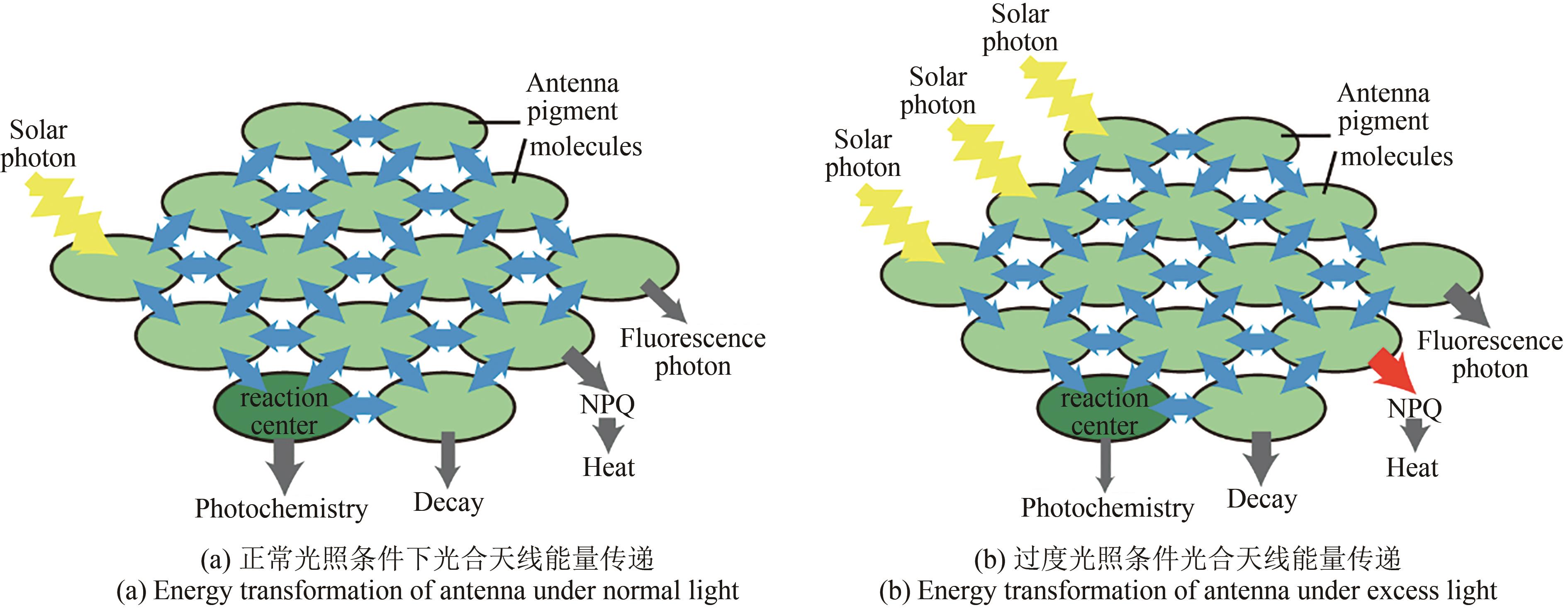
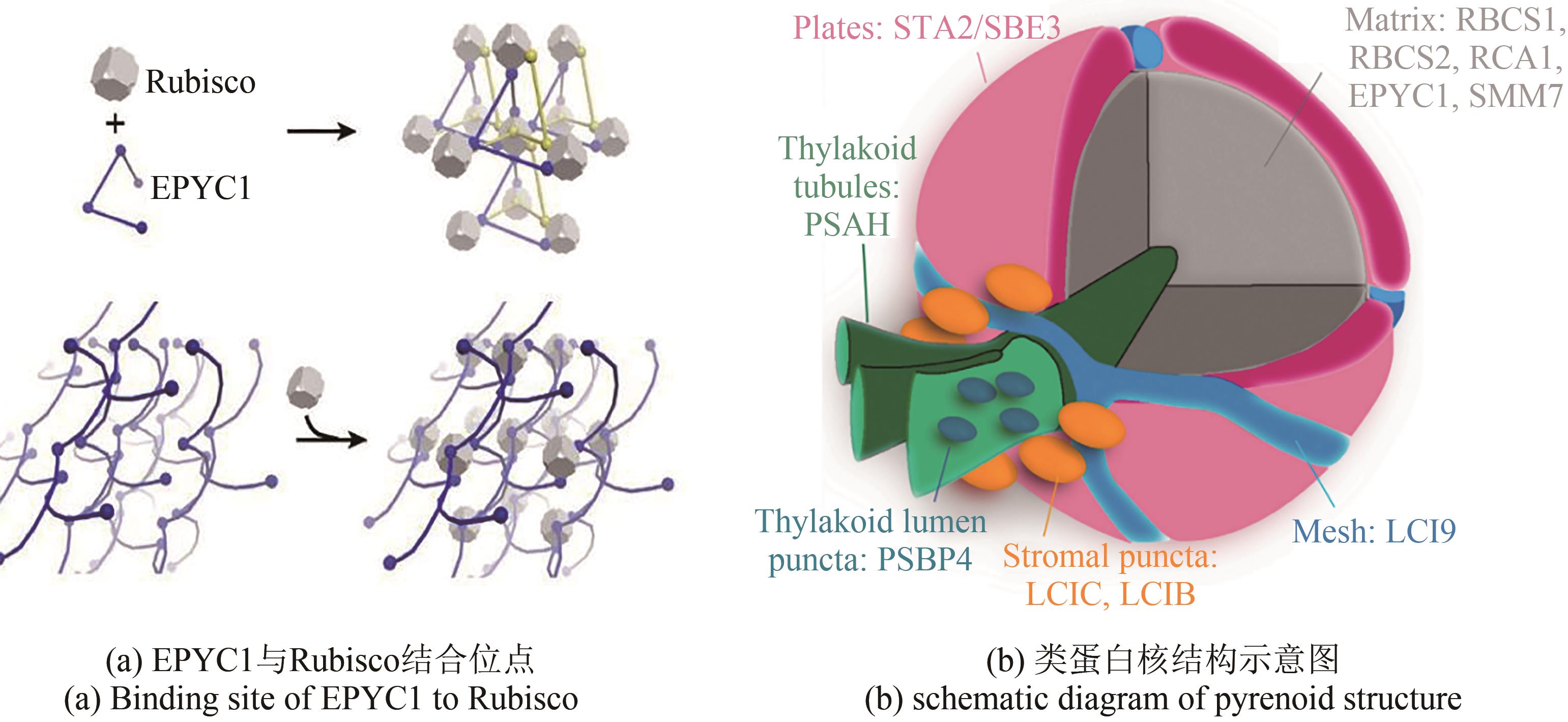
合成生物学 ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (5): 985-1005.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2022-002
植物二氧化碳代谢途径改造研究进展
史梦琳1,2, 周琳1,3, 王庆1,3, 赵磊1,2,3
- 1.中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所,天津 300308
2.中国科学院系统微生物工程重点实验室,天津 300308
3.国家合成生物技术创新中心,天津 300308
-
收稿日期:2022-01-12修回日期:2022-02-17出版日期:2022-10-31发布日期:2022-11-16 -
通讯作者:赵磊 -
作者简介:史梦琳 (1991—),女,博士后。研究方向为植物固碳途径解析与改造等。 E-mail:shiml@tib.cas.cn赵磊 (1985—),男,博士,研究员。研究方向为植物合成生物学与代谢工程等。 E-mail:zhaol@tib.cas.cn -
基金资助:天津市合成生物技术创新能力提升行动项目(TSBICIP-CXRC-027);中国科技部科技合作计划项目(KY202001017)
Advances in the study on the modification of carbon dioxide metabolic pathways in plants
SHI Menglin1,2, ZHOU Lin1,3, WANG Qing1,3, ZHAO Lei1,2,3
- 1.Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Tianjin 300308,China
2.Key Laboratory of Systems Microbial Biotechnology,Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Tianjin 300308,China
3.National Center of Technology Innovation for Synthetic Biology,Tianjin 300308,China
-
Received:2022-01-12Revised:2022-02-17Online:2022-10-31Published:2022-11-16 -
Contact:ZHAO Lei
摘要:
降碳减排是我国可持续发展过程中的一项重大战略决策。为如期实现“碳达峰、碳中和”宏伟目标,我国需在提高生态碳汇能力上取得突破。植物光合作用有利于增加地球碳汇,而光呼吸和呼吸作用过程则释放CO2。自然状态下,上述CO2代谢过程能量利用率低、人工改造并提高植物CO2固定的难度较大。因此,在植物体内重构新的人工代谢途径,有望大幅提高植物CO2固定能力,是解决人类社会发展瓶颈的有效途径之一。本文分别介绍了植物光合作用、光呼吸和呼吸作用中与CO2固定、释放相关途径,并指出可用于改造的潜在靶点;重点综述了植物体内已构建的人工固碳途径及其代谢原理,系统分析评价了不同途径的CO2固定能力和限制因素;最后,对人工设计及合成植物CO2代谢通路、基于零碳排放的新型物质生产等关键问题进行了探讨,并对植物CO2代谢途径的改造发展趋势进行了展望。
中图分类号:
引用本文
史梦琳, 周琳, 王庆, 赵磊. 植物二氧化碳代谢途径改造研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(5): 985-1005.
SHI Menglin, ZHOU Lin, WANG Qing, ZHAO Lei. Advances in the study on the modification of carbon dioxide metabolic pathways in plants[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(5): 985-1005.
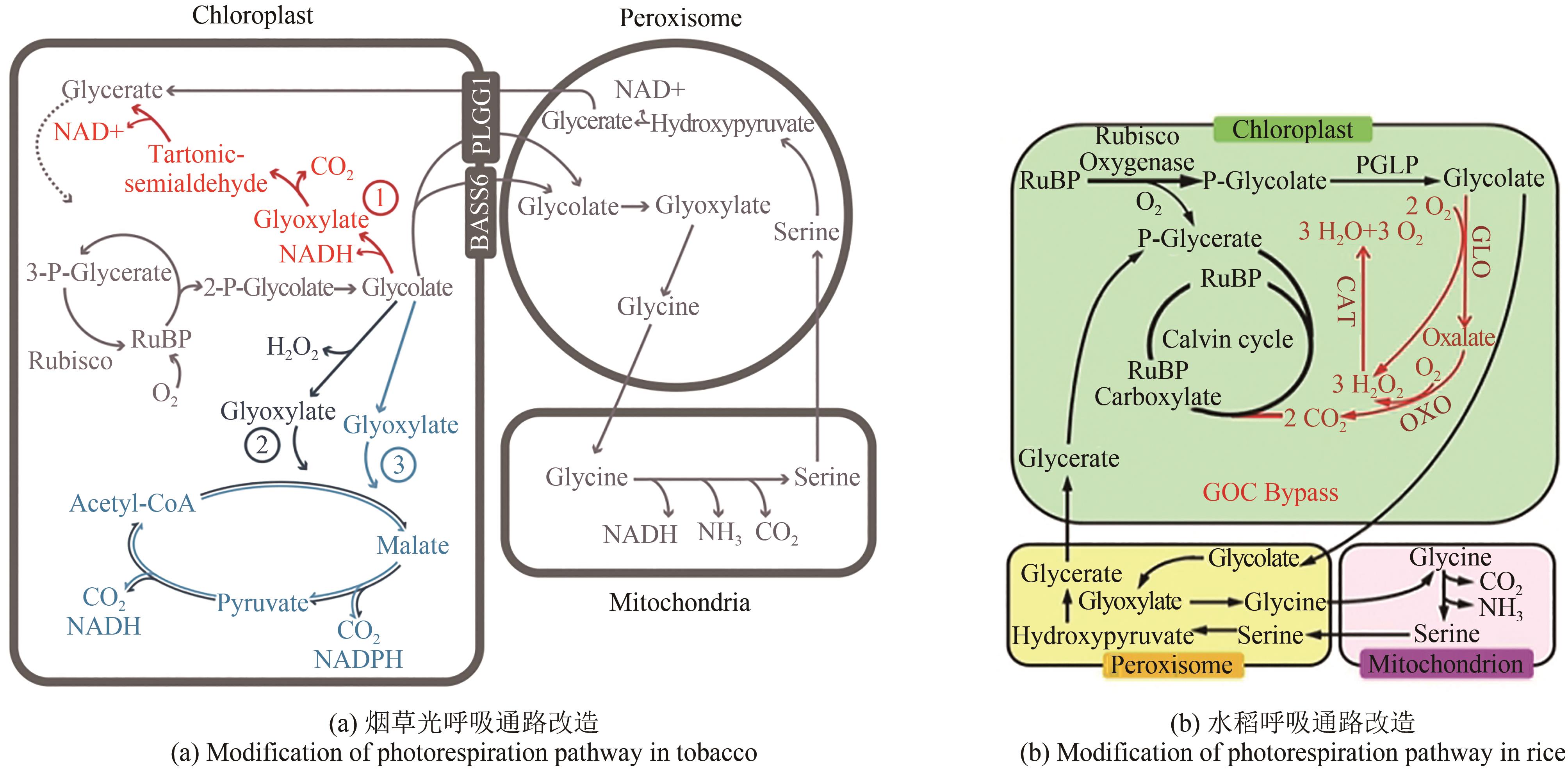
图4 以增加叶绿体中CO2浓度为目的的光呼吸通路改造[106,118-119]
Fig. 4 Photorespiration pathway modification aimed at increasing CO2 concentration in chloroplasts[106, 118-119]

图5 植物碳代谢改造潜在靶点图示(★光合固碳改造;★光呼吸途径改造;★:呼吸作用途径改造)1—天然光合作用元件改造;2—外源蛋白导入以优化光合效率;3—Rubisco优化设计以提高其羧化能力;4—增加CO2供给能力;5—天然光呼吸途径的改造或新型光呼吸替代途径的构建;6,7—增加光呼吸通量或代谢中间产物再利用;8—呼吸作用途径改造(AOX调整)
Fig. 5 Schematic diagram of potential targets for carbon metabolism modification in plants(★Photosynthesis modification; ★Photorespiration modification; ★Respiration modification) 1—Modification of natural photosynthetic elements; 2—Exogenous protein are introduced to optimize photosynthetic efficiency; 3—Rubisco optimization design to improve its carboxylation capacity; 4—Increase CO2 supply capacity; 5—Reconstruction of natural photorespiration pathway or construction of alternative pathway for new photorespiration; 6, 7—Increase photorespiration flux or reuse of metabolic intermediates; 8—Modification of respiratory pathway (AOX adjustment)
| 涉及部分 | 改造对象或方式 | 改造效果 |
|---|---|---|
| 光合作用 | 光系统天线 | 降低光损耗、提高光能利用率和生物量 |
| 光系统对波动光的响应能力 | 有望提高光系统对波动光的响应能力,减少光抑制 | |
| 天然光合系统吸光范围 | 有望将植物吸光范围扩展到远红区域,进而增强光合效率 | |
| CO2扩散能力 | 可改善叶片内部CO2扩散特性,是提高光合效率的有效途径;其扩散能力与温度、细胞壁厚度和组成等均相关。由于叶片CO2扩散速率测定较为困难,致该部分研究缓慢 | |
| Rubisco催化特性 | Rubisco催化特性改造尚未取得实质性进展;通过筛选不同物种特异性Rubisco或将Rubisco与碳浓缩机制改造相结合,有望改善植物固碳能力 | |
| Rubisco附近的CO2浓度 | 通过将CCM系统、蛋白核或将C4光合系统引入C3作物等,可增加CO2供给。但需要考虑光合过程中生化反应的变化及叶片结构的改变,C3向C4植物转化研究仍待加强 | |
| 光呼吸 | 天然光呼吸途径 | 改造较为复杂,需考虑较多因素;增加光呼吸通量可使植物更好地应对高光呼吸胁迫,提高生物量,但具体改造靶点和策略仍待探索 |
| 新型光呼吸替代途径 | 导入新型光呼吸替代途径,可将毒性副产物化为其他生物质,同时将CO2重新释放到叶绿体中,在提高CO2浓度的同时减少植物固碳损失;基于零CO2释放的新型替代通路,可避免光呼吸中的碳损失,在增加植物固碳方面有较大潜力 | |
| 光呼吸代谢通量模型计算 | 将计算技术与基因组工程、合成生物学技术等技术结合,进行代谢通量模型分析,可简化和评估光呼吸通路改造设计,优化实验设计 | |
| 呼吸作用 | 交替氧化酶AOX | 呼吸作用对植物基础代谢尤为重要,对其进行改造的操作空间较小;不同体系和生长条件下,AOX表达量变化对固碳和生长影响不同,对其进行有效改造的策略仍待探索中 |
表1 植物固碳改造策略与效果
Tab.1 Modification strategies for plant carbon sequestration and their effects
| 涉及部分 | 改造对象或方式 | 改造效果 |
|---|---|---|
| 光合作用 | 光系统天线 | 降低光损耗、提高光能利用率和生物量 |
| 光系统对波动光的响应能力 | 有望提高光系统对波动光的响应能力,减少光抑制 | |
| 天然光合系统吸光范围 | 有望将植物吸光范围扩展到远红区域,进而增强光合效率 | |
| CO2扩散能力 | 可改善叶片内部CO2扩散特性,是提高光合效率的有效途径;其扩散能力与温度、细胞壁厚度和组成等均相关。由于叶片CO2扩散速率测定较为困难,致该部分研究缓慢 | |
| Rubisco催化特性 | Rubisco催化特性改造尚未取得实质性进展;通过筛选不同物种特异性Rubisco或将Rubisco与碳浓缩机制改造相结合,有望改善植物固碳能力 | |
| Rubisco附近的CO2浓度 | 通过将CCM系统、蛋白核或将C4光合系统引入C3作物等,可增加CO2供给。但需要考虑光合过程中生化反应的变化及叶片结构的改变,C3向C4植物转化研究仍待加强 | |
| 光呼吸 | 天然光呼吸途径 | 改造较为复杂,需考虑较多因素;增加光呼吸通量可使植物更好地应对高光呼吸胁迫,提高生物量,但具体改造靶点和策略仍待探索 |
| 新型光呼吸替代途径 | 导入新型光呼吸替代途径,可将毒性副产物化为其他生物质,同时将CO2重新释放到叶绿体中,在提高CO2浓度的同时减少植物固碳损失;基于零CO2释放的新型替代通路,可避免光呼吸中的碳损失,在增加植物固碳方面有较大潜力 | |
| 光呼吸代谢通量模型计算 | 将计算技术与基因组工程、合成生物学技术等技术结合,进行代谢通量模型分析,可简化和评估光呼吸通路改造设计,优化实验设计 | |
| 呼吸作用 | 交替氧化酶AOX | 呼吸作用对植物基础代谢尤为重要,对其进行改造的操作空间较小;不同体系和生长条件下,AOX表达量变化对固碳和生长影响不同,对其进行有效改造的策略仍待探索中 |
| 1 | KEENAN T F, WILLIAMS C A. The terrestrial carbon sink[J]. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 2018, 43: 219-243. |
| 2 | DUSENGE M E, DUARTE A G, WAY D A. Plant carbon metabolism and climate change: elevated CO2 and temperature impacts on photosynthesis, photorespiration and respiration[J]. The New Phytologist, 2019, 221(1): 32-49. |
| 3 | BAUWE H, KOLUKISAOGLU Ü. Genetic manipulation of glycine decarboxylation[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2003, 54(387): 1523-1535. |
| 4 | PETERHANSEL C, HORST I, NIESSEN M, et al. Photorespiration[J]. Arabidopsis Book, 2010, 8: e0130. |
| 5 | TIMM S, HAGEMANN M. Photorespiration—how is it regulated and how does it regulate overall plant metabolism? [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2020, 71(14): 3955-3965. |
| 6 | LONG S P, MARSHALL-COLON A, ZHU X G. Meeting the global food demand of the future by engineering crop photosynthesis and yield potential[J]. Cell, 2015, 161(1): 56-66. |
| 7 | MELIS A. Solar energy conversion efficiencies in photosynthesis: minimizing the chlorophyll antennae to maximize efficiency[J]. Plant Science, 2009, 177(4): 272-280. |
| 8 | ORT D R, ZHU X G, et al. Optimizing antenna size to maximize photosynthetic efficiency[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 155(1): 79-85. |
| 9 | ORT D R, MERCHANT S S, ALRIC J, et al. Redesigning photosynthesis to sustainably meet global food and bioenergy demand[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(28): 8529-8536. |
| 10 | MITRA M, KIRST H, DEWEZ D, et al. Modulation of the light-harvesting chlorophyll antenna size in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by TLA1 gene over-expression and RNA interference[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B, Biological Sciences, 2012, 367(1608): 3430-3443. |
| 11 | KIRST H, GARCÍA-CERDÁN J G, ZURBRIGGEN A, et al. Assembly of the light-harvesting chlorophyll antenna in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii requires expression of the TLA2-CpFTSY gene[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 158(2): 930-945. |
| 12 | ZHU X G, LONG S P, ORT D R. Improving photosynthetic efficiency for greater yield[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010, 61: 235-261. |
| 13 | MURCHIE E H, NIYOGI K K. Manipulation of photoprotection to improve plant photosynthesis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 155(1): 86-92. |
| 14 | NILKENS M, KRESS E, LAMBREV P, et al. Identification of a slowly inducible Zeaxanthin-dependent component of non-photochemical quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence generated under steady-state conditions in Arabidopsis [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 2010, 1797(4): 466-475. |
| 15 | NOCTOR G, REES D, YOUNG A, et al. The relationship between Zeaxanthin, energy-dependent quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence, and trans-thylakoid pH gradient in isolated chloroplasts[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 1991, 1057(3): 320-330. |
| 16 | LI X P, BJÖRKMAN O, SHIH C, et al. A pigment-binding protein essential for regulation of photosynthetic light harvesting[J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6768): 391-395. |
| 17 | CROUCHMAN S, RUBAN A, HORTON P. PsbS enhances nonphotochemical fluorescence quenching in the absence of Zeaxanthin[J]. FEBS Letters, 2006, 580(8): 2053-2058. |
| 18 | LI X P, MULLER-MOULE P, GILMORE A M, et al. PsbS-dependent enhancement of feedback de-excitation protects photosystem II from photoinhibition[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(23): 15222-15227. |
| 19 | GŁOWACKA K, KROMDIJK J, KUCERA K, et al. Photosystem II Subunit S overexpression increases the efficiency of water use in a field-grown crop[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 868. |
| 20 | NIYOGI K K, GROSSMAN A R, BJÖRKMAN O. Arabidopsis mutants define a central role for the xanthophyll cycle in the regulation of photosynthetic energy conversion[J]. The Plant Cell, 1998, 10(7): 1121-1134. |
| 21 | JAHNS P, LATOWSKI D, STRZALKA K. Mechanism and regulation of the violaxanthin cycle: the role of antenna proteins and membrane lipids[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics, 2009, 1787(1): 3-14. |
| 22 | LI L, NELSON C J, TRÖSCH J, et al. Protein degradation rate in Arabidopsis thaliana leaf growth and development[J]. The Plant Cell, 2017, 29(2): 207-228. |
| 23 | LI L, ARO E M, MILLAR A H. Mechanisms of photodamage and protein turnover in photoinhibition[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2018, 23(8): 667-676. |
| 24 | KROMDIJK J, GŁOWACKA K, LEONELLI L, et al. Improving photosynthesis and crop productivity by accelerating recovery from photoprotection[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6314): 857-861. |
| 25 | BLANKENSHIP R E, CHEN M. Spectral expansion and antenna reduction can enhance photosynthesis for energy production[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2013, 17(3): 457-461. |
| 26 | LI Y Q, CHEN M. Novel chlorophylls and new directions in photosynthesis research[J]. Functional Plant Biology: FPB, 2015, 42(6): 493-501. |
| 27 | EVANS J R, VON CAEMMERER S. Carbon dioxide diffusion inside leaves[J]. Plant Physiology, 1996, 110(2): 339-346. |
| 28 | FLEXAS J, NIINEMETS U, GALLÉ A, et al. Diffusional conductances to CO2 as a target for increasing photosynthesis and photosynthetic water-use efficiency[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2013, 117(1/2/3): 45-59. |
| 29 | VON CAEMMERER S, EVANS J R. Temperature responses of mesophyll conductance differ greatly between species[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2015, 38(4): 629-637. |
| 30 | GROSZMANN M, OSBORN H L, EVANS J R. Carbon dioxide and water transport through plant aquaporins[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2017, 40(6): 938-961. |
| 31 | UBIERNA N, GANDIN A, BOYD R A, et al. Temperature response of mesophyll conductance in three C4 species calculated with two methods: 18O discrimination and in vitro Vpmax [J]. The New Phytologist, 2017, 214(1): 66-80. |
| 32 | EVANS J R, KALDENHOFF R, GENTY B, et al. Resistances along the CO2 diffusion pathway inside leaves[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2009, 60(8): 2235-2248. |
| 33 | ELLSWORTH P V, ELLSWORTH P Z, KOTEYEVA N K, et al. Cell wall properties in Oryza sativa influence mesophyll CO2 conductance[J]. The New Phytologist, 2018, 219(1): 66-76. |
| 34 | SOMERVILLE C R, OGREN W L. Genetic modification of photorespiration[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 1982, 7(5): 171-174. |
| 35 | MUELLER-CAJAR O, WHITNEY S M. Directing the evolution of Rubisco and Rubisco activase: first impressions of a new tool for photosynthesis research[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2008, 98(1/2/3): 667-675. |
| 36 | WHITNEY S M, SHARWOOD R E. Construction of a tobacco master line to improve Rubisco engineering in chloroplasts[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2008, 59(7): 1909-1921. |
| 37 | TCHERKEZ G G B, FARQUHAR G D, ANDREWS T J. Despite slow catalysis and confused substrate specificity, all ribulose bisphosphate carboxylases may be nearly perfectly optimized[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(19): 7246-7251. |
| 38 | SAVIR Y, NOOR E, MILO R, et al. Cross-species analysis traces adaptation of Rubisco toward optimality in a low-dimensional landscape[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(8): 3475-3480. |
| 39 | YOUNG J N, HEUREUX A M C, SHARWOOD R E, et al. Large variation in the Rubisco kinetics of diatoms reveals diversity among their carbon-concentrating mechanisms[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(11): 3445-3456. |
| 40 | ORR D J, ALCÂNTARA A, KAPRALOV M V, et al. Surveying Rubisco diversity and temperature response to improve crop photosynthetic efficiency[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 172(2): 707-717. |
| 41 | PRINS A, ORR D J, ANDRALOJC P J, et al. Rubisco catalytic properties of wild and domesticated relatives provide scope for improving wheat photosynthesis[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(6): 1827-1838. |
| 42 | LIN M T, OCCHIALINI A, ANDRALOJC P J, et al. A faster Rubisco with potential to increase photosynthesis in crops[J]. Nature, 2014, 513(7519): 547-550. |
| 43 | LIN M T, HANSON M R. Red algal Rubisco fails to accumulate in transplastomic tobacco expressing Griffithsia monilis rbcL and rbcS genes[J]. Plant Direct, 2018, 2(2): e00045. |
| 44 | AIGNER H, WILSON R H, BRACHER A, et al. Plant RuBisCo assembly in E. coli with five chloroplast chaperones including BSD2[J]. Science, 2017, 358(6368): 1272-1278. |
| 45 | VALEGÅRD K, HASSE D, ANDERSSON I, et al. Structure of rubisco from Arabidopsis thaliana in complex with 2-carboxyarabinitol-1, 5-bisphosphate[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section D, Structural Biology, 2018, 74(Pt 1): 1-9. |
| 46 | VALEGÅRD K, ANDRALOJC P J, HASLAM R P, et al. Structural and functional analyses of Rubisco from arctic diatom species reveal unusual posttranslational modifications[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2018, 293(34): 13033-13043. |
| 47 | SASCHENBRECKER S, BRACHER A, RAO K V, et al. Structure and function of RbcX, an assembly chaperone for hexadecameric Rubisco[J]. Cell, 2007, 129(6): 1189-1200. |
| 48 | FEIZ L, WILLIAMS-CARRIER R, WOSTRIKOFF K, et al. Ribulose-1,5-bis-phosphate carboxylase/oxygenase accumulation Factor1 is required for holoenzyme assembly in maize[J]. The Plant Cell, 2012, 24(8): 3435-3446. |
| 49 | WHITNEY S M, BIRCH R, KELSO C, et al. Improving recombinant Rubisco biogenesis, plant photosynthesis and growth by coexpressing its ancillary RAF1 chaperone[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(11): 3564-3569. |
| 50 | RAE B D, LONG B M, FÖRSTER B, et al. Progress and challenges of engineering a biophysical CO2-concentrating mechanism into higher plants[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2017, 68(14): 3717-3737. |
| 51 | MORITA E, ABE T, TSUZUKI M, et al. Presence of the CO2-concentrating mechanism in some species of the pyrenoid-less free-living algal genus Chloromonas (Volvocales, Chlorophyta)[J]. Planta, 1998, 204(3): 269-276. |
| 52 | KINNEY J N, AXEN S D, KERFELD C A. Comparative analysis of carboxysome shell proteins[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2011, 109(1/2/3): 21-32. |
| 53 | NIEDERHUBER M J, LAMBERT T J, YAPP C, et al. Superresolution microscopy of the β-carboxysome reveals a homogeneous matrix[J]. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 2017, 28(20): 2734-2745. |
| 54 | SHARWOOD R E. Engineering chloroplasts to improve Rubisco catalysis: prospects for translating improvements into food and fiber crops[J]. The New Phytologist, 2017, 213(2): 494-510. |
| 55 | SOMMER M, CAI F, MELNICKI M, et al. β-Carboxysome bioinformatics: identification and evolution of new bacterial microcompartment protein gene classes and core locus constraints[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2017, 68(14): 3841-3855. |
| 56 | RAE B D, LONG B M, WHITEHEAD L F, et al. Cyanobacterial carboxysomes: microcompartments that facilitate CO2 fixation[J]. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2013, 23(4/5): 300-307. |
| 57 | SHARWOOD R E. A step forward to building an algal pyrenoid in higher plants[J]. The New Phytologist, 2017, 214(2): 496-499. |
| 58 | HANSON M R, LIN M T, CARMO-SILVA A E, et al. Towards engineering carboxysomes into C3 plants[J]. The Plant Journal: for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2016, 87(1): 38-50. |
| 59 | OCCHIALINI A, LIN M T, ANDRALOJC P J, et al. Transgenic tobacco plants with improved cyanobacterial Rubisco expression but no extra assembly factors grow at near wild-type rates if provided with elevated CO2 [J]. The Plant Journal, 2016, 85(1): 148-160. |
| 60 | WANG H, YAN X, AIGNER H, et al. Rubisco condensate formation by CcmM in β-carboxysome biogenesis[J]. Nature, 2019, 566(7742): 131-135. |
| 61 | LONG B M, HEE W Y, SHARWOOD R E, et al. Carboxysome encapsulation of the CO2-fixing enzyme Rubisco in tobacco chloroplasts[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3570. |
| 62 | MEYER M T, GENKOV T, SKEPPER J N, et al. Rubisco small-subunit α-helices control pyrenoid formation in Chlamydomonas [J]. PNAS, 2012, 109(47): 19474-19479. |
| 63 | MACKINDER L C M, MEYER M T, METTLER-ALTMANN T, et al. A repeat protein links Rubisco to form the eukaryotic carbon-concentrating organelle[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(21): 5958-5963. |
| 64 | ATKINSON N, LEITÃO N, ORR D J, et al. Rubisco small subunits from the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas complement Rubisco-deficient mutants of Arabidopsis [J]. The New Phytologist, 2017, 214(2): 655-667. |
| 65 | MACKINDER L C M, CHEN C, LEIB R D, et al. A spatial interactome reveals the protein organization of the algal CO2-concentrating mechanism[J]. Cell, 2017, 171(1): 133-147.e14. |
| 66 | SAGE R F, SAGE T L, KOCACINAR F. Photorespiration and the evolution of C4 photosynthesis[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2012, 63: 19-47. |
| 67 | SCHLÜTER U, WEBER A P M. The road to C4 photosynthesis: evolution of a complex trait via intermediary states[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2016, 57(5): 881-889. |
| 68 | FURBANK R T. Walking the C4 pathway: past, present, and future[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(14): 4057-4066. |
| 69 | MATSUOKA M, FURBANK R T, FUKAYAMA H, et al. Molecular engineering of C4 photosynthesis[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 2001, 52: 297-314. |
| 70 | SCHULER M L, MANTEGAZZA O, WEBER A P. Engineering C4 photosynthesis into C3 chassis in the synthetic biology age[J]. The Plant Journal, 2016, 87(1): 51-65. |
| 71 | VON CAEMMERER S, QUICK W P, FURBANK R T. The development of C₄ rice: current progress and future challenges[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6089): 1671-1672. |
| 72 | LAKSHMI N M, BINOD P, SINDHU R, et al. Microbial engineering for the production of isobutanol: current status and future directions[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(2): 12308-12321. |
| 73 | VANHERCKE T, BELIDE S, TAYLOR M C, et al. Up-regulation of lipid biosynthesis increases the oil content in leaves of Sorghum bicolor [J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17(1): 220-232. |
| 74 | LI P H, BRUTNELL T P. Setaria viridis and Setaria italica, model genetic systems for the Panicoid grasses[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(9): 3031-3037. |
| 75 | BAR-EVEN A, NOOR E, LEWIS N E, et al. Design and analysis of synthetic carbon fixation pathways[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(19): 8889-8894. |
| 76 | SHIH P M, ZARZYCKI J, NIYOGI K K, et al. Introduction of a synthetic CO2-fixing photorespiratory bypass into a cyanobacterium[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2014, 289(14): 9493-9500. |
| 77 | PETTIGREW W T, HESKETH J D, PETERS D B, et al. Characterization of canopy photosynthesis of chlorophyll-deficient soybean isolines[J]. Crop Science, 1989, 29(4): 1025-1029. |
| 78 | KIRST H, GABILLY S T, NIYOGI K K, et al. Photosynthetic antenna engineering to improve crop yields[J]. Planta, 2017, 245(5): 1009-1020. |
| 79 | JIN H L, LI M S, DUAN S J, et al. Optimization of light-harvesting pigment improves photosynthetic efficiency[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 172(3): 1720-1731. |
| 80 | DECKER J P. A rapid, postillumination deceleration of respiration in green leaves[J]. Plant Physiology, 1955, 30(1): 82-84. |
| 81 | ZELITCH I. Increased rate of net photosynthetic carbon dioxide uptake caused by the inhibition of glycolate oxidase[J]. Plant Physiology, 1966, 41(10): 1623-1631. |
| 82 | ZELITCH I. The effect of glycidate, an inhibitor of glycolate synthesis, on photorespiration and net photosynthesis[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 1974, 163(1): 367-377. |
| 83 | TOLBERT N E. Microbodies-peroxisomes and glyoxysomes[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology, 1971, 22: 45-74. |
| 84 | GRIFFITHS H. Designs on Rubisco[J]. Nature, 2006, 441(7096): 940-941. |
| 85 | EHLERINGER J R, SAGE R F, FLANAGAN L B, et al. Climate change and the evolution of C4 photosynthesis[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 1991, 6(3): 95-99. |
| 86 | DELLERO Y, JOSSIER M, SCHMITZ J, et al. Photorespiratory glycolate-glyoxylate metabolism[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(10): 3041-3052. |
| 87 | ZABALETA E, MARTIN M V, BRAUN H P. A basal carbon concentrating mechanism in plants? [J]. Plant Science, 2012, 187: 97-104. |
| 88 | ANDERSON L E. Chloroplast and cytoplasmic enzymes (II): Pea leaf triose phosphate isomerases[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Enzymology, 1971, 235(1): 237-244. |
| 89 | KELLY G J, LATZKO E. Inhibition of spinach-leaf phosphofructokinase by 2-phosphoglycollate[J]. FEBS Letters, 1976, 68(1): 55-58. |
| 90 | ENGQVIST M K M, SCHMITZ J, GERTZMANN A, et al. GLYCOLATE OXIDASE3, a glycolate oxidase homolog of yeast l-lactate cytochrome c oxidoreductase, supports l-lactate oxidation in roots of Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiology, 2015, 169(2): 1042-1061. |
| 91 | CAMPBELL W J, OGREN W L. Glyoxylate inhibition of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activation in intact, lysed, and reconstituted chloroplasts[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 1990, 23(3): 257-268. |
| 92 | COOK C M, MULLIGAN R M, TOLBERT N E. Inhibition and stimulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase by glyoxylate[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 1985, 240(1): 392-401. |
| 93 | CHASTAIN C J, OGREN W L. Photorespiration-induced reduction of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activation level[J]. Plant Physiology, 1985, 77(4): 851-856. |
| 94 | WALKER B J, VANLOOCKE A, BERNACCHI C J, et al. The costs of photorespiration to food production now and in the future[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2016, 67: 107-129. |
| 95 | RAINES C A. Transgenic approaches to manipulate the environmental responses of the C3 carbon fixation cycle[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2006, 29(3): 331-339. |
| 96 | PETERHANSEL C, BLUME C, OFFERMANN S. Photorespiratory bypasses: how can they work? [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 64(3): 709-715. |
| 97 | MAURINO V G, WEBER A P M. Engineering photosynthesis in plants and synthetic microorganisms[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 64(3): 743-751. |
| 98 | SOMERVILLE C R, OGREN W L. A phosphoglycolate phosphatase-deficient mutant of Arabidopsis [J]. Nature, 1979, 280(5725): 833-836. |
| 99 | HALL N P, KENDALL A C, LEA P J, et al. Characteristics of a photorespiratory mutant of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) deficient in phosphogly collate phosphatase[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 1987, 11(1): 89-96. |
| 100 | MURRAY A J S, BLACKWELL R D, LEA P J. Metabolism of hydroxypyruvate in a mutant of barley lacking NADH-dependent hydroxypyruvate reductase, an important photorespiratory enzyme activity[J]. Plant Physiology, 1989, 91(1): 395-400. |
| 101 | BOLDT R, EDNER C, KOLUKISAOGLU U, et al. D-GLYCERATE 3-KINASE, the last unknown enzyme in the photorespiratory cycle in Arabidopsis, belongs to a novel kinase family[J]. The Plant Cell, 2005, 17(8): 2413-2420. |
| 102 | SCHWARTE S, BAUWE H. Identification of the photorespiratory 2-phosphoglycolate phosphatase, PGLP1, in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiology, 2007, 144(3): 1580-1586. |
| 103 | TIMM S, NUNES-NESI A, PÄRNIK T, et al. A cytosolic pathway for the conversion of hydroxypyruvate to glycerate during photorespiration in Arabidopsis [J]. The Plant Cell, 2008, 20(10): 2848-2859. |
| 104 | TIMM S, FLORIAN A, ARRIVAULT S, et al. Glycine decarboxylase controls photosynthesis and plant growth[J]. FEBS Letters, 2012, 586(20): 3692-3697. |
| 105 | PICK T R, BRÄUTIGAM A, SCHULZ M A, et al. PLGG1, a plastidic glycolate glycerate transporter, is required for photorespiration and defines a unique class of metabolite transporters[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(8): 3185-3190. |
| 106 | SOUTH P F, WALKER B J, CAVANAGH A P, et al. Bile acid sodium symporter BASS6 can transport glycolate and is involved in photorespiratory metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. The Plant Cell, 2017, 29(4): 808-823. |
| 107 | ALIYEV J A. Photosynthesis, photorespiration and productivity of wheat and soybean genotypes[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2012, 145(3): 369-383. |
| 108 | ZELITCH I, DAY P R. The effect on net photosynthesis of pedigree selection for low and high rates of photorespiration in tobacco[J]. Plant Physiology, 1973, 52(1): 33-37. |
| 109 | ZELITCH I. Selection and characterization of tobacco plants with novel O2-resistant photosynthesis[J]. Plant Physiology, 1989, 90(4): 1457-1464. |
| 110 | ZELITCH I. Control of plant productivity by regulation of photorespiration[J]. BioScience, 1992, 42(7): 510-516. |
| 111 | SAGE T L, SAGE R F. The functional anatomy of rice leaves: implications for refixation of photorespiratory CO2 and efforts to engineer C4 photosynthesis into rice[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2009, 50(4): 756-772. |
| 112 | BUSCH F A, SAGE T L, COUSINS A B, et al. C3 plants enhance rates of photosynthesis by reassimilating photorespired and respired CO2 [J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2013, 36(1): 200-212. |
| 113 | TIMM S, WITTMIß M, GAMLIEN S, et al. Mitochondrial dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase activity shapes photosynthesis and photorespiration of Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. The Plant Cell, 2015, 27(7): 1968-1984. |
| 114 | SIMKIN A J, LOPEZ-CALCAGNO P E, DAVEY P A, et al. Simultaneous stimulation of sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphatase, fructose 1,6-bisphophate aldolase and the photorespiratory glycine decarboxylase-H protein increases CO2 assimilation, vegetative biomass and seed yield in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017, 15(7): 805-816. |
| 115 | LÓPEZ-CALCAGNO P E, FISK S, BROWN K L, et al. Overexpressing the H-protein of the glycine cleavage system increases biomass yield in glasshouse and field-grown transgenic tobacco plants[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17(1): 141-151. |
| 116 | TIMM S, FLORIAN A, FERNIE A R, et al. The regulatory interplay between photorespiration and photosynthesis[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(10): 2923-2929. |
| 117 | BAUWE H, HAGEMANN M, FERNIE A R. Photorespiration: players, partners and origin[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2010, 15(6): 330-336. |
| 118 | SHEN B R, WANG L M, LIN X L, et al. Engineering a new chloroplastic photorespiratory bypass to increase photosynthetic efficiency and productivity in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(2): 199-214. |
| 119 | WANG L M, SHEN B R, LI B D, et al. A synthetic photorespiratory shortcut enhances photosynthesis to boost biomass and grain yield in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(12): 1802-1815. |
| 120 | SOUTH P F, CAVANAGH A P, LIU H W, et al. Synthetic glycolate metabolism pathways stimulate crop growth and productivity in the field[J]. Science, 2019, 363(6422): eaat9077. |
| 121 | KEBEISH R, NIESSEN M, THIRUVEEDHI K, et al. Chloroplastic photorespiratory bypass increases photosynthesis and biomass production in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2007, 25(5): 593-599. |
| 122 | NÖLKE G, HOUDELET M, KREUZALER F, et al. The expression of a recombinant glycolate dehydrogenase polyprotein in potato (Solanum tuberosum) plastids strongly enhances photosynthesis and tuber yield[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2014, 12(6): 734-742. |
| 123 | DALAL J, LOPEZ H, VASANI N B, et al. A photorespiratory bypass increases plant growth and seed yield in biofuel crop Camelina sativa [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2015, 8: 175. |
| 124 | DE F C CARVALHO J, MADGWICK P J, POWERS S J, et al. An engineered pathway for glyoxylate metabolism in tobacco plants aimed to avoid the release of ammonia in photorespiration[J]. BMC Biotechnology, 2011, 11: 111. |
| 125 | MAIER A, FAHNENSTICH H, VON CAEMMERER S, et al. Transgenic introduction of a glycolate oxidative cycle into A. thaliana chloroplasts leads to growth improvement[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2012, 3: 38. |
| 126 | XIN C P, THOLEN D, DEVLOO V, et al. The benefits of photorespiratory bypasses: how can they work? [J]. Plant Physiology, 2014, 167(2): 574-585. |
| 127 | PETERHANSEL C, KRAUSE K, BRAUN H P, et al. Engineering photorespiration: current state and future possibilities[J]. Plant Biology (Stuttgart, Germany), 2013, 15(4): 754-758. |
| 128 | ABOELMY M H, PETERHANSEL C. Enzymatic characterization of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii glycolate dehydrogenase and its nearest proteobacterial homologue[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2014, 79: 25-30. |
| 129 | SCHMITZ J, SRIKANTH N V, HÜDIG M, et al. The ancestors of diatoms evolved a unique mitochondrial dehydrogenase to oxidize photorespiratory glycolate[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2017, 132(2): 183-196. |
| 130 | TRUDEAU D L, EDLICH-MUTH C, ZARZYCKI J, et al. Design and in vitro realization of carbon-conserving photorespiration[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(49): E11455-E11464. |
| 131 | SCHEFFEN M, MARCHAL D G, BENEYTON T, et al. A new-to-nature carboxylation module to improve natural and synthetic CO2 fixation[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2021, 4(2): 105-115. |
| 132 | BAR-EVEN A. Daring metabolic designs for enhanced plant carbon fixation[J]. Plant Science, 2018, 273: 71-83. |
| 133 | ENGLER C, GRUETZNER R, KANDZIA R, et al. Golden gate shuffling: a one-pot DNA shuffling method based on type IIs restriction enzymes[J]. PLoS One, 2009, 4(5): e5553. |
| 134 | GIBSON D G, YOUNG L, CHUANG R Y, et al. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases[J]. Nature Methods, 2009, 6(5): 343-345. |
| 135 | SOMERVILLE C R, OGREN W L. Mutants of the cruciferous plant Arabidopsis thaliana lacking glycine decarboxylase activity[J]. The Biochemical Journal, 1982, 202(2): 373-380. |
| 136 | RACHMILEVITCH S, COUSINS A B, BLOOM A J. Nitrate assimilation in plant shoots depends on photorespiration[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(31): 11506-11510. |
| 137 | TIMM S, MIELEWCZIK M, FLORIAN A, et al. High-to-low CO2 acclimation reveals plasticity of the photorespiratory pathway and indicates regulatory links to cellular metabolism of Arabidopsis [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(8): e42809. |
| 138 | FLÜGEL F, TIMM S, ARRIVAULT S, et al. The photorespiratory metabolite 2-phosphoglycolate regulates photosynthesis and starch accumulation in Arabidopsis [J]. The Plant Cell, 2017, 29(10): 2537-2551. |
| 139 | FERNIE A R, BAUWE H, EISENHUT M, et al. Perspectives on plant photorespiratory metabolism[J]. Plant Biology, 2013, 15(4): 748-753. |
| 140 | TIMM S, BAUWE H. The variety of photorespiratory phenotypes-employing the current status for future research directions on photorespiration[J]. Plant Biology, 2013, 15(4): 737-747. |
| 141 | BUSCH F A, SAGE R F, FARQUHAR G D. Plants increase CO2 uptake by assimilating nitrogen via the photorespiratory pathway[J]. Nature Plants, 2018, 4(1): 46-54. |
| 142 | HAGEMANN M, KERN R, MAURINO V G, et al. Evolution of photorespiration from cyanobacteria to land plants, considering protein phylogenies and acquisition of carbon concentrating mechanisms[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(10): 2963-2976. |
| 143 | WHEELER R M, MACKOWIAK C L, SAGER J C, et al. Proximate composition of CELSS crops grown in NASA's biomass production chamber[J]. Advances in Space Research, 1996, 18(4/5): 43-47. |
| 144 | LONG S P, ZHU X G, NAIDU S L, et al. Can improvement in photosynthesis increase crop yields? [J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2006, 29(3): 315-330. |
| 145 | MCGRATH J M, LONG S P. Can the cyanobacterial carbon-concentrating mechanism increase photosynthesis in crop species? A theoretical analysis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2014, 164(4): 2247-2261. |
| 146 | NÖLKE G, BARSOUM M, HOUDELET M, et al. The integration of algal carbon concentration mechanism components into tobacco chloroplasts increases photosynthetic efficiency and biomass[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 14(3): e1800170. |
| 147 | TCHERKEZ G, GAUTHIER P, BUCKLEY T N, et al. Leaf day respiration: low CO2 flux but high significance for metabolism and carbon balance[J]. The New Phytologist, 2017, 216(4): 986-1001. |
| 148 | FEILER H S, NEWTON K J. Altered mitochondrial gene expression in the nonchromosomal stripe 2 mutant of maize[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1987, 6(6): 1535-1539. |
| 149 | ROUSSELL D L, THOMPSON D L, PALLARDY S G, et al. Chloroplast structure and function is altered in the NCS2 maize mitochondrial mutant[J]. Plant Physiology, 1991, 96(1): 232-238. |
| 150 | BARTOLI C G, PASTORI G M, FOYER C H. Ascorbate biosynthesis in mitochondria is linked to the electron transport chain between complexes Ⅲ and Ⅳ[J]. Plant Physiology, 2000, 123(1): 335-344. |
| 151 | SARADADEVI K, RAGHAVENDRA A S. Dark respiration protects photosynthesis against photoinhibition in mesophyll protoplasts of pea (Pisum sativum)[J]. Plant Physiology, 1992, 99(3): 1232-1237. |
| 152 | HANNING I, HELDT H W. On the function of mitochondrial metabolism during photosynthesis in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) leaves (partitioning between respiration and export of redox equivalents and precursors for nitrate assimilation products)[J]. Plant Physiology, 1993, 103(4): 1147-1154. |
| 153 | SMITH C A, MELINO V J, SWEETMAN C, et al. Manipulation of alternative oxidase can influence salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2009, 137(4): 459-472. |
| 154 | ATKIN O K, MACHEREL D. The crucial role of plant mitochondria in orchestrating drought tolerance[J]. Annals of Botany, 2008, 103(4): 581-597. |
| 155 | LEE B H, LEE H, XIONG L M, et al. A mitochondrial complex I defect impairs cold-regulated nuclear gene expression[J]. The Plant Cell, 2002, 14(6): 1235-1251. |
| 156 | DUTILLEUL C, GARMIER M, NOCTOR G, et al. Leaf mitochondria modulate whole cell redox homeostasis, set antioxidant capacity, and determine stress resistance through altered signaling and diurnal regulation[J]. The Plant Cell, 2003, 15(5): 1212-1226. |
| 157 | LEAKEY A D B, XU F X, GILLESPIE K M, et al. Genomic basis for stimulated respiration by plants growing under elevated carbon dioxide[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(9): 3597-3602. |
| 158 | CONSIDINE M J, HOLTZAPFFEL R C, DAY D A, et al. Molecular distinction between alternative oxidase from monocots and dicots[J]. Plant Physiology, 2002, 129(3): 949-953. |
| 159 | NOCTOR G, FOYER C H. Homeostasis of adenylate status during photosynthesis in a fluctuating environment[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2000, 51(): 347-356. |
| 160 | KRAMER D M, EVANS J R. The importance of energy balance in improving photosynthetic productivity[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 155(1): 70-78. |
| 161 | HUANG P, BRUTNELL T P. A synthesis of transcriptomic surveys to dissect the genetic basis of C4 photosynthesis[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2016, 31: 91-99. |
| 162 | GIRAUD E, HO L H M, CLIFTON R, et al. The absence of ALTERNATIVE OXIDASE1a in Arabidopsis results in acute sensitivity to combined light and drought stress[J]. Plant Physiology, 2008, 147(2): 595-610. |
| 163 | CVETKOVSKA M, VANLERBERGHE G C. Alternative oxidase modulates leaf mitochondrial concentrations of superoxide and nitric oxide[J]. The New Phytologist, 2012, 195(1): 32-39. |
| 164 | IGAMBERDIEV A U, BYKOVA N V, SHAH J K, et al. Anoxic nitric oxide cycling in plants: participating reactions and possible mechanisms[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2010, 138(4): 393-404. |
| 165 | AMIRSADEGHI S, ROBSON C A, MCDONALD A E, et al. Changes in plant mitochondrial electron transport alter cellular levels of reactive oxygen species and susceptibility to cell death signaling molecules[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2006, 47(11): 1509-1519. |
| 166 | PASQUALINI S, PAOLOCCI F, BORGOGNI A, et al. The overexpression of an alternative oxidase gene triggers ozone sensitivity in tobacco plants[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2007, 30(12): 1545-1556. |
| 167 | WATANABE C K, HACHIYA T, TERASHIMA I, et al. The lack of alternative oxidase at low temperature leads to a disruption of the balance in carbon and nitrogen metabolism, and to an up-regulation of antioxidant defence systems in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2008, 31(8): 1190-1202. |
| 168 | WANG J, RAJAKULENDRAN N, AMIRSADEGHI S, et al. Impact of mitochondrial alternative oxidase expression on the response of Nicotiana tabacum to cold temperature[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2011, 142(4): 339-351. |
| 169 | VISHWAKARMA A, BASHYAM L, SENTHILKUMARAN B, et al. Physiological role of AOX1a in photosynthesis and maintenance of cellular redox homeostasis under high light in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2014, 81: 44-53. |
| 170 | DAHAL K, VANLERBERGHE G C. Alternative oxidase respiration maintains both mitochondrial and chloroplast function during drought[J]. The New Phytologist, 2017, 213(2): 560-571. |
| 171 | HUANG S B, VAN AKEN O, SCHWARZLÄNDER M, et al. The roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cellular signaling and stress response in plants[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 171(3): 1551-1559. |
| 172 | NG S, DE CLERCQ I, VAN AKEN O, et al. Anterograde and retrograde regulation of nuclear genes encoding mitochondrial proteins during growth, development, and stress[J]. Molecular Plant, 2014, 7(7): 1075-1093. |
| 173 | CVETKOVSKA M, VANLERBERGHE G C. Alternative oxidase impacts the plant response to biotic stress by influencing the mitochondrial generation of reactive oxygen species[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2013, 36(3): 721-732. |
| 174 | FIORANI F, UMBACH A L, SIEDOW J N. The alternative oxidase of plant mitochondria is involved in the acclimation of shoot growth at low temperature. A study of Arabidopsis AOX1a transgenic plants[J]. Plant Physiology, 2005, 139(4): 1795-1805. |
| 175 | Murakami Y, Toriyama K. Enhanced high temperature tolerance in transgenic rice seedlings with elevated levels of alternative oxidase, osaox1a[J]. Plant Biotechnology, 2008, 25:361-364. |
| MURAKAMI Y, TORIYAMA K. Enhanced high temperature tolerance in transgenic rice seedlings with elevated levels of alternative oxidase, OsAOX1a[J]. Plant Biotechnology, 2008, 25(4): 361-364. | |
| 176 | Yoshida K, Watanabe C K, Terashima I, et al. Physiological impact of mitochondrial alternative oxidase on photosynthesis and growth in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2011, 34:1890-9. |
| YOSHIDA K, WATANABE C K, TERASHIMA I, et al. Physiological impact of mitochondrial alternative oxidase on photosynthesis and growth in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2011, 34(11): 1890-1899. | |
| 177 | LI C R, LIANG D D, XU R F, et al. Overexpression of an alternative oxidase gene, OsAOX1a, improves cold tolerance in Oryza sativa L[J]. Genetics and Molecular Research: GMR, 2013, 12(4): 5424-5432. |
| 178 | DAHAL K, VANLERBERGHE G C. Improved chloroplast energy balance during water deficit enhances plant growth: more crop per drop[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2017, 69(5): 1183-1197. |
| 179 | YANG H L, DENG L B, LIU H F, et al. Overexpression of BnaAOX1b confers tolerance to osmotic and salt stress in rapeseed[J]. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics, 2019, 9(10): 3501-3511. |
| 180 | MATHY G, CARDOL P, DINANT M, et al. Proteomic and functional characterization of a Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutant lacking the mitochondrial alternative oxidase 1[J]. Journal of Proteome Research, 2010, 9(6): 2825-2838. |
| 181 | SKIRYCZ A, DE BODT S, OBATA T, et al. Developmental stage specificity and the role of mitochondrial metabolism in the response of Arabidopsis leaves to prolonged mild osmotic stress[J]. Plant Physiology, 2009, 152(1): 226-244. |
| 182 | SWEETMAN C, WATERMAN C D, RAINBIRD B M, et al. AtNDB2 is the main external NADH dehydrogenase in mitochondria and is important for tolerance to environmental stress[J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 181(2): 774-788. |
| 183 | PHAM H M, KEBEDE H, RITCHIE G, et al. Alternative oxidase (AOX) over-expression improves cell expansion and elongation in cotton seedling exposed to cool temperatures[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2018, 131(11): 2287-2298. |
| 184 | WANG J, VANLERBERGHE G C. A lack of mitochondrial alternative oxidase compromises capacity to recover from severe drought stress[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2013, 149(4): 461-473. |
| 185 | FENG H Q, GUAN D D, SUN K, et al. Expression and signal regulation of the alternative oxidase genes under abiotic stresses[J]. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica, 2013, 45(12): 985-994. |
| 186 | VANLERBERGHE G C. Alternative oxidase: a mitochondrial respiratory pathway to maintain metabolic and signaling homeostasis during abiotic and biotic stress in plants[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2013, 14(4): 6805-6847. |
| 187 | DEL-SAZ N F, RIBAS-CARBO M, MCDONALD A E, et al. An in vivo perspective of the role(s) of the alternative oxidase pathway[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2018, 23(3): 206-219. |
| 188 | LOUGHLIN P, LIN Y K, CHEN M. Chlorophyll d and Acaryochloris marina: current status[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 2013, 116(2/3): 277-293. |
| 189 | HO M Y, SHEN G Z, CANNIFFE D P, et al. Light-dependent chlorophyll f synthase is a highly divergent paralog of PsbA of photosystem II[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6302): aaf9178. |
| 190 | ENGLER C, YOULES M, GRUETZNER R, et al. A golden gate modular cloning toolbox for plants[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2014, 3(11): 839-843. |
| 191 | LIU W S, STEWART C N JR. Plant synthetic biology[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2015, 20(5): 309-317. |
| 192 | PATRON N J, ORZAEZ D, MARILLONNET S, et al. Standards for plant synthetic biology: a common syntax for exchange of DNA parts[J]. The New Phytologist, 2015, 208(1): 13-19. |
| 193 | FUENTES P, ZHOU F, ERBAN A, et al. A new synthetic biology approach allows transfer of an entire metabolic pathway from a medicinal plant to a biomass crop[J]. eLife, 2016, 5: e13664. |
| 194 | SHIH P M, VUU K, MANSOORI N, et al. A robust gene-stacking method utilizing yeast assembly for plant synthetic biology[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 13215. |
| 195 | MATZKE M A, MATZKE A J M. Homology-dependent gene silencing in transgenic plants: what does it really tell us? [J]. Trends in Genetics, 1995, 11(1): 1-3. |
| 196 | MEYER P, SAEDLER H. Homology-dependent gene silencing in plants[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 1996, 47:23-48. |
| 197 | MATZKE M A, AUFSATZ W, KANNO T, et al. Homology-dependent gene silencing and host defense in plants[J]. Advances in Genetics, 2002, 46: 235-275. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 董颖, 马孟丹, 黄卫人. CRISPR-Cas系统的小型化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 105-117. |
| [3] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [11] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [12] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [13] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [14] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [15] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||