New technologies and industrialization progress in healthy sugar biomanufacturing based on in vitro synthetic biology
SHI Ting1,2, CHEN Xuemei2, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job1,2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Engineering Biology for Low-Carbon Manufacturing,Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Tianjin 300308,China
2.In vitro Synthetic Biology Center,Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Tianjin 300308,China
-
Received:2025-06-04Revised:2025-08-05 -
Contact:ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job
基于体外合成生物学的健康糖生物制造新技术与产业化进展
石婷1,2, 陈雪梅2, 张以恒1,2
- 1.低碳合成工程生物学全国重点实验室,中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所,天津 300308
2.中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所体外合成生物学中心,天津 300308
-
通讯作者:张以恒 -
作者简介:石婷 (1984—),女,博士,中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所正高级工程师。2008年本科毕业于合肥工业大学生物与食品工程学院,2010年和2014年分别获得天津大学化工学院生物化工专业硕士和博士学位。主要研究方向为体外合成生物学、酶工程与微生物代谢工程。E-mail:shi_ting@tib.cas.cn张以恒 (1971—),低碳合成工程生物学全国重点实验室主任,中国科学院天津工业生物技术研究所体外合成生物学与生物制造中心主任,曾经任美国弗吉尼亚理工大学终身正教授。他是体外合成生物学的奠基人之一与产业化领跑者,创建体外生物转化(ivBT)技术平台,率先提出“人工多酶分子机器”概念并实现万吨级产业化。在秸秆制粮、体外呼吸作用(无氧呼吸作用产氢、有氧呼吸作用制电)、人工合成淀粉、淀粉制塔格糖与肌醇等方向取得了一系列原创性(0-1)突破。E-mail:zhang_xw@tib.cas.cn -
基金资助:科技部重点专项(2022YFA0912300);国家自然科学基金面上项目(NSFC32271544);合成生物学海河实验室颠覆性创新项目(22HHSWSS000155);天津市合成生物技术创新能力提升行动项目(TSBICIP-CXRC-067)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SHI Ting, CHEN Xuemei, ZHANG Yi-Heng P. Job. New technologies and industrialization progress in healthy sugar biomanufacturing based on in vitro synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-054.
石婷, 陈雪梅, 张以恒. 基于体外合成生物学的健康糖生物制造新技术与产业化进展[J]. 合成生物学, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-054.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2025-054
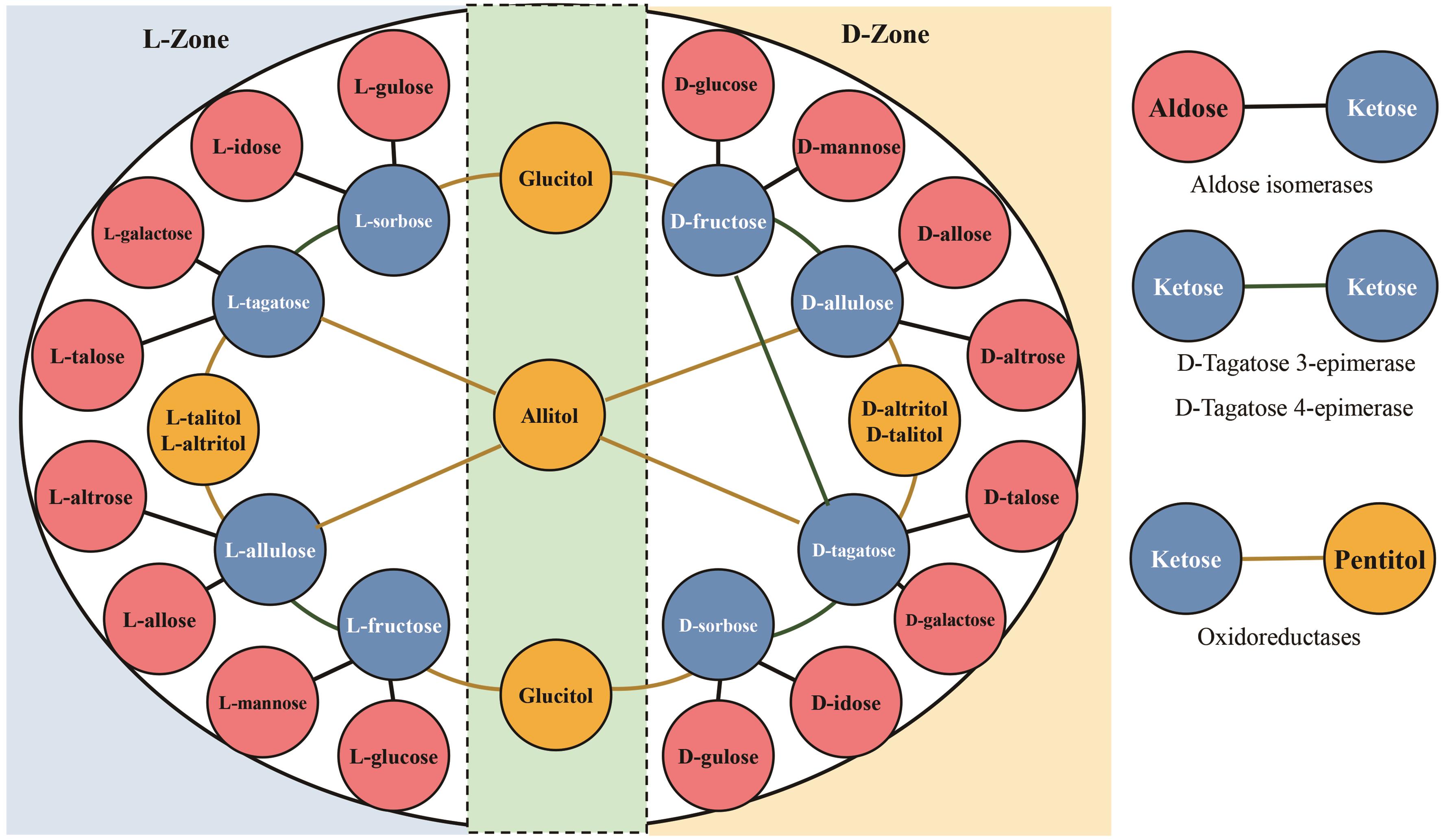
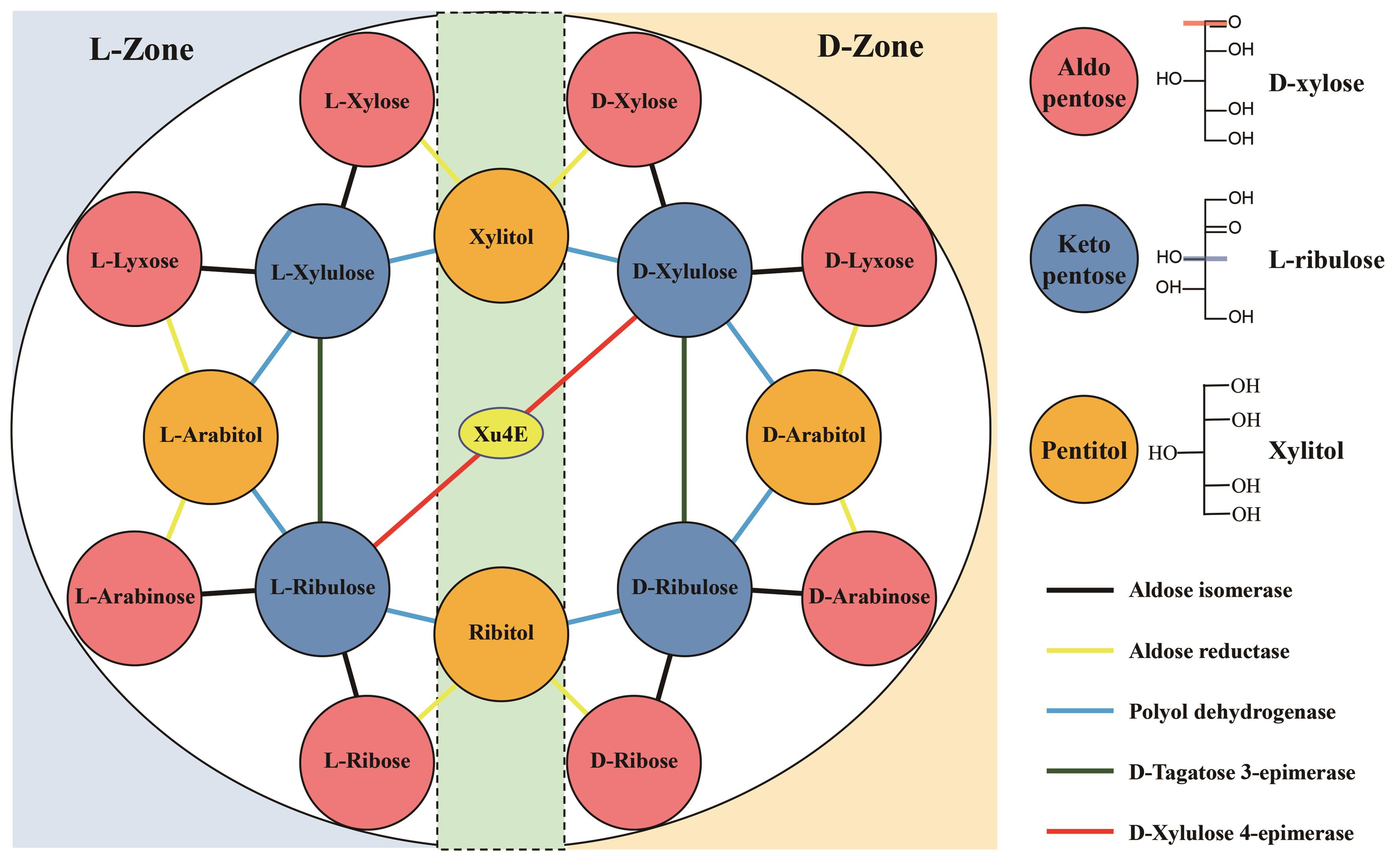
Fig. 1 Updated Izumoring strategy for hexoses(Add D-tagatose 4-epimerase to catalyze the synthesis of D-tagatose from D-fructose; omit ketose reductases that catalyze the synthesis of hexitol from D, L-ketose)
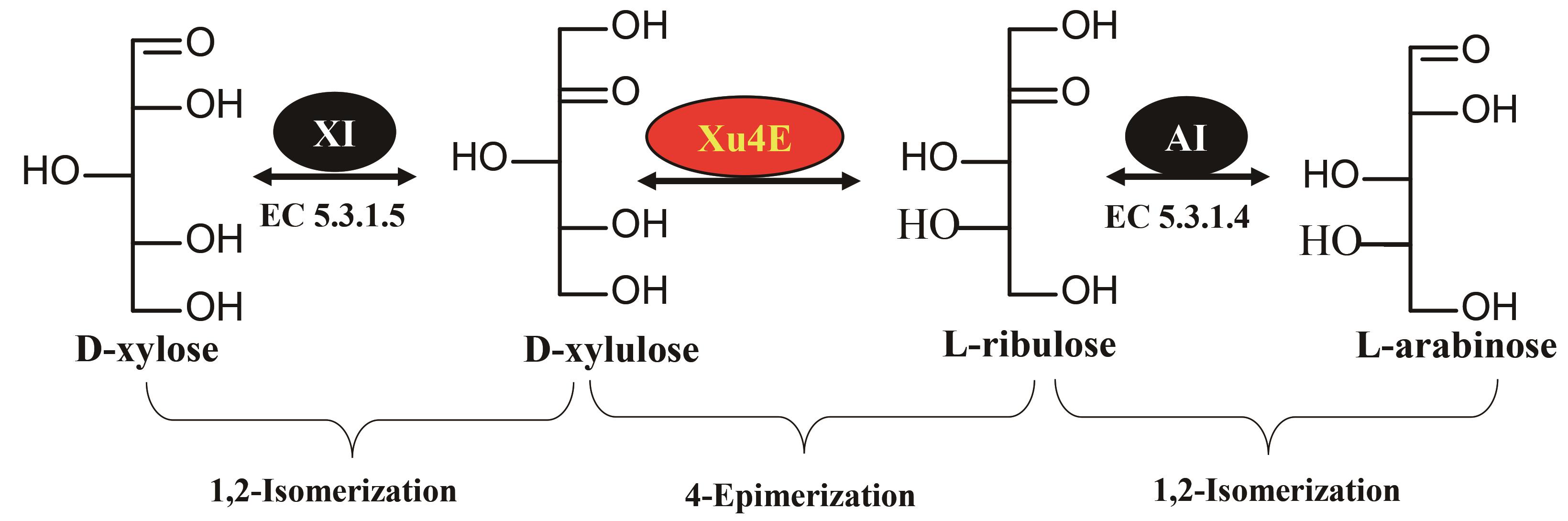
Fig. 3 Production of L-arabinose using D-L sugar epimerase based on in vitro Biotransformation (ivBT)(XI, D-xylose isomerase; Xu4E, D-xylulose 4-epimerase; AI, L-arabinose isomerase)
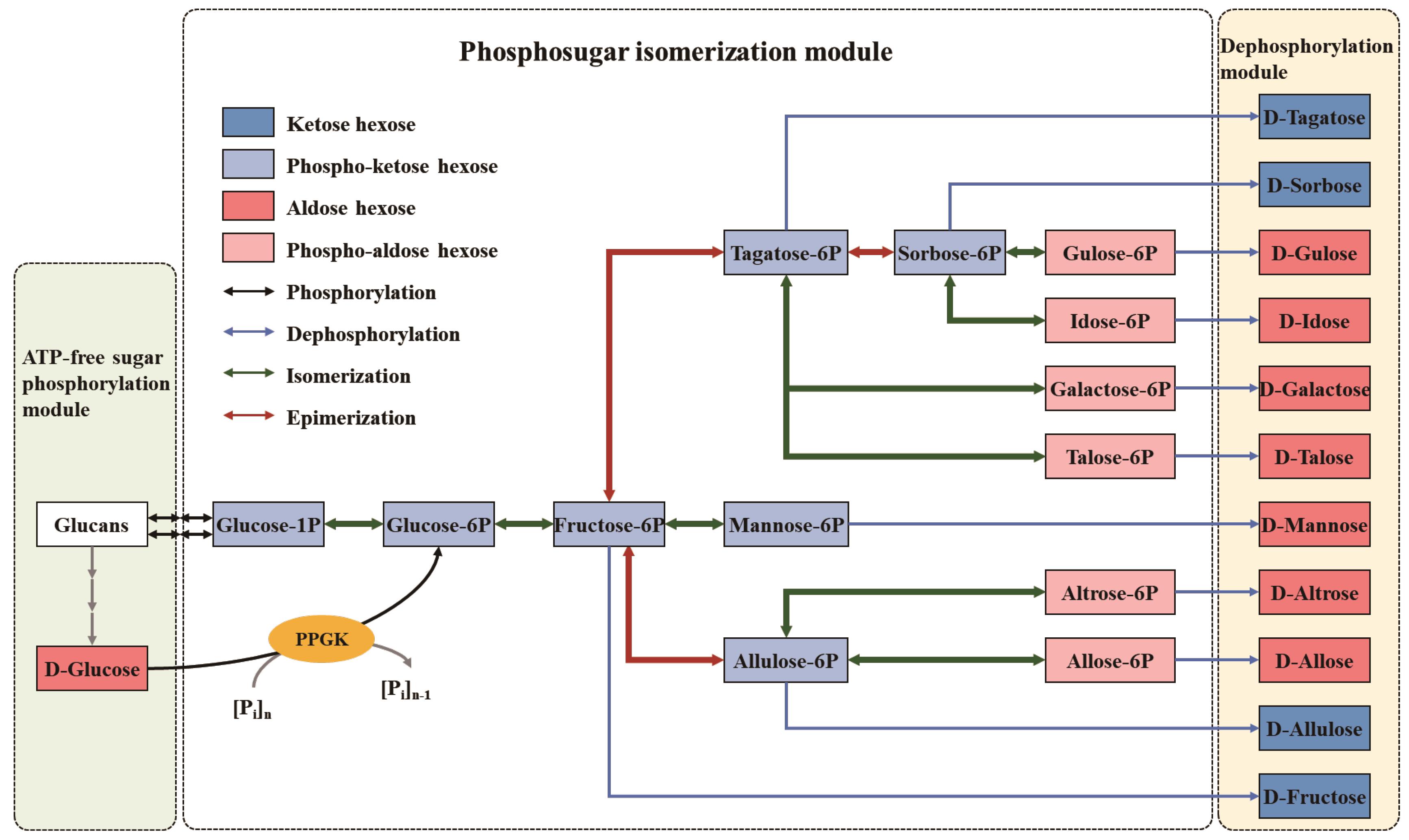
Fig. 4 Application of Zhang Strategy ("ATP-free Phosphorylation-Isomerization-Dephosphorylation" strategy) in in vitro Biotransformation (ivBT): A multi-enzyme molecular machine for healthy sugars
| Production method | Enzyme | Substrate | Titer (g/L) | Yield (%) | Productivity (g/L/h) | Temp (oC) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzymatic isomerization | L-AI from Arthrobacter sp. 22c | 100 g/L D-galactose | 30 | 30 | 0.25 | 30 | [ |
| L-AI from G. stearothermophilus | 100 g/L D-galactose | 30.6 | 30.6 | 1.9 | 60 | [ | |
| L-AI from G. thermodenitrificans | 300 g/L D-galactose | 158 | 52.7 | 8 | 60 | [ | |
| L-AI from Thermoanaerobacter mathranii | 300 g/L D-galactose | 126 | 42.0 | 2.6 | 65 | [ | |
| L-AI from Thermotaga maritima | 1.8 g/L D-galactose | 1.0 | 56.0 | 0.2 | 80 | [ | |
| Tagaturonate 3-epimerase from Thermotoga petrophila | 700 g/L D-fructose | 213 | 30.0 | 107 | 80 | [ | |
| Tagatose-4-epimerase from Thermotogae bacterium | 200 g/L D-fructose | 28 | 14.0 | 14 | 70 | [ | |
| D-tagaturonate epimerase from Thermotoga neapolitana | 100 g/L D-fructose | 21.8 | 21.8 | 7.3 | 65 | [ | |
| Tagatose 4-epimerase from Thermoprotei archaeon | 100 g/L D-fructose | 18.9 | 18.9 | 7.6 | 70 | [ | |
| Whole-cell biosynthesis | E. coli BL21/pET28a-P3-LfaraAD390V/V468LlacZ | 500 g/L lactose | 115 | 23.1 | 2.4 | 50 | [ |
| E. coli/pETDuet-αgp-pgm andpCDFDuet-pgi-gatz-pgp | 20 g/L maltodextrin | 3.2 | 16.0 | 0.13 | 60 | [ | |
| E. coli ER-2GatZ (ΔpΔz) | 10 g/L maltodextrin | 3.38 | 33.8 | 1.13 | 60 | [ | |
| Fermentation | S. cerevisiae EJ2g_iXiG_pXpG | 114 g/L lactose | 37.7 | 33 | 0.13 | 30 | [ |
| B. subtilis BS-3CA4 | 72 g/L D-galactose | 39.6 | 0.55 | 0.33 | 45 | [ | |
| ivBT | αGP, PGM, PGI, TPE, and TPP from B. subtilis | 100 g/L maltodextrin | 78 | 78 | 2.0 | 37 | [ |
| αGP, PGM, PGI, TPE, and TPP from E.coli BL21 | 20 g/L maltodextrin | 17.7 | 88.5 | 0.74 | 50 | [ | |
| αGP, PGM, PGI, TPE, and TPP from E.coli BL21 | 50 g/L maltodextrin | 37.6 | 75 | 1.57 | 50 | [ |
Table 1 Comparison of Key Technical Indicators for D-Tagatose Synthesis via Enzymatic Isomerization, Whole-cell Biosynthesis, Microbial Fermentation, and in vitro BioTransformation (ivBT)
| Production method | Enzyme | Substrate | Titer (g/L) | Yield (%) | Productivity (g/L/h) | Temp (oC) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzymatic isomerization | L-AI from Arthrobacter sp. 22c | 100 g/L D-galactose | 30 | 30 | 0.25 | 30 | [ |
| L-AI from G. stearothermophilus | 100 g/L D-galactose | 30.6 | 30.6 | 1.9 | 60 | [ | |
| L-AI from G. thermodenitrificans | 300 g/L D-galactose | 158 | 52.7 | 8 | 60 | [ | |
| L-AI from Thermoanaerobacter mathranii | 300 g/L D-galactose | 126 | 42.0 | 2.6 | 65 | [ | |
| L-AI from Thermotaga maritima | 1.8 g/L D-galactose | 1.0 | 56.0 | 0.2 | 80 | [ | |
| Tagaturonate 3-epimerase from Thermotoga petrophila | 700 g/L D-fructose | 213 | 30.0 | 107 | 80 | [ | |
| Tagatose-4-epimerase from Thermotogae bacterium | 200 g/L D-fructose | 28 | 14.0 | 14 | 70 | [ | |
| D-tagaturonate epimerase from Thermotoga neapolitana | 100 g/L D-fructose | 21.8 | 21.8 | 7.3 | 65 | [ | |
| Tagatose 4-epimerase from Thermoprotei archaeon | 100 g/L D-fructose | 18.9 | 18.9 | 7.6 | 70 | [ | |
| Whole-cell biosynthesis | E. coli BL21/pET28a-P3-LfaraAD390V/V468LlacZ | 500 g/L lactose | 115 | 23.1 | 2.4 | 50 | [ |
| E. coli/pETDuet-αgp-pgm andpCDFDuet-pgi-gatz-pgp | 20 g/L maltodextrin | 3.2 | 16.0 | 0.13 | 60 | [ | |
| E. coli ER-2GatZ (ΔpΔz) | 10 g/L maltodextrin | 3.38 | 33.8 | 1.13 | 60 | [ | |
| Fermentation | S. cerevisiae EJ2g_iXiG_pXpG | 114 g/L lactose | 37.7 | 33 | 0.13 | 30 | [ |
| B. subtilis BS-3CA4 | 72 g/L D-galactose | 39.6 | 0.55 | 0.33 | 45 | [ | |
| ivBT | αGP, PGM, PGI, TPE, and TPP from B. subtilis | 100 g/L maltodextrin | 78 | 78 | 2.0 | 37 | [ |
| αGP, PGM, PGI, TPE, and TPP from E.coli BL21 | 20 g/L maltodextrin | 17.7 | 88.5 | 0.74 | 50 | [ | |
| αGP, PGM, PGI, TPE, and TPP from E.coli BL21 | 50 g/L maltodextrin | 37.6 | 75 | 1.57 | 50 | [ |
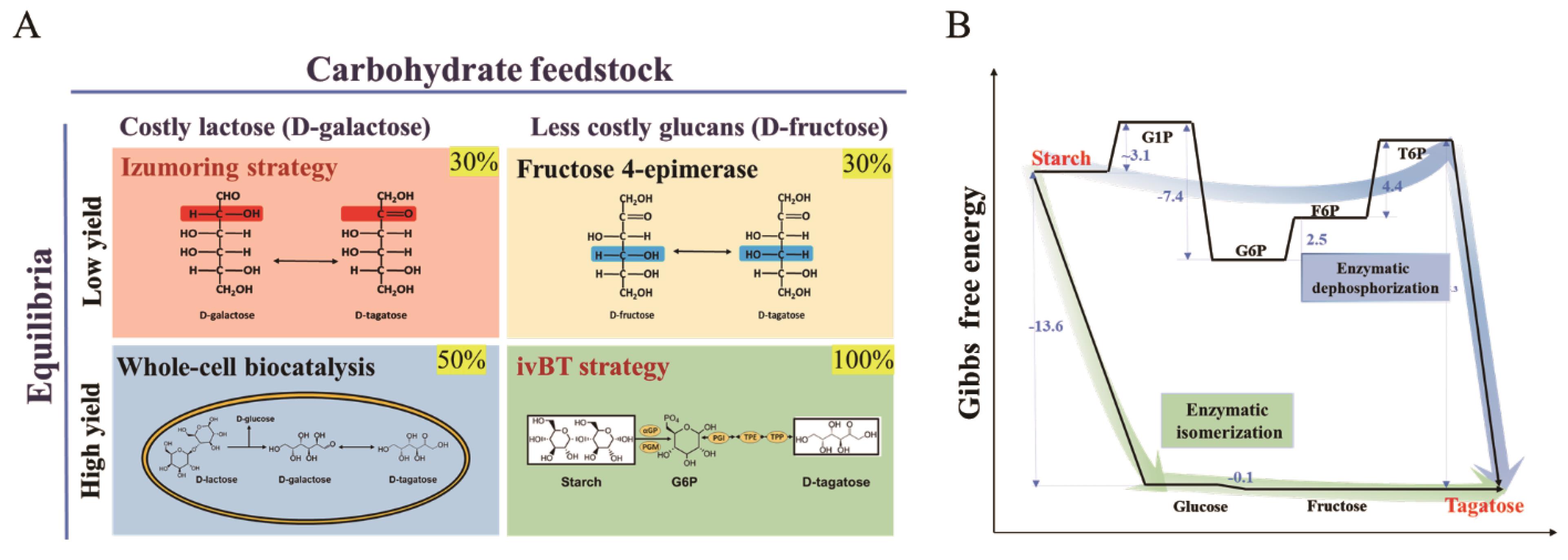
Fig. 5 Comparison of biotechnological methods for D-tagatose production(A, Theoretical molar yield: 30%-100%; B, Sources of Gibbs free energy data: eQuilibrator: The Biochemical Thermodynamics Calculator (weizmann.ac.il))
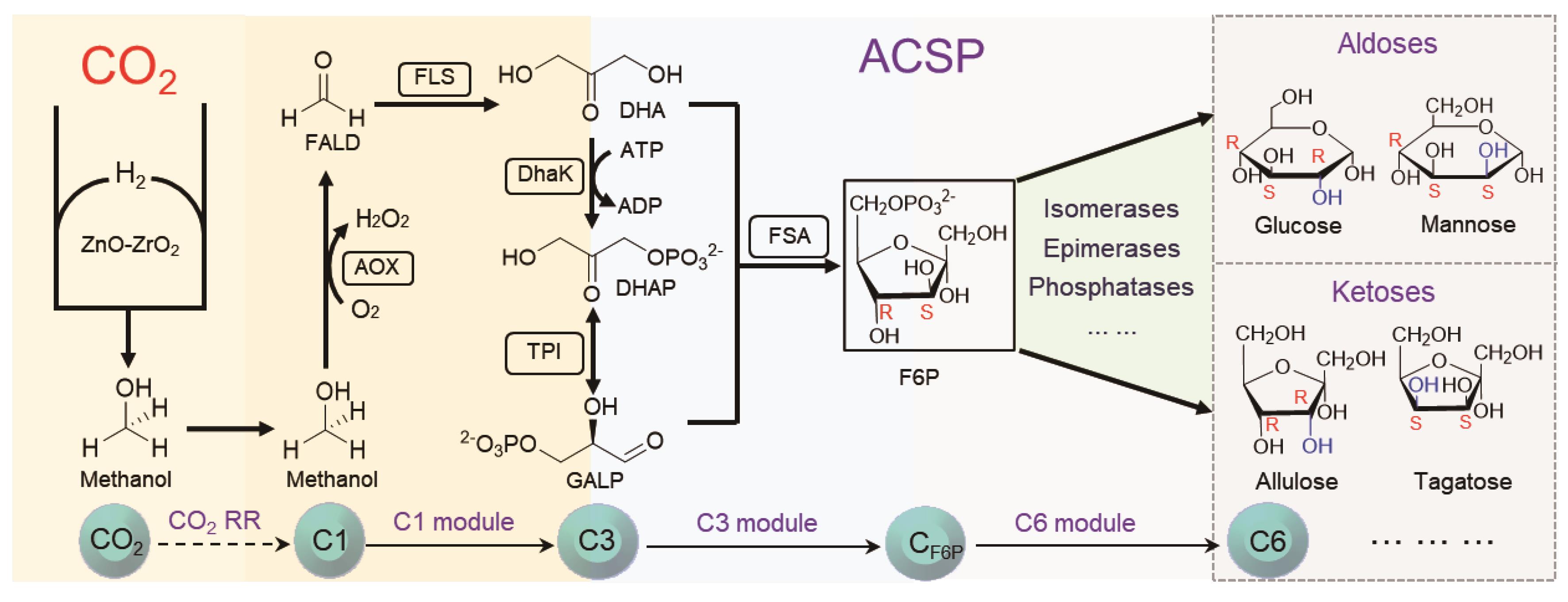
Fig. 6 Design of artificial CO2-to-sugars route (ACSP)FALD: formaldehyde; DHA: dihydroxyacetone; DHAP: dihydroxyacetone phosphate; GALP: glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate; F6P: fructose-6-phosphate; AOX: alcoholoxidase; FLS: formolase; DhaK: dihydroxyacetone kinase; TPI: triosephosphate isomerase; FSA: fructose 6-phosphate aldolase.
| [1] | VALENCIA G A. Natural additives in foods[M]. 2023: Cham, Switzerland : Springer. |
| [2] | 2024年甜味剂市场现状与发展趋势分析. 2024; Available from: . |
| [3] | PHILIPPE R N, DE MEY M, ANDERSON J, et al. Biotechnological production of natural zero-calorie sweeteners[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2014. 26: 155-161. |
| [4] | XU Y M, WU Y K, LIU Y F, et al. Sustainable bioproduction of natural sugar substitutes: strategies and challenges[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2022. 129: 512-527. |
| [5] | DHAARINI C, TEJASHWINI S, and GAYATHRI M. Biotechnological intervention in production of bioactive compounds: biosynthesis, characterization and applications[M]. 2025: Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland. |
| [6] | SUN S, ARAKI Y, HANZAWA F, et al. High sucrose diet-induced dysbiosis of gut microbiota promotes fatty liver and hyperlipidemia in rats[J]. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 2021. 93: 108621. |
| [7] | YU S, LI C, JI G, et al. The contribution of dietary fructose to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2021. 12: 783393. |
| [8] | WANG S and TONG T. Progress of research on sweeteners and human health[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024. 50(17): 371-379. |
| [9] | DEBRAS C, DESCHASAUX-TANGUY M, CHAZELAS E, et al. Artificial sweeteners and risk of type 2 diabetes in the prospective NutriNet-Santé cohort[J]. Diabetes Care, 2023. 46(9): 1681-1690. |
| [10] | ZANI F, BLAGIH J, GRUBER T, et al. The dietary sweetener sucralose is a negative modulator of T cell-mediated responses[J]. Nature, 2023. 615(7953): 705-711. |
| [11] | Aspartame | EFSA. 2023; Available from: . |
| [12] | WU W J, SUI W H, CHEN S Z, et al. Sweetener aspartame aggravates atherosclerosis through insulin-triggered inflammation[J]. Cell Metabolism, 2025. 37(5): 1075-1088. |
| [13] | WITKOWSKI M, WILCOX J, PROVINCE V, et al. Ingestion of the non-nutritive sweetener erythritol, but not glucose, enhances platelet reactivity and thrombosis potential in healthy volunteers-brief report[J]. Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis and Vascular Biology, 2024. 44(9): 2136-2141. |
| [14] | WITKOWSKI M, NEMET I, ALAMRI H, et al. The artificial sweetener erythritol and cardiovascular event risk[J]. Nature Medicine, 2023. 29(3): 710-718. |
| [15] | FAN L, SHI T, CHEN X, et al. Biosynthesis of a healthy natural sugar D-tagatose: advances and opportunities[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2025: 1-16. |
| [16] | HAO L, LU X, SUN M, et al. Protective effects of L-arabinose in high-carbohydrate, high-fat diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats[J]. Food & Nutrition Research, 2015. 59: 28886. |
| [17] | KROG-MIKKELSEN I, HELS O, TETENS I, et al. The effects of L-arabinose on intestinal sucrase activity: dose-response studies in vitro and in humans[J]. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2011. 94(2): 472-478. |
| [18] | WANG Y, ZHAO J, LI Q, et al. L-Arabinose improves hypercholesterolemia via regulating bile acid metabolism in high-fat-high-sucrose diet-fed mice[J]. Nutrition & Metabolism, 2022. 19(1): 30. |
| [19] | LIU K, DONG H, LI X, et al. L-Arabinose alleviates functional constipation in mice by regulating gut microbiota and metabolites[J]. Foods, 2025. 14(5): 900. |
| [20] | GIBSON G R and ROBERFROID M B. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota introducing the concept of prebiotics[J]. The Journal of Nutrition, 1995. 125(6): 1401-1412. |
| [21] | POL K and MARS M. L-arabinose and D-xylose: sweet pentoses that may reduce postprandial glucose and insulin responses[J]. Food & Nutrition Research, 2021. 65(10): 29219. |
| [22] | PASMANS K, MEEX R C R, TROMMELEN J, et al. L-arabinose co-ingestion delays glucose absorption derived from sucrose in healthy men and women: a double-blind, randomised crossover trial[J]. The British Journal of Nutrition, 2022. 128(6): 1072-1081. |
| [23] | POL K, PUHLMANN M L, and MARS M. Efficacy of L-arabinose in lowering glycemic and insulinemic responses: the modifying effect of starch and fat[J]. Foods, 2022. 11(2): 157. |
| [24] | MATSUO T, SUZUKI H, HASHIGUCHI M, et al. D-Psicose is a rare sugar that provides no energy to growing rats[J]. Journal of Nutritional Science & Vitaminology, 2002. 48(1): 77-80. |
| [25] | O'CHAROEN S, HAYAKAWA S, and OGAWA M. Food properties of egg white protein modified by rare ketohexoses through Maillard reaction[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 2014. 50(1): 194-202. |
| [26] | KANASAKI A, IIDA T, MURAO K, et al. D-Allulose enhances uptake of HDL-cholesterol into rat's primary hepatocyte via SR-B1[J]. Cytotechnology, 2020. 72(2): 295-301. |
| [27] | MOON S, KIM Y H, and CHOI K. Inhibition of 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation by D-allulose[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2020. 25(1): 22-28. |
| [28] | 石婷, 宋展, 宋世怡, et al. 体外生物转化 (in vitro BioTransformation, ivBT):生物制造的新前沿[J]. 合成生物学, 2024. 5(6): 1-24. |
| [29] | ZHANG Y-H P J, ZHU Z, YOU C, et al. In vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): Definitions, opportunities, and challenges[J]. Synthetic Biology and Engineering, 2023. 1(2): 10013. |
| [30] | ZAREZADEH M, DEHGHANI A, FAGHFOURI A H, et al. Inositol supplementation and body mass index: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials[J]. Obesity Science & Practice, 2022. 8(3): 387-397. |
| [31] | GREFF D, JUHASZ A E, VANCSA S, et al. Inositol is an effective and safe treatment in polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology, 2023. 21(1): 10. |
| [32] | LOPEZ-GAMBERO A J, SANJUAN C, SERRANO-CASTRO P J, et al. The biomedical uses of inositols: a nutraceutical approach to metabolic dysfunction in aging and neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Biomedicines, 2020. 8(9): 295. |
| [33] | YOU C, SHI T, LI Y, et al. An in vitro synthetic biology platform for the industrial biomanufacturing of myo-inositol from starch[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2017. 114(8): 1855-1864. |
| [34] | 欧阳平凯. 我国工业生物技术发展回顾及展望[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022. 38(11): 3991-4000. |
| [35] | GRANSTRöM T B, TAKATA G, TOKUDA M, et al. Izumoring: a novel and complete strategy for bioproduction of rare sugars[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2004. 97(2): 89-94. |
| [36] | IZUMORI K. Izumoring: a strategy for bioproduction of all hexoses[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2006. 124(4): 717-722. |
| [37] | ZHANG W, CHEN D, CHEN J, et al. D-allulose, a versatile rare sugar: recent biotechnological advances and challenges[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2023. 63(22): 5661-5679. |
| [38] | WU H, ZHANG W, and MU W. Recent studies on the biological production of D-mannose[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019. 103(21-22): 8753-8761. |
| [39] | SHEN J D, XU B P, YU T L, et al. Identification of hyperthermophilic D-allulose 3-epimerase from Thermotoga sp. and its application as a high-performance biocatalyst for D-allulose synthesis[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2024. 47(6): 841-850. |
| [40] | JIAJUN CHEN Z H, TING SHI, DAWEI NI, YINGYING ZHU, WEI XU, WENLI ZHANG, WANMENG MU. Engineering D-allulose 3-epimerase from Clostridium cellulolyticum for improved thermostability using directed evolution facilitated by a nonenzymatic colorimetric screening assay[J]. Food Bioscience, 2023. 53: 102607. |
| [41] | YANG J, TIAN C, ZHANG T, et al. Development of food-grade expression system for D-allulose 3-epimerase preparation with tandem isoenzyme genes in Corynebacterium glutamicum and its application in conversion of cane molasses to D-allulose[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2019. 116(4): 745-756. |
| [42] | GAO X, FANG S B, MA X Z, et al. Customized self-assembled bimetallic hybrid nanoflowers promoting the robustness of D-allulose 3-epimerase[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024. 484: 149453. |
| [43] | LI Z Y, LIU T, PEI W W, et al. Immobilization of a novel D-allulose 3-epimerase from Bacillus cihuensis within metal-organic frameworks[J]. Food Bioscience, 2024. 59: 104202. |
| [44] | XIAO Z Q, JIANG B, CHEN J J, et al. Immobilization and stabilization of D-allulose 3-epimerase for continuous D-allulose synthesis in packed-bed reactors[J]. Food Bioscience, 2025. 64: 105959. |
| [45] | WEN X, LIN H B, LIU G W, et al. Immobilization of cells expressing D-allulose 3-epimerase and their application in D-allulose bioproduction with the assistance of boric acid[J]. Food Bioscience, 2025. 65: 106027. |
| [46] | SHEN J D, XU B P, HUANG L G, et al. Study on immobilization of hyperthermophilic D-allulose 3-epimerase and properties of immobilized enzyme[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2025. 43(2): 42-50. |
| [47] | REN S, LI C, JIAO X, et al. Recent progress in multienzymes co-immobilization and multienzyme system applications[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019. 373: 1254-1278. |
| [48] | LIM B C, KIM H J, and OH D K. High production of D-tagatose by the addition of boric acid[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2007. 23(4): 824-828. |
| [49] | K-C SHIN, LEE T-E, SEO M-J, et al. Development of tagaturonate 3-epimerase into tagatose 4-epimerase with a biocatalytic route from fructose to tagatose[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020. 10(20): 12212-12222. |
| [50] | CHEN J J, NI D W, ZHU Y Y, et al. Discovery of a thermostable tagatose 4-epimerase powered by structure- and sequence-based protein clustering[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024. 72(33): 18585-18593. |
| [51] | KHERSONSKY O, ROODVELDT C, and TAWFIK D S. Enzyme promiscuity: evolutionary and mechanistic aspects[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2006. 10(5): 498-508. |
| [52] | HULT K and BERGLUND P. Enzyme promiscuity: mechanism and applications[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2007. 25(5): 231-238. |
| [53] | RODIONOVA I A, SCOTT D A, GRISHIN N V, et al. Tagaturonate-fructuronate epimerase UxaE, a novel enzyme in the hexuronate catabolic network in Thermotoga maritima [J]. Environmental microbiology, 2012. 14(11): 2920-2934. |
| [54] | WILLE D, HAURI-HOHL M, VONBACH P, et al. Too much of too little: xylitol, an unusual trigger of a chronic metabolic hyperchloremic acidosis[J]. European Journal of Pediatrics, 2010. 169(12): 1549-1551. |
| [55] | OKU T and NAKAMURA S. Threshold for transitory diarrhea induced by ingestion of xylitol and lactitol in young male and female adults[J]. Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology, 2007. 53(1): 13-20. |
| [56] | LI Y, SHI T, HAN P, et al. Thermodynamics-driven production of value-added D-allulose from inexpensive starch by an in vitro enzymatic synthetic biosystem[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021. 11(9): 5088-5099. |
| [57] | TIAN C, YANG J, LI Y, et al. Artificially designed routes for the conversion of starch to value-added mannosyl compounds through coupling in vitro and in vivo metabolic engineering strategies[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2020. 61: 215-224. |
| [58] | WANG P Y, ZHENG Y T, LI Y P, et al. Recent advances in biotransformation, extraction and green production of D-mannose[J]. Current Research in Food Science, 2022. 5: 49-56. |
| [59] | WICHELECKI D J, VETTING M W, CHOU L, et al. ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transport system solute-binding protein-guided identification of novel D-altritol and galactitol catabolic pathways in Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2015. 290(48): 28963-28976. |
| [60] | MORADIAN A and BENNER S A. A biomimetic biotechnological process for converting starch to fructose: thermodynamic and evolutionary considerations in applied enzymology[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1992. 114(18): 6980-6987. |
| [61] | WICHELECKI D J and ZHANG Y-H P, Enzymatic synthesis of D-tagatose : US62236226[P]. 2015-10-02. |
| [62] | ZHANG Y H, EVANS B R, MIELENZ J R, et al. High-yield hydrogen production from starch and water by a synthetic enzymatic pathway[J]. PLoS One, 2007. 2(5): e456. |
| [63] | HUANG H, PANDYA C, LIU C, et al. Panoramic view of a superfamily of phosphatases through substrate profiling[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2015. 112(16): 1974-1983. |
| [64] | 马延和, 孙媛霞, 杨建刚, al et, 一种全细胞催化制备塔格糖的方法 : CN107988286A[P]. 2017-11-02. |
| [65] | MA Y H, SUN Y X, YANG J G, al et, Engineering strain for producing tagatose, and construction method and application thereof : CN109666620B[P]. 2019-02-20. |
| [66] | MA Y H, SHI T, LI Y J, al et, Bacillus subtilis gene engineering bacteria for producing tagatose and method for preparing tagatose : CN112342179B[P]. 2021-01-05. |
| [67] | HAN P, WANG X, LI Y, et al. Synthesis of a healthy sweetener D-tagatose from starch catalyzed by semiartificial cell factories[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023. 71(8): 3813-3820. |
| [68] | LIU Y, QIAO Z, ZHANG H, et al. One-step whole-cell synthesis of D-tagatose from lactose catalyzed by recombinant Escherichia coli [J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2025. 41(5): 1974-1993. |
| [69] | DAI Y, ZHANG J, ZHANG T, et al. Characteristics of a fructose 6-phosphate 4-epimerase from Caldilinea aerophila DSM 14535 and its application for biosynthesis of tagatose[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2020. 139: 109594. |
| [70] | DAI Y W, LI M L, JIANG B, et al. Whole-cell biosynthesis of D-tagatose from maltodextrin by engineered Escherichia coli with multi-enzyme co-expression system[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2021. 145 |
| [71] | DAI Y, ZHANG T, JIANG B, et al. Dictyoglomus turgidum DSM 6724 alpha-Glucan phosphorylase: characterization and its application in multi-enzyme cascade reaction for D-tagatose production[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2021. 193(11): 3719-3731. |
| [72] | DAI Y, LI C, ZHENG L, et al. Enhanced biosynthesis of D-tagatose from maltodextrin through modular pathway engineering of recombinant Escherichia coli [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2022. 178: 108303. |
| [73] | CHEETHAM P S J and WOOTTON A N. Bioconversion of D-galactose into D-tagatose[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 1993. 15: 105-108. |
| [74] | CHEN J, WEI Y, NI D, et al. Biochemical characterization and biocatalytic application of a hyperthermostable tagatose 4-epimerase from Infirmifilum uzonense [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2025. 305(Pt 1): 141168. |
| [75] | LIU J J, ZHANG G C, KWAK S, et al. Overcoming the thermodynamic equilibrium of an isomerization reaction through oxidoreductive reactions for biotransformation[J]. Nature Communications, 2019. 10(1): 1356. |
| [76] | ZHANG G, AN Y, ZABED H M, et al. Rewiring Bacillus subtilis and bioprocess optimization for oxidoreductive reaction-mediated biosynthesis of D-tagatose[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023. 389: 129843. |
| [77] | LIU Z, WANG K, CHEN Y, et al. Third-generation biorefineries as the means to produce fuels and chemicals from CO2 [J]. Nature Catalysis, 2020. 3(3): 274-288. |
| [78] | WEYMOUTH-WILSON A C. The role of carbohydrates in biologically active natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 1997. 14(2): 99-110. |
| [79] | KEELING P L and MYERS A M. Biochemistry and genetics of starch synthesis[J]. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology, 2010. 1: 271-303. |
| [80] | CAI T, SUN H, QIAO J, et al. Cell-free chemoenzymatic starch synthesis from carbon dioxide[J]. Science, 2021. 373(6562): 1523-1527. |
| [81] | BLANKENSHIP R E, TIEDE D M, BARBER J, et al. Comparing photosynthetic and photovoltaic efficiencies and recognizing the potential for improvement[J]. Science, 2011. 332(6031): 805-809. |
| [82] | YANG J, ZHANG T, TIAN C, et al. Multi-enzyme systems and recombinant cells for synthesis of valuable saccharides: advances and perspectives[J]. Biotechnology advances, 2019. 37(7): 107406. |
| [83] | DESMONS S, GRAYSON-STEEL K, NUNEZ-DALLOS N, et al. Enantioselective reductive oligomerization of carbon dioxide into L-erythrulose via a chemoenzymatic catalysis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021. 143(39): 16274-16283. |
| [84] | YANG J, SONG W, CAI T, et al. De novo artificial synthesis of hexoses from carbon dioxide[J]. Science Bulletin, 2023. 68(20): 2370-2381. |
| [85] | ZHANG Y-H P J. The enlightenment of the chinese philosophy "Tao-Fa-Shu-Qi" to industrial biomanufacturing[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal 2023. 4: 1-11. |
| [86] | PAN Y, LIU Y, LONG T, et al. Biomanufacturing of inositol from corn stover with biological pretreatment by an in vitro synthetic biology platform[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2025. 13(1): 436-446. |
| [87] | CHENG K, ZHENG W, CHEN H, et al. Upgrade of wood sugar D-xylose to a value-added nutraceutical by in vitro metabolic engineering[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019. 52: 1-8. |
| [88] | YOU C, CHEN H, MYUNG S, et al. Enzymatic transformation of nonfood biomass to starch[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013. 110(18): 7182-7187. |
| [89] | TANG S, LIAO D, LI X, et al. Cell-free biosynthesis system: methodology and perspective of in vitro efficient platform for pyruvate biosynthesis and transformation[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2021. 10(10): 2417-2433. |
| [90] | ROLLIN J A, MARTIN DEL CAMPO J, MYUNG S, et al. High-yield hydrogen production from biomass by in vitro metabolic engineering: mixed sugars coutilization and kinetic modeling[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015. 112(16): 4964-4969. |
| [91] | OPGENORTH P H, KORMAN T P, and BOWIE J U. A synthetic biochemistry module for production of bio-based chemicals from glucose[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2016. 12(6): 393-395. |
| [92] | SHI T, LIU S, and ZHANG Y-H P J. CO2 fixation for malate synthesis energized by starch via in vitro metabolic engineering[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2019. 55: 152-160. |
| [93] | MOXLEY G and ZHANG Y-H P. More accurate determination of acid-labile carbohydrates in lignocellulose by modified quantitative saccharificatio[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2007. 21(6): 3684-3688. |
| [94] | 舒国伟, 张璐, 刘谕, et al. 玉米芯中提取木聚糖的研究[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2008. 043(002): 131-135. |
| [95] | 樊洪玉, 卫民, 赵剑, et al. 玉米芯木聚糖的提取及其相对分子质量分布研究[J]. 生物质化学工程, 2019. 53(3): 24-32. |
| [96] | 张以恒, 陈雪梅, and 韩平平. 生物制造的PE值与PX值:定义与应用[J]. 合成生物学, 2025. 6: 1-14. |
| [97] | YE J, LI Y J, BAI Y Q, et al. A facile and robust T7-promoter-based high-expression of heterologous proteins in Bacillus subtilis [J]. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 2022. 9(56): 1-12. |
| [98] | NINH P H, HONDA K, SAKAI T, et al. Assembly and multiple gene expression of thermophilic enzymes in Escherichia coli for in vitro metabolic engineering[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2015. 112(1): 189-196. |
| [99] | SHELDON R A and VAN PELT S. Enzyme immobilisation in biocatalysis: why, what and how[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2013. 42: 6223-6235. |
| [100] | BETANCOR L and LUCKARIFT H. Co-immobilized coupled enzyme systems in biotechnology[J]. Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering Reviews, 2010. 27: 95-114. |
| [101] | HAN P, YOU C, LI Y, et al. High-titer production of myo-inositol by a co-immobilized four-enzyme cocktail in biomimetic mineralized microcapsules[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023. 461: 141946. |
| [102] | 刘宗利, 王乃强, 王明珠, et al. 模拟移动床色谱分离技术在功能糖生产中的应用[J]. 中国食品添加剂, 2012. 23(S1): 200-204. |
| [103] | GABSI K, TRIGUI M, HELAL A N, et al. Simulated moving bed technology for the separation of fructose from date syrup[J]. International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology, 2015. 5(2): 1183-1190. |
| [104] | WANARSKA M KUR J. A method for the production of D-tagatose using a recombinant Pichia pastoris strain secreting beta-D-galactosidase from Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus and a recombinant L-arabinose isomerase from Arthrobacter sp. 22c[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2012. 11: 113. |
| [105] | KIM H J, RYU S A, KIM P, et al. A feasible enzymatic process for D-tagatose production by an immobilized thermostable L-arabinose isomerase in a packed-bed bioreactor[J]. Biotechnology Progress, 2003. 19(2): 400-404. |
| [106] | JORGENSEN F, HANSEN O C, and STOUGAARD P. Enzymatic conversion of D-galactose to D-tagatose: heterologous expression and characterisation of a thermostable L-arabinose isomerase from Thermoanaerobacter mathranii [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2004. 64(6): 816-822. |
| [107] | LEE D W, JANG H J, CHOE E A, et al. Characterization of a thermostable L-arabinose (D-galactose) isomerase from the hyperthermophilic eubacterium Thermotoga maritima [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2004. 70(3): 1397-1404. |
| [108] | WANG L, TAN Z, XIE X, et al. Discovery and characterization of a novel tagatose-4-epimerase[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2023. 63: 4197-4207. |
| [109] | XIA W, LIU S, HUANG L, et al. Reshaping the binding pocket of D-tagaturonate epimerase UxaE to improve the epimerization activity of C4-OH for enabling green synthesis of D-tagatose[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2024. 566: 114439. |
| [110] | MA Y H and SUN Y X, Tagatose preparation method : CN106399427A[P]. 2016-11-01. |
| [1] | Ding Yi, Su Min, Gao Xiaodong, Wang Ning. Advances in Research of N-Glycan Synthesis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-16. |
| [2] | WANG Kunkun, CHEN Hongyu, ZHANG Andong, LU Xiaoyun, TAN Dan. A preliminary study on the regulation and analysis of indole mediated bidirectional chemotaxis behavior of Escherichia coli [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-22. |
| [3] | YANG Shuai, XU YunDong, JIN Fan. Applications and Ethical Governance of Synthetic Biology in Medical Diagnosis and Treatment: Technological Breakthroughs and Value Boundaries [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-19. |
| [4] | CUI Zhongxin, WANG Yi, ZHANG Lei, QI Haishan. Engineering fungal antifreeze proteins through ‘EKylation’ and mechanism analysis [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-12. |
| [5] | LI Yi, LI Yinshuang, LI Shuang, LING Peixue, FANG Junqiang. Recent Progress on the in vitro Bio-transformation Synthesis of Human Milk Oligosaccharides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-16. |
| [6] | HUANG Yang, LI Yiye, NIE Guangjun. Synthetic Biology-Powered Cell Membrane-Derived Nanoparticles for Precision Theranostics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-24. |
| [7] | LI Quanfei, CHEN Qian, YANG Kai, LIU Hao, LI Sha, LEI Peng, GU Yian, SUN Liang, WANG Rui, XU Hong. Biosynthesis and applications of high-adhesion protein materials [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-20. |
| [8] | ZHU Yueming, YANG Jiangang, ZENG Yan, DONG Qianzhen, SUN Yuanxia. Advances and applications of in vitro biosynthesis of carbohydrates [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-16. |
| [9] | HU Die, XU Daozhu, LU Zhiyi, TANG Wei, FAN Bo, HE Yucai. Biosynthesis of xylo-oligosaccharides from wheat straw xylan via the synergistic hydrolysis by xylanase Xyn11A and arabinofuranosidase Abf62A [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-15. |
| [10] | MA Muqing, WU Yan, QU Maohua, LU Xiafeng, CAO Min, DU Feng, JI Rongtao, DONG Leichi, LUO Zhibo. Extracellular Multi-enzyme Assembly and Biocatalytic Cascade: Advances and Prospects [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-20. |
| [11] | XIAO He, YAO Mingju, QIAO Xue. Advances in the biosynthesis of long sugar-chain saponins [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, (): 1-7. |
| [12] | . [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 493-496. |
| [13] | YANG Ying, LI Xia, LIU Lizhong. Applications of synthetic biology to stem-cell-derived modeling of early embryonic development [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 669-684. |
| [14] | LI Mingchen, ZHONG Bozitao, YU Yuanxi, JIANG Fan, ZHANG Liang, TAN Yang, YU Huiqun, FAN Guisheng, HONG Liang. DeepSeek model analysis and its applications in AI-assistant protein engineering [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 636-650. |
| [15] | HUANG Yi, SI Tong, LU Anjing. Standardization for biomanufacturing: global landscape, critical challenges, and pathways forward [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 701-714. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||