合成生物学 ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (3): 612-630.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2023-087
放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展
谢皇1,2, 郑义蕾1,2, 苏依婷1,2, 阮静怡1,2, 李永泉1,2
- 1.浙江大学药物生物技术研究所,浙江 杭州 310058
2.浙江省微生物生化与代谢工程重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310058
-
收稿日期:2023-11-28修回日期:2024-01-16出版日期:2024-06-30发布日期:2024-07-12 -
通讯作者:李永泉 -
作者简介:谢皇 (1997—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为微生物次级代谢产物调控,底盘构建与天然产物的异源表达。E-mail:xiehuang@zju.edu.cn郑义蕾 (1996—),男,博士研究生。研究方向为微生物异源生物合成,微生物次级代谢的生物化学机理。E-mail:yl_zheng@zju.edu.cn李永泉 (1962—),男,博士,浙江大学求是特聘教授。研究方向为微生物合成生物学、微生物次级代谢调控和微生物制药。E-mail:lyq@zju.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(32170057);国家重点研发计划(2019YFA09005400)
An overview on reconstructing the biosynthetic system of actinomycetes for polyketides production
XIE Huang1,2, ZHENG Yilei1,2, SU Yiting1,2, RUAN Jingyi1,2, LI Yongquan1,2
- 1.Institute of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310058,Zhejiang,China
2.Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory for Microbial Biochemistry and Metabolic Engineering,Hangzhou 310058,Zhejiang,China
-
Received:2023-11-28Revised:2024-01-16Online:2024-06-30Published:2024-07-12 -
Contact:LI Yongquan
摘要:
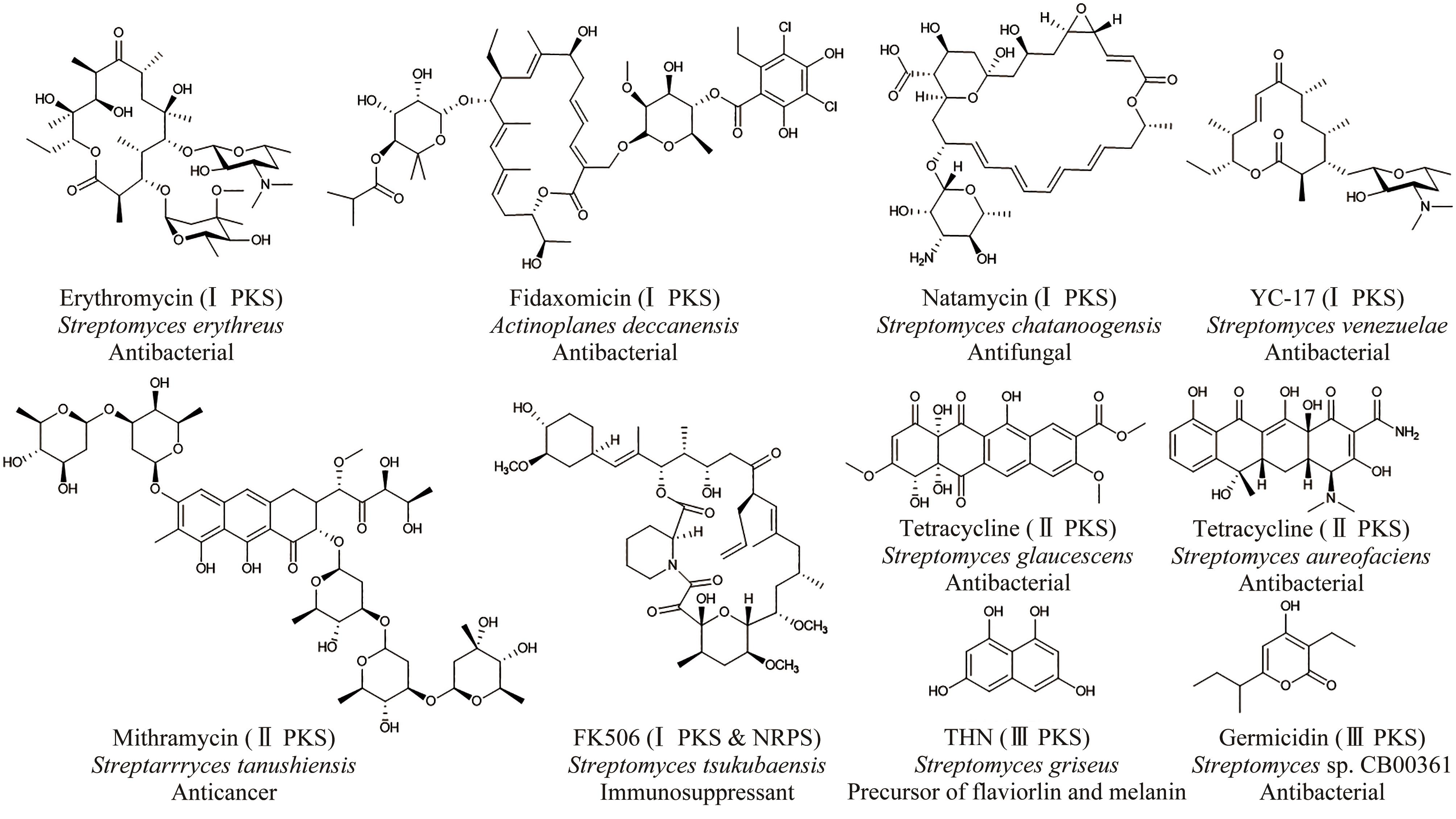
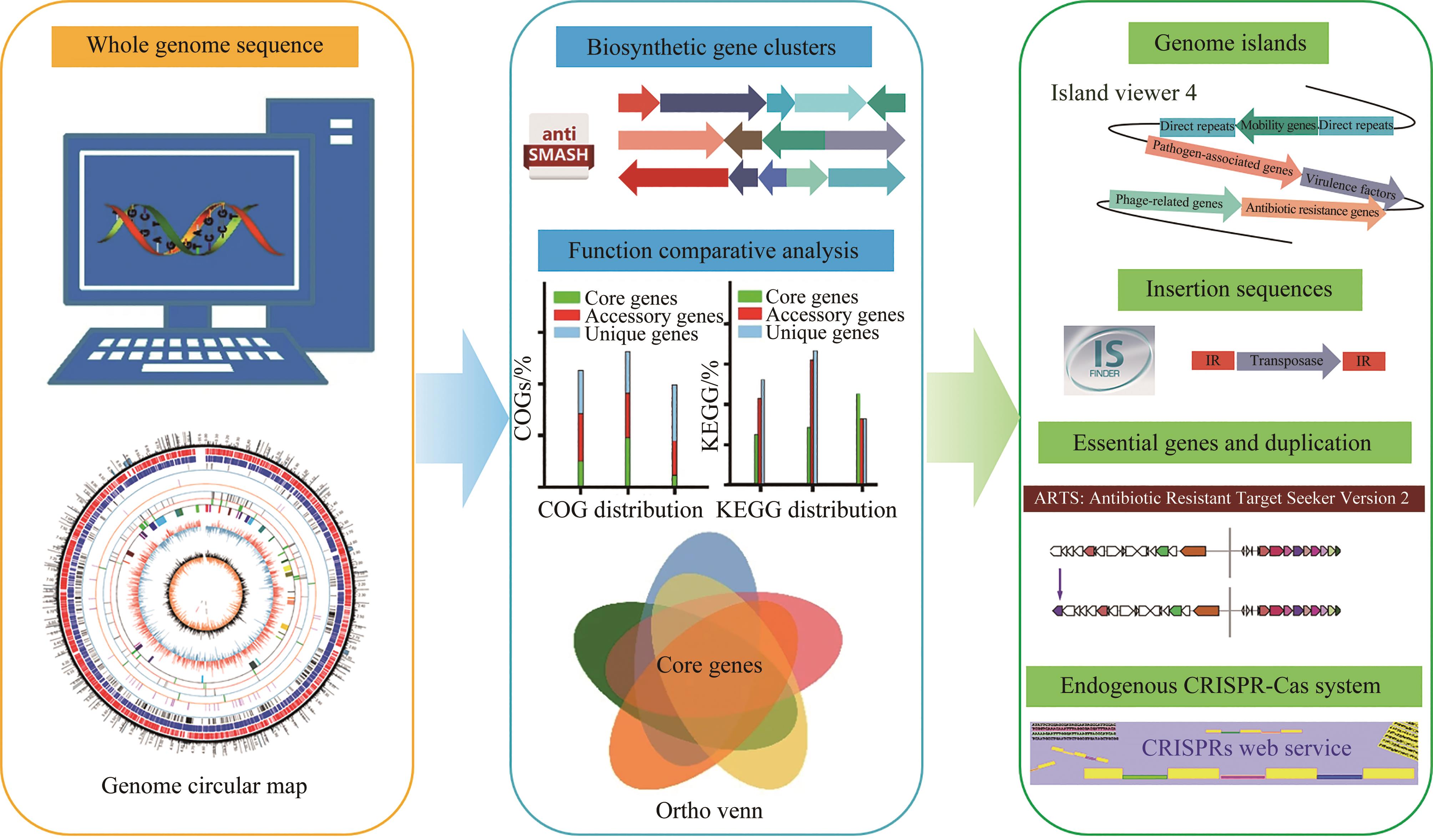
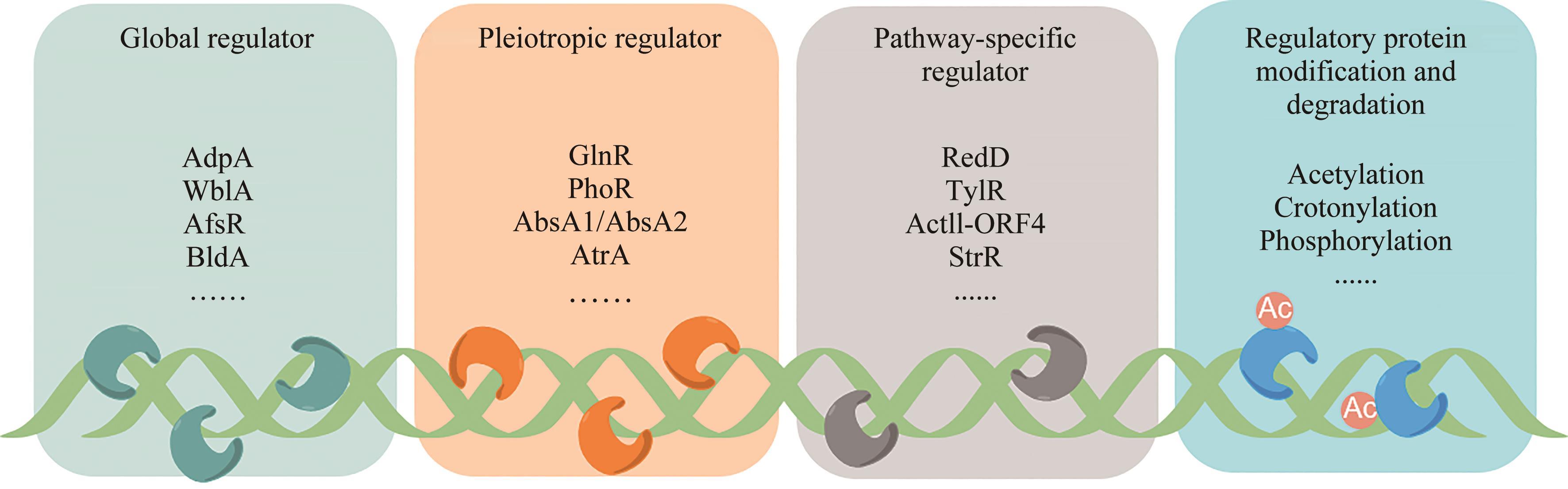
放线菌因其丰富的次级代谢产物而成为候选药物发掘的宝贵资源库,其蕴含的活性化合物包含聚酮类、非核糖体肽类、氨基糖苷类、萜类等,其中聚酮类化合物占比最大。大环内酯是聚酮类化合物的典型,常常被用作抗生素、抗肿瘤剂、免疫抑制剂、抗寄生虫剂等,具有重要的生物学意义。本文立足聚酮类大环内酯的生物合成过程,提出了从基因组重塑、调控通路重组、组合代谢工程及聚酮类化合物结构的衍生与多样化等多角度,实现放线菌聚酮类生物合成体系的优化,为工业规模生产聚酮类药物及其新型衍生物提供技术支撑。通过这种多维度的方法,结合最新的合成生物学使能技术,遵循绿色、环保、高效和可持续的策略,可以更有效地优化和增强放线菌中聚酮类化合物的生产,为未来药物的开发和生产提供新的可能性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
谢皇, 郑义蕾, 苏依婷, 阮静怡, 李永泉. 放线菌聚酮类化合物生物合成体系重构研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(3): 612-630.
XIE Huang, ZHENG Yilei, SU Yiting, RUAN Jingyi, LI Yongquan. An overview on reconstructing the biosynthetic system of actinomycetes for polyketides production[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2024, 5(3): 612-630.
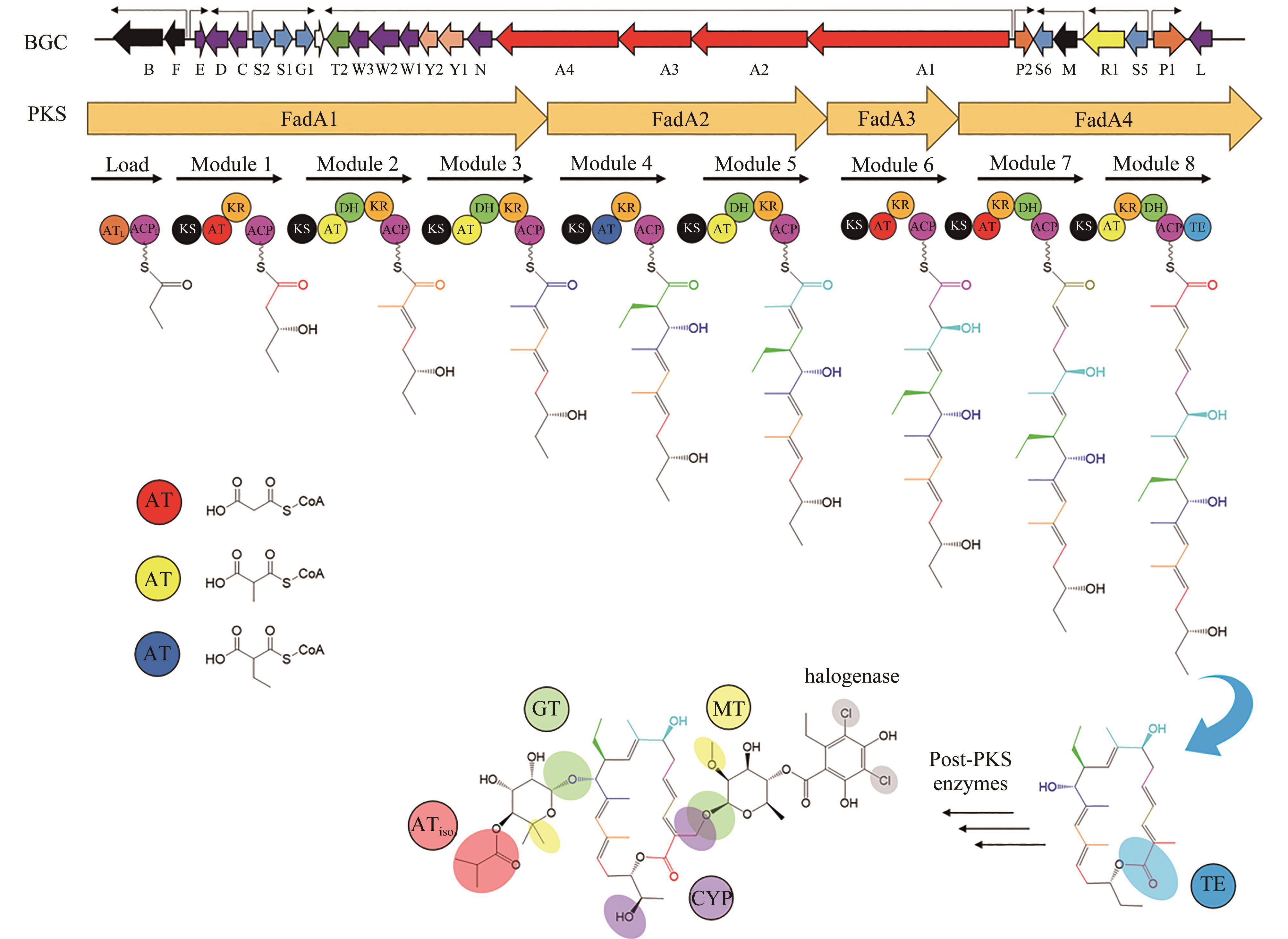
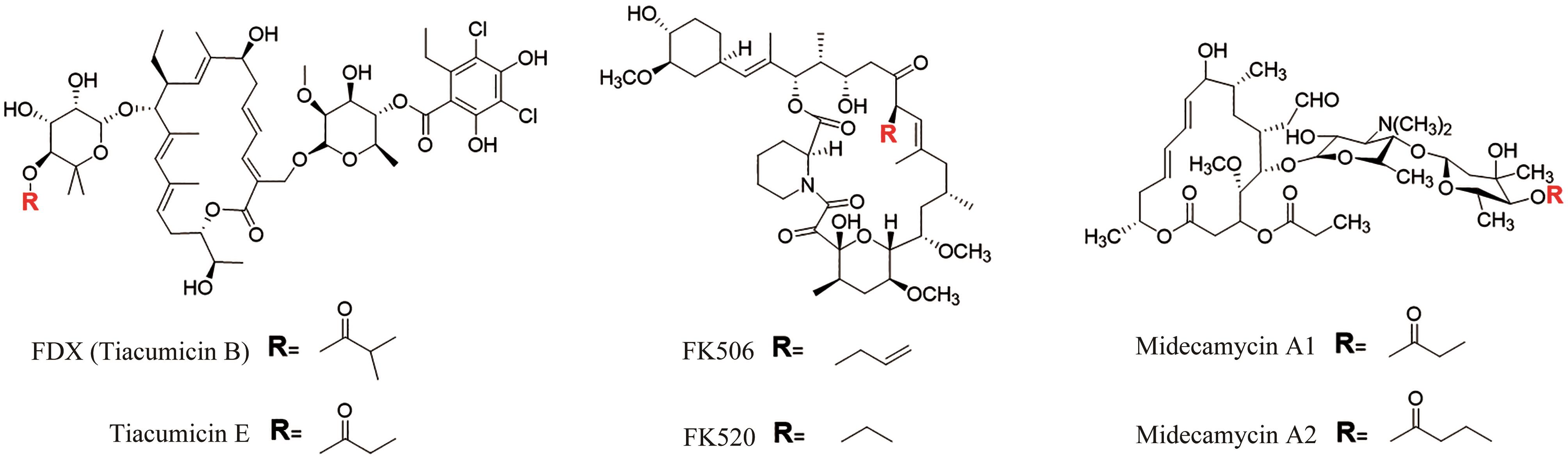
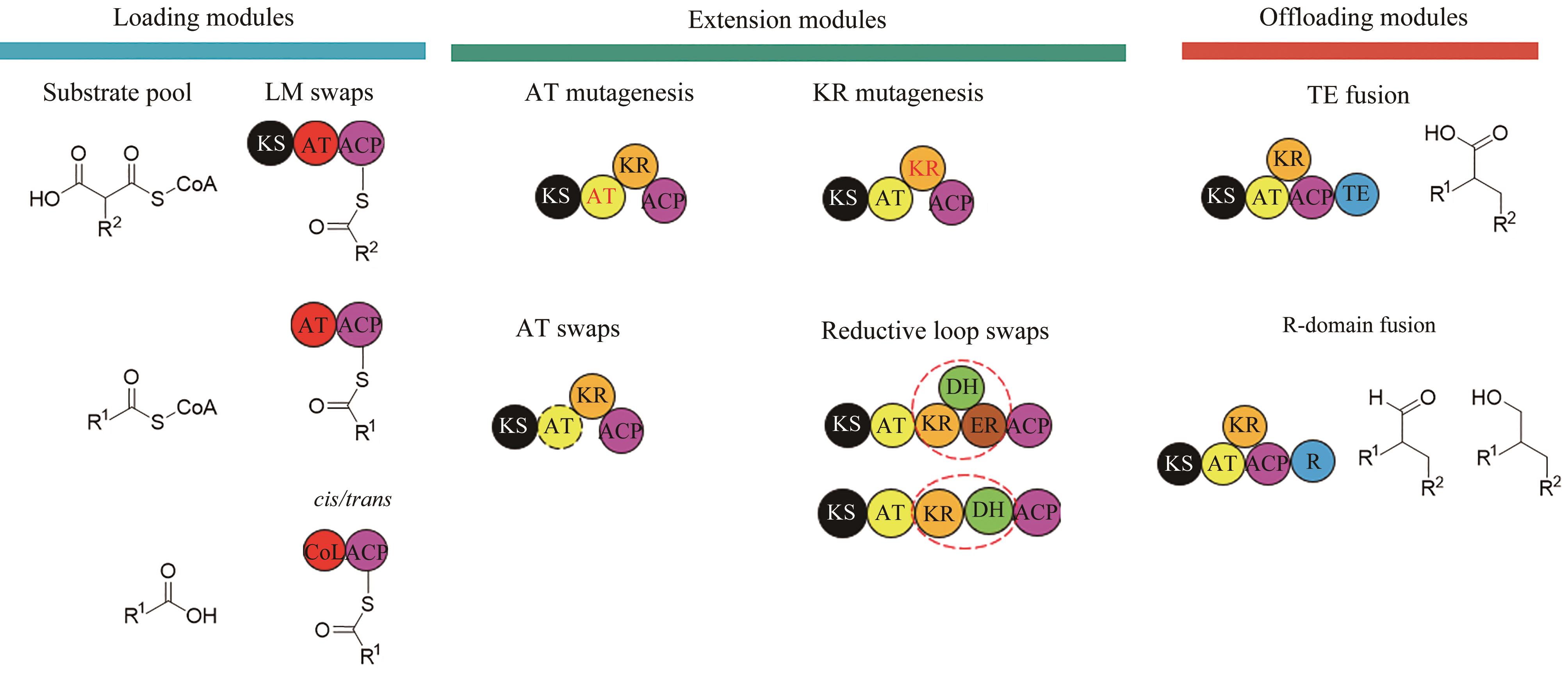
图2 非达霉素生物合成基因簇的模块化组装(图中展示了不同延长单元的缩合和修饰,形成了糖苷配体骨架,然后通过不同的后修饰酶进行催化进一步形成非达霉素)
Fig. 2 Assembly of the gene clusters for fidaxomicin biosynthesis(Condensations and modifications of different extender units to form fidaxomicin aglycone are illustrated, which is further processed with different post-modifications to form fidaxomicin.)
| 120 | MALMIERCA M G, PÉREZ-VICTORIA I, MARTÍN J, et al. New sipanmycin analogues generated by combinatorial biosynthesis and mutasynthesis approaches relying on the substrate flexibility of key enzymes in the biosynthetic pathway[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2020, 86(3): e02453-19. |
| 121 | LI L Y, HU Y L, SUN J L, et al. Resistance and phylogeny guided discovery reveals structural novelty of tetracycline antibiotics[J]. Chemical Science, 2022, 13(43): 12892-12898. |
| 122 | DHAKAL D, SOHNG J K, PANDEY R P. Engineering actinomycetes for biosynthesis of macrolactone polyketides[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18(1): 137. |
| 123 | YUAN Y J, CHENG S, BIAN G K, et al. Efficient exploration of terpenoid biosynthetic gene clusters in filamentous fungi[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2022, 5(4): 277-287. |
| 124 | DENG L, ZHAO Z H, LIU L, et al. Dissection of 3D chromosome organization in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) leads to biosynthetic gene cluster overexpression[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(11): e2222045120. |
| 125 | TU R, ZHANG Y, HUA E B, et al. Droplet-based microfluidic platform for high-throughput screening of Streptomyces [J]. Communications Biology, 2021, 4(1): 647. |
| 1 | WAKSMAN S A, REILLY H C, JOHNSTONE D B. Isolation of streptomycin-producing strains of Streptomyces griseus [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1946, 52(3): 393-397. |
| 2 | MARSCHNER P. Rhizosphere biology[M/OL]// Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants. 3rd Edition. New York: Academic Press, 2012: 369-388 [2023-12-01]. . |
| 3 | NETT M, IKEDA H, MOORE B S. Genomic basis for natural product biosynthetic diversity in the actinomycetes[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2009, 26(11): 1362-1384. |
| 4 | KOMAKI H, SAKURAI K, HOSOYAMA A, et al. Diversity of nonribosomal peptide synthetase and polyketide synthase gene clusters among taxonomically close Streptomyces strains[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 6888. |
| 5 | BELKNAP K C, PARK C J, BARTH B M, et al. Genome mining of biosynthetic and chemotherapeutic gene clusters in Streptomyces bacteria[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 2003. |
| 6 | HE X M, LIU H W. Formation of unusual sugars: mechanistic studies and biosynthetic applications[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2002, 71: 701-754. |
| 7 | DUTTA S, WHICHER J R, HANSEN D A, et al. Structure of a modular polyketide synthase[J]. Nature, 2014, 510(7506): 512-517. |
| 8 | WHICHER J R, DUTTA S, HANSEN D A, et al. Structural rearrangements of a polyketide synthase module during its catalytic cycle[J]. Nature, 2014, 510(7506): 560-564. |
| 9 | PARK S R, HAN A R, BAN Y H, et al. Genetic engineering of macrolide biosynthesis: past advances, current state, and future prospects[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 85(5): 1227-1239. |
| 10 | CHEN A Y, SCHNARR N A, KIM C Y, et al. Extender unit and acyl carrier protein specificity of ketosynthase domains of the 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128(9): 3067-3074. |
| 11 | FISCHBACH M A, WALSH C T. Assembly-line enzymology for polyketide and nonribosomal peptide antibiotics: logic, machinery, and mechanisms[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2006, 106(8): 3468-3496. |
| 12 | XU W, QIAO K J, TANG Y. Structural analysis of protein-protein interactions in type Ⅰ polyketide synthases[J]. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2013, 48(2): 98-122. |
| 13 | XIAO Y, LI S M, NIU S W, et al. Characterization of tiacumicin B biosynthetic gene cluster affording diversified tiacumicin analogues and revealing a tailoring dihalogenase[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(4): 1092-1105. |
| 14 | ERB W, ZHU J P. From natural product to marketed drug: the tiacumicin odyssey[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2013, 30(1): 161-174. |
| 15 | LI Y P, YU P, LI J F, et al. FadR1, a pathway-specific activator of fidaxomicin biosynthesis in Actinoplanes deccanensis Yp-1[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(18): 7583-7596. |
| 16 | MYRONOVSKYI M, ROSENKRÄNZER B, NADMID S, et al. Generation of a cluster-free Streptomyces albus chassis strains for improved heterologous expression of secondary metabolite clusters[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2018, 49: 316-324. |
| 17 | GOMEZ-ESCRIBANO J P, BIBB M J. Engineering Streptomyces coelicolor for heterologous expression of secondary metabolite gene clusters[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2011, 4(2): 207-215. |
| 18 | JONES A C, GUST B, KULIK A, et al. Phage p1-derived artificial chromosomes facilitate heterologous expression of the FK506 gene cluster[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(7): e69319. |
| 19 | NAH H J, WOO M W, CHOI S S, et al. Precise cloning and tandem integration of large polyketide biosynthetic gene cluster using Streptomyces artificial chromosome system[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 140. |
| 20 | TANG X Y, LI J, MILLÁN-AGUIÑAGA N, et al. Identification of thiotetronic acid antibiotic biosynthetic pathways by target-directed genome mining[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2015, 10(12): 2841-2849. |
| 21 | QIAN Z Y, BRUHN T, D’AGOSTINO P M, et al. Discovery of the streptoketides by direct cloning and rapid heterologous expression of a cryptic PKS Ⅱ gene cluster from Streptomyces sp. Tü 6314[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2020, 85(2): 664-673. |
| 22 | GREN T, WHITFORD C M, MOHITE O S, et al. Characterization and engineering of Streptomyces griseofuscus DSM 40191 as a potential host for heterologous expression of biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 18301. |
| 23 | BLIN K, SHAW S, KLOOSTERMAN A M, et al. antiSMASH 6.0: improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(W1): W29-W35. |
| 24 | LU C Y, ZHANG X J, JIANG M, et al. Enhanced salinomycin production by adjusting the supply of polyketide extender units in Streptomyces albus [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2016, 35: 129-137. |
| 25 | KORMANEC J, REZUCHOVA B, HOMEROVA D, et al. Recent achievements in the generation of stable genome alterations/mutations in species of the genus Streptomyces [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(14): 5463-5482. |
| 26 | CRAMERI R, KIESER T, ONO H, et al. Chromosomal instability in Streptomyces glaucescens: mapping of streptomycin-sensitive mutants[J]. Microbiology, 1983, 129(2): 519-527. |
| 27 | PENG M X, LIANG Z H. Degeneration of industrial bacteria caused by genetic instability[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2020, 36(8): 119. |
| 28 | FISHMAN S E, HERSHBERGER C L. Amplified DNA in Streptomyces fradiae [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1983, 155(2): 459-466. |
| 29 | ROTH M, NOACK D. Genetic stability of differentiated functions in Streptomyces hygroscopicus in relation to conditions of continuous culture[J]. Microbiology, 1982, 128(1): 107-114. |
| 30 | LI Y P, BU Q T, LI J F, et al. Genome-based rational engineering of Actinoplanes deccanensis for improving fidaxomicin production and genetic stability[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 330: 124982. |
| 31 | BU Q T, YU P, WANG J, et al. Rational construction of genome-reduced and high-efficient industrial Streptomyces chassis based on multiple comparative genomic approaches[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2019, 18(1): 16. |
| 32 | GOMEZ-ESCRIBANO J P, BIBB M J. Streptomyces coelicolor as an expression host for heterologous gene clusters[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2012, 517: 279-300. |
| 33 | JUGUET M, LAUTRU S, FRANCOU F X, et al. An iterative nonribosomal peptide synthetase assembles the pyrrole-amide antibiotic congocidine in Streptomyces ambofaciens [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2009, 16(4): 421-431. |
| 34 | IKEDA H, KAZUO S Y, OMURA S. Genome mining of the Streptomyces avermitilis genome and development of genome-minimized hosts for heterologous expression of biosynthetic gene clusters[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2014, 41(2): 233-250. |
| 35 | KOMATSU M, KOMATSU K, KOIWAI H, et al. Engineered Streptomyces avermitilis host for heterologous expression of biosynthetic gene cluster for secondary metabolites[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2013, 2(7): 384-396. |
| 36 | LOPATNIUK M, MYRONOVSKYI M, LUZHETSKYY A. Streptomyces albus: a new cell factory for non-canonical amino acids incorporation into ribosomally synthesized natural products[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2017, 12(9): 2362-2370. |
| 37 | BATE N, STRATIGOPOULOS G, CUNDLIFFE E. Differential roles of two SARP-encoding regulatory genes during tylosin biosynthesis[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2002, 43(2): 449-458. |
| 38 | AIGLE B, PANG X H, DECARIS B, et al. Involvement of AlpV, a new member of the Streptomyces antibiotic regulatory protein family, in regulation of the duplicated type Ⅱ polyketide synthase alp gene cluster in Streptomyces ambofaciens [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2005, 187(7): 2491-2500. |
| 39 | YIN S L, WANG W S, WANG X F, et al. Identification of a cluster-situated activator of oxytetracycline biosynthesis and manipulation of its expression for improved oxytetracycline production in Streptomyces rimosus [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2015, 14: 46. |
| 40 | ZHANG Y Y, HE H R, LIU H, et al. Characterization of a pathway-specific activator of milbemycin biosynthesis and improved milbemycin production by its overexpression in Streptomyces bingchenggensis [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15(1): 152. |
| 41 | ZHANG X S, LUO H D, TAO Y, et al. FkbN and Tcs7 are pathway-specific regulators of the FK506 biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces tsukubaensis L19[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2016, 43(12): 1693-1703. |
| 42 | ANTÓN N, MENDES M V, MARTÍN J F, et al. Identification of PimR as a positive regulator of pimaricin biosynthesis in Streptomyces natalensis [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2004, 186(9): 2567-2575. |
| 43 | WILSON D J, XUE Y, REYNOLDS K A, et al. Characterization and analysis of the PikD regulatory factor in the pikromycin biosynthetic pathway of Streptomyces venezuelae [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2001, 183(11): 3468-3475. |
| 44 | ZHU Z H, LI H, YU P, et al. SlnR is a positive pathway-specific regulator for salinomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces albus [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(4): 1547-1557. |
| 45 | KUSCER E, COATES N, CHALLIS I, et al. Roles of rapH and rapG in positive regulation of rapamycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces hygroscopicus [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2007, 189(13): 4756-4763. |
| 46 | PARK S S, YANG Y H, SONG E, et al. Mass spectrometric screening of transcriptional regulators involved in antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2009, 36(8): 1073-1083. |
| 47 | MAO X M, LUO S, ZHOU R C, et al. Transcriptional regulation of the daptomycin gene cluster in Streptomyces roseosporus by an autoregulator, AtrA[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2015, 290(12): 7992-8001. |
| 48 | YU P, LIU S P, BU Q T, et al. WblAch, a pivotal activator of natamycin biosynthesis and morphological differentiation in Streptomyces chattanoogensis L10, is positively regulated by AdpAch[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 80(22): 6879-6887. |
| 49 | FU Y, DONG Y Q, SHEN J L, et al. A meet-up of acetyl phosphate and c-di-GMP modulates BldD activity for development and antibiotic production[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2023, 51(13): 6870-6882. |
| 50 | MARTÍN J F, LIRAS P, SÁNCHEZ S. Modulation of gene expression in Actinobacteria by translational modification of transcriptional factors and secondary metabolite biosynthetic enzymes[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 630694. |
| 51 | DE CRÉCY-LAGARD V, SERVANT-MOISSON P, VIALA J, et al. Alteration of the synthesis of the Clp ATP-dependent protease affects morphological and physiological differentiation in Streptomyces [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 1999, 32(3): 505-517. |
| 52 | MAO X M, SUN N, WANG F, et al. Dual positive feedback regulation of protein degradation of an extra-cytoplasmic function σ factor for cell differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor [J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2013, 288(43): 31217-31228. |
| 53 | MAO X M, REN N N, SUN N, et al. Proteasome involvement in a complex cascade mediating SigT degradation during differentiation of Streptomyces coelicolor [J]. FEBS Letters, 2014, 588(4): 608-613. |
| 54 | SHEN J J, CHEN F, WANG X X, et al. Substrate specificity of acyltransferase domains for efficient transfer of acyl groups[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 1840. |
| 55 | STUTZMAN-ENGWALL K, CONLON S, FEDECHKO R, et al. Semi-synthetic DNA shuffling of aveC leads to improved industrial scale production of doramectin by Streptomyces avermitilis [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2005, 7(1): 27-37. |
| 56 | GRABOWSKA A D, BRISON Y, MAVEYRAUD L, et al. Molecular basis for extender unit specificity of mycobacterial polyketide synthases[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2020, 15(12): 3206-3216. |
| 57 | INGRAHAM J B, BARANOV M, COSTELLO Z, et al. Illuminating protein space with a programmable generative model[J]. Nature, 2023, 623(7989): 1070-1078. |
| 58 | BOIKO D A, MACKNIGHT R, KLINE B, et al. Autonomous chemical research with large language models[J]. Nature, 2023, 624(7992): 570-578. |
| 59 | BERQUEZ M, CHEN Z Y, FESTA B P, et al. Lysosomal cystine export regulates mTORC1 signaling to guide kidney epithelial cell fate specialization[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 3994. |
| 60 | SUN J, KELEMEN G H, FERNÁNDEZ-ABALOS J M, et al. Green fluorescent protein as a reporter for spatial and temporal gene expression in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)[J]. Microbiology, 1999, 145( Pt 9): 2221-2227. |
| 61 | MYRONOVSKYI M, WELLE E, FEDORENKO V, et al. β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile reporter in actinomycetes[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(15): 5370-5383. |
| 62 | ZHENG J T, SAGAR V, SMOLINSKY A, et al. Structure and function of the macrolide biosensor protein, MphR(A), with and without erythromycin[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2009, 387(5): 1250-1260. |
| 63 | CHEN Y, DENG W, WU J Q, et al. Genetic modulation of the overexpression of tailoring genes eryK and eryG leading to the improvement of erythromycin A purity and production in Saccharopolyspora erythraea fermentation[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 74(6): 1820-1828. |
| 64 | ZHANG J, HE Z L, XU J T, et al. Semi-rational mutagenesis of an industrial Streptomyces fungicidicus strain for improved enduracidin productivity[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(8): 3459-3471. |
| 65 | CHEN H T, ZHANG X Y, WU Q B, et al. Production improvement of FK506 in Streptomyces tsukubaensis by metabolic engineering strategy[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2023, 134(7): lxad142. |
| 66 | LI L, WEI K K, LIU X C, et al. aMSGE: advanced multiplex site-specific genome engineering with orthogonal modular recombinases in actinomycetes[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019, 52: 153-167. |
| 67 | MURAKAMI T, SUMIDA N, BIBB M, et al. ZouA, a putative relaxase, is essential for DNA amplification in Streptomyces kanamyceticus [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2011, 193(8): 1815-1822. |
| 68 | MURAKAMI T, BURIAN J, YANAI K, et al. A system for the targeted amplification of bacterial gene clusters multiplies antibiotic yield in Streptomyces coelicolor [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(38): 16020-16025. |
| 69 | SHAN Y M, GUO D, GU Q S, et al. Genome mining and homologous comparison strategy for digging exporters contributing self-resistance in natamycin-producing Streptomyces strains[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(2): 817-831. |
| 70 | QIU J F, ZHUO Y, ZHU D Q, et al. Overexpression of the ABC transporter AvtAB increases avermectin production in Streptomyces avermitilis [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2011, 92(2): 337-345. |
| 71 | YU L, YAN X Y, WANG L, et al. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of an ATP-binding cassette transporter OtrC from Streptomyces rimosus [J]. BMC Biotechnology, 2012, 12: 52. |
| 72 | WANG X R, WEI J H, XIAO Y F, et al. Efflux identification and engineering for ansamitocin P-3 production in Actinosynnema pretiosum [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2021, 105(2): 695-706. |
| 73 | CHU L Y, LI S S, DONG Z X, et al. Mining and engineering exporters for titer improvement of macrolide biopesticides in Streptomyces [J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2022, 15(4): 1120-1132. |
| 74 | ROKEM J S, LANTZ A E, NIELSEN J. Systems biology of antibiotic production by microorganisms[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2007, 24(6): 1262-1287. |
| 75 | KIM E, MOORE B S, YOON Y J. Reinvigorating natural product combinatorial biosynthesis with synthetic biology[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2015, 11(9): 649-659. |
| 76 | BREITLING R, TAKANO E. Synthetic biology of natural products[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2016, 8(10): a023994. |
| 77 | MICHAEL J B, PER B, SRDJAN J, et al. Engineering of Primary carbon metabolism for improved antibiotic production in Streptomyces lividans [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2002, 68(10): 4731-4739. |
| 78 | ZABALA D, BRAÑA A F, FLÓREZ A B, et al. Engineering precursor metabolite pools for increasing production of antitumor mithramycins in Streptomyces argillaceus [J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2013, 20: 187-197. |
| 79 | HUANG D, LI S S, XIA M L, et al. Genome-scale metabolic network guided engineering of Streptomyces tsukubaensis for FK506 production improvement[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2013, 12: 52. |
| 80 | DANG L Q, LIU J, WANG C, et al. Enhancement of rapamycin production by metabolic engineering in Streptomyces hygroscopicus based on genome-scale metabolic model[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2017, 44(2): 259-270. |
| 81 | BAI C X, ZHANG Y, ZHAO X J, et al. Exploiting a precise design of universal synthetic modular regulatory elements to unlock the microbial natural products in Streptomyces [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(39): 12181-12186. |
| 82 | WANG T, BAI L Q, ZHU D Q, et al. Enhancing macrolide production in Streptomyces by coexpressing three heterologous genes[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2012, 50(1): 5-9. |
| 83 | GERTH K, BEDORF N, HÖFLE G, et al. Epothilons A and B: antifungal and cytotoxic compounds from Sorangium cellulosum (Myxobacteria). Production, physico-chemical and biological properties[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 1996, 49(6): 560-563. |
| 84 | GRIFFITH R S, BLACK H R. Erythromycin[J]. The Medical Clinics of North America, 1970, 54(5): 1199-1215. |
| 85 | DUTCHER J D. The discovery and development of amphotericin B[J]. Diseases of the Chest, 1968, 54: 296-298. |
| 86 | KUHSTOSS S, HUBER M, TURNER J R, et al. Production of a novel polyketide through the construction of a hybrid polyketide synthase[J]. Gene, 1996, 183(1-2): 231-236. |
| 87 | LONG P F, WILKINSON C J, BISANG C P, et al. Engineering specificity of starter unit selection by the erythromycin-producing polyketide synthase[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2002, 43(5): 1215-1225. |
| 88 | DUTTON C J, GIBSON S P, GOUDIE A C, et al. Novel avermectins produced by mutational biosynthesis[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 1991, 44(3): 357-365. |
| 89 | YUZAWA S, ENG C H, KATZ L, et al. Broad substrate specificity of the loading didomain of the lipomycin polyketide synthase[J]. Biochemistry, 2013, 52(22): 3791-3793. |
| 90 | MUSIOL-KROLL E M, ZUBEIL F, SCHAFHAUSER T, et al. Polyketide bioderivatization using the promiscuous acyltransferase KirCⅡ[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(3): 421-427. |
| 91 | REEVES C D, MURLI S, ASHLEY G W, et al. Alteration of the substrate specificity of a modular polyketide synthase acyltransferase domain through site-specific mutations[J]. Biochemistry, 2001, 40(51): 15464-15470. |
| 92 | 沈洁洁, 毛旭明, 陈新爱, 等. Ⅰ型聚酮合酶中酰基转移酶结构域的研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2018, 38(9): 2377-2385. |
| SHEN J J, MAO X M, CHEN X A, et al. Recent advances in acyltransferase domain of type Ⅰ polyktide synthases[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2018, 38(9): 2377-2385. | |
| 93 | MARSDEN A F, WILKINSON B, CORTÉS J, et al. Engineering broader specificity into an antibiotic-producing polyketide synthase[J]. Science, 1998, 279(5348): 199-202. |
| 94 | STASSI D L, KAKAVAS S J, REYNOLDS K A, et al. Ethyl-substituted erythromycin derivatives produced by directed metabolic engineering[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1998, 95(13): 7305-7309. |
| 95 | HANS M, HORNUNG A, DZIARNOWSKI A, et al. Mechanistic analysis of acyl transferase domain exchange in polyketide synthase modules[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(18): 5366-5374. |
| 96 | MUSIOL E M, WEBER T. Discrete acyltransferases involved in polyketide biosynthesis[J]. MedChemComm, 2012, 3(8): 871-886. |
| 97 | BARAJAS J F, BLAKE-HEDGES J M, BAILEY C B, et al. Engineered polyketides: synergy between protein and host level engineering[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology, 2017, 2(3): 147-166. |
| 98 | PETKOVIĆ H, SANDMANN A, CHALLIS I R, et al. Substrate specificity of the acyl transferase domains of EpoC from the epothilone polyketide synthase[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2008, 6(3): 500-506. |
| 99 | JIANG H, WANG Y Y, GUO Y Y, et al. An acyltransferase domain of FK506 polyketide synthase recognizing both an acyl carrier protein and coenzyme A as acyl donors to transfer allylmalonyl and ethylmalonyl units[J]. The FEBS Journal, 2015, 282(13): 2527-2539. |
| 100 | SUNDERMANN U, BRAVO-RODRIGUEZ K, KLOPRIES S, et al. Enzyme-directed mutasynthesis: a combined experimental and theoretical approach to substrate recognition of a polyketide synthase[J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2013, 8(2): 443-450. |
| 101 | BRAVO-RODRIGUEZ K, ISMAIL-ALI A F, KLOPRIES S, et al. Predicted incorporation of non-native substrates by a polyketide synthase yields bioactive natural product derivatives[J]. ChemBioChem, 2014, 15(13): 1991-1997. |
| 102 | BAERGA-ORTIZ A, POPOVIC B, SISKOS A P, et al. Directed mutagenesis alters the stereochemistry of catalysis by isolated ketoreductase domains from the erythromycin polyketide synthase[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2006, 13(3): 277-285. |
| 103 | O′HARE H M, BAERGA-ORTIZ A, POPOVIC B, et al. High-throughput mutagenesis to evaluate models of stereochemical control in ketoreductase domains from the erythromycin polyketide synthase[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2006, 13(3): 287-296. |
| 104 | REID R, PIAGENTINI M, RODRIGUEZ E, et al. A model of structure and catalysis for ketoreductase domains in modular polyketide synthases[J]. Biochemistry, 2003, 42(1): 72-79. |
| 105 | ZHOU Y J, LI J L, ZHU J, et al. Incomplete β-ketone processing as a mechanism for polyene structural variation in the FR-008/candicidin complex[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2008, 15(6): 629-638. |
| 106 | BRAUTASET T, SLETTA H, NEDAL A, et al. Improved antifungal polyene macrolides via engineering of the nystatin biosynthetic genes in Streptomyces noursei [J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2008, 15(11): 1198-1206. |
| 107 | YONG J H, BYEON W H. Alternative production of avermectin components in Streptomyces avermitilis by gene replacement[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2005, 43(3): 277-284. |
| 108 | KEATINGE-CLAY A T. Stereocontrol within polyketide assembly lines[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2016, 33(2): 141-149. |
| 109 | KWAN D H, SUN Y H, SCHULZ F, et al. Prediction and manipulation of the stereochemistry of enoylreduction in modular polyketide synthases[J]. Chemistry & Biology, 2008, 15(11): 1231-1240. |
| 110 | QI Z, ZHOU Y C, KANG Q J, et al. Directed accumulation of less toxic pimaricin derivatives by improving the efficiency of a polyketide synthase dehydratase domain[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 101(6): 2427-2436. |
| 111 | ZHANG X L, CHEN Z, LI M, et al. Construction of ivermectin producer by domain swaps of avermectin polyketide synthase in Streptomyces avermitilis [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 72(5): 986-994. |
| 112 | MCDANIEL R, THAMCHAIPENET A, GUSTAFSSON C, et al. Multiple genetic modifications of the erythromycin polyketide synthase to produce a library of novel “unnatural” natural products[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(5): 1846-1851. |
| 113 | CORTES J, WIESMANN K E, ROBERTS G A, et al. Repositioning of a domain in a modular polyketide synthase to promote specific chain cleavage[J]. Science, 1995, 268(5216): 1487-1489. |
| 114 | PIEPER R, GOKHALE R S, LUO G, et al. Purification and characterization of bimodular and trimodular derivatives of the erythromycin polyketide synthase[J]. Biochemistry, 1997, 36(7): 1846-1851. |
| 115 | WEISSMAN K J, BYCROFT M, STAUNTON J, et al. Origin of starter units for erythromycin biosynthesis[J]. Biochemistry, 1998, 37(31): 11012-11017. |
| 116 | ENGLUND E, SCHMIDT M, NAVA A A, et al. Biosensor guided polyketide synthases engineering for optimization of domain exchange boundaries[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 4871. |
| 117 | HOCHLOWSKI J E, JACKSON M, RASMUSSEN R R, et al. Production of brominated tiacumicin derivatives[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 1997, 50(3): 201-205. |
| 118 | GROTE M, SCHULZ F. Exploring the promiscuous enzymatic activation of unnatural polyketide extender units in vitro and in vivo for monensin biosynthesis[J]. ChemBioChem, 2019, 20(9): 1183-1189. |
| 119 | ZHANG H B, TIAN X X, PU X H, et al. Tiacumicin congeners with improved antibacterial activity from a halogenase-inactivated mutant[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2018, 81(5): 1219-1224. |
| [1] | 郭姝媛, 张倩楠, 姑丽克孜·买买提热夏提, 杨一群, 于涛. 液体生物燃料合成与炼制的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 18-44. |
| [2] | 高歌, 边旗, 王宝俊. 合成基因线路的工程化设计研究进展与展望[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 45-64. |
| [3] | 李冀渊, 吴国盛. 合成生物学视域下有机体的两种隐喻[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 190-202. |
| [4] | 焦洪涛, 齐蒙, 邵滨, 蒋劲松. DNA数据存储技术的法律治理议题[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 177-189. |
| [5] | 唐兴华, 陆钱能, 胡翌霖. 人类世中对合成生物学的哲学反思[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 203-212. |
| [6] | 徐怀胜, 石晓龙, 刘晓光, 徐苗苗. DNA存储的关键技术:编码、纠错、随机访问与安全性[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(1): 157-176. |
| [7] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, 张以恒. 体外生物转化(ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1437-1460. |
| [8] | 柴猛, 王风清, 魏东芝. 综合利用木质纤维素生物转化合成有机酸[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1242-1263. |
| [9] | 邵明威, 孙思勉, 杨时茂, 陈国强. 基于极端微生物的生物制造[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1419-1436. |
| [10] | 赵亮, 李振帅, 付丽平, 吕明, 王士安, 张全, 刘立成, 李福利, 刘自勇. 生物转化一碳化合物原料产油脂与单细胞蛋白研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1300-1318. |
| [11] | 竺方欢, 岑雪聪, 陈振. 微生物合成二元醇研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(6): 1367-1385. |
| [12] | 陈雨, 张康, 邱以婧, 程彩云, 殷晶晶, 宋天顺, 谢婧婧. 微生物电合成技术转化二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1142-1168. |
| [13] | 郑皓天, 李朝风, 刘良叙, 王嘉伟, 李恒润, 倪俊. 负碳人工光合群落的设计、优化与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1189-1210. |
| [14] | 夏孔晨, 徐维华, 吴起. 光酶催化混乱性反应的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 997-1020. |
| [15] | 禹伟, 高教琪, 周雍进. 一碳生物转化合成有机酸的研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, 2024, 5(5): 1169-1188. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||