合成生物学 ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (5): 980-999.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-018
原位电离质谱技术在微生物菌株筛选中的应用进展
刘欢1,2,3, 崔球1,2,3
- 1.中国科学院青岛生物能源与过程研究所,中国科学院生物燃料重点实验室,山东省合成生物学重点实验室,山东 青岛 266101
2.山东能源研究院,山东 青岛 266101
3.青岛新能源山东省实验室,山东 青岛 266101
-
收稿日期:2023-03-01修回日期:2023-07-27出版日期:2023-10-31发布日期:2023-11-15 -
通讯作者:崔球 -
作者简介:刘欢 (1988—),女,项目副研究员。研究方向为生物质谱、直接质谱的高通量筛选平台和方法体系。E-mail:liuhuan@qibebt.ac.cn崔球 (1975—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为蛋白质及代谢物层面的组学分析、低值生物质的生物降解利用及生物智造相关的自动化装备。E-mail:cuiqiu@qibebt.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(32001053);山东能源研究院科研创新基金(SEI I202123);山东省重点研发计划(2021ZDSYS29)
Advances and applications of ambient ionization mass spectrometry in screening of microbial strains
LIU Huan1,2,3, CUI Qiu1,2,3
- 1.Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Synthetic Biology,CAS Key Laboratory of Biofuels,Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Qingdao 266101,Shandong,China
2.Shandong Energy Institute,Qingdao 266101,Shandong,China
3.Qingdao New Energy Shandong Laboratory,Qingdao 266101,Shandong,China
-
Received:2023-03-01Revised:2023-07-27Online:2023-10-31Published:2023-11-15 -
Contact:CUI Qiu
摘要:
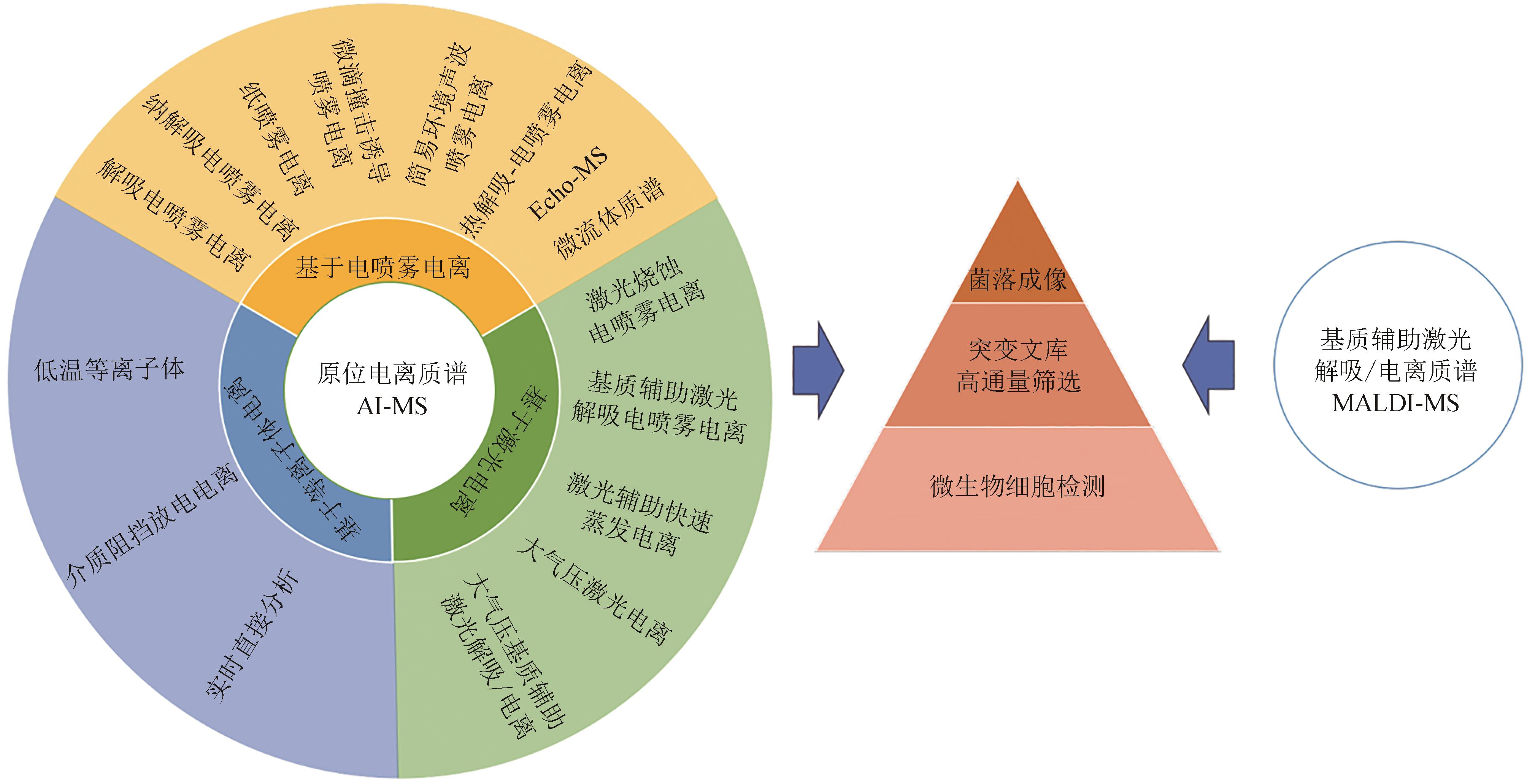
质谱是一种强大的分析工具,可提供分子量和化学结构信息。它具有高特异性、高灵敏度、快速、普适性、微量和非标记等优点。在合成生物学的“设计-构建-测试-学习”工程化策略中,质谱具有重要的应用潜力。随着质谱仪器及其方法体系的不断发展,质谱,特别是原位电离质谱技术,已经成为检测和筛选微生物菌株的重要工具。它能够获取完整的细胞代谢表型,用于合成生物学中的“测试”环节高通量筛选和成像。本文重点介绍了经典的基质辅助激光解吸/电离质谱技术和基于电喷雾、激光和等离子体的原位电离质谱技术的工作机制。此外,还综述了这些质谱技术可以在无需样品预处理的情况下直接检测完整的微生物细胞,以及在微生物突变文库的高通量筛选和活微生物菌落的质谱成像方面的研究进展。最后,总结了原位电离质谱技术在合成生物学中的应用。原位电离质谱技术具有微量、无标记、高通量、普适性、高灵敏度等特点,将在合成生物学“测试”环节的高通量筛选装备中发挥重要作用。
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘欢, 崔球. 原位电离质谱技术在微生物菌株筛选中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 980-999.
LIU Huan, CUI Qiu. Advances and applications of ambient ionization mass spectrometry in screening of microbial strains[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 980-999.
| 电离技术 | 电离机理 | 应用场景 | 应用案例 |
|---|---|---|---|
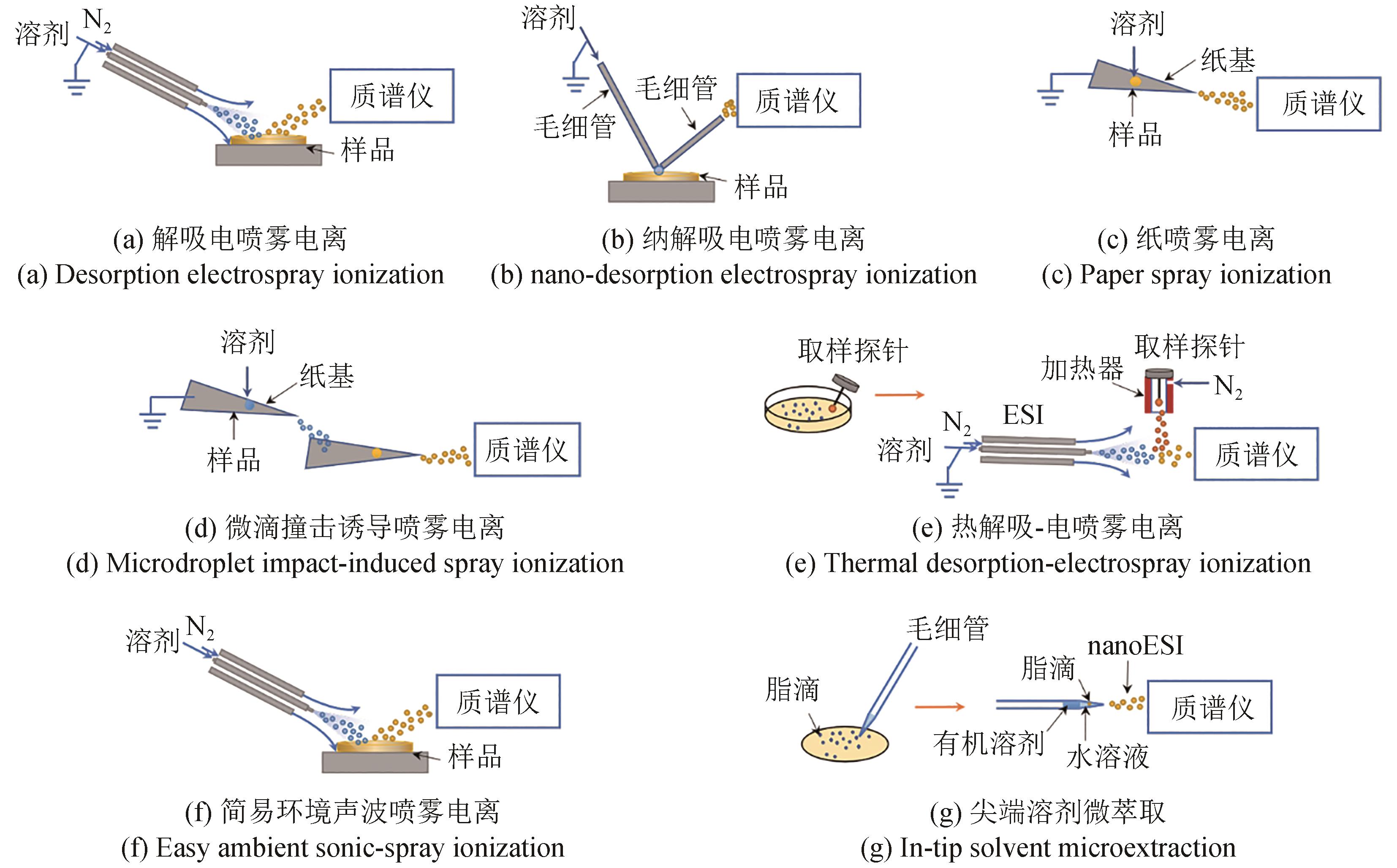
| DESI | 电喷雾电离 气动辅助 | 细胞液干燥 | 亚种分化:大肠杆菌,鼠伤寒沙门氏菌菌株[ |
| 菌落 | 菌株表征:枯草芽孢杆菌[ | ||
| 微生物相互作用:大肠杆菌和黄色黏球菌[ | |||
| 表型分析:大肠杆菌[ | |||
| nano-DESI | 电喷雾电离 | 菌落 | 代谢分析:希瓦氏菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、链霉菌[ |
| 分子网络:枯草芽孢杆菌,链霉菌,分枝杆菌和铜绿假单胞菌[ | |||
| PSI | 电喷雾电离 纸基 | 菌落置于纸基 | 细菌区分:革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌的8个属16个物种[ |
| 藻液置于纸基 | 微藻表征:小球藻和微拟球藻[ | ||
| MISI | 电喷雾电离 多级纸基 | 菌置于纸基 | 细菌鉴别:枯草芽孢杆菌、大肠杆菌和恶臭假单胞菌[ |
| TD-ESI | 热解吸-电喷雾电离 | 菌落 | 细菌区分:5种革兰氏阳性菌和5种革兰氏阴性菌[ |
| EASI | 声波电离 | 细胞液 | 膜脂质分析:蓝藻[ |
| ITSME | 电喷雾电离 | 细胞脂滴 | 油脂检测:HepG2细胞[ |
| Sciex Echo-MS | 电喷雾电离 | 细胞上清液或粗细胞提取液 | 酶筛选:二酰基甘油酰基转移酶2抑制剂[ |
微流体-ESI 微流体-MALDI | 电喷雾电离 激光电离 | 纳升液滴 纳升液滴 | 酶促反应:转氨酶ATA-117[ 酶分泌分析:酵母细胞中植酸酶[ |
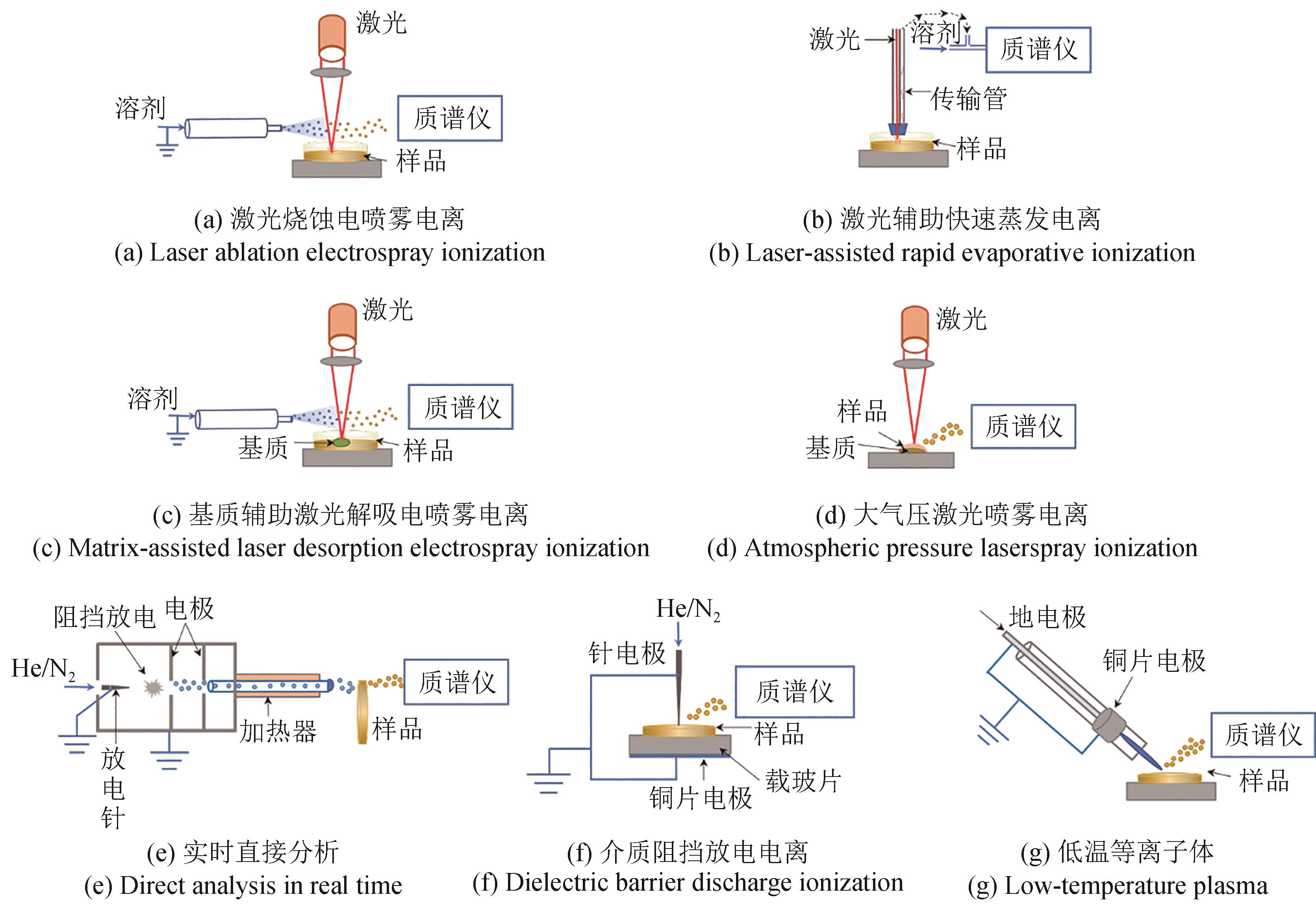
| LA-ESI | 激光烧蚀电喷雾电离 | 菌落 | 生长、代谢和抗生素抑制研究的分子成像:枯草芽孢杆菌和大肠杆菌[ |
| 表征:蓝藻[ | |||
| 微生物周转率:莱茵衣藻[ | |||
| LA-REI | 激光蒸发电离 | 菌落 | 菌株分类:细菌和酵母[ |
| MALDESI | 激光解吸电喷雾电离 | 细胞分散于载玻片上 | 脂质组学分析:HeLa细胞[ |
| AP-LSI | 激光解吸电离 | 细胞液与基质共结晶 | 细菌区分:12个属的21种食源性细菌[ |
| AP-MALDI | 激光解吸电离 | 菌落 | 成像:球状芽孢杆菌[ |
| DART | 等离子体 | 全细胞悬浮液 | 细菌鉴定:化脓链球菌、大肠杆菌、γ-射线贝氏考克斯菌[ |
| DBDI | 等离子体 | 细胞 | 化合物检测:洋葱细胞和PANC-1细胞[ |
| LTP | 等离子体 | 细胞液沉积载玻片上 | 细菌区分:16种细菌的脂肪酸乙酯检测[ |
表1 原位电离技术及在微生物检测中的应用案例
Table 1 AI techniques and their application examples in microbial detection
| 电离技术 | 电离机理 | 应用场景 | 应用案例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DESI | 电喷雾电离 气动辅助 | 细胞液干燥 | 亚种分化:大肠杆菌,鼠伤寒沙门氏菌菌株[ |
| 菌落 | 菌株表征:枯草芽孢杆菌[ | ||
| 微生物相互作用:大肠杆菌和黄色黏球菌[ | |||
| 表型分析:大肠杆菌[ | |||
| nano-DESI | 电喷雾电离 | 菌落 | 代谢分析:希瓦氏菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、链霉菌[ |
| 分子网络:枯草芽孢杆菌,链霉菌,分枝杆菌和铜绿假单胞菌[ | |||
| PSI | 电喷雾电离 纸基 | 菌落置于纸基 | 细菌区分:革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌的8个属16个物种[ |
| 藻液置于纸基 | 微藻表征:小球藻和微拟球藻[ | ||
| MISI | 电喷雾电离 多级纸基 | 菌置于纸基 | 细菌鉴别:枯草芽孢杆菌、大肠杆菌和恶臭假单胞菌[ |
| TD-ESI | 热解吸-电喷雾电离 | 菌落 | 细菌区分:5种革兰氏阳性菌和5种革兰氏阴性菌[ |
| EASI | 声波电离 | 细胞液 | 膜脂质分析:蓝藻[ |
| ITSME | 电喷雾电离 | 细胞脂滴 | 油脂检测:HepG2细胞[ |
| Sciex Echo-MS | 电喷雾电离 | 细胞上清液或粗细胞提取液 | 酶筛选:二酰基甘油酰基转移酶2抑制剂[ |
微流体-ESI 微流体-MALDI | 电喷雾电离 激光电离 | 纳升液滴 纳升液滴 | 酶促反应:转氨酶ATA-117[ 酶分泌分析:酵母细胞中植酸酶[ |
| LA-ESI | 激光烧蚀电喷雾电离 | 菌落 | 生长、代谢和抗生素抑制研究的分子成像:枯草芽孢杆菌和大肠杆菌[ |
| 表征:蓝藻[ | |||
| 微生物周转率:莱茵衣藻[ | |||
| LA-REI | 激光蒸发电离 | 菌落 | 菌株分类:细菌和酵母[ |
| MALDESI | 激光解吸电喷雾电离 | 细胞分散于载玻片上 | 脂质组学分析:HeLa细胞[ |
| AP-LSI | 激光解吸电离 | 细胞液与基质共结晶 | 细菌区分:12个属的21种食源性细菌[ |
| AP-MALDI | 激光解吸电离 | 菌落 | 成像:球状芽孢杆菌[ |
| DART | 等离子体 | 全细胞悬浮液 | 细菌鉴定:化脓链球菌、大肠杆菌、γ-射线贝氏考克斯菌[ |
| DBDI | 等离子体 | 细胞 | 化合物检测:洋葱细胞和PANC-1细胞[ |
| LTP | 等离子体 | 细胞液沉积载玻片上 | 细菌区分:16种细菌的脂肪酸乙酯检测[ |
| 电离技术 | 优劣势及适用场景 | 单个菌样 分析时间 | 空间分辨率 | 应用案例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MALDI | 优势:方法成熟、样品制备简单、高通量 劣势:真空取样,限制不稳定或挥发性小分子的检测 适用场景:菌落 | 约2 s | 中链脂肪酸合成酶突变体库筛选:酿酒酵母 (m/z 730/758峰比值>1)[ 脂肪酸合成酶突变文库筛选:酿酒酵母(脂肪酸酰基片段C16:1/C18:1比值为18.1±1.1)、大肠杆菌(脂肪酸酰基片段C16:1/C16比值为1.11±0.04)和荧光假单胞菌(C16:1/C16比值为0.45±0.06)[ | |
| 1~2.5 s | 多步酶促反应:产肽类抗生素类似物的大肠杆菌和产鼠李糖脂的大肠杆菌[ | |||
| 5 s | 环二肽合酶定向进化:产二酮哌嗪的大肠杆菌[ | |||
| 约1 s | 120 μm× 120 μm | 菌落成像:铜绿假单胞菌、枯草芽孢杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌[ | ||
| 约1 s | 250 μm | 菌落生物膜成像:枯草芽孢杆菌[ | ||
| DESI | 优势:常压敞开条件下取样,原位、实时、高通量,适于细胞外泌代谢物和细胞膜相关分子 劣势:难以直接提供细胞内代谢物 适用场景:菌落、完整微生物细胞 | 10 s | 100 μm | 生物催化剂筛选:表达氨裂解酶和P450单加氧酶的大肠杆菌(L-苯丙氨酸检测限为>50 nmol/mm2)[ |
| 约7 s | 50 μm× 250 μm | 菌落成像:生产过量游离脂肪酸的大肠杆菌[ | ||
| Nano-DESI | 同DESI | 1 mm × 1 mm | 质谱成像:希瓦氏菌、枯草芽孢杆菌和链霉菌[ | |
| 20 s | 约200 μm | 菌落质谱分子网络:枯草芽孢杆菌、链霉菌、分枝杆菌和铜绿假单胞菌[ | ||
| LA-REI | 优势:常压敞开条件下取样,原位、实时、高通量、高分辨 劣势:限制细胞内代谢物直接分析 适用场景:菌落 | 8 s | 约500 μm | 微生物菌种分类:大肠杆菌等25种微生物[ |
| 10 s | 0.8 cm2 | 突变文库筛选:产紫色素和白桦酸的酿酒酵母(白桦酸线性范围2~2×10-5 g/L)[ | ||
| LAESI | 优势:常压敞开条件下取样,原位、实时、高通量、高分辨 劣势:限制低极性化合物的分析 适用场景:菌落 | 150 μm | 菌落成像:枯草芽孢杆菌和大肠杆菌[ |
表2 主要原位电离技术及在菌株筛选和成像中的应用案例
Table 2 Main AI techniques and their application examples in microbial strain screening and imaging
| 电离技术 | 优劣势及适用场景 | 单个菌样 分析时间 | 空间分辨率 | 应用案例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MALDI | 优势:方法成熟、样品制备简单、高通量 劣势:真空取样,限制不稳定或挥发性小分子的检测 适用场景:菌落 | 约2 s | 中链脂肪酸合成酶突变体库筛选:酿酒酵母 (m/z 730/758峰比值>1)[ 脂肪酸合成酶突变文库筛选:酿酒酵母(脂肪酸酰基片段C16:1/C18:1比值为18.1±1.1)、大肠杆菌(脂肪酸酰基片段C16:1/C16比值为1.11±0.04)和荧光假单胞菌(C16:1/C16比值为0.45±0.06)[ | |
| 1~2.5 s | 多步酶促反应:产肽类抗生素类似物的大肠杆菌和产鼠李糖脂的大肠杆菌[ | |||
| 5 s | 环二肽合酶定向进化:产二酮哌嗪的大肠杆菌[ | |||
| 约1 s | 120 μm× 120 μm | 菌落成像:铜绿假单胞菌、枯草芽孢杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌[ | ||
| 约1 s | 250 μm | 菌落生物膜成像:枯草芽孢杆菌[ | ||
| DESI | 优势:常压敞开条件下取样,原位、实时、高通量,适于细胞外泌代谢物和细胞膜相关分子 劣势:难以直接提供细胞内代谢物 适用场景:菌落、完整微生物细胞 | 10 s | 100 μm | 生物催化剂筛选:表达氨裂解酶和P450单加氧酶的大肠杆菌(L-苯丙氨酸检测限为>50 nmol/mm2)[ |
| 约7 s | 50 μm× 250 μm | 菌落成像:生产过量游离脂肪酸的大肠杆菌[ | ||
| Nano-DESI | 同DESI | 1 mm × 1 mm | 质谱成像:希瓦氏菌、枯草芽孢杆菌和链霉菌[ | |
| 20 s | 约200 μm | 菌落质谱分子网络:枯草芽孢杆菌、链霉菌、分枝杆菌和铜绿假单胞菌[ | ||
| LA-REI | 优势:常压敞开条件下取样,原位、实时、高通量、高分辨 劣势:限制细胞内代谢物直接分析 适用场景:菌落 | 8 s | 约500 μm | 微生物菌种分类:大肠杆菌等25种微生物[ |
| 10 s | 0.8 cm2 | 突变文库筛选:产紫色素和白桦酸的酿酒酵母(白桦酸线性范围2~2×10-5 g/L)[ | ||
| LAESI | 优势:常压敞开条件下取样,原位、实时、高通量、高分辨 劣势:限制低极性化合物的分析 适用场景:菌落 | 150 μm | 菌落成像:枯草芽孢杆菌和大肠杆菌[ |
| 1 | 杨永富, 耿碧男, 宋皓月, 等. 合成生物学时代基于非模式细菌的工业底盘细胞研究现状与展望[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37(3): 874-910. |
| YANG Y F, GENG B N, SONG H Y, et al. Progress and perspective on development of non-model industrial bacteria as chassis cells for biochemical production in the synthetic biology era[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37(3): 874-910. | |
| 2 | 刘宜嵩, 王壬, 钮成拓, 等. 荧光探针在高通量筛选技术上的应用进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2021, 47(11): 266-271. |
| LIU Y S, WANG R, NIU C T, et al. Application of fluorescence probe in high throughput screening[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(11): 266-271. | |
| 3 | YANG G Y, WITHERS S G. Ultrahigh-throughput FACS-based screening for directed enzyme evolution[J]. Chembiochem, 2009, 10(17): 2704-2715. |
| 4 | 王喜先, 孙晴, 刁志钿, 等. 拉曼光谱技术在单细胞表型检测与分选中的应用进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(1): 204-224. |
| WANG X X, SUN Q, DIAO Z D, et al. Advances with applications of Raman spectroscopy in single-cell phenotype sorting and analysis[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 204-224. | |
| 5 | MAY J C, MCLEAN J A. Advanced multidimensional separations in mass spectrometry: navigating the big data deluge[J]. Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 9: 387-409. |
| 6 | FENN J B, MANN M, MENG C K, et al. Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of large biomolecules[J]. Science, 1989, 246(4926): 64-71. |
| 7 | KARAS M, HILLENKAMP F. Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10, 000 Daltons[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1988, 60(20): 2299-2301. |
| 8 | CARROLL D I, DZIDIC I, STILLWELL R N, et al. Atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometry. Corona discharge ion source for use in a liquid chromatograph-mass spectrometer-computer analytical system[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1975, 47(14): 2369-2373. |
| 9 | RIGOUIN C, CROUX C, BORSENBERGER V, et al. Increasing medium chain fatty acids production in Yarrowia lipolytica by metabolic engineering[J].Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17(1): 142. |
| 10 | COOKS R G, OUYANG Z, TAKATS Z, et al. Ambient mass spectrometry[J]. Science, 2006, 311(5767): 1566-1570. |
| 11 | FEIDER C L, KRIEGER A, DEHOOG R J, et al. Ambient ionization mass spectrometry: recent developments and applications[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(7): 4266-4290. |
| 12 | SINGHAL N, KUMAR M, KANAUJIA P K, et al. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: an emerging technology for microbial identification and diagnosis[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2015, 6: 791. |
| 13 | SANDRIN T R, GOLDSTEIN J E, SCHUMAKER S. MALDI TOF MS profiling of bacteria at the strain level: a review[J]. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 2013, 32(3): 188-217. |
| 14 | CLAYDON M A, DAVEY S N, EDWARDS-JONES V, et al. The rapid identification of intact microorganisms using mass spectrometry[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 1996, 14(11): 1584-1586. |
| 15 | HOLLAND R D, WILKES J G, RAFII F, et al. Rapid identification of intact whole bacteria based on spectral patterns using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization with time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 1996, 10(10): 1227-1232. |
| 16 | POPOVIĆ N T, KAZAZIĆ S P, STRUNJAK-PEROVIĆ I, et al. Differentiation of environmental aquatic bacterial isolates by MALDI-TOF MS[J]. Environmental Research, 2017, 152: 7-16. |
| 17 | TOPIĆ POPOVIĆ N, KAZAZIĆ S P, BOJANIĆ K, et al. Sample preparation and culture condition effects on MALDI-TOF MS identification of bacteria: a review[J/OL]. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 2021[2023-02-01]. . |
| 18 | JANG K S, KIM Y H. Rapid and robust MALDI-TOF MS techniques for microbial identification: a brief overview of their diverse applications[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2018, 56(4): 209-216. |
| 19 | SANDRIN T R, DEMIREV P A. Characterization of microbial mixtures by mass spectrometry[J]. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 2018, 37(3): 321-349. |
| 20 | XUE P, SI T, ZHAO H M. Optically guided mass spectrometry to screen microbial colonies for directed enzyme evolution[M/OL]//Methods in enzymology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2020, 644: 255-273 [2023-02-01]. . |
| 21 | XUE P, SI T, MISHRA S, et al. A mass spectrometry-based high-throughput screening method for engineering fatty acid synthases with improved production of medium-chain fatty acids[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2020, 117(7): 2131-2138. |
| 22 | SI T, LI B, COMI T J, et al. Profiling of microbial colonies for high-throughput engineering of multistep enzymatic reactions via optically guided matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(36): 12466-12473. |
| 23 | TAKÁTS Z, WISEMAN J M, GOLOGAN B, et al. Mass spectrometry sampling under ambient conditions with desorption electrospray ionization[J]. Science, 2004, 306(5695): 471-473. |
| 24 | SONG Y S, TALATY N, TAO W A, et al. Rapid ambient mass spectrometric profiling of intact, untreated bacteria using desorption electrospray ionization[J]. Chemical Communications, 2007(1): 61-63. |
| 25 | SONG Y S, TALATY N, DATSENKO K, et al. In vivo recognition of Bacillus subtilis by desorption electrospray ionizationmass spectrometry (DESI-MS)[J]. Analyst, 2009, 134(5): 838-841. |
| 26 | ELLIS B M, FISCHER C N, MARTIN L B, et al. Spatiochemically profiling microbial interactions with membrane scaffolded desorption electrospray ionization-ion mobility-imaging mass spectrometry and unsupervised segmentation[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(21): 13703-13711. |
| 27 | ELLIS B M, BABELE P K, MAY J C, et al. Accelerating strain phenotyping with desorption electrospray ionization-imaging mass spectrometry and untargeted analysis of intact microbial colonies[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(49): e2109633118. |
| 28 | WATROUS J, ROACH P, HEATH B, et al. Metabolic profiling directly from the Petri dish using nanospray desorption electrospray ionization imaging mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 85(21): 10385-10391. |
| 29 | LANEKOFF I, GEYDEBREKHT O, PINCHUK G E, et al. Spatially resolved analysis of glycolipids and metabolites in living Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 using nanospray desorption electrospray ionization[J]. Analyst, 2013, 138(7): 1971-1978. |
| 30 | WATROUS J, ROACH P, ALEXANDROV T, et al. Mass spectral molecular networking of living microbial colonies[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(26): E1743-E1752. |
| 31 | HAMID A M, JARMUSCH A K, PIRRO V, et al. Rapid discrimination of bacteria by paper spray mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(15): 7500-7507. |
| 32 | ORADU S A, COOKS R G. Multistep mass spectrometry methodology for direct characterization of polar lipids in green microalgae using paper spray ionization[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84(24): 10576-10585. |
| 33 | BASURI P, DAS S, JENIFER S K, et al. Microdroplet impact-induced spray ionization mass spectrometry (MISI MS) for online reaction monitoring and bacteria discrimination[J]. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2021, 32(1): 355-363. |
| 34 | SU H, JIANG Z H, CHIOU S F, et al. Rapid characterization of bacterial lipids with ambient ionization mass spectrometry for species differentiation[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(9): 2772. |
| 35 | MAVROUDAKIS L, VALSAMI E A, GRAFANAKI S, et al. The effect of nitrogen starvation on membrane lipids of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 investigated by using easy ambient sonic-spray ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes, 2019, 1861(10): 183027. |
| 36 | LIU Y Q, ZHANG J L, NIE H G, et al. Study on variation of lipids during different growth phases of living cyanobacteria using easy ambient sonic-spray ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(14): 7096-7102. |
| 37 | ZHAO Y Y, CHEN Z, WU Y, et al. Separating and profiling phosphatidylcholines and triglycerides from single cellular lipid droplet by in-tip solvent microextraction mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(7): 4466-4471. |
| 38 | WEN X J, LIU C, GHISLAIN L, et al. Direct analysis from phase-separated liquid samples using ADE-OPI-MS: applicability to high-throughput screening for inhibitors of diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(15): 6071-6079. |
| 39 | HOLLAND-MORITZ D A, WISMER M K, MANN B F, et al. Mass activated droplet sorting (MADS) enables high-throughput screening of enzymatic reactions at nanoliter scale[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(11): 4470-4477. |
| 40 | HAIDAS D, BACHLER S, KÖHLER M, et al. Microfluidic platform for multimodal analysis of enzyme secretion in nanoliter droplet arrays[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(3): 2066-2073. |
| 41 | LI H, BALAN P, VERTES A. Molecular imaging of growth, metabolism, and antibiotic inhibition in bacterial colonies by laser ablation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(48): 15035-15039. |
| 42 | PARSIEGLA G, SHRESTHA B, CARRIÈRE F, et al. Direct analysis of phycobilisomal antenna proteins and metabolites in small cyanobacterial populations by laser ablation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84(1): 34-38. |
| 43 | STOPKA S A, MANSOUR T R, SHRESTHA B, et al. Turnover rates in microorganisms by laser ablation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and pulse-chase analysis[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2016, 902: 1-7. |
| 44 | CAMERON S J S, PERDONES-MONTERO A, VAN MEULEBROEK L, et al. Sample preparation free mass spectrometry using laser-assisted rapid evaporative ionization mass spectrometry: applications to microbiology, metabolic biofluid phenotyping, and food authenticity[J]. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2021, 32(6): 1393-1401. |
| 45 | XI Y, TU A Q, MUDDIMAN D C. Lipidomic profiling of single mammalian cells by infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization (IR-MALDESI)[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2020, 412(29): 8211-8222. |
| 46 | LIU S Y, ZUO J, LU Y W, et al. Direct bacteria analysis using laserspray ionization miniature mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2019, 411(18): 4031-4040. |
| 47 | KOMPAUER M, HEILES S, SPENGLER B. Atmospheric pressure MALDI mass spectrometry imaging of tissues and cells at 1.4-μm lateral resolution[J]. Nature Methods, 2017, 14(1): 90-96. |
| 48 | PIERCE C Y, BARR J R, CODY R B, et al. Ambient generation of fatty acid methyl ester ions from bacterial whole cells by direct analysis in real time (DART) mass spectrometry[J]. Chemical Communications, 2007(8): 807-809. |
| 49 | LIU Q L, LAN J Y, WU R, et al. Hybrid ionization source combining nanoelectrospray and dielectric barrier discharge ionization for the simultaneous detection of polar and nonpolar compounds in single cells[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 94(6): 2873-2881. |
| 50 | ZHANG J I, COSTA A B, TAO W A, et al. Direct detection of fatty acid ethyl esters using low temperature plasma (LTP) ambient ionization mass spectrometry for rapid bacterial differentiation[J]. Analyst, 2011, 136(15): 3091-3097. |
| 51 | TAKÁTS Z, WISEMAN J M, COOKS R G. Ambient mass spectrometry using desorption electrospray ionization (DESI): instrumentation, mechanisms and applications in forensics, chemistry, and biology[J]. Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2005, 40(10): 1261-1275. |
| 52 | COSTA A B, COOKS R G. Simulated splashes: elucidating the mechanism of desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2008, 464(1/2/3): 1-8. |
| 53 | IFA D R, WU C P, OUYANG Z, et al. Desorption electrospray ionization and other ambient ionization methods: current progress and preview[J]. Analyst, 2010, 135(4): 669-681. |
| 54 | WESTON D J. Ambient ionization mass spectrometry: current understanding of mechanistic theory; analytical performance and application areas[J]. Analyst, 2010, 135(4): 661-668. |
| 55 | HARRIS G A, GALHENA A S, FERNÁNDEZ F M. Ambient sampling/ionization mass spectrometry: applications and current trends[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 83(12): 4508-4538. |
| 56 | HUANG M Z, CHENG S C, CHO Y T, et al. Ambient ionization mass spectrometry: a tutorial[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2011, 702(1): 1-15. |
| 57 | VENTER A R, DOUGLASS K A, SHELLEY J T, et al. Mechanisms of real-time, proximal sample processing during ambient ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(1): 233-249. |
| 58 | LEBEDEV A T. Ambient ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Russian Chemical Reviews, 2015, 84(7): 665-692. |
| 59 | MANIKANDAN M, KAZIBWE Z, HASAN N, et al. Biological desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (DESI MS)-unequivocal role of crucial ionization factors, solvent system and substrates[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 78: 109-119. |
| 60 | ROACH P J, LASKIN J, LASKIN A. Nanospray desorption electrospray ionization: an ambient method for liquid-extraction surface sampling in mass spectrometry[J]. Analyst, 2010, 135(9): 2233-2236. |
| 61 | NGUYEN S N, LIYU A V, CHU R K, et al. Constant-distance mode nanospray desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging of biological samples with complex topography[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(2): 1131-1137. |
| 62 | LIU J J, WANG H, MANICKE N E, et al. Development, characterization, and application of paper spray ionization[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 82(6): 2463-2471. |
| 63 | WANG H, LIU J J, COOKS R G, et al. Paper spray for direct analysis of complex mixtures using mass spectrometry[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(5): 877-880. |
| 64 | ESPY R D, MULIADI A R, OUYANG Z, et al. Spray mechanism in paper spray ionization[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2012, 325/326/327: 167-171. |
| 65 | ZHANG Z P, LIU X N, ZHENG Y J. Ambient ionization-paper spray ionization and its application[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 42(1): 145-152. |
| 66 | 刘婧靖, 何晓伟, 何燕, 等. 纸喷雾敞开式质谱法的发展和应用[J]. 化学进展, 2017, 29(6): 659-666. |
| LIU J J, HE X W, HE Y, et al. Development and application of paper spray ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2017, 29(6): 659-666. | |
| 67 | LIU H, GAO W, TIAN Y, et al. Rapidly detecting tetrabromobisphenol A in soils and sediments by paper spray ionization mass spectrometry combined with isotopic internal standard[J]. Talanta, 2019, 191: 272-276. |
| 68 | HADDAD R, SPARRAPAN R, EBERLIN M N. Desorption sonic spray ionization for (high) voltage-free ambient mass spectrometry[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2006, 20(19): 2901-2905. |
| 69 | HADDAD R, MILAGRE H M S, CATHARINO R R, et al. Easy ambient sonic-spray ionization mass spectrometry combined with thin-layer chromatography[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80(8): 2744-2750. |
| 70 | TEUNISSEN S F, FERNANDES A M A P, EBERLIN M N, et al. Celebrating 10 years of easy ambient sonic-spray ionization[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 90: 135-141. |
| 71 | GONG X Y, ZHAO Y Y, CAI S Q, et al. Single cell analysis with probe ESI-mass spectrometry: detection of metabolites at cellular and subcellular levels[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(8): 3809-3816. |
| 72 | ZHANG X C, ZANG Q C, ZHAO H S, et al. Combination of droplet extraction and pico-ESI-MS allows the identification of metabolites from single cancer cells[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(16): 9897-9903. |
| 73 | ZHANG H, LIU C, HUA W Y, et al. Acoustic ejection mass spectrometry for high-throughput analysis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(31): 10850-10861. |
| 74 | KEMPA E E, SMITH C A, LI X, et al. Coupling droplet microfluidics with mass spectrometry for ultrahigh-throughput analysis of complex mixtures up to and above 30 Hz[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(18): 12605-12612. |
| 75 | HAIDAS D, NAPIORKOWSKA M, SCHMITT S, et al. Parallel sampling of nanoliter droplet arrays for noninvasive protein analysis in discrete yeast cultivations by MALDI-MS[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(5): 3810-3818. |
| 76 | NEMES P, VERTES A. Laser ablation electrospray ionization for atmospheric pressure, in vivo, and imaging mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2007, 79(21): 8098-8106. |
| 77 | WANG H, FEI Z H, LI Z X, et al. Coupling laser desorption with corona beam ionization for ambient mass spectrometric analysis of solution and powder samples[J]. Talanta, 2018, 179: 364-368. |
| 78 | FOWBLE K L, TERAMOTO K, CODY R B, et al. Development of "laser ablation direct analysis in real time imaging" mass spectrometry: application to spatial distribution mapping of metabolites along the biosynthetic cascade leading to synthesis of atropine and scopolamine in plant tissue[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 89(6): 3421-3429. |
| 79 | BIERSTEDT A, RIEDEL J. High-repetition rate laser ablation coupled to dielectric barrier discharge postionization for ambient mass spectrometry[J]. Methods, 2016, 104: 3-10. |
| 80 | BENHAM K, HODYSS R, FERNÁNDEZ F M, et al. Laser-induced acoustic desorption atmospheric pressure photoionization via VUV-generating microplasmas[J]. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2016, 27(11): 1805-1812. |
| 81 | CALEB BAGLEY M, GARRARD K P, MUDDIMAN D C. The development and application of matrix assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization: the teenage years[J]. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 2023, 42(1): 35-66. |
| 82 | DIXON R B, SAMPSON J S, HAWKRIDGE A M, et al. Ambient aerodynamic ionization source for remote analyte sampling and mass spectrometric analysis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80(13): 5266-5271. |
| 83 | CHEN Z Y, VERTES A. Early plume expansion in atmospheric pressure midinfrared laser ablation of water-rich targets[J]. Physical Review E, 2008, 77(3): 036316. |
| 84 | SHRESTHA B, VERTES A. High-throughput cell and tissue analysis with enhanced molecular coverage by laser ablation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry using ion mobility separation[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(9): 4308-4315. |
| 85 | JACOBSON R S, THURSTON R L, SHRESTHA B, et al. In situ analysis of small populations of adherent mammalian cells using laser ablation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry in transmission geometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(24): 12130-12136. |
| 86 | STOPKA S A, SAMARAH L Z, SHAW J B, et al. Ambient metabolic profiling and imaging of biological samples with ultrahigh molecular resolution using laser ablation electrospray ionization 21 tesla FTICR mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(8): 5028-5035. |
| 87 | AGTUCA B J, STOPKA S A, EVANS S, et al. Metabolomic profiling of wild-type and mutant soybean root nodules using laser-ablation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry reveals altered metabolism[J]. The Plant Journal, 2020, 103(5): 1937-1958. |
| 88 | TAYLOR M J, LIYU A, VERTES A, et al. Ambient single-cell analysis and native tissue imaging using laser-ablation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry with increased spatial resolution[J]. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2021, 32(9): 2490-2494. |
| 89 | TAYLOR M J, MATTSON S, LIYU A, et al. Optical microscopy-guided laser ablation electrospray ionization ion mobility mass spectrometry: ambient single cell metabolomics with increased confidence in molecular identification[J]. Metabolites, 2021, 11(4): 200. |
| 90 | SAMARAH L Z, VERTES A. Mass spectrometry imaging of biological tissues by laser desorption ionization from silicon nanopost arrays[M/OL]//Methods in molecular biology: mass spectrometry imaging of small molecules. New York, NY: Springer US, 2022, 2437: 89-98 [2023-02-01]. . |
| 91 | SHIEA J, HUANG M Z, HSU H J, et al. Electrospray-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for direct ambient analysis of solids[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2005, 19(24): 3701-3704. |
| 92 | SAMARAH L Z, TRAN T H, STACEY G, et al. In vivo chemical analysis of plant sap from the xylem and single parenchymal cells by capillary microsampling electrospray ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(10): 7299-7306. |
| 93 | SAMPSON J S, HAWKRIDGE A M, MUDDIMAN D C. Generation and detection of multiply-charged peptides and proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization (MALDESI) Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2006, 17(12): 1712-1716. |
| 94 | BOKHART M T, MUDDIMAN D C. Infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging analysis of biospecimens[J]. Analyst, 2016, 141(18): 5236-5245. |
| 95 | ROBICHAUD G, BARRY J A, MUDDIMAN D C. IR-MALDESI mass spectrometry imaging of biological tissue sections using ice as a matrix[J]. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2014, 25(3): 319-328. |
| 96 | CHEN B M, OUYANG C Z, TIAN Z C, et al. A high resolution atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-quadrupole-orbitrap MS platform enables in situ analysis of biomolecules by multi-mode ionization and acquisition[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2018, 1007: 16-25. |
| 97 | MADONNA A J, VOORHEES K J, TARANENKO N I, et al. Detection of cyclic lipopeptide biomarkers from Bacillus species using atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2003, 75(7): 1628-1637. |
| 98 | CODY R B, LARAMÉE J A, DURST H D. Versatile new ion source for the analysis of materials in open air under ambient conditions[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2005, 77(8): 2297-2302. |
| 99 | CODY R B, MCALPIN C R, COX C R, et al. Identification of bacteria by fatty acid profiling with direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2015, 29(21): 2007-2012. |
| 100 | NA N, ZHAO M X, ZHANG S C, et al. Development of a dielectric barrier discharge ion source for ambient mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2007, 18(10): 1859-1862. |
| 101 | LIU Q L, GE W J, WANG T T, et al. High-throughput single-cell mass spectrometry reveals abnormal lipid metabolism in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(46): 24534-24542. |
| 102 | HARPER J D, CHARIPAR N A, MULLIGAN C C, et al. Low-temperature plasma probe for ambient desorption ionization[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80(23): 9097-9104. |
| 103 | ZHANG S Y, ZHU J, FAN S, et al. Directed evolution of a cyclodipeptide synthase with new activities via label-free mass spectrometric screening[J]. Chemical Science, 2022, 13(25): 7581-7586. |
| 104 | CHOE K, XUE P, ZHAO H M, et al. MacroMS: image-guided analysis of random objects by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2021, 32(5): 1180-1188. |
| 105 | BROCKMANN E U, POTTHOFF A, TORTORELLA S, et al. Infrared MALDI mass spectrometry with laser-induced postionization for imaging of bacterial colonies[J]. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 2021, 32(4): 1053-1064. |
| 106 | SI T, LI B, ZHANG K, et al. Characterization of Bacillus subtilis colony biofilms via mass spectrometry and fluorescence imaging[J]. Journal of Proteome Research, 2016, 15(6): 1955-1962. |
| 107 | YAN C Y, PARMEGGIANI F, JONES E A, et al. Real-time screening of biocatalysts in live bacterial colonies[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(4): 1408-1411. |
| 108 | GOWERS G O F, CAMERON S J S, PERDONES-MONTERO A, et al. Off-colony screening of biosynthetic libraries by rapid laser-enabled mass spectrometry[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(11): 2566-2575. |
| 109 | GUO E P, FU L H, FANG X T, et al. Robotic construction and screening of lanthipeptide variant libraries in Escherichia coli [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(12): 3900-3911. |
| 110 | CHEN K, BALUYA D, TOSUN M, et al. Imaging mass spectrometry: a new tool to assess molecular underpinnings of neurodegeneration[J]. Metabolites, 2019, 9(7): 135. |
| 111 | RIVERA E S, WEISS A, MIGAS L G, et al. Imaging mass spectrometry reveals complex lipid distributions across Staphylococcus aureus biofilm layers[J]. Journal of Mass Spectrometry and Advances in the Clinical Lab, 2022, 26: 36-46. |
| 112 | MCCAUGHEY CATHERINE S, TREBINO MICHAEL A, YILDIZ FITNAT H, et al. Utilizing imaging mass spectrometry to analyze microbial biofilm chemical responses to exogenous compounds[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2022, 665: 281-304. |
| 113 | LI B, COMI T J, SI T, et al. A one-step matrix application method for MALDI mass spectrometry imaging of bacterial colony biofilms[J]. Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2016, 51(11): 1030-1035. |
| 114 | QI K K, WU L T, LIU C Y, et al. Recent advances of ambient mass spectrometry imaging and its applications in lipid and metabolite analysis[J]. Metabolites, 2021, 11(11): 780. |
| 115 | XIAO Y P, DENG J W, YAO Y, et al. Recent advances of ambient mass spectrometry imaging for biological tissues: A review[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2020, 1117: 74-88. |
| 116 | LI N, NIE H G, JIANG L P, et al. Recent advances of ambient ionization mass spectrometry imaging in clinical research[J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2020, 43(15): 3146-3163. |
| 117 | XUE J J, BAI Y, LIU H W. Recent advances in ambient mass spectrometry imaging[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 120: 115659. |
| 118 | PEREZ C J, BAGGA A K, PROVA S S, et al. Review and perspectives on the applications of mass spectrometry imaging under ambient conditions[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2019, 33(S3): 27-53. |
| 119 | DUNHAM S J B, ELLIS J F, LI B, et al. Mass spectrometry imaging of complex microbial communities[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2017, 50(1): 96-104. |
| 120 | STASULLI N M, SHANK E A. Profiling the metabolic signals involved in chemical communication between microbes using imaging mass spectrometry[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2016, 40(6): 807-813. |
| 121 | LASKIN J, LANEKOFF I. Ambient mass spectrometry imaging using direct liquid extraction techniques[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 88(1): 52-73. |
| 122 | SHIH C J, CHEN P Y, LIAW C C, et al. Bringing microbial interactions to light using imaging mass spectrometry[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2014, 31(6): 739-755. |
| 123 | WU C P, DILL A L, EBERLIN L S, et al. Mass spectrometry imaging under ambient conditions[J]. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 2013, 32(3): 218-243. |
| 124 | WATROUS J D, DORRESTEIN P C. Imaging mass spectrometry in microbiology[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2011, 9(9): 683-694. |
| 125 | LI H, SMITH B K, MARK L, et al. Ambient molecular imaging by laser ablation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry with ion mobility separation[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2015, 377: 681-689. |
| 126 | STOPKA S A, RONG C, KORTE A R, et al. Molecular imaging of biological samples on nanophotonic laser desorption ionization platforms[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(14): 4482-4486. |
| 127 | LUKOWSKI J K, BHATTACHARJEE A, YANNARELL S M, et al. Expanding molecular coverage in mass spectrometry imaging of microbial systems using metal-assisted laser desorption/ionization[J]. Microbiology Spectrum, 2021, 9(1): e00520-21. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [3] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [4] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [5] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [6] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [7] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [8] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [9] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [10] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [11] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [12] | 陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [13] | 蔡冰玉, 谭象天, 李伟. 合成生物学在干细胞工程化改造中的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| [14] | 谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630. |
| [15] | 查文龙, 卜兰, 訾佳辰. 中药药效成分群的合成生物学研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 631-657. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||