合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (5): 870-883.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-019
光合作用碳同化的合成生物学研究进展
盛阳阳, 徐秀美, 张巧红, 张立新
- 河南大学生命科学学院,省部共建作物逆境适应与改良国家重点实验室,河南 开封 475004
-
收稿日期:2022-04-02修回日期:2022-06-29出版日期:2022-10-31发布日期:2022-11-16 -
通讯作者:张立新 -
作者简介:盛阳阳 (1990—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为光合作用碳同化。 E-mail:shengyangyang727@163.com张立新 (1970—),男,教授。研究方向为光合作用功能调控机理。 E-mail:zhanglixin@henu.edu.cn
Advances in synthetic biology for photosynthetic carbon assimilation
SHENG Yangyang, XU Xiumei, ZHANG Qiaohong, ZHANG Lixin
- State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Adaptation and Improvement,School of Life Sciences,Henan University,Kaifeng 475004,Henan,China
-
Received:2022-04-02Revised:2022-06-29Online:2022-10-31Published:2022-11-16 -
Contact:ZHANG Lixin
摘要:
随着人口增多及耕地面积的减少,人类对粮食的需求日益增加,因此保障足够的粮食供给尤为重要。光合作用通过光反应和碳同化把无机物转换成有机物,是地球上最重要的化学反应。90%以上的植物干物质来源于光合作用固碳反应,光合作用同化的有机物是作物产量形成的物质基础,因此提高作物光能利用效率是提高作物产量的重要途径。近年来,合成生物学在能源、材料、健康和环境等多领域的快速发展,为提高植物光合效率提供了新的机遇。本文着重讨论了合成生物学在提高光合作用碳同化效率方面的研究进展,主要集中在提高Rubisco酶的羧化活性、引进CO2浓缩机制、降低光呼吸等方面;最后,对新型光合固碳回路进行探讨,通过合成生物学对光合作用碳同化模块进行设计、改造、优化和重组,必将有效提高碳同化效率,最终提高作物产量。
中图分类号:
引用本文
盛阳阳, 徐秀美, 张巧红, 张立新. 光合作用碳同化的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(5): 870-883.
SHENG Yangyang, XU Xiumei, ZHANG Qiaohong, ZHANG Lixin. Advances in synthetic biology for photosynthetic carbon assimilation[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 870-883.
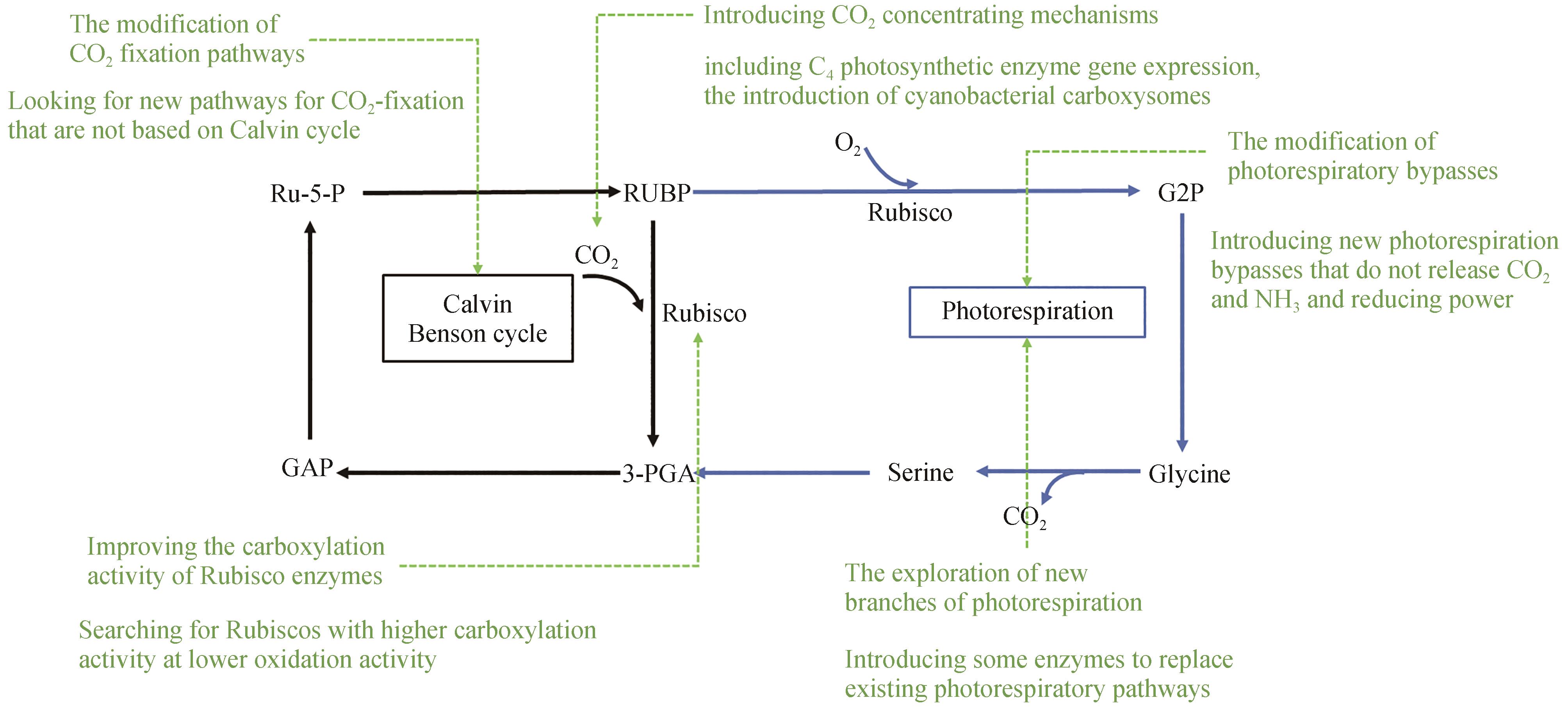
图1 提高光合作用碳同化效率总思路Ru-5-P—5-磷酸核酮糖;RUBP—1,5-二磷酸核酮糖;G2P—2-磷酸甘油酸;3-PGA—3-磷酸甘油酸;GAP—丙糖磷酸Ru-5-P—Ribulose 5-phosphate; RUBP—Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate; G2P—2-phosphoglyceric acid; 3-PGA—3-磷酸甘油酸; GAP—Triose phosphate
Fig. 1 Overview of improving carbon assimilation efficiency of photosynthesis
| 提高Rubisco酶的羧化活性 | 研究策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 寻找其他物种中高活性的Rubisco酶 | 高羧化酶活性 | [ |
| 高亲和力 | [ | |
| 筛选Rubisco酶高活性品种 | 高羧化酶活性 | [ |
| 人工合成肽 | 无明显作用 | [ |
| 引进Rubisco生物合成依赖的辅助因子 | 折叠伴侣蛋白、组装伴侣蛋白及活化酶 | [ |
表1 Rubisco酶活性的合成生物学研究汇总
Tab. 1 Summary of Rubisco enzyme activity by synthetic biological research
| 提高Rubisco酶的羧化活性 | 研究策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 寻找其他物种中高活性的Rubisco酶 | 高羧化酶活性 | [ |
| 高亲和力 | [ | |
| 筛选Rubisco酶高活性品种 | 高羧化酶活性 | [ |
| 人工合成肽 | 无明显作用 | [ |
| 引进Rubisco生物合成依赖的辅助因子 | 折叠伴侣蛋白、组装伴侣蛋白及活化酶 | [ |
| 引进CO2浓缩机制 | 研究策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| GLK基因的引入 | 促进产量增加 | [ |
| 转运蛋白的引入 | 条件促进,可以提高光合速率和碳同化率 | [ |
| 蓝藻羧酶体的引入 | 有待进一步探索研究 | [ |
表2 CO2浓缩机制的合成生物学研究汇总
Tab. 2 Summary of CO2 enrichment mechanisms by synthetic biological research
| 引进CO2浓缩机制 | 研究策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| GLK基因的引入 | 促进产量增加 | [ |
| 转运蛋白的引入 | 条件促进,可以提高光合速率和碳同化率 | [ |
| 蓝藻羧酶体的引入 | 有待进一步探索研究 | [ |
| 降低光呼吸 | 研究策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 叶绿体甘油酸支路 | 叶绿体乙醇酸转化为甘油酸,生物量增加,无NH3的释放 | [ |
| 过氧化物酶体甘油酸支路 | 绕过了线粒体中的甘氨酸到丝氨酸的转化,同时将CO2释放的位置从线粒体转移到过氧化物酶体,无NH3的释放 | [ |
| 叶绿体乙醇酸氧化支路 | 光呼吸途径的碳全部丢失,无NH3的释放 | [ |
| 3-羟基丙酸盐支路 | 实现光呼吸期间CO2的净同化,无NH3的释放 | [ |
表3 光呼吸支路的合成生物学研究汇总
Tab. 3 Summary of photorespiration pathways by synthetic biological research
| 降低光呼吸 | 研究策略 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 叶绿体甘油酸支路 | 叶绿体乙醇酸转化为甘油酸,生物量增加,无NH3的释放 | [ |
| 过氧化物酶体甘油酸支路 | 绕过了线粒体中的甘氨酸到丝氨酸的转化,同时将CO2释放的位置从线粒体转移到过氧化物酶体,无NH3的释放 | [ |
| 叶绿体乙醇酸氧化支路 | 光呼吸途径的碳全部丢失,无NH3的释放 | [ |
| 3-羟基丙酸盐支路 | 实现光呼吸期间CO2的净同化,无NH3的释放 | [ |

图2 天然和合成的光呼吸支路黑色箭头,经典的光呼吸旁路;蓝色箭头,叶绿体甘油酸支路;橙色箭头,过氧化物酶体甘油酸支路;绿色箭头,叶绿体乙醇酸氧化支路;紫色箭头,3-羟基丙酸盐支路;红色箭头,水稻中新的光呼吸支路RUBP—1,5-二磷酸核酮糖;G2P—2-磷酸甘油酸;3-PGA—3-磷酸甘油酸
Fig. 2 Natural and synthetic photorespiratory bypassesBlack arrow, classic photorespiratory bypass; Blue arrow, chloroplastic glycerate bypass; Orange arrow, peroxisomal glycerate bypass; Green arrow, chloroplastic glycolate oxidation bypass; Purple arrow, 3-hydroxypropionate bypass; Red arrow, A new photorespiratory bypasses in riceRUBP—Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate; G2P—2-phosphoglyceric acid; 3-PGA—3-phosphoglyceric acid
| 59 | RAVEN J A, COCKELL C S, DE LA ROCHA C L. The evolution of inorganic carbon concentrating mechanisms in photosynthesis[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B, Biological Sciences, 2008, 363(1504): 2641-2650. |
| 60 | LANGDALE J A. C4 cycles: past, present, and future research on C4 photosynthesis[J]. The Plant Cell, 2011, 23(11): 3879-3892. |
| 61 | KLAVSEN S K, MADSEN T V, MABERLY S C. Crassulacean acid metabolism in the context of other carbon-concentrating mechanisms in freshwater plants: a review[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2011, 109(1/2/3): 269-279. |
| 62 | VON CAEMMERER S, QUICK W P, FURBANK R T. The development of C₄ rice: current progress and future challenges[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6089): 1671-1672. |
| 63 | LONG S P, MARSHALL-COLON A, ZHU X G. Meeting the global food demand of the future by engineering crop photosynthesis and yield potential[J]. Cell, 2015, 161(1): 56-66. |
| 64 | MIYAO M, MASUMOTO C, MIYAZAWA S I, et al. Lessons from engineering a single-cell C4 photosynthetic pathway into rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(9): 3021-3029. |
| 65 | WANG P, KHOSHRAVESH R, KARKI S, et al. Re-creation of a key step in the evolutionary switch from C3 to C4 leaf anatomy[J]. Current Biology, 2017, 27(21): 3278-3287.e6. |
| 66 | YEH S Y, LIN H H, CHANG Y M, et al. Maize Golden2-like transcription factors boost rice chloroplast development, photosynthesis, and grain yield[J]. Plant Physiology, 2021, 188(1): 442-459. |
| 67 | MCGRATH J M, LONG S P. Can the cyanobacterial carbon-concentrating mechanism increase photosynthesis in crop species? A theoretical analysis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2014, 164(4): 2247-2261. |
| 68 | YANG S M, CHANG C Y, YANAGISAWA M, et al. Transgenic rice expressing cyanobacterial bicarbonate transporter exhibited enhanced photosynthesis, growth and grain yield[J]. Photosynthesis Energy from the Sun, 2008:1247-1250. |
| 69 | HAY W T, BIHMIDINE S, MUTLU N, et al. Enhancing soybean photosynthetic CO2 assimilation using a cyanobacterial membrane protein, ictB [J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2017, 212: 58-68. |
| 70 | ROLLAND V, BADGER M R, PRICE G D. Redirecting the cyanobacterial bicarbonate transporters BicA and SbtA to the chloroplast envelope: soluble and membrane cargos need different chloroplast targeting signals in plants[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 185. |
| 71 | UEHARA S, ADACHI F, ITO-INABA Y, et al. Specific and efficient targeting of cyanobacterial bicarbonate transporters to the inner envelope membrane of chloroplasts in Arabidopsis [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 16. |
| 72 | ATKINSON N, FEIKE D, MACKINDER L C M, et al. Introducing an algal carbon-concentrating mechanism into higher plants: location and incorporation of key components[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 14(5): 1302-1315. |
| 73 | BADGER M R, HANSON D, PRICE G D. Evolution and diversity of CO2 concentrating mechanisms in cyanobacteria[J]. Functional Plant Biology: FPB, 2002, 29(3): 161-173. |
| 74 | LONG B M, RAE B D, ROLLAND V, et al. Cyanobacterial CO2-concentrating mechanism components: function and prospects for plant metabolic engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2016, 31: 1-8. |
| 75 | RAE B D, LONG B M, BADGER M R, et al. Functions, compositions, and evolution of the two types of carboxysomes: polyhedral microcompartments that facilitate CO2 fixation in cyanobacteria and some proteobacteria[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews: MMBR, 2013, 77(3): 357-379. |
| 76 | LONG B M, BADGER M R, WHITNEY S M, et al. Analysis of carboxysomes from Synechococcus PCC7942 reveals multiple Rubisco complexes with carboxysomal proteins CcmM and CcaA[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2007, 282(40): 29323-29335. |
| 77 | PRICE G D, BADGER M R, WOODGER F J, et al. Advances in understanding the cyanobacterial CO2-concentrating-mechanism (CCM): functional components, Ci transporters, diversity, genetic regulation and prospects for engineering into plants[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2007, 59(7): 1441-1461. |
| 78 | PRICE G D. Inorganic carbon transporters of the cyanobacterial CO2 concentrating mechanism[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2011, 109(1/2/3): 47-57. |
| 79 | SHIVELY J M, BALL F, BROWN D H, et al. Functional organelles in prokaryotes: polyhedral inclusions (carboxysomes) of Thiobacillus neapolitanus [J]. Scientific Reports, 1973, 182(4112): 584-586. |
| 80 | CANNON G C, HEINHORST S, KERFELD C A. Carboxysomal carbonic anhydrases: structure and role in microbial CO2 fixation[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Proteins and Proteomics, 2010, 1804(2): 382-392. |
| 81 | SO A K C, ESPIE G S, WILLIAMS E B, et al. A novel evolutionary lineage of carbonic anhydrase (ε class) is a component of the carboxysome shell[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2004, 186(3): 623-630. |
| 82 | MANGAN N M, FLAMHOLZ A, HOOD R D, et al. pH determines the energetic efficiency of the cyanobacterial CO2 concentrating mechanism[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(36): E5354-E5362. |
| 83 | GONZALEZ-ESQUER C R, SHUBITOWSKI T B, KERFELD C A. Streamlined construction of the cyanobacterial CO2-fixing organelle via protein domain fusions for use in plant synthetic biology[J]. The Plant Cell, 2015, 27(9): 2637-2644. |
| 84 | LIN M T, OCCHIALINI A, ANDRALOJC P J, et al. β-Carboxysomal proteins assemble into highly organized structures in Nicotiana chloroplasts[J]. The Plant Journal, 2014, 79(1): 1-12. |
| 85 | BONACCI W, TENG P K, AFONSO B, et al. Modularity of a carbon-fixing protein organelle[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(2): 478-483. |
| 86 | PENGELLY J J L, FÖRSTER B, VON CAEMMERER S, et al. Transplastomic integration of a cyanobacterial bicarbonate transporter into tobacco chloroplasts[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2014, 65(12): 3071-3080. |
| 87 | LONG B M, HEE W Y, SHARWOOD R E, et al. Carboxysome encapsulation of the CO2-fixing enzyme Rubisco in tobacco chloroplasts[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3570. |
| 88 | HANSON M R, LIN M T, CARMO-SILVA A E, et al. Towards engineering carboxysomes into C3 plants[J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2016, 87(1): 38-50. |
| 89 | TCHERKEZ G. The mechanism of Rubisco-catalysed oxygenation[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2016, 39(5): 983-997. |
| 90 | MAURINO V G, PETERHANSEL C. Photorespiration: current status and approaches for metabolic engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2010, 13(3): 248-255. |
| 91 | PETERHANSEL C, MAURINO V G. Photorespiration redesigned[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 155(1): 49-55. |
| 92 | FIELD C B, BEHRENFELD M J, RANDERSON J T, et al. Primary production of the biosphere: integrating terrestrial and oceanic components[J]. Science, 1998, 281(5374): 237-240. |
| 93 | GIORDANO M, BEARDALL J, RAVEN J A. CO2 concentrating mechanisms in algae: mechanisms, environmental modulation, and evolution[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2005, 56: 99-131. |
| 94 | WINGLER A, LEA P J, QUICK W P, et al. Photorespiration: metabolic pathways and their role in stress protection[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 2000, 355(1402): 1517-1529. |
| 95 | SOUTH P F, CAVANAGH A P, LIU H W, et al. Synthetic glycolate metabolism pathways stimulate crop growth and productivity in the field[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6422): eaat9077. |
| 96 | TIMM S, NUNES-NESI A, PÄRNIK T, et al. A cytosolic pathway for the conversion of hydroxypyruvate to glycerate during photorespiration in Arabidopsis [J]. The Plant Cell, 2008, 20(10): 2848-2859. |
| 1 | SILVIA M. Agriculture has to increase production by 70%: FAO chief[EB/OL]. [2009-10-14]. . |
| 2 | TILMAN D, CASSMAN K G, MATSON P A, et al. Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices[J]. Nature, 2002, 418(6898): 671-677. |
| 3 | MAURINO V G, WEBER A P M. Engineering photosynthesis in plants and synthetic microorganisms[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 64(3): 743-751. |
| 4 | WHITNEY S M, HOUTZ R L, ALONSO H. Advancing our understanding and capacity to engineer nature's CO2-sequestering enzyme, Rubisco[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 155(1): 27-35. |
| 5 | ZHU X G, LONG S P, ORT D R. Improving photosynthetic efficiency for greater yield[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010, 61: 235-261. |
| 6 | 程建峰, 沈允钢. 试析光合作用的研究动向[J]. 植物学报, 2011, 46(6): 694-704. |
| CHENG J F, SHEN Y G. On the trends of photosynthesis research[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2011, 46(6): 694-704. | |
| 7 | 朱观林, 郭龙彪, 钱前. 水稻的高光效分子育种[J]. 中国稻米, 2009, 15(5): 5-10. |
| ZHU G L, GUO L B, QIAN Q. Molecular breeding of rice with high light efficiency[J]. China Rice, 2009, 15(5): 5-10. | |
| 8 | 张立新, 卢从明, 彭连伟, 等. 利用合成生物学原理提高光合作用效率的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2017, 33(3): 486-493. |
| ZHANG L X, LU C M, PENG L W, et al. Progress in improving photosynthetic efficiency by synthetic biology[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2017, 33(3): 486-493. | |
| 9 | 程建峰, 沈允钢. 作物高光效之管见[J]. 作物学报, 2010, 36(8): 1235-1247. |
| CHENG J F, SHEN Y G. My humble opinions on high photosynthetic efficiency of crop[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2010, 36(8): 1235-1247. | |
| 10 | 张春霆. 合成生物学: 我国急需发展的前沿科学[J]. 前沿科学, 2007, 1(3): 55. |
| ZHANG C T. Synthetic biology: frontier science in urgent need of development in China[J]. Frontier Science, 2007, 1(3): 55. | |
| 11 | DRUBIN D A, WAY J C, SILVER P A. Designing biological systems[J]. Genes & Development, 2007, 21(3): 242-254. |
| 12 | 熊燕, 陈大明, 杨琛, 等. 合成生物学发展现状与前景[J]. 生命科学, 2011, 23(9): 826-837. |
| XIONG Y, CHEN D M, YANG C, et al. Progress and perspective of synthetic biology[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2011, 23(9): 826-837. | |
| 13 | STEEN E J, KANG Y S, BOKINSKY G, et al. Microbial production of fatty-acid-derived fuels and chemicals from plant biomass[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7280):559-563. |
| 14 | DEKISHIMA Y, LAN E I, SHEN C R, et al. Extending carbon chain length of 1-butanol pathway for 1-hexanol synthesis from glucose by engineered Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(30):11399-11401. |
| 15 | MAHISHI L H, TRIPATHI G, RAWAL S K. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) synthesis by recombinant Escherichia coli harbouring Streptomyces aureofaciens PHB biosynthesis genes: effect of various carbon and nitrogen sources[J]. Microbiological Research, 2003, 158(1): 19-27. |
| 16 | YANG T H, KIM T W, KANG H O, et al. Biosynthesis of polylactic acid and its copolymers using evolved propionate CoA transferase and PHA synthase[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2010, 105(1): 150-160. |
| 17 | AJIKUMAR P K, XIAO W H, TYO K E J, et al. Isoprenoid pathway optimization for taxol precursor overproduction in Escherichia coli [J]. Science, 2010, 330(6000): 70-74. |
| 18 | LEVSKAYA A, CHEVALIER A A, TABOR J J, et al. Engineering Escherichia coli to see light[J]. Nature, 2005, 438(7067): 441-442. |
| 97 | AHMAD R, BILAL M, JEON J H, et al. Improvement of biomass accumulation of potato plants by transformation of cyanobacterial photorespiratory glycolate catabolism pathway genes[J]. Plant Biotechnology Reports, 2016, 10(5): 269-276. |
| 98 | DE F C CARVALHO J, MADGWICK P J, POWERS S J, et al. An engineered pathway for glyoxylate metabolism in tobacco plants aimed to avoid the release of ammonia in photorespiration[J]. BMC Biotechnology, 2011, 11: 111. |
| 99 | MAIER A, FAHNENSTICH H, VON CAEMMERER S, et al. Transgenic introduction of a glycolate oxidative cycle into A. thaliana chloroplasts leads to growth improvement[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2012, 3: 38. |
| 100 | KEBEISH R, NIESSEN M, THIRUVEEDHI K, et al. Chloroplastic photorespiratory bypass increases photosynthesis and biomass production in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2007, 25(5): 593-599. |
| 101 | SHIH P M, ZARZYCKI J, NIYOGI K K, et al. Introduction of a synthetic CO2-fixing photorespiratory bypass into a Cyanobacterium[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2014, 289(14): 9493-9500. |
| 102 | ERB T J, ZARZYCKI J. Biochemical and synthetic biology approaches to improve photosynthetic CO2-fixation[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2016, 34: 72-79. |
| 103 | DALAL J, LOPEZ H, VASANI N B, et al. A photorespiratory bypass increases plant growth and seed yield in biofuel crop Camelina sativa [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2015, 8: 175. |
| 104 | NÖLKE G, HOUDELET M, KREUZALER F, et al. The expression of a recombinant glycolate dehydrogenase polyprotein in potato (Solanum tuberosum) plastids strongly enhances photosynthesis and tuber yield[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2014, 12(6): 734-742. |
| 105 | FAHNENSTICH H, SCARPECI T E, VALLE E M, et al. Generation of hydrogen peroxide in chloroplasts of Arabidopsis overexpressing glycolate oxidase as an inducible system to study oxidative stress[J]. Plant Physiology, 2008, 148(2): 719-729. |
| 106 | OLIVER D J. The effect of glyoxylate on photosynthesis and photorespiration by isolated soybean mesophyll cells[J]. Plant Physiology, 1980, 65(5): 888-892. |
| 107 | XIN C P, THOLEN D, DEVLOO V, et al. The benefits of photorespiratory bypasses: how can they work? [J]. Plant Physiology, 2014, 167(2): 574-585. |
| 108 | PETERHANSEL C, BLUME C, OFFERMANN S. Photorespiratory bypasses: how can they work? [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 64(3): 709-715. |
| 19 | TOPP S, GALLIVAN J P. Riboswitches in unexpected places - a synthetic riboswitch in a protein coding region[J]. RNA, 2008, 14(12): 2498-2503. |
| 20 | WERLEN C, JASPERS M C M, VAN DER MEER J R. Measurement of biologically available naphthalene in gas and aqueous phases by use of a Pseudomonas putida biosensor[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70(1): 43-51. |
| 21 | ATSUMI S, HANAI T, LIAO J C. Non-fermentative pathways for synthesis of branched-chain higher alcohols as biofuels[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7174): 86-89. |
| 22 | ZHANG K C, SAWAYA M R, EISENBERG D S, et al. Expanding metabolism for biosynthesis of nonnatural alcohols[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(52): 20653-20658. |
| 23 | SHEN C R, LAN E I, DEKISHIMA Y, et al. Driving forces enable high-titer anaerobic 1-butanol synthesis in Escherichia coli [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(9): 2905-2915. |
| 24 | HANANIA U, ARIEL T, TEKOAH Y, et al. Establishment of a tobacco BY2 cell line devoid of plant-specific xylose and fucose as a platform for the production of biotherapeutic proteins[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(9): 1120-1129. |
| 25 | ČERMÁK T, CURTIN S J, GIL-HUMANES J, et al. A multipurpose toolkit to enable advanced genome engineering in plants[J]. The Plant Cell, 2017, 29(6): 1196-1217. |
| 26 | PARRY M A J, KEYS A J, MADGWICK P J, et al. Rubisco regulation: a role for inhibitors[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2008, 59(7): 1569-1580. |
| 27 | ANDERSSON I, BACKLUND A. Structure and function of Rubisco[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2008, 46(3): 275-291. |
| 28 | ANDERSSON I. Catalysis and regulation in Rubisco[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2008, 59(7): 1555-1568. |
| 29 | WHITNEY S M, BALDET P, HUDSON G S, et al. Form I Rubiscos from non-green algae are expressed abundantly but not assembled in tobacco chloroplasts[J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2001, 26(5): 535-547. |
| 30 | LIN M T, OCCHIALINI A, ANDRALOJC P J, et al. A faster Rubisco with potential to increase photosynthesis in crops[J]. Nature, 2014, 513(7519): 547-550. |
| 31 | ZHU X G, PORTIS A R, LONG S P. Would transformation of C3 crop plants with foreign Rubisco increase productivity? A computational analysis extrapolating from kinetic properties to canopy photosynthesis[J]. Plant, Cell and Environment, 2004, 27(2): 155-165. |
| 32 | MATSUMURA H, SHIOMI K, YAMAMOTO A, et al. Hybrid Rubisco with complete replacement of rice Rubisco small subunits by sorghum counterparts confers C4 plant-like high catalytic activity[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(11): 1570-1581. |
| 33 | PRINS A, ORR D J, ANDRALOJC P J, et al. Rubisco catalytic properties of wild and domesticated relatives provide scope for improving wheat photosynthesis[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(6): 1827-1838. |
| 34 | WHITNEY S M, KANE H J, HOUTZ R L, et al. Rubisco oligomers composed of linked small and large subunits assemble in tobacco plastids and have higher affinities for CO2 and O2 [J]. Plant Physiology, 2009, 149(4): 1887-1895. |
| 35 | DURÃO P, AIGNER H, NAGY P, et al. Opposing effects of folding and assembly chaperones on evolvability of Rubisco[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(2): 148-155. |
| 46 | GUTTERIDGE S, GATENBY A A. Rubisco synthesis, assembly, mechanism, and regulation[J]. The Plant Cell, 1995, 7(7): 809-819. |
| 37 | QU Y C, SAKODA K, FUKAYAMA H, et al. Overexpression of both Rubisco and Rubisco activase rescues rice photosynthesis and biomass under heat stress[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2021, 44(7): 2308-2320. |
| 38 | KANEVSKI I, MALIGA P, RHOADES D F, et al. Plastome engineering of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in tobacco to form a sunflower large subunit and tobacco small subunit hybrid[J]. Plant Physiology, 1999, 119(1): 133-142. |
| 39 | WHITNEY S M, ANDREWS T J. Plastome-encoded bacterial ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RubisCO) supports photosynthesis and growth in tobacco[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2001, 98(25): 14738-14743. |
| 40 | ISHIKAWA C, HATANAKA T, MISOO S, et al. Functional incorporation of sorghum small subunit increases the catalytic turnover rate of Rubisco in transgenic rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(3): 1603-1611. |
| 41 | MARTIN-AVILA E, LIM Y L, BIRCH R, et al. Modifying plant photosynthesis and growth via simultaneous chloroplast transformation of Rubisco large and small subunits[J]. The Plant Cell, 2020, 32(9): 2898-2916. |
| 42 | PARRY M A J, ANDRALOJC P J, MITCHELL R A C, et al. Manipulation of Rubisco: the amount, activity, function and regulation[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2003, 54(386): 1321-1333. |
| 43 | SPREITZER R J, SALVUCCI M E. Rubisco: structure, regulatory interactions, and possibilities for a better enzyme[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2002, 53: 449-475. |
| 44 | PORTIS A R JR. Rubisco activase-rubisco's catalytic chaperone[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2003, 75(1): 11-27. |
| 45 | 张国, 王玮, 邹琦. Rubisco活化酶的分子生物学[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2004, 40(5): 633-637. |
| ZHANG G, WANG W, ZOU Q. Molecular biology of rubisco activase[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2004, 40(5): 633-637. | |
| 46 | REITH M, CATTOLICO R A. Inverted repeat of Olisthodiscus luteus chloroplast DNA contains genes for both subunits of ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase and the 32,000-dalton QB protein: phylogenetic implications[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1986, 83(22): 8599-8603. |
| 47 | DELWICHE C F, PALMER J D. Rampant horizontal transfer and duplication of Rubisco genes in eubacteria and plastids[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 1996, 13(6): 873-882. |
| 48 | TABITA F R. Microbial ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase: a different perspective[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 1999, 60(1):1-28. |
| 49 | JOSHI J, MUELLER-CAJAR O, TSAI Y C C, et al. Role of small subunit in mediating assembly of red-type form I Rubisco[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2015, 290(2): 1066-1074. |
| 50 | GUNN L H, MARTIN AVILA E, BIRCH R, et al. The dependency of red Rubisco on its cognate activase for enhancing plant photosynthesis and growth[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(41): 25890-25896. |
| 51 | SALESSE-SMITH C E, SHARWOOD R E, BUSCH F A, et al. Overexpression of Rubisco subunits with RAF1 increases Rubisco content in maize[J]. Nature Plants, 2018, 4(10): 802-810. |
| 52 | WHITNEY S M, BIRCH R, KELSO C, et al. Improving recombinant Rubisco biogenesis, plant photosynthesis and growth by coexpressing its ancillary RAF1 chaperone[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(11): 3564-3569. |
| 53 | FLECKEN M, WANG H P, POPILKA L, et al. Dual functions of a Rubisco activase in metabolic repair and recruitment to carboxysomes[J]. Cell, 2020, 183(2): 457-473.e20. |
| 54 | SASCHENBRECKER S, BRACHER A, RAO K V, et al. Structure and function of RbcX, an assembly chaperone for hexadecameric rubisco[J]. Cell, 2007, 129(6): 1189-1200. |
| 55 | XIA L Y, JIANG Y L, KONG W W, et al. Molecular basis for the assembly of RuBisCO assisted by the chaperone Raf1[J]. Nature Plants, 2020, 6(6): 708-717. |
| 56 | HUANG F, KONG W W, SUN Y Q, et al. Rubisco accumulation factor 1 (Raf1) plays essential roles in mediating Rubisco assembly and carboxysome biogenesis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(29): 17418-17428. |
| 57 | PARRY M A J, ANDRALOJC P J, SCALES J C, et al. Rubisco activity and regulation as targets for crop improvement[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 64(3): 717-730. |
| 58 | CAI Z, LIU G X, ZHANG J L, et al. Development of an activity-directed selection system enabled significant improvement of the carboxylation efficiency of Rubisco[J]. Protein & Cell, 2014, 5(7): 552-562. |
| 109 | BETTI M, BAUWE H, BUSCH F A, et al. Manipulating photorespiration to increase plant productivity: recent advances and perspectives for crop improvement[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(10): 2977-2988. |
| 110 | SAGE T L, SAGE R F. The functional anatomy of rice leaves: implications for refixation of photorespiratory CO2 and efforts to engineer C4 photosynthesis into rice[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2009, 50(4): 756-772. |
| 111 | BUSCH F A, SAGE T L, COUSINS A B, et al. C3 plants enhance rates of photosynthesis by reassimilating photorespired and respired CO2 [J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2013, 36(1): 200-212. |
| 112 | BRAUN H P, ZABALETA E. Carbonic anhydrase subunits of the mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase complex (complex I) in plants[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2007, 129(1): 114-122. |
| 113 | KHURSHID G, ABBASSI A Z, KHALID M F, et al. A cyanobacterial photorespiratory bypass model to enhance photosynthesis by rerouting photorespiratory pathway in C3 plants[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 20879. |
| 114 | SHEN B R, WANG L M, LIN X L, et al. Engineering a new chloroplastic photorespiratory bypass to increase photosynthetic efficiency and productivity in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(2): 199-214. |
| 115 | Online computer library center: future agriculture project[EB/OL]. http: . |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [12] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [13] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [14] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [15] | 查文龙, 卜兰, 訾佳辰. 中药药效成分群的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
