合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (2): 353-368.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-055
合成生物技术助力纳米颗粒疫苗理性设计时代的到来
马雪璟1,2, 郭畅3, 华兆琳1,2,3, 侯百东1,2,3
- 1.中国科学院生物物理研究所,感染与免疫重点实验室,北京 100101
2.中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3.昌平实验室,北京 102206
-
收稿日期:2023-08-16修回日期:2023-11-10出版日期:2024-04-30发布日期:2024-04-28 -
通讯作者:华兆琳,侯百东 -
作者简介:马雪璟 (1995—),女,博士研究生。研究方向为B细胞的分化与纳米颗粒疫苗的免疫机制。E-mail:maxuejing1217@126.com郭畅 (1994—),女,博士后。研究方向为基于病原样抗原疫苗策略的新型疫苗研发。E-mail:guochang201212@126.com华兆琳 (1974—),女,博士,副研究员,教授。研究方向为B细胞细胞活化和记忆细胞等不同细胞分化阶段中的转录调控机制,并以此为理论基础指导纳米颗粒为载体的新型疫苗的研发。 E-mail:zlhua@ibp.ac.cn侯百东 (1971—),男,研究员,教授,博士生导师,昌平实验室(CPNL)领衔科学家。长期从事感染免疫学基础理论研究,在B细胞TLR信号启动抗病毒免疫应答功能、新一代病原样抗原(PLA)疫苗策略研究等方面取得原创性理论突破。E-mail:baidong_hou@ibp.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(81991495);国家重点研发计划(2019YFA0508901)
Dawn of the rational design of nanoparticle vaccines aided by the advance of synthetic biology techniques
MA Xuejing1,2, GUO Chang3, HUA Zhaolin1,2,3, HOU Baidong1,2,3
- 1.CAS Key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity,Institute of Biophysics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100101,China
2.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
3.Changping Laboratory,Beijing 102206,China
-
Received:2023-08-16Revised:2023-11-10Online:2024-04-30Published:2024-04-28 -
Contact:HUA Zhaolin, HOU Baidong
摘要:
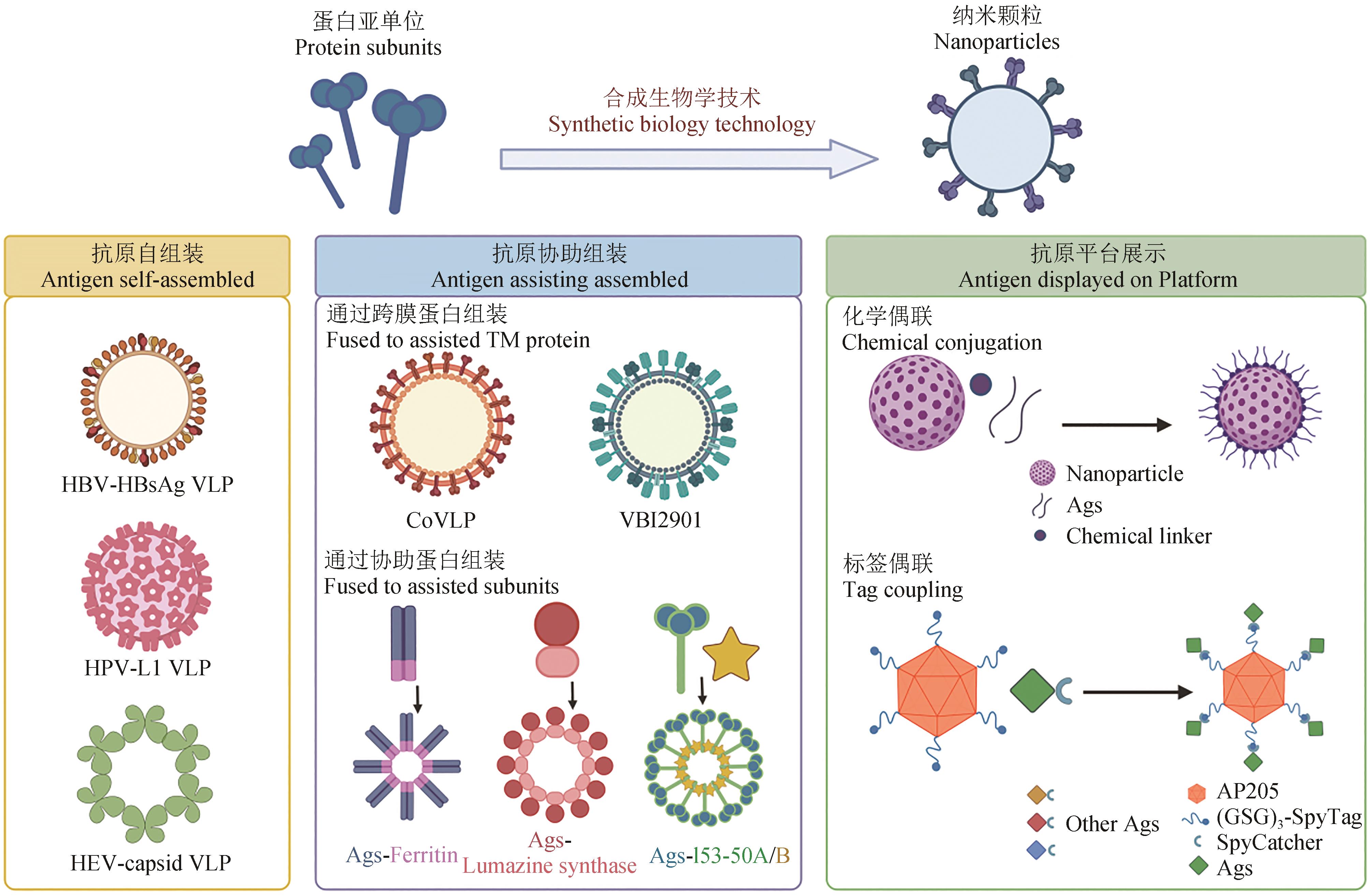
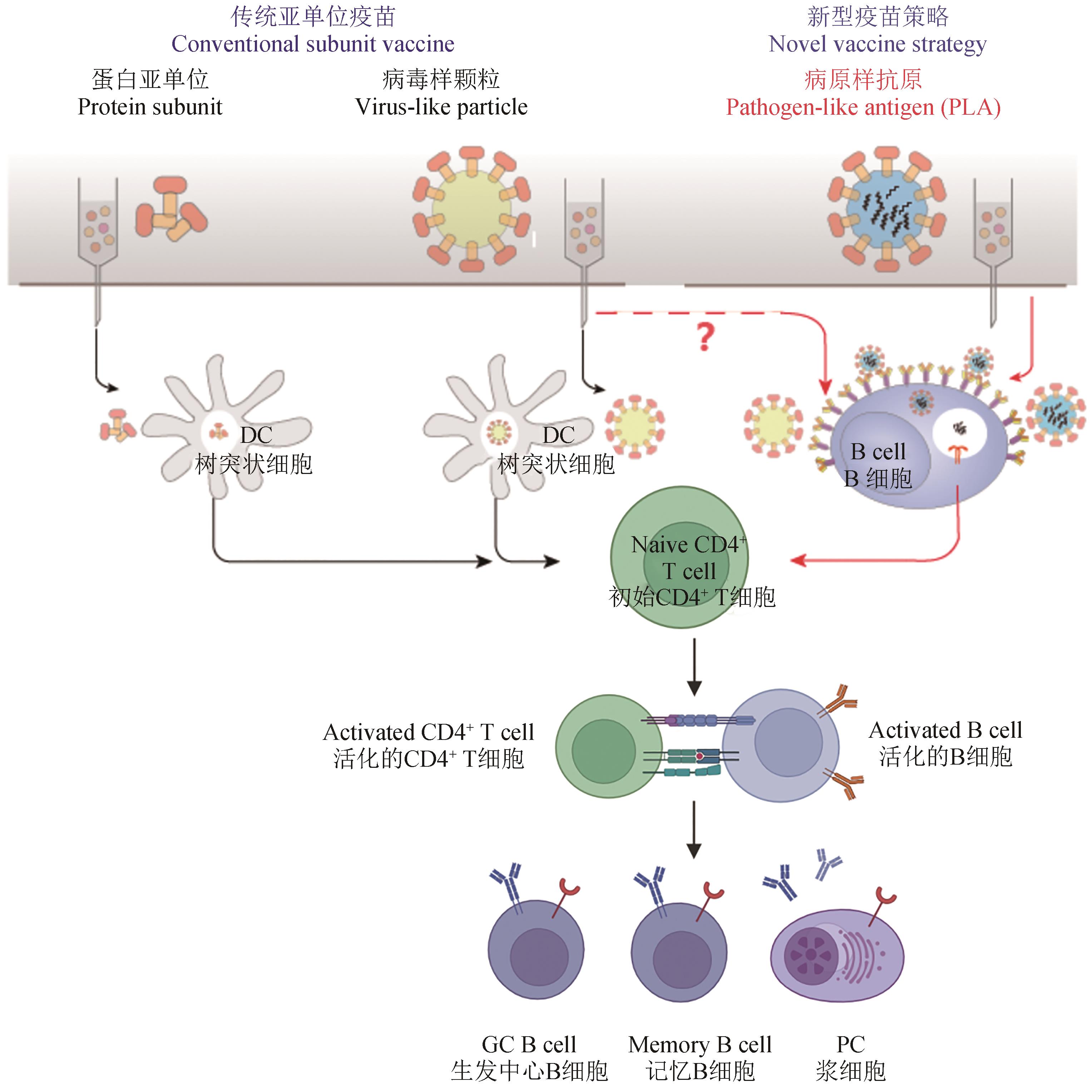
纳米颗粒疫苗自1981年首次应用于人体以来,经历逾40年的发展历程,在临床应用方面已取得了极大成功。尤其是在乙型肝炎病毒(hepatitis B virus,HBV)、人乳头瘤病毒(human papillomavirus,HPV)等疫苗领域,纳米颗粒疫苗以显著的免疫原性和良好的安全性在遏制病毒传播和疾病防控方面发挥了不可替代的作用,为人类社会的健康安全作出了巨大贡献。自新型冠状病毒疫情爆发以来,迫切的防控需要进一步推动了包括纳米颗粒疫苗在内的各类新型疫苗技术的发展。然而,由于被相对更经验化的设计方式和更复杂的制备工艺制约,纳米颗粒疫苗临床转化应用的速度并不突出。因此,通过理性设计来提升纳米颗粒疫苗的研制效率和应用范围,正成为其未来发展的重要方向和关键目标。合成生物技术在纳米颗粒疫苗发展的过程中一直起着重要作用。近年来,新型合成生物技术的应用在推动纳米颗粒平台灵活性方面取得了显著进展,有望满足未来对抗原承载多样性的需求。本文首先综述了纳米颗粒疫苗发展的技术沿革与进展,从抗原自组装形成的纳米颗粒疫苗到抗原协助组装的纳米颗粒疫苗,再到抗原平台展示的纳米颗粒疫苗。其次,总结了纳米颗粒疫苗提高抗原淋巴引流效率、抗原增强B细胞信号活化、抗原具有独特的抗原提呈方式等增强抗原免疫原性的特殊作用。最后概括了纳米颗粒疫苗在新型冠状病毒流行中的转化应用,如新型冠状病毒刺突蛋白三聚体疫苗、协助组装的新冠纳米颗粒疫苗、标签偶联展示的新冠纳米颗粒疫苗。随着对免疫应答机理的深入研究和对抗原提呈新规律的发现,利用合成生物技术也将有助于充分发掘纳米颗粒疫苗的独特免疫功能、满足高难度疫苗研制的要求。因此有理由相信:在合成生物技术助力下,未来纳米颗粒疫苗将在新突发及重大传染性疾病的防控中做出更突出的贡献。
中图分类号:
引用本文
马雪璟, 郭畅, 华兆琳, 侯百东. 合成生物技术助力纳米颗粒疫苗理性设计时代的到来[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(2): 353-368.
MA Xuejing, GUO Chang, HUA Zhaolin, HOU Baidong. Dawn of the rational design of nanoparticle vaccines aided by the advance of synthetic biology techniques[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(2): 353-368.
| 项目 | 自组装 | 协助组装 | 平台展示 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 商品名 | Nuvaxovid | SCTV01E | CoVLP | VBI-2901/VBI-2902/VBI-2905 | GBP510 | ABNCoV2 | LYB001 |
| 开发商 | Novavax | Sinoce lltech | Medicao | VBI Vaccines | SK Biosciene | Radboud University | Yantai Patronus Biotech |
| 抗原靶点 | S蛋白 | S蛋白 | S蛋白 | S蛋白 | RBD蛋白 | RBD蛋白 | RBD蛋白 |
| 佐剂 | Matrix-M | SCT-VA02B | AS03 | E6020 | AS03 | MF59 | 氢氧化铝 |
| 接种策略 | Day0 + 21 | Day0 | Day0 + 21 | Day0 + 28 | Day0 + 28 | Day0 + 28 | Day0 + 28+56 |
| 临床阶段 | 三期 | 三期 | 三期 | 一期 | 三期 | 三期 | 三期 |
表1 新型冠状病毒纳米颗粒疫苗总结
Table 1 Overview of nanoparticle vaccines for SARS-CoV-2
| 项目 | 自组装 | 协助组装 | 平台展示 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 商品名 | Nuvaxovid | SCTV01E | CoVLP | VBI-2901/VBI-2902/VBI-2905 | GBP510 | ABNCoV2 | LYB001 |
| 开发商 | Novavax | Sinoce lltech | Medicao | VBI Vaccines | SK Biosciene | Radboud University | Yantai Patronus Biotech |
| 抗原靶点 | S蛋白 | S蛋白 | S蛋白 | S蛋白 | RBD蛋白 | RBD蛋白 | RBD蛋白 |
| 佐剂 | Matrix-M | SCT-VA02B | AS03 | E6020 | AS03 | MF59 | 氢氧化铝 |
| 接种策略 | Day0 + 21 | Day0 | Day0 + 21 | Day0 + 28 | Day0 + 28 | Day0 + 28 | Day0 + 28+56 |
| 临床阶段 | 三期 | 三期 | 三期 | 一期 | 三期 | 三期 | 三期 |
| 1 | ROYCHOUDHURY S, DAS A, SENGUPTA P, et al. Viral pandemics of the last four decades: pathophysiology, health impacts and perspectives[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(24): 9411. |
| 2 | PAVLI A, MALTEZOU H C. Travel vaccines throughout history[J]. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease, 2022, 46: 102278. |
| 3 | ZAPPA A, AMENDOLA A, ROMANÒ L, et al. Emerging and re-emerging viruses in the era of globalisation[J]. Blood Transfusion, 2009, 7(3): 167-171. |
| 4 | DI MARCO M, BAKER M L, DASZAK P, et al. Sustainable development must account for pandemic risk[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(8): 3888-3892. |
| 5 | ALFVÉN T, ERKKOLA T, GHYS P, et al. Global AIDS reporting-2001 to 2015: lessons for monitoring the sustainable development goals[J]. AIDS and Behavior, 2017, 21(1): 5-14. |
| 6 | FALCARO M, CASTAÑON A, NDLELA B, et al. The effects of the national HPV vaccination programme in England, UK, on cervical cancer and grade 3 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia incidence: a register-based observational study[J]. The Lancet, 2021, 398(10316): 2084-2092. |
| 7 | KRUGMAN S. The newly licensed hepatitis B vaccine: characteristics and indications for use[J]. JAMA, 1982, 247(14): 2012. |
| 8 | HILLEMAN M R. Vaccines in historic evolution and perspective: a narrative of vaccine discoveries[J]. Vaccine, 2000, 18(15): 1436-1447. |
| 9 | SZMUNESS W, STEVENS C E, HARLEY E J, et al. Hepatitis B vaccine: demonstration of efficacy in a controlled clinical trial in a high-risk population in the United States[J]. New England Journal of Medicine, 1980, 303(15): 833-841. |
| 10 | FRANCIS D P. The safety of the hepatitis B vaccine: inactivation of the AIDS virus during routine vaccine manufacture[J]. JAMA, 1986, 256(7): 869. |
| 11 | VALENZUELA P, MEDINA A, RUTTER W J, et al. Synthesis and assembly of hepatitis B virus surface antigen particles in yeast[J]. Nature, 1982, 298(5872): 347-350. |
| 12 | MCALEER W J, BUYNAK E B, MAIGETTER R Z, et al. Human hepatitis B vaccine from recombinant yeast[J]. Nature, 1984, 307(5947): 178-180. |
| 13 | SIMON P, DUPOND I. Anti-HPV vaccination: preventing cervical cancer[J]. Revue Medicale De Bruxelles, 2006, 27(4): S338-S340. |
| 14 | WIDDICE L E, KAHN J A. Using the new HPV vaccines in clinical practice[J]. Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine, 2006, 73(10): 929-935. |
| 15 | FAIT T, DVOŘÁK V, PILKA R. Nine-valent HPV vaccine-new generation of HPV vaccine[J]. Ceska Gynekologie, 2015, 80(6): 397-400. |
| 16 | BASU P, MALVI S G, JOSHI S, et al. Vaccine efficacy against persistent human papillomavirus (HPV) 16/18 infection at 10 years after one, two, and three doses of quadrivalent HPV vaccine in girls in India: a multicentre, prospective, cohort study[J]. The Lancet Oncology, 2021, 22(11): 1518-1529. |
| 17 | KIRNBAUER R, BOOY F, CHENG N, et al. Papillomavirus L1 major capsid protein self-assembles into virus-like particles that are highly immunogenic[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1992, 89(24): 12180-12184. |
| 18 | ROSE R C, BONNEZ W, REICHMAN R C, et al. Expression of human papillomavirus type 11 L1 protein in insect cells: in vivo and in vitro assembly of viruslike particles[J]. Journal of Virology, 1993, 67(4): 1936-1944. |
| 19 | LOWY D R, SHILLER J T. Prophylactic human papillomavirus vaccines[J]. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2006, 116(5): 1167-1173. |
| 20 | LI S W, ZHAO Q J, WU T, et al. The development of a recombinant hepatitis E vaccine HEV 239[J]. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, 2015, 11(4): 908-914. |
| 21 | ZHANG J, SHIH J W K, XIA N S. Long-term efficacy of a hepatitis E vaccine[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2015, 372(23): 2265-2266. |
| 22 | ZHU F C, ZHANG J, ZHANG X F, et al. Efficacy and safety of a recombinant hepatitis E vaccine in healthy adults: a large-scale, randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial[J]. The Lancet, 2010, 376(9744): 895-902. |
| 23 | WU G X, JI H Y, GUO X Y, et al. Nanoparticle reinforced bacterial outer-membrane vesicles effectively prevent fatal infection of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae [J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2020, 24: 102148. |
| 24 | SHEN A R, JIN X X, TANG T T, et al. Exosomal vaccine loading T cell epitope peptides of SARS-CoV-2 induces robust CD8+ T cell response in HLA-a transgenic mice[J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2022, 17: 3325-3341. |
| 25 | PRATES-SYED W A, CHAVES L C S, CREMA K P, et al. VLP-based COVID-19 vaccines: an adaptable technology against the threat of new variants[J]. Vaccines, 2021, 9(12): 1409. |
| 26 | MORRISON C. Landmark green light for Mosquirix malaria vaccine[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(10): 1015-1016. |
| 27 | RTS, Clinical Trials Partnership S. Efficacy and safety of RTS, S/AS01 malaria vaccine with or without a booster dose in infants and children in Africa: final results of a phase 3, individually randomised, controlled trial[J]. The Lancet, 2015, 386(9988): 31-45. |
| 28 | LEE L A, WANG Q. Adaptations of nanoscale viruses and other protein cages for medical applications[J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2006, 2(3): 137-149. |
| 29 | CHO K J, SHIN H J, LEE J H, et al. The crystal structure of ferritin from Helicobacter pylori reveals unusual conformational changes for iron uptake[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2009, 390(1): 83-98. |
| 30 | KANEKIYO M, WEI C J, YASSINE H M, et al. Self-assembling influenza nanoparticle vaccines elicit broadly neutralizing H1N1 antibodies[J]. Nature, 2013, 499(7456): 102-106. |
| 31 | LÓPEZ-SAGASETA J, MALITO E, RAPPUOLI R, et al. Self-assembling protein nanoparticles in the design of vaccines[J]. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 14: 58-68. |
| 32 | KANEKIYO M, JOYCE M G, GILLESPIE R A, et al. Mosaic nanoparticle display of diverse influenza virus hemagglutinins elicits broad B cell responses[J]. Nature Immunology, 2019, 20(3): 362-372. |
| 33 | QU Z H, GUO Y L, LI M Z, et al. Recombinant ferritin nanoparticles can induce dendritic cell maturation through TLR4/NF-κB pathway[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2020, 42(12): 2489-2500. |
| 34 | LADENSTEIN R, FISCHER M, BACHER A. The lumazine synthase/riboflavin synthase complex: shapes and functions of a highly variable enzyme system[J]. The FEBS Journal, 2013, 280(11): 2537-2563. |
| 35 | JARDINE J, JULIEN J P, MENIS S, et al. Rational HIV immunogen design to target specific germline B cell receptors[J]. Science, 2013, 340(6133): 711-716. |
| 36 | KATO Y, ABBOTT R K, FREEMAN B L, et al. Multifaceted effects of antigen valency on B cell response composition and differentiation in vivo [J]. Immunity, 2020, 53(3): 548-563.e8. |
| 37 | LEGGAT D J, COHEN K W, WILLIS J R, et al. Vaccination induces HIV broadly neutralizing antibody precursors in humans[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6623): eadd6502. |
| 38 | COHEN K W, DE ROSA S C, FULP W J, et al. A first-in-human germline-targeting HIV nanoparticle vaccine induced broad and publicly targeted helper T cell responses[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2023, 15(697): eadf3309. |
| 39 | BALE J B, GONEN S, LIU Y X, et al. Accurate design of megadalton-scale two-component icosahedral protein complexes[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6297): 389-394. |
| 40 | NGUYEN B, TOLIA N H. Protein-based antigen presentation platforms for nanoparticle vaccines[J]. NPJ Vaccines, 2021, 6: 70. |
| 41 | MARCANDALLI J, FIALA B, OLS S, et al. Induction of potent neutralizing antibody responses by a designed protein nanoparticle vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus[J]. Cell, 2019, 176(6): 1420-1431.e17. |
| 42 | MCLELLAN J S, CHEN M, JOYCE M G, et al. Structure-based design of a fusion glycoprotein vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus[J]. Science, 2013, 342(6158): 592-598. |
| 43 | CRANK M C, RUCKWARDT T J, CHEN M, et al. A proof of concept for structure-based vaccine design targeting RSV in humans[J]. Science, 2019, 365(6452): 505-509. |
| 44 | CHANG L A, PHUNG E, CRANK M C, et al. A prefusion-stabilized RSV F subunit vaccine elicits B cell responses with greater breadth and potency than a postfusion F vaccine[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2022, 14(676): eade0424. |
| 45 | KRARUP A, TRUAN D, FURMANOVA-HOLLENSTEIN P, et al. A highly stable prefusion RSV F vaccine derived from structural analysis of the fusion mechanism[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 8143. |
| 46 | OLS S, LENART K, ARCOVERDE CERVEIRA R, et al. Multivalent antigen display on nanoparticle immunogens increases B cell clonotype diversity and neutralization breadth to pneumoviruses[J]. Immunity, 2023, 56(10): 2425-2441.e14. |
| 47 | Two vaccines (Arexvy and Abrysvo) for prevention of RSV disease[J]. The Medical Letter on Drugs and Therapeutics, 2023, 65(1686): 155-156. |
| 48 | SONI A, KABRA S K, LODHA R. Respiratory syncytial virus infection: an update[J]. Indian Journal of Pediatrics, 2023, 90(12): 1245-1253. |
| 49 | LUA L H L, FAN Y Y, CHANG C, et al. Synthetic biology design to display an 18 kDa rotavirus large antigen on a modular virus-like particle[J]. Vaccine, 2015, 33(44): 5937-5944. |
| 50 | KRATZ P A, BÖTTCHER B, NASSAL M. Native display of complete foreign protein domains on the surface of hepatitis B virus capsids[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(5): 1915-1920. |
| 51 | CHARLTON HUME H K, VIDIGAL J, CARRONDO M J T, et al. Synthetic biology for bioengineering virus-like particle vaccines[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2019, 116(4): 919-935. |
| 52 | MAURER P, BACHMANN M F. Vaccination against nicotine: an emerging therapy for tobacco dependence[J]. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs, 2007, 16(11): 1775-1783. |
| 53 | THRANE S, JANITZEK C M, AGERBÆK M Ø, et al. A novel virus-like particle based vaccine platform displaying the placental malaria antigen VAR2CSA[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(11): e0143071. |
| 54 | THRANE S, JANITZEK C M, MATONDO S, et al. Bacterial superglue enables easy development of efficient virus-like particle based vaccines[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2016, 14: 30. |
| 55 | BRUNE K D, BULDUN C M, LI Y Y, et al. Dual plug-and-display synthetic assembly using orthogonal reactive proteins for twin antigen immunization[J]. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2017, 28(5): 1544-1551. |
| 56 | BRUNE K D, LENEGHAN D B, BRIAN I J, et al. Plug-and-Display: decoration of virus-like particles via isopeptide bonds for modular immunization[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 19234. |
| 57 | LENEGHAN D B, MIURA K, TAYLOR I J, et al. Nanoassembly routes stimulate conflicting antibody quantity and quality for transmission-blocking malaria vaccines[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 3811. |
| 58 | BRUUN T U J, ANDERSSON A M C, DRAPER S J, et al. Engineering a rugged nanoscaffold to enhance plug-and-display vaccination[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(9): 8855-8866. |
| 59 | SHISHOVS M, RUMNIEKS J, DIEBOLDER C, et al. Structure of AP205 coat protein reveals circular permutation in ssRNA bacteriophages[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2016, 428(21): 4267-4279. |
| 60 | GUO C, PENG Y N, LIN L, et al. A pathogen-like antigen-based vaccine confers immune protection against SARS-CoV-2 in non-human Primates[J]. Cell Reports Medicine, 2021, 2(11): 100448. |
| 61 | MA X C, ZOU F, YU F, et al. Nanoparticle vaccines based on the receptor binding domain (RBD) and heptad repeat (HR) of SARS-CoV-2 elicit robust protective immune responses[J]. Immunity, 2020, 53(6): 1315-1330.e9. |
| 62 | MA J P, LEE S M Y, YI C Q, et al. Controllable synthesis of functional nanoparticles by microfluidic platforms for biomedical applications-a review[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2017, 17(2): 209-226. |
| 63 | MANOLOVA V, FLACE A, BAUER M, et al. Nanoparticles target distinct dendritic cell populations according to their size[J]. European Journal of Immunology, 2008, 38(5): 1404-1413. |
| 64 | BAKALAR M H, JOFFE A M, SCHMID E M, et al. Size-dependent segregation controls macrophage phagocytosis of antibody-opsonized targets[J]. Cell, 2018, 174(1): 131-142.e13. |
| 65 | SWARTZ M. The physiology of the lymphatic system[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2001, 50(1/2): 3-20. |
| 66 | REDDY S T, REHOR A, SCHMOEKEL H G, et al. In vivo targeting of dendritic cells in lymph nodes with poly(propylene sulfide) nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2006, 112(1): 26-34. |
| 67 | OUSSOREN C, ZUIDEMA J, CROMMELIN D J A, et al. Lymphatic uptake and biodistribution of liposomes after subcutaneous injection. Ⅱ. Influence of liposomal size, lipid composition and lipid dose[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes, 1997, 1328(2): 261-272. |
| 68 | BACHMANN M F, ZINKERNAGEL R M. Neutralizing antiviral B cell responses[J]. Annual Review of Immunology, 1997, 15: 235-270. |
| 69 | FELDMANN M, EASTEN A. The relationship between antigenic structure and the requirement for thymus-derived cells in the immune response[J]. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 1971, 134(1): 103-119. |
| 70 | BROOKS J F, RIGGS J, MUELLER J L, et al. Molecular basis for potent B cell responses to antigen displayed on particles of viral size[J]. Nature Immunology, 2023, 24(10): 1762-1777. |
| 71 | CARTER R H, MYERS R. Germinal center structure and function: lessons from CD19[J]. Seminars in Immunology, 2008, 20(1): 43-48. |
| 72 | GATTO D, PFISTER T, JEGERLEHNER A, et al. Complement receptors regulate differentiation of bone marrow plasma cell precursors expressing transcription factors Blimp-1 and XBP-1[J]. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 2005, 201(6): 993-1005. |
| 73 | MARTINS G, CALAME K. Regulation and functions of Blimp-1 in T and B lymphocytes[J]. Annual Review of Immunology, 2008, 26: 133-169. |
| 74 | KOZLOVSKA T M, CIELĒNS I, DREILINŅA D, et al. Recombinant RNA phage Qβ capsid particles synthesized and self-assembled in Escherichia coli [J]. Gene, 1993, 137(1): 133-137. |
| 75 | HOU B D, SAUDAN P, OTT G, et al. Selective utilization of toll-like receptor and MyD88 signaling in B cells for enhancement of the antiviral germinal center response[J]. Immunity, 2011, 34(3): 375-384. |
| 76 | TIAN M J, HUA Z L, HONG S, et al. B cell–intrinsic MyD88 signaling promotes initial cell proliferation and differentiation to enhance the germinal center response to a virus-like particle[J]. The Journal of Immunology, 2018, 200(3): 937-948. |
| 77 | HONG S, ZHANG Z M, LIU H T, et al. B cells are the dominant antigen-presenting cells that activate naive CD4+ T cells upon immunization with a virus-derived nanoparticle antigen[J]. Immunity, 2018, 49(4): 695-708.e4. |
| 78 | HUA Z L, HOU B D. The role of B cell antigen presentation in the initiation of CD4+ T cell response[J]. Immunological Reviews, 2020, 296(1): 24-35. |
| 79 | ITANO A A, MCSORLEY S J, REINHARDT R L, et al. Distinct dendritic cell populations sequentially present antigen to CD4 T cells and stimulate different aspects of cell-mediated immunity[J]. Immunity, 2003, 19(1): 47-57. |
| 80 | 华兆琳, 侯百东. “自我”与“非我”免疫识别新机理与创新疫苗发展[J]. 中国科学基金, 2020, 34(5): 565-572. |
| HUA Z L, HOU B D. New immune mechanism of “self vs non-self” discrimination and its implication in designing novel vaccines[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2020, 34(5): 565-572. | |
| 81 | QU L, YI Z Y, SHEN Y, et al. Circular RNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(10): 1728-1744.e16. |
| 82 | KOBIYAMA K, ISHII K J. Making innate sense of mRNA vaccine adjuvanticity[J]. Nature Immunology, 2022, 23(4): 474-476. |
| 83 | WHO. COVID-19 vaccine tracker and landscape[EB/OL]. (2023-03-30)[2023-03-30]. . |
| 84 | TIAN J H, PATEL N, HAUPT R, et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein vaccine candidate NVX-CoV2373 immunogenicity in baboons and protection in mice[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 372. |
| 85 | REIMER J M, KARLSSON K H, LÖVGREN-BENGTSSON K, et al. Matrix-M™ adjuvant induces local recruitment, activation and maturation of central immune cells in absence of antigen[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(7): e41451. |
| 86 | HEATH P T, GALIZA E P, BAXTER D N, et al. Safety and efficacy of NVX-CoV2373 COVID-19 vaccine[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2021, 385(13): 1172-1183. |
| 87 | WANG R, HUANG H P, YU C L, et al. A spike-trimer protein-based tetravalent COVID-19 vaccine elicits enhanced breadth of neutralization against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants and other variants[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2023, 66(8): 1818-1830. |
| 88 | MEIER S, GÜTHE S, KIEFHABER T, et al. Foldon, the natural trimerization domain of T4 fibritin, dissociates into a monomeric A-state form containing a stable β-hairpin: atomic details of trimer dissociation and local β-hairpin stability from residual dipolar couplings[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2004, 344(4): 1051-1069. |
| 89 | WANG R, HUANG X, CAO T S, et al. Development of a thermostable SARS-CoV-2 variant-based bivalent protein vaccine with cross-neutralizing potency against Omicron subvariants[J]. Virology, 2022, 576: 61-68. |
| 90 | WANG R, SUN C Y, MA J, et al. A bivalent COVID-19 vaccine based on alpha and beta variants elicits potent and broad immune responses in mice against SARS-CoV-2 variants[J]. Vaccines, 2022, 10(5): 702. |
| 91 | HANNAWI S, SAIFELDIN L, ABUQUTA A, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a tetravalent and bivalent SARS-CoV-2 protein booster vaccine in men[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 4043. |
| 92 | WARD B J, GOBEIL P, SÉGUIN A, et al. Phase 1 randomized trial of a plant-derived virus-like particle vaccine for COVID-19[J]. Nature Medicine, 2021, 27(6): 1071-1078. |
| 93 | HAGER K J, PÉREZ MARC G, GOBEIL P, et al. Efficacy and safety of a recombinant plant-based adjuvanted covid-19 vaccine[J]. New England Journal of Medicine, 2022, 386(22): 2084-2096. |
| 94 | KIRCHMEIER M, FLUCKIGER A C, SOARE C, et al. Enveloped virus-like particle expression of human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B antigen induces antibodies with potent and broad neutralizing activity[J]. Clinical and Vaccine Immunology, 2014, 21(2): 174-180. |
| 95 | FLUCKIGER A C, ONTSOUKA B, BOZIC J, et al. An enveloped virus-like particle vaccine expressing a stabilized prefusion form of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein elicits highly potent immunity[J]. Vaccine, 2021, 39(35): 4988-5001. |
| 96 | WALLS A, FIALA B, SCHÄFER A, et al. Elicitation of potent neutralizing antibody responses by designed protein nanoparticle vaccines for SARS-CoV-2[J]. Cell, 2020, 183: 1367-1382.e17. |
| 97 | JACOB-DOLAN C, YU J Y, MCMAHAN K, et al. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of GBP510/AS03 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 delta challenge in rhesus macaques[J]. NPJ Vaccines, 2023, 8: 23. |
| 98 | FOUGEROUX C, GOKSØYR L, IDORN M, et al. Capsid-like particles decorated with the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain elicit strong virus neutralization activity[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 324. |
| 99 | LI Y Y, ZHANG Y N, ZHOU Y, et al. An RBD virus-like particle vaccine for SARS-CoV-2 induces cross-variant antibody responses in mice and macaques[J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2023, 8: 173. |
| 100 | MIQUEL C H, ABBAS F, CENAC C, et al. B cell-intrinsic TLR7 signaling is required for neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 and pathogen-like COVID-19 vaccines[J]. European Journal of Immunology, 2023, 53(10): e2350437. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [12] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [13] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [14] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [15] | 查文龙, 卜兰, 訾佳辰. 中药药效成分群的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||