Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (3): 371-383.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-084
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
DNA data storage: preservation approach and data encryption
ZHOU Tingyao, LUO Yuan, JIANG Xingyu
- Department of Biomedical Engineering,Southern University of Science and Technology,Shenzhen 518055,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2020-12-01Revised:2021-03-03Online:2021-07-13Published:2021-06-30 -
Contact:JIANG Xingyu
DNA数据存储:保存策略与数据加密
周廷尧, 罗源, 蒋兴宇
- 南方科技大学生物医学工程系,广东 深圳 518055
-
通讯作者:蒋兴宇 -
作者简介:周廷尧 (1986—),男,博士,副研究员。研究方向为DNA生物矿化、纳米材料制备与可控组装。 E-mail:zhouty@sustech.edu.cn蒋兴宇 (1977—),男,博士,讲席教授。研究方向为生物医学工程、DNA存储、微流控。 E-mail:jiang@sustech.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0902600);国家自然科学基金(21907032)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHOU Tingyao, LUO Yuan, JIANG Xingyu. DNA data storage: preservation approach and data encryption[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 371-383.
周廷尧, 罗源, 蒋兴宇. DNA数据存储:保存策略与数据加密[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(3): 371-383.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2020-084
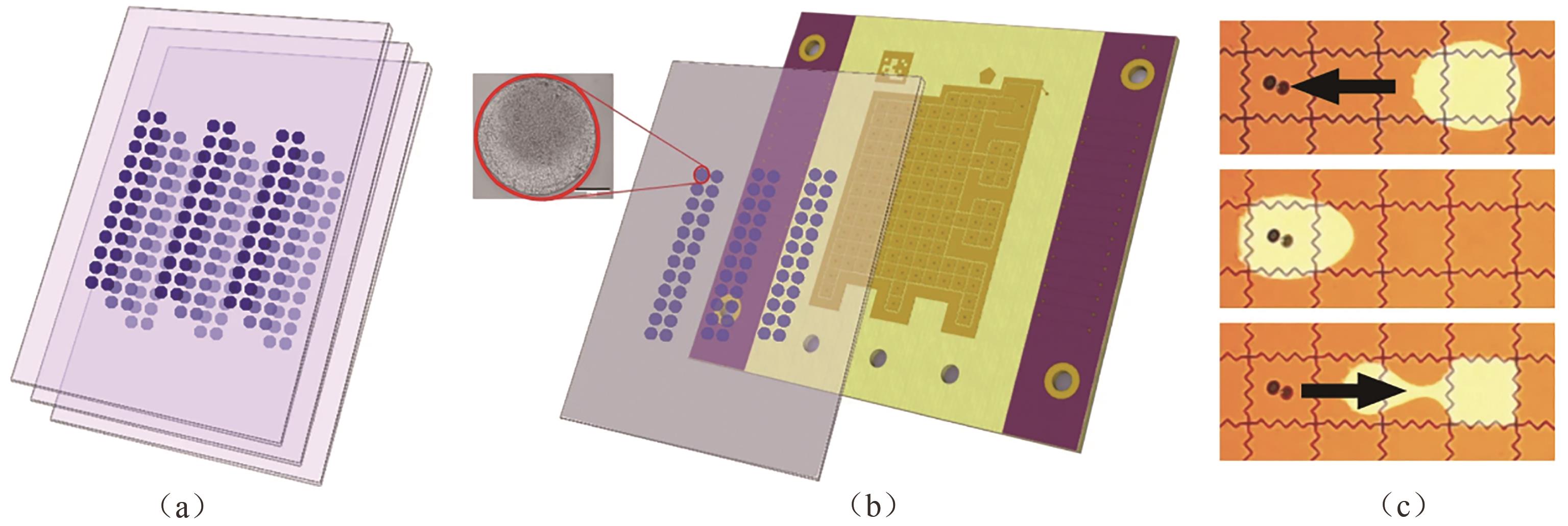
Fig. 2 High density dehydrated DNA data storage with digital microfluidic retrieval[(a) Dehydrated DNA stored on glass cartridges; (b) Cartridge was loaded onto digital microfluidic device to retrieve data, and inset showed photograph of an actual magnified spot, scale bar: 275 μm; (c) A water droplet sandwiched between cartridge and electrodes was actuated to move under spotted DNA for rehydration[39]]
| Storage media | DNA loading | Year of invention | Half life | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Earth alkaline salts | >30% | 2020 | about 109 years | [ |
| DNA in silica | 0.7% | 2013 | about 527 years | [ |
| DNA in magnetic NPs | 3.4% | 2019 | about 527 years | [ |
Tab. 1 Comparison of different DNA storage media
| Storage media | DNA loading | Year of invention | Half life | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Earth alkaline salts | >30% | 2020 | about 109 years | [ |
| DNA in silica | 0.7% | 2013 | about 527 years | [ |
| DNA in magnetic NPs | 3.4% | 2019 | about 527 years | [ |
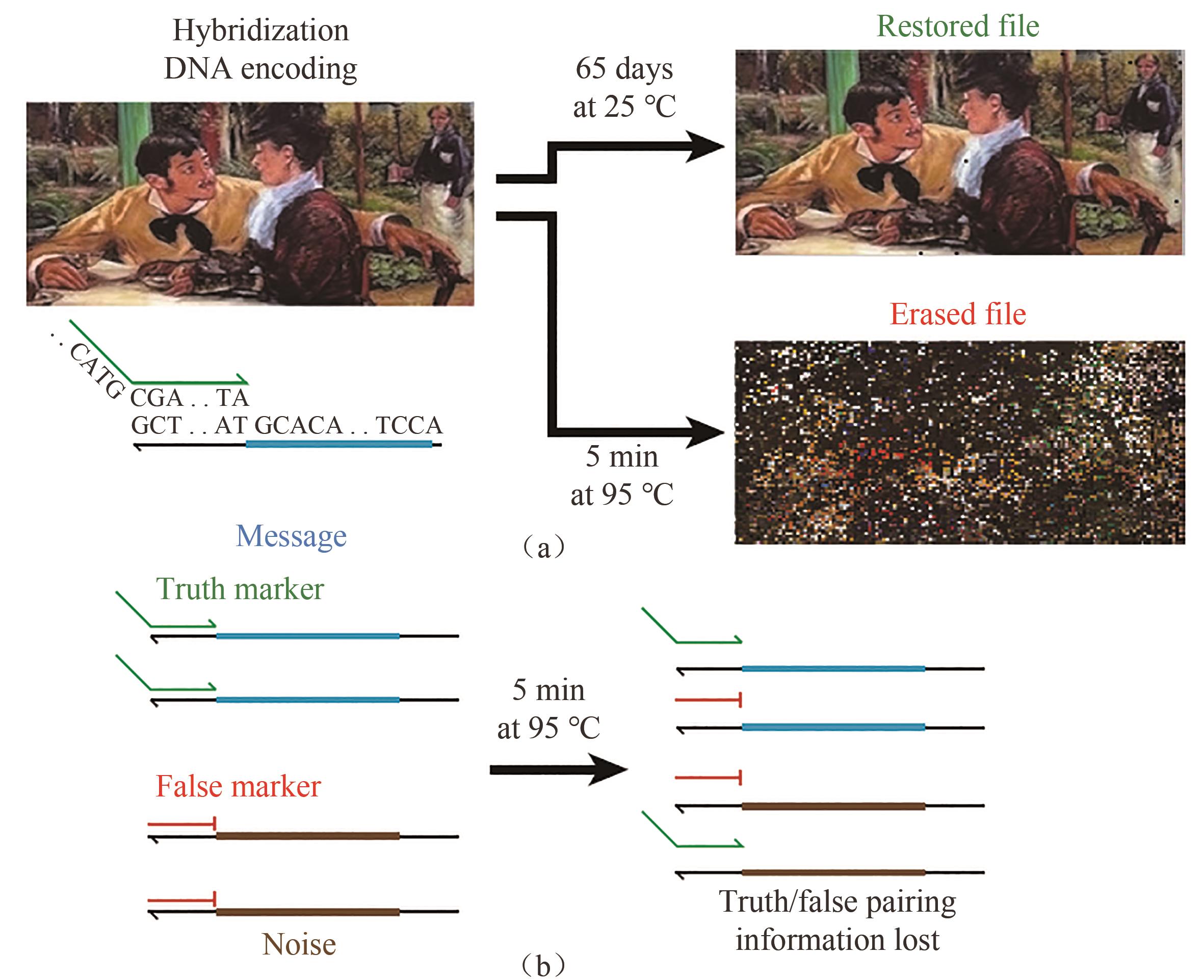
Fig. 5 Metastable hybridization-based DNA data storage[(a) Image file was encoded as DNA sequences, which could be stored steadily at room temperature for long periods of time, but was permanently and quickly erased when exposed to 95 ℃. (b) Truthful information encoding based on DNA hybridization[98]]
| 1 | ZHIRNOV V, ZADEGAN R M, SANDHU G S, et al. Nucleic acid memory [J]. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(4): 366-370. |
| 2 | SHRIVASTAVA S, BADLANI R. Data storage in DNA [J]. International Journal of Electrical Energy, 2014, 2(2): 119-124. |
| 3 | GODA K, KITSUREGAWA M. The history of storage systems [J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100: 1433-1440. |
| 4 | WIENER N. Interview: machines smarter than men? [J]. US News World Report, 1964, 56: 84-86. |
| 5 | NEIMAN M S. On the molecular memory systems and the directed mutations [J]. Radiotekhnika, 1965, 6: 1-8. |
| 6 | DAVIS J. Microvenus [J]. Art Journal, 1996, 55(1): 70-74. |
| 7 | CLELLAND C T, RISCA V, BANCROFT C. Hiding messages in DNA microdots [J]. Nature, 1999, 399(6736): 533-534. |
| 8 | BANCROFT C, BOWLER T, BLOOM B, et al. Long-term storage of information in DNA [J]. Science, 2001, 2939(5536): 1763-1765. |
| 9 | CHURCH G M, GAO Y, KOSURI S. Next-generation digital information storage in DNA [J]. Science, 2012, 337(6102): 1628. |
| 10 | GOLDMAN N, BERTONE P, CHEN S, et al. Towards practical, high-capacity, low-maintenance information storage in synthesized DNA [J]. Nature, 2013, 494(7435): 77-80. |
| 11 | BORNHOLT J, LOPEZ R, CARMEAN D. M,et al. Toward a DNA-based archival storage system [J]. IEEE Micro, 2017, 37(3): 98-104. |
| 12 | ERLICH Y, ZIELINSKI D. DNA Fountain enables a robust and efficient storage architecture [J]. Science, 2017, 355(6328): 950-954. |
| 13 | 张淑芳, 彭康, 宋香明, 等. DNA 数据存储技术研究进展[J]. 计算机科学, 2019, 46(6): 21-28. |
| ZHANG S F, PENG K, SONG X M, et al. Research progress on DNA data storage technology [J]. Computer Science, 2019, 46(6): 21-28. | |
| 14 | 许鹏, 方刚, 石晓龙, 等. DNA存储及其研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1326-1331. |
| XU P, FANG G, SHI X, et al. DNA storage and its research progress [J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1326-1331. | |
| 15 | DONG Y, SUN F, PING Z, et al. DNA storage: research landscape and future prospects [J]. National Science Review, 2020, 7(6): 1092-1107. |
| 16 | ORGANICK L, CHEN Y J, ANG S D, et al. Experimental assessment of PCR specificity and copy number for reliable data retrieval in DNA storage [EB/OL]. [2021-05-24]. . |
| 17 | CHEN Y J, TAKAHASHI C N, ORGANICK L, et al. Quantifying molecular bias in DNA data storage [J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3264. |
| 18 | CAMPBELL M. DNA data storage: automated DNA synthesis and sequencing are key to unlocking virtually unlimited data storage [J]. Computer, 2020, 53(4): 63-67. |
| 19 | CEZE L, NIVALA J, STRAUSS K. Molecular digital data storage using DNA [J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2019, 20(8): 456-466. |
| 20 | GAO X, LEPROUST E, ZHANG H, et al. A flexible light-directed DNA chip synthesis gated by deprotection using solution photogenerated acids [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2001, 29(22): 4744-4750. |
| 21 | XIONG A S, YAO Q H, PENG R H, et al. A simple, rapid, high-fidelity and cost-effective PCR-based two-step DNA synthesis method for long gene sequences [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32(12): e98. |
| 22 | KOZLOV I, DANG M. SIKES K,et al. Significant improvement of quality for long oligonucleotides by using controlled pore glass with large pores [J]. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids, 2005, 24(5/6/7): 1037-1041. |
| 23 | PALLUK S, ARLOW D H, DE ROND T, et al. De novo DNA synthesis using polymerase-nucleotide conjugates [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(7): 645-650. |
| 24 | GRASS R N, HECKEL R, PUDDU M, et al. Robust chemical preservation of digital information on DNA in silica with error-correcting codes [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(8): 2552-2555. |
| 25 | ORGANICK L, ANG S D, CHEN Y J, et al. Random access in large-scale DNA data storage [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(3): 242-248. |
| 26 | TOMEK K J, VOLKEL K, SIMPSON A, et al. Driving the scalability of DNA-based information storage systems [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(6): 1241-1248. |
| 27 | GOODWIN S, MCPHERSON J D, MCCOMBIE W R. Coming of age: ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies [J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2016, 17(6): 333-351. |
| 28 | DRMANAC R, SPARKS A B, CALLOW M J, et al. Human genome sequencing using unchained base reads on self-assembling DNA nanoarrays [J]. Science, 2010, 327(5961): 78-81. |
| 29 | DEAMER D, AKESON M, BRANTON D. Three decades of nanopore sequencing [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2016, 34(5): 518-524. |
| 30 | DABNEY J, KNAPP M, GLOCKE I, et al. Complete mitochondrial genome sequence of a Middle Pleistocene cave bear reconstructed from ultrashort DNA fragments [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(39): 15758. |
| 31 | MEYER M, FU Q, AXIMU-PETRI A, et al. A mitochondrial genome sequence of a hominin from Sima de los Huesos [J]. Nature, 2014, 505(7483): 403-406. |
| 32 | BONNET J, COLOTTE M, COUDY D, et al. Chain and conformation stability of solid-state DNA: implications for room temperature storage [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 38(5): 1531-1546. |
| 33 | DEAGLE B E, EVESON J P, JARMAN S N. Quantification of damage in DNA recovered from highly degraded samples - a case study on DNA in faeces [J]. Frontiers in Zoology, 2006, 3: 11. |
| 34 | ALLENTOFT M E, COLLINS M, HARKER D, et al. The half-life of DNA in bone: measuring decay kinetics in 158 dated fossils [J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 2012, 279(1748): 4724-4733. |
| 35 | BAOUTINA A, BHAT S, PARTIS L, et al. Storage stability of solutions of DNA standards [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(19): 12268-12274. |
| 36 | TABATABAEI YAZDI S M H, YUAN Y, MA J, et al. A rewritable, random-access DNA-based storage system [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 14138. |
| 37 | YAZDI S M H T, GABRYS R, MILENKOVIC O. Portable and error-free DNA-based data storage [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 5011. |
| 38 | IVANOVA N V, KUZMINA M L. Protocols for dry DNA storage and shipment at room temperature [J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2013, 13(5): 890-898. |
| 39 | NEWMAN S, STEPHENSON A P, WILLSEY M, et al. High density DNA data storage library via dehydration with digital microfluidic retrieval [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1706. |
| 40 | BURGOYNE L A, Solid medium and method for DNA storage: US 5807527 [P]. 1998-09-15. |
| 41 | KOHLL A X, ANTKOWIAK P L, CHEN W D, et al. Stabilizing synthetic DNA for long-term data storage with earth alkaline salts [J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(25): 3613-3616. |
| 42 | PAUNESCU D, FUHRER R, GRASS R N. Protection and deprotection of DNA-high-temperature stability of nucleic acid barcodes for polymer labeling [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(15): 4269-4272. |
| 43 | CHEN W D, KOHLL A X, NGUYEN B H, et al. Combining data longevity with high storage capacity-layer‐by‐layer DNA encapsulated in magnetic nanoparticles [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(28): 1901672. |
| 44 | LINDAHL T, NYBERG B. Rate of depurination of native deoxyribonucleic acid [J]. Biochemistry, 1972, 11(19): 3610-3618. |
| 45 | KOCH J, GANTENBEIN S, MASANIA K, et al. A DNA-of-things storage architecture to create materials with embedded memory [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(1): 39-43. |
| 46 | KHALIFEHZADEH R, ARAMI H. DNA-templated strontium-doped calcium phosphate nanoparticles for gene delivery in bone cells [J]. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2019, 5(7): 3201-3211. |
| 47 | ANASTASSACOS F M, ZHAO Z, ZENG Y, et al. Glutaraldehyde cross-linking of oligolysines coating DNA origami greatly reduces susceptibility to nuclease degradation [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(7): 3311-3315. |
| 48 | NGUYEN M K, NGUYEN V H, NATARAJAN A K, et al. Ultrathin silica coating of DNA origami nanostructures [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(15): 6657-6665. |
| 49 | SHANG Y, LI N, LIU S, et al. Site-specific synthesis of silica nanostructures on DNA origami templates [J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(21): e2000294. |
| 50 | LIU X, ZHANG F, JING X, et al. Complex silica composite nanomaterials templated with DNA origami [J]. Nature, 2018, 559(7715): 593-598. |
| 51 | LIU X, JING X, LIU P, et al. DNA framework-encoded mineralization of calcium phosphate [J]. Chem, 2020, 6(2): 472-485. |
| 52 | SHETH R U, WANG H H. DNA-based memory devices for recording cellular events [J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2018, 19(11): 718-732. |
| 53 | 元英进, 韩明哲, 陈为刚,等. 基于DNA的信息存储方法: CN201811377712.X [P]. 2018-11-19. |
| YUAN Y J, HAN M Z, CHEN W G, et al. Information storage means based on DNA: CN201811377712.X[P]. 2018-11-19. | |
| 54 | HAO M, QIAO H, GAO Y, et al. A mixed culture of bacterial cells enables an economic DNA storage on a large scale [J]. Communications Biology, 2020, 3(1): 416. |
| 55 | WIRTH D, GAMA-NORTON L, RIEMER P, et al. Road to precision: recombinase-based targeting technologies for genome engineering [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2007, 18(5): 411-419. |
| 56 | BIBIKOVA M, BEUMER K, TRAUTMAN J K, et al. Enhancing gene targeting with designed zinc finger nucleases [J]. Science, 2003, 300(5620): 764. |
| 57 | YANG L, NIELSEN A A K, FERNANDEZ-RODRIGUEZ J, et al. Permanent genetic memory with >1-byte capacity [J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(12): 1261-1266. |
| 58 | BONNET J, SUBSOONTORN P, ENDY D. Rewritable digital data storage in live cells via engineered control of recombination directionality [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(23): 8884. |
| 59 | MARRAFFINI L A. CRISPR-Cas immunity in prokaryotes [J]. Nature, 2015, 526(7571): 55-61. |
| 60 | XIE Z X, MITCHELL L A, LIU H M, et al. Rapid and efficient CRISPR/Cas9-based mating-type switching of saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. G3-Genes Genomes Genetics, 2018, 8(1): 173-183. |
| 61 | DOUDNA J A, CHARPENTIER E. The new frontier of genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9 [J]. Science, 2014, 346(6213): 1258096. |
| 62 | FRIEDA K L, LINTON J M, HORMOZ S, et al. Synthetic recording and in situ readout of lineage information in single cells [J]. Nature, 2017, 541(7635): 107-111. |
| 63 | MCKENNA A, FINDLAY G M, GAGNON J A, et al. Whole-organism lineage tracing by combinatorial and cumulative genome editing [J]. Science, 2016, 353(6298): aaf7907. |
| 64 | KALHOR R, MALI P, CHURCH G M. Rapidly evolving homing CRISPR barcodes [J]. Nature Methods, 2017, 14(2): 195-200. |
| 65 | ZETSCHE B, GOOTENBERG J S, ABUDAYYEH O O, et al. Cpf1 is a single RNA-guided endonuclease of a class 2 CRISPR-Cas system [J]. Cell, 2015, 163(3): 759-771. |
| 66 | KIM Y G, CHA J, CHANDRASEGARAN S. Hybrid restriction enzymes: zinc finger fusions to FokI cleavage domain [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1996, 93(3): 1156-1160. |
| 67 | MILLER J C, HOLMES M C, WANG J, et al. An improved zinc-finger nuclease architecture for highly specific genome editing [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2007, 25(7): 778-785. |
| 68 | BOCH J, SCHOLZE H, SCHORNACK S, et al. Breaking the code of DNA binding specificity of TAL-type III effectors [J]. Science, 2009, 326(5959): 1509-1512. |
| 69 | CHRISTIAN M, CERMAK T, DOYLE E L, et al. Targeting DNA double-strand breaks with TAL effector nucleases [J]. Genetics, 2010, 186(2): 757-761. |
| 70 | LIM C K, NIRANTAR S, YEW W S, et al. Novel modalities in DNA data storage [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2021. DOI:10.1016/j.tibtech.2020.12.008 . |
| 71 | YACHIE N, OHASHI Y, TOMITA M. Stabilizing synthetic data in the DNA of living organisms [J]. Systems and Synthetic Biology, 2008, 2(1): 19-25. |
| 72 | SONG L, ZENG A P. Orthogonal information encoding in living cells with high error-tolerance, safety, and fidelity [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(3): 866-874. |
| 73 | DE SILVA P Y, GANEGODA G U. New trends of digital data storage in DNA [J]. BioMed Research International, 2016, 2016: 8072463. |
| 74 | BORDA M, TORNEA O. DNA secret writing techniques [C]// International Conference on Communications. Piscataway: IEEE, 2010. |
| 75 | SANGWAN N. Text encryption with huffman compression [J]. International Journal of Computer Applications, 2012, 54(6): 29-32. |
| 76 | AKRAM F, HAQ I U, ALI H, et al. Trends to store digital data in DNA: an overview [J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2018, 45(5): 1479-1490. |
| 77 | MARGULIES D, FELDER C E, MELMAN G, et al. A molecular keypad lock: a photochemical device capable of authorizing password entries [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(2): 347-354. |
| 78 | LIU Y, REN J, QIN Y, et al. An aptamer-based keypad lock system [J]. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(6): 802-804. |
| 79 | SHOSHANI S, PIRAN R, ARAVA Y, et al. A molecular cryptosystem for images by DNA computing [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(12): 2883-2887. |
| 80 | WONG N Y, XING H, TAN L H, et al. Nano-encrypted morse code: a versatile approach to programmable and reversible nanoscale assembly and disassembly [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(8): 2931-2934. |
| 81 | CHEN Z, XU J. One-time-pads encryption in the tile assembly model [J]. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience, 2010, 7(5): 848-855. |
| 82 | ADLEMAN L M. Molecular computation of solutions to combinatorial problems [J]. Science, 1994, 266(5187): 1021-1024. |
| 83 | LI J, GREEN A A, YAN H, et al. Engineering nucleic acid structures for programmable molecular circuitry and intracellular biocomputation [J]. Nature Chemistry, 2017, 9(11): 1056-1067. |
| 84 | QIAN L, WINFREE E, BRUCK J. Neural network computation with DNA strand displacement cascades [J]. Nature, 2011, 475(7356): 368-372. |
| 85 | SONG X, REIF J. Nucleic Acid databases and molecular-scale computing [J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(6): 6256-6268. |
| 86 | CARMEAN D, CEZE L, SEELIG G, et al. DNA data storage and hybrid molecular-electronic computing [J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2019, 107(1): 63-72. |
| 87 | 陈智华, 石晓龙, 程珍. DNA计算在信息安全领域的影响与应用[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2014, 29(1): 70-82. |
| CHEN Z H, SHI X L. CHENG Z. Impact and application of DNA nanotechnology in information security [J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014, 29(1): 70-82. | |
| 88 | LEIER A, RICHTER C, BANZHAF W, et al. Cryptography with DNA binary strands [J]. Biosystems, 2000, 57: 13-22. |
| 89 | GEHANI A, LABEAN T H, REIF J H. DNA-based cryptography, in dimacs deries in discrete mathematics [J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2000, 54: 233-251. |
| 90 | ZHANG Y, WANG F, CHAO J, et al. DNA origami cryptography for secure communication [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 5469. |
| 91 | LI S Y, LIU J K, ZHAO G P, et al. CADS: CRISPR/Cas12a-assisted DNA steganography for securing the storage and transfer of DNA-encoded information [J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(4): 1174-1178. |
| 92 | ZHANG Y, LI F, LI M, et al. Encoding carbon nanotubes with tubular nucleic acids for information storage [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(44): 17861-17866. |
| 93 | BESARATINIA A, YOON J I, SCHROEDER C, et al. Wavelength dependence of ultraviolet radiation-induced DNA damage as determined by laser irradiation suggests that cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers are the principal DNA lesions produced by terrestrial sunlight [J]. The FASEB Journal, 2011, 25(9): 3079-3091. |
| 94 | DIETRICH D, UHL B, SAILER V, et al. Improved PCR performance using template DNA from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues by overcoming PCR inhibition [J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(10): e77771. |
| 95 | PAUNESCU D, PUDDU M, SOELLNER J O B, et al. Reversible DNA encapsulation in silica to produce ROS-resistant and heat-resistant synthetic DNA 'fossils' [J]. Nature Protocols, 2013, 8(12): 2440-2448. |
| 96 | KARNI M, ZIDON D, POLAK P, et al. Thermal degradation of DNA [J]. DNA and Cell Biology, 2013, 32(6): 298-301. |
| 97 | KEMP B M, SMITH D G. Use of bleach to eliminate contaminating DNA from the surface of bones and teeth [J]. Forensic Science International, 2005, 154(1): 53-61. |
| 98 | KIM J, BAE J H, BAYM M, et al. Metastable hybridization-based DNA information storage to allow rapid and permanent erasure [J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5008. |
| 99 | LIN K N, VOLKEL K, TUCK J M, et al. Dynamic and scalable DNA-based information storage [J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 2981. |
| 100 | SONG Y, KIM S, HELLER M J, et al. DNA multi-bit non-volatile memory and bit-shifting operations using addressable electrode arrays and electric field-induced hybridization [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 281. |
| 101 | PUDDU M, PAUNESCU D, STARK W J, et al. Magnetically recoverable, thermostable, hydrophobic DNA/silica encapsulates and their application as invisible oil tags [J]. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(3): 2677-2685. |
| 102 | MIKUTIS G, DEUBER C A, SCHMID L, et al. Silica-encapsulated DNA-based tracers for aquifer characterization [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(21): 12142-12152. |
| 103 | KOSURI S, CHURCH G M. Large-scale de novo DNA synthesis: technologies and applications [J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(5): 499-507. |
| 104 | HUGHES R A, ELLINGTON A D. Synthetic DNA synthesis and assembly: putting the synthetic in synthetic biology [J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2017, 9(1): a023812. |
| [1] | JIAO Hongtao, QI Meng, SHAO Bin, JIANG Jinsong. Legal issues for the storage of DNA data [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [2] | XU Huaisheng, SHI Xiaolong, LIU Xiaoguang, XU Miaomiao. Key technologies for DNA storage: encoding, error correction, random access, and security [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [3] | LIU Zijian, MU Baiyang, DUAN Zhiqiang, WANG Xuan, LU Xiaojie. Advances in the development of DNA-compatible chemistries [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1102-1124. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xuanliang, LI Qingting, WANG Fei. Data writing in DNA storage systems [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(5): 1125-1141. |
| [5] | CHEN Yongcan, SI Tong, ZHANG Jianzhi. Applications of automated synthetic biotechnology in DNA assembly and microbial chassis manipulation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 857-876. |
| [6] | MA Mengdan, LIU Yuchen. Potential application of synthetic biology in disease information recording and real-time monitoring [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(2): 301-317. |
| [7] | YANG Yi, MAO Yufeng, YANG Chunhe, WANG Meng, LIAO Xiaoping, MA Hongwu. Recent progress in computational tools for designing editing sequences used in microbial genetic manipulations [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(1): 30-46. |
| [8] | SHI Qian, WU Yuanyuan, YANG yang. DNA nanotechnology and synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(2): 302-319. |
| [9] | HE Bo, FU Zongheng, WU Yi, ZHAO Guangrong. Research progress of synthetic mammalian genomics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(1): 78-97. |
| [10] | JIANG Chanjuan, CUI Tianqi, SUN Hongluan, JIAO Nianzhi, FU Jun, ZHANG Youming, WANG Hailong. Efficient capture and assembly of AT-rich genomic fragments using ExoCET-BAC strategy [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2022, 3(1): 238-251. |
| [11] | PING Zhi, ZHANG Haoling, CHEN Shihong, NI Ming, XU Xun, ZHU Sha, SHEN Yue. Chamaeleo: an integrated evaluation platform for DNA storage [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 412-427. |
| [12] | CHEN Daming, ZHANG Xuebo, LIU Xiao, MA Yue, XIONG Yan. A global patent analysis: trends in DNA synthesis and information storage [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 399-411. |
| [13] | YANG Yang, FAN Chunhai. The current advance in artificial chromosome based DNA information storage [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 305-308. |
| [14] | HUANG Xiaoluo, DAI Junbiao. DNA synthesis technology: foundation of DNA data storage [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 335-353. |
| [15] | CHEN Weigang, GE Qi, WANG Panpan, HAN Mingzhe, GUO Jian. Multiple interleaved RS codes for data storage using up to Mb-scale synthetic DNA in living cells [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 428-443. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||