合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (4): 795-812.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-106
类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展
陈子苓, 向阳飞
- 上海科技大学生命科学与技术学院,上海 201210
-
收稿日期:2023-12-09修回日期:2024-02-23出版日期:2024-08-31发布日期:2024-09-19 -
通讯作者:向阳飞 -
作者简介:陈子苓 (2000—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为神经类器官。E-mail:chenzl2022@shanghaitech.edu.cn向阳飞 (1983—),男,博士,研究员。研究方向为干细胞与神经生物学。E-mail:xiangyf@shanghaitech.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFF1200800);国家自然科学基金(32170836);中央引导地方项目(YDZX20233100001002)
Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology
CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei
- School of Life Science and Technology,ShanghaiTech University,Shanghai 201210,China
-
Received:2023-12-09Revised:2024-02-23Online:2024-08-31Published:2024-09-19 -
Contact:XIANG Yangfei
摘要:
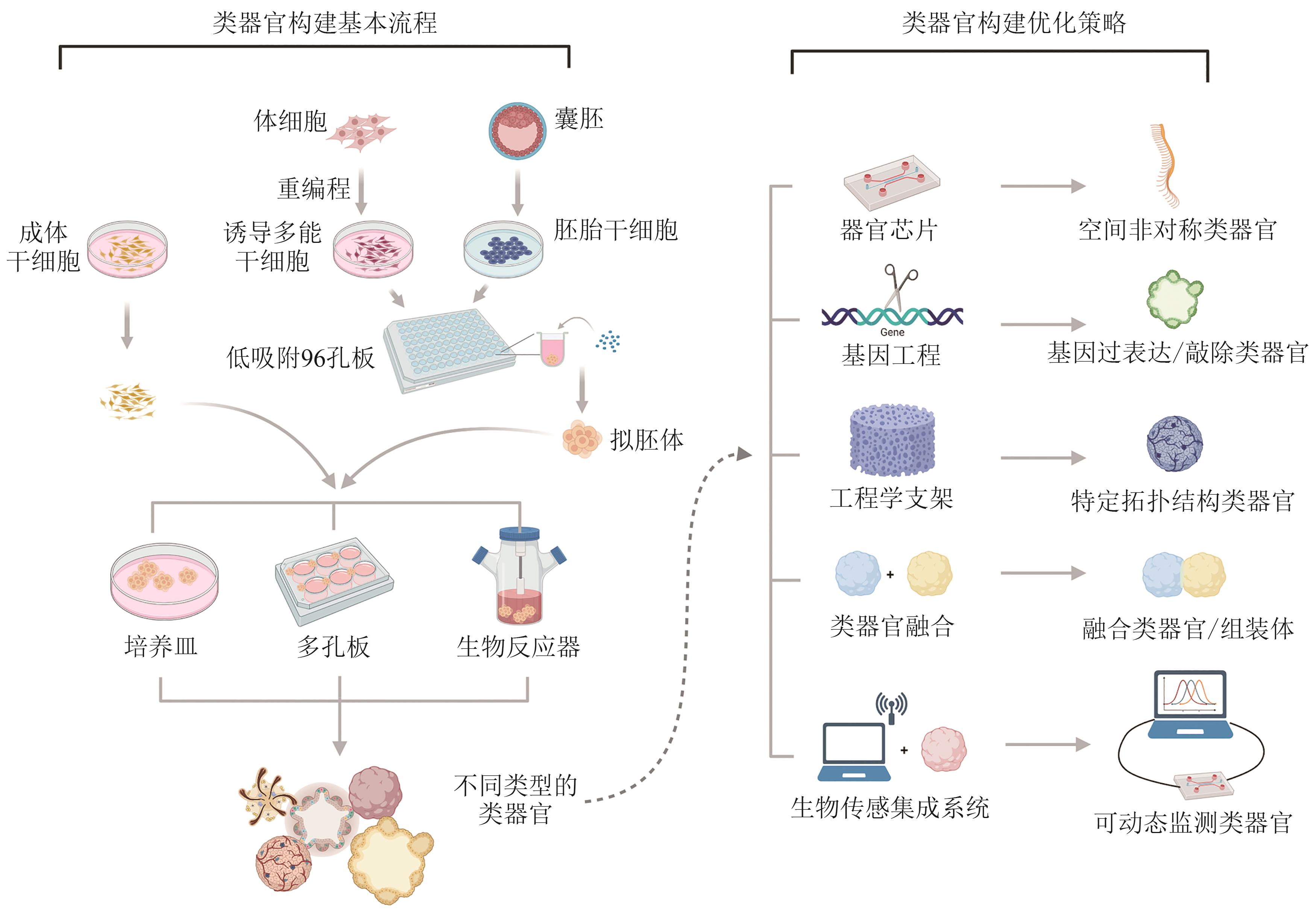
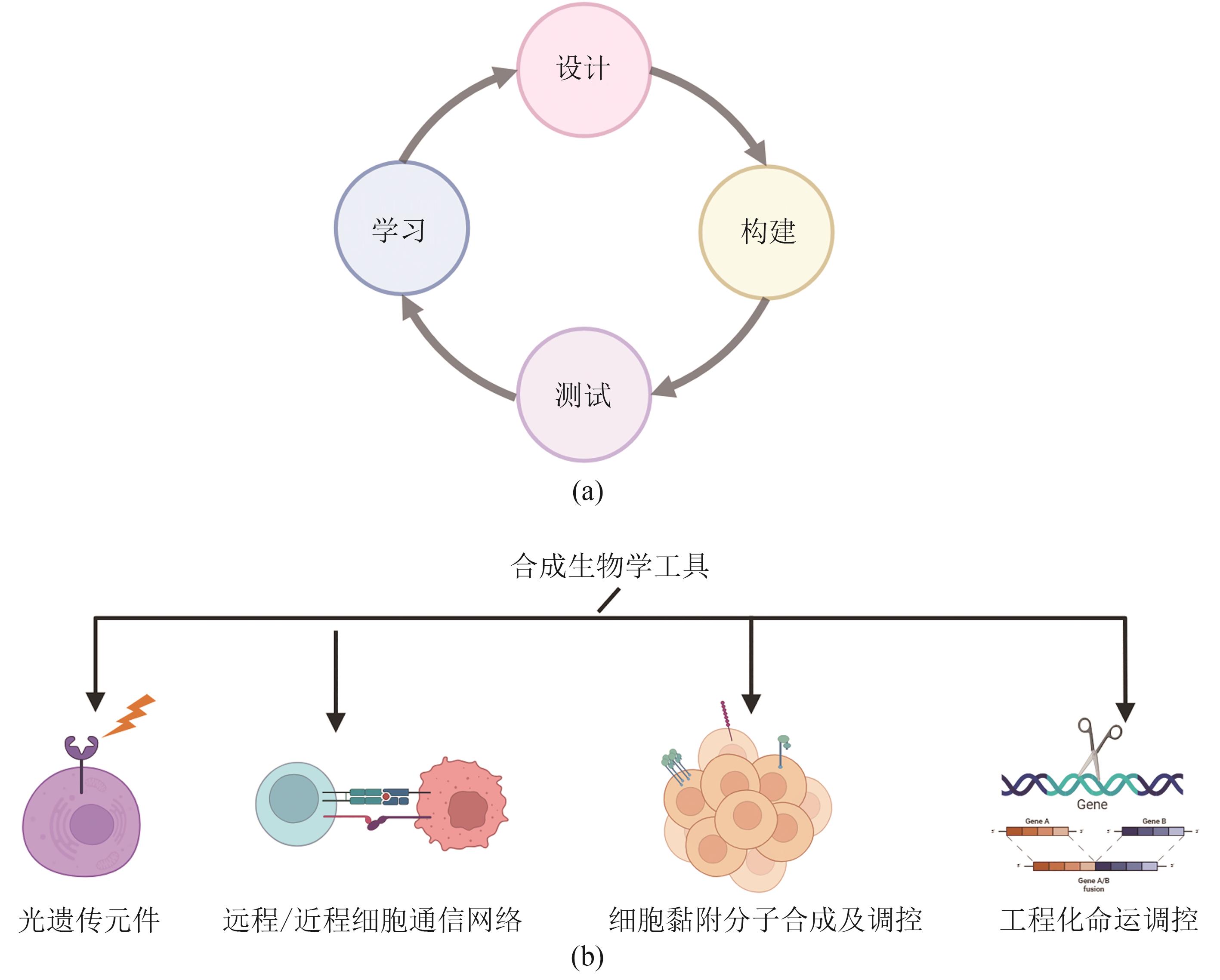
类器官由成体干细胞或多能干细胞在体外分化而来,可以在细胞类型、空间结构及生理功能上实现对体内组织器官的模拟。类器官的构建及技术完善,推动了发育生物学、遗传学、病理毒理学等发展。合成生物学是一门多学科交叉的新兴学科,以工程学思想为指导,旨在通过工程化、模块化的方法设计、改造、构建生物元件、系统、功能等。近年来类器官构建的优化方案体现了与合成生物学契合的研究理念,而合成生物学的发展及相关方法的产生也为类器官技术的发展起到了推动作用。本文将概述类器官和合成生物学的发展历程与面对的挑战,探讨类器官优化过程中合成生物学策略的体现与新兴的合成生物学工具对于类器官在时空命运调控、结构自组织及功能形成等方面的优化作用,简述基于类器官模型的研究对于合成生物学发展的促进作用。总的来说,本文旨在阐述合成生物学与类器官构建及优化之间相辅相成、互相促进的关系,并进一步探讨合成生物学与类器官在未来结合应用的潜力。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈子苓, 向阳飞. 类器官技术与合成生物学协同研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 795-812.
CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812.
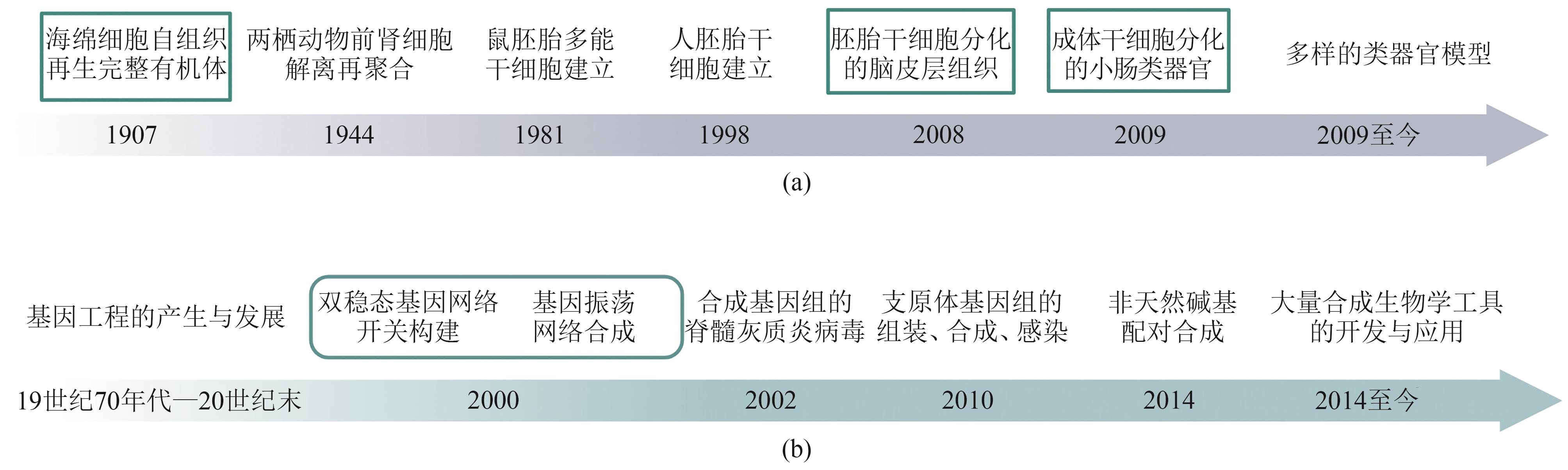
| 1 | LANCASTER M A, KNOBLICH J A. Generation of cerebral organoids from human pluripotent stem cells[J]. Nature Protocols, 2014, 9(10): 2329-2340. |
| 2 | XIANG Y F, CAKIR B, PARK I H. Generation of regionally specified human brain organoids resembling thalamus development[J]. STAR Protocols, 2020, 1(1): 100001. |
| 3 | WANG J Y, NIELSEN J, LIU Z H. Synthetic biology advanced natural product discovery[J]. Metabolites, 2021, 11(11): 785. |
| 4 | 李童, 杨劲树, 杨卫军. 肺成体干细胞体外培养模型的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(9): 3255-3266. |
| LI T, YANG J S, YANG W J. Advances of in vitro culture models derived from lung adult stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 38(9): 3255-3266. | |
| 5 | NIKOLAEV M, MITROFANOVA O, BROGUIERE N, et al. Homeostatic mini-intestines through scaffold-guided organoid morphogenesis[J]. Nature, 2020, 585(7826): 574-578. |
| 6 | CLEVERS H. Modeling development and disease with organoids[J]. Cell, 2016, 165(7): 1586-1597. |
| 7 | LI M, IZPISUA BELMONTE J C. Organoids - preclinical models of human disease[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2019, 380(6): 569-579. |
| 8 | LANCASTER M A. Brain organoids: a new frontier of human neuroscience research[J]. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 2021, 111: 1-3. |
| 9 | MEIER A B, ZAWADA D, DE ANGELIS M T, et al. Epicardioid single-cell genomics uncovers principles of human epicardium biology in heart development and disease[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2023, 41(12): 1787-1800. |
| 10 | UZQUIANO A, KEDAIGLE A J, PIGONI M, et al. Proper acquisition of cell class identity in organoids allows definition of fate specification programs of the human cerebral cortex[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(20): 3770-3788. |
| 11 | BOUFFI C, WIKENHEISER-BROKAMP K A, CHATURVEDI P, et al. In vivo development of immune tissue in human intestinal organoids transplanted into humanized mice[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2023, 41(6): 824-831. |
| 12 | GABRIEL E, ALBANNA W, PASQUINI G, et al. Human brain organoids assemble functionally integrated bilateral optic vesicles[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2021, 28(10): 1740-1757. |
| 13 | SCHMIDT C, DEYETT A, ILMER T, et al. Multi-chamber cardioids unravel human heart development and cardiac defects[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(25): 5587-5605. |
| 14 | FAUSTINO MARTINS J M, FISCHER C, URZI A, et al. Self-organizing 3D human trunk neuromuscular organoids[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2020, 26(2): 172-186. |
| 15 | PELLEGRINI L, LANCASTER M A. Modeling neurodegeneration with mutant-tau organoids[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(17): 4377-4379. |
| 16 | JIANG S W, ZHAO H R, ZHANG W J, et al. An automated organoid platform with inter-organoid homogeneity and inter-patient heterogeneity[J]. Cell Reports Medicine, 2020, 1(9): 100161. |
| 17 | CORRÒ C, NOVELLASDEMUNT L, LI V S W. A brief history of organoids[J]. American Journal of Physiology Cell Physiology, 2020, 319(1): C151-C165. |
| 18 | BIJUKUMAR G, SOMVANSHI P R. Reverse engineering in biotechnology: the role of genetic engineering in synthetic biology[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2024, 2719: 307-324. |
| 19 | CAMERON D E, BASHOR C J, COLLINS J J. A brief history of synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2014, 12(5): 381-390. |
| 20 | SMITH E, COCHRANE W J. Cystic organoid teratoma; report of a case[J]. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 1946, 55(2): 151. |
| 21 | WILSON H V. A new method by which sponges may be artificially reared[J]. Science, 1907, 25(649): 912-915. |
| 22 | TUNG T C, KÜ S H. Experimental studies on the development of the pronephric duct in anuran embryos[J]. Journal of Anatomy, 1944, 78(1/2): 52-57. |
| 23 | WEISS P, TAYLOR A C. Reconstitution of complete organs from single-cell suspensions of chick embryos in advanced stages of differentiation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1960, 46(9): 1177-1185. |
| 24 | EIRAKU M, WATANABE K, MATSUO-TAKASAKI M, et al. Self-organized formation of polarized cortical tissues from ESCs and its active manipulation by extrinsic signals[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2008, 3(5): 519-532. |
| 25 | SATO T, VRIES R G, SNIPPERT H J, et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche[J]. Nature, 2009, 459(7244): 262-265. |
| 26 | KIM T H, SHIVDASANI R A. Stomach development, stem cells and disease[J]. Development, 2016, 143(4): 554-565. |
| 27 | BROUTIER L, ANDERSSON-ROLF A, HINDLEY C J, et al. Culture and establishment of self-renewing human and mouse adult liver and pancreas 3D organoids and their genetic manipulation[J]. Nature Protocols, 2016, 11(9): 1724-1743. |
| 28 | HUCH M, GEHART H, VAN BOXTEL R, et al. Long-term culture of genome-stable bipotent stem cells from adult human liver[J]. Cell, 2015, 160(1/2): 299-312. |
| 29 | NARAYANAN S, SURETTE F A, HAHN Y S. The immune landscape in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Immune Network, 2016, 16(3): 147-158. |
| 30 | TAKEBE T, SEKINE K, ENOMURA M, et al. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant[J]. Nature, 2013, 499(7459): 481-484. |
| 31 | MORIZANE R, BONVENTRE J V. Generation of nephron progenitor cells and kidney organoids from human pluripotent stem cells[J]. Nature Protocols, 2017, 12(1): 195-207. |
| 32 | CHEN Y W, HUANG S X, DE CARVALHO A L R T, et al. A three-dimensional model of human lung development and disease from pluripotent stem cells[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2017, 19(5): 542-549. |
| 33 | LANCASTER M A, RENNER M, MARTIN C A, et al. Cerebral organoids model human brain development and microcephaly[J]. Nature, 2013, 501(7467): 373-379. |
| 34 | QIAN X Y, NGUYEN H N, SONG M M, et al. Brain-region-specific organoids using mini-bioreactors for modeling ZIKV exposure[J]. Cell, 2016, 165(5): 1238-1254. |
| 35 | ASSAWACHANANONT J, MANDAI M, OKAMOTO S, et al. Transplantation of embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived 3D retinal sheets into retinal degenerative mice[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2014, 2(5): 662-674. |
| 36 | KIM M S, MUN H M, SUNG C O, et al. Patient-derived lung cancer organoids as in vitro cancer models for therapeutic screening[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 3991. |
| 37 | QU M L, XIONG L, LÜ Y L, et al. Establishment of intestinal organoid cultures modeling injury-associated epithelial regeneration[J]. Cell Research, 2021, 31(3): 259-271. |
| 38 | LU X X, YANG J J, XIANG Y F. Modeling human neurodevelopmental diseases with brain organoids[J]. Cell Regeneration, 2022, 11(1): 1. |
| 39 | TANG X Y, WU S S, WANG D, et al. Human organoids in basic research and clinical applications[J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2022, 7(1): 168. |
| 40 | CAKIR B, XIANG Y F, TANAKA Y, et al. Engineering of human brain organoids with a functional vascular-like system[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(11): 1169-1175. |
| 41 | ZHAO Z X, CHEN X Y, DOWBAJ A M, et al. Organoids[J]. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 2022, 2: 94. |
| 42 | TAO T T, DENG P W, WANG Y Q, et al. Microengineered multi-organoid system from hiPSCs to recapitulate human liver-islet axis in normal and type 2 diabetes[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(5): e2103495. |
| 43 | ZHANG W J, LI J W, ZHOU J Q, et al. Translational organoid technology — the convergence of chemical, mechanical, and computational biology[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2022, 40(9): 1121-1135. |
| 44 | PARK S E, GEORGESCU A, HUH D. Organoids-on-a-chip[J]. Science, 2019, 364(6444): 960-965. |
| 45 | JI S Y, FENG L, FU Z L, et al. Pharmaco-proteogenomic characterization of liver cancer organoids for precision oncology[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2023, 15(706): eadg3358. |
| 46 | LIN L, DEMARTINO J, WANG D S, et al. Unbiased transcription factor CRISPR screen identifies ZNF800 as master repressor of enteroendocrine differentiation[J]. Science, 2023, 382(6669): 451-458. |
| 47 | HENDRIKS D, BROUWERS J F, HAMER K, et al. Engineered human hepatocyte organoids enable CRISPR-based target discovery and drug screening for steatosis[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2023, 41(11): 1567-1581. |
| 48 | HANSEN S L, LARSEN H L, PIKKUPEURA L M, et al. An organoid-based CRISPR-Cas9 screen for regulators of intestinal epithelial maturation and cell fate[J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(28): eadg4055. |
| 49 | GARDNER T S, CANTOR C R, COLLINS J J. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 339-342. |
| 50 | ELOWITZ M B, LEIBLER S. A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators[J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 335-338. |
| 51 | MUELLER S, CAO X M, WELKER R, et al. Interaction of the poliovirus receptor CD155 with the dynein light chain Tctex-1 and its implication for poliovirus pathogenesis[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2002, 277(10): 7897-7904. |
| 52 | GIBSON D G, GLASS J I, LARTIGUE C, et al. Creation of a bacterial cell controlled by a chemically synthesized genome[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5987): 52-56. |
| 53 | GIBSON D G, YOUNG L, CHUANG R Y, et al. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases[J]. Nature Methods, 2009, 6(5): 343-345. |
| 54 | LI L J, DEGARDIN M, LAVERGNE T, et al. Natural-like replication of an unnatural base pair for the expansion of the genetic alphabet and biotechnology applications[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(3): 826-829. |
| 55 | SHI Y C, WU Q, WANG X Q. Modeling brain development and diseases with human cerebral organoids[J]. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 2021, 66: 103-115. |
| 56 | MENG F K, ELLIS T. The second decade of synthetic biology: 2010—2020[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5174. |
| 57 | ANDREWS L B, NIELSEN A A K, VOIGT C A. Cellular checkpoint control using programmable sequential logic[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6408): eaap8987. |
| 58 | MIURA Y, LI M Y, BIREY F, et al. Generation of human striatal organoids and cortico-striatal assembloids from human pluripotent stem cells[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(12): 1421-1430. |
| 59 | TODA S, BLAUCH L R, TANG S K Y, et al. Programming self-organizing multicellular structures with synthetic cell-cell signaling[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6398): 156-162. |
| 60 | MCCRACKEN K W, CATÁ E M, CRAWFORD C M, et al. Modelling human development and disease in pluripotent stem-cell-derived gastric organoids[J]. Nature, 2014, 516(7531): 400-404. |
| 61 | EIRAKU M, TAKATA N, ISHIBASHI H, et al. Self-organizing optic-cup morphogenesis in three-dimensional culture[J]. Nature, 2011, 472(7341): 51-56. |
| 62 | CRUZ N M, SONG X W, CZERNIECKI S M, et al. Organoid cystogenesis reveals a critical role of microenvironment in human polycystic kidney disease[J]. Nature Materials, 2017, 16(11): 1112-1119. |
| 63 | CEDERQUIST G Y, ASCIOLLA J J, TCHIEU J, et al. Specification of positional identity in forebrain organoids[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(4): 436-444. |
| 64 | DEMERS C J, SOUNDARARAJAN P, CHENNAMPALLY P, et al. Development-on-chip: in vitro neural tube patterning with a microfluidic device[J]. Development, 2016, 143(11): 1884-1892. |
| 65 | RIFES P, ISAKSSON M, RATHORE G S, et al. Modeling neural tube development by differentiation of human embryonic stem cells in a microfluidic WNT gradient[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(11): 1265-1273. |
| 66 | LEE K K, MCCAULEY H A, BRODA T R, et al. Human stomach-on-a-chip with luminal flow and peristaltic-like motility[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(20): 3079-3085. |
| 67 | HOMAN K A, GUPTA N, KROLL K T, et al. Flow-enhanced vascularization and maturation of kidney organoids in vitro [J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(3): 255-262. |
| 68 | WANG Y Q, WANG H, DENG P W, et al. In situ differentiation and generation of functional liver organoids from human iPSCs in a 3D perfusable chip system[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(23): 3606-3616. |
| 69 | TAO T T, WANG Y Q, CHEN W W, et al. Engineering human islet organoids from iPSCs using an organ-on-chip platform[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2019, 19(6): 948-958. |
| 70 | LIU X, CHENG Y L, ABRAHAM J M, et al. Modeling Wnt signaling by CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing recapitulates neoplasia in human Barrett epithelial organoids[J]. Cancer Letters, 2018, 436: 109-118. |
| 71 | ZHAO H, CHENG Y L, KALRA A, et al. Generation and multiomic profiling of a TP53/CDKN2A double-knockout gastroesophageal junction organoid model[J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2022, 14(673): eabq6146. |
| 72 | TRUJILLO C A, RICE E S, SCHAEFER N K, et al. Reintroduction of the archaic variant of NOVA1 in cortical organoids alters neurodevelopment[J]. Science, 2021, 371(6530): eaax2537. |
| 73 | ARTEGIANI B, HENDRIKS D, BEUMER J, et al. Fast and efficient generation of knock-in human organoids using homology-independent CRISPR-Cas9 precision genome editing[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2020, 22(3): 321-331. |
| 74 | ESK C, LINDENHOFER D, HAENDELER S, et al. A human tissue screen identifies a regulator of ER secretion as a brain-size determinant[J]. Science, 2020, 370(6519): 935-941. |
| 75 | BORTOLOMAI I, SANDRI M, DRAGHICI E, et al. Gene modification and three-dimensional scaffolds as novel tools to allow the use of postnatal thymic epithelial cells for Thymus regeneration approaches[J]. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 2019, 8(10): 1107-1122. |
| 76 | ROTHENBÜCHER T S P, GÜRBÜZ H, PEREIRA M P, et al. Next generation human brain models: engineered flat brain organoids featuring gyrification[J]. Biofabrication, 2021, 13(1): 011001. |
| 77 | CHEN S S, CHEN X, GENG Z, et al. The horizon of bone organoid: a perspective on construction and application[J]. Bioactive Materials, 2022, 18: 15-25. |
| 78 | Jamaluddin M F B, Ghosh A, Ingle A, et al. Bovine and human endometrium-derived hydrogels support organoid culture from healthy and cancerous tissues. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2022, 119(44): e2208040119 |
| 79 | XIANG Y F, TANAKA Y, PATTERSON B, et al. Fusion of regionally specified hPSC-derived organoids models human brain development and interneuron migration[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2017, 21(3): 383-398. e7. |
| 80 | ANDERSEN J, REVAH O, MIURA Y, et al. Generation of functional human 3D cortico-motor assembloids[J]. Cell, 2020, 183(7): 1913-1929. |
| 81 | LIND J U, BUSBEE T A, VALENTINE A D, et al. Instrumented cardiac microphysiological devices via multimaterial three-dimensional printing[J]. Nature Materials, 2017, 16(3): 303-308. |
| 82 | ZHANG Y S, ALEMAN J, SHIN S R, et al. Multisensor-integrated organs-on-chips platform for automated and continual in situ monitoring of organoid behaviors[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(12): E2293-E2302. |
| 83 | STEPHENSON A, LASTRA L, NGUYEN B, et al. Physical laboratory automation in synthetic biology[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2023, 12(11): 3156-3169. |
| 84 | CHIA N, LEE S Y, TONG Y J. Optogenetic tools for microbial synthetic biology[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2022, 59: 107953. |
| 85 | REPINA N A, JOHNSON H J, BAO X P, et al. Optogenetic control of Wnt signaling models cell-intrinsic embryogenic patterning using 2D human pluripotent stem cell culture[J]. Development, 2023, 150(14): dev201386. |
| 86 | LEGNINI I, EMMENEGGER L, ZAPPULO A, et al. Spatiotemporal, optogenetic control of gene expression in organoids[J]. Nature Methods, 2023, 20(10): 1544-1552. |
| 87 | MANHAS J, EDELSTEIN H I, LEONARD J N, et al. The evolution of synthetic receptor systems[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2022, 18(3): 244-255. |
| 88 | WANG H F, ZANG C Z, LIU X S, et al. The role of Notch receptors in transcriptional regulation[J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 2015, 230(5): 982-988. |
| 89 | MORSUT L, ROYBAL K T, XIONG X, et al. Engineering customized cell sensing and response behaviors using synthetic Notch receptors[J]. Cell, 2016, 164(4): 780-791. |
| 90 | MALAGUTI M, PORTERO MIGUELES R, ANNOH J, et al. SyNPL: synthetic Notch pluripotent cell lines to monitor and manipulate cell interactions in vitro and in vivo [J]. Development, 2022, 149(12): dev200226. |
| 91 | TODA S, MCKEITHAN W L, HAKKINEN T J, et al. Engineering synthetic morphogen systems that can program multicellular patterning[J]. Science, 2020, 370(6514): 327-331. |
| 92 | FOTY R A, STEINBERG M S. The differential adhesion hypothesis: a direct evaluation[J]. Developmental Biology, 2005, 278(1): 255-263. |
| 93 | STEVENS A J, HARRIS A R, GERDTS J, et al. Programming multicellular assembly with synthetic cell adhesion molecules[J]. Nature, 2023, 614(7946): 144-152. |
| 94 | TRENTESAUX C, YAMADA T, KLEIN O D, et al. Harnessing synthetic biology to engineer organoids and tissues[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(1): 10-19. |
| 95 | ZHU J W, CHU P, FU X F. Unbalanced response to growth variations reshapes the cell fate decision landscape[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2023, 19(9): 1097-1104. |
| 96 | CAMP J G, BADSHA F, FLORIO M, et al. Human cerebral organoids recapitulate gene expression programs of fetal neocortex development[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(51): 15672-15677. |
| 97 | PAULSEN B, VELASCO S, KEDAIGLE A J, et al. Autism genes converge on asynchronous development of shared neuron classes[J]. Nature, 2022, 602(7896): 268-273. |
| 98 | AMIN N D, KELLEY K W, HAO J, et al. Generating human neural diversity with a multiplexed morphogen screen in organoids[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2023: 2023.05.31.541819[2023-12-01]. . |
| 99 | HE Z S, DONY L, Fleck J S, et al. An integrated transcriptomic cell atlas of human neural organoids[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2023: 2023.10.05.561097[2023-12-01]. . |
| 100 | MENG X L, YAO D, IMAIZUMI K, et al. Assembloid CRISPR screens reveal impact of disease genes in human neurodevelopment[J]. Nature, 2023, 622(7982): 359-366. |
| [1] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | 董颖, 马孟丹, 黄卫人. CRISPR-Cas系统的小型化研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 105-117. |
| [3] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [11] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [12] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [13] | 艾宗勇, 张成庭, 牛宝华, 尹宇, 杨洁, 李天晴. 人胚胎早期发育与干细胞[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 700-718. |
| [14] | 胡可儿, 王汉奇, 黄儒麒, 张灿阳, 邢新会, 马少华. 整合设计策略下的工程化类器官与类器官芯片技术[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 883-897. |
| [15] | 李石开, 曾东鳌, 杜方舟, 张京钟, 余爽. 血管化类器官的构建方法及生物材料[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(4): 851-866. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||