾剑红, 杨玲玲, 刘安安, 庞代文. “时-空耦合”活细胞合成量子点[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(2): 385-398.
JIA Jianhong, YANG Lingling, LIU An’an, PANG Daiwen. Space-time-coupled live-cell synthesis of quantum dots[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(2): 385-398.
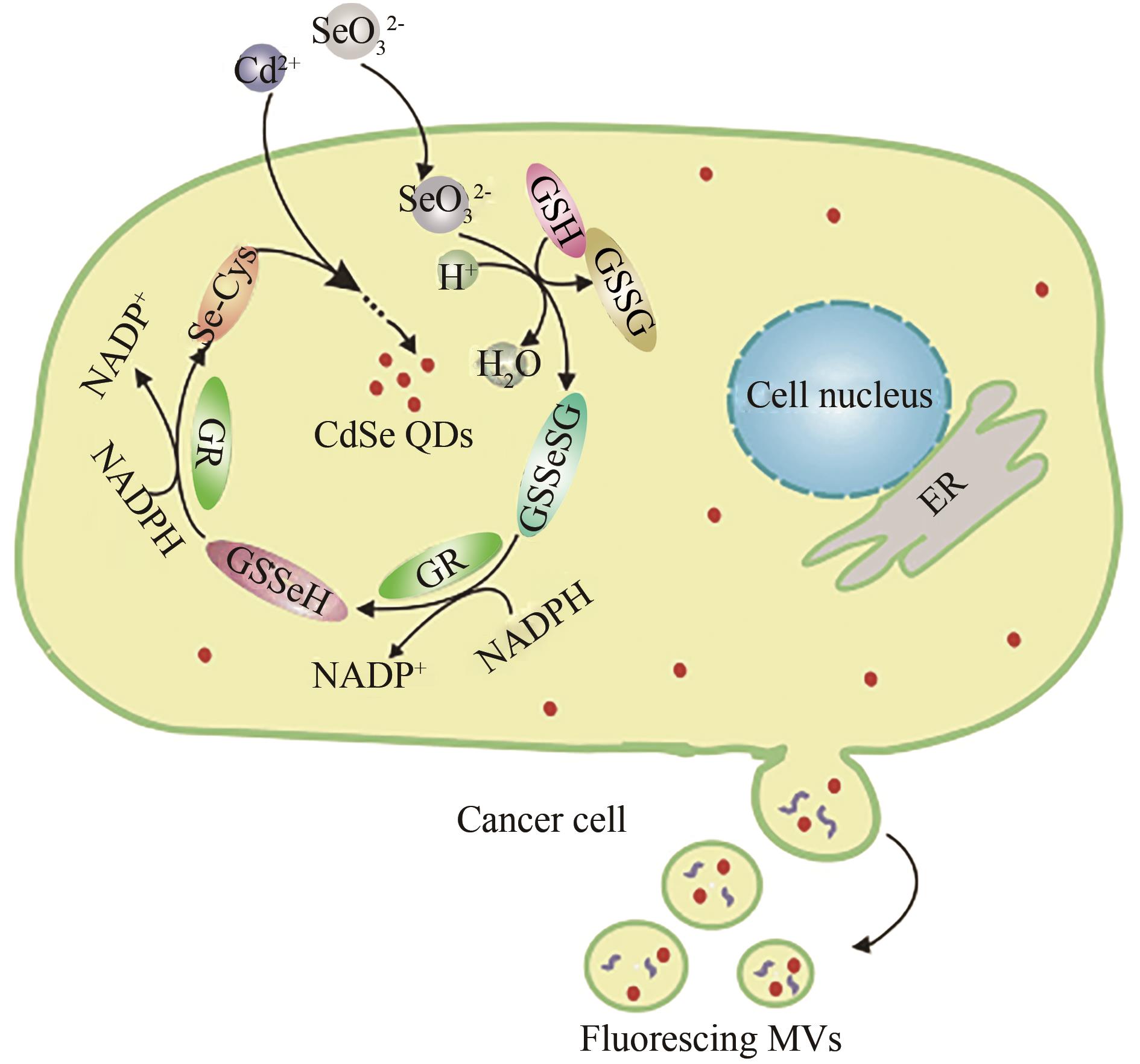
图3 通过MCF-7胞内合成荧光量子点一步标记微囊泡的示意图[40]
Fig. 3 Schematic illustration for one-step labeling of microvesicles by coupling the intracellular synthesis of fluorescent quantum dots in live MCF-7 cells[40]
| 1 | ROSS-MACDONALD P, COELHO P S R, ROEMER T, et al. Large-scale analysis of the yeast genome by transposon tagging and gene disruption[J]. Nature, 1999, 402(6760): 413-418. |
| 2 | UETZ P, GIOT L, CAGNEY G, et al. A comprehensive analysis of protein-protein interactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6770): 623-627. |
| 3 | GAVIN A C, ALOY P, GRANDI P, et al. Proteome survey reveals modularity of theyeastcell machinery[J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7084): 631-636. |
| 4 | REITH F, ETSCHMANN B, GROSSE C, et al. Mechanisms of gold biomineralization in the bacterium Cupriavidus metallidurans [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(42): 17757-17762. |
| 5 | KLAUS T, JOERGER R, OLSSON E, et al. Silver-based crystalline nanoparticles, microbially fabricated[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(24): 13611-13614. |
| 6 | PAULSEN I T, SAIER M H JR. A novel family of ubiquitous heavy metal ion transport proteins[J]. The Journal of Membrane Biology, 1997, 156(2): 99-103. |
| 7 | KLAUS-JOERGER T, JOERGER R, OLSSON E, et al. Bacteria as workers in the living factory: metal-accumulating bacteria and their potential for materials science[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2001, 19(1): 15-20. |
| 8 | ADAMIS P D B, MANNARINO S C, ELEUTHERIO E C A. Glutathione and gamma-glutamyl transferases are involved in the formation of cadmium-glutathione complex[J]. FEBS Letters, 2009, 583(9): 1489-1492. |
| 9 | DAMERON C T, REESE R N, MEHRA R K, et al. Biosynthesis of cadmium sulphide quantum semiconductor crystallites[J]. Nature, 1989, 338(6216): 596-597. |
| 10 | KOWSHIK M, VOGEL W, URBAN J, et al. Microbial synthesis of semiconductor PbS nanocrystallites[J]. Advanced Materials, 2002, 14(11): 815-818. |
| 11 | SWEENEY R Y, MAO C B, GAO X X, et al. Bacterial biosynthesis of cadmium sulfide nanocrystals[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2004, 11(11): 1553-1559. |
| 12 | LABRENZ M, DRUSCHEL G K, THOMSEN-EBERT T, et al. Formation of sphalerite (ZnS) deposits in natural biofilms of sulfate-reducing bacteria[J]. Science, 2000, 290(5497): 1744-1747. |
| 13 | AHMAD A, SENAPATI S, KHAN M I, et al. Intracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles by a novel alkalotolerant actinomycete, Rhodococcus species[J]. Nanotechnology, 2003, 14(7): 824-828. |
| 14 | ALIVISATOS A P. Perspectives on the physical chemistry of semiconductor nanocrystals[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1996, 100(31): 13226-13239. |
| 15 | ALIVISATOS A P. Birth of a nanoscience building block[J]. ACS Nano, 2008, 2(8): 1514-1516. |
| 16 | BRUS L E. Electron-electron and electron-hole interactions in small semiconductor crystallites: The size dependence of the lowest excited electronic state[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1984, 80(9): 4403-4409. |
| 17 | ALIVISATOS A P. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots[J]. Science, 1996, 271(5251): 933-937. |
| 18 | LEACH A D P, MACDONALD J E. Optoelectronic properties of CuInS2 nanocrystals and their origin[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2016, 7(3): 572-583. |
| 19 | YU X J, LIU X Y, YANG K, et al. Pnictogen semimetal (Sb, Bi)-based nanomaterials for cancer imaging and therapy: a materials perspective[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(2): 2038-2067. |
| 20 | JING L H, KERSHAW S V, LI Y L, et al. Aqueous based semiconductor nanocrystals[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(18): 10623-10730. |
| 21 | LI C Y, WANG Q B. Challenges and opportunities for intravital near-infrared fluorescence imaging technology in the second transparency window[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(10): 9654-9659. |
| 22 | WU X Y, LIU H J, LIU J Q, et al. Immunofluorescent labeling of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor quantum dots[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2003, 21(1): 41-46. |
| 23 | BRUNS O T, BISCHOF T S, HARRIS D K, et al. Next-generation in vivo optical imaging with short-wave infrared quantum dots[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 1: 56. |
| 24 | LIU S L, WANG Z G, XIE H Y, et al. Single-virus tracking: from imaging methodologies to virological applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(3): 1936-1979. |
| 25 | ZHANG J J, LIN Y, ZHOU H, et al. Cell membrane-camouflaged NIR II fluorescent Ag2Te quantum dots-based nanobioprobes for enhanced in vivo homotypic tumor imaging[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2019, 8(14): 1900341. |
| 26 | WANG Z G, WANG L, LAMB D C, et al. Real-time dissecting the dynamics of drug transportation in the live brain[J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(1): 642-650. |
| 27 | CHEN G, ZHU J Y, ZHANG Z L, et al. Transformation of cell-derived microparticles into quantum-dot-labeled nanovectors for antitumor siRNA delivery[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(3): 1036-1040. |
| 28 | WANG L, SHI X H, ZHANG Y F, et al. CdZnSeS quantum dots condensed with ordered mesoporous carbon for high-sensitive electrochemiluminescence detection of hydrogen peroxide in live cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 362: 137107. |
| 29 | WANG J J, LIN Y, JIANG Y Z, et al. Multifunctional cellular beacons with in situ synthesized quantum dots make pathogen detectable with the naked eye[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(11): 7280-7287. |
| 30 | JIANG P, TIAN Z Q, ZHU C N, et al. Emission-tunable near-infrared Ag2S quantum dots[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2012, 24(1): 3-5. |
| 31 | MA J J, YU M X, ZHANG Z, et al. Gd-DTPA-coupled Ag2Se quantum dots for dual-modality magnetic resonance imaging and fluorescence imaging in the second near-infrared window[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(22): 10699-10704. |
| 32 | CHIN P T K, DE MELLO DONEGÁ C, BAVEL S S VAN, et al. Highly luminescent CdTe/CdSe colloidal heteronanocrystals with temperature-dependent emission color[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(48): 14880-14886. |
| 33 | YU W W, PENG X G. Formation of high-quality CdS and other II-VI semiconductor nanocrystals in noncoordinating solvents: tunable reactivity of monomers[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2002, 41(13): 2368-2371. |
| 34 | JIANG P, ZHU C N, ZHANG Z L, et al. Water-soluble Ag2S quantum dots for near-infrared fluorescence imaging in vivo [J]. Biomaterials, 2012, 33(20): 5130-5135. |
| 35 | LIU P, WANG Q S, LI X. Studies on CdSe/L-cysteine quantum dots synthesized in aqueous solution for biological labeling[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113(18): 7670-7676. |
| 36 | MA J, CHEN J Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Photochemical instability of thiol-capped CdTe quantum dots in aqueous solution and living cells: process and mechanism[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2007, 111(41): 12012-12016. |
| 37 | MUSSA FARKHANI S, VALIZADEH A. Review: three synthesis methods of CdX (X = Se, S or Te) quantum dots[J]. IET Nanobiotechnology, 2014, 8(2): 59-76. |
| 38 | CUI R, LIU H H, XIE H Y, et al. Living yeast cells as a controllable biosynthesizer for fluorescent quantum dots[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2009, 19(15): 2359-2364. |
| 39 | XIONG L H, CUI R, ZHANG Z L, et al. Uniform fluorescent nanobioprobes for pathogen detection[J]. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(5): 5116-5124. |
| 40 | XIONG L H, TU J W, ZHANG Y N, et al. Designer cell-self-implemented labeling of microvesicles in situ with the intracellular-synthesized quantum dots[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2020, 63(4): 448-453. |
| 41 | WU S M, SU Y L, LIANG R R, et al. Crucial factors in biosynthesis of fluorescent CdSe quantum dots in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(96): 79184-79191. |
| 42 | YAN Z Y, QIAN J, GU Y Q, et al. Green biosynthesis of biocompatible CdSe quantum dots in living Escherichia coli cells[J]. Materials Research Express, 2014, 1(1): 015401. |
| 43 | BURK R F, HILL K E. Regulation of selenium metabolism and transport[J]. Annual Review of Nutrition, 2015, 35: 109-134. |
| 44 | GANTHER H E J C. Selenium metabolism, selenoproteins and mechanisms of cancer prevention: complexities with thioredoxin reductase[J]. Carcinogenesis, 1999, 20(9): 1657-1666. |
| 45 | WHITE P J. Selenium metabolism in plants[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2018, 1862(11): 2333-2342. |
| 46 | SEALE L A, HA H Y, HASHIMOTO A C, et al. Relationship between selenoprotein P and selenocysteine lyase: insights into selenium metabolism[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2018, 127: 182-189. |
| 47 | BROOKS J, LEFEBVRE D D. Optimization of conditions for cadmium selenide quantum dot biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(7): 2735-2745. |
| 48 | SHAO M, ZHANG R, WANG C, et al. Living cell synthesis of CdSe quantum dots: manipulation based on the transformation mechanism of intracellular Se-precursors[J]. Nano Research, 2018, 11(5): 2498-2511. |
| 49 | WEEKLEY C M, HARRIS H H. Which form is that? The importance of selenium speciation and metabolism in the prevention and treatment of disease[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2013, 42(23): 8870-8894. |
| 50 | ZANETTI T A, BIAZI B I, BARANOSKI A, et al. Response of HepG2/C3A cells supplemented with sodium selenite to hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress[J]. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 2018, 50: 209-215. |
| 51 | GEETHA N, BHAVYA G, ABHIJITH P, et al. Insights into nanomycoremediation: secretomics and mycogenic biopolymer nanocomposites for heavy metal detoxification[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 409: 124541. |
| 52 | TARZE A, DAUPLAIS M, GRIGORAS I, et al. Extracellular production of hydrogen selenide accounts for thiol-assisted toxicity of selenite against Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2007, 282(12): 8759-8767. |
| 53 | XU P, LIU L, ZENG G M, et al. Heavy metal-induced glutathione accumulation and its role in heavy metal detoxification in Phanerochaete chrysosporium [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(14): 6409-6418. |
| 54 | LUO Q Y, LIN Y, LI Y, et al. Nanomechanical analysis ofyeastcells in CdSe quantum dot biosynthesis[J]. Small, 2014, 10(4): 699-704. |
| 55 | ORTIZ D F, RUSCITTI T, MCCUE K F, et al. Transport of metal-binding peptides by HMT1, a fission yeast ABC-type vacuolar membrane protein[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1995, 270(9): 4721-4728. |
| 56 | LI Y, CUI R, ZHANG P, et al. Mechanism-oriented controllability of intracellular quantum dots formation: the role of glutathione metabolic pathway[J]. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(3): 2240-2248. |
| 57 | ZHANG R, SHAO M, HAN X, et al. ATP synthesis in the energy metabolism pathway: a new perspective for manipulating CdSe quantum dots biosynthesized in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2017, 12: 3865-3879. |
| 58 | TIAN L J, LI W W, ZHU T T, et al. Directed biofabrication of nanoparticles through regulating extracellular electron transfer[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(35): 12149-12152. |
| 59 | TIAN L J, MIN Y, WANG X M, et al. Biogenic quantum dots for sensitive, label-free detection of mercury ions[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2019, 2(6): 2661-2667. |
| 60 | TIAN L J, LI W W, ZHU T T, et al. Acid-stimulated bioassembly of high-performance quantum dots in Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(31): 18480-18487. |
| 61 | SAKIMOTO K K, WONG A B., YANG P D. Self-photosensitization of nonphotosynthetic bacteria for solar-to-chemical production[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6268): 74-77. |
| 62 | KORNIENKO N, SAKIMOTO K K, HERLIHY D M, et al. Spectroscopic elucidation of energy transfer in hybrid inorganic-biological organisms for solar-to-chemical production[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(42): 11750-11755. |
| 63 | WANG B, ZENG C P, CHU K H, et al. Enhanced biological hydrogen production from Escherichia coli with surface precipitated cadmium sulfide nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(20): 1700611. |
| 64 | CUI Y H, TIAN L J, LI W W, et al. Solar-energy-facilitated CdS x Se1- x quantum dot bio-assembly in Escherichia coli and Tetrahymena pyriformis [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(11): 6205-6212. |
| 65 | CUI R, ZHANG M X, TIAN Z Q, et al. Intermediate-dominated controllable biomimetic synthesis of gold nanoparticles in a quasi-biological system[J]. Nanoscale, 2010, 2(10): 2120-2125. |
| 66 | ZHANG M X, CUI R, TIAN Z Q, et al. Kinetics-controlled formation of gold clusters using a quasi-biological system[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 20(21): 3673-3677. |
| 67 | ZHANG M X, CUI R, ZHAO J Y, et al. Synthesis of sub-5 nm Au-Ag alloy nanoparticles using bio-reducing agent in aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(43): 17080-17082. |
| 68 | XIONG L H, CUI R, ZHANG Z L, et al. Harnessing intracellular biochemical pathways for in vitro synthesis of designer tellurium nanorods[J]. Small, 2015, 11(40): 5416-5422. |
| 69 | CUI R, GU Y P, ZHANG Z L, et al. Controllable synthesis of PbSe nanocubes in aqueous phase using a quasi-biosystem[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(9): 3713-3716. |
| 70 | GU Y P, CUI R, ZHANG Z L, et al. Ultrasmall near-infrared Ag2Se quantum dots with tunable fluorescence for in vivo imaging[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(1): 79-82. |
| 71 | ZHAO J Y, CUI R, ZHANG Z L, et al. Cytotoxicity of nucleus-targeting fluorescent gold nanoclusters[J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(21): 13126-13134. |
| 72 | CUI R, GU Y P, BAO L, et al. Near-infrared electrogenerated chemiluminescence of ultrasmall Ag2Se quantum dots for the detection of dopamine[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84(21): 8932-8935. |
| 73 | LÜ C, ZHANG T Y, LIN Y, et al. Transformation of viral light particles into near-infrared fluorescence quantum dot-labeled active tumor-targeting nanovectors for drug delivery[J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(10): 7035-7042. |
| 74 | ZHAO J Y, CHEN G, GU Y P, et al. Ultrasmall magnetically engineered Ag2Se quantum dots for instant efficient labeling and whole-body high-resolution multimodal real-time tracking of cell-derived microvesicles[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(6): 1893-1903. |
| 75 | YU Z L, ZHANG W, ZHAO J Y, et al. Development of a dual-modally traceable nanoplatform for cancer theranostics using natural circulating cell-derived microparticles in oral cancer patients[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(40): 1703482. |
| 76 | WANG W, YANG Q L, DU Y H, et al. Metabolic labeling of peptidoglycan with NIR-II dye enables in vivo imaging of gut microbiota[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(7): 2628-2633. |
| 77 | HUANG J S, JIANG Y Y, LI J C, et al. Molecular chemiluminescent probes with a very long near-infrared emission wavelength for in vivo imaging[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(8): 3999-4003. |
| 78 | FANG Y, SHANG J Z, LIU D K, et al. Design, synthesis, and application of a small molecular NIR-II fluorophore with maximal emission beyond 1200 nm[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(36): 15271-15275. |
| 79 | CHEN D D, LIU Y, ZHANG Z, et al. NIR-II fluorescence imaging reveals bone marrow retention of small polymer nanoparticles[J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(1): 798-805. |
| 80 | HUANG J S, HUANG J G, CHENG P H, et al. Near-infrared chemiluminescent reporters for in vivo imaging of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in kidneys[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(39): 2003628. |
| 81 | FAN Y, WANG P Y, LU Y B, et al. Lifetime-engineered NIR-II nanoparticles unlock multiplexed in vivo imaging[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2018, 13(10): 941-946. |
| 82 | YU T Y, WEI D M, LI Z, et al. Target-modulated sensitization of upconversion luminescence by NIR-emissive quantum dots: a new strategy to construct upconversion biosensors[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(13): 1976-1979. |
| 83 | ZHANG Y J, YANG H C, AN X Y, et al. Controlled synthesis of Ag2Te@Ag2S core-shell quantum dots with enhanced and tunable fluorescence in the second near-infrared window[J]. Small, 2020, 16(14): 2001003. |
| 84 | PEREIRA C F, VIEGAS I M A, SOUZA SOBRINHA I G, et al. Surface-enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy using silver selenide quantum dots[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2020, 8(30): 10448-10455. |
| 85 | DONG L L, LI W J, YU L D, et al. Ultrasmall Ag2Te quantum dots with rapid clearance for amplified computed tomography imaging and augmented photonic tumor hyperthermia[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(38): 42558-42566. |
| 86 | YU M X, MA J J, WANG J M, et al. Ag2Te quantum dots as contrast agents for near-infrared fluorescence and computed tomography imaging[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2020, 3(6): 6071-6077. |
| 87 | KARGOZAR S, HOSEINI S J, MILAN P B, et al. Quantum dots: A review from concept to clinic[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 15(12): 2000117. |
| 88 | BAHY R M. Autofocus microscope system based on blur measurement approach[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 1721(1): 012058. |
| 89 | ZHANG L Q, YANG T T, DU C N, et al. Lithium whisker growth and stress generation in an in situ atomic force microscope-environmental transmission electron microscope set-up[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2020, 15(2): 94-98. |
| 90 | HAGE F S, RADTKE G, KEPAPTSOGLOU D M, et al. Single-atom vibrational spectroscopy in the scanning transmission electron microscope[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6482): 1124-1127. |
| 91 | WANG D Q, HE P S, WANG Z J, et al. Advances in single cell Raman spectroscopy technologies for biological and environmental applications[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2020, 64: 218-229. |
| 92 | YUAN Y, RAJ P, ZHANG J, et al. Furin-mediated self-assembly of olsalazine nanoparticles for targeted Raman imaging of tumors[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(8): 3923-3927. |
| 93 | DE MOLINER F, KNOX K, GORDON D, et al. A palette of minimally tagged sucrose analogues for real-time Raman imaging of intracellular plant metabolism[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(14): 7637-7642. |
| 94 | GU Y Q, BI X Y, YE J. Gap-enhanced resonance Raman tags for live-cell imaging[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2020, 8(31): 6944-6955. |
| 95 | HE Q, ZABOTINA O A, YU C X. Principal component analysis facilitated fast and noninvasive Raman spectroscopic imaging of plant cell wall pectin distribution and interaction with enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2020, 51(12): 2458-2467. |
| 96 | TIAN S D, LI H Z, LI Z, et al. Polydiacetylene-based ultrastrong bioorthogonal Raman probes for targeted live-cell Raman imaging[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 6223. |
| 97 | PARK T J, LEE S Y, HEO N S, et al. In vivo synthesis of diverse metal nanoparticles by recombinant Escherichia coli [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(39): 7019-7024. |
| 98 | ZHOU X, LI H D, SHI C, et al. An APN-activated NIR photosensitizer for cancer photodynamic therapy and fluorescence imaging[J]. Biomaterials, 2020, 253: 120089. |
| 99 | WANG X N, NIU M T, FAN J X, et al. Photoelectric bacteria enhance the in situ production of tetrodotoxin for antitumor therapy[J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(10): 4270-4279. |
| 100 | ZHANG Z W, CHEN J, YANG Q L, et al. Eco-friendly intracellular microalgae synthesis of fluorescent CdSe QDs as a sensitive nanoprobe for determination of imatinib[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2018, 263: 625-633. |
| 101 | ÓRDENES-AENISHANSLINS N, ANZIANI-OSTUNI G, QUEZADA C P, et al. Biological synthesis of CdS/CdSe core/shell nanoparticles and its application in quantum dot sensitized solar cells[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 1587. |
| [1] | 郭姝媛, 张倩楠, 姑丽克孜·买买提热夏提, 杨一群, 于涛. 液体生物燃料合成与炼制的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 18-44. |
| [2] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [3] | 董颖, 马孟丹, 黄卫人. CRISPR-Cas系统的小型化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 105-117. |
| [4] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [5] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [6] | 任家卫, 张金鹏, 徐国强, 张晓梅, 许正宏, 张晓娟. 大肠杆菌中终止子对下游转录单元基因表达的影响[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 213-227. |
| [7] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [8] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [9] | 仲泉周, 单依怡, 裴清云, 金艳芸, 王艺涵, 孟璐远, 王歆韵, 张雨鑫, 刘坤媛, 王慧中, 冯尚国. 生物合成法生产α-熊果苷的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 118-135. |
| [10] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [11] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [12] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [13] | 赵亮, 李振帅, 付丽平, 吕明, 王士安, 张全, 刘立成, 李福利, 刘自勇. 生物转化一碳化合物原料产油脂与单细胞蛋白研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [14] | 王子渊, 杨立荣, 吴坚平, 郑文隆. 酶促合成手性氨基酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1319-1349. |
| [15] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||