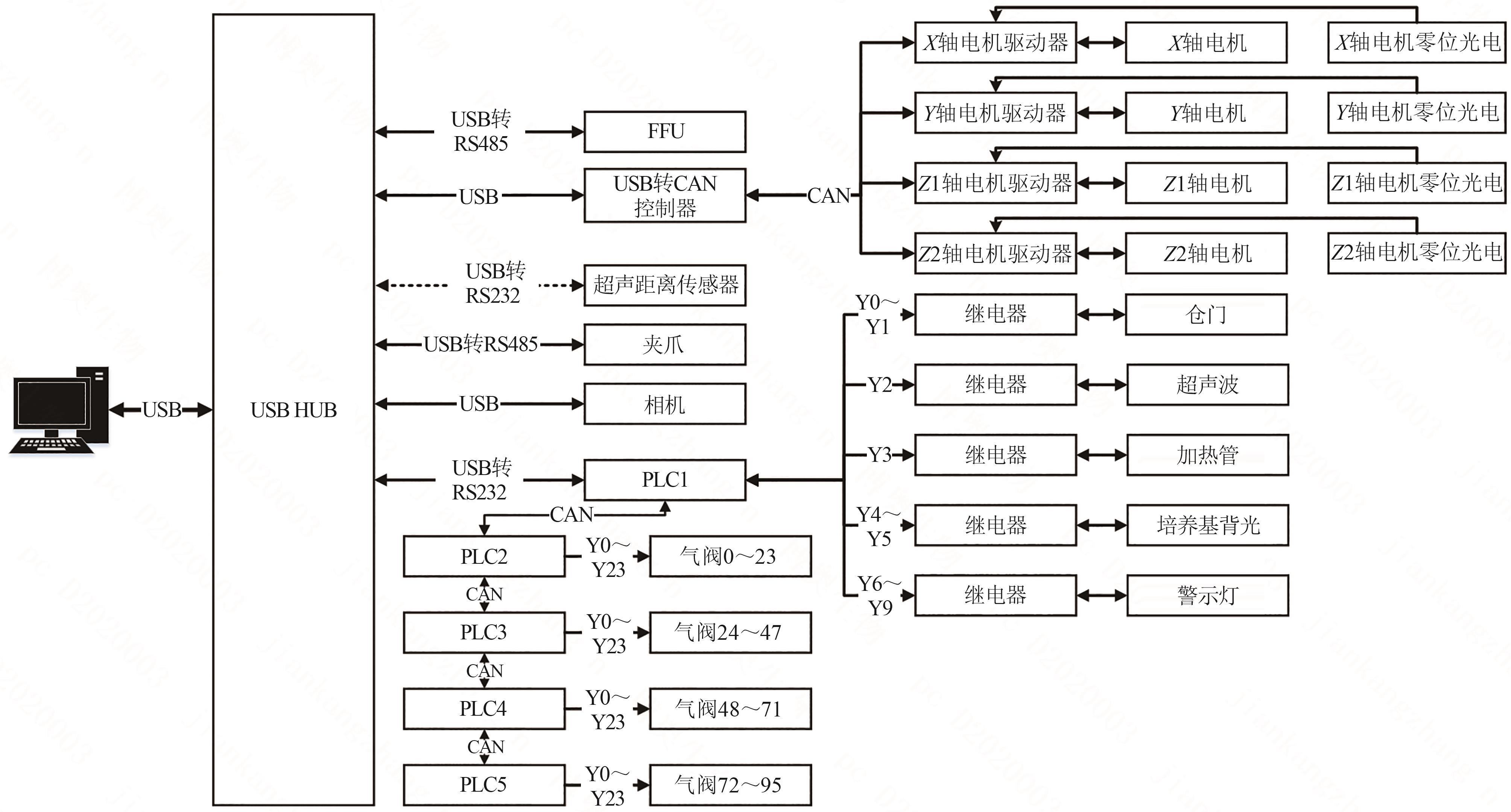
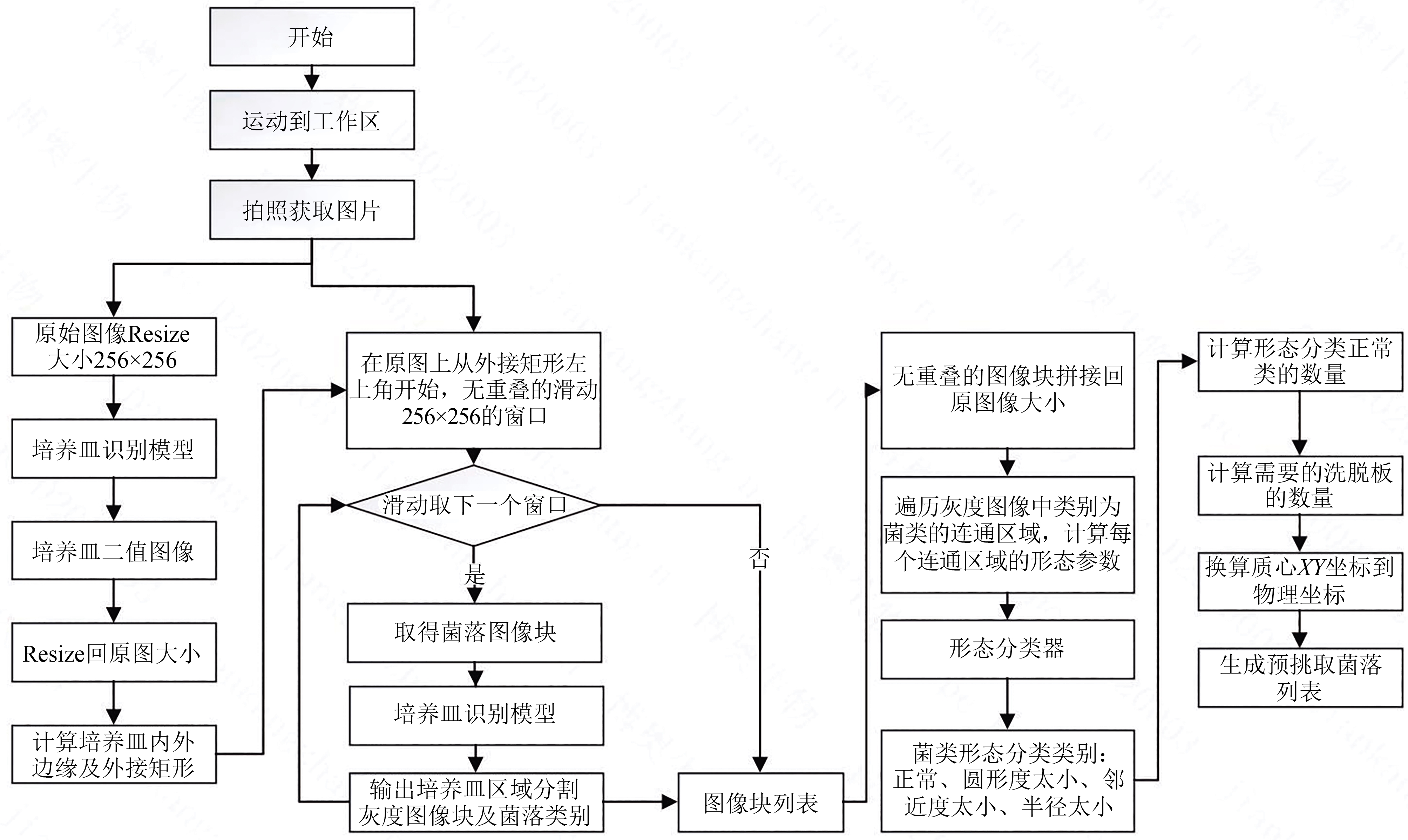
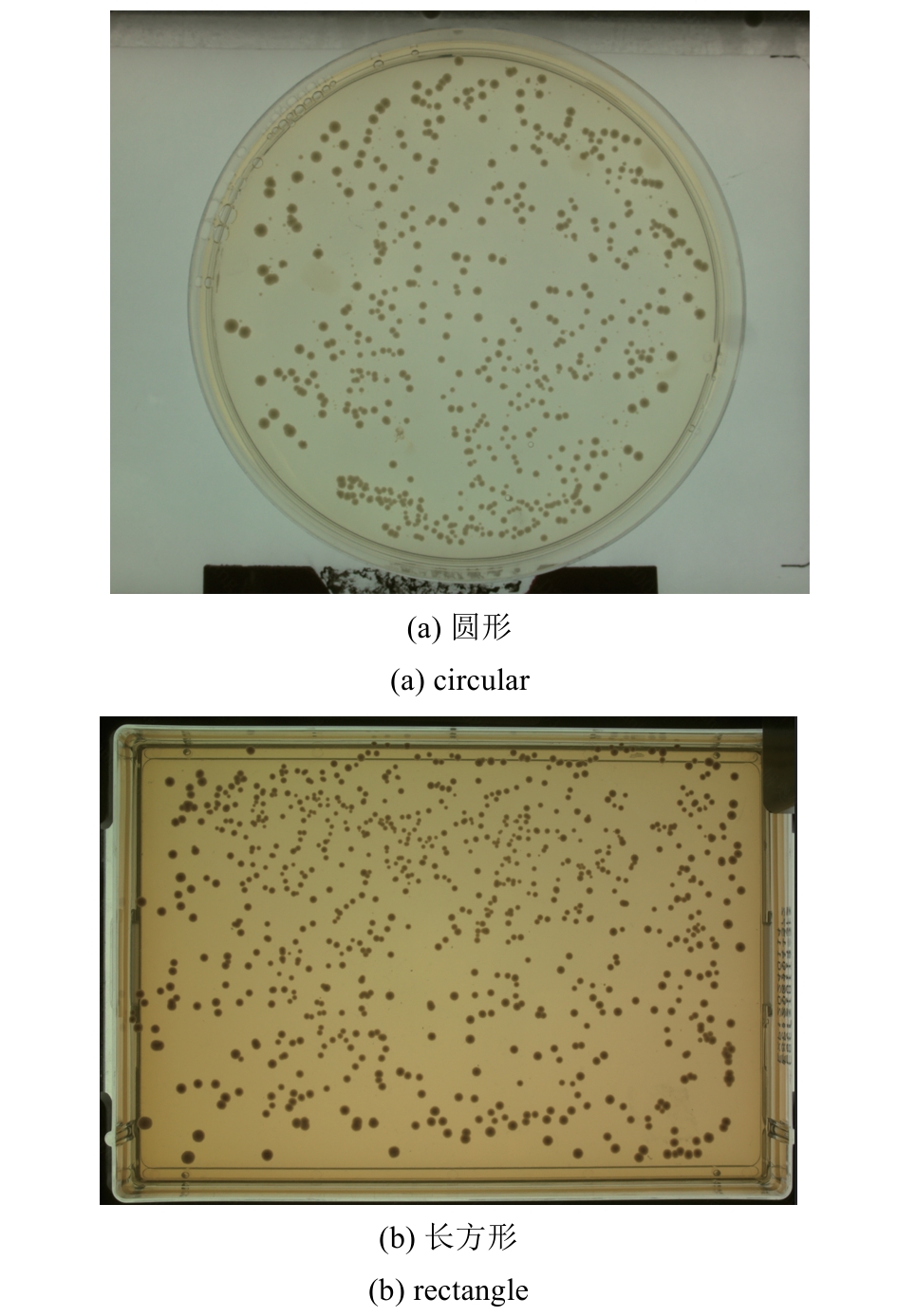
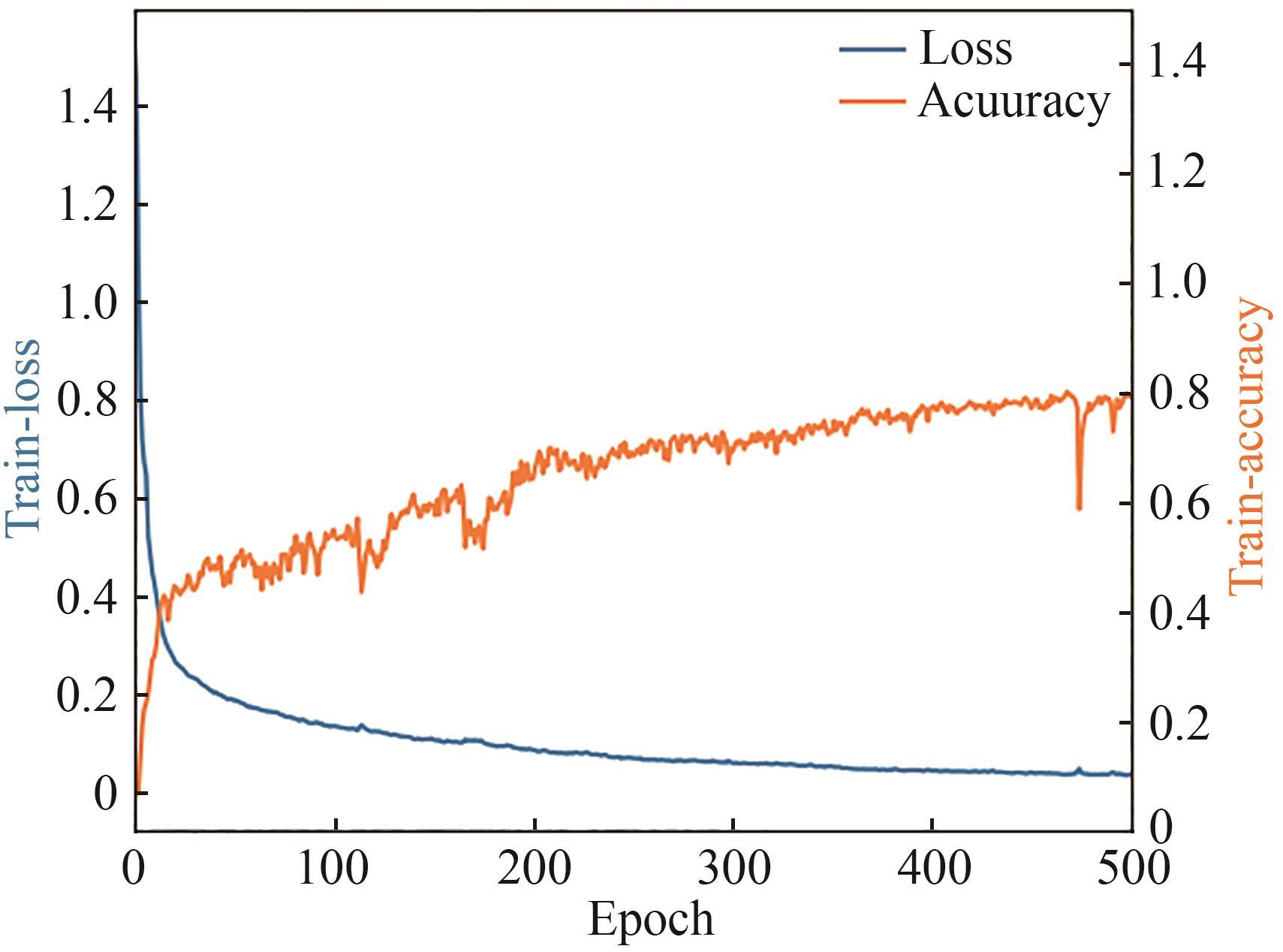
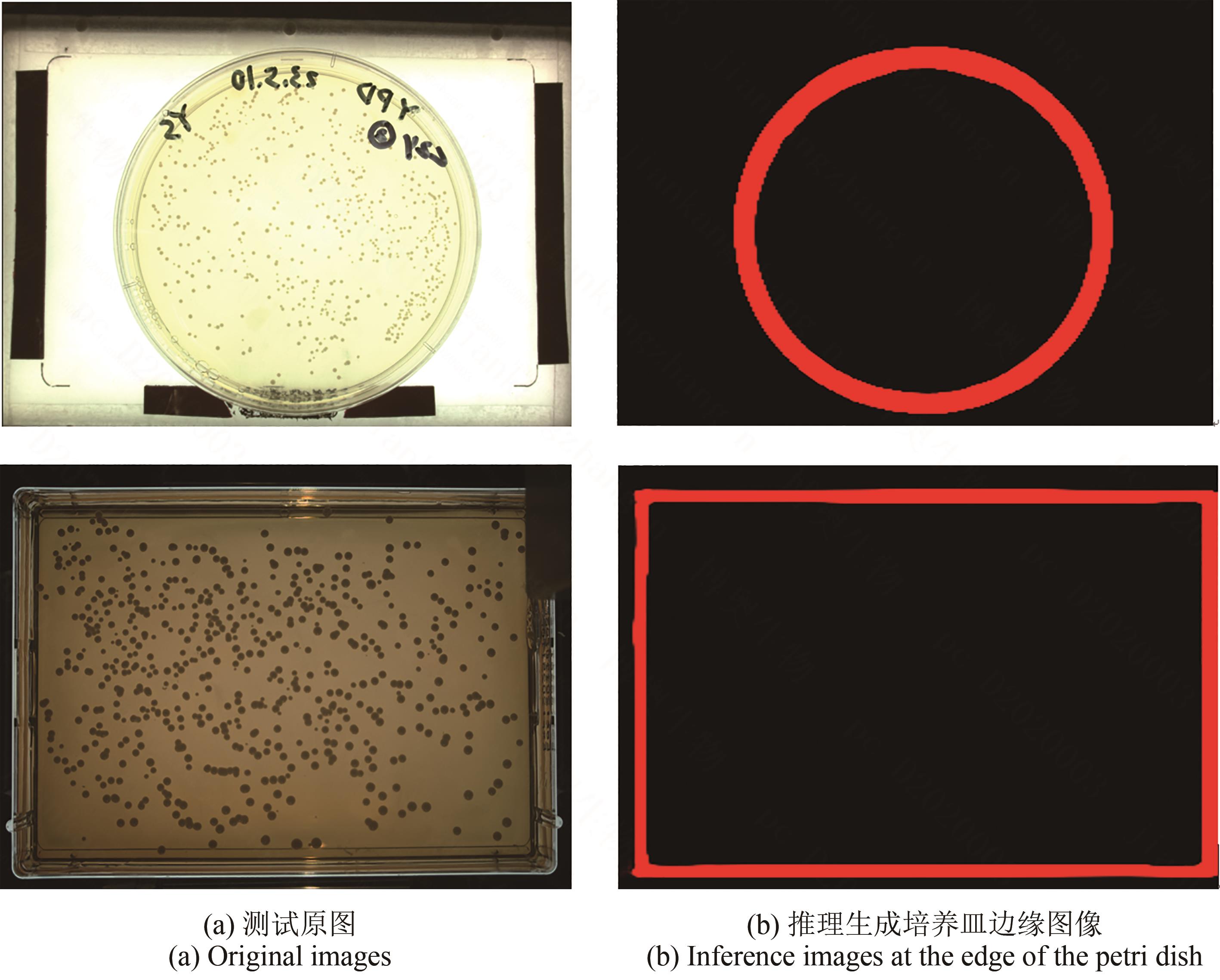
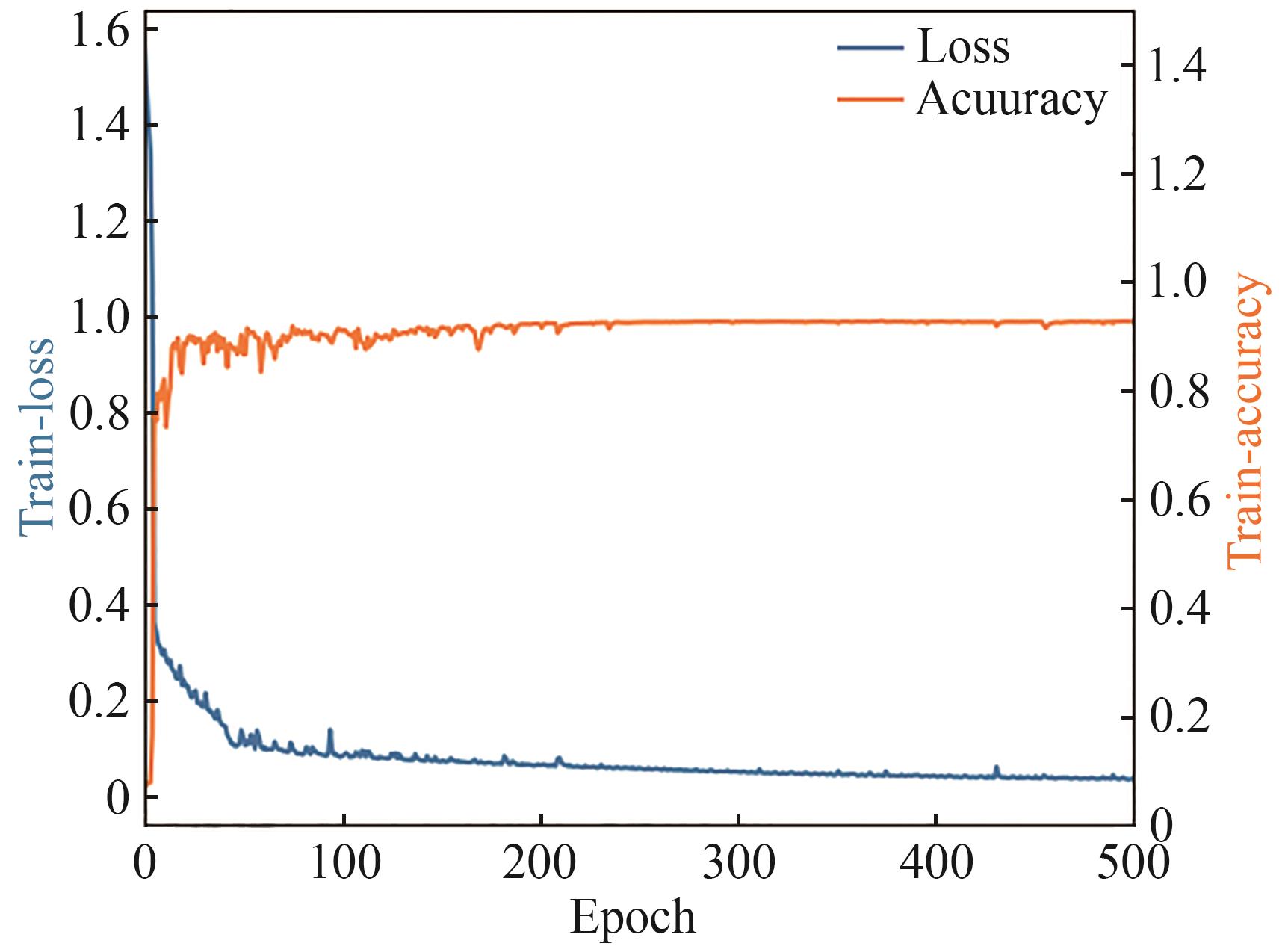
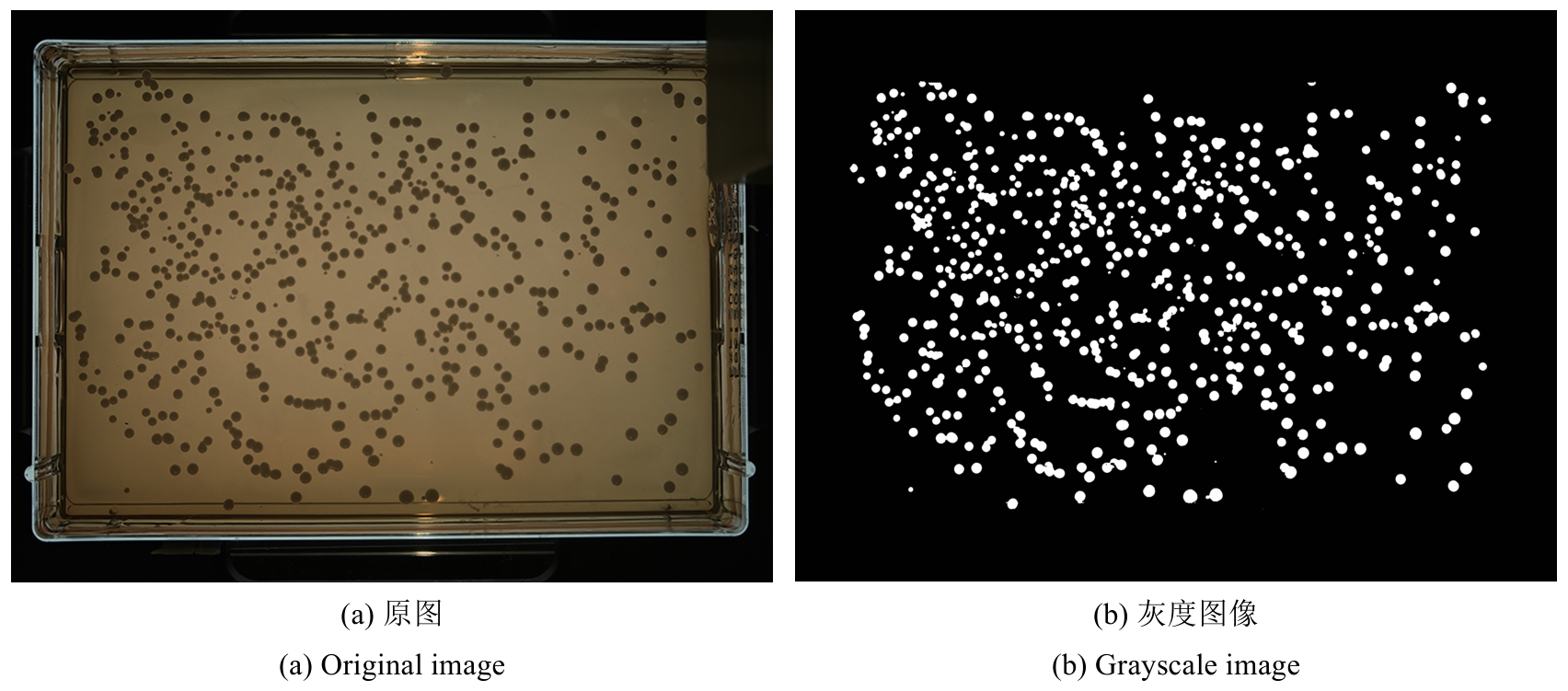
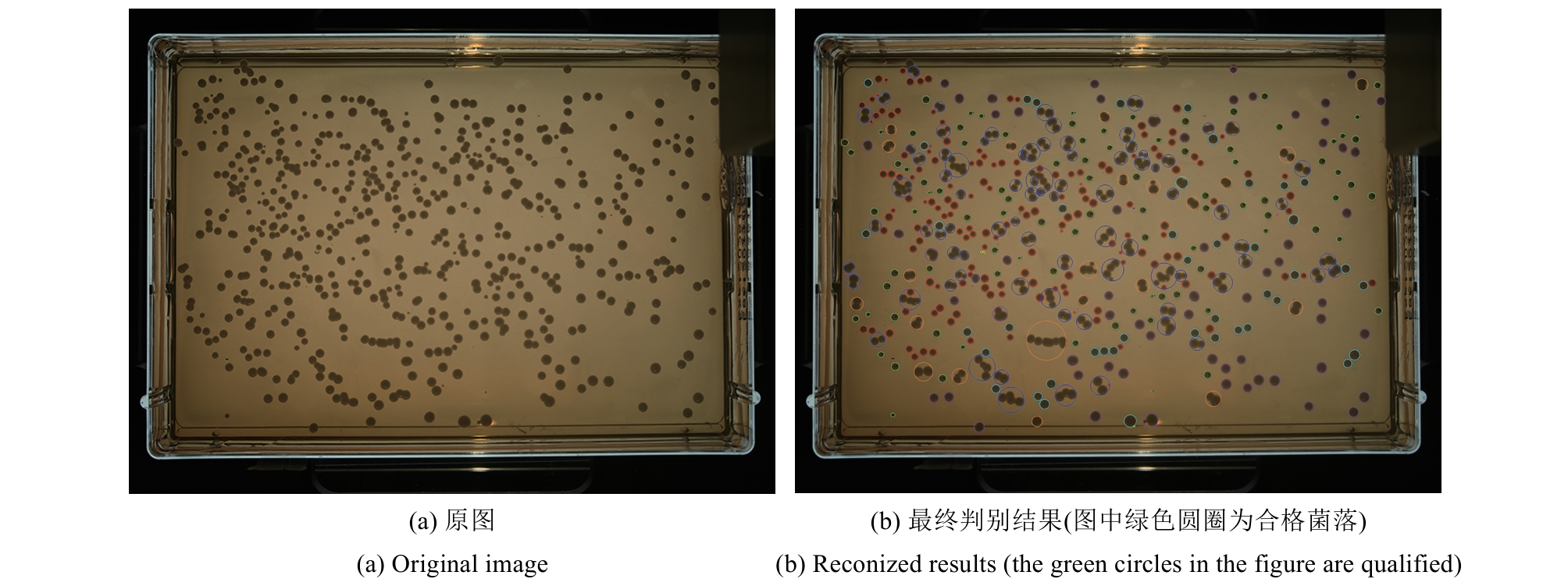
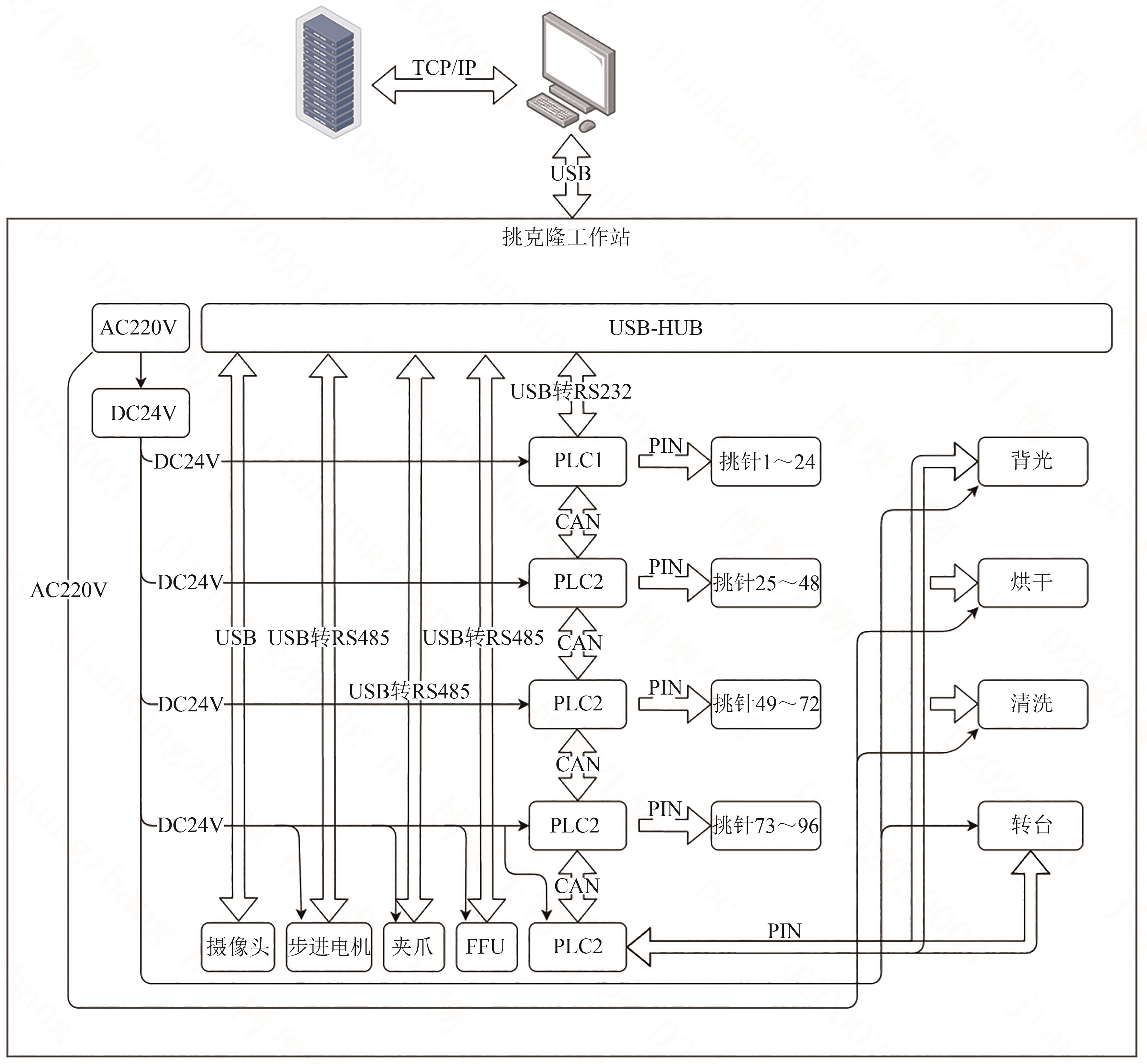
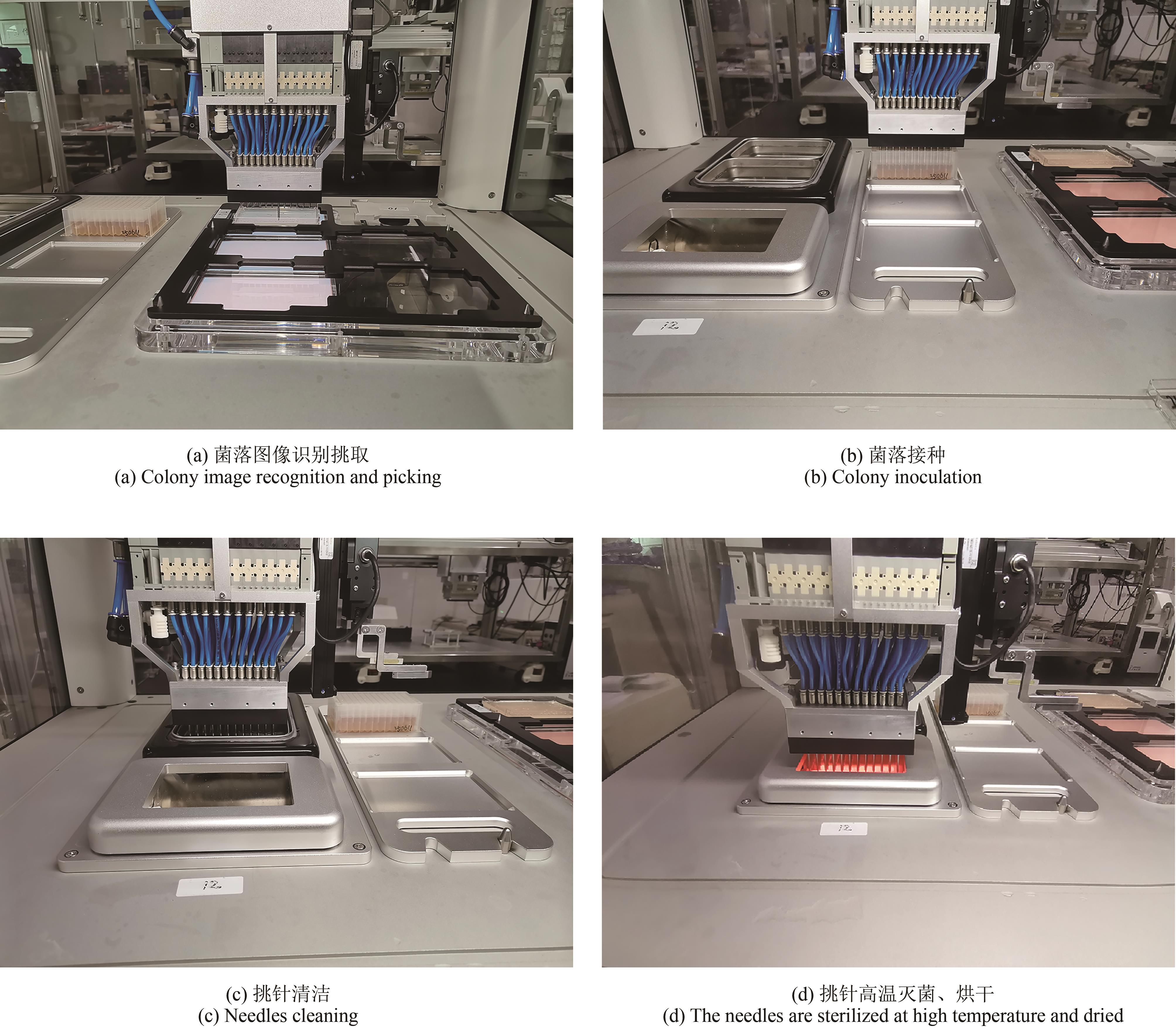
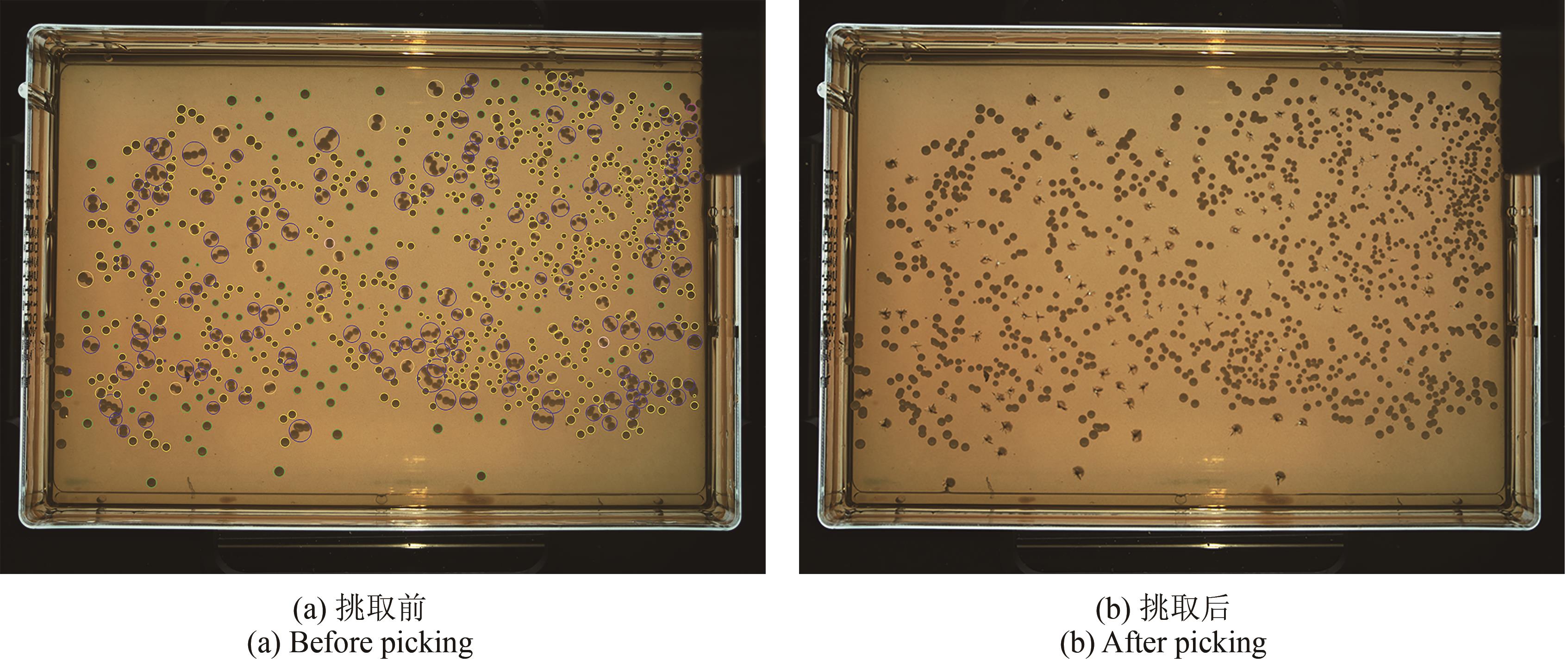
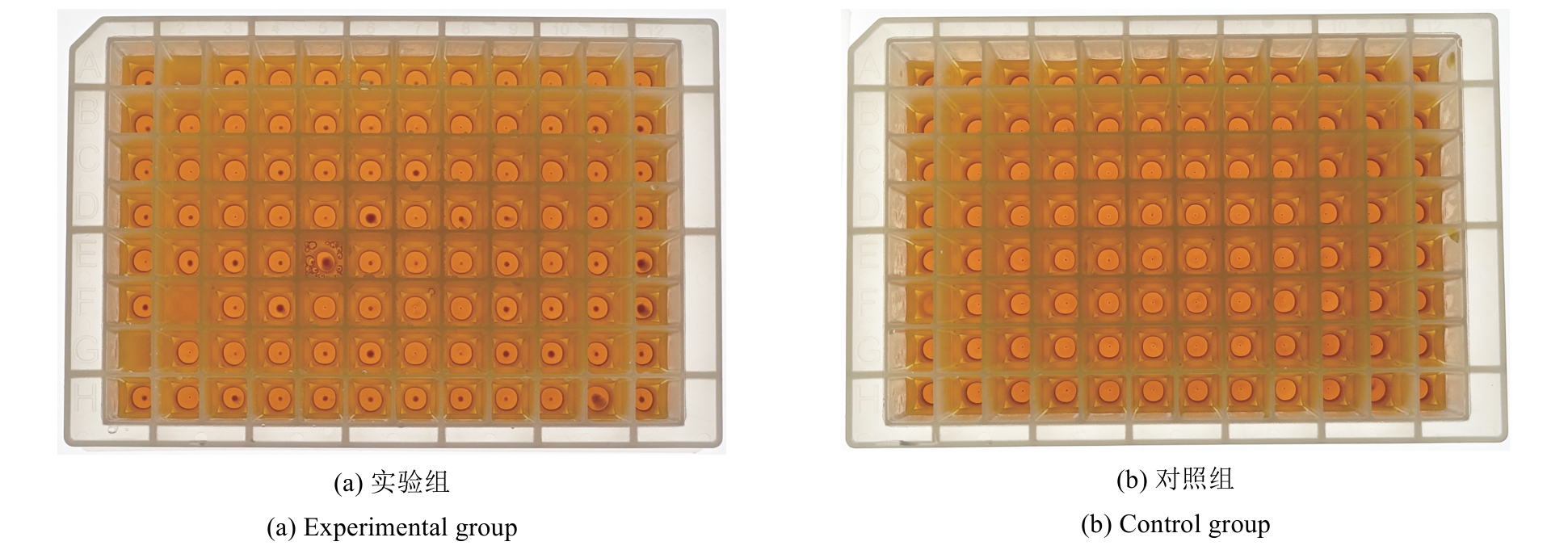
Synthetic Biology Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 6 ›› Issue (4): 956-971.DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-038
• Research Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
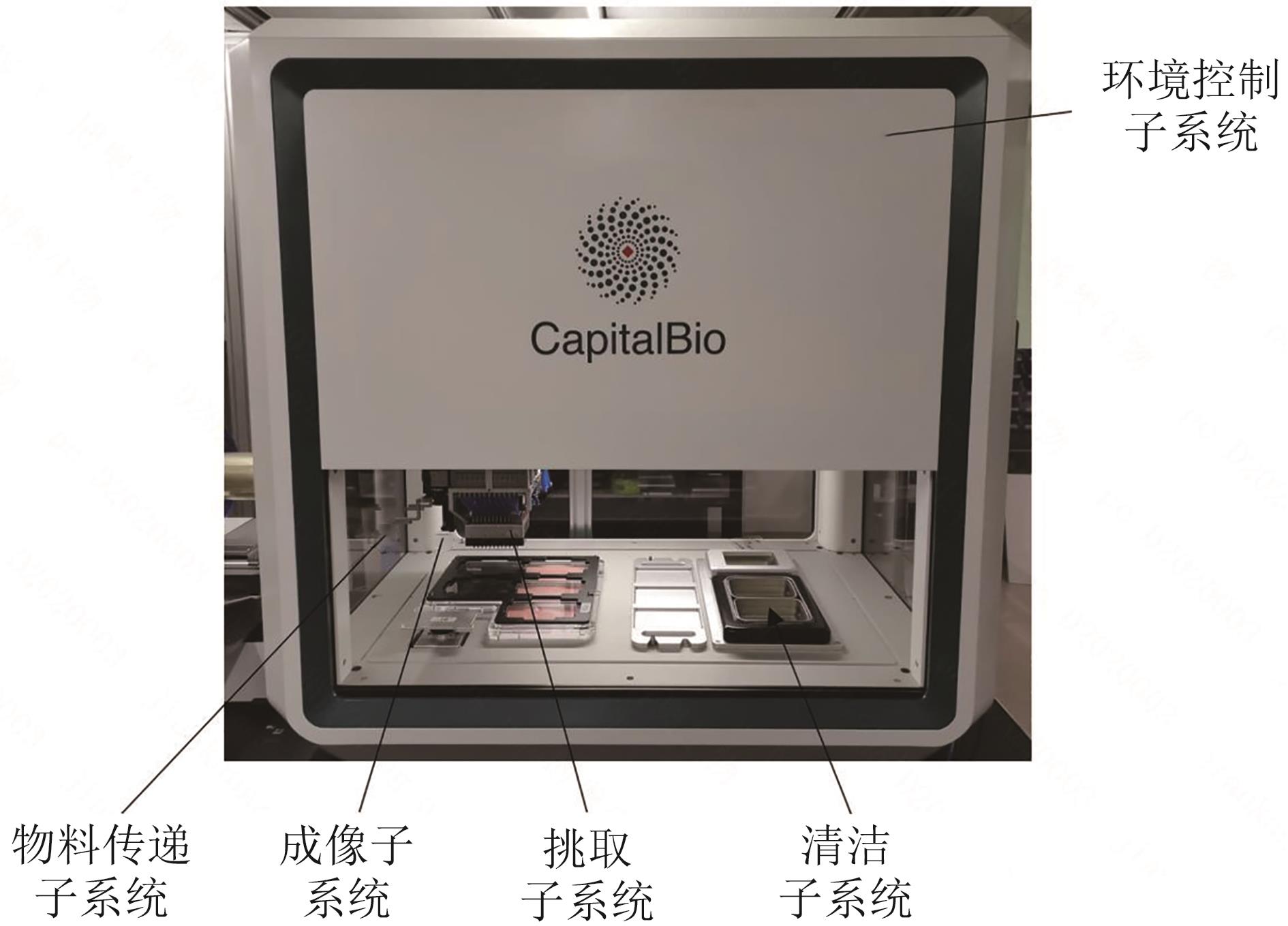
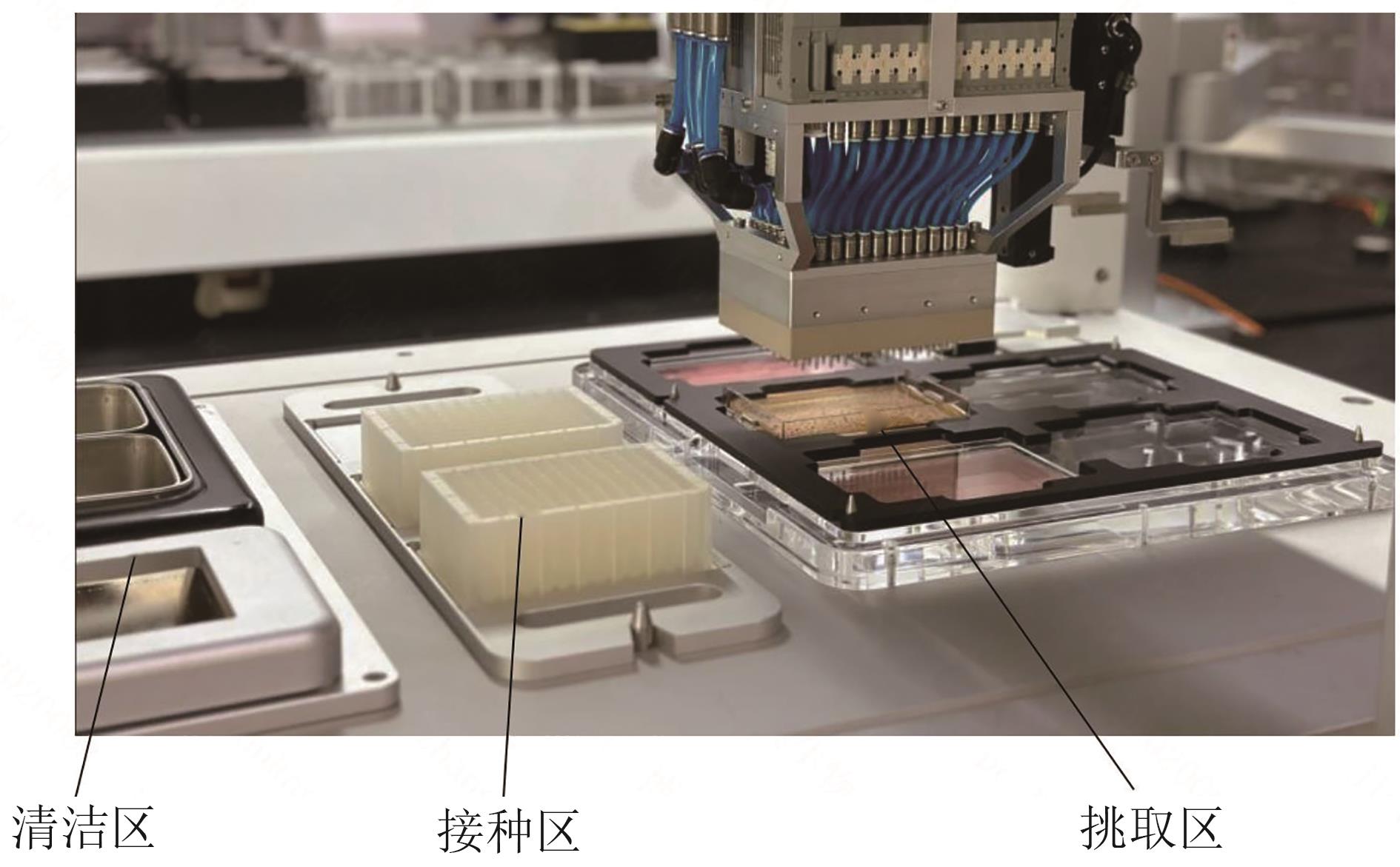
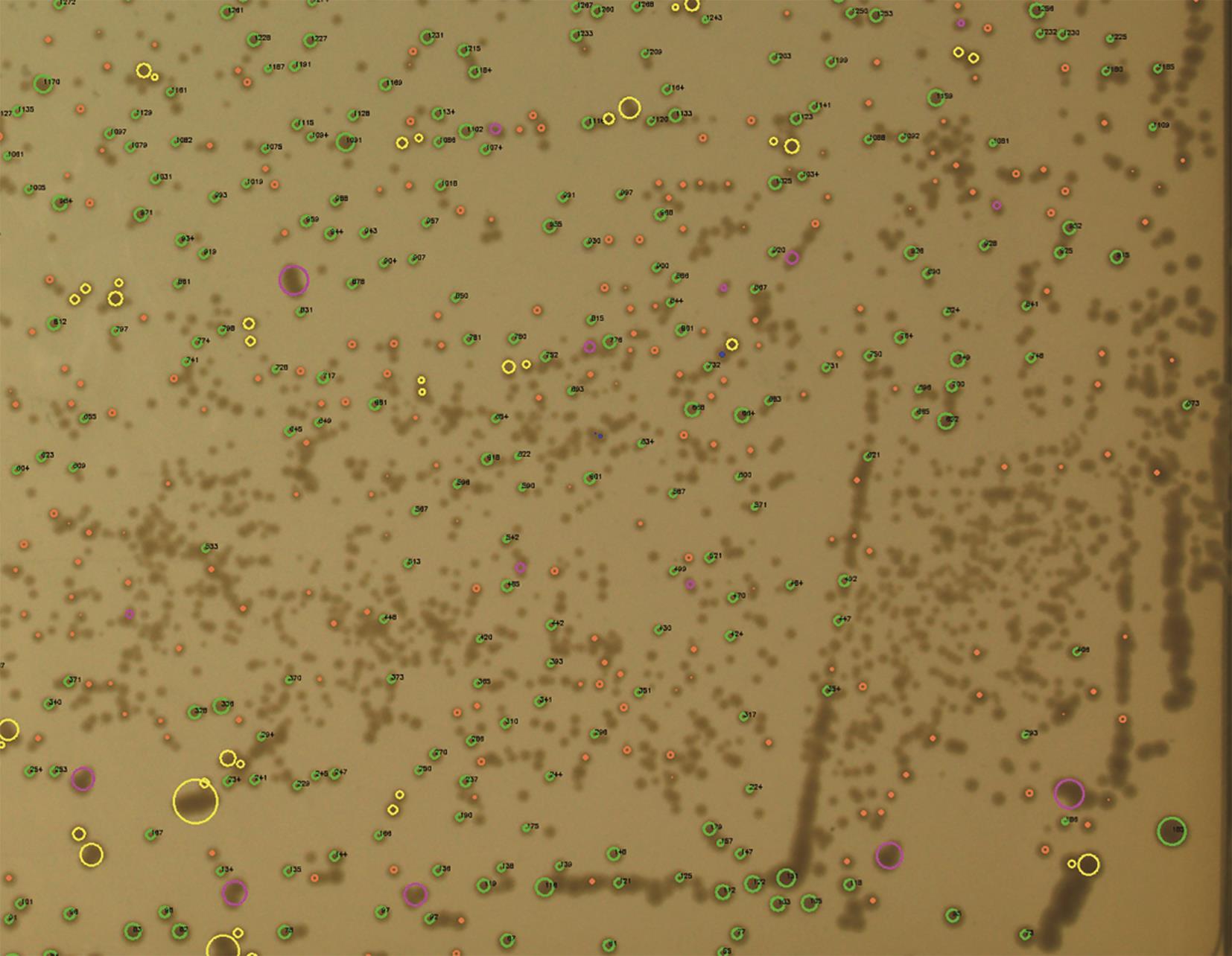
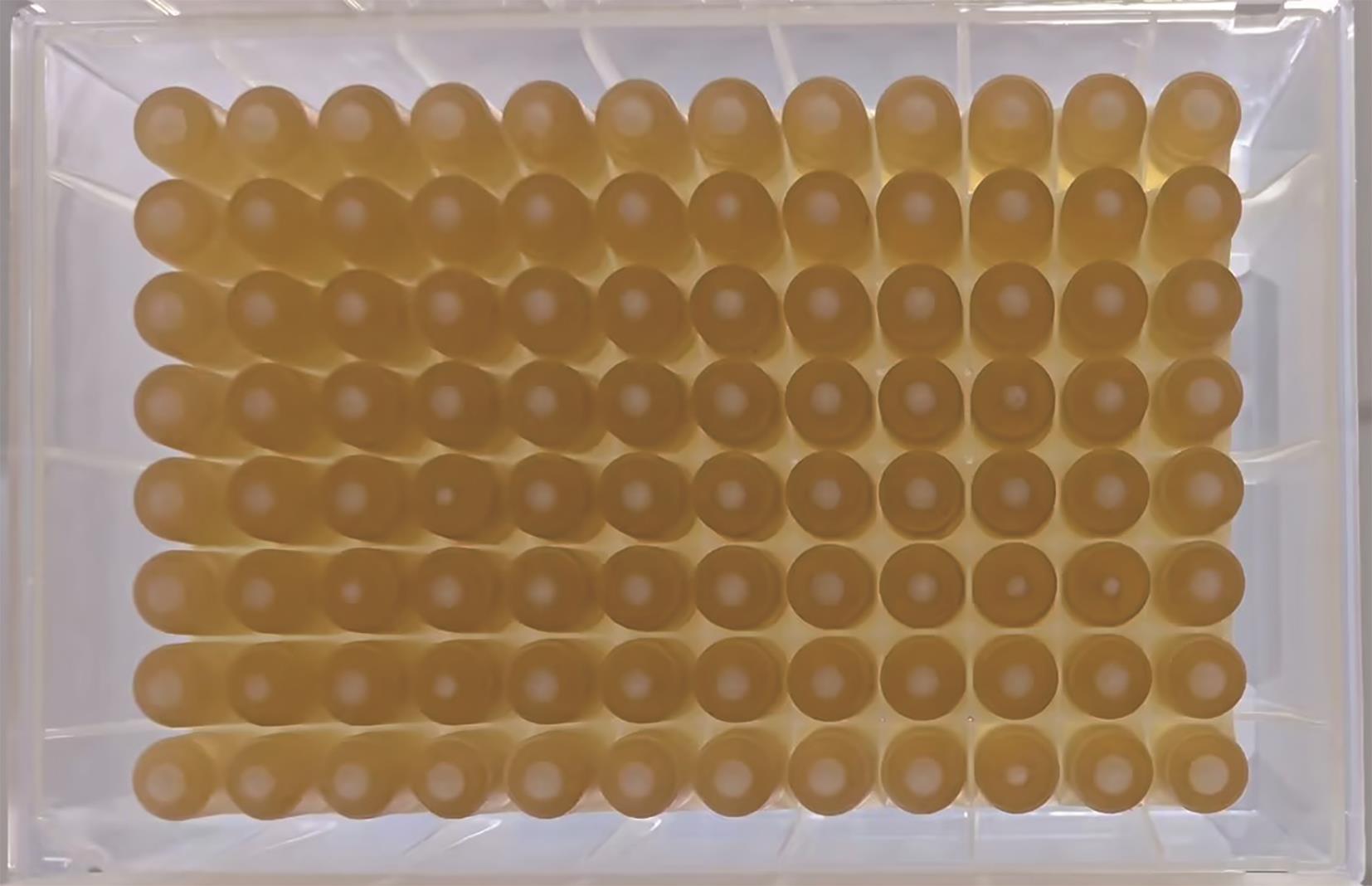
Development and application of a high-throughput microbial clone picking workstation based on machine vision
ZHANG Jiankang1,2, WANG Wenjun1,2, GUO Hongju1,2, BAI Beichen1,2, ZHANG Yafei1,2, YUAN Zheng1,2, LI Yanhui1,2, LI Hang1,2
- 1.National Engineering Research Center for Beijing Biochip Technology,Beijing 102206,China
2.CapitalBio Corporation,Beijing 102206,China
-
Received:2025-04-29Revised:2025-06-25Online:2025-09-03Published:2025-08-31 -
Contact:LI Hang
基于机器视觉的高通量微生物克隆挑选工作站研制及应用
张建康1,2, 王文君1,2, 郭洪菊1,2, 白北辰1,2, 张亚飞1,2, 袁征1,2, 李彦辉1,2, 李航1,2
- 1.生物芯片北京国家工程研究中心,北京 102206
2.博奥生物集团有限公司,北京 102206
-
通讯作者:李航 -
作者简介:张建康 (1986—),男,高级工程师。研究方向为实验室自动化系统开发、机器人技术应用、智能装备研发。 E-mail:jiankangzhang@capitalbio.com李航 (1971—),男,技术负责人,工程师。研究方向为工业自动化系统集成、精密机电设备研发、智能检测技术工程化应用。 E-mail:hli@capitalbio.com -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0902302);国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0902304)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Jiankang, WANG Wenjun, GUO Hongju, BAI Beichen, ZHANG Yafei, YUAN Zheng, LI Yanhui, LI Hang. Development and application of a high-throughput microbial clone picking workstation based on machine vision[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 956-971.
张建康, 王文君, 郭洪菊, 白北辰, 张亚飞, 袁征, 李彦辉, 李航. 基于机器视觉的高通量微生物克隆挑选工作站研制及应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025, 6(4): 956-971.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2025-038
数据集 Data set | 训练集 Training set | 测试集 Test set |
|---|---|---|
完整菌落图像 Complete colony images | 34 | 4 |
挑选出小图像块 Small image blocks selected | 5160 | 1466 |
Table 1 Distribution of the dataset
数据集 Data set | 训练集 Training set | 测试集 Test set |
|---|---|---|
完整菌落图像 Complete colony images | 34 | 4 |
挑选出小图像块 Small image blocks selected | 5160 | 1466 |
| 设备型号 | 通道数量 | 挑取 方式 | CCD分辨率/(Pixel/mm) | 菌落识 别尺寸/mm | 菌落识别准确度/% | 挑取准确率/% | 有效像素/万 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QPix 420 | 96 | 挑针 | 22 | ≥ 0.1 | 0.5~0.7mm菌落,>97% | > 98% | 500 |
| Hedylax T200智能微生物菌落挑选工作站 | 单通道或8通道 | 吸头 | — | — | — | ≥ 98% | 2500 |
| 全自动菌落挑选工作站G3000 | 2或4 | 挑针 | — | ≥ 0.5 | — | 1 mm以上98% | 600~2000 |
| 本设备 | 96 | 挑针 | 30 | ≥0.2 | ≥ 98% | ≥ 98% | 1000 |
Table 2 A comparison of technical parameters of this device with other three clone picking workstations
| 设备型号 | 通道数量 | 挑取 方式 | CCD分辨率/(Pixel/mm) | 菌落识 别尺寸/mm | 菌落识别准确度/% | 挑取准确率/% | 有效像素/万 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QPix 420 | 96 | 挑针 | 22 | ≥ 0.1 | 0.5~0.7mm菌落,>97% | > 98% | 500 |
| Hedylax T200智能微生物菌落挑选工作站 | 单通道或8通道 | 吸头 | — | — | — | ≥ 98% | 2500 |
| 全自动菌落挑选工作站G3000 | 2或4 | 挑针 | — | ≥ 0.5 | — | 1 mm以上98% | 600~2000 |
| 本设备 | 96 | 挑针 | 30 | ≥0.2 | ≥ 98% | ≥ 98% | 1000 |
| [1] | MACARRÓN R, HERTZBERG R P. Design and implementation of high throughput screening assays[J]. Molecular Biotechnology, 2011, 47(3): 270-285. |
| [2] | HUGHES S R, BUTT T R, BARTOLETT S, et al. Design and construction of a first-generation high-throughput integrated robotic molecular biology platform for bioenergy applications[J]. SLAS Technology, 2011, 16(4): 292-307. |
| [3] | 孙梦楚, 陆亮宇, 申晓林, 等. 基于荧光检测的高通量筛选技术和装备助力细胞工厂构建[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 947-965. |
| SUN M C, LU L Y, SHEN X L, et al. Fluorescence detection-based high-throughput screening systems and devices facilitate cell factories construction[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 947-965. | |
| [4] | 卢挥, 张芳丽, 黄磊. 合成生物学自动化装置iBioFoundry的构建与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2023, 4(5): 877-891. |
| LU H, ZHANG F L, HUANG L. Establishment of iBioFoundry for synthetic biology applications[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2023, 4(5): 877-891. | |
| [5] | STEPHENSON A, LASTRA L, NGUYEN B, et al. Physical laboratory automation in synthetic biology[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2023, 12(11): 3156-3169. |
| [6] | PAVAN M. Setting up an automated biomanufacturing laboratory[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2021, 2229: 137-155. |
| [7] | MARTIN V J J, PITERA D J, WITHERS S T, et al. Engineering a mevalonate pathway in Escherichia coli for production of terpenoids[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2003, 21(7): 796-802. |
| [8] | WIN M N, SMOLKE C D. Higher-order cellular information processing with synthetic RNA devices[J]. Science, 2008, 322(5900): 456-460. |
| [9] | PADDON C J, WESTFALL P J, PITERA D J, et al. High-level semi-synthetic production of the potent antimalarial artemisinin[J]. Nature, 2013, 496(7446): 528-532. |
| [10] | CHAO R, MISHRA S, SI T, et al. Engineering biological systems using automated biofoundries[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 42: 98-108. |
| [11] | 唐婷, 付立豪, 郭二鹏, 等. 自动化合成生物技术与工程化设施平台[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(3): 300-309. |
| TANG T, FU L H, GUO E P, et al. Automation in synthetic biology using biological foundries[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(3): 300-309. | |
| [12] | ZIMMERMANN M, ZIMMERMANN-KOGADEEVA M, WEGMANN R, et al. Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes[J]. Nature, 2019, 570(7762): 462-467. |
| [13] | CERBINI T, LUO Y Q, RAO M S, et al. Transfection, selection, and colony-picking of human induced pluripotent stem cells TALEN-targeted with a GFP gene into the AAVS1 safe harbor[J]. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 2015(96): 52504. |
| [14] | DJATNA T, HADI M Z. Implementation of an ant colony approach to solve multi-objective order picking problem in beverage warehousing with drive-in rack system[C]//2017 International Conference on Advanced Computer Science and Information Systems (ICACSIS), 28-29 October 2017, Bali, Indonesia, 2017: 137-142. |
| [15] | HUANG C, HE K, LIU C L, et al. A colony picking robot with multi-pin synchronous manipulator[C]//2018 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation(ICIA), 11-13 August 2018, Wuyi Mountain, Fujian, China, 2018: 7-12. |
| [16] | 张依朗. 基于机器视觉的高通量自动菌落挑取系统研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2021. |
| ZHANG Y L. Research on high throughput automatic colony picking sysetem based on machine vision[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2021. | |
| [17] | CHEN W B, ZHANG C C. Automated bacterial colony counting for clonogenic assay[M]//Dental Computing and Applications. New York: IGI Global, 2009: 134-145. |
| [18] | GOROKHOV O, FAZYLOV R, KAZACHUK M, et al. Bacterial colony detection method for microbiological photographic images[C]//2022 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). July 18-23, 2022, Padua, Italy. IEEE, 2022: 1-8. |
| [19] | ZHANG L. Phase contrast microscopy cell population segmentation: a survey[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2019: 1911.11111. (2019-11-29)[2025-03-01]. . |
| [20] | LAWLESS C, WILKINSON D J, YOUNG A, et al. Colonyzer: automated quantification of micro-organism growth characteristics on solid agar[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2010, 11: 287. |
| [21] | REHMAN A, SALEEM Z, AMJAD J, et al. A comparison of bacterial colonies count from petri dishes utilizing hough transform and traditional manual counting[EB/OL].arXiv, 2025: 2505.20365. (2025-05-26)[2025-06-01]. . |
| [22] | RUSS J C, NEAL F B. The image processing handbook[M/OL]. 7th ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2016. (2018-09-03)[2025-06-25]. . |
| [23] | MOEN E, BANNON D, KUDO T, et al. Deep learning for cellular image analysis[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(12): 1233-1246. |
| [24] | WAKABAYASHI R, AOYANAGI A, TOMINAGA T. Rapid counting of coliforms and Escherichia coli by deep learning-based classifier[J]. Journal of Food Safety, 2024, 44(4): e13158. |
| [25] | SHEN B Y, CHEN X, CAI D L, et al. Real-Space Imaging of the Ordered Small Molecule Orientations in Porous Frameworks by Electron Microscopy[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2020: 2001.09588.(2020-01-27)[2025-06-01]. . |
| [26] | AKBAR S ALI, GHAZALI K H, HASAN H, et al. Rapid bacterial colony classification using deep learning[J]. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 2022, 26(1): 352. |
| [27] | ANDREINI P, BONECHI S, BIANCHINI M, et al. a deep learning approach to bacterial colony segmentation[C/OL]//KŮRKOVÁ V, MANOLOPOULOS Y, HAMMER B, et al. Artificial neural networks and machine learning-ICANN 2018. 27th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Rhodes, Greece, October 4-7, 2018 , Proceedings, Part III. Cham: Springer, 2018. (2018-09-18)[2025-06-01]. . |
| [28] | RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROXET T, et al. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2015: 1505.04597. (2015-05-18)[2025-06-01]. . |
| [29] | OKTAY O, SCHLEMPER J, LE FOLGOC L, et al. Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2018: 1804.03999. (2018-05-20)[2025-06-01]. . |
| [30] | HE K M, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁRET P, et al. Mask R-CNN for object detection and instance segmentation[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2017: 1703.06870. (2018-01-24)[2025-06-01]. . |
| [31] | JHA D, SMEDSRUD P H, JOHANSEN D, et al. A comprehensive study on colorectal polyp segmentation with ResUNet++, conditional random field and test-time augmentation[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2021, 25(6): 2029-2040. |
| [32] | 曹淑艳, 陈雪景, 张洵洋. 中国塑料行业绿色低碳发展研究报告[R/OL]. [2025-06-01]. . |
| CAO S Y, CHEN X J, ZHANG X Y. Green and low carbon development of the plastics industry in China[R/OL]. [2025-06-01]. . |
| [1] | FANG Xinyi, SUN Lichao, HUO Yixin, WANG Ying, YUE Haitao. Trends and challenges in microbial synthesis of higher alcohols [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 873-898. |
| [2] | WU Xiaoyan, SONG Qi, XU Rui, DING Chenjun, CHEN Fang, GUO Qing, ZHANG Bo. A comparative analysis of global research and development competition in synthetic biology [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 940-955. |
| [3] | LI Quanfei, CHEN Qian, LIU Hao, HE Kundong, PAN Liang, LEI Peng, GU Yi’an, SUN Liang, LI Sha, QIU Yibin, WANG Rui, XU Hong. Synthetic biology and applications of high-adhesion protein materials [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(4): 806-828. |
| [4] | WU Ke, LUO Jiahao, LI Feiran. Applications of machine learning in the reconstruction and curation of genome-scale metabolic models [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 566-584. |
| [5] | TIAN Xiao-jun, ZHANG Rixin. “Economics Paradox” with cells in synthetic gene circuits [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 532-546. |
| [6] | ZHANG Yiqing, LIU Gaowen. Exploration of gene functions and library construction for engineering strains from a synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 685-700. |
| [7] | ZHANG Chengxin. Challenges and opportunities in text mining-based protein function annotation [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 603-616. |
| [8] | YANG Ying, LI Xia, LIU Lizhong. Applications of synthetic biology to stem-cell-derived modeling of early embryonic development [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 669-684. |
| [9] | LI Mingchen, ZHONG Bozitao, YU Yuanxi, JIANG Fan, ZHANG Liang, TAN Yang, YU Huiqun, FAN Guisheng, HONG Liang. DeepSeek model analysis and its applications in AI-assistant protein engineering [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 636-650. |
| [10] | HUANG Yi, SI Tong, LU Anjing. Standardization for biomanufacturing: global landscape, critical challenges, and pathways forward [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 701-714. |
| [11] | SONG Chengzhi, LIN Yihan. AI-enabled directed evolution for protein engineering and optimization [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 617-635. |
| [12] | ZHANG Mengyao, CAI Peng, ZHOU Yongjin. Synthetic biology drives the sustainable production of terpenoid fragrances and flavors [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 334-356. |
| [13] | ZHANG Lu’ou, XU Li, HU Xiaoxu, YANG Ying. Synthetic biology ushers cosmetic industry into the “bio-cosmetics” era [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 479-491. |
| [14] | YI Jinhang, TANG Yulin, LI Chunyu, WU Heyun, MA Qian, XIE Xixian. Applications and advances in the research of biosynthesis of amino acid derivatives as key ingredients in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 254-289. |
| [15] | WEI Lingzhen, WANG Jia, SUN Xinxiao, YUAN Qipeng, SHEN Xiaolin. Biosynthesis of flavonoids and their applications in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||