Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (3): 429-444.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2021-032
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Artificial intelligence-assisted protein engineering
BIAN Jiahao, YANG Guangyu
- State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism,School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 200240,China
-
Received:2021-03-16Revised:2021-05-24Online:2022-07-13Published:2022-06-30 -
Contact:YANG Guangyu
人工智能辅助的蛋白质工程
卞佳豪, 杨广宇
- 上海交通大学 生命科学技术学院,微生物代谢国家重点实验室,上海 200240
-
通讯作者:杨广宇 -
作者简介:卞佳豪 (1997—),男,硕士研究生。研究方向为人工智能辅助定向进化的组合方法。 E-mail:bjh2170@sjtu.edu.cn杨广宇 (1980—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为酶定向进化、酶高通量筛选、酶技术应用、体外合成生物学等。E-mail:yanggy@sjtu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(32030063)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
BIAN Jiahao, YANG Guangyu. Artificial intelligence-assisted protein engineering[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(3): 429-444.
卞佳豪, 杨广宇. 人工智能辅助的蛋白质工程[J]. 合成生物学, 2022, 3(3): 429-444.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2021-032

Fig. 1 Schematic diagram for rational design, directed evolution and artificial intelligence-assisted protein engineering(Rational design relies on sequence and structural information to design mutant libraries accurately. However, it is difficult for being applied to proteins lacking structural and functional information. In the directed evolution strategy, multiple rounds of mutation and screening experiments are performed on target genes, which are not limited by structural and functional information, but high-throughput screening methods are required. Artificial intelligence-assisted protein engineering requires a large amount of sequence-function data, which can be derived from experiments, calculations, and databases. Through the predictive model, the sequence space of protein mutants can be explored more effectively)
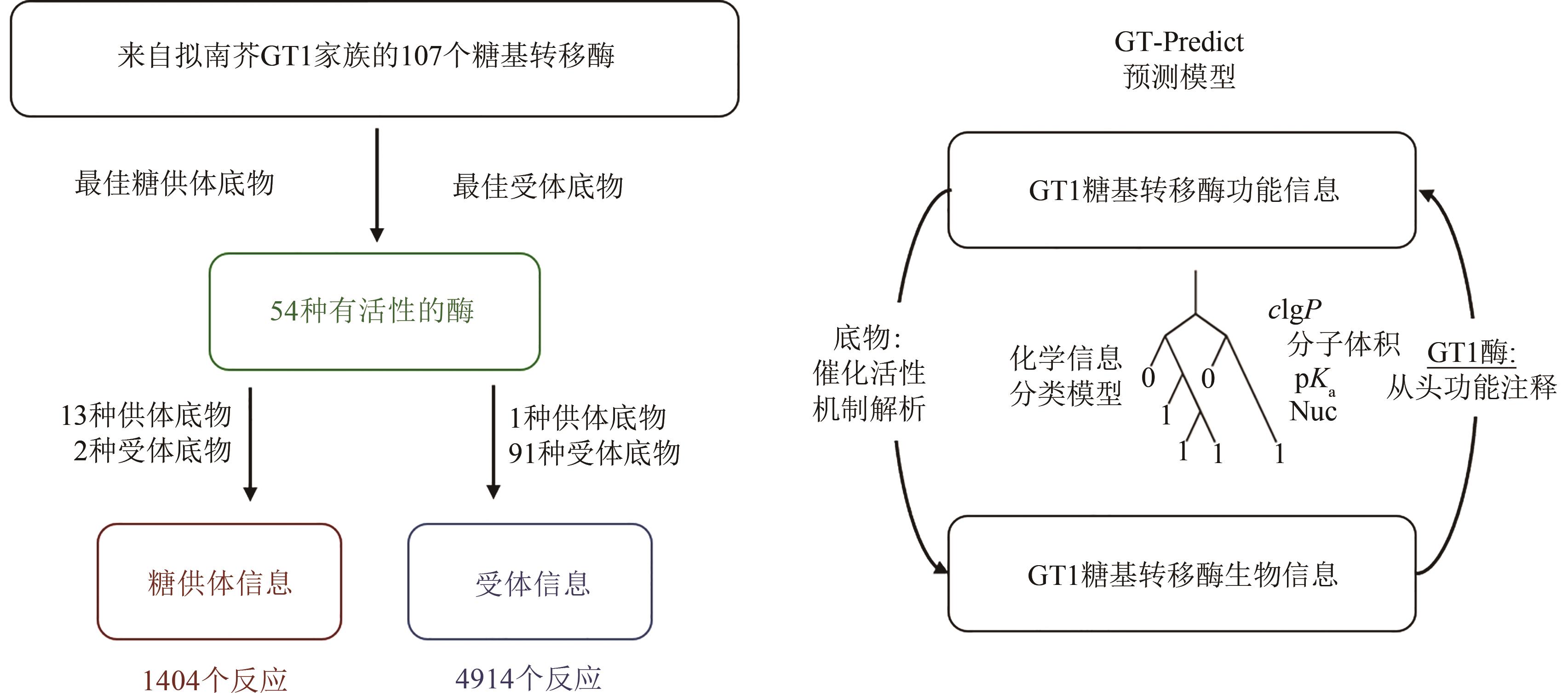
Fig. 2 Workflow for predicting the GT1 glycosyltransferase model (GT-Predict)[19](The function-based algorithmic learning approach, GT-Predict, uses a diverse training set of enzymes, electrophiles, and nucleophiles to create a physicochemical and local-sequence-based classifier for predicting the novel transformations and functional annotation of GT group-transfer enzymes.)
| 名称 | 发表日期 | 分子描述符 | 程序/算法 | 软件/工具包地址 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRIAM | 2003年 11月15日 | 序列比对构建的同源模块 | PSI-BLAST序列比对程序 | http://genopole.toulouse.inra.fr/bioinfo/priam/ |
| CatFam | 2008年 07月17日 | 序列比对和分层聚类 | ClustalW和PSI-BLAST 序列比对程序 | http://www.bhsai.org/downloads/catfam.tar.gz |
| EFICAz2.5 | 2012年 08月24日 | 序列比对和分层聚类 | 支持向量机(SVM)和 分类树(classification trees) | http://cssb.biology.gatech.edu/EFICAz2.5 |
| SVM-Prot | 2016年 08月15日 | 多种分子描述符(多种氨基酸 残基特性描述符和整体描述符) | 支持向量机(SVM), K最近邻(KNN)和概率 神经网络(sPNN) | http://bidd2.nus.edu.sg/cgi-bin/svmprot/svmprot.cgi |
| COFACTOR | 2017年 05月02日 | 来自BioLiP文库的结构信息 | 基于TM分数的蛋白质结构比对算法 | http://zhanglab.ccmb.med.umich.edu/COFACTOR/。 |
| DEEPre | 2017年 10月23日 | 序列独热编码,位置特异性得分矩阵,溶剂可及性,二级结构独热编码和功能结构域 | 卷积神经网络(CNN) 和循环神经网络(RNN) | http://www.cbrc.kaust.edu.sa/DEEPre |
| DETECT v2 | 2018年 05月02日 | 酶EC编号的正负密度分布图 | 贝叶斯框架(Bayesian framework) | https://github.com/ParkinsonLab/DETECT-v2 |
| ECPred | 2018年 09月21日 | 三种基于子序列,序列相似性和氨基酸物理化学特征的分子描述符:SPMap,BLAST-kNN和Pepstats-SVM | 二进制分类算法 | https://ecpred.kansil.org/ |
| DeepEC | 2019年 06月20日 | 独热编码 | 卷积神经网络(CNN) | https://bitbucket.org/kaistsystemsbiology/deepec |
Tab. 1 Forecast tools for EC numbers
| 名称 | 发表日期 | 分子描述符 | 程序/算法 | 软件/工具包地址 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRIAM | 2003年 11月15日 | 序列比对构建的同源模块 | PSI-BLAST序列比对程序 | http://genopole.toulouse.inra.fr/bioinfo/priam/ |
| CatFam | 2008年 07月17日 | 序列比对和分层聚类 | ClustalW和PSI-BLAST 序列比对程序 | http://www.bhsai.org/downloads/catfam.tar.gz |
| EFICAz2.5 | 2012年 08月24日 | 序列比对和分层聚类 | 支持向量机(SVM)和 分类树(classification trees) | http://cssb.biology.gatech.edu/EFICAz2.5 |
| SVM-Prot | 2016年 08月15日 | 多种分子描述符(多种氨基酸 残基特性描述符和整体描述符) | 支持向量机(SVM), K最近邻(KNN)和概率 神经网络(sPNN) | http://bidd2.nus.edu.sg/cgi-bin/svmprot/svmprot.cgi |
| COFACTOR | 2017年 05月02日 | 来自BioLiP文库的结构信息 | 基于TM分数的蛋白质结构比对算法 | http://zhanglab.ccmb.med.umich.edu/COFACTOR/。 |
| DEEPre | 2017年 10月23日 | 序列独热编码,位置特异性得分矩阵,溶剂可及性,二级结构独热编码和功能结构域 | 卷积神经网络(CNN) 和循环神经网络(RNN) | http://www.cbrc.kaust.edu.sa/DEEPre |
| DETECT v2 | 2018年 05月02日 | 酶EC编号的正负密度分布图 | 贝叶斯框架(Bayesian framework) | https://github.com/ParkinsonLab/DETECT-v2 |
| ECPred | 2018年 09月21日 | 三种基于子序列,序列相似性和氨基酸物理化学特征的分子描述符:SPMap,BLAST-kNN和Pepstats-SVM | 二进制分类算法 | https://ecpred.kansil.org/ |
| DeepEC | 2019年 06月20日 | 独热编码 | 卷积神经网络(CNN) | https://bitbucket.org/kaistsystemsbiology/deepec |
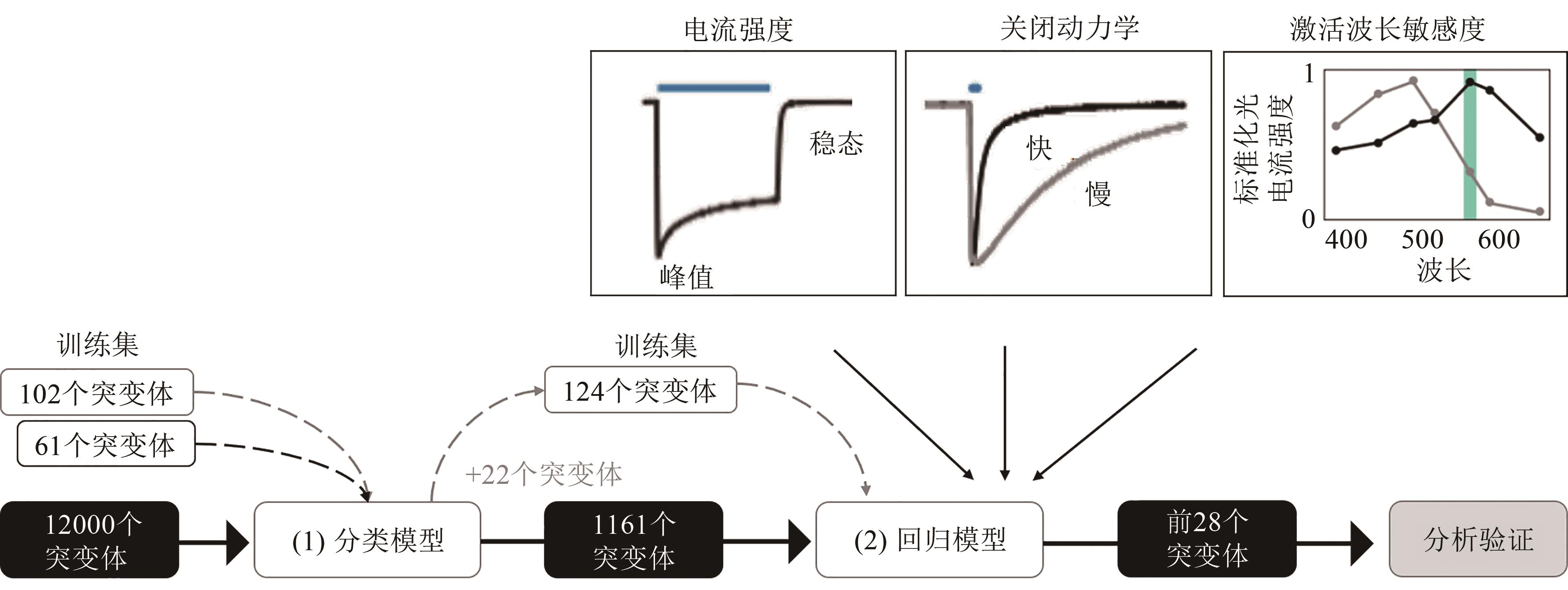
Fig. 3 Workflow for machine learning-guided channelrhodopsin engineering[26][102 ChR proteins characterized in the recombinant library, together with 61 variants reported in the literature, constitute the training set of the classification model (1). Then the trained classification model was used to predict whether 12000 uncharacterized ChR sequence variants are functional, and three regression models (2) were trained, one for each of the ChR photocurrent properties of interest: photocurrent strength, off-kinetics and wavelength sensitivity of the photocurrents.]
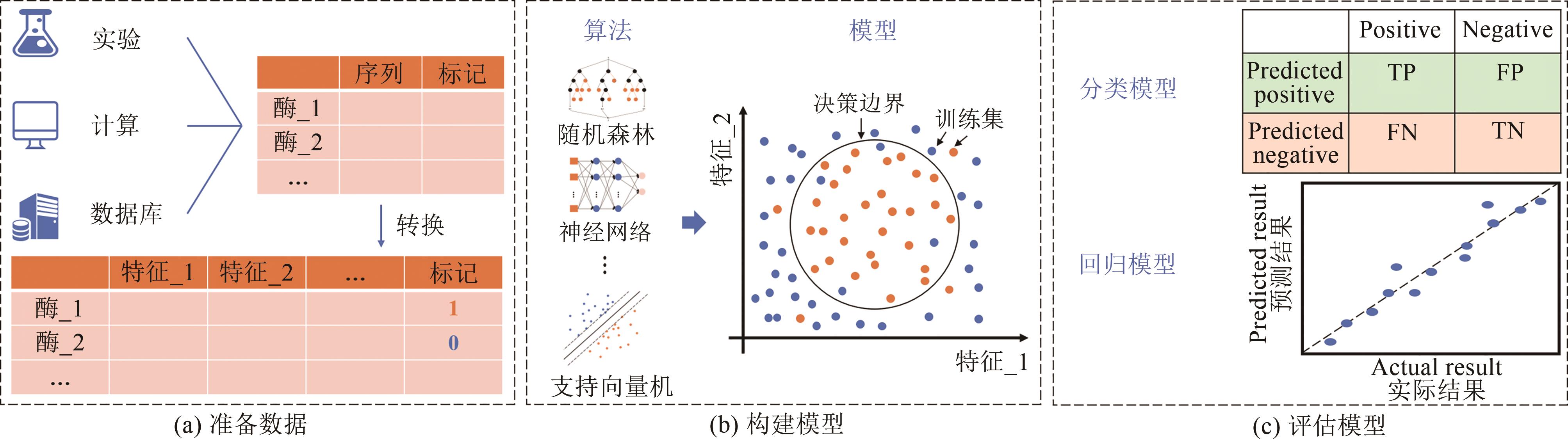
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of the supervised learning process[27]Step (a): Preparing data. The data from experiments, calculations or databases are usually converted to a format that the computer can recognize and split into the training and test parts. Step(b): Constructing a predictive model. Using the training set to train different algorithms to find decision boundaries, such as random forests, neural networks and support vector machines, so as to build predictive models. Step (c): Validating the model. An appropriate evaluation method should be selected for tasks with classification or regression.
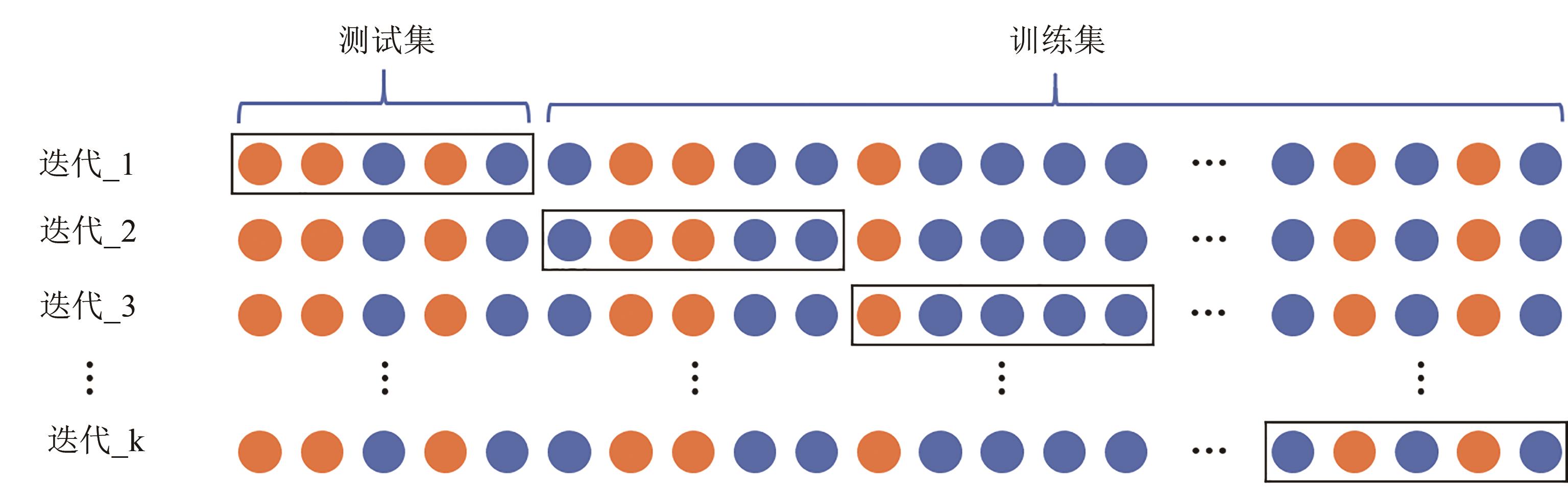
Fig. 5 Schematic diagram for k-fold cross-validation(The training data is further subsplit into k subsets, and the training workflow is repeated k times with each of the k subsets holding for evaluation and the remaining k-1 subsets used for training)
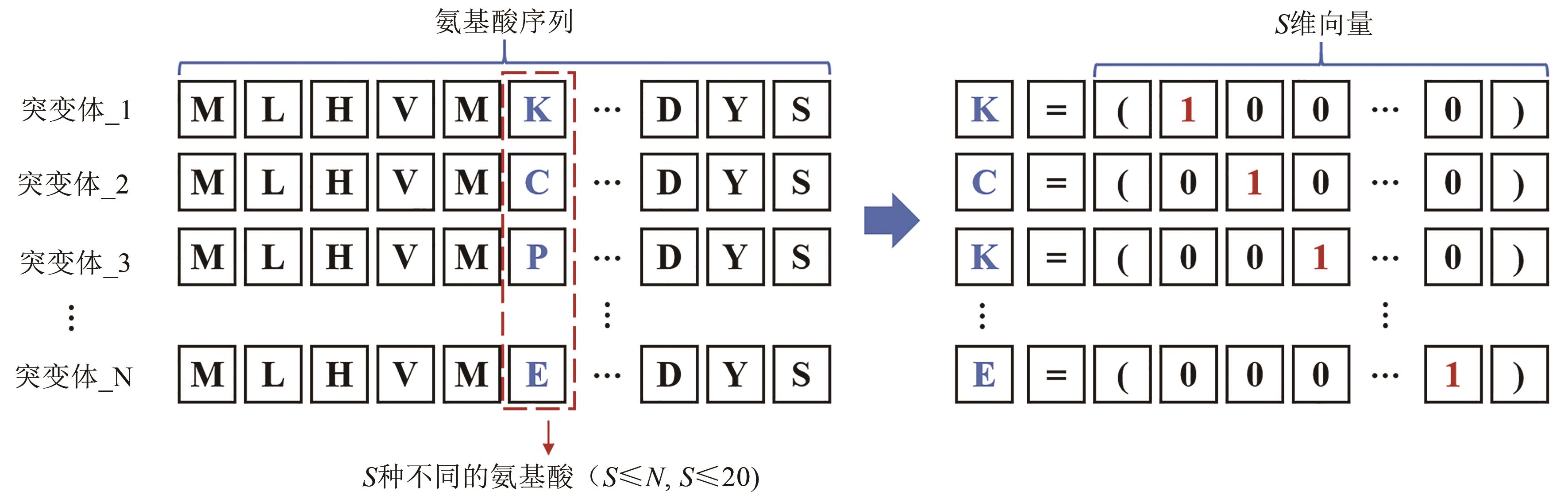
Fig. 6 Schematic diagram for one-hot encoding(A certain position of the L amino acids in the N protein mutant sequence contains S different amino acids. The one-hot encoding represents all S amino acids as an S-dimensional vector including S-1 zeros and one 1. The position of 1 indicates the type of amino acid at that position.)
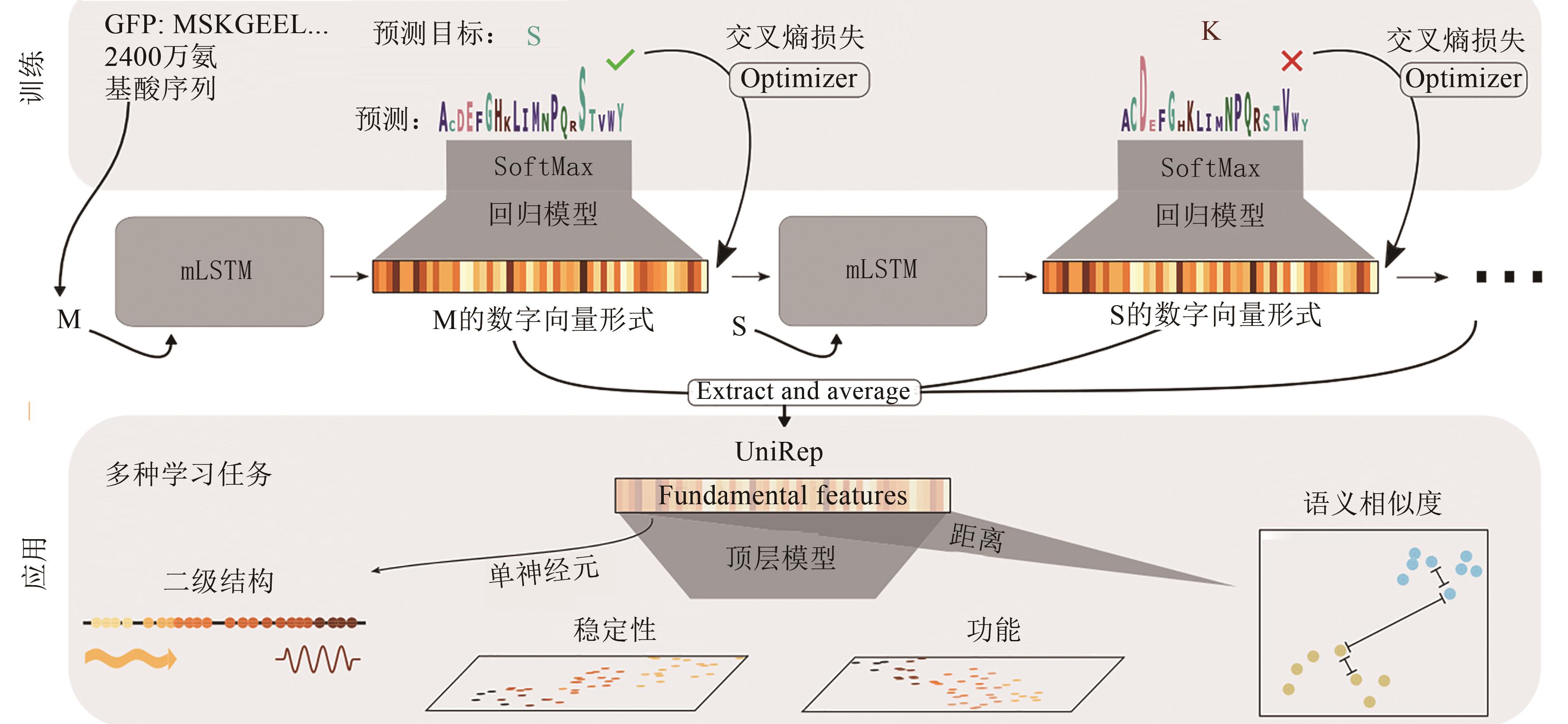
Fig. 7 Workflow for the UniRep model[67][In the training part, 24 million amino acid sequences are used to train the UniRep model. Then the trained model is used to predict the next amino acid (minimizing the cross-entropy loss), so as to learn how to correctly represent the amino acid. In the application part, by extracting and assessing the numerical vector associated with the amino acid, the trained model is used to generate a single fixed-length vector representing the input sequence. Next, these vectors can be used to train top models, which can be applied to various sequence-function prediction tasks.]
| 名称 | 类型 | 数目/大小 | 参考文献 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UniProtKB | 蛋白质序列、功能信息、研究论文索引的蛋白质数据库 | UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot包括560 000多条手动注释的蛋白序列,UniProtKB/TrEMBL则包括了2亿多条自动注释的蛋白序列 | [ | 已有学者利用该数据库提供的大量蛋白质序列信息,利用自然语言处理技术成功构建预测模型[ |
| Protein Data Bank | 生物大分子三维结构的数据库 | 145 000多个来源于X射线单晶衍射、核磁共振、电子衍射等实验手段确定的蛋白质、DNA、RNA等生物大分子结构 | [ | 该数据库为蛋白质结构预测模型的构建提供了大量的初始数据 |
| ProThermDB | 蛋白质信息、结构信息、实验条件、文献信息和实验热力学数据库 | 32 000多条数据 | [ | 突变体数据中突变类型包括野生型、单点突变和多点突变 |
| FireProtDB | 蛋白质稳定性数据的数据库 | 242个蛋白质的6715个变体数据 | [ | 手动管理,仅包含单点突变体蛋白质数据 |
| SoluProtMut DB | 突变体蛋白质溶解度数据库 | 917条突变数据 | [ | 手动管理,数据已经针对机器学习应用进行了整理 |
| ProtaBank | 蛋白质工程数据的数据库 | 700多种蛋白质的1 800 000多个突变体 | [ | 手动输入,不仅仅储存各种类型的突变信息,还提供完整的序列信息 |
Tab. 2 Commonly used database
| 名称 | 类型 | 数目/大小 | 参考文献 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UniProtKB | 蛋白质序列、功能信息、研究论文索引的蛋白质数据库 | UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot包括560 000多条手动注释的蛋白序列,UniProtKB/TrEMBL则包括了2亿多条自动注释的蛋白序列 | [ | 已有学者利用该数据库提供的大量蛋白质序列信息,利用自然语言处理技术成功构建预测模型[ |
| Protein Data Bank | 生物大分子三维结构的数据库 | 145 000多个来源于X射线单晶衍射、核磁共振、电子衍射等实验手段确定的蛋白质、DNA、RNA等生物大分子结构 | [ | 该数据库为蛋白质结构预测模型的构建提供了大量的初始数据 |
| ProThermDB | 蛋白质信息、结构信息、实验条件、文献信息和实验热力学数据库 | 32 000多条数据 | [ | 突变体数据中突变类型包括野生型、单点突变和多点突变 |
| FireProtDB | 蛋白质稳定性数据的数据库 | 242个蛋白质的6715个变体数据 | [ | 手动管理,仅包含单点突变体蛋白质数据 |
| SoluProtMut DB | 突变体蛋白质溶解度数据库 | 917条突变数据 | [ | 手动管理,数据已经针对机器学习应用进行了整理 |
| ProtaBank | 蛋白质工程数据的数据库 | 700多种蛋白质的1 800 000多个突变体 | [ | 手动输入,不仅仅储存各种类型的突变信息,还提供完整的序列信息 |
| 名称 | 主要功能 | 类型 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PseAAC | 从蛋白质序列生成氨基酸的疏水性、亲水性、侧链质量、α-COOH的pK值、α-NH3+的pK值以及25 °C时的pI值6种特征 | 网页平台 | [ |
| PROFEAT | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含11种不同类型分子描述符 | 网页平台 | [ |
| propy | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含13种不同类型分子描述符 | Python工具包 | [ |
| PseAAC-General | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含13种基于PseAAC的分子描述符 | Linux/Windows软件 | [ |
| protr/ProtrWeb | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含22种分子描述符 | R工具包/网页平台 | [ |
| Rcpi | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含10种分子描述符 | R/Bioconductor工具包 | [ |
| Pse-in-One | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含8种分子描述符 | 网页平台 | [ |
| ProFET | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,不支持PSSM矩阵和GO注释等非基于序列的特征 | Python工具包 | [ |
| PseKRAAC | 从蛋白质序列生成多种基于PseAAC的特征,并且利用氨基酸簇的概念,降低了特征向量的维度 | 网页平台 | [ |
| POSSUM | 从蛋白质序列生成21种基于PSSM矩阵的特征 | 网页平台 | [ |
| iFeature | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含18种分子描述符,并且提供12种常用的特征聚类,选择和降维算法 | Python工具包/ 网页平台 | [ |
| BioSeq-Analysis2.0 | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征;提供多种人工智能算法构建预测模型;提供特征选择算法和模型验证方法 | Windows/Linux/ Unix软件/网页平台 | [ |
| iLearn | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征;提供多种人工智能算法构建预测模型;提供特征选择算法和模型验证方法 | Python工具包/ 网页平台 | [ |
| SOLart | 支持从特征提取、预测模型构建到性能评估的完整流程。但是用户不能获得特征信息,不能选择算法和评估方式 | 网页平台 | [ |
Tab. 3 Feature generation tools based on protein sequences
| 名称 | 主要功能 | 类型 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PseAAC | 从蛋白质序列生成氨基酸的疏水性、亲水性、侧链质量、α-COOH的pK值、α-NH3+的pK值以及25 °C时的pI值6种特征 | 网页平台 | [ |
| PROFEAT | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含11种不同类型分子描述符 | 网页平台 | [ |
| propy | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含13种不同类型分子描述符 | Python工具包 | [ |
| PseAAC-General | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含13种基于PseAAC的分子描述符 | Linux/Windows软件 | [ |
| protr/ProtrWeb | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含22种分子描述符 | R工具包/网页平台 | [ |
| Rcpi | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含10种分子描述符 | R/Bioconductor工具包 | [ |
| Pse-in-One | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含8种分子描述符 | 网页平台 | [ |
| ProFET | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,不支持PSSM矩阵和GO注释等非基于序列的特征 | Python工具包 | [ |
| PseKRAAC | 从蛋白质序列生成多种基于PseAAC的特征,并且利用氨基酸簇的概念,降低了特征向量的维度 | 网页平台 | [ |
| POSSUM | 从蛋白质序列生成21种基于PSSM矩阵的特征 | 网页平台 | [ |
| iFeature | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征,包含18种分子描述符,并且提供12种常用的特征聚类,选择和降维算法 | Python工具包/ 网页平台 | [ |
| BioSeq-Analysis2.0 | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征;提供多种人工智能算法构建预测模型;提供特征选择算法和模型验证方法 | Windows/Linux/ Unix软件/网页平台 | [ |
| iLearn | 从蛋白质序列生成多种氨基酸分子的结构和物理化学特征;提供多种人工智能算法构建预测模型;提供特征选择算法和模型验证方法 | Python工具包/ 网页平台 | [ |
| SOLart | 支持从特征提取、预测模型构建到性能评估的完整流程。但是用户不能获得特征信息,不能选择算法和评估方式 | 网页平台 | [ |
| 1 | WAY J C, COLLINS J J, KEASLING J D, et al. Integrating biological redesign: Where synthetic biology came from and where it needs to go[J]. Cell, 2014, 157(1): 151-161. |
| 2 | XIE M Q, HAELLMAN V, FUSSENEGGER M. Synthetic biology—application-oriented cell engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2016, 40: 139-148. |
| 3 | BOYLE P M, SILVER P A. Parts plus pipes: Synthetic biology approaches to metabolic engineering[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2012, 14(3): 223-232. |
| 4 | FOO J L, CHING C B, CHANG M W, et al. The imminent role of protein engineering in synthetic biology[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2012, 30(3): 541-549. |
| 5 | ERB T J, JONES P R, BAR-EVEN A. Synthetic metabolism: Metabolic engineering meets enzyme design[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2017, 37: 56-62. |
| 6 | PLEISS J. Protein design in metabolic engineering and synthetic biology[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2011, 22(5): 611-617. |
| 7 | CHEN R P, GAYNOR A S, CHEN W. Synthetic biology approaches for targeted protein degradation[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(8): 107446. |
| 8 | GAINZA-CIRAUQUI P, CORREIA B E. Computational protein design—the next generation tool to expand synthetic biology applications[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2018, 52: 145-152. |
| 9 | BADENHORST C P S, BORNSCHEUER U T. Getting momentum: From biocatalysis to advanced synthetic biology[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2018, 43(3): 180-198. |
| 10 | EASON M G, DAMRY A M, CHICA R A. Structure-guided rational design of red fluorescent proteins: Towards designer genetically-encoded fluorophores[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2017, 45: 91-99. |
| 11 | ZEYMER C, HILVERT D. Directed evolution of protein catalysts[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2018, 87: 131-157. |
| 12 | RIBEIRO L F, AMARELLE V, ALVES L F, et al. Genetically engineered proteins to improve biomass conversion: New advances and challenges for tailoring biocatalysts[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(16): 2879. |
| 13 | MARKEL U, ESSANI K D, BESIRLIOGLU V, et al. Advances in ultrahigh-throughput screening for directed enzyme evolution[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(1): 233-262. |
| 14 | LIU Q, XUN G H, FENG Y. The state-of-the-art strategies of protein engineering for enzyme stabilization[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2019, 37(4): 530-537. |
| 15 | LIAO J, WARMUTH M K, GOVINDARAJAN S, et al. Engineering proteinase K using machine learning and synthetic genes[J]. BMC Biotechnology, 2007, 7: 16. |
| 16 | YANG K K, WU Z, ARNOLD F H. Machine-learning-guided directed evolution for protein engineering[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(8): 687-694. |
| 17 | SENIOR A W, EVANS R, JUMPER J, et al. Improved protein structure prediction using potentials from deep learning[J]. Nature, 2020, 577(7792): 706-710. |
| 18 | YANG J Y, ANISHCHENKO I, PARK H, et al. Improved protein structure prediction using predicted interresidue orientations[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(3): 1496-1503. |
| 19 | YANG M, FEHL C, LEES K V, et al. Functional and informatics analysis enables glycosyltransferase activity prediction[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2018, 14(12): 1109-1117. |
| 20 | RYU J Y, KIM H U, LEE S Y. Deep learning enables high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(28): 13996-14001. |
| 21 | HAN X, WANG X N, ZHOU K. Develop machine learning-based regression predictive models for engineering protein solubility[J]. Bioinformatics, 2019, 35(22): 4640-4646. |
| 22 | CHEN J W, ZHENG S J, ZHAO H Y, et al. Structure-aware protein solubility prediction from sequence through graph convolutional network and predicted contact map. Journal of Cheminformatics, 2021, 13: 7. |
| 23 | SAITO Y, OIKAWA M, NAKAZAWA H, et al. Machine-learning-guided mutagenesis for directed evolution of fluorescent proteins[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(9): 2014-2022. |
| 24 | WU Z, KAN S B J, LEWIS R D, et al. Machine learning-assisted directed protein evolution with combinatorial libraries[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(18): 8852-8858. |
| 25 | CADET F, FONTAINE N, LI G Y, et al. A machine learning approach for reliable prediction of amino acid interactions and its application in the directed evolution of enantioselective enzymes[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 16757. |
| 26 | BEDBROOK C N, YANG K K, ROBINSON J E, et al. Machine learning-guided channelrhodopsin engineering enables minimally invasive optogenetics[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(11): 1176-1184. |
| 27 | MAZURENKO S, PROKOP Z, DAMBORSKY J. Machine learning in enzyme engineering[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(2): 1210-1223. |
| 28 | YANG X, WANG Y F, BYRNE R, et al. Concepts of artificial intelligence for computer-assisted drug discovery[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(18): 10520-10594. |
| 29 | BADILLO S, BANFAI B, BIRZELE F, et al. An introduction to machine learning[J]. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2020, 107(4): 871-885. |
| 30 | 蒋迎迎, 曲戈, 孙周通. 机器学习助力酶定向进化[J]. 生物学杂志, 2020, 37(4): 1-11. |
| JIANG Y Y, QU G, SUN Z T. Machine learning-assisted enzyme directed evolution[J]. Journal of Biology, 2020, 37(4): 1-11. | |
| 31 | 胡如云, 张嵩亚, 蒙海林, 等. 面向合成生物学的机器学习方法及应用[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(3): 284-299. |
| HU R Y, ZHANG S Y, MENG H L, et al. Machine learning for synthetic biology: Methods and applications[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(3): 284-299. | |
| 32 | CONSORTIUM T U. UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 47(D1): D506-D515. |
| 33 | MUGGLETON S, KING R D, STENBERG M J E. Protein secondary structure prediction using logic-based machine learning[J]. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection, 1992, 5(7): 647-657. |
| 34 | ALQURAISHI M. AlphaFold at CASP13[J]. Bioinformatics, 2019, 35(22): 4862-4865. |
| 35 | KINCH L N, SHI S Y, CHENG H, et al. CASP9 target classification[J]. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, 2011, 79(S10): 21-36. |
| 36 | LI Y, WANG S, UMAROV R, et al. DEEPre: sequence-based enzyme EC number prediction by deep learning[J]. Bioinformatics, 2017, 34(5): 760-769. |
| 37 | BOUTET E, LIEBERHERR D, TOGNOLLI M, et al. UniProtKB/Swiss-prot, the manually annotated section of the UniProt KnowledgeBase: How to use the entry view[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2016, 1374: 23-54. |
| 38 | CLAUDEL-RENARD C, CHEVALET C, FARAUT T, et al. Enzyme-specific profiles for genome annotation: PRIAM[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2003, 31(22): 6633-6639. |
| 39 | YU C G, ZAVALJEVSKI N, DESAI V, et al. Genome-wide enzyme annotation with precision control: Catalytic families (CatFam) databases[J]. Proteins, 2009, 74(2): 449-460. |
| 40 | KUMAR N, SKOLNICK J. EFICAz2.5: application of a high-precision enzyme function predictor to 396 proteomes[J]. Bioinformatics, 2012, 28(20): 2687-2688. |
| 41 | LI Y H, XU J Y, TAO L, et al. SVM-prot 2016: A web-server for machine learning prediction of protein functional families from sequence irrespective of similarity[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(8): e0155290. |
| 42 | ZHANG C X, FREDDOLINO P L, ZHANG Y. COFACTOR: improved protein function prediction by combining structure, sequence and protein-protein interaction information[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(W1): W291-W299. |
| 43 | NURSIMULU N, XU L L, WASMUTH J D, et al. Improved enzyme annotation with EC-specific cutoffs using DETECT v2[J]. Bioinformatics, 2018, 34(19): 3393-3395. |
| 44 | DALKIRAN A, RIFAIOGLU A S, MARTIN M J, et al. ECPred: a tool for the prediction of the enzymatic functions of protein sequences based on the EC nomenclature[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2018, 19(1): 334. |
| 45 | HOU Q Z, BOURGEAS R, PUCCI F, et al. Computational analysis of the amino acid interactions that promote or decrease protein solubility[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 14661. |
| 46 | BHANDARI B K, GARDNER P P, LIM C S. Solubility-Weighted Index: Fast and accurate prediction of protein solubility[J]. Bioinformatics, 2020, 36(18): 4691-4698. |
| 47 | LI G Y, DONG Y J, REETZ M T. Can machine learning revolutionize directed evolution of selective enzymes? [J]. Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis, 2019, 361(11): 2377-2386. |
| 48 | SONG H, BREMER B J, HINDS E C, et al. Inferring protein sequence-function relationships with large-scale positive-unlabeled learning[J]. Cell Systems, 2021, 12(1): 92-101.e8. |
| 49 | YU L A, WANG S Y, LAI K K. An integrated data preparation scheme for neural network data analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2006, 18(2): 217-230. |
| 50 | YANG Y, UROLAGIN S, NIROULA A, et al. PON-tstab: Protein variant stability predictor. importance of training data quality[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(4): 1009. |
| 51 | SIEDHOFF N E, SCHWANEBERG U, DAVARI M D. Machine learning-assisted enzyme engineering[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2020, 643: 281-315. |
| 52 | BASTIAN F B, CHIBUCOS M C, GAUDET P, et al. The Confidence Information Ontology: A step towards a standard for asserting confidence in annotations[J]. Database, 2015, 2015:bav043. |
| 53 | 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016. |
| ZHOU Z H. Machine learning[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2016. | |
| 54 | KAWASHIMA S, POKAROWSKI P, POKAROWSKA M, et al. AAindex: amino acid index database, progress report 2008[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2007, 36(): D202-D205. |
| 55 | XU Y T, VERMA D, SHERIDAN R P, et al. Deep dive into machine learning models for protein engineering[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2020, 60(6): 2773-2790. |
| 56 | LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-444. |
| 57 | ABDI H. Partial least squares regression and projection on latent structure regression (PLS Regression)[J]. WIREs Computational Statistics, 2010, 2(1): 97-106. |
| 58 | CORTES C, VAPNIK V. Support-vector networks[J]. Machine Learning, 1995, 20(3): 273-297. |
| 59 | QUINLAN J R. Induction of decision trees[J]. Machine Learning, 1986, 1(1): 81-106. |
| 60 | HECKERMAN D. A tutorial on learning with Bayesian networks [M]//HOLMES D E, JAIN L C. Innovations in Bayesian networks: theory and applications. Berlin, Heidelberg; Springer, 2008: 33-82. |
| 61 | SINAI S, KELSIC E, CHURCH G M, et al. Variational auto-encoding of protein sequences[EB/OL]. 2017: arXiv: 1712.03346[q-bio.QM]. |
| 62 | LECUN Y, BENGIO Y. Convolutional networks for images, speech, and time series[J]. The handbook of brain theory and neural networks, 1995, 3361(10): 1995. |
| 63 | LOHMANN R, SCHNEIDER G, BEHRENS D, et al. A neural network model for the prediction of membrane-spanning amino acid sequences[J]. Protein Science, 1994, 3(9): 1597-1601. |
| 64 | 曲戈, 朱彤, 蒋迎迎, 等. 蛋白质工程:从定向进化到计算设计[J]. 生物工程学报, 2019, 35(10): 1843-1856. |
| QU G, ZHU T, JIANG Y Y, et al. Protein engineering: From directed evolution to computational design[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2019, 35(10): 1843-1856. | |
| 65 | WOLPERT D H. The lack of A priori distinctions between learning algorithms[J]. Neural Computation, 1996, 8(7): 1341-1390. |
| 66 | YANG K K, WU Z, BEDBROOK C N, et al. Learned protein embeddings for machine learning[J]. Bioinformatics, 2018, 34(15): 2642-2648. |
| 67 | ALLEY E C, KHIMULYA G, BISWAS S, et al. Unified rational protein engineering with sequence-based deep representation learning[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(12): 1315-1322. |
| 68 | CONSORTIUM T U, BATEMAN A, MARTIN M J, et al. UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase in 2021[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 49(D1): D480-D489. |
| 69 | RIVES A, MEIER J, SERCU T, et al. Biological structure and function emerge from scaling unsupervised learning to 250 million protein sequences[EB/OL]. bioRxiv, 2020, DOI:10.1101/622803 . |
| 70 | BURLEY S K, BHIKADIYA C, BI C X, et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Powerful new tools for exploring 3D structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 49(D1): D437-D451. |
| 71 | NIKAM R, KULANDAISAMY A, HARINI K, et al. ProThermDB: thermodynamic database for proteins and mutants revisited after 15 years[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 49(D1): D420-D424. |
| 72 | STOURAC J, DUBRAVA J, MUSIL M, et al. FireProtDB: database of manually curated protein stability data[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 49(D1): D319-D324. |
| 73 | TIAN Y, DEUTSCH C, KRISHNAMOORTHY B. Scoring function to predict solubility mutagenesis[J]. Algorithms for Molecular Biology: AMB, 2010, 5: 33. |
| 74 | SORMANNI P, APRILE F A, VENDRUSCOLO M. The CamSol method of rational design of protein mutants with enhanced solubility[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2015, 427(2): 478-490. |
| 75 | ZAMBRANO R, JAMROZ M, SZCZASIUK A, et al. AGGRESCAN3D (A3D): Server for prediction of aggregation properties of protein structures[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 43(W1): W306-W313. |
| 76 | YANG Y, NIROULA A, SHEN B R, et al. PON-Sol: Prediction of effects of amino acid substitutions on protein solubility[J]. Bioinformatics, 2016, 32(13): 2032-2034. |
| 77 | PALADIN L, PIOVESAN D, TOSATTO S C E. SODA: prediction of protein solubility from disorder and aggregation propensity[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(W1): W236-W240. |
| 78 | MAZURENKO S. Predicting protein stability and solubility changes upon mutations: data perspective[J]. Chem Cat Chem, 2020, 12,5590-5598. |
| 79 | WANG C Y, CHANG P M, ARY M L, et al. ProtaBank: A repository for protein design and engineering data[J]. Protein Science: a Publication of the Protein Society, 2018, 27(6): 1113-1124. |
| 80 | SHEN H B, CHOU K C. PseAAC: A flexible web server for generating various kinds of protein pseudo amino acid composition[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2008, 373(2): 386-388. |
| 81 | RAO H B, ZHU F, YANG G B, et al. Update of PROFEAT: A web server for computing structural and physicochemical features of proteins and peptides from amino acid sequence[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, 39(): W385-W390. |
| 82 | CAO D S, XU Q S, LIANG Y Z. Propy: a tool to generate various modes of Chou's PseAAC[J]. Bioinformatics, 2013, 29(7): 960-962. |
| 83 | DU P F, GU S W, JIAO Y S. PseAAC-General: Fast building various modes of general form of Chou's pseudo-amino acid composition for large-scale protein datasets[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2014, 15(3): 3495-3506. |
| 84 | XIAO N, CAO D S, ZHU M F, et al. Protr/ProtrWeb: R package and web server for generating various numerical representation schemes of protein sequences[J]. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(11): 1857-1859. |
| 85 | CAO D S, XIAO N, XU Q S, et al. Rcpi: R/Bioconductor package to generate various descriptors of proteins, compounds and their interactions[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 31(2): 279-281. |
| 86 | LIU B, LIU F L, WANG X L, et al. Pse-in-One: a web server for generating various modes of pseudo components of DNA, RNA, and protein sequences[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 43(W1): W65-W71. |
| 87 | OFER D, LINIAL M. ProFET: Feature engineering captures high-level protein functions[J]. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(21): 3429-3436. |
| 88 | ZUO Y C, LI Y, CHEN Y L, et al. PseKRAAC: a flexible web server for generating pseudo K-tuple reduced amino acids composition[J]. Bioinformatics, 2016, 33(1): 122-124. |
| 89 | WANG J W, YANG B J, REVOTE J, et al. POSSUM: a bioinformatics toolkit for generating numerical sequence feature descriptors based on PSSM profiles[J]. Bioinformatics, 2017, 33(17): 2756-2758. |
| 90 | CHEN Z, ZHAO P, LI F Y, et al. iFeature: a Python package and web server for features extraction and selection from protein and peptide sequences[J]. Bioinformatics, 2018, 34(14): 2499-2502. |
| 91 | LIU B, GAO X, ZHANG H Y. BioSeq-Analysis2.0: An updated platform for analyzing DNA, RNA and protein sequences at sequence level and residue level based on machine learning approaches[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(20): e127. |
| 92 | CHEN Z, ZHAO P, LI F Y, et al. iLearn: an integrated platform and meta-learner for feature engineering, machine-learning analysis and modeling of DNA, RNA and protein sequence data[J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2019, 21(3): 1047-1057. |
| 93 | HOU Q Z, KWASIGROCH J M, ROOMAN M, et al. SOLart: a structure-based method to predict protein solubility and aggregation[J]. Bioinformatics, 2019, 36(5): 1445-1452. |
| 94 | LIU Y M, WANG X L, LIU B. IDP-CRF: intrinsically disordered protein/region identification based on conditional random fields[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(9): 2483. |
| 95 | CHEN Z, HE N N, HUANG Y, et al. Integration of A deep learning classifier with A random forest approach for predicting malonylation sites[J]. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics, 2018, 16(6): 451-459. |
| 96 | SCHNOES A M, REAM D C, THORMAN A W, et al. Biases in the experimental annotations of protein function and their effect on our understanding of protein function space[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2013, 9(5): e1003063. |
| 97 | ZHOU N H, JIANG Y X, BERGQUIST T R, et al. The CAFA challenge reports improved protein function prediction and new functional annotations for hundreds of genes through experimental screens[J]. Genome Biology, 2019, 20(1): 244. |
| 98 | GERLT J A, ALLEN K N, ALMO S C, et al. The enzyme function initiative[J]. Biochemistry, 2011, 50(46): 9950-9962. |
| 99 | ROBERTS R J, CHANG Y C, HU Z J, et al. COMBREX: a project to accelerate the functional annotation of prokaryotic genomes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 39(S1): D11-D14. |
| 100 | FOWLER D M, FIELDS S. Deep mutational scanning: A new style of protein science[J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(8): 801-807. |
| 101 | FOWLER D M, STEPHANY J J, FIELDS S. Measuring the activity of protein variants on a large scale using deep mutational scanning[J]. Nature Protocols, 2014, 9(9): 2267-2284. |
| 102 | NEWBERRY R W, LEONG J T, CHOW E D, et al. Deep mutational scanning reveals the structural basis for α-synuclein activity[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2020, 16(6): 653-659. |
| 103 | Riesselman A J, Ingraham J B, Marks D S. Deep generative models of genetic variation capture the effects of mutations[J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(10): 816-822. |
| [1] | GAO Ge, BIAN Qi, WANG Baojun. Synthetic genetic circuit engineering: principles, advances and prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [2] | DONG Ying, MA Mengdan, HUANG Weiren. Progress in the miniaturization of CRISPR-Cas systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 105-117. |
| [3] | LI Jiyuan, WU Guosheng. Two hypothesises for the origins of organisms from the synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | TANG Xinghua, LU Qianneng, HU Yilin. Philosophical reflections on synthetic biology in the Anthropocene [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | WEN Yanhua, LIU Hedong, CAO Chunlai, WU Ruibo. Applications of protein engineering in pharmaceutical industry [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 65-86. |
| [8] | SHI Ting, SONG Zhan, SONG Shiyi, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): a new frontier of industrial biomanufacturing [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [9] | CHAI Meng, WANG Fengqing, WEI Dongzhi. Synthesis of organic acids from lignocellulose by biotransformation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [10] | SHAO Mingwei, SUN Simian, YANG Shimao, CHEN Guoqiang. Bioproduction based on extremophiles [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [11] | WANG Ziyuan, YANG Lirong, WU Jianping, ZHENG Wenlong. A review on enzyme-catalyzed synthesis of chiral amino acids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(6): 1319-1349. |
| [12] | CHEN Yu, ZHANG Kang, QIU Yijing, CHENG Caiyun, YIN Jingjing, SONG Tianshun, XIE Jingjing. Progress of microbial electrosynthesis for conversion of CO2 [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [13] | ZHENG Haotian, LI Chaofeng, LIU Liangxu, WANG Jiawei, LI Hengrun, NI Jun. Design, optimization and application of synthetic carbon-negative phototrophic community [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [14] | CHEN Ziling, XIANG Yangfei. Integrated development of organoid technology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 795-812. |
| [15] | CAI Bingyu, TAN Xiangtian, LI Wei. Advances in synthetic biology for engineering stem cell [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(4): 782-794. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||