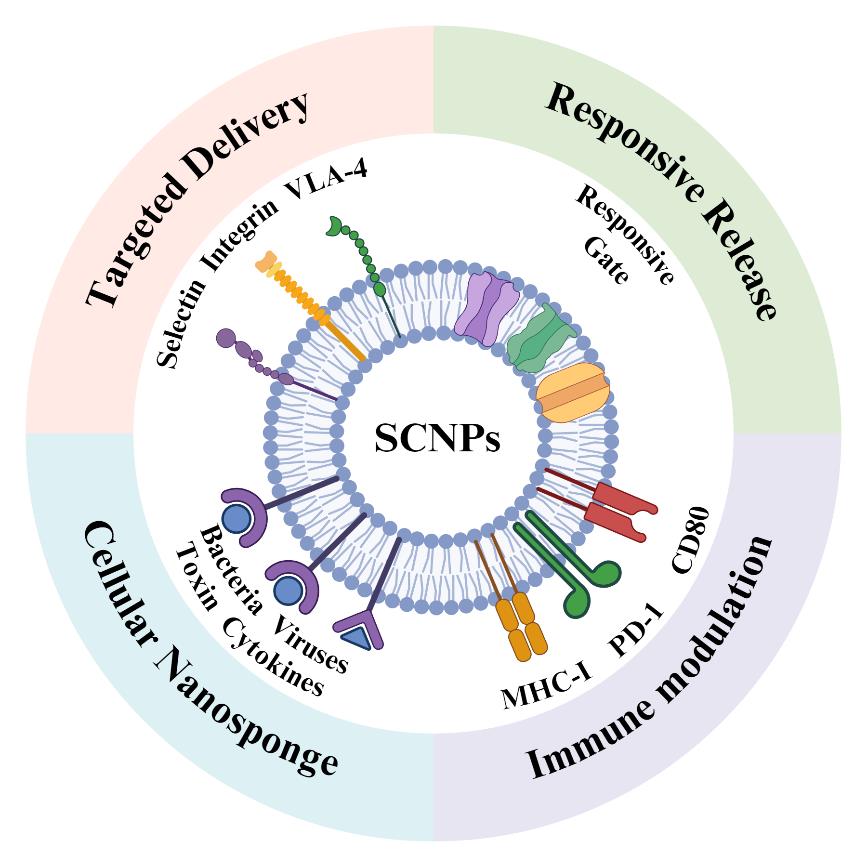
Synthetic Biology-Powered Cell Membrane-Derived Nanoparticles for Precision Theranostics
HUANG Yang1,2, LI Yiye1,3, NIE Guangjun1,2,3
- 1.CAS Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety,CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience,National Center for Nanoscience and Technology of China,Beijing 100190,China
2.School of Nanoscience and Engineering,University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
3.College of Materials Science and Opto-Electronic Technology,University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
-
Received:2025-06-30Revised:2025-07-23Published:2025-07-28 -
Contact:LI Yiye, NIE Guangjun
合成生物学赋能细胞膜纳米颗粒的精准诊疗
黄扬1,2, 李一叶1,3, 聂广军1,2,3
- 1.国家纳米科学中心,中国科学院纳米生物效应与安全性重点实验室,中国科学院纳米科学卓越创新中心,北京,100190
2.中国科学院大学,纳米科学与工程学院,北京,100049
3.中国科学院大学,材料科学与光电技术学院,北京,100049
-
通讯作者:李一叶,聂广军 -
作者简介:黄扬 (2001—),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为纳米材料在骨相关疾病中的应用。E-mail:huangy2023@nanoctr.cn李一叶 (1977—),女,博士,研究员,研究方向为纳米生物医学与纳米药物。E-mail:liyy@nanoctr.cn聂广军 (1974—),男,博士,研究员,研究方向为纳米生物学与智能纳米药物。 E-mail:niegj@nanoctr.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(2021YFA1201103);国家自然科学基金(2023YFC2509900)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HUANG Yang, LI Yiye, NIE Guangjun. Synthetic Biology-Powered Cell Membrane-Derived Nanoparticles for Precision Theranostics[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-069.
黄扬, 李一叶, 聂广军. 合成生物学赋能细胞膜纳米颗粒的精准诊疗[J]. 合成生物学, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-069.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2025-069
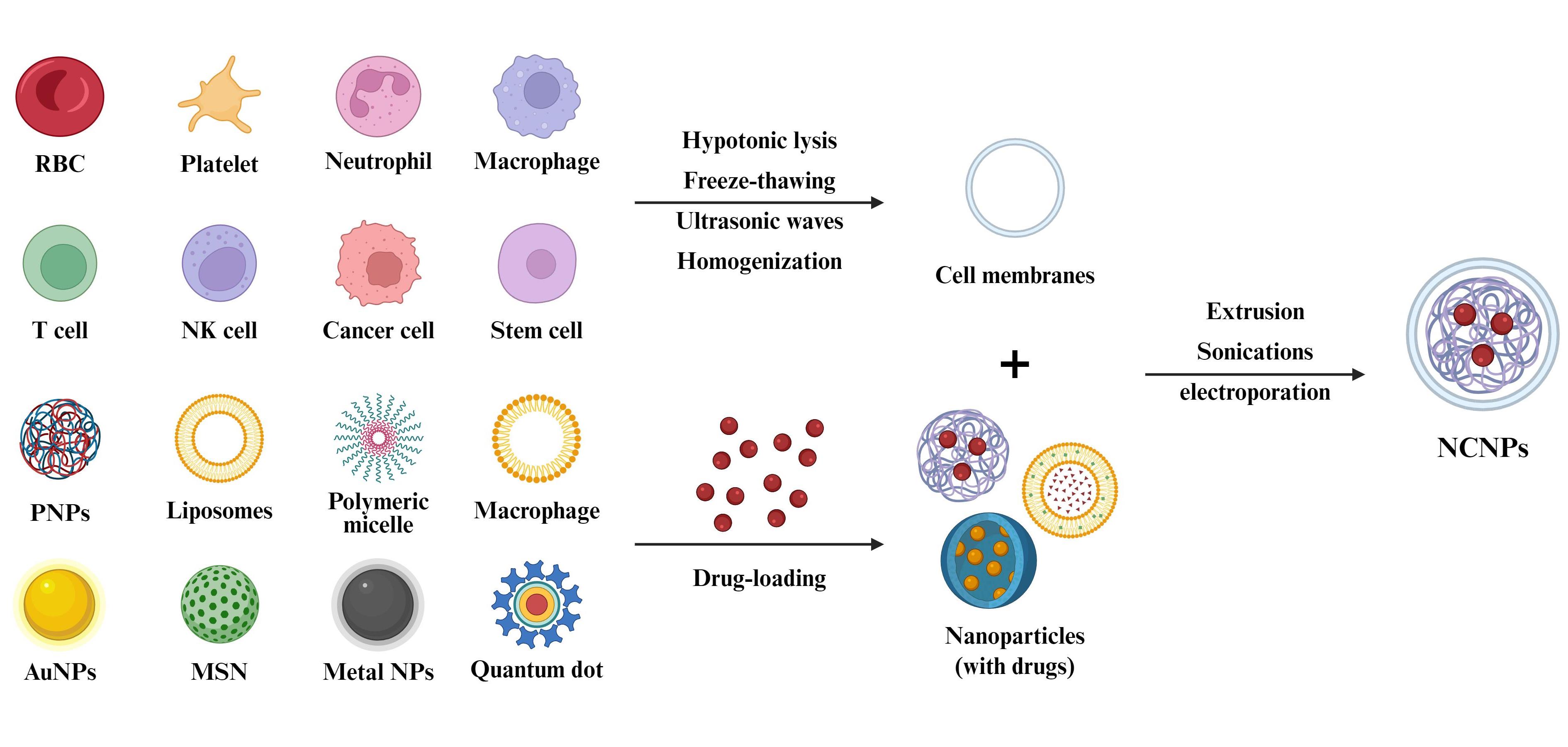
Fig. 1 Preparation of NCNPs. Created in BioRender. Huang Yang (2025)[The preparation of NCNPs usually involves three steps: (1) natural cell membrane extraction, mainly involves techniques such as hypotonic lysis, freeze-thawing, ultrasonic waves, and homogenization; (2) preparation of nanocores; (3) fusion of cell membrane and nanocore, mainly involves techniques such as extrusion, sonication, and electroporation.]
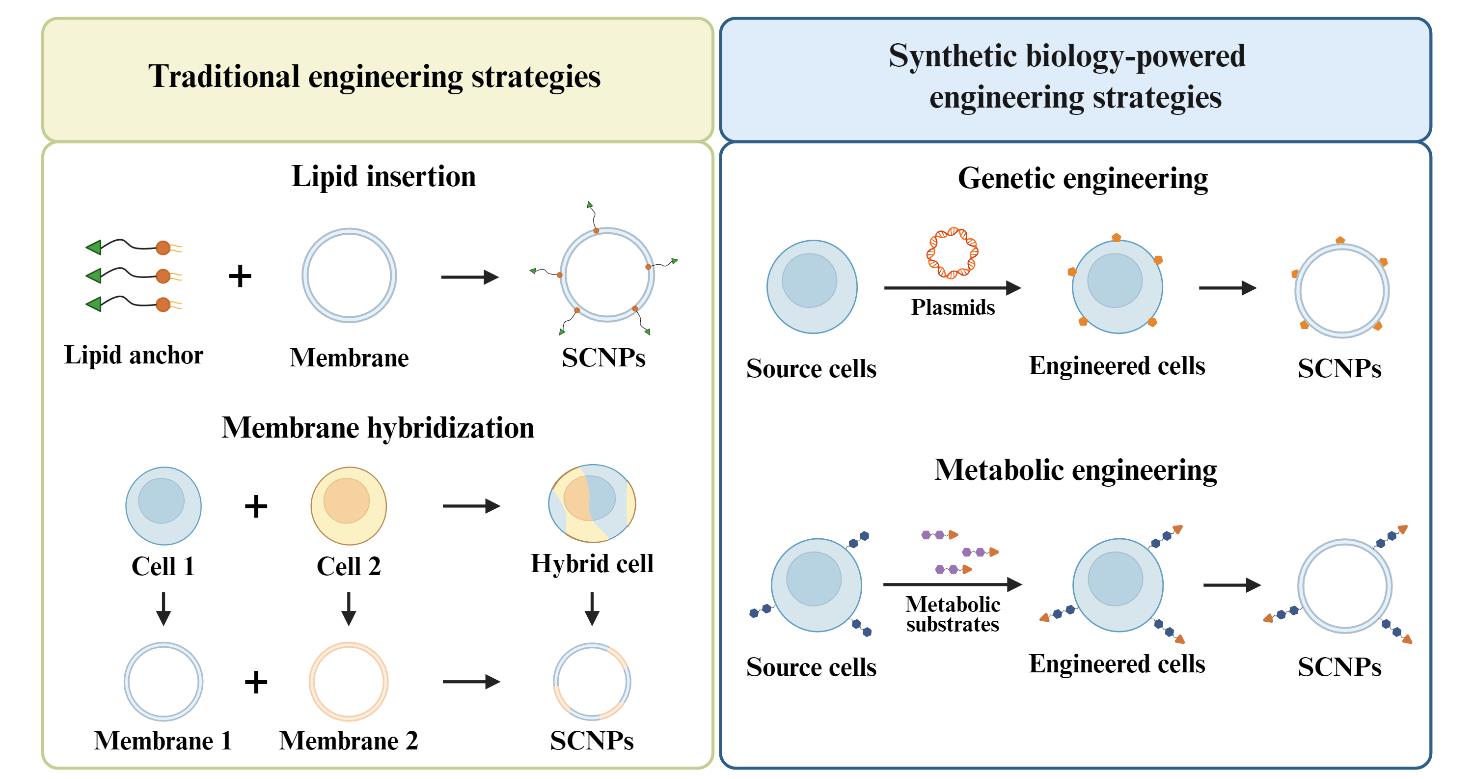
Fig. 2 Engineering strategies for SCNPs. Created in BioRender. Huang Yang (2025)[Mainly includes: (1) lipid insertion, which incorporates functional ligands onto natural cell membranes through a lipid anchor;(2) membrane hybridization, which derives the membrane from individual cell types and then fuse them or fuses different live cells and then derives membrane from the cell hybrids;(3) genetic engineering, which alters protein expression on the cell surfaces through selective gene editing and (4) metabolic engineering, which conjugates functional moieties with metabolic substrates to anchor them to the cell surfaces through natural metabolic pathways.]
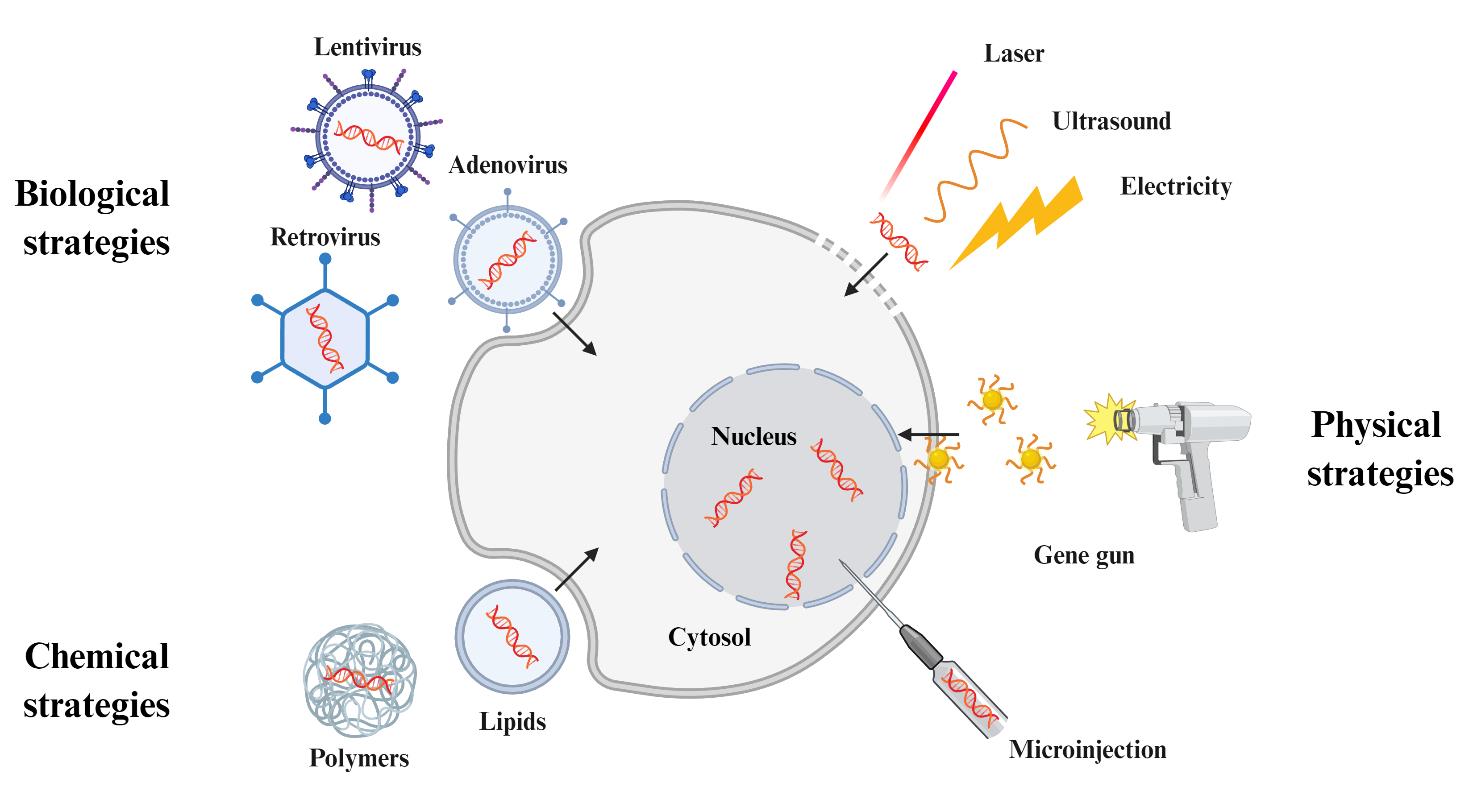
Fig. 3 Strategies of gene transfection. Created in BioRender. Huang Yang (2025)[It mainly includes physical strategies (e.g., electricity/ultrasound/laser -assisted perforation, gene gun and microinjection), chemical strategies (e.g., cationic lipids/polymers -mediated transmembrane transport), and biological strategies (e.g., viral transduction).]
| 基因递送载体 | 细胞膜来源 | 特异表达蛋白 | 生物医学应用 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病毒载体 | 逆转录病毒载体 | 脂肪来源干细胞 | CXCR4 | 通过CXCR4/SDF-1靶向炎症部位 | [ |
| 慢病毒载体 | RAW 264.7 | CCR2 | 通过CCR2/CCL2靶向炎症部位,阻断炎症信号,缓解炎症 | [ | |
| LX2 | TRAIL | 通过TRAIL-受体相互作用诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡 | [ | ||
| 神经干细胞 | CXCR4 | 通过CXCR4/SDF-1靶向炎症部位,跨越血脑屏障 | [ | ||
| CT26 | HER2抗体 | 通过HER2抗体/HER靶向肿瘤部位,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ | ||
| RAW 264.7 | HA,RAGE | 通过RAGE/S100A9靶向炎症受损心肌,缓解炎症和心肌损伤;通过HA实现内体逃逸 | [ | ||
| 腺病毒载体 | DCs | MHC-I,PD 1,B7 | 通过MHC-I/PD-1/B7活化T细胞,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ | |
| 神经干细胞 | Lamp 2b-RVG | 通过RVG/乙酰胆碱受体靶向神经细胞,跨越血脑屏障 | [ | ||
| 非病毒载体 | 阳离子脂质体 | B16-F10 | 卵清白蛋白,CD80 | 通过卵清白蛋白/CD80活化T细胞,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ |
| B16-F10 | HA | 通过HA实现内体逃逸 | [ | ||
| C1498 | VLA-4 | 通过VLA-4/VCAM-1靶向炎症部位 | [ | ||
| HEK293T | PD-1 | 通过PD-1/PD-L1靶向肿瘤部位,阻断免疫检查点,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ | ||
| 阳离子聚合物 | 4T1-Fluc | KillerRed | 通过KillerRed实现光动力治疗,杀伤肿瘤 | [ | |
| B16-F10 | CD 47 KO/CRT | 激活肿瘤免疫 | [ | ||
Table 1 Biomedical applications of nanoparticles with genetically engineered membranes
| 基因递送载体 | 细胞膜来源 | 特异表达蛋白 | 生物医学应用 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病毒载体 | 逆转录病毒载体 | 脂肪来源干细胞 | CXCR4 | 通过CXCR4/SDF-1靶向炎症部位 | [ |
| 慢病毒载体 | RAW 264.7 | CCR2 | 通过CCR2/CCL2靶向炎症部位,阻断炎症信号,缓解炎症 | [ | |
| LX2 | TRAIL | 通过TRAIL-受体相互作用诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡 | [ | ||
| 神经干细胞 | CXCR4 | 通过CXCR4/SDF-1靶向炎症部位,跨越血脑屏障 | [ | ||
| CT26 | HER2抗体 | 通过HER2抗体/HER靶向肿瘤部位,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ | ||
| RAW 264.7 | HA,RAGE | 通过RAGE/S100A9靶向炎症受损心肌,缓解炎症和心肌损伤;通过HA实现内体逃逸 | [ | ||
| 腺病毒载体 | DCs | MHC-I,PD 1,B7 | 通过MHC-I/PD-1/B7活化T细胞,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ | |
| 神经干细胞 | Lamp 2b-RVG | 通过RVG/乙酰胆碱受体靶向神经细胞,跨越血脑屏障 | [ | ||
| 非病毒载体 | 阳离子脂质体 | B16-F10 | 卵清白蛋白,CD80 | 通过卵清白蛋白/CD80活化T细胞,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ |
| B16-F10 | HA | 通过HA实现内体逃逸 | [ | ||
| C1498 | VLA-4 | 通过VLA-4/VCAM-1靶向炎症部位 | [ | ||
| HEK293T | PD-1 | 通过PD-1/PD-L1靶向肿瘤部位,阻断免疫检查点,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ | ||
| 阳离子聚合物 | 4T1-Fluc | KillerRed | 通过KillerRed实现光动力治疗,杀伤肿瘤 | [ | |
| B16-F10 | CD 47 KO/CRT | 激活肿瘤免疫 | [ | ||
| 代谢工程 | 生物合成途径 | 代谢底物 | 生物医学应用 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糖工程 | 唾液酸途径 | N-乙酰甘露糖胺 ManNAc | 插入N3偶联肝素,中和SARS-CoV-2 | [ |
N-叠氮基乙酰基甘露糖胺 ManNAz | 插入N3偶联抗 CD3ε抗体,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ | ||
| 插入N3,增强细胞膜-纳米核结合 | [ | |||
| 插入N3偶联ALN,靶向骨组织 | [ | |||
| GalNAc补救合成途径 | N-乙酰半乳糖胺 GalNAc | 插入N3,靶向肿瘤细胞BCN | [ | |
| 脂质工程 | CDP-胆碱途径 | 胆碱 Choline | 插入N3偶联RGD,靶向肿瘤 | [ |
| 插入N3偶联pMHC-I/CD28,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ | |||
| 插入N3偶联抗CD205,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ |
Table 2 Biomedical applications and synthesis of nanoparticles with metabolically engineered membranes
| 代谢工程 | 生物合成途径 | 代谢底物 | 生物医学应用 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糖工程 | 唾液酸途径 | N-乙酰甘露糖胺 ManNAc | 插入N3偶联肝素,中和SARS-CoV-2 | [ |
N-叠氮基乙酰基甘露糖胺 ManNAz | 插入N3偶联抗 CD3ε抗体,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ | ||
| 插入N3,增强细胞膜-纳米核结合 | [ | |||
| 插入N3偶联ALN,靶向骨组织 | [ | |||
| GalNAc补救合成途径 | N-乙酰半乳糖胺 GalNAc | 插入N3,靶向肿瘤细胞BCN | [ | |
| 脂质工程 | CDP-胆碱途径 | 胆碱 Choline | 插入N3偶联RGD,靶向肿瘤 | [ |
| 插入N3偶联pMHC-I/CD28,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ | |||
| 插入N3偶联抗CD205,激活肿瘤免疫 | [ |
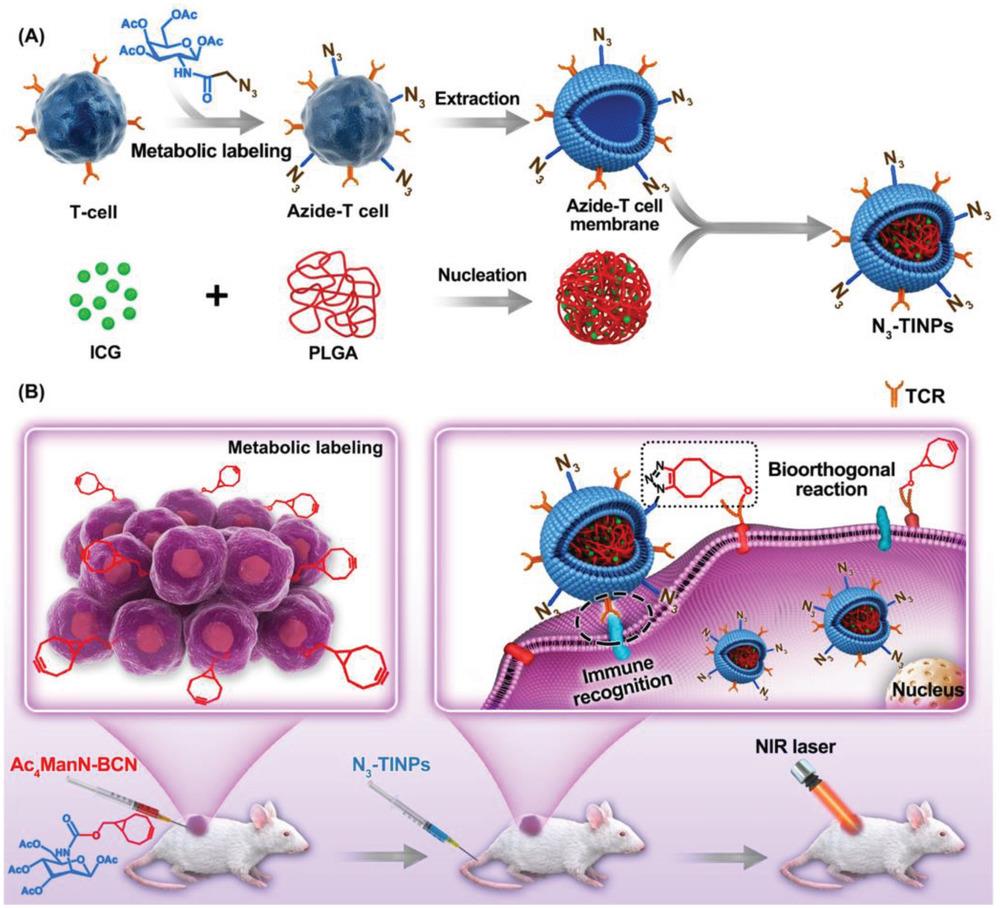
Fig. 4 Schematic illustration of N3-labeled T cell membrane-biomimetic nanoparticles with dual-targeting mechanism [91][A) Synthesis of N3-TINPs. B) Tumor cells carrying the BCN group via natural glycometabolic labeling by pretreatment with Ac4ManN-BCN. N3-TINPs could target tumor through immune recognition of T cell membrane and bioorthogonal reaction between BCN and N3 groups.]
| 应用 | 功能 | 机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 恶性肿瘤 | 肿瘤靶向 | 修饰靶向分子,如RGD、NGR | [110,35] |
| 免疫疗法 | 表达免疫检测点抗体或受体,阻断PD-1/PD-L1 信号轴; | [ | |
| 修饰肿瘤抗原和/或肿瘤细胞膜固有抗原激活肿瘤免疫,发挥疫苗功效 | [ | ||
| 心血管疾病 | 炎症靶向和缓解 | 修饰靶向蛋白如VLA-4; 血小板、巨噬细胞等固有炎症靶向和免疫调节能力 | [111,112,81] |
| 感染性疾病 | 中和病原体 | 修饰对应受体/配体/抗体,如肝素 | [ |
| 激活免疫应答 | 展示病毒特异性抗原表位 | [ | |
| 自身免疫性疾病 | 抑制免疫激活 | 修饰对应受体,如OX40、CD40,阻断免疫激活信号 | [ |
| 神经退行性疾病 | 跨越血脑屏障实现靶向递送 | 神经干细胞脑归巢效应; 修饰靶向分子,如CCR2 | [ |
| 骨相关疾病 | 骨靶向 | 修饰靶向分子,如CXCR4、ALN | [ |
| 中和破骨因子 | 过表达对应受体,如RANK | [ |
Table 3 The application of SCNPs in disease diagnosis and treatment
| 应用 | 功能 | 机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 恶性肿瘤 | 肿瘤靶向 | 修饰靶向分子,如RGD、NGR | [110,35] |
| 免疫疗法 | 表达免疫检测点抗体或受体,阻断PD-1/PD-L1 信号轴; | [ | |
| 修饰肿瘤抗原和/或肿瘤细胞膜固有抗原激活肿瘤免疫,发挥疫苗功效 | [ | ||
| 心血管疾病 | 炎症靶向和缓解 | 修饰靶向蛋白如VLA-4; 血小板、巨噬细胞等固有炎症靶向和免疫调节能力 | [111,112,81] |
| 感染性疾病 | 中和病原体 | 修饰对应受体/配体/抗体,如肝素 | [ |
| 激活免疫应答 | 展示病毒特异性抗原表位 | [ | |
| 自身免疫性疾病 | 抑制免疫激活 | 修饰对应受体,如OX40、CD40,阻断免疫激活信号 | [ |
| 神经退行性疾病 | 跨越血脑屏障实现靶向递送 | 神经干细胞脑归巢效应; 修饰靶向分子,如CCR2 | [ |
| 骨相关疾病 | 骨靶向 | 修饰靶向分子,如CXCR4、ALN | [ |
| 中和破骨因子 | 过表达对应受体,如RANK | [ |
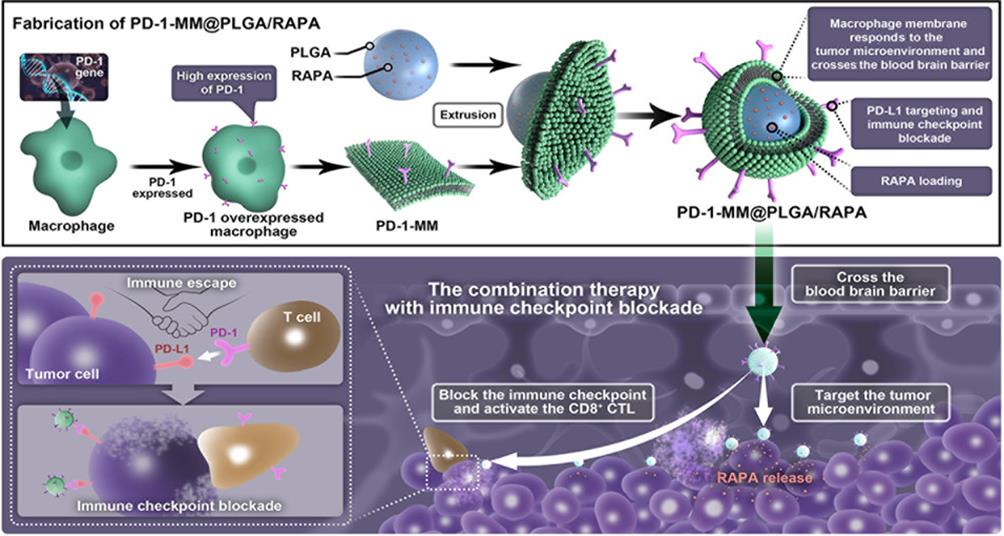
Fig. 6 Schematic Illustration of Preparing Engineered Macrophage-Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles with Enhanced PD-1 Expression[61][Macrophage membrane-derived NPs permeate the blood-brain-barrier and conduct targeted drug delivery; in situ engineered overexpression of PD-1 on the macrophage membrane competitively binds to PD-L1 and effectively blocks the PD-1/PD-L1 signaling axis.]
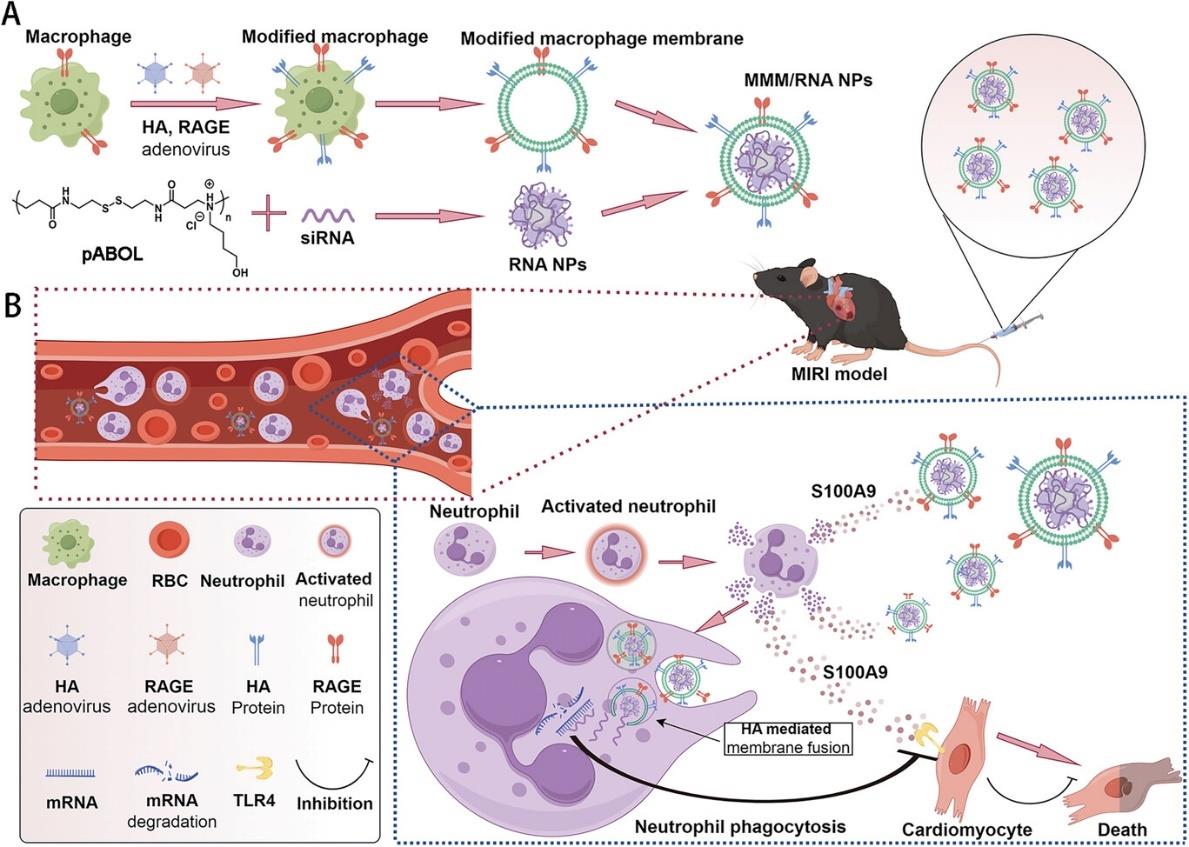
Fig.7 Schematic representation of MMM/RNA NPs-mediated siRNA delivery for the treatment of MIRI[81][A) Depiction of the MMM/RNA NPs preparation. Macrophages were transfected with adenoviruses encoding for HA and RAGE to construct engineered macrophages. B) Diagram of MMM/RNA NPs injected into the tail vein of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion mice. Myocardial ischemic injury recruits a large number of neutrophils in the blood, which activate and release S100A9 inflammatory factors. MMM/RNA NPs rely on their cell membrane protein RAGE to recruit to the myocardial injury area along the concentration of S100A9. Neutrophils engulf MMM/RNA NPs, and MMM/RNA NPs rely on their cell membrane protein HA to play an endosomal escape role, transporting siRNA to the cytoplasm.]
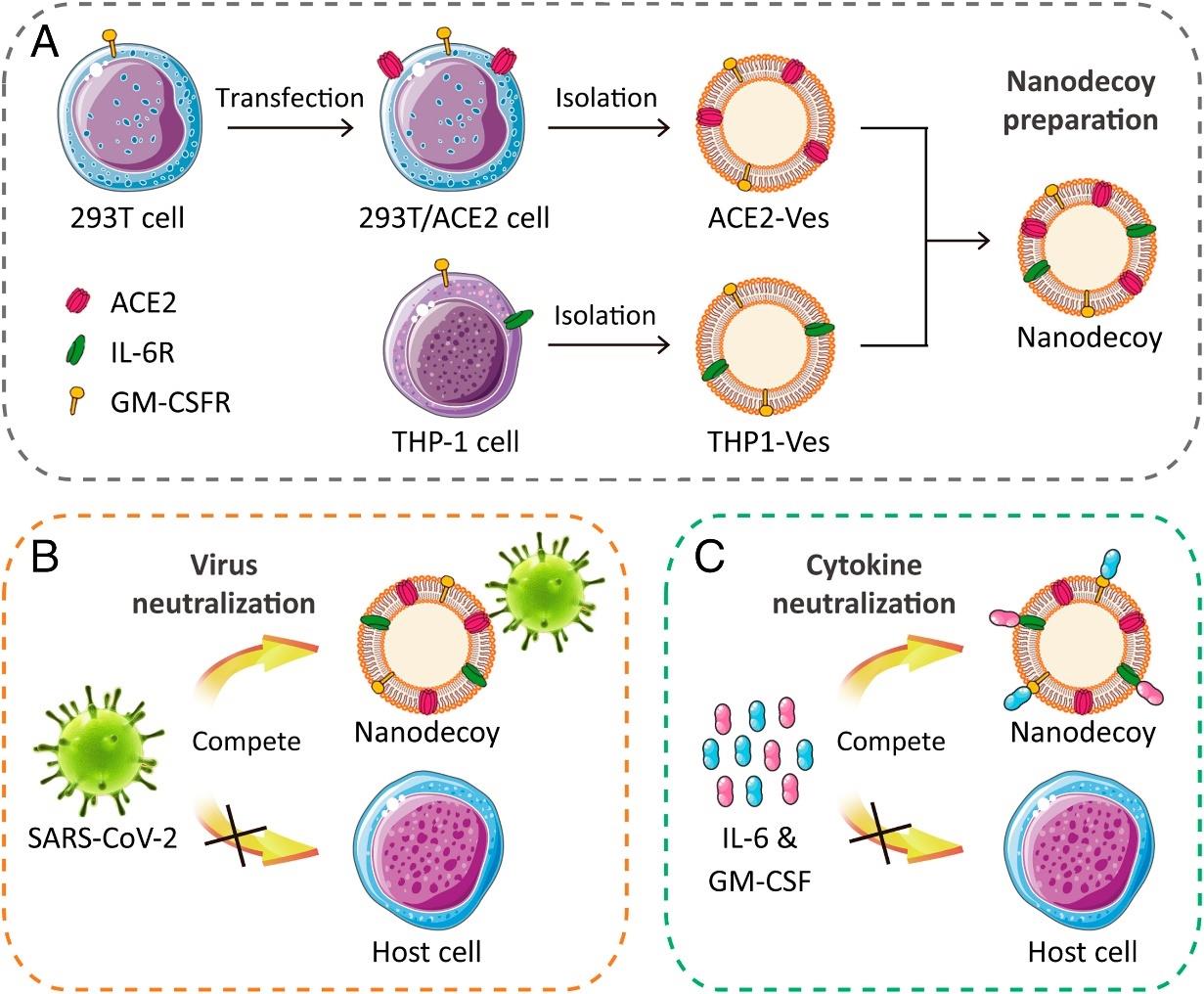
Fig. 8 Schematic illustration of nanosponges against COVID-19[106][A) Preparation of nanosponges by fusing cellular membrane nanovesicles derived from genetically edited 293T/ACE2 and THP-1 cells. The nanosponges, displaying abundant ACE2 and cytokine receptors, compete with host cells to bind (B) SARS-CoV-2 and (C) inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and GM-CSF.]
| [117] | Zhou Y., Deng Y. K., Liu Z. M., et al. Cytokine-scavenging nanodecoys reconstruct osteoclast/osteoblast balance toward the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(48): eabl6432. |
| [118] | Jiang X. B., Zhang X. Y., Guo C., et al. Genetically engineered cell membrane-coated magnetic nanoparticles for high-performance isolation of circulating tumor cells [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(7): 2304426. |
| [119] | Song Y. N., Zhang N., Li Q. Y., et al. Biomimetic liposomes hybrid with platelet membranes for targeted therapy of atherosclerosis [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 408: 127296. |
| [120] | Su T., Huang K., Ma H., et al. Platelet-inspired nanocells for targeted heart repair after ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(4): 1803567. |
| [121] | Pang X., Liu X., Cheng Y., et al. Sono-immunotherapeutic nanocapturer to combat multidrug-resistant bacterial infections [J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(35): 1902530. |
| [122] | Fang T. L., Li B. Q., Li M., et al. Engineered cell membrane vesicles expressing cd40 alleviate system lupus nephritis by intervening b cell activation [J]. Small Methods, 2023, 7(3): 2200925. |
| [123] | Anzalone A. V., Randolph P. B., Davis J. R., et al. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA [J]. Nature, 2019, 576(7785): 149-157. |
| [1] | Beach M. A., Nayanathara U., Gao Y. T., et al. Polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2024, 124(9): 5505-5616. |
| [2] | Dams E. T. M., Laverman P., Oyen W. J. G., et al. Accelerated blood clearance and altered biodistribution of repeated injections of sterically stabilized liposomes [J]. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 2000, 292(3): 1071-1079. |
| [3] | Mohamed M., Abu Lila A. S., Shimizu T., et al. Pegylated liposomes: Immunological responses [J]. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2019, 20(1): 710-724. |
| [4] | Sanna V., Pala N., Sechi M.. Targeted therapy using nanotechnology: Focus on cancer [J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2014, 9(1): 467-483. |
| [5] | An Y. Q., Ji C., Zhang H., et al. Engineered cell membrane coating technologies for biomedical applications: From nanoscale to macroscale [J]. Acs Nano, 2025, 19(12): 11517-11546. |
| [6] | Le Q. V., Lee J., Lee H., et al. Cell membrane-derived vesicles for delivery of therapeutic agents [J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2021, 11(8): 2096-2113. |
| [7] | Hu C. M. J., Zhang L., Aryal S., et al. Erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged polymeric nanoparticles as a biomimetic delivery platform [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(27): 10980-10985. |
| [8] | Parodi A., Quattrocchi N., Van De Ven A. L., et al. Synthetic nanoparticles functionalized with biomimetic leukocyte membranes possess cell-like functions [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2013, 8(1): 61-68. |
| [9] | Cao B. R., Yang M. Y., Zhu Y., et al. Stem cells loaded with nanoparticles as a drug carrier for in vivo breast cancer therapy [J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(27): 4627-4631. |
| [10] | Deng G. J., Sun Z. H., Li S. P., et al. Cell-membrane immunotherapy based on natural killer cell membrane coated nanoparticles for the effective inhibition of primary and abscopal tumor growth [J]. Acs Nano, 2018, 12(12): 12096-12108. |
| [11] | Fang R. H., Hu C. M. J., Luk B. T., et al. Cancer cell membrane-coated nanoparticles for anticancer vaccination and drug delivery [J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(4): 2181-2188. |
| [12] | Gong H., Zhang Q. Z., Komarla A., et al. Nanomaterial biointerfacing via mitochondrial membrane coating for targeted detoxification and molecular detection [J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(6): 2603-2609. |
| [13] | Jiang L. X., Zhu Y. Y., Luan P. W., et al. Bacteria-anchoring hybrid liposome capable of absorbing multiple toxins for antivirulence therapy of escherichia coli infection [J]. Acs Nano, 2021, 15(3): 4173-4185. |
| [14] | Xuan M. J., Shao J. X., Dai L. R., et al. Macrophage cell membrane camouflaged mesoporous silica nanocapsules for in vivo cancer therapy [J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2015, 4(11): 1645-1652. |
| [15] | Hu C. M. J., Fang R. H., Copp J., et al. A biomimetic nanosponge that absorbs pore-forming toxins [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2013, 8(5): 336-340. |
| [16] | Yang L., Froio R. M., Sciuto T. E., et al. Icam-1 regulates neutrophil adhesion and transcellular migration of tnf-α-activated vascular endothelium under flow [J]. Blood, 2005, 106(2): 584-592. |
| [17] | Zhou K., Yang C. L., Shi K., et al. Activated macrophage membrane-coated nanoparticles relieve osteoarthritis-induced synovitis and joint damage [J]. Biomaterials, 2023, 295: 122036. |
| [18] | Guo J., Pan X. T., Wu Q. Y., et al. Bio-barrier-adaptable biomimetic nanomedicines combined with ultrasound for enhanced cancer therapy [J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2025, 10(1): 137. |
| [19] | Lei S. B., Li J. M., Zhu M. F., et al. Chimeric antigen receptor-engineered cell membrane-coated nanoparticles promote dual-targeted mrna-based cancer gene therapy [J]. Acs Nano, 2025, 19(16): 15668-15684. |
| [20] | Liu H., Su Y. Y., Jiang X. C., et al. Cell membrane-coated nanoparticles: A novel multifunctional biomimetic drug delivery system [J]. Drug Delivery and Translational Research, 2023, 13(3): 716-737. |
| [21] | Tuo Z., He Q. Y., Zhang Z. J., et al. Irradiation conditioning of adjuvanted, autologous cancer cell membrane nanoparticle vaccines [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 134437. |
| [22] | Wang X. X., Zhu X. Q., Li B. Y., et al. Intelligent biomimetic nanoplatform for systemic treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer via enhanced egfr-targeted therapy and immunotherapy [J]. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(20): 23152-23163. |
| [23] | Zhu J. Y., Zheng D. W., Zhang M. K., et al. Preferential cancer cell self-recognition and tumor self-targeting by coating nanoparticles with homotypic cancer cell membranes [J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(9): 5895-5901. |
| [24] | Wang S. Y., Wang D., Kai M. X., et al. Design strategies for cellular nanosponges as medical countermeasures [J]. Bme Frontiers, 2023, 4: 0018. |
| [25] | Zhang J. A., Feng K. L., Shen W. T., et al. Research advances of cellular nanoparticles as multiplex countermeasures [J]. Acs Nano, 2024, 18(44): 30211-30223. |
| [26] | Pang Z. Q., Hu C. M. J., Fang R. H., et al. Detoxification of organophosphate poisoning using nanoparticle bioscavengers [J]. Acs Nano, 2015, 9(6): 6450-6458. |
| [27] | Ai X. Z., Wang S. Y., Duan Y. O., et al. Emerging approaches to functionalizing cell membrane-coated nanoparticles [J]. Biochemistry, 2021, 60(13): 941-955. |
| [28] | Fang R. H., Gao W. W., Zhang L. F.. Targeting drugs to tumours using cell membrane-coated nanoparticles [J]. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology, 2023, 20(1): 33-48. |
| [29] | Yi W. Z., Xiao P., Liu X. C., et al. Recent advances in developing active targeting and multi-functional drug delivery systems via bioorthogonal chemistry [J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2022, 7(1): 386. |
| [30] | Zhang X. E., Liu C. L., Dai J. B., et al. Enabling technology and core theory of synthetic biology [J]. Science China-Life Sciences, 2023, 66(8): 1742-1785. |
| [31] | Jiang Y., Krishnan N., Zhou J. R., et al. Engineered cell-membrane-coated nanoparticles directly present tumor antigens to promote anticancer immunity [J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(30): 2001808. |
| [32] | Krishnan N., Jiang Y., Zhou J. R., et al. A modular approach to enhancing cell membrane-coated nanoparticle functionality using genetic engineering [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2024, 19(3): 345–353. |
| [33] | Ma W. J., Zhu D. M., Li J. H., et al. Coating biomimetic nanoparticles with chimeric antigen receptor t cell-membrane provides high specificity for hepatocellular carcinoma photothermal therapy treatment [J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(3): 1281-1295. |
| [34] | Ai X. Z., Wang D., Honko A., et al. Surface glycan modification of cellular nanosponges to promote sars-cov-2 inhibition [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(42): 17615-17621. |
| [35] | Zhang F., Zhao L. J., Wang S. M., et al. Construction of a biomimetic magnetosome and its application as a sirna carrier for high-performance anticancer therapy [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(1): 1703326. |
| [36] | Chugh V., Krishna K. V., Pandit A.. Cell membrane-coated mimics: A methodological approach for fabrication, characterization for therapeutic applications, and challenges for clinical translation [J]. Acs Nano, 2021, 15(11): 17080-17123. |
| [37] | Wang Y., Zhang K., Qin X., et al. Biomimetic nanotherapies: Red blood cell based core-shell structured nanocomplexes for atherosclerosis management [J]. Advanced Science, 2019, 6(12): 1900172. |
| [38] | Wei X. L., Gao J., Fang R. H., et al. Nanoparticles camouflaged in platelet membrane coating as an antibody decoy for the treatment of immune thrombocytopenia [J]. Biomaterials, 2016, 111: 116-123. |
| [39] | Park J. H., Jiang Y., Zhou J. R., et al. Genetically engineered cell membrane-coated nanoparticles for targeted delivery of dexamethasone to inflamed lungs [J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(25): eabf7820. |
| [40] | He Y. L., Zhang S. Q., She Y. G., et al. Innovative utilization of cell membrane-coated nanoparticles in precision cancer therapy [J]. Exploration, 2024, 4(6): 20230164. |
| [41] | Rao L., Cai B., Bu L. L., et al. Microfluidic electroporation-facilitated synthesis of erythrocyte membrane-coated magnetic nanoparticles for enhanced imaging-guided cancer therapy [J]. Acs Nano, 2017, 11(4): 3496-3505. |
| [42] | Hu C. M. J., Fang R. H., Wang K. C., et al. Nanoparticle biointerfacing by platelet membrane cloaking [J]. Nature, 2015, 526(7571): 118–121. |
| [43] | Sekhon U. D. S., Swingle K., Girish A., et al. Platelet-mimicking procoagulant nanoparticles augment hemostasis in animal models of bleeding [J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2022, 14(629): eabb8975. |
| [44] | Lavergne M., Janus-Bell E., Schaff M., et al. Platelet integrins in tumor metastasis: Do they represent a therapeutic target? [J]. Cancers, 2017, 9(10): 133. |
| [45] | Chen L., Zhou Z. Y., Hu C., et al. Platelet membrane-coated nanocarriers targeting plaques to deliver anti-cd47 antibody for atherosclerotic therapy [J]. Research, 2022, 2022: 9845459. |
| [46] | Li Y., Xiang Q., Zhang Y., et al. Mechanical biomimetic nanocomposites for multidimensional treatment of arterial thrombosis [J]. Advanced Science, 2025, 12(25): 2501134. |
| [47] | Song Y. J., He Y. H., Rong L., et al. "Platelet-coated bullets" biomimetic nanoparticles to ameliorate experimental colitis by targeting endothelial cells [J]. Biomaterials Advances, 2023, 148: 213378. |
| [48] | Tao W. H., Zhao D. Y., Li G. T., et al. Artificial tumor microenvironment regulated by first hemorrhage for enhanced tumor targeting and then occlusion for synergistic bioactivation of hypoxia-sensitive platesomes [J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2022, 12(3): 1487-1499. |
| [49] | Gao C., Huang Q. X., Liu C. H., et al. Treatment of atherosclerosis by macrophage-biomimetic nanoparticles via targeted pharmacotherapy and sequestration of proinflammatory cytokines [J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 2622. |
| [50] | Song W. L., Jia P. F., Ren Y. P., et al. Engineering white blood cell membrane-camouflaged nanocarriers for inflammation-related therapeutics [J]. Bioactive Materials, 2023, 23: 80-100. |
| [51] | Wu Y. S., Wan S. L., Yang S., et al. Macrophage cell membrane-based nanoparticles: A new promising biomimetic platform for targeted delivery and treatment [J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2022, 20(1): 542. |
| [52] | Zhu K. H., Xu Y. C., Zhong R., et al. Hybrid liposome-erythrocyte drug delivery system for tumor therapy with enhanced targeting and blood circulation [J]. Regenerative Biomaterials, 2023, 10: rbad045. |
| [53] | Ren E., Liu C., Lv P., et al. Genetically engineered cellular membrane vesicles as tailorable shells for therapeutics [J]. Advanced Science, 2021, 8(21): 2100460. |
| [54] | Mcmahon H. T., Gallop J. L.. Membrane curvature and mechanisms of dynamic cell membrane remodelling [J]. Nature, 2005, 438(7068): 590-596. |
| [55] | Owji H., Nezafat N., Negandaripour M., et al. A comprehensive review of signal peptides: Structure, roles, and applications [J]. European Journal of Cell Biology, 2018, 97(6): 422-441. |
| [56] | Voorhees R. M., Hegde R. S.. Toward a structural understanding of co-translational protein translocation [J]. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 2016, 41: 91-99. |
| [57] | Jiang R. Z., Yuan S. T., Zhou Y. L., et al. Strategies to overcome the challenges of low or no expression of heterologous proteins in escherichia coli [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2024, 75: 108417. |
| [58] | Manandhar M., Chun E., Romesberg F. E.. Genetic code expansion: Inception, development, commercialization [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(13): 4859-4878. |
| [59] | Parvathy S. T., Udayasuriyan V., Bhadana V.. Codon usage bias [J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2022, 49(1): 539-565. |
| [60] | Guo X., Ye S. P., Cheng X. Y., et al. Engineered P2Y12-overexpressing cell-membrane-wrapped nanoparticles for the functional reversal of ticagrelor and clopidogrel [J]. Nano Letters, 2024, 24(34): 10482-10489. |
| [61] | Yin T. Y., Fan Q., Hu F. F., et al. Engineered macrophage-membrane-coated nanoparticles with enhanced pd-1 expression induce immunomodulation for a synergistic and targeted antiglioblastoma activity [J]. Nano Letters, 2022, 22(16): 6606-6614. |
| [62] | Krishnan N., Peng F. X., Mohapatra A., et al. Genetically engineered cellular nanoparticles for biomedical applications [J]. Biomaterials, 2023, 296: 122065. |
| [63] | Sayed N., Allawadhi P., Khurana A., et al. Gene therapy: Comprehensive overview and therapeutic applications [J]. Life Sciences, 2022, 294: 120375. |
| [64] | Stewart M. P., Langer R., Jensen K. F.. Intracellular delivery by membrane disruption: Mechanisms, strategies, and concepts [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(16): 7409-7531. |
| [65] | Shi J. F., Ma Y. F., Zhu J., et al. A review on electroporation-based intracellular delivery [J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(11): 3044. |
| [66] | Tsong T. Y.. Electroporation of cell-membranes [J]. Biophysical Journal, 1991, 60(2): 297-306. |
| [67] | Chong Z. X., Yeap S. K., Ho W. Y.. Transfection types, methods and strategies: A technical review [J]. Peerj, 2021, 9: e11165. |
| [68] | Meng L., Liu X. F., Wang Y. C., et al. Sonoporation of cells by a parallel stable cavitation microbubble array [J]. Advanced Science, 2019, 6(17): 1900557. |
| [69] | Pylaev T., Vanzha E., Avdeeva E., et al. A novel cell transfection platform based on laser optoporation mediated by au nanostar layers [J]. Journal of Biophotonics, 2019, 12(1): e201800166. |
| [70] | Chow Y. T., Chen S. X., Wang R., et al. Single cell transfection through precise microinjection with quantitatively controlled injection volumes [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 24127. |
| [71] | Zhang J. Q., Hu Y. X., Yang J. X., et al. Non-viral, specifically targeted car-t cells achieve high safety and efficacy in b-nhl [J]. Nature, 2022, 609(7926): 369-374. |
| [72] | Kiefer K., Clement J., Garidel P., et al. Transfection efficiency and cytotoxicity of nonviral gene transfer reagents in human smooth muscle and endothelial cells [J]. Pharmaceutical Research, 2004, 21(6): 1009-1017. |
| [73] | Kim H. Y., Kang M., Choo Y. W., et al. Immunomodulatory lipocomplex functionalized with photosensitizer-embedded cancer cell membrane inhibits tumor growth and metastasis [J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(8): 5185-5193. |
| [74] | Liu S. Y., Wu J. Y., Feng Y. J., et al. Cd47ko/crt dual-bioengineered cell membrane-coated nanovaccine combined with anti-pd-l1 antibody for boosting tumor immunotherapy [J]. Bioactive Materials, 2023, 22: 211-224. |
| [75] | Zhang X. D., Wang C., Wang J. Q., et al. Pd-1 blockade cellular vesicles for cancer immunotherapy [J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(22): 1707112. |
| [76] | Bose R. J. C., Kim B. J., Arai Y., et al. Bioengineered stem cell membrane functionalized nanocarriers for therapeutic targeting of severe hindlimb ischemia [J]. Biomaterials, 2018, 185: 360-370. |
| [77] | Gu C. J., Geng X. W., Wu Y. C., et al. Engineered macrophage membrane-coated nanoparticles with enhanced ccr2 expression promote spinal cord injury repair by suppressing neuroinflammation and neuronal death [J]. Small, 2024, 20(10): 2305659. |
| [78] | Huang D. H., Wang Q. W., Cao Y. H., et al. Multiscale nir-ii imaging-guided brain-targeted drug delivery using engineered cell membrane nanoformulation for alzheimer's disease therapy [J]. Acs Nano, 2023, 17(5): 5033-5046. |
| [79] | Liu C., Liu X., Xiang X. C., et al. A nanovaccine for antigen self-presentation and immunosuppression reversal as a personalized cancer immunotherapy strategy [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2022, 17(5): 531-540. |
| [80] | Liu Z. M., Zhou X. F., Li Q., et al. Macrophage-evading and tumor-specific apoptosis inducing nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy [J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2023, 13(1): 327-343. |
| [81] | Lu H., Wang J. Z., Chen Z. W., et al. Engineered macrophage membrane-coated s100a9-sirna for ameliorating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(41): 2403542. |
| [82] | Ma J. N., Zhang S. Q., Liu J., et al. Targeted drug delivery to stroke via chemotactic recruitment of nanoparticles coated with membrane of engineered neural stem cells [J]. Small, 2019, 15(35): 1902011. |
| [83] | Bulcha J. T., Wang Y., Ma H., et al. Viral vector platforms within the gene therapy landscape [J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2021, 6(1): 53. |
| [84] | Crystal R. G.. Adenovirus: The first effective in vivo gene delivery vector [J]. Human Gene Therapy, 2014, 25(1): 3-11. |
| [85] | Milone M. C., O'doherty U.. Clinical use of lentiviral vectors [J]. Leukemia, 2018, 32(7): 1529-1541. |
| [86] | Park J. H., Mohapatra A., Zhou J. R., et al. Virus-mimicking cell membrane-coated nanoparticles for cytosolic delivery of mrna [J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2022, 61(2): e202113671. |
| [87] | Ai X. Z., Wang D., Noh I., et al. Glycan-modified cellular nanosponges for enhanced neutralization of botulinum toxin [J]. Biomaterials, 2023, 302. |
| [88] | Xiao P., Wang J., Zhao Z. T., et al. Engineering nanoscale artificial antigen-presenting cells by metabolic dendritic cell labeling to potentiate cancer immunotherapy [J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(5): 2094-2103. |
| [89] | Zhang X. L., Zhen X. Y., Yang Y. X., et al. Precise assembly of inside-out cell membrane camouflaged nanoparticles via bioorthogonal reactions for improving drug leads capturing [J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2023, 13(2): 852-862. |
| [90] | Huang Y., Chen M. W., Shen Y. D., et al. Bone-targeting cell membrane-engineered caco3-based nanoparticles restore local bone homeostasis for microenvironment-responsive osteoporosis treatment [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 470: 144145. |
| [91] | Han Y. T., Pan H., Li W. J., et al. T cell membrane mimicking nanoparticles with bioorthogonal targeting and immune recognition for enhanced photothermal therapy [J]. Advanced Science, 2019, 6(15): 1900251. |
| [92] | Zhang Q. B., Wei W., Wang P. L., et al. Biomimetic magnetosomes as versatile artificial antigen-presenting cells to potentiate t-cell-based anticancer therapy [J]. Acs Nano, 2017, 11(11): 10724-10732. |
| [93] | Li F., Nie W. D., Zhang F., et al. Engineering magnetosomes for high-performance cancer vaccination [J]. Acs Central Science, 2019, 5(5): 796-807. |
| [94] | Yoon H. Y., Koo H., Kim K., et al. Molecular imaging based on metabolic glycoengineering and bioorthogonal click chemistry [J]. Biomaterials, 2017, 132: 28-36. |
| [95] | Krishnan N., Fang R. N. H., Zhang L. F.. Engineering of stimuli-responsive self-assembled biomimetic nanoparticles [J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2021, 179: 114006. |
| [96] | Boussiotis V. A.. Molecular and biochemical aspects of the pd-1 checkpoint pathway [J]. New England Journal of Medicine, 2016, 375(18): 1767-1778. |
| [97] | Tang Q. S., Sun S. H., Wang P., et al. Genetically engineering cell membrane-coated bto nanoparticles for mmp2-activated piezocatalysis-immunotherapy [J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(18): 2300964. |
| [98] | Xu S. Y., Shi X. X., Ren E., et al. Genetically engineered nanohyaluronidase vesicles: A smart sonotheranostic platform for enhancing cargo penetration of solid tumors [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(22): 2112989. |
| [99] | Han J. H., Sul J. H., Lee J. M., et al. Engineered exosomes with a photoinducible protein delivery system enable crispr-cas-based epigenome editing in alzheimer's disease [J]. Science Translational Medicine, 2024, 16(759): eadi4830. |
| [100] | Yang Y. X., Wang K., Pan Y. W., et al. Engineered cell membrane-derived nanoparticles in immune modulation [J]. Advanced Science, 2021, 8(24): 2102330. |
| [101] | Zhou J. R., Kroll A. V., Holay M., et al. Biomimetic nanotechnology toward personalized vaccines [J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(13): 1901255. |
| [102] | Wang K. Y., Zhang X. B., Ye H., et al. Biomimetic nanovaccine-mediated multivalent il-15 self-transpresentation (mist) for potent and safe cancer immunotherapy [J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 6748. |
| [103] | Yi M., Zheng X. L., Niu M. K., et al. Combination strategies with pd-1/pd-l1 blockade: Current advances and future directions [J]. Molecular Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 28. |
| [104] | Ding L., Zhang X. L., Yu P. W., et al. Genetically engineered nanovesicles mobilize synergistic antitumor immunity by adar1 silence and pdl1 blockade [J]. Molecular Therapy, 2023, 31(8): 2489-2506. |
| [105] | Wang S. Y., Wang D., Duan Y. O., et al. Cellular nanosponges for biological neutralization [J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(13): 2107719. |
| [106] | Rao L., Xia S., Xu W., et al. Decoy nanoparticles protect against covid-19 by concurrently adsorbing viruses and inflammatory cytokines [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(44): 27141-27147. |
| [107] | Schlapschy M., Binder U., Börger C., et al. Pasylation: A biological alternative to pegylation for extending the plasma half-life of pharmaceutically active proteins [J]. Protein Engineering Design & Selection, 2013, 26(8): 489-501. |
| [108] | Duan Y. U., Zhou J. R., Zhou Z. D., et al. Extending the in vivo residence time of macrophage membrane-coated nanoparticles through genetic modification [J]. Small, 2023, 19(52): 2305551. |
| [109] | Krishnamurthy S., Muthukumaran P., Jayakumar M. K. G., et al. Surface protein engineering increases the circulation time of a cell membrane-based nanotherapeutic [J]. Nanomedicine-Nanotechnology Biology and Medicine, 2019, 18: 169-178. |
| [110] | Lv P., Liu X., Chen X. M., et al. Genetically engineered cell membrane nanovesicles for oncolytic adenovirus delivery: A versatile platform for cancer virotherapy [J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(5): 2993-3001. |
| [111] | Chen T. Y., Lv W. T., Yang M. X., et al. Treatment of atherosclerosis by biomimetic responsive-targeting hybrid nanoparticles enabled by genetically engineering cell membranes and nucleic acid nanostructures for atorvastatin delivery [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 511: 162130. |
| [112] | Li Y. Y., Che J. Y., Chang L., et al. Cd47-and integrin α4/β1-comodified-macrophage-membrane-coated nanoparticles enable delivery of colchicine to atherosclerotic plaque [J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2022, 11(4): 2101788. |
| [113] | Zhang P. F., Chen Y. X., Zeng Y., et al. Virus-mimetic nanovesicles as a versatile antigen-delivery system [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(45): E6129-E6138. |
| [114] | Fu Y., Wang L. L., Liu W., et al. Ox40l blockade cellular nanovesicles for autoimmune diseases therapy [J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2021, 337: 557-570. |
| [115] | Lin R. R., Jin L. L., Xue Y. Y., et al. Hybrid membrane-coated nanoparticles for precise targeting and synergistic therapy in alzheimer's disease [J]. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(24): 2306675. |
| [116] | Liu H., Song P. R., Zhang H., et al. Synthetic biology-based bacterial extracellular vesicles displaying bmp-2 and cxcr4 to ameliorate osteoporosis [J]. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 2024, 13(4): e12429. |
| [1] | WU Ke, LUO Jiahao, LI Feiran. Applications of machine learning in the reconstruction and curation of genome-scale metabolic models [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 566-584. |
| [2] | TIAN Xiao-jun, ZHANG Rixin. “Economics Paradox” with cells in synthetic gene circuits [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 532-546. |
| [3] | LI Yongzhu, CHEN Yu. Advances and prospects in genome-scale models of yeast [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 585-602. |
| [4] | ZHANG Yiqing, LIU Gaowen. Exploration of gene functions and library construction for engineering strains from a synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 685-700. |
| [5] | YANG Ying, LI Xia, LIU Lizhong. Applications of synthetic biology to stem-cell-derived modeling of early embryonic development [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 669-684. |
| [6] | HUANG Yi, SI Tong, LU Anjing. Standardization for biomanufacturing: global landscape, critical challenges, and pathways forward [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 701-714. |
| [7] | SONG Chengzhi, LIN Yihan. AI-enabled directed evolution for protein engineering and optimization [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 617-635. |
| [8] | GAO Qi, XIAO Wenhai. Advances in the biosynthesis of monoterpenes by yeast [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 357-372. |
| [9] | ZHANG Mengyao, CAI Peng, ZHOU Yongjin. Synthetic biology drives the sustainable production of terpenoid fragrances and flavors [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 334-356. |
| [10] | ZHANG Lu’ou, XU Li, HU Xiaoxu, YANG Ying. Synthetic biology ushers cosmetic industry into the “bio-cosmetics” era [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 479-491. |
| [11] | YI Jinhang, TANG Yulin, LI Chunyu, WU Heyun, MA Qian, XIE Xixian. Applications and advances in the research of biosynthesis of amino acid derivatives as key ingredients in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 254-289. |
| [12] | WEI Lingzhen, WANG Jia, SUN Xinxiao, YUAN Qipeng, SHEN Xiaolin. Biosynthesis of flavonoids and their applications in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| [13] | XIAO Sen, HU Litao, SHI Zhicheng, WANG Fayin, YU Siting, DU Guocheng, CHEN Jian, KANG Zhen. Research advances in biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid with controlled molecular weights [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 445-460. |
| [14] | WANG Qian, GUO Shiting, XIN Bo, ZHONG Cheng, WANG Yu. Advances in biosynthesis of L-arginine using engineered microorganisms [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 290-305. |
| [15] | ZUO Yimeng, ZHANG Jiaojiao, LIAN Jiazhang. Enabling technology for the biosynthesis of cosmetic raw materials with Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 233-253. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||