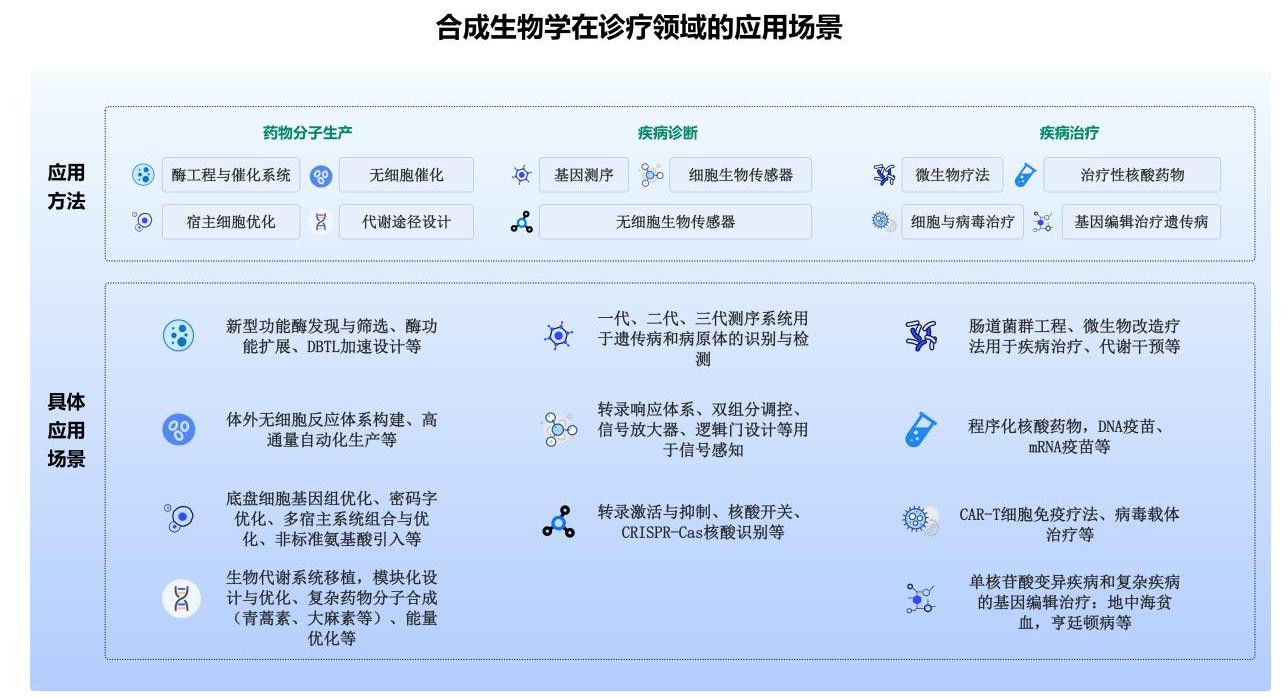
Applications and Ethical Governance of Synthetic Biology in Medical Diagnosis and Treatment: Technological Breakthroughs and Value Boundaries
YANG Shuai1,2, XU YunDong1,2, JIN Fan3
- 1.National Science Library (Chengdu),Chinese Academy of Sciences,Chengdu 610299
2.Department of Information Resources Management,School of Economics and Management,University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049
3.Institute of Synthetic Biology,Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenzhen 518055
-
Received:2025-04-08Revised:2025-07-30Published:2025-08-01 -
Contact:JIN Fan
合成生物学在医学诊疗中的应用与伦理治理:技术突破与价值边界
杨帅1,2, 徐韵东1,2, 金帆3
- 1.中国科学院成都文献情报中心 成都 610299
2.中国科学院大学经济与管理学院信息资源管理系 北京 100049
3.中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,合成生物学研究所,深圳 518055
-
通讯作者:金帆 -
作者简介:杨帅 (1990—),男,副研究员,硕士生导师。具有合成生物学与情报科学的交叉学科研究背景,主要研究方向包括:智能情报分析与决策;生物安全与科技伦理治理;生物技术预见与战略情报研究;AI驱动的科研情报挖掘与知识发现。金帆 (1978—),男,研究员,博士生导师。研究方向为微生物学合成生物学,包括人工合成细胞的设计与构建;基于环鸟苷二磷酸通用基因调控线路的创建;创建的可控生物底盘以及新型的基因线路去尝试解决和环境、健康直接相关的重大问题。E-mail:fan.jin@siat.ac.cn -
基金资助:中国科学院成都文献情报中心创新基金项目(E3Z0000903);四川省科技计划项目(2023JDR0329)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YANG Shuai, XU YunDong, JIN Fan. Applications and Ethical Governance of Synthetic Biology in Medical Diagnosis and Treatment: Technological Breakthroughs and Value Boundaries[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-033.
杨帅, 徐韵东, 金帆. 合成生物学在医学诊疗中的应用与伦理治理:技术突破与价值边界[J]. 合成生物学, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-033.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2025-033
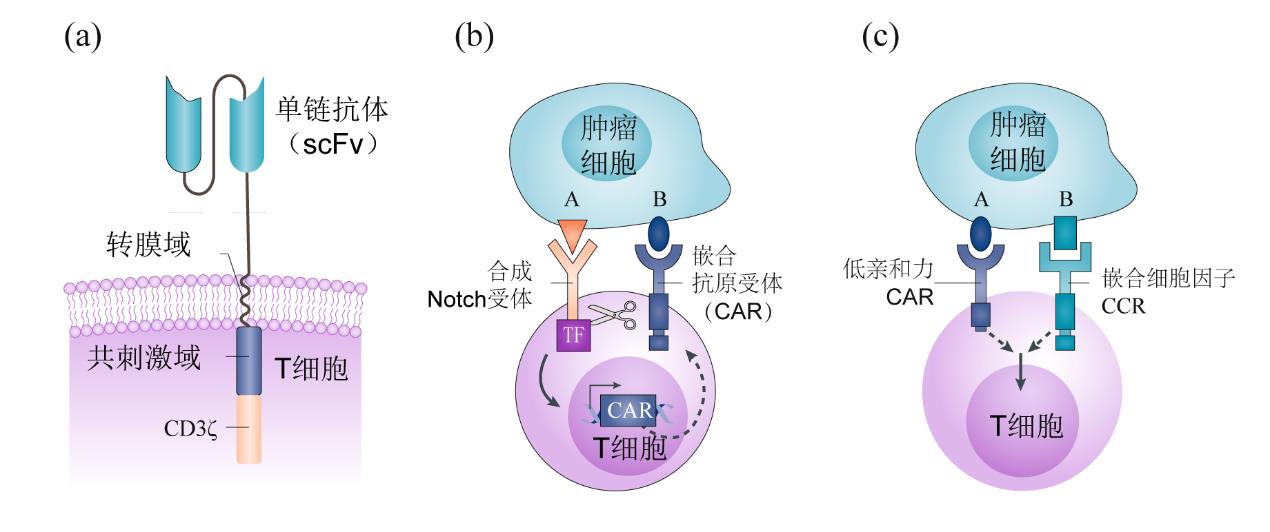
Fig. 3 Synthetic biology in the design of chimeric antigen receptors (CAR)a. The basic structure of second-generation CAR, highlighting the critical improvements of costimulatory domains on T cell function.b. An "AND gate" logic recognition system based on synNotch receptors (A AND B).c. An "AND gate" system based on CAR and CCR (chimeric costimulatory receptors).
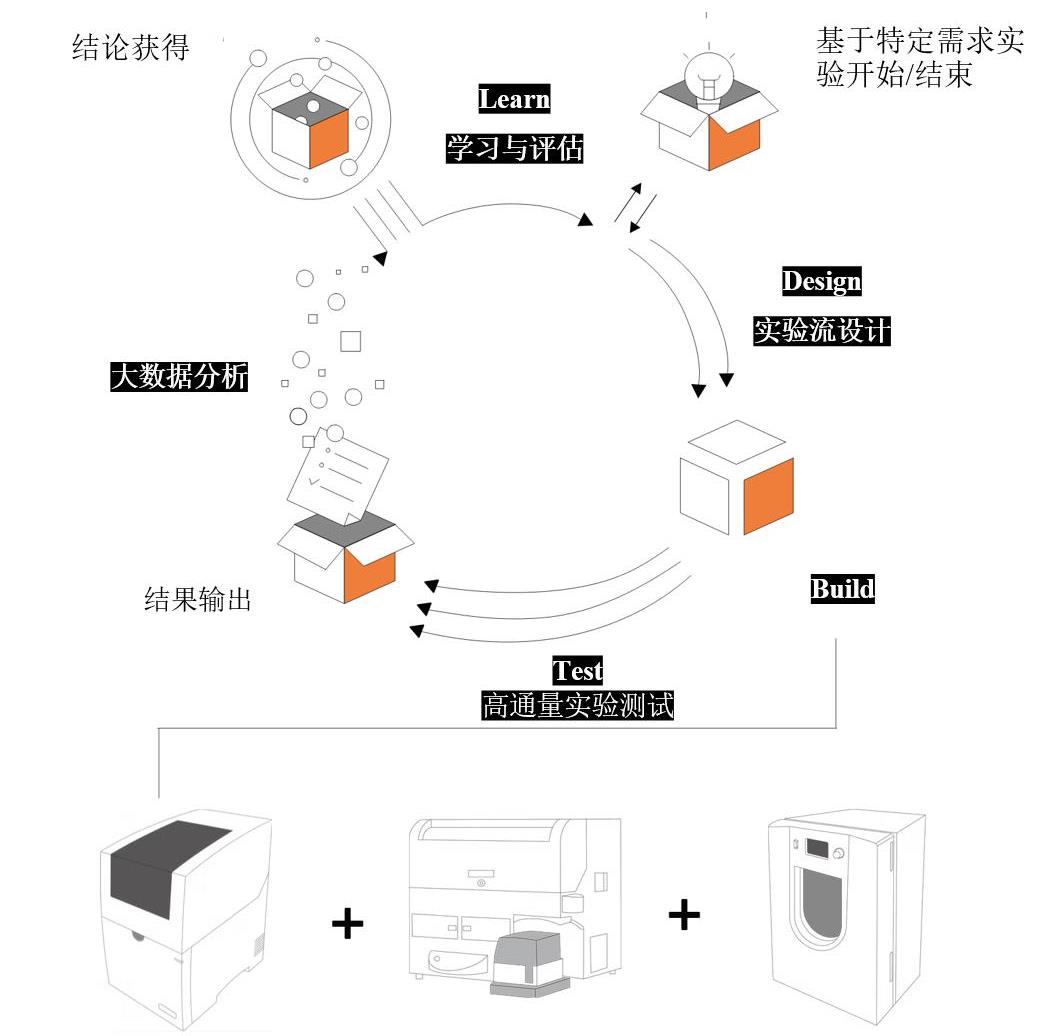
Fig. 4 Promoting the rapid translation of synthetic biology from laboratory research to diagnostic and therapeutic applications through iterative DBTL (Design–Build–Test–Learn) optimization supported by standardized synthetic biology facility platforms
| [1] | Cameron D. E.; Bashor C. J.; Collins J. J. A brief history of synthetic biology. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2014, 12 (5), 381-390. DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro3239 . |
| [2] | 袁伯川; 金义光.基于工程化细菌的活体生物药: 现状与未来[J].药学学报:1-34. |
| Bo-chuan Y., Yi-guang J.Living biotherapeutic products based on engineered bacteria:current status and future prospects[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica:1-34. | |
| [3] | Yan X.; Liu X.; Zhao C.; Chen G.-Q. Applications of synthetic biology in medical and pharmaceutical fields. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2023, 8 (1), 199. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01440-5 . |
| [4] | Ruder W. C.; Lu T.; Collins J. J. Synthetic Biology Moving into the Clinic. Science 2011, 333 (6047), 1248-1252. DOI: 10.1126/science.1206843 (acccessed 2025/04/03). |
| [5] | Le Duc S. The mechanism of life; Rebman Company, 1914. |
| [6] | Shapira P.; Kwon S.; Youtie J. Tracking the emergence of synthetic biology. Scientometrics 2017, 112 (3), 1439-1469. DOI: 10.1007/s11192-017-2452-5 From NLM . |
| [7] | Elowitz M. B.; Leibler S. A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators. Nature 2000, 403 (6767), 335-338. DOI: 10.1038/35002125 . |
| [8] | Gardner T. S.; Cantor C. R.; Collins J. J. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli. Nature 2000, 403 (6767), 339-342. DOI: 10.1038/35002131 . |
| [9] | Mukherji S.; van Oudenaarden A. Synthetic biology: understanding biological design from synthetic circuits. Nature Reviews Genetics 2009, 10 (12), 859-871. DOI: 10.1038/nrg2697 . |
| [10] | 李雨蒙; 田旭彤; 罗掬月; 鲍彤彤; 吴信.烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸(NAD+)合成代谢及其调控机体衰老研究进展[J].中国科学:生命科学,2025,55(04):596-606. |
| YuMeng L., XuTong T., JuYue L., TongTong B., Xin W.Advances in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)anabolism and itsregulation of aging[J]. Scientia Sinica(Vitae), 2025,55(04):596-606. | |
| [11] | Khoshnood S.; Ghanavati R.; Shirani M.; Ghahramanpour H.; Sholeh M.; Shariati A.; Sadeghifard N.; Heidary M. Viral vector and nucleic acid vaccines against COVID-19: A narrative review. Frontiers in Microbiology 2022, 13, Review. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.984536 . |
| [12] | Wang Z.; Koirala B.; Hernandez Y.; Zimmerman M.; Brady S. F. Bioinformatic prospecting and synthesis of a bifunctional lipopeptide antibiotic that evades resistance. Science 2022, 376 (6596), 991-996. DOI: doi:10.1126/science.abn4213 . |
| [13] | Zhang X.; Zhang H.; Lan H.; Wu J.; Xiao Y. CAR-T cell therapy in multiple myeloma: Current limitations and potential strategies. Frontiers in Immunology 2023, 14, Review. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1101495 . |
| [14] | Bashor C. J.; Hilton I. B.; Bandukwala H.; Smith D. M.; Veiseh O. Engineering the next generation of cell-based therapeutics. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2022, 21 (9), 655-675. DOI: 10.1038/s41573-022-00476-6 . |
| [15] | 史天宇; 孟凡岩.基于合成生物学的CAR-T细胞治疗实体肿瘤的研究进展[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2023,30(03):261-266. |
| Tianyu S., Fanyan M.Research progress of synthetic biology-based CAR-T cell therapy for solid tumors[J]. Chinese Journal of Cancer Biotherapy, 2023,30(03):261-266. | |
| [16] | Inda M. E.; Mimee M.; Lu T. K. Cell-based biosensors for immunology, inflammation, and allergy. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2019, 144 (3), 645-647. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.07.024 (acccessed 2025/04/03). |
| [17] | Zhao N.; Song Y.; Xie X.; Zhu Z.; Duan C.; Nong C.; Wang H.; Bao R. Synthetic biology-inspired cell engineering in diagnosis, treatment and drug development. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2023, 8 (1), 112. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01375-x . |
| [18] | Tan X.; Letendre J. H.; Collins J. J.; Wong W. W. Synthetic biology in the clinic: engineering vaccines, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Cell 2021, 184 (4), 881-898. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.017 . |
| [19] | Feng Y.; Su C.; Mao G.; Sun B.; Cai Y.; Dai J.; Ma Y. When synthetic biology meets medicine. Life Medicine 2024, 3 (1). DOI: 10.1093/lifemedi/lnae010 (acccessed 4/2/2025). |
| [20] | Nazir A.; Hussain F. H. N.; Raza A. Advancing microbiota therapeutics: the role of synthetic biology in engineering microbial communities for precision medicine. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2024, 12, 1511149. |
| [21] | 杜治政.医学技术发展的新阶段:医学新质高技术[J].医学与哲学,2025,46(04):1-9. |
| Zhizheng D.A New Stage in Medical Technology Development: Medical New-quality Advanced Technology[J]. Medicine & Philosophy, 2025,46(04):1-9. | |
| [22] | Philp J. C. Emerging policy issues in synthetic biology. Industrial Biotechnology 2014, 10 (4), 256-258. |
| [23] | Kaebnick G. E. Synthetic biology and morality: Artificial life and the bounds of nature; MIT Press, 2013. |
| [24] | Marchant G. E. The growing gap between emerging technologies and the law. The growing gap between emerging technologies and legal-ethical oversight: The pacing problem 2011, 19-33. |
| [25] | 王琳琳; 李红玲.CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑技术在精准肿瘤学研究中的应用[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2024,31(05):519-527. |
| Linlin W., Hongling L.Application of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology in the research of precisiononcology[J]. Chinese Journal of Cancer Biotherapy, 2024,31(05):519-527. | |
| [26] | Dever D. P.; Bak R. O.; Reinisch A.; Camarena J.; Washington G.; Nicolas C. E.; Pavel-Dinu M.; Saxena N.; Wilkens A. B.; Mantri S.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9 β-globin gene targeting in human haematopoietic stem cells. Nature 2016, 539 (7629), 384-389. DOI: 10.1038/nature20134 . |
| [27] | Yang S.; Chang R.; Yang H.; Zhao T.; Hong Y.; Kong H. E.; Sun X.; Qin Z.; Jin P.; Li S.; Li X.-J. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing ameliorates neurotoxicity in mouse model of Huntington's disease. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 2017, 127 (7), 2719-2724. DOI: 10.1172/JCI92087 . |
| [28] | Rafeeq M. M.; Murad H. A. S. Cystic fibrosis: current therapeutic targets and future approaches. Journal of Translational Medicine 2017, 15 (1), 84. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-017-1193-9 . |
| [29] | Krokan H. E.; Bjørås M. Base Excision Repair. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 2013, 5 (4). DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012583 . |
| [30] | Geurts M. H.; de Poel E.; Amatngalim G. D.; Oka R.; Meijers F. M.; Kruisselbrink E.; van Mourik P.; Berkers G.; de Winter-de Groot K. M.; Michel S.; et al. CRISPR-Based Adenine Editors Correct Nonsense Mutations in a Cystic Fibrosis Organoid Biobank. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26 (4), 503-510.e507. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.01.019 (acccessed 2025/04/04). |
| [31] | Chemello F.; Chai A. C.; Li H.; Rodriguez-Caycedo C.; Sanchez-Ortiz E.; Atmanli A.; Mireault A. A.; Liu N.; Bassel-Duby R.; Olson E. N. Precise correction of Duchenne muscular dystrophy exon deletion mutations by base and prime editing. Science Advances 2021, 7 (18), eabg4910. DOI: doi:10.1126/sciadv.abg4910 . |
| [32] | Li M.; Lin Y.; Cheng Q.; Wei T. Prime Editing: A Revolutionary Technology for Precise Treatment of Genetic Disorders. Cell Proliferation 2025, 58 (4), e13808. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.13808 . |
| [33] | Flanigan K. M.; Dunn D. M.; von Niederhausern A.; Soltanzadeh P.; Gappmaier E.; Howard M. T.; Sampson J. B.; Mendell J. R.; Wall C.; King W. M.; et al. Mutational spectrum of DMD mutations in dystrophinopathy patients: application of modern diagnostic techniques to a large cohort. Human Mutation 2009, 30 (12), 1657-1666. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.21114 |
| [34] | Chen P. J.; Liu D. R. Prime editing for precise and highly versatile genome manipulation. Nature Reviews Genetics 2023, 24 (3), 161-177. DOI: 10.1038/s41576-022-00541-1 . |
| [35] | Zhou M.; Tang S.; Duan N.; Xie M.; Li Z.; Feng M.; Wu L.; Hu Z.; Liang D. Targeted-Deletion of a Tiny Sequence via Prime Editing to Restore SMN Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23 (14), 7941. |
| [36] | Yuan Q.; Gao X. Multiplex base- and prime-editing with drive-and-process CRISPR arrays. Nature Communications 2022, 13 (1), 2771. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30514-1 . |
| [37] | Pinglay S.; Lalanne J .-B.; Daza R. M.; Kottapalli S.; Quaisar F.; Koeppel J.; Garge R. K.; Li X.; Lee D. S.; Shendure J. Multiplex generation and single-cell analysis of structural variants in mammalian genomes. Science 387 (6733), eado5978. DOI: 10.1126/science.ado5978 (acccessed 2025/04/04). |
| [38] | Kalhor R.; Kalhor K.; Mejia L.; Leeper K.; Graveline A.; Mali P.; Church G. M. Developmental barcoding of whole mouse via homing CRISPR. Science 2018, 361 (6405), eaat9804. DOI: doi:10.1126/science.aat9804 . |
| [39] | Cho J. H.; Collins J. J.; Wong W. W. Universal Chimeric Antigen Receptors for Multiplexed and Logical Control of T Cell Responses. Cell 2018, 173 (6), 1426-1438.e1411. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.038 (acccessed 2025/04/04). |
| [40] | Lajoie M. J.; Boyken S. E.; Salter A. I.; Bruffey J.; Rajan A.; Langan R. A.; Olshefsky A.; Muhunthan V.; Bick M. J.; Gewe M.; et al. Designed protein logic to target cells with precise combinations of surface antigens. Science 2020, 369 (6511), 1637-1643. DOI: doi:10.1126/science.aba6527 . |
| [41] | Labanieh L.; Mackall, immune cells C. L. CAR : principles design, resistance and the next generation. Nature 2023, 614 (7949), 635-648. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-05707-3 . |
| [42] | Magee M. S.; Snook A. Challenges to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy for cancer. Discovery Medicine 2014, 18 (100), 265-271. |
| [43] | Chung J. B.; Brudno J. N.; Borie D.; Kochenderfer J. N. Chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy for autoimmune disease. Nature Reviews Immunology 2024, 24 (11), 830-845. DOI: 10.1038/s41577-024-01035-3 . |
| [44] | Wu M.-R.; Jusiak B.; Lu T. K. Engineering advanced cancer therapies with synthetic biology. Nature Reviews Cancer 2019, 19 (4), 187-195. DOI: 10.1038/s41568-019-0121-0 . |
| [45] | Thirumalaisamy R.; Vasuki S.; Sindhu S. M.; Mothilal T. M.; Srimathi V.; Poornima B.; Bhuvaneswari M.; Hariharan M. FDA-Approved Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T Cell Therapy for Different Cancers-A Recent Perspective. Molecular Biotechnology 2025, 67 (2), 469-483. DOI: 10.1007/s12033-024-01090-0 . |
| [46] | Li H .-S.; Wong N. M.; Tague E.; Ngo J. T.; Khalil A. S.; Wong W. W. High-performance multiplex drug-gated CAR circuits. Cancer Cell 2022, 40 (11), 1294-1305.e1294. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.08.008 (acccessed 2025/04/04). |
| [47] | Kosti P.; Opzoomer J. W.; Larios-Martinez K. I.; Henley-Smith R.; Scudamore C. L.; Okesola M.; Taher M. Y. M.; Davies D. M.; Muliaditan T.; Larcombe-Young D.; et al. Hypoxia-sensing CAR T cells provide safety and efficacy in treating solid tumors. Cell Reports Medicine 2021, 2 (4). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100227 (acccessed 2025/04/04). |
| [48] | 卢俊南; 罗周卿; 姜双英; 沈玥; 吴毅; 杨焕明; 元英进; 戴俊彪.DNA的合成、组装及转移技术[J].中国科学院院刊,2018,33(11):1174-1183. |
| Junnan L., Zhouqing L., Shuangying J., Yue S., Yi W., Huanming Y., Yingjin Y., Junbiao D.Technologies for DNA Synthesis, Assembly, and Transplantation[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018,33(11):1174-1183. | |
| [49] | 李诗渊; 赵国屏; 王金.合成生物学技术的研究进展——DNA合成、组装与基因组编辑[J].生物工程学报,2017,33(03):343-360. |
| Li S., Zhao G., Wang J.Enabling technologies in synthetic biology——DNA synthesis,assembly and editing[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2017,33(03):343-360. | |
| [50] | Yadav M.; Chauhan N. S. Overview of the rules of the microbial engagement in the gut microbiome: a step towards microbiome therapeutics. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2021, 130 (5), 1425-1441. DOI: 10.1111/jam.14883 (acccessed 4/3/2025). |
| [51] | Gibson D. G.; Young L.; Chuang R.-Y.; Venter J. C.; Hutchison C. A.; Smith H. O. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nature Methods 2009, 6 (5), 343-345. DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1318 . |
| [52] | Engler C.; Kandzia R.; Marillonnet S. A One Pot, One Step, Precision Cloning Method with High Throughput Capability. PLOS ONE 2008, 3 (11), e3647. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003647 . |
| [53] | Semkum P.; Thangthamniyom N.; Chankeeree P.; Keawborisuth C.; Theerawatanasirikul S.; Lekcharoensuk P. The Application of the Gibson Assembly Method in the Production of Two pKLS3 Vector-Derived Infectious Clones of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus. Vaccines 2023, 11 (6), 1111. |
| [54] | Hoose A.; Vellacott R.; Storch M.; Freemont P. S.; Ryadnov M. G. DNA synthesis technologies to close the gene writing gap. Nature Reviews Chemistry 2023, 7 (3), 144-161. DOI: 10.1038/s41570-022-00456-9 . |
| [55] | 彭鹏; 陈明海; 李芹; 张先恩.合成启动子:理论、设计与展望[J].生物工程学报:1-37. |
| Peng P., Minghai C., Qin L., Xian'en Z.Synthetic promoters: theory, design, and prospects[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology:1-37. | |
| [56] | Robinson, P. K. Enzymes: principles and biotechnological applications. Essays in Biochemistry 2015, 59, 1-41. DOI: 10.1042/bse0590001 (acccessed 4/3/2025). |
| [57] | Kavita K.; Breaker R. R. Discovering riboswitches: the past and the future. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 2023, 48 (2), 119-141. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.08.009 (acccessed 2025/04/03). |
| [58] | Santarpia G.; Carnes E. Therapeutic Applications of Aptamers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2024, 25 (12), 6742. |
| [59] | Yu Y.; Jain B.; Anand G.; Heidarian M.; Lowe A.; Kalra A. Technologies for non-invasive physiological sensing: Status, challenges, and future horizons. Biosensors and Bioelectronics: X 2024, 16, 100420. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosx.2023.100420 . |
| [60] | 方建军; 汪新; 钟卫鸿.微生物法生产鸟氨酸的代谢工程研究进展[J].食品研究与开发,2008,(11):182-185. |
| Jian-jun F., Xin W., Wei-hong Z.PROGRESS OF APPLICATION OF METEBOLIC ENGINEERING IN MICROBIAL BIOSYNTHESIS OF ORNITHINE[J]. Food Research and Development, 2008,(11):182-185. | |
| [61] | 张世哲; 江鸿标; 卢玥晴; 马慧慧; 陈亮宇; 赵心清; 苏春.抗补体活性物质临床应用及开发研究进展[J].微生物学通报,2022,49(06):2347-2361. |
| Shizhe Z., Hongbiao J., Yueqing L., Huihui M., Liangyu C., Xinqing Z., Chun S.Clinical application and development of anti-complementagents: a review[J]. Microbiology China, 2022,49(06):2347-2361. | |
| [62] | 杨博楠; 刘春立; 郝云鹏; 许广博; 刘秀霞; 杨艳坤; 白仲虎.代谢工程改造大肠杆菌从头合成木香烃内酯[J].食品与发酵工业:1-9. |
| Bonan Y., Chunli L., Yunpeng H., Guangbo X., Xiuxia L., Yankun Y., Zhonghu B.Metabolic engineering Escherichia coli for de novo biosynthesis of costunolide[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries:1-9. | |
| [63] | 李国民; 闫思翰; 尤甲甲; 饶志明.代谢工程改造大肠杆菌高效合成l-缬氨酸[J].生物工程学报:1-20. |
| Guomin L., Sihan Y., Jiajia Y., Zhiming R.Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for efficientproduction of L-valine[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology:1-20. | |
| [64] | 徐龙兴; 孙悦嘉; 张玮辰; 庞昆; 刘鹏才; 刘顺成; 袁丽杰.代谢工程改造解脂耶氏酵母合成β-榄香烯及其发酵优化[J].食品与发酵工业:1-9. |
| Longxing X., Yuejia S., Weichen Z., Kun P., Pengcai L., Shuncheng L., Lijie Y.Metabolic engineering and medium optimization for β-elemene production inYarrowia lipolytica[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries:1-9. | |
| [65] | 盛华康; 张博; 申晓林; 孙新晓; 王佳; 袁其朋.微生物合成白藜芦醇及其衍生物[J].化工进展:1-16. |
| Huakang S., Bo Z., Xiaolin S., Xinxiao S., Jia W., Qipeng Y.Microbial synthesis of resveratrol and its derivatives[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress:1-16. | |
| [66] | Lee D.-H.; Kim H.; Sung B.-H.; Cho B. K.; Lee S.-G. Biofoundries: Bridging Automation and Biomanufacturing in Synthetic Biology. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering 2023, 28 (6), 892-904. DOI: 10.1007/s12257-023-0226-x . |
| [67] | Zhang R.; Huang Y.; Li M.; Wang L.; Li B.; Xia A.; Li Y.; Yang S.; Jin F. High-throughput, microscopy-based screening and quantification of genetic elements. mLife 2023, 2 (4), 450-461. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/mlf2.12096 . |
| [68] | Crone M. A.; Priestman M.; Ciechonska M.; Jensen K.; Sharp D. J.; Anand A.; Randell P.; Storch M.; Freemont P. S. A role for Biofoundries in rapid development and validation of automated SARS-CoV-2 clinical diagnostics. Nature Communications 2020, 11 (1), 4464. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18130-3 . |
| [69] | Fu S.; Zhang R.; Gao Y.; Xiong J.; Li Y.; Pu L.; Xia A.; Jin F. Programming the lifestyles of engineered bacteria for cancer therapy. National Science Review 2023, 10 (5). DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwad031 (acccessed 4/6/2025). |
| [70] | Li H.; Yang Y.; Hong W.; Huang M.; Wu M.; Zhao X. Applications of genome editing technology in the targeted therapy of human diseases: mechanisms, advances and prospects. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2020, 5 (1), 1. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-019-0089-y . |
| [71] | Kurtoğlu A.; Yıldız A.; Arda B. The view of synthetic biology in the field of ethics: a thematic systematic review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2024, 12, 1397796. DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1397796 From NLM . |
| [72] | Ou Y.; Guo S. Safety risks and ethical governance of biomedical applications of synthetic biology. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2023, 11, Policy and Practice Reviews. DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1292029 . |
| [73] | Segers S. Heritable genome editing: ethical aspects of a developing domain. Human Reproduction 2023, 38 (11), 2055-2061. DOI: 10.1093/humrep/dead167 (acccessed 4/2/2025). |
| [74] | 陈天; 赵旭.当代生命科技的身体伦理学反思——以干细胞、脑科学和合成生物学为例[J].医学与哲学,2024,45(12):11-15+33. |
| Tian C., Xu Z.Reflections on Contemporary Life Science Technology Based on Ethics of the Body: Take Stem Cells Technology, BrainScience Research and Synthetic Biology Researches as the Examples[J]. Medicine & Philosophy, 2024,45(12):11-15+33. | |
| [75] | 张巍巍; 管同.基因治疗伦理研究的主题聚类与演进[J].医学与哲学,2025,46(04):39-44. |
| Weiwei Z., Tong G.Thematic Clustering and Evolution of Gene Therapy Ethical Research[J]. Medicine & Philosophy, 2025,46(04):39-44. | |
| [76] | Duan D. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Gene Therapy in 2023: Status, Perspective, and Beyond. Human Gene Therapy 2023, 34 (9-10), 345-349. DOI: 10.1089/hum.2023.29242.ddu (acccessed 2025/04/05). |
| [77] | Lek A.; Wong B.; Keeler A.; Blackwood M.; Ma K.; Huang S.; Sylvia K.; Batista A. R.; Artinian R.; Kokoski D.; et al. Unexpected Death of a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Patient in an N-of-1 Trial of rAAV9-delivered CRISPR-transactivator. medRxiv 2023, 2023.2005.2016.23289881. DOI: 10.1101/2023.05.16.23289881 . |
| [78] | Marshall E. Gene Therapy Death Prompts Review of Adenovirus Vector. Science 1999, 286 (5448), 2244-2245. DOI: doi:10.1126/science.286.5448.2244 . |
| [79] | Marshal E. FDA Halts All Gene Therapy Trials at Penn. Science 2000, 287 (5453), 565-567. DOI: doi:10.1126/science.287.5453.565b . |
| [80] | 何包钢; 吴进进.中国公众对基因编辑技术的态度及其转变——以构建多元协商治理体系为视角[J].学习与探索,2025,(02):33-43+175+172. |
| Baogang H., Jinjin W.China's Public Attitudes Toward Gene Editing and Transformation--From the Perspective of Constructing a Diversified Consultative Governance System[J]. Study & Exploration, 2025,(02):33-43+175+172. | |
| [81] | Killingley B.; Mann A. J.; Kalinova M.; Boyers A.; Goonawardane N.; Zhou J.; Lindsell K.; Hare S. S.; Brown J.; Frise R.; et al. Safety, tolerability and viral kinetics during SARS-CoV-2 human challenge in young adults. Nature Medicine 2022, 28 (5), 1031-1041. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-01780-9 . |
| [82] | Williams E.; Craig K.; Chiu C.; Davies H.; Ellis S.; Emerson C.; Jamrozik E.; Jefford M.; Kang G.; Kapulu M.; et al. Ethics review of COVID-19 human challenge studies: A joint HRA/WHO workshop. Vaccine 2022, 40 (26), 3484-3489. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.02.004 . |
| [83] | Organization W. H. Laboratory biosafety manual ; World Health Organization, 2004. |
| [84] | Pei L.; Garfinkel M.; Schmidt M. Bottlenecks and opportunities for synthetic biology biosafety standards. Nature Communications 2022, 13 (1), 2175. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29889-y . |
| [85] | 左锟澜; 邹诗施; 吴宗震; 国原源; 徐雁龙; 刘欢.病原体相关合成生物学的生物安全风险和应对策略研究[J].中国生物工程杂志,2023,43(09):120-130. |
| Kun-lan Z., Shi-shi Z., Zong-zhen W., Yuan-yuan G., Yan-long X., Huan L.Biosafety Risks and Countermeasures of Pathogen Related Synthetic Biology[J]. China Biotechnology, 2023,43(09):120-130. | |
| [86] | Hewett J. P.; Wolfe A. K.; Bergmann R. A.; Stelling S. C.; Davis K. L. Human Health and Environmental Risks Posed by Synthetic Biology R&D for Energy Applications: A Literature Analysis. Applied Biosafety 2016, 21 (4), 177-184. DOI: 10.1177/1535676016672377 (acccessed 2025/04/05). |
| [87] | Sciences N. A. o.; Medicine; Earth D. o.; Studies L.; Sciences B. o. L.; Sciences B. o. C.; Identifying C. o. S. f.; Biology A. P. B. V. P. b. S. Biodefense in the age of synthetic biology; National Academies Press, 2018. |
| [88] | Chen D .-Y.; Kenney D.; Chin C. V.; Tavares A. H.; Khan N.; Conway H. L.; Liu G.; Choudhary M. C.; Gertje H. P.; O'Connell A. K.; et al. Role of spike in the pathogenic and antigenic behavior of SARS-CoV-2 BA.1 Omicron. bioRxiv 2023, 2022.2010.2013.512134. DOI: 10.1101/2022.10.13.512134 . |
| [89] | Melin A. Overstatements and Understatements in the Debate on Synthetic Biology, Bioterrorism and Ethics. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2021, 9, Perspective. |
| [90] | Eslami E.; Siamian H.; Rezaei Orimi J.; Aghabeiglooei Z.; Salimi-Sabour E.; Amrollahi-Sharifabadi M. Pattern of bioterrorism in ancient times: lessons to be learned from the microbial and toxicological aspects. Wiener Medizinische Wochenschrift 2024, 174 (13), 288-298. DOI: 10.1007/s10354-023-01029-1 . |
| [91] | Poor Toulabi B. The Myth of the "Poor Man's Atomic Bomb": Knowledge, Method, and Ideology in the Study of Chemical, Biological, and Nuclear Weapons. Journal of Global Security Studies 2023, 8 (1). DOI: 10.1093/jogss/ogac037 (acccessed 4/5/2025). |
| [92] | Ikemoto, DIY Bio L. C. : hacking life in biotech's backyard. UCDL Rev. 2017, 51, 539. |
| [93] | Landrain T.; Meyer M.; Perez A. M.; Sussan R. Do-it-yourself biology: challenges and promises for an open science and technology movement. Systems and Synthetic Biology 2013, 7 (3), 115-126. DOI: 10.1007/s11693-013-9116-4 . |
| [94] | Bohua L.; Yuexin W.; Yakun O.; Kunlan Z.; Huan L.; Ruipeng L. Ethical framework on risk governance of synthetic biology. Journal of Biosafety and Biosecurity 2023, 5 (2), 45-56. |
| [95] | 张娟娟; 卢阳旭; 赵延东; 何光喜."基因治疗"还是"基因增强"?——公众对基因编辑技术的接受度及其影响因素[J].科学与社会,2023,13(02):107-122. |
| Juan-juan Z., Yang-xu L., Yan-dong Z., Guang-xi H.'Gene Therapy' or 'Gene Enhancement'?—Public acceptance of gene editing technology andits influencing factors[J]. Science and Society, 2023,13(02):107-122. | |
| [96] | 张慧; 闫瑞峰.基因编辑技术与合成生物技术的伦理问题比较[J].科技导报,2022,40(18):56-62. |
| Hui Z., Ruifeng Y.Comparison of ethical issues between gene editing technology andsynthetic biology technology[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2022,40(18):56-62. | |
| [97] | Baylis F. Human genome editing. Issues in Science and Technology 2019, 35 (3), 42-44. |
| [98] | Silver L. M.; Silver S. R. Confused heritage and the absurdity of genetic ownership. Harv. JL & Tech. 1997, 11, 593. |
| [99] | Feeney O.; Julian C.; Michael M.; Lisa D.; Kristof V. A.; and Sterckx S. Patenting Foundational Technologies: Lessons From CRISPR and Other Core Biotechnologies. The American Journal of Bioethics 2018, 18 (12), 36-48. DOI: 10.1080/15265161.2018.1531160 . |
| [100] | Buchanan A.; Brock D. W. From chance to choice: Genetics and justice; Cambridge University Press, 2000. |
| [101] | Conrad D. F.; Keebler J. E. M.; DePristoM. A.; LindsayS. J.; ZhangY.; CasalsF.; IdaghdourY.; HartlC. L.; TorrojaC.; GarimellaK. V.; et al. Variation in genome-wide mutation rates within and between human families. Nature Genetics 2011, 43 (7), 712-714. DOI: 10.1038/ng.862 . |
| [102] | Auton A.; Abecasis G. R.; Altshuler D. M.; Durbin R. M.; Abecasis G. R.; Bentley D. R.; Chakravarti A.; Clark A. G.; Donnelly P.; Eichler E. E.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526 (7571), 68-74. DOI: 10.1038/nature15393 . |
| [103] | 朱菊隐; 展进涛.合成生物学科技风险的管理与规制:国际防范逻辑与中国应对策略[J].科技管理研究,2023,43(10):36-42. |
| Juyin Z., Jintao Z.Management and Regulation of Scientific and Technological Risks in Synthetic Biology:International Preventive Logic and China's Response Strategy[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2023,43(10):36-42. | |
| [104] | 薛杨; 俞晗之.前沿生物技术发展的安全威胁:应对与展望[J].国际安全研究,2020,38(04):136-156+160. |
| Yang X., Hanzhi Y.Security Threats Associated with the Cutting-edge Biotechnology:Responses and Prospects[J]. Journal of International Security Studies, 2020,38(04):136-156+160. | |
| [105] | Feinberg J. The child's right to an open future. In Justice, politics, and the family, Routledge, 2015; pp 145-158. |
| [106] | Oakley, Choosing Children J. : Genes, Disability, and Design. JSTOR: 2008. |
| [107] | COUNCIL O. E. Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being with regard to the Application of Biology and Medicine: Convention on Human Rights and Biomedicine. Oviedo: COE 1997. |
| [108] | Raposo, Gene Editing V. L., the Mystic Threat to Human Dignity. Journal of Bioethical Inquiry 2019, 16 (2), 249-257. DOI: 10.1007/s11673-019-09906-4 . |
| [109] | Cutas D.-E. Looking for the Meaning of Dignity in the Bioethics Convention and the Cloning Protocol. Health Care Analysis 2005, 13 (4), 303-313. DOI: 10.1007/s10728-005-8127-z . |
| [110] | WOOPEN C.; NYS, H.; O'SULLIVAN S. Opinion on Ethics of Genome Editing. |
| [111] | Rohregger R.; Sganzerla A.; Simão-Silva D. P. Synthetic biology and genetic manipulation: risks, promises and responsibilities. Ambiente & Sociedade 2020, 23, e01963. |
| [112] | Jasanoff S.; Hurlbut J. B.; Saha K. CRISPR democracy: Gene editing and the need for inclusive deliberation. Issues in Science and Technology 2015, 32 (1), 25-32. |
| [113] | König H. The illusion of control in germline-engineering policy. Nature Biotechnology 2017, 35 (6), 502-506. DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3884 . |
| [114] | Ethikrat D. Intervening in the human germline. Opinion-Executive summary & recommendations 2019. |
| [115] | Organization W. H. Human genome editing: Position paper. In Human genome editing: position paper, 2021. |
| [116] | Society T. R.; Medicine N. A. o.; Editing I. C. o. t. C. U. o. H. G. G. Heritable Human Genome Editing; National Academies Press, 2021. |
| [117] | Almeida M.; Ranisch R. Beyond safety: mapping the ethical debate on heritable genome editing interventions. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications 2022, 9 (1), 139. DOI: 10.1057/s41599-022-01147-y . |
| [118] | Waltz E. First results from us trial of genetically modified mosquitoes. Nature 2022, 604, 608-609. |
| [119] | Association W. M. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310 (20), 2191-2194. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2013.281053 (acccessed 4/6/2025). |
| [120] | Berg C. Sustainable action: Overcoming the barriers; Routledge, 2019. |
| [121] | Harrington L. M. B. Sustainability Theory and Conceptual Considerations: A Review of Key Ideas for Sustainability, and the Rural Context. Papers in Applied Geography 2016, 2 (4), 365-382. DOI: 10.1080/23754931.2016.1239222 . |
| [122] | Munthe C.; Fumagalli D.; Malmqvist E. Sustainability principle for the ethics of healthcare resource allocation. Journal of Medical Ethics 2021, 47 (2), 90. DOI: 10.1136/medethics-2020-106644 . |
| [123] | Zwart H.; Landeweerd L.; van Rooij A. Adapt or perish? Assessing the recent shift in the European research funding arena from 'ELSA' to 'RRI'. Life Sciences, Society and Policy 2014, 10 (1), 11. DOI: 10.1186/s40504-014-0011-x . |
| [124] | Holm S.; Stokes, Precautionary Principle. E. In Encyclopedia of Applied Ethics (Second Edition), Chadwick, R. Ed.; Academic Press, 2012; pp 569-575. |
| [125] | Gregorowius D.; Deplazes-Zemp A. Societal impact of synthetic biology: responsible research and innovation (RRI). Essays in Biochemistry 2016, 60 (4), 371-379. DOI: 10.1042/EBC20160039 (acccessed 4/6/2025). |
| [126] | Grunwald A. Synthetic biology as technoscience and the EEE concept of responsibility. In Synthetic biology: character and impact, Springer, 2014; pp 249-265. |
| [127] | Chan S. Research Translation and Emerging Health Technologies: Synthetic Biology and Beyond. Health Care Analysis 2018, 26 (4), 310-325. DOI: 10.1007/s10728-016-0334-2 . |
| [128] | Newson A. J. Current Ethical Issues in Synthetic Biology: Where Should We Go from Here? Accountability in Research 2011, 18 (3), 181-193. DOI: 10.1080/08989621.2011.575035 . |
| [129] | Selin, C. The Sociology of the Future: Tracing Stories of Technology and Time. Sociology Compass 2008, 2 (6), 1878-1895. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-9020.2008.00147.x |
| [130] | Betten A. W.; Rerimassie V.; Broerse J. E. W.; Stemerding D.; Kupper F. Constructing future scenarios as a tool to foster responsible research and innovation among future synthetic biologists. Life Sciences, Society and Policy 2018, 14 (1), 21. DOI: 10.1186/s40504-018-0082-1 . |
| [131] | Undheim T. A. The whack-a-mole governance challenge for AI-enabled synthetic biology: literature review and emerging frameworks. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2024, 12, Review. |
| [132] | 袁志明.合成生物学技术发展带来的机遇与挑战[J].华中科技大学学报(社会科学版),2020,34(01):5-7. |
| ming Y. Z.Opportunities and Challenges from the Developmentof Synthetic Biology Technology[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Social Science Edition), 2020,34(01):5-7. | |
| [133] | 梁慧刚; 黄翠; 宋冬林; 陈宗胜; 袁志明.合成生物学研究和应用的生物安全问题[J].科技导报,2016,34(02):307-312. |
| Huigang L., Cui H., Donglin S., Zongsheng C., Zhiming Y.Biosafety issue on researches and applications of Synthetic Biology[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2016,34(02):307-312. | |
| [134] | 张维; 杨敬宇; 化得良.合成生物学治理的国外经验综述及启示[J].医学与哲学,2020,41(03):54-58. |
| Wei Z., Jing-yu Y., De-liang H.Review and Implication of Synthetic Biology Governance in Foreign Countries[J]. Medicine & Philosophy, 2020,41(03):54-58. | |
| [135] | 李真真; 董永亮; 高旖蔚.设计生命:合成生物学的安全风险与伦理挑战[J].中国科学院院刊,2018,33(11):1269-1276. |
| Zhenzhen L., Yongliang D., Yiwei G.Design Life: Safety Risks and Ethical Challenges in Synthetic Biology[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018,33(11):1269-1276. | |
| [136] | 张慧; 闫瑞峰; 邱惠丽.欧美合成生物学伦理治理比较及启示[J].科学技术哲学研究,2023,40(01):86-93. |
| Hui Z., Rui-feng Y., Hui-li Q.Comparison of the Ethical Governance ofSynthetic Biology in Europe and America and Its Enlightenment[J]. Studies in Philosophy of Science and Technology, 2023,40(01):86-93. | |
| [137] | 翟晓梅; 邱仁宗.合成生物学:伦理和管治问题[J].科学与社会,2014,4(04):43-52. |
| Xiao-mei Z., Ren-zong Q.Ethical and Governance Issues in Synthetic Biology[J]. Science and Society, 2014,4(04):43-52. | |
| [138] | Safety G. C. C. o. B. Synthetic biology; Berlin, 2018. |
| [139] | Pariotti E.; Gerotto S.; Muratorio A.; Piccinni M.; Guerra G.; Neri A. Ethical and regulatory challenges raised by synthetic biology. 2010. |
| [140] | Report F. Identification of ethical issues and analysis of public discourse; Brussels, 2010. |
| [141] | Biosecurity N. S. A. B. f. Addressing Biosecurity Concerns Related to Synthetic Biology. US Department of Health & Human Services, NSABBWashington, DC: 2010. |
| [142] | Sciences N. A. o.; Medicine; Earth D. o.; Studies L.; Sciences B. o. C.; Sciences B. o. L.; Products C. o. F. B.; System O. t. E. C. o. t. B. R. Preparing for future products of biotechnology; National Academies Press, 2017. |
| [143] | Trump B. A Comparative Analysis of Variations in Synthetic Biology Regulation. 2016. |
| [144] | 赵雪梅; 邓益志; 孟点点.分层分类科技伦理治理体系构建、国际经验与中国策略[J].中国医学伦理学:1-13. |
| Xuemei Z., Yizhi D., Diandian M.The construction of a hierarchical and classified science and technology ethics governancesystem, international experience, and Chinese strategies[J]. Chinese Medical Ethics:1-13. |
| [1] | WU Ke, LUO Jiahao, LI Feiran. Applications of machine learning in the reconstruction and curation of genome-scale metabolic models [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 566-584. |
| [2] | TIAN Xiao-jun, ZHANG Rixin. “Economics Paradox” with cells in synthetic gene circuits [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 532-546. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yiqing, LIU Gaowen. Exploration of gene functions and library construction for engineering strains from a synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 685-700. |
| [4] | YANG Ying, LI Xia, LIU Lizhong. Applications of synthetic biology to stem-cell-derived modeling of early embryonic development [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 669-684. |
| [5] | HUANG Yi, SI Tong, LU Anjing. Standardization for biomanufacturing: global landscape, critical challenges, and pathways forward [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 701-714. |
| [6] | SONG Chengzhi, LIN Yihan. AI-enabled directed evolution for protein engineering and optimization [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 617-635. |
| [7] | ZHANG Mengyao, CAI Peng, ZHOU Yongjin. Synthetic biology drives the sustainable production of terpenoid fragrances and flavors [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 334-356. |
| [8] | ZHANG Lu’ou, XU Li, HU Xiaoxu, YANG Ying. Synthetic biology ushers cosmetic industry into the “bio-cosmetics” era [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 479-491. |
| [9] | YI Jinhang, TANG Yulin, LI Chunyu, WU Heyun, MA Qian, XIE Xixian. Applications and advances in the research of biosynthesis of amino acid derivatives as key ingredients in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 254-289. |
| [10] | WEI Lingzhen, WANG Jia, SUN Xinxiao, YUAN Qipeng, SHEN Xiaolin. Biosynthesis of flavonoids and their applications in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| [11] | XIAO Sen, HU Litao, SHI Zhicheng, WANG Fayin, YU Siting, DU Guocheng, CHEN Jian, KANG Zhen. Research advances in biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid with controlled molecular weights [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 445-460. |
| [12] | WANG Qian, GUO Shiting, XIN Bo, ZHONG Cheng, WANG Yu. Advances in biosynthesis of L-arginine using engineered microorganisms [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 290-305. |
| [13] | ZUO Yimeng, ZHANG Jiaojiao, LIAN Jiazhang. Enabling technology for the biosynthesis of cosmetic raw materials with Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 233-253. |
| [14] | TANG Chuan′gen, WANG Jing, ZHANG Shuo, ZHANG Haoning, KANG Zhen. Advances in synthesis and mining strategies for functional peptides [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 461-478. |
| [15] | GUO Tingting, HAN Xiangning, HUANG Xiting, ZHANG Tingting, KONG Jian. Advances in synthetic biology tools for lactic acid bacteria and their application in the development of skin beneficial products [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 320-333. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||