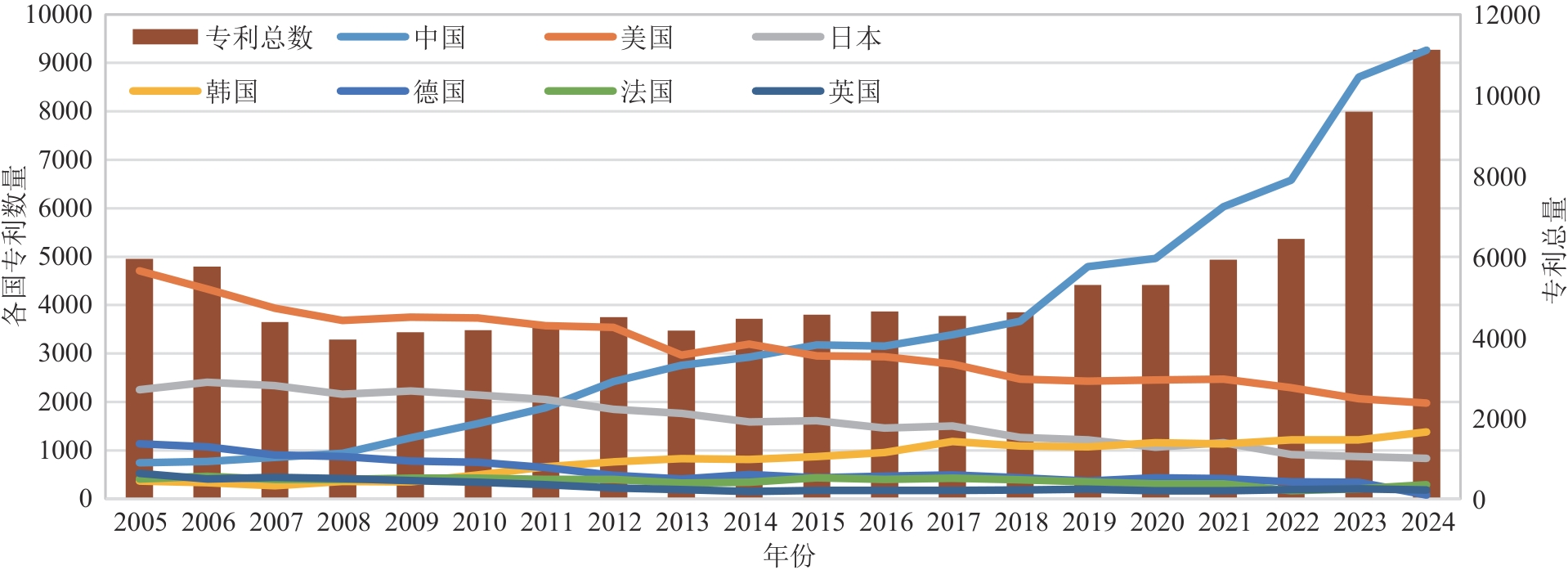
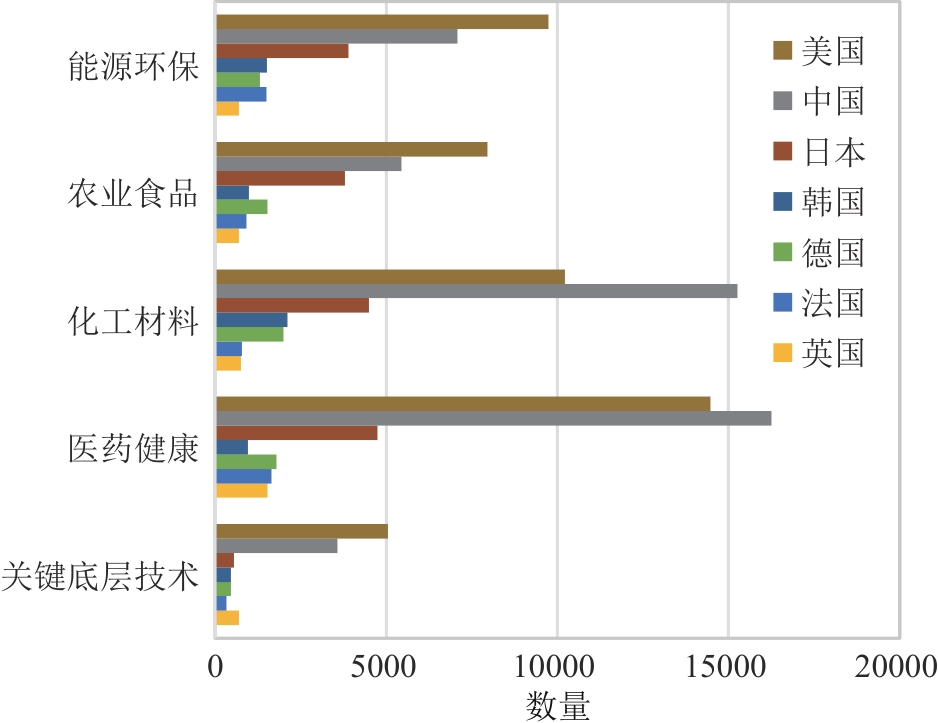
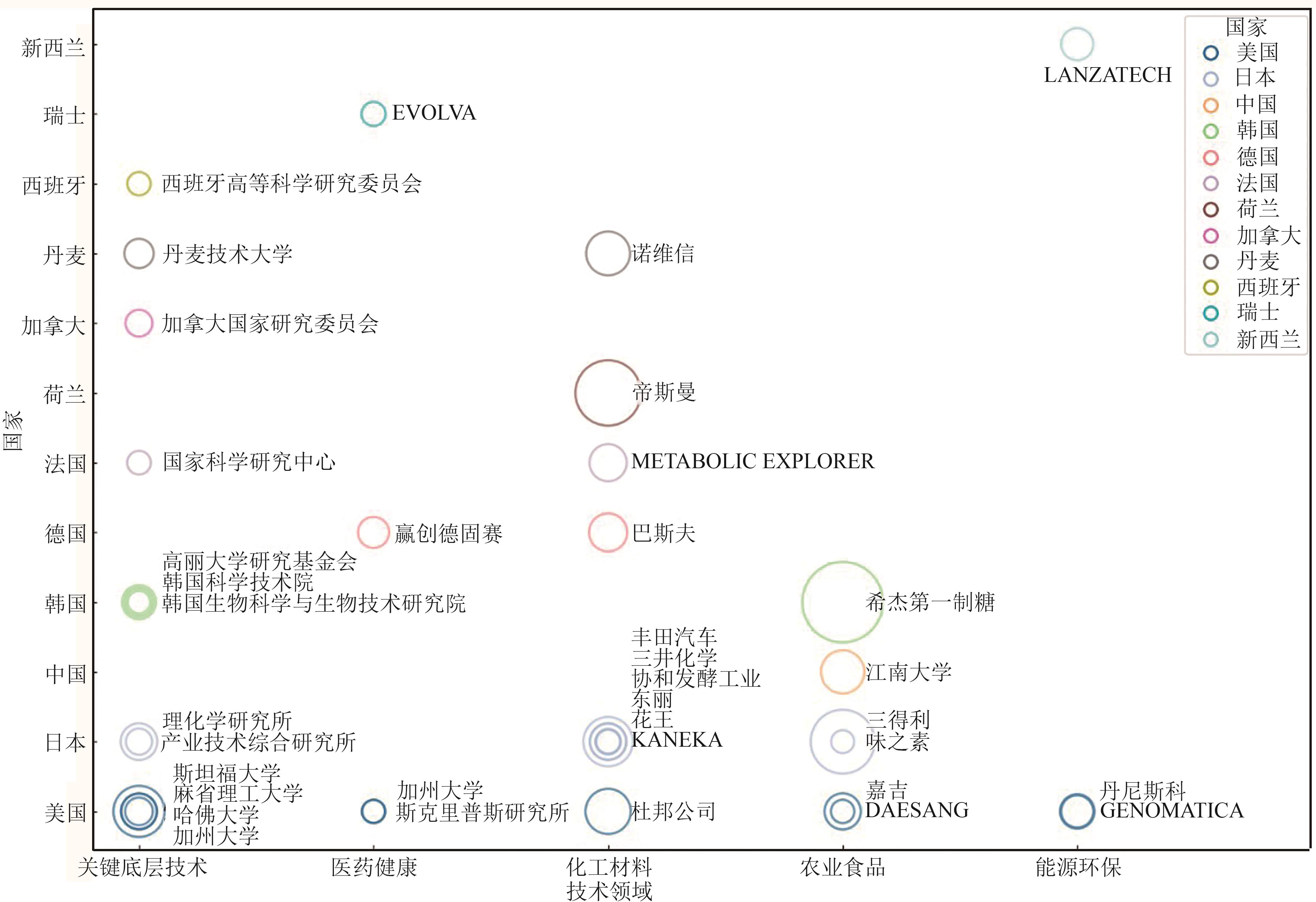
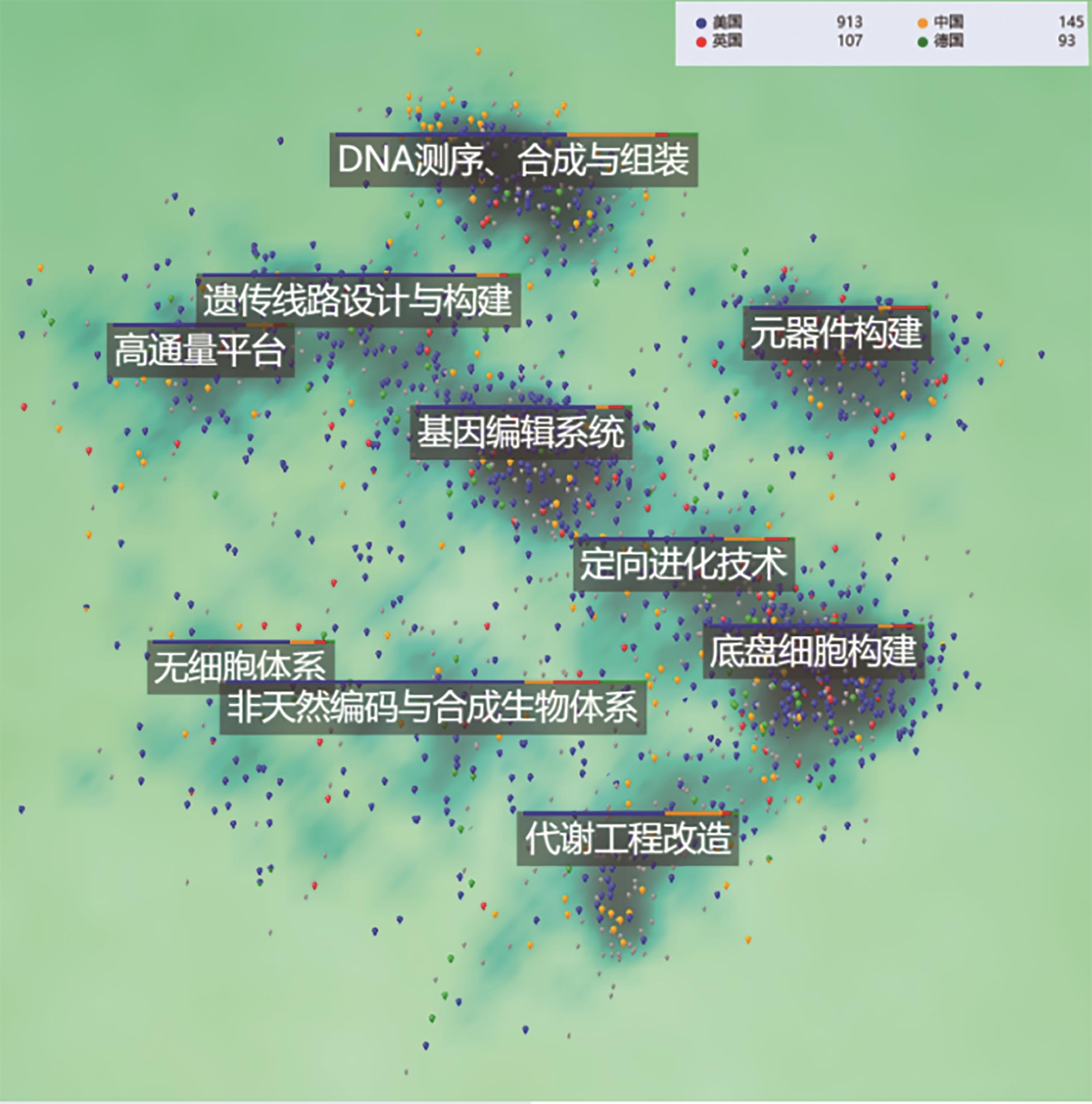
Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (4): 940-955.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2024-087
• Invited Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
A comparative analysis of global research and development competition in synthetic biology
WU Xiaoyan1, SONG Qi1, XU Rui1, DING Chenjun1, CHEN Fang1, GUO Qing2, ZHANG Bo2
- 1.National Science Library(Chengdu),Chinese Academy of Sciences,Chengdu 610299,Sichuan,China
2.Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Qingdao 266101,Shandong,China
-
Received:2024-12-02Revised:2025-05-23Online:2025-09-03Published:2025-08-31 -
Contact:DING Chenjun
合成生物学研发竞争态势对比分析
吴晓燕1, 宋琪1, 许睿1, 丁陈君1, 陈方1, 郭勍2, 张波2
- 1.中国科学院成都文献情报中心,四川 成都 610299
2.中国科学院青岛生物能源与过程研究所,山东 青岛 266101
-
通讯作者:丁陈君 -
作者简介:吴晓燕 (1992—),女,助理研究员。专注于合成生物制造产业分析、市场与政策研究,对合成生物制造产业的发展动态、市场趋势和政策导向有深入研究,为推动合成生物制造产业的创新发展提供理论支持和政策建议。 E-mail:wuxy@clas.ac.cn丁陈君 (1981—),女,博士,副研究员。中国科学院成都文献情报中心生物科技战略研究中心副主任。长期致力于生物科技领域的科技战略、创新政策及战略情报研究,聚焦合成生物学等前沿技术领域发展趋势,为国家和企业战略决策提供关键依据,推动领域科技创新与战略布局。 E-mail:dingcj@clas.ac.cn -
基金资助:山东省合成生物技术产业发展战略研究(202202SDZD05);2024年中国科学院文献情报能力建设专项项目“科技领域态势分析与服务”(E4290425)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WU Xiaoyan, SONG Qi, XU Rui, DING Chenjun, CHEN Fang, GUO Qing, ZHANG Bo. A comparative analysis of global research and development competition in synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 940-955.
吴晓燕, 宋琪, 许睿, 丁陈君, 陈方, 郭勍, 张波. 合成生物学研发竞争态势对比分析[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 940-955.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2024-087
| 项目 | 美国/中国 | 全球/中国 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 关键底层技术 | 总发文量 | 1.56 | 5.35 |
| 篇均被引 | 1.99 | — | |
| 高被引论文数 | 1.53 | 3.42 | |
| CNS顶刊发文量 | 8.29 | 10.86 | |
| CNS顶刊被引次数 | 15.59 | 18.86 | |
| CNS顶刊篇均被引 | 1.88 | 1.80 | |
| 医药健康 | 总发文量 | 0.82 | 4.96 |
| 篇均被引 | 2.09 | — | |
| 高被引论文数 | 1.13 | 3.94 | |
| CNS顶刊发文量 | 12.67 | 17.33 | |
| CNS顶刊被引次数 | 12.39 | 17.59 | |
| CNS顶刊篇均被引 | 0.98 | 1.01 | |
| 化工材料 | 总发文量 | 0.88 | 4.67 |
| 篇均被引 | 2.07 | 1.36 | |
| 高被引论文数 | 0.84 | 3.29 | |
| CNS顶刊发文量 | 10.70 | 14.30 | |
| CNS顶刊被引次数 | 12.85 | 16.56 | |
| CNS顶刊篇均被引 | 1.20 | 1.16 | |
| 农业食品 | 总发文量 | 0.90 | 4.67 |
| 篇均被引 | 1.78 | 1.26 | |
| 高被引论文数 | 0.91 | 3.57 | |
| CNS顶刊发文量 | 1.79 | 1.55 | |
| CNS顶刊被引次数 | 4.00① | 8.00① | |
| 能源环保 | 总发文量 | 0.64 | 4.41 |
| 篇均被引 | 2.04 | 1.24 | |
| 高被引论文数 | 0.89 | 4.22 | |
| CNS顶刊发文量 | 1.72 | 1.35 | |
| CNS顶刊被引次数 | 12.00① | 16.00① | |
Table 1 China-US research impact in synthetic biology
| 项目 | 美国/中国 | 全球/中国 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 关键底层技术 | 总发文量 | 1.56 | 5.35 |
| 篇均被引 | 1.99 | — | |
| 高被引论文数 | 1.53 | 3.42 | |
| CNS顶刊发文量 | 8.29 | 10.86 | |
| CNS顶刊被引次数 | 15.59 | 18.86 | |
| CNS顶刊篇均被引 | 1.88 | 1.80 | |
| 医药健康 | 总发文量 | 0.82 | 4.96 |
| 篇均被引 | 2.09 | — | |
| 高被引论文数 | 1.13 | 3.94 | |
| CNS顶刊发文量 | 12.67 | 17.33 | |
| CNS顶刊被引次数 | 12.39 | 17.59 | |
| CNS顶刊篇均被引 | 0.98 | 1.01 | |
| 化工材料 | 总发文量 | 0.88 | 4.67 |
| 篇均被引 | 2.07 | 1.36 | |
| 高被引论文数 | 0.84 | 3.29 | |
| CNS顶刊发文量 | 10.70 | 14.30 | |
| CNS顶刊被引次数 | 12.85 | 16.56 | |
| CNS顶刊篇均被引 | 1.20 | 1.16 | |
| 农业食品 | 总发文量 | 0.90 | 4.67 |
| 篇均被引 | 1.78 | 1.26 | |
| 高被引论文数 | 0.91 | 3.57 | |
| CNS顶刊发文量 | 1.79 | 1.55 | |
| CNS顶刊被引次数 | 4.00① | 8.00① | |
| 能源环保 | 总发文量 | 0.64 | 4.41 |
| 篇均被引 | 2.04 | 1.24 | |
| 高被引论文数 | 0.89 | 4.22 | |
| CNS顶刊发文量 | 1.72 | 1.35 | |
| CNS顶刊被引次数 | 12.00① | 16.00① | |
| 项目 | 序号 | 专利申请机构 | 专利数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 关键底层技术 | 1 | 江南大学 | 307 |
| 2 | 美国哈佛大学 | 163 | |
| 3 | 美国桑加莫治疗公司 | 113 | |
| 4 | 美国加州大学 | 96 | |
| 5 | 美国英拜奥斯公司 | 93 | |
| 项目 | 序号 | 专利申请机构 | 专利数量 |
| 医药健康 | 1 | 美国基因泰克公司 | 220 |
| 2 | 美国加利福尼亚大学 | 149 | |
| 3 | 法国巴斯德研究所 | 142 | |
| 4 | 英国葛兰素史克生物制品公司 | 141 | |
| 5 | 瑞士诺华公司 | 140 | |
| 项目 | 序号 | 专利申请机构 | 专利数量 |
| 化工材料 | 1 | 韩国希杰第一制糖公司 | 535 |
| 2 | 波兰弗罗茨瓦夫环境与生命科学大学 | 221 | |
| 3 | 日本味之素株式会社 | 202 | |
| 4 | 德国赢创德固赛公司 | 180 | |
| 5 | 美国基因泰克公司 | 161 | |
| 项目 | 序号 | 专利申请机构 | 专利数量 |
| 农业食品 | 1 | 荷兰帝斯曼知识产权有限公司 | 282 |
| 2 | 江南大学 | 163 | |
| 3 | 德国巴斯夫植物科学 | 149 | |
| 4 | 日本三得利控股公司 | 123 | |
| 5 | 美国孟山都科技有限公司 | 122 | |
| 项目 | 序号 | 专利申请机构 | 专利数量 |
| 能源环保 | 1 | 江南大学 | 438 |
| 2 | 丹麦诺维信 | 269 | |
| 3 | 南京工业大学 | 216 | |
| 4 | 清华大学 | 209 | |
| 5 | 美国xyleco | 194 |
Table 2 Major patent applicants
| 项目 | 序号 | 专利申请机构 | 专利数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 关键底层技术 | 1 | 江南大学 | 307 |
| 2 | 美国哈佛大学 | 163 | |
| 3 | 美国桑加莫治疗公司 | 113 | |
| 4 | 美国加州大学 | 96 | |
| 5 | 美国英拜奥斯公司 | 93 | |
| 项目 | 序号 | 专利申请机构 | 专利数量 |
| 医药健康 | 1 | 美国基因泰克公司 | 220 |
| 2 | 美国加利福尼亚大学 | 149 | |
| 3 | 法国巴斯德研究所 | 142 | |
| 4 | 英国葛兰素史克生物制品公司 | 141 | |
| 5 | 瑞士诺华公司 | 140 | |
| 项目 | 序号 | 专利申请机构 | 专利数量 |
| 化工材料 | 1 | 韩国希杰第一制糖公司 | 535 |
| 2 | 波兰弗罗茨瓦夫环境与生命科学大学 | 221 | |
| 3 | 日本味之素株式会社 | 202 | |
| 4 | 德国赢创德固赛公司 | 180 | |
| 5 | 美国基因泰克公司 | 161 | |
| 项目 | 序号 | 专利申请机构 | 专利数量 |
| 农业食品 | 1 | 荷兰帝斯曼知识产权有限公司 | 282 |
| 2 | 江南大学 | 163 | |
| 3 | 德国巴斯夫植物科学 | 149 | |
| 4 | 日本三得利控股公司 | 123 | |
| 5 | 美国孟山都科技有限公司 | 122 | |
| 项目 | 序号 | 专利申请机构 | 专利数量 |
| 能源环保 | 1 | 江南大学 | 438 |
| 2 | 丹麦诺维信 | 269 | |
| 3 | 南京工业大学 | 216 | |
| 4 | 清华大学 | 209 | |
| 5 | 美国xyleco | 194 |
| 国家 | 合享价值度为10的专利 | 转让专利 | 维持年限超过10年的专利 | 简单同族数量大于3的专利 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国 | 2937 | 4482 | 5603 | 3391 |
| 美国 | 11783 | 11493 | 17069 | 19750 |
| 日本 | 3988 | 4107 | 7721 | 8128 |
| 韩国 | 1749 | 1103 | 2553 | 2477 |
| 德国 | 1530 | 1657 | 1891 | 3423 |
| 法国 | 879 | 846 | 1140 | 1813 |
| 英国 | 830 | 710 | 890 | 1861 |
Table 3 High-value patent comparison by country
| 国家 | 合享价值度为10的专利 | 转让专利 | 维持年限超过10年的专利 | 简单同族数量大于3的专利 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国 | 2937 | 4482 | 5603 | 3391 |
| 美国 | 11783 | 11493 | 17069 | 19750 |
| 日本 | 3988 | 4107 | 7721 | 8128 |
| 韩国 | 1749 | 1103 | 2553 | 2477 |
| 德国 | 1530 | 1657 | 1891 | 3423 |
| 法国 | 879 | 846 | 1140 | 1813 |
| 英国 | 830 | 710 | 890 | 1861 |
| 国家 | PCT专利占比 | 海外专利占比 | 主要受理地区(占比) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 中国 | 5.75% | 5.27% | 美国(45.27%)、日本(13.66%)、EPO(11.11%) |
| 美国 | 21.77% | 61.13% | EPO(15.25%)、日本(15.03%)、加拿大(10.72%) |
| 日本 | 18.42% | 60.93% | 美国(27.09%)、EPO(17.04%)、德国(11.67%) |
| 韩国 | 16.88% | 49.63% | 美国(24.89%)、日本(13.98%)、中国(13.33%) |
| 德国 | 18.78% | 86.41% | 美国(26.07%)、EPO(18.47%)、西班牙(9.35%) |
| 法国 | 18.91% | 87.06% | 美国(24.06%)、EPO(15.60%)、德国(9.67%) |
| 英国 | 17.23% | 95.72% | 美国(26.78%)、日本(12.05%)、EPO(10.19%) |
Table 4 Overseas patent distribution by country
| 国家 | PCT专利占比 | 海外专利占比 | 主要受理地区(占比) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 中国 | 5.75% | 5.27% | 美国(45.27%)、日本(13.66%)、EPO(11.11%) |
| 美国 | 21.77% | 61.13% | EPO(15.25%)、日本(15.03%)、加拿大(10.72%) |
| 日本 | 18.42% | 60.93% | 美国(27.09%)、EPO(17.04%)、德国(11.67%) |
| 韩国 | 16.88% | 49.63% | 美国(24.89%)、日本(13.98%)、中国(13.33%) |
| 德国 | 18.78% | 86.41% | 美国(26.07%)、EPO(18.47%)、西班牙(9.35%) |
| 法国 | 18.91% | 87.06% | 美国(24.06%)、EPO(15.60%)、德国(9.67%) |
| 英国 | 17.23% | 95.72% | 美国(26.78%)、日本(12.05%)、EPO(10.19%) |
| 国家 | 关键底层技术 | 医药健康 | 化工材料 | 农业食品 | 能源环保 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 美国 | 85 | 200 | 161 | 111 | 188 |
| 日本 | 15 | 150 | 162 | 135 | 116 |
| 韩国 | 15 | 28 | 81 | 22 | 38 |
| 德国 | 10 | 40 | 67 | 25 | 25 |
| 荷兰 | 8 | 31 | 25 | 45 | 53 |
| 法国 | 5 | 21 | 17 | 25 | 47 |
| 瑞士 | 7 | 28 | 16 | 31 | 18 |
| 丹麦 | 3 | 17 | 17 | 29 | 20 |
| 英国 | 16 | 24 | 12 | 8 | 18 |
| 加拿大 | 2 | 15 | 5 | 6 | 14 |
Table 5 Patents entering China
| 国家 | 关键底层技术 | 医药健康 | 化工材料 | 农业食品 | 能源环保 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 美国 | 85 | 200 | 161 | 111 | 188 |
| 日本 | 15 | 150 | 162 | 135 | 116 |
| 韩国 | 15 | 28 | 81 | 22 | 38 |
| 德国 | 10 | 40 | 67 | 25 | 25 |
| 荷兰 | 8 | 31 | 25 | 45 | 53 |
| 法国 | 5 | 21 | 17 | 25 | 47 |
| 瑞士 | 7 | 28 | 16 | 31 | 18 |
| 丹麦 | 3 | 17 | 17 | 29 | 20 |
| 英国 | 16 | 24 | 12 | 8 | 18 |
| 加拿大 | 2 | 15 | 5 | 6 | 14 |
| 分类 | 中国 | 国外 |
|---|---|---|
| 技术创新平台 | 合成生物研究重大科技基础设施(深圳) 国家合成生物技术创新中心(天津) 上海合成生物学创新中心 | 美国敏捷生物工厂厂(Agile BioFoundry,ABF) 英国过程创新研究中心心 (The Centre for Process Innovation,CPI) 丹麦诺和诺德基金会生物可持续发展中心(The Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Biosustainability,DTU Biosustain) |
| 中试放大平台 | 天津华熙生物平台 江苏华泰疫苗平台 北京千升级中试基地 深圳合成生物产业园 | 美国生物工业制造和设计生态系统(BioMADE) 欧盟Pilots4U 英国生物试点项目(BioPilots UK) |
| 产业孵化平台 | 中关村生命科学园孵化器 滨海新区生物制造谷 上海徐汇基地 成都天河园孵化基地 | 英国合成生物学创新知识中心(SynbiCITE) 荷兰代尔夫特生物技术园区(Biotech Campus Delft) 美国IndieBio |
Table 6 Representative platform facilities of the global synthetic biology industry[40]
| 分类 | 中国 | 国外 |
|---|---|---|
| 技术创新平台 | 合成生物研究重大科技基础设施(深圳) 国家合成生物技术创新中心(天津) 上海合成生物学创新中心 | 美国敏捷生物工厂厂(Agile BioFoundry,ABF) 英国过程创新研究中心心 (The Centre for Process Innovation,CPI) 丹麦诺和诺德基金会生物可持续发展中心(The Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Biosustainability,DTU Biosustain) |
| 中试放大平台 | 天津华熙生物平台 江苏华泰疫苗平台 北京千升级中试基地 深圳合成生物产业园 | 美国生物工业制造和设计生态系统(BioMADE) 欧盟Pilots4U 英国生物试点项目(BioPilots UK) |
| 产业孵化平台 | 中关村生命科学园孵化器 滨海新区生物制造谷 上海徐汇基地 成都天河园孵化基地 | 英国合成生物学创新知识中心(SynbiCITE) 荷兰代尔夫特生物技术园区(Biotech Campus Delft) 美国IndieBio |
| [1] | “中国学科及前沿领域发展战略研究( 2021—2035)”项目组. 中国合成生物学2035发展战略[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2023. |
| Research Group of “China’s Discipline and Frontier Field Development Strategy (2021—2035)”. China’s synthetic biology development strategy 2035[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2023. | |
| [2] | RABINOVITCH-DEERE C A, OLIVER J W K, RODRIGUEZ G M, et al. Synthetic biology and metabolic engineering approaches to produce biofuels[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113(7): 4611-4632. |
| [3] | MEZZINA M P, MANOLI M T, PRIETO M A, et al. Engineering native and synthetic pathways in Pseudomonas putida for the production of tailored polyhydroxyalkanoates[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 16(3): 2000165. |
| [4] | SMANSKI M J, ZHOU H, CLAESEN J, et al. Synthetic biology to access and expand nature’s chemical diversity[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(3): 135-149. |
| [5] | CRAVENS A, PAYNE J, SMOLKE C D. Synthetic biology strategies for microbial biosynthesis of plant natural products[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 2142. |
| [6] | GALANIE S, THODEY K, TRENCHARD I J, et al. Complete biosynthesis of opioids in yeast[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6252): 1095-1100. |
| [7] | CUBILLOS-RUIZ A, GUO T X, SOKOLOVSKA A, et al. Engineering living therapeutics with synthetic biology[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2021, 20(12): 941-960. |
| [8] | KE J, WANG B, YOSHIKUNI Y. Microbiome engineering: synthetic biology of plant-associated microbiomes in sustainable agriculture[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2021, 39(3): 244-261. |
| [9] | GUPTA A, LEE S G, SUNG B H, et al. Advancing biofoundry development: strategies and challenges[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2024, 29(5): 771-778. |
| [10] | Engineering Biology | EBRC Research Roadmap[EB/OL]. [2025-01-20]. . |
| [11] | LEE E D, AURAND E R, FRIEDMAN D C, et al. Engineering microbiomes-looking ahead[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(12): 3181-3183. |
| [12] | Engineering Biology & Materials Science | EBRC Research Roadmap[EB/OL]. [2025-01-20]. . |
| [13] | The United States innovation and competition act of 2021[EB/OL]. (2021-06)[2025-01-20]. . |
| [14] | NSF 17-557 : Semiconductor synthetic biology for information processing and storage technologies (SemiSynBio) | NSF-National Science Foundation[EB/OL]. [2025-01-20]. . |
| [15] | FACT SHEET: The United States announces new investments and resources to advance president Biden’s national biotechnology and biomanufacturing initiative[EB/OL]. (2022-09-14)[2025-01-20]. . |
| [16] | FACT SHEET: Biden-Harris administration announces new bold goals and priorities to advance American biotechnology and biomanufacturing | OSTP[EB/OL]. (2023-03-22)[2025-01-20]. . |
| [17] | TESSY Achievements and future perspectives in synthetic biology[EB/OL]. (2008-12-1)[2025-01-20]. . |
| [18] | Computational models of cell factories for a sustainable future[EB/OL]. (2021-05-14)[2025-01-20]. |
| [19] | UK Synthetic Biology Roadmap coordination Group. A synthetic biology roadmap for the UK[EB/OL]. (2012-07)[2025-01-20]. . |
| [20] | MOLLOY J. UK synthetic biology strategic plan 2016 launched: biodesign for the bioeconomy[EB/OL]. (2016-02-24)[2025-01-20]. . |
| [21] | National vision for engineering biology[EB/OL]. [2025-01-20]. . |
| [22] | Government announces £ UK 100 Million fund for AI in life sciences and healthcare[EB/OL]. [2025-01-20]. . |
| [23] | 合成生物学が切り拓く技術領域と適用分野―日本における微生物発酵の歴史と知見をいかした新産業創出の可能性[EB/OL]. (2022-09)[2025-01-20]. . |
| The technological domains and application fields opened up by synthetic biology-the possibility of creating new industries utilizing the history and insights of microbial fermentation in Japan[EB/OL]. (2022-09)[2025-01-20]. . | |
| [24] | Australia’s synthetic biology roadmap[EB/OL].(2021-08)[2025-01-20]. . |
| [25] | NUS SynCTI cofounds the Global BioFoundry Alliance[EB/OL]. (2019-06-27)[2025-01-20]. . |
| [26] | 张先恩. 中国合成生物学发展回顾与展望[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2019, 49(12): 1543-1572. |
| ZHANG X E. Synthetic biology in China: review and prospects[J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2019, 49(12): 1543-1572. | |
| [27] | 刘陈立, 张先恩, 傅雄飞, 等. 合成生物学发展与展望[J]. 前进论坛, 2024(4): 57-62. |
| LIU C L, ZHANG X E, FU X F, et al. Development and prospects of synthetic biology[J]. Forward Forum, 2024(4): 57-62. | |
| [28] | 科技部关于印发《“十三五”生物技术创新专项规划》的通知[EB/OL]. [2024-08-13]. . |
| Notice of the Ministry of Science and Technology on Issuing the “Special Plan for Biotechnology Innovation during the 13th Five-Year Plan”[EB/OL]. [2024-08-13]. . | |
| [29] | 科技部关于印发国家技术创新中心建设工作指引的通 [EB/OL]. [2024-08-13]. . |
| Notice of the Ministry of Science and Technology on Issuing the Guidelines for the Construction of National Technology Innovation Centers[EB/OL]. [2024-08-13]. . | |
| [30] | 国家发展改革委关于印发《“十四五”生物经济发展规划》的通知 [EB/OL]. [2024-08-13]. . |
| Notice of the National Development and Reform Commission on Issuing the “14th Five Year Plan for the Development of Bioeconomy”[EB/OL]. [2024-08-13]. . | |
| [31] | 国家发展改革委等部门关于印发《绿色低碳先进技术示范工程实施方案》的通知[EB/OL]. [2024-08-13]. . |
| Notice from the National Development and Reform Commission and other departments on the issuance of the Implementation Plan for Green and Low Carbon Advanced Technology Demonstration Projects [EB/OL]. [2024-08-13]. . | |
| [32] | 辛竹琳, 何微, 王晓梅, 等. 全球合成生物学专利发展格局及对中国的启示[J]. 农业展望, 2023, 19(7): 105-113. |
| XIN Z L, HE W, WANG X M, et al. Landscape of synthetic biology based on global patents and its enlightenment to China[J]. Agricultural Outlook, 2023, 19(7): 105-113. | |
| [33] | 江洪, 李晓南, 高倩. 合成生物学领域技术发展态势与研究进展[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2024, 44(5): 118-133. |
| JIANG H, LI X N, GAO Q. Technology development trend and research progress of synthetic biology[J]. China Biotechnology, 2024, 44(5): 118-133. | |
| [34] | 吴晓燕, 丁陈君, 陈方, 等. 合成生物学专利态势分析[J]. 科学观察, 2020, 15(1): 11-21. |
| WU X Y, DING C J, CHEN F, et al. International patent analysis on synthetic biology[J]. Science Focus, 2020, 15(1): 11-21. | |
| [35] | 合成生物学发展战略研究组. 合成生物学路线图-2030: 驱动下一代生物制造的引擎[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2024. |
| Synthetic Biology Development Strategy Research Group. Synthetic Biology Roadmap2023: Engine Driving Next-Generation Biomanufacturing[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2024. | |
| [36] | 陈大明, 周光明, 刘晓, 等. 从全球专利分析看合成生物学技术发展趋势[J]. 合成生物学, 2020, 1(3): 372-384. |
| CHEN D M, ZHOU G M, LIU X, et al. Analysis of global patents for the trend of synthetic biology inventions[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2020, 1(3): 372-384. | |
| [37] | 叶文力, 王建, 冯茜, 等. 我国高价值专利评估问题与指标模型构建[J]. 江苏科技信息, 2024, 41(14): 51-54, 84. |
| YE W L, WANG J, FENG Q, et al. Evaluation issues and indicator model construction of high-value patents in China[J]. Jiangsu Science and Technology Information, 2024, 41(14): 51-54, 84. | |
| [38] | 李凤侠. 基于简单专利族和BCP指数方法探讨专利“睡美人”的识别与分析[J]. 情报探索, 2021(3): 69-77. |
| LI F X. Identification and analysis on “sleeping beauties” patents based on simple patent family and parameter free BCP index[J]. Information Research, 2021(3): 69-77. | |
| [39] | 韩祺, 姜江, 汪琪琦, 等. 我国工业生物技术和产业的现状、差距与任务[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(11): 4035-4042. |
| HAN Q, JIANG J, WANG Q Q, et al. The current situation and developmental trends of industrial biotechnology and biomanufacturing in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 38(11): 4035-4042. | |
| [40] | 吴晓燕, 陈方, 单耀莹, 等. 全球生物制造产业关键平台设施建设现状分析与思考[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2025, 40(1): 116-126. |
| WU X Y, CHEN F, SHAN Y Y, et al. Analysis and reflections on key platform facilities construction of global biomanufacturing industry[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2025, 40(1): 116-126. | |
| [41] | 单晓冰. 中国合成生物产业知识产权运营中心28日在津揭牌[EB/OL]. . |
| SHAN X B. China Synthetic Biology Industry Intellectual Property Operation Center was inaugurated in Tianjin on the 28th[EB/OL]. . | |
| [42] | 万玉航. 全球最大的中试转化平台建成, 华熙生物引领生物制造走向5.0时代[EB/OL]. . |
| WAN Y H. The world’s largest pilot-scale transformation platform has been built, leading the way for Huaxi Bio to usher in the 5.0 era of biomanufacturing[EB/OL]. . | |
| [43] | 《2023中国生物医药产业园区竞争力评价及分析报告》正式发布[EB/OL]. (2023-11-01)[2024-10-29]. . |
| “ The 2023 China Biomedical Industry Park Competitiveness Evaluation and Analysis Report” was officially released[EB/OL]. (2023-11-01)[2024-10-29]. . |
| [1] | FANG Xinyi, SUN Lichao, HUO Yixin, WANG Ying, YUE Haitao. Trends and challenges in microbial synthesis of higher alcohols [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 873-898. |
| [2] | ZHANG Jiankang, WANG Wenjun, GUO Hongju, BAI Beichen, ZHANG Yafei, YUAN Zheng, LI Yanhui, LI Hang. Development and application of a high-throughput microbial clone picking workstation based on machine vision [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 956-971. |
| [3] | LI Quanfei, CHEN Qian, LIU Hao, HE Kundong, PAN Liang, LEI Peng, GU Yi’an, SUN Liang, LI Sha, QIU Yibin, WANG Rui, XU Hong. Synthetic biology and applications of high-adhesion protein materials [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 806-828. |
| [4] | WU Ke, LUO Jiahao, LI Feiran. Applications of machine learning in the reconstruction and curation of genome-scale metabolic models [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 566-584. |
| [5] | TIAN Xiao-jun, ZHANG Rixin. “Economics Paradox” with cells in synthetic gene circuits [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 532-546. |
| [6] | ZHANG Yiqing, LIU Gaowen. Exploration of gene functions and library construction for engineering strains from a synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 685-700. |
| [7] | YANG Ying, LI Xia, LIU Lizhong. Applications of synthetic biology to stem-cell-derived modeling of early embryonic development [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 669-684. |
| [8] | HUANG Yi, SI Tong, LU Anjing. Standardization for biomanufacturing: global landscape, critical challenges, and pathways forward [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 701-714. |
| [9] | SONG Chengzhi, LIN Yihan. AI-enabled directed evolution for protein engineering and optimization [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 617-635. |
| [10] | ZHANG Mengyao, CAI Peng, ZHOU Yongjin. Synthetic biology drives the sustainable production of terpenoid fragrances and flavors [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 334-356. |
| [11] | ZHANG Lu’ou, XU Li, HU Xiaoxu, YANG Ying. Synthetic biology ushers cosmetic industry into the “bio-cosmetics” era [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 479-491. |
| [12] | YI Jinhang, TANG Yulin, LI Chunyu, WU Heyun, MA Qian, XIE Xixian. Applications and advances in the research of biosynthesis of amino acid derivatives as key ingredients in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 254-289. |
| [13] | WEI Lingzhen, WANG Jia, SUN Xinxiao, YUAN Qipeng, SHEN Xiaolin. Biosynthesis of flavonoids and their applications in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| [14] | XIAO Sen, HU Litao, SHI Zhicheng, WANG Fayin, YU Siting, DU Guocheng, CHEN Jian, KANG Zhen. Research advances in biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid with controlled molecular weights [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 445-460. |
| [15] | WANG Qian, GUO Shiting, XIN Bo, ZHONG Cheng, WANG Yu. Advances in biosynthesis of L-arginine using engineered microorganisms [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 290-305. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||