Progress on synthetic methods and applications of sialyllactose based on synthetic biology
LAI Xia1, ZHANG Yanmei2, ZHANG Hongtao1,5, DU Yuguang3, ZHAN Xiaobei1, CHAI Wengang4
- 1.Jiangnan University,School of Biotechnology,Key Laboratory of Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biotechnology of Ministry of Education,Wuxi 214122,Jiangsu,China
2.Luwu Eurasia Sugar Industry Co. ,Ltd. ,Lingshan County,Qinzhou City,Guangxi
3.State Key Laboratory of Biopharmaceutical Preparation and Delivery,Institue of Process Engineering,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100190,China
4.Glycosciences Laboratory,Faculty of Medicine,Imperial College London,Hammersmith Campus,London,W12 0NN,United Kingdom
5.Inner Mongolia Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism and Green Fermentation Engineering,Huhehaote 010000,Neimenggu China
-
Received:2025-06-16Revised:2025-09-01Published:2025-09-02 -
Contact:ZHANG Hongtao
基于合成生物学的唾液酸乳糖合成方法及其应用研究进展
赖霞1, 张燕梅2, 张洪涛1,5, 杜昱光3, 詹晓北1, 柴文刚4
- 1.江南大学生物工程学院,糖化学与生物技术教育部重点实验室,江苏 无锡 214122
2.广西壮族自治区钦州市灵山县陆屋欧亚糖业公司
3.中国科学院过程工程研究所,生物制药制备与递送国家重点实验室,北京 100190
4.伦敦帝国理工学院医学院,糖科学实验室,英国 伦敦
5.内蒙古自治区微生物代谢与绿色发酵工程重点实验室,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010000
-
通讯作者:张洪涛 -
作者简介:赖霞 (2001—),女,硕士研究生。研究方向为以廉价碳源为底物合成功能寡糖链。E-mail:1265518031@qq.com张洪涛 (1979—),男,博士,副教授,博士生导师,研究方向为功能糖的生物合成及其与益生菌的协同效应研究。E-mail:htzhang@jiangnan.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LAI Xia, ZHANG Yanmei, ZHANG Hongtao, DU Yuguang, ZHAN Xiaobei, CHAI Wengang. Progress on synthetic methods and applications of sialyllactose based on synthetic biology[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-061.
赖霞, 张燕梅, 张洪涛, 杜昱光, 詹晓北, 柴文刚. 基于合成生物学的唾液酸乳糖合成方法及其应用研究进展[J]. 合成生物学, DOI: 10.12211/2096-8280.2025-061.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://synbioj.cip.com.cn/EN/10.12211/2096-8280.2025-061
| 中文名称 | 简称 | 英文名称 | 结构 | 分子量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
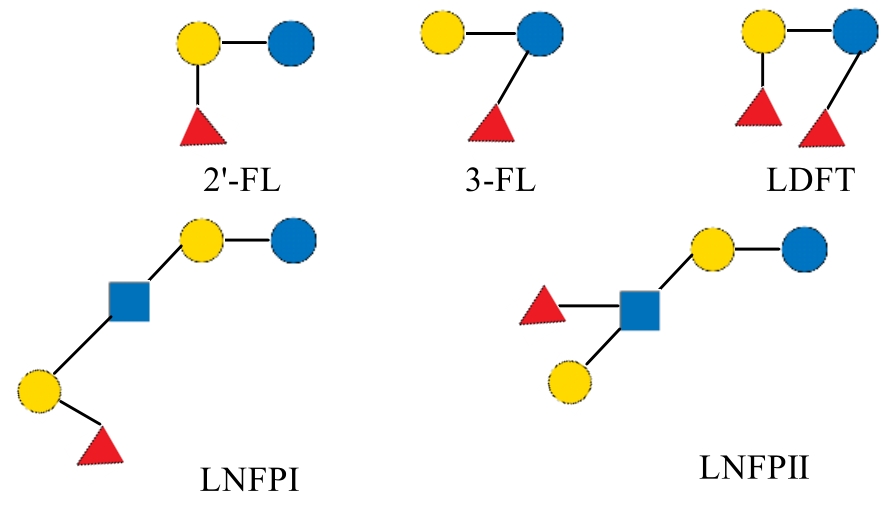
| 2'-岩藻糖基乳糖 | 2'-FL | 2'-fucosyllactose | Fucα1-2Galβ1-4Glc | 488.44 |
| 3-岩藻糖基乳糖 | 3-FL | 3-fucosyllactose | Galβ1-4(Fucα1-3)Glc | 488.44 |
| 二岩藻糖基乳糖 | LDFT | lactodifucotetraose | Fucα1-2Galβ1-4(Fucα1-3)Glc | 634.58 |
| 乳-N-岩藻五糖-Ⅰ | LNFP-Ⅰ | lacto-N fucopentaose I | Fuc-α-1,2-Gal-β-1,3-GlcNAc-β1,3-Gal-β1,4-Glc | 853.77 |
| 乳-N-岩藻五糖-Ⅱ | LNFP-Ⅱ | lacto-N difucotetraose II | Gal-β-1,3-(Fuc-α1,4-)GlcNAcβ1,3Gal-β-1,4-Glc | 853.77 |
| 乳-N-岩藻五糖-Ⅲ | LNFP-Ⅲ | lacto-N fucopentaose III | Gal-β-1,4-(Fuc-α1,3-)GlcNAc-β1,3-Gal-β-1,4-Glc | 853.77 |
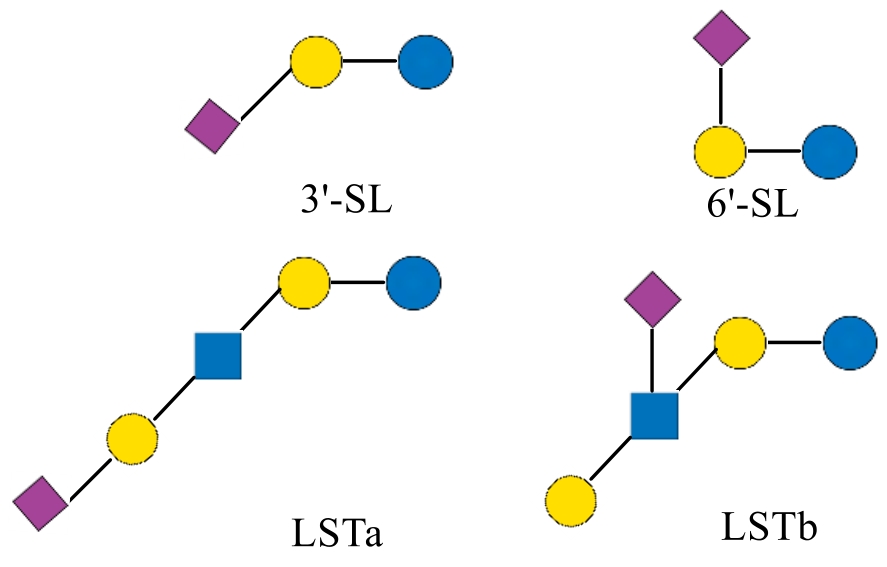
| 3'-唾液酸乳糖 | 3'-SL | 3'-sialyllactose | Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-4Glc | 633.53 |
| 6'-唾液酸乳糖 | 6'-SL | 6'-sialyllactose | Neu5Acα2-6Galβ1-4Glc | 633.53 |
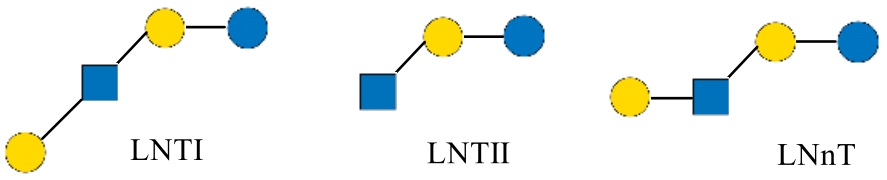
| 乳-N-四糖 | LNT | Lacto-N-tetraose | Galβ1-3GlcNAcβ1-3Galβ1-4Glc | 707.63 |
| 乳-N-新四糖 | LNnT | lacto-N-neotetraose | Galβ1-4GlcNAcβ1-3Galβ1-4Glc | 707.63 |
| 乳-N-六糖 | LNH | lacto-N-hexaose | Gal-β-1,3- GlcNAc-β-1,3-(Gal-β-1,4-GlcNAc-β1,6-)Gal-β-1,4- Glc | 1072.96 |
Table 1 Main information of common human milk oligosaccharides
| 中文名称 | 简称 | 英文名称 | 结构 | 分子量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2'-岩藻糖基乳糖 | 2'-FL | 2'-fucosyllactose | Fucα1-2Galβ1-4Glc | 488.44 |
| 3-岩藻糖基乳糖 | 3-FL | 3-fucosyllactose | Galβ1-4(Fucα1-3)Glc | 488.44 |
| 二岩藻糖基乳糖 | LDFT | lactodifucotetraose | Fucα1-2Galβ1-4(Fucα1-3)Glc | 634.58 |
| 乳-N-岩藻五糖-Ⅰ | LNFP-Ⅰ | lacto-N fucopentaose I | Fuc-α-1,2-Gal-β-1,3-GlcNAc-β1,3-Gal-β1,4-Glc | 853.77 |
| 乳-N-岩藻五糖-Ⅱ | LNFP-Ⅱ | lacto-N difucotetraose II | Gal-β-1,3-(Fuc-α1,4-)GlcNAcβ1,3Gal-β-1,4-Glc | 853.77 |
| 乳-N-岩藻五糖-Ⅲ | LNFP-Ⅲ | lacto-N fucopentaose III | Gal-β-1,4-(Fuc-α1,3-)GlcNAc-β1,3-Gal-β-1,4-Glc | 853.77 |
| 3'-唾液酸乳糖 | 3'-SL | 3'-sialyllactose | Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-4Glc | 633.53 |
| 6'-唾液酸乳糖 | 6'-SL | 6'-sialyllactose | Neu5Acα2-6Galβ1-4Glc | 633.53 |
| 乳-N-四糖 | LNT | Lacto-N-tetraose | Galβ1-3GlcNAcβ1-3Galβ1-4Glc | 707.63 |
| 乳-N-新四糖 | LNnT | lacto-N-neotetraose | Galβ1-4GlcNAcβ1-3Galβ1-4Glc | 707.63 |
| 乳-N-六糖 | LNH | lacto-N-hexaose | Gal-β-1,3- GlcNAc-β-1,3-(Gal-β-1,4-GlcNAc-β1,6-)Gal-β-1,4- Glc | 1072.96 |
| 配方奶粉品牌 | 阶段 | 3'-SL含量 (mg/100mL) | 6'-SL含量 (mg/100mL) | 其他HMOs成分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雀巢 BEBA®Supreme | 第1阶段 | 4 | 20 | 2'-FL、LNT、DFL |
| 第2阶段 | 1 | 5 | 2'-FL、LNT、DFL | |
| 第3阶段 | 1 | 4 | 2'-FL、LNT、DFL | |
| 第4阶段 | 5 | 5 | 2'-FL、LNT、DFL | |
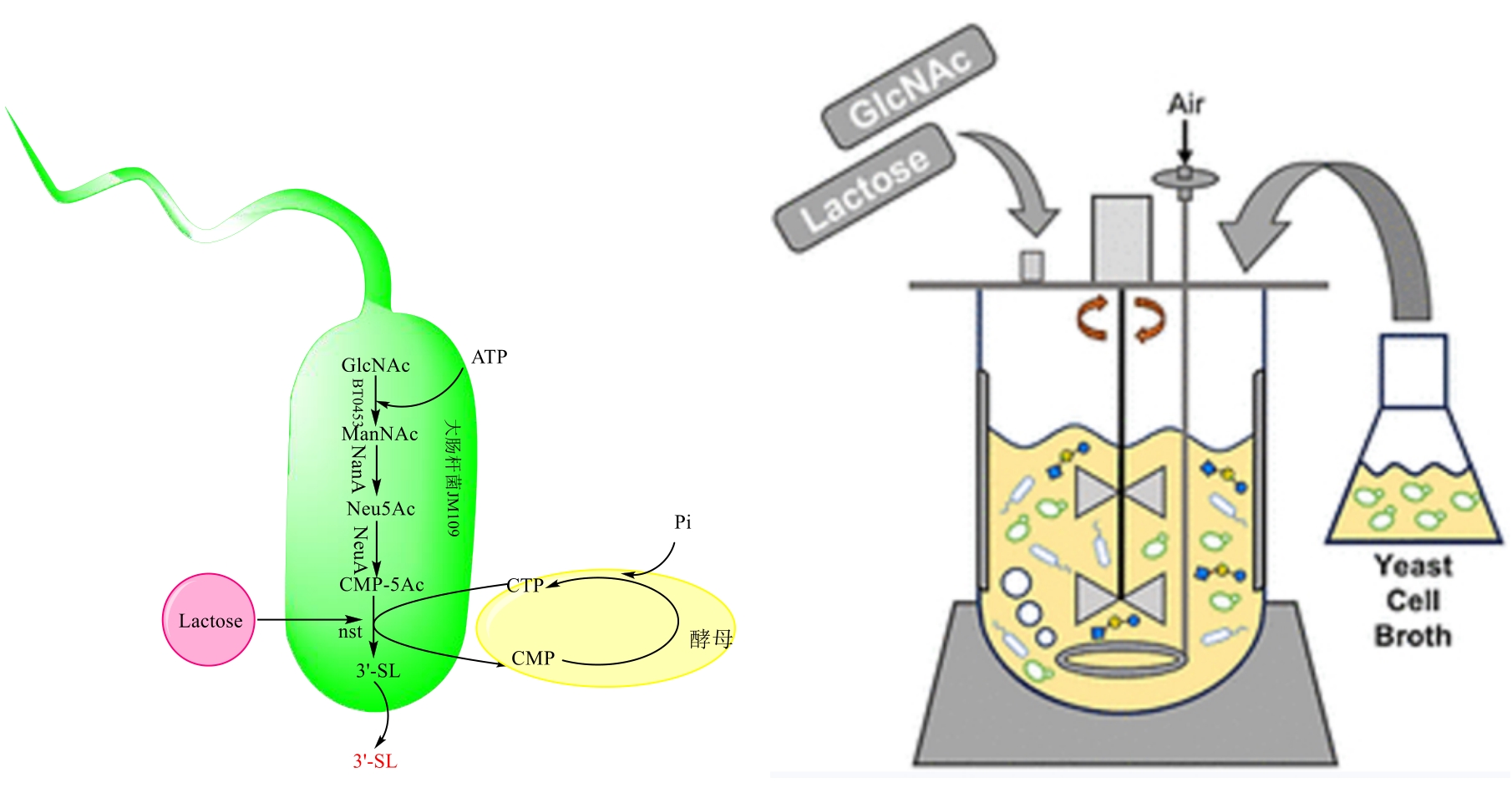
| 惠氏 Illuma®LUXA 启赋未来 | 第1阶段 | 10 | 18 | 2'-FL、LNT、LNnT、DFL |
| 第2阶段 | 4.9 | 4.6 | 2'-FL、LNT、LNnT、DFL | |
| 第3阶段 | 4.9 | 4.6 | 2'-FL、LNT、LNnT、DFL | |
| 第4阶段 | 5 | 4.6 | 2'-FL、LNT、LNnT、DFL |
Table 2 Addition of 3'-SL, 6'-SL, and other human milk oligosaccharides to enriched formulas
| 配方奶粉品牌 | 阶段 | 3'-SL含量 (mg/100mL) | 6'-SL含量 (mg/100mL) | 其他HMOs成分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雀巢 BEBA®Supreme | 第1阶段 | 4 | 20 | 2'-FL、LNT、DFL |
| 第2阶段 | 1 | 5 | 2'-FL、LNT、DFL | |
| 第3阶段 | 1 | 4 | 2'-FL、LNT、DFL | |
| 第4阶段 | 5 | 5 | 2'-FL、LNT、DFL | |
| 惠氏 Illuma®LUXA 启赋未来 | 第1阶段 | 10 | 18 | 2'-FL、LNT、LNnT、DFL |
| 第2阶段 | 4.9 | 4.6 | 2'-FL、LNT、LNnT、DFL | |
| 第3阶段 | 4.9 | 4.6 | 2'-FL、LNT、LNnT、DFL | |
| 第4阶段 | 5 | 4.6 | 2'-FL、LNT、LNnT、DFL |
| [1] | Aaron L, Franco OE, Hayward SW. Review of Prostate Anatomy and Embryology and the Etiology of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Urol Clin North Am. 2016;43(3):279-288. |
| [2] | Faijes M, Castejón-Vilatersana M, Val-Cid C, Planas A. Enzymatic and cell factory approaches to the production of human milk oligosaccharides. Biotechnol Adv. 2019;37(5):667-697. |
| [3] | Borewicz K, Gu F, Saccenti E, et al. Correlating Infant Fecal Microbiota Composition and Human Milk Oligosaccharide Consumption by Microbiota of 1-Month-Old Breastfed Infants. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019;63(13):e1801214. |
| [4] | Sato K, Nakamura Y, Fujiyama K, et al. Absolute quantification of eight human milk oligosaccharides in breast milk to evaluate their concentration profiles and associations with infants' neurodevelopmental outcomes. J Food Sci. 2024;89(12):10152-10170. |
| [5] | Garrido D, Dallas DC, Mills DA. Consumption of human milk glycoconjugates by infant-associated bifidobacteria: mechanisms and implications. Microbiology (Reading). 2013;159(Pt 4):649-664. |
| [6] | Meredith-Dennis L, Xu G, Goonatilleke E, Lebrilla CB, Underwood MA, Smilowitz JT. Composition and Variation of Macronutrients, Immune Proteins, and Human Milk Oligosaccharides in Human Milk From Nonprofit and Commercial Milk Banks. J Hum Lact. 2018;34(1):120-129. |
| [7] | Smilowitz JT, Lebrilla CB, Mills DA, German JB, Freeman SL. Breast milk oligosaccharides: structure-function relationships in the neonate. Annu Rev Nutr. 2014;34:143-169. |
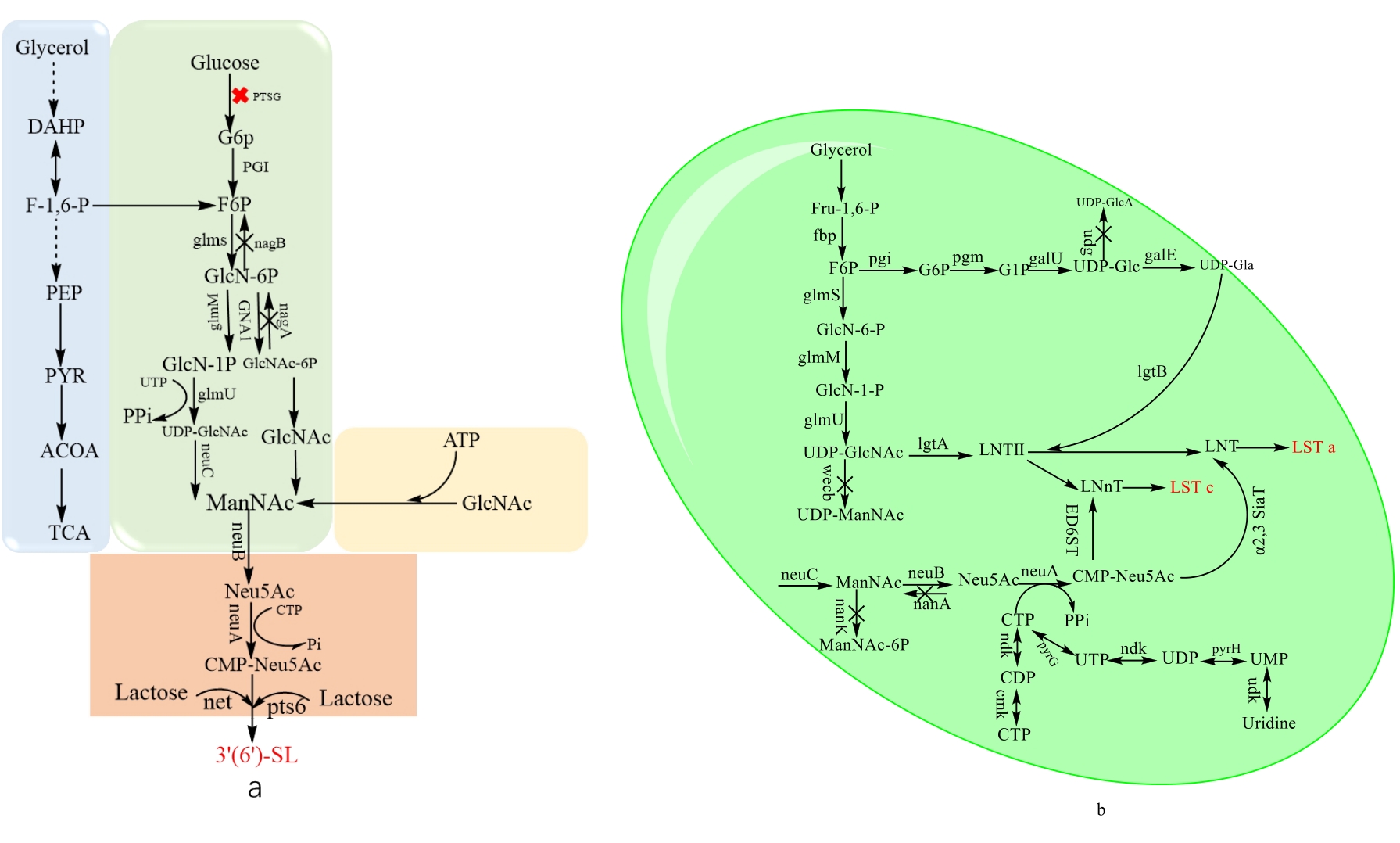
| [8] | Nguyen TLL, Nguyen DV, Heo KS. Potential biological functions and future perspectives of sialylated milk oligosaccharides. Arch Pharm Res. 2024;47(4):325-340. |
| [9] | Bode L. Human milk oligosaccharides: every baby needs a sugar mama.Glycobiology. 2012;22(9):1147-1162. |
| [10] | Okburan G, Kızıler S. Human milk oligosaccharides as prebiotics. Pediatr Neonatol. 2023;64(3):231-238. |
| [11] | Bode L, Contractor N, Barile D, et al. Overcoming the limited availability of human milk oligosaccharides: challenges and opportunities for research and application. Nutr Rev. 2016;74(10):635-644. . |
| [12] | Ninonuevo MR, Park Y, Yin H, et al. A strategy for annotating the human milk glycome. J Agric Food Chem. 2006;54(20):7471-7480. |
| [13] | Newburg DS, Ruiz-Palacios GM, Morrow AL. Human milk glycans protect infants against enteric pathogens. Annu Rev Nutr. 2005;25:37-58. |
| [14] | Morrow AL, Ruiz-Palacios GM, Altaye M, et al. Human milk oligosaccharides are associated with protection against diarrhea in breast-fed infants. J Pediatr. 2004;145(3):297-303. |
| [15] | Coppa GV, Zampini L, Galeazzi T, et al. Human milk oligosaccharides inhibit the adhesion to Caco-2 cells of diarrheal pathogens: Escherichia coli, Vibrio cholerae, and Salmonella fyris. Pediatr Res. 2006;59(3):377-382. |
| [16] | Tonon KM, Chutipongtanate S, Morrow AL, Newburg DS. Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Infants. Adv Nutr. 2024;15(6):100218.. |
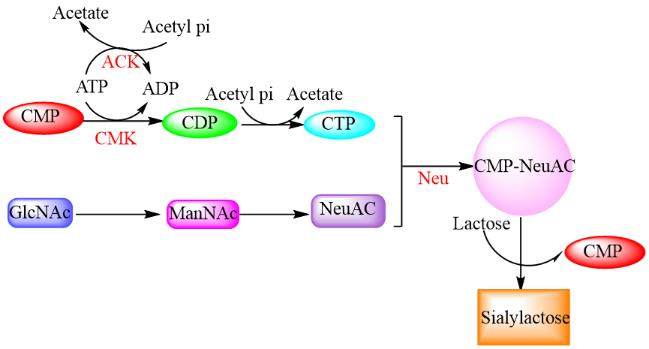
| [17] | Ben Hamed S, Tavares Ranzani-Paiva MJ, Tachibana L, de Carla Dias D, Ishikawa CM, Esteban MA. Fish pathogen bacteria: Adhesion, parameters influencing virulence and interaction with host cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018;80:550-562. |
| [18] | Ruiz-Palacios GM, Cervantes LE, Ramos P, Chavez-Munguia B, Newburg DS. Campylobacter jejuni binds intestinal H(O) antigen (Fuc alpha 1, 2Gal beta 1, 4GlcNAc), and fucosyloligosaccharides of human milk inhibit its binding and infection. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(16):14112-14120. |
| [19] | Nilsen M, Madelen Saunders C, Leena Angell I, et al. Butyrate Levels in the Transition from an Infant- to an Adult-Like Gut Microbiota Correlate with Bacterial Networks Associated with Eubacterium Rectale and Ruminococcus Gnavus. Genes (Basel). 2020;11(11):1245. Published 2020 Oct 22. |
| [20] | Fukuda S, Toh H, Hase K, et al. Bifidobacteria can protect from enteropathogenic infection through production of acetate. Nature. 2011;469(7331):543-547. |
| [21] | Albrecht S, Lane JA, Mariño K, et al. A comparative study of free oligosaccharides in the milk of domestic animals. Br J Nutr. 2014;111(7):1313-1328. |
| [22] | Craft KM, Townsend SD. The Human Milk Glycome as a Defense Against Infectious Diseases: Rationale, Challenges, and Opportunities. ACS Infect Dis. 2018;4(2):77-83. |
| [23] | Antunes KH, Fachi JL, de Paula R, et al. Microbiota-derived acetate protects against respiratory syncytial virus infection through a GPR43-type 1 interferon response. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3273. Published 2019 Jul 22. |
| [24] | Yu ZT, Chen C, Kling DE, et al. The principal fucosylated oligosaccharides of human milk exhibit prebiotic properties on cultured infant microbiota.Glycobiology. 2013;23(2):169-177. |
| [25] | Plaza-Díaz J, Fontana L, Gil A. Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Immune System Development. Nutrients. 2018;10(8):1038.. |
| [26] | Zhang S, Li T, Xie J, et al. Correction to: Gold standard for nutrition: a review of human milk oligosaccharide and its effects on infant gut microbiota. Microb Cell Fact. 2021;20(1):140. |
| [27] | Fan Y, McMath AL, Donovan SM. Review on the Impact of Milk Oligosaccharides on the Brain and Neurocognitive Development in Early Life. Nutrients. 2023; 15(17):3743. |
| [28] | Hauser J, Pisa E, Arias Vásquez A, et al. Sialylated human milk oligosaccharides program cognitive development through a non-genomic transmission mode. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26(7):2854-2871. |
| [29] | Wang B. Sialic acid is an essential nutrient for brain development and cognition. Annu Rev Nutr. 2009;29:177-222. |
| [30] | Thum C, Wall CR, Weiss GA, Wang W, Szeto IM-Y, Day L. Changes in HMO Concentrations throughout Lactation: Influencing Factors, Health Effects and Opportunities.Nutrients. 2021;13(7):2272.. |
| [31] | Craft KM, Townsend SD. Mother Knows Best: Deciphering the Antibacterial Properties of Human Milk Oligosaccharides.Acc Chem Res. 2019;52(3):760-768. |
| [32] | Lis-Kuberka J, Orczyk-Pawiłowicz M. Sialylated Oligosaccharides and Glycoconjugates of Human Milk. The Impact on Infant and Newborn Protection, Development and Well-Being. Nutrients. 2019;11(2):306. |
| [33] | Kobata A. Structures and application of oligosaccharides in human milk.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2010;86(7):731-747. |
| [34] | Puccio G, Alliet P, Cajozzo C, et al. Effects of Infant Formula With Human Milk Oligosaccharides on Growth and Morbidity: A Randomized Multicenter Trial. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017;64(4):624-631.. |
| [35] | Gabrielli O, Zampini L, Galeazzi T, et al. Preterm milk oligosaccharides during the first month of lactation. Pediatrics. 2011;128(6):e1520-e1531. |
| [36] | Corona L, Lussu A, Bosco A, et al. Human Milk Oligosaccharides: A Comprehensive Review towards Metabolomics. Children (Basel). 2021;8(9):804. |
| [37] | Jiao R, Peng X, Wang B, Du Y, Qian EW, Li J. Highly efficient and economical one-pot two-step multienzymatic synthesis of 6'/3'-sialyllactosamine from in situ-produced N-acetyllactosamine. J Agric Food Chem. 2025;73(23):14444-14452. |
| [38] | Laursen MF, Pekmez CT, Larsson MW, et al. Maternal milk microbiota and oligosaccharides contribute to the infant gut microbiota assembly. ISME Commun. 2021;1(1):21.. |
| [39] | 刘雯娴,彭晶,程海娜,等.母乳低聚糖的生物合成研究进展[J].中国食品学报,2024,24(11):388-398. |
| Liu WX, Peng J, Cheng HN, et al. Research progress on the biosynthesis of human milk oligosaccharides. J Chin Inst Food Sci Technol. 2024;24(11):388-398.. | |
| [40] | 王司琪,张宇,彭小雨,等.母乳中的活性成分——HMOs对机体的益处及应用现状[J].食品研究与开发,2025,46(06):191-196. |
| Wang SQ, Zhang Y, Peng XY, et al. Active components in human milk—benefits and applications of human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs). Food Res Dev. 2025;46(6):191-196. | |
| [41] | Xiao M, Tang L, Fu X, et al. Structural characterization of bacterial fucose-containing tetrasaccharide and its potential enhancement on intestinal barrier function. Food Biosci. 2025;66:106256. |
| [42] | Wang M, Monaco MH, Daniels VC, et al. Individual and Combined Effects of 2'-Fucosyllactose and Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis on the Gut Microbiota Composition of Piglets. J Nutr. 2025;155(2):509-522. |
| [43] | An P, Lan D, Feng D, et al. Quantitative nuclear magnetic analysis of human milk oligosaccharides 2'-fucosyllactose and 3-fucosyllactose in complicated food matrices. Food Chem. 2025;473:142821. |
| [44] | Pitt J, Bond J, Roper J, et al. A 21-day safety evaluation of biotechnologically produced 3-fucosyllactose (3-FL) in neonatal farm piglets to support use in infant formulas. Food Chem Toxicol. 2024;187:114592. |
| [45] | Cheng L, Akkerman R, Kong C, Walvoort MTC, de Vos P. More than sugar in the milk: human milk oligosaccharides as essential bioactive molecules in breast milk and current insight in beneficial effects. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61(7):1184-1200. |
| [46] | Bode L. Human Milk Oligosaccharides: Next-Generation Functions and Questions. Nestle Nutr Inst Workshop Ser. 2019;90:191-201. |
| [47] | Wu S, Tao N, German JB, Grimm R, Lebrilla CB. Development of an annotated library of neutral human milk oligosaccharides. J Proteome Res. 2010;9(8):4138-4151. |
| [48] | Qian Q, Yang L, Zhao C, et al. Highly efficient production of lacto-N-tetraose in plasmid-free Escherichia coli through chromosomal integration of multicopy key glycosyltransferase genes. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025;284(Pt 1):137987. |
| [49] | Slater AS, McDonald AG, Hickey RM, Davey GP. Glycosyltransferases: glycoengineers in human milk oligosaccharide synthesis and manufacturing. Front Mol Biosci. 2025;12:1587602. |
| [50] | Conze DB, Kruger CL, Symonds JM, et al. Weighted analysis of 2'-fucosyllactose, 3-fucosyllactose, lacto-N-tetraose, 3'-sialyllactose, and 6'-sialyllactose concentrations in human milk. Food Chem Toxicol. 2022;163:112877. |
| [51] | Orczyk-Pawiłowicz M, Lis-Kuberka J. The Impact of Dietary Fucosylated Oligosaccharides and Glycoproteins of Human Milk on Infant Well-Being. Nutrients. 2020;12(4):1105. |
| [52] | Li Y, Du G, Chen J, Lv X, Liu L. Glycosyltransferases in human milk oligosaccharide synthesis: structural mechanisms and rational design. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2025;93:103315. |
| [53] | Sheng M, Liu Y, Zhu Y, Wang R, Zhang W, Mu W. Efficient biosynthesis of sialyllacto-N-tetraose a by a metabolically engineered escherichia coli BL21(DE3) strain. J Agric Food Chem. 2025;73(11):6820-6827. |
| [54] | 张新景.石家庄地区乳母乳汁中低聚糖含量检测及其影响因素分析[D].河北医科大学,2020 |
| Zhang X J. Detection of oligosaccharide content in breast milk of lactating women in Shijiazhuang area and analysis of influencing factors[D]. Hebei Medical University, 2020. | |
| [55] | 周钰,姜珊,王淑霞,等.母乳低聚糖水平与6月龄内婴儿体格生长的关系[J].卫生研究,2025,54(03):358-365 |
| Zhou Y, Jiang S, Wang SX, et al. Relationship between human milk oligosaccharide levels and physical growth of infants within 6 months of age. J Hyg Res. 2025;54(3):358-365. | |
| [56] | Bode L, Jantscher-Krenn E. Structure-function relationships of human milk oligosaccharides. Adv Nutr. 2012;3(3):383S-91S. |
| [57] | Wu S, Grimm R, German JB, Lebrilla CB. Annotation and structural analysis of sialylated human milk oligosaccharides. J Proteome Res. 2011;10(2):856-868.. |
| [58] | Duman H, Bechelany M, Karav S. Human Milk Oligosaccharides: Decoding Their Structural Variability, Health Benefits, and the Evolution of Infant Nutrition. Nutrients. 2024;17(1):118. |
| [59] | Zhou Q, Lu S, Feng K, et al. Comparative effect of sialic acid and 3'-sialyllactose on fecal microbiota fermentation and prebiotic activity in ETEC-challenged IPEC-J2 cells. J Sci Food Agric. 2025;105(12):6615-6629. ,. |
| [60] | 游星,郭进,张洪涛,等.基于混菌耦合发酵策略合成3'-唾液酸乳糖[J].食品与发酵工业,2021,47(17):8-14 |
| You X, Guo J, Zhang HT, et al. Biosynthesis of 3'-sialyllactose using a mixed-culture coupling fermentation strategy. Food Ferment Ind. 2021;47(17):8-14. | |
| [61] | Weishaupt M, Eller S, Seeberger PH. Solid phase synthesis of oligosaccharides. Methods Enzymol. 2010;478:463-484. |
| [62] | Seeberger PH, Werz DB. Automated synthesis of oligosaccharides as a basis for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(9):751-763. |
| [63] | Routenberg Love K, Seeberger PH. Automated solid-phase synthesis of protected tumor-associated antigen and blood group determinant oligosaccharides. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2004;43(5):602-605. |
| [64] | Gilbert M, Bayer R, Cunningham AM, et al. The synthesis of sialylated oligosaccharides using a CMP-Neu5Ac synthetase/sialyltransferase fusion. Nat Biotechnol. 1998;16(8):769-772. |
| [65] | 靳文斌, 张潇潇, 李玉, 等. 合成唾液酸乳糖重组大肠杆菌的构建[J]. 生物技术通报, 2014, 10:201-206. |
| Jin WB, Zhang XX, Li Y, et al. Construction of recombinant Escherichia coli for sialyllactose synthesis. Biotechnol Bull. 2014, 10:201-206. | |
| [66] | Endo T, Koizumi S, Tabata K, Ozaki A. Large-scale production of CMP-NeuAc and sialylated oligosaccharides through bacterial coupling. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2000;53(3):257-261.. |
| [67] | 杨双红. 利用微生物合成唾液酸寡糖的研究进展[J]. 齐鲁渔业, 2015, 32(5): 51-52. |
| Yang SH. Research advances in microbial synthesis of sialyloligosaccharides. J Shandong Fish. 2015;32(5):51-52. | |
| [68] | Lee SG, Lee JO, Yi JK, Kim BG. Production of cytidine 5'-monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid using recombinant Escherichia coli as a biocatalyst. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2002;80(5):516-524. |
| [69] | Han NS, Kim TJ, Park YC, Kim J, Seo JH. Biotechnological production of human milk oligosaccharides. Biotechnol Adv. 2012;30(6):1268-1278. |
| [70] | Vibhute AM, Komura N, Tanaka HN, Imamura A, Ando H. Advanced Chemical Methods for Stereoselective Sialylation and Their Applications in Sialoglycan Syntheses. Chem Rec. 2021;21(11):3194-3223. |
| [71] | Adak AK, Yu CC, Liang CF, Lin CC. Synthesis of sialic acid-containing saccharides. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013;17(6):1030-1038. |
| [72] | Chen J, Hansen T, Zhang QJ, et al. 1-Picolinyl-5-azido Thiosialosides: Versatile Donors for the Stereoselective Construction of Sialyl Linkages. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019;58(47):17000-17008. |
| [73] | Cao H, Chen X. General consideration on sialic acid chemistry.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;808:31-56.. |
| [74] | Nielsen MM, Pedersen CM. Catalytic Glycosylations in Oligosaccharide Synthesis.Chem Rev. 2018;118(17):8285-8358.. |
| [75] | Li C, Liu Z, Li M, Miao M, Zhang T. Review on bioproduction of sialylated human milk oligosaccharides: synthesis methods, physiologic functions, and applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2025;352:123177. |
| [76] | Juge N, Tailford L, Owen CD. Sialidases from gut bacteria: a mini-review. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016;44(1):166-175. |
| [77] | 孟欣. 双唾液酸化四糖抗原表位的化学酶法合成研究[D]. 山东:山东大学,2014. |
| Meng X. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of disialylated tetrasaccharide antigen epitopes [D]. Jinan: Shandong University; 2014.. | |
| [78] | Tanaka H, Ito F, Iwasaki T. A system for sialic acid transfer by colominic acid and a sialidase that preferentially hydrolyzes sialyl alpha-2,8 linkages. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1995;59(4):638-643. |
| [79] | Guo Y, Jers C, Meyer AS, et al. A Pasteurella multocida sialyltransferase displaying dual trans-sialidase activities for production of 3'-sialyl and 6'-sialyl glycans. J Biotechnol. 2014;170:60-67. |
| [80] | 韩乐闪,于潇頔,栾庆民,等.唾液酸乳糖的功能及制备研究进展[J].中国食品添加剂,2024,35(12):242-250. |
| Han LS, Yu XD, Luan QM, et al. Research progress on the functionality and preparation of sialyllactose. China Food Addit. 2024;35(12):242-250. | |
| [81] | Westers L, Westers H, Quax WJ. Bacillus subtilis as cell factory for pharmaceutical proteins: a biotechnological approach to optimize the host organism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1694(1-3):299-310. |
| [82] | 朱咏莲.代谢工程改造枯草芽孢杆菌合成3'-唾液酸乳糖[D].江南大学,2023. |
| Zhu Y L. Metabolic engineering of Bacillus subtilis for 3'-sialyllactose production[D]. Jiangnan University, 2023. | |
| [83] | Efficient production of 3 '-sialyllactose using escherichia coli | journal of agricultural and food chemistry. Accessed August 16, 2025. |
| [84] | Liu Y, Chen X, Lv X, Yuan L, Wu J, Yao J. Engineered Escherichia coli as a Microbial Cell Factory for De Novo 6'-Sialyllactose Biosynthesis. J Agric Food Chem. 2025;73(25):15880-15888. |
| [85] | Li C, Li M, Hu M, Miao M, Zhang T. Metabolic engineering of escherichia coli for high-titer biosynthesis of 3'-sialyllactose. J Agric Food Chem. 2024;72(10):5379-5390. |
| [86] | Priem B, Gilbert M, Wakarchuk WW, Heyraud A, Samain E. A new fermentation process allows large-scale production of human milk oligosaccharides by metabolically engineered bacteria.Glycobiology. 2002;12(4):235-240.. |
| [87] | Fierfort N, Samain E. Genetic engineering of Escherichia coli for the economical production of sialylated oligosaccharides. J Biotechnol. 2008;134(3-4):261-265. |
| [88] | Zhang J, Zhu Y, Zhang W, Mu W. Efficient Production of a Functional Human Milk Oligosaccharide 3'-Sialyllactose in Genetically Engineered Escherichia coli. ACS Synth Biol. 2022;11(8):2837-2845. |
| [89] | Liu Y, Zhu Y, Qiao L, et al. Simonsiella muelleri α2,6-sialyltransferase enables efficient biosynthesis of 6'-sialyllactose in both plasmid-dependent and plasmid-free engineered Escherichia coli. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025;320(Pt 1):145718. |
| [90] | 黄传超,邓阳.代谢工程改造大肠杆菌合成3'-唾液酸乳糖[J/OL].食品与发酵工业,1-11[2025-05-29]. |
| Huang CC, Deng Y. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for 3'-sialyllactose synthesis [J/OL]. Food Ferment Ind. 2025:1-11 [2025-05-29]. | |
| [91] | 周文,游星,张洪涛,等.多细胞耦合转化N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖和乳糖生产唾液酸乳糖[J].生物工程学报,2023,39(11):4621-4634. |
| Zhou W, You X, Zhang HT, et al. Multi-cell coupling conversion of N-acetylglucosamine and lactose for sialyllactose production [J]. Chin J Biotechnol. 2023;39(11):4621-4634. | |
| [92] | Zhang Z, Zhang H, Wang Z, et al. A Cellular Coupling Strategy Leveraging Pathway Modularization and Cofactor Regeneration for the Biosynthesis of 3'-Sialyllactose. J Agric Food Chem. 2025;73(29):18380-18389. |
| [93] | Zhao M, Zhu Y, Wang H, Zhang J, Xu W, Mu W. Efficient Production of N-Acetylneuraminic Acid in Escherichia coli Based on the UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine Biosynthetic Pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 2023;71(28):10701-10709. |
| [94] | Liu Y, Lin Q, Sheng M, et al. Highly Efficient In Vivo Production of Sialyllacto-N-tetraose C via Screening of Beneficial β1,4-galactosyltransferase and α2,6-sialyltransferase. J Agric Food Chem. 2025;73(9):5376-5384. |
| [95] | Zhu Y, Zhang J, Zhang W, Mu W. Recent progress on health effects and biosynthesis of two key sialylated human milk oligosaccharides, 3'-sialyllactose and 6'-sialyllactose. Biotechnol Adv. 2023;62:108058. |
| [96] | 陈奇.代谢工程改造枯草芽孢杆菌高效合成6'-唾液酸乳糖[D].江南大学,2024. |
| Chen Q. High-efficiency biosynthesis of 6'-sialyllactose through metabolic engineering of Bacillus subtilis[D]. Jiangnan University, 2024. | |
| [97] | Mao S, Zhao A, Jiang H, et al. Patterns of Human Milk Oligosaccharides in Mature Milk Are Associated with Certain Gut Microbiota in Infants. Nutrients. 2024;16(9):1287.. |
| [98] | Kang J, Gu P, Wang Y, et al. Engineering of an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetic pathway in Escherichia coli.Metab Eng. 2012;14(6):623-629.. |
| [99] | EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA), Turck D, Bohn T, et al. Safety of 3'-sialyllactose (3'-SL) sodium salt produced by a derivative strain (Escherichia coli NEO3) of E. coli W (ATCC 9637) as a Novel Food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2023;21(9):e08224 |
| [100] | Bénet T, Frei N, Spichtig V, Cuany D, Austin S. Determination of Seven Human Milk Oligosaccharides (HMOs) in Infant Formula and Adult Nutritionals: First Action 2022.07. J AOAC Int. 2024;107(2):286-302. |
| [101] | Yang M, Jiang Z, Zhou L, et al. 3'-Sialyllactose and B. infantis synergistically alleviate gut inflammation and barrier dysfunction by enriching cross-feeding bacteria for short-chain fatty acid biosynthesis. Gut Microbes. 2025;17(1):248651. |
| [102] | Ding J, Ouyang R, Zheng S, et al. Effect of Breastmilk Microbiota and Sialylated Oligosaccharides on the Colonization of Infant Gut Microbial Community and Fecal Metabolome. Metabolites. 2022;12(11):1136. |
| [103] | Bajic D, Wiens F, Wintergerst E, Deyaert S, Baudot A, Van den Abbeele P. HMOs Exert Marked Bifidogenic Effects on Children's Gut Microbiota Ex Vivo, Due to Age-Related Bifidobacterium Species Composition. Nutrients. 2023;15(7):1701. |
| [104] | Zhu L, Wang M, Li H, et al. Supplementation of 3'-Sialyllactose During the Growth Period Improves Learning and Memory Development in Mice. J Agric Food Chem. 2024;72(44):24518-24529. |
| [105] | Golden RK, Sutkus LT, Donovan SM, Dilger RN. Dietary supplementation of 3'-sialyllactose or 6'-sialyllactose elicits minimal influence on cognitive and brain development in growing pigs. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024;17:1337897. |
| [106] | Thomson P, Medina DA, Garrido D. Human milk oligosaccharides and infant gut bifidobacteria: Molecular strategies for their utilization. Food Microbiol. 2018;75:37-46. |
| [107] | Bauer J, Osborn HM. Sialic acids in biological and therapeutic processes: opportunities and challenges. Future Med Chem. 2015;7(16):2285-2299. |
| [108] | Kim J, Kim YJ, Kim JW. Bacterial Clearance Is Enhanced by α2,3- and α2,6-Sialyllactose via Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis and Phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 2018;87(1):e00694-18. |
| [109] | Kang LJ, Kwon ES, Lee KM, et al. 3'-Sialyllactose as an inhibitor of p65 phosphorylation ameliorates the progression of experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Pharmacol. 2018;175(23):4295-4309. |
| [110] | Duan Q, Yu B, Huang Z, et al. Sialyllactose Attenuates Inflammation and Injury of Intestinal Epithelial Cells upon Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Infection. Int J Mol Sci. 2025;26(8):3860. |
| [111] | Park DB, Kim L, Hwang JH, et al. Temporal quantitative profiling of sialyllactoses and sialic acids after oral administration of sialyllactose to mini-pigs with osteoarthritis. RSC Adv. 2023;13(2):1115-1124. |
| [112] | Yamabe M, Kaihatsu K, Ebara Y. Binding inhibition of various influenza viruses by sialyllactose-modified trimer DNAs. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019;29(5):744-748. |
| [113] | Cooper P, Bolton KD, Velaphi S, et al. Early Benefits of a Starter Formula Enriched in Prebiotics and Probiotics on the Gut Microbiota of Healthy Infants Born to HIV+ Mothers: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Clin Med Insights Pediatr. 2017;10:119-130. |
| [114] | Lim B, Kim KS, Ahn JY, Na K. Overcoming antibiotic resistance caused by genetic mutations of Helicobacter pylori with mucin adhesive polymer-based therapeutics. Biomaterials. 2024;308:122541. |
| [115] | Schelch S, Zhong C, Petschacher B, Nidetzky B. Bacterial sialyltransferases and their use in biocatalytic cascades for sialo-oligosaccharide production. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;44:107613. |
| [1] | WU Ke, LUO Jiahao, LI Feiran. Applications of machine learning in the reconstruction and curation of genome-scale metabolic models [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 566-584. |
| [2] | TIAN Xiao-jun, ZHANG Rixin. “Economics Paradox” with cells in synthetic gene circuits [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 532-546. |
| [3] | ZHANG Yiqing, LIU Gaowen. Exploration of gene functions and library construction for engineering strains from a synthetic biology perspective [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 685-700. |
| [4] | YANG Ying, LI Xia, LIU Lizhong. Applications of synthetic biology to stem-cell-derived modeling of early embryonic development [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 669-684. |
| [5] | HUANG Yi, SI Tong, LU Anjing. Standardization for biomanufacturing: global landscape, critical challenges, and pathways forward [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 701-714. |
| [6] | SONG Chengzhi, LIN Yihan. AI-enabled directed evolution for protein engineering and optimization [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(3): 617-635. |
| [7] | SHENG Zhouhuang, CHEN Zhixian, ZHANG Yan. Research progress of yeast mannoproteins [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 408-421. |
| [8] | ZHANG Mengyao, CAI Peng, ZHOU Yongjin. Synthetic biology drives the sustainable production of terpenoid fragrances and flavors [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 334-356. |
| [9] | ZHANG Lu’ou, XU Li, HU Xiaoxu, YANG Ying. Synthetic biology ushers cosmetic industry into the “bio-cosmetics” era [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 479-491. |
| [10] | LU Jinchang, WU Yaokang, LV Xueqin, LIU Long, CHEN Jian, LIU Yanfeng. Green biomanufacturing of ceramide sphingolipids [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 422-444. |
| [11] | YI Jinhang, TANG Yulin, LI Chunyu, WU Heyun, MA Qian, XIE Xixian. Applications and advances in the research of biosynthesis of amino acid derivatives as key ingredients in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 254-289. |
| [12] | WEI Lingzhen, WANG Jia, SUN Xinxiao, YUAN Qipeng, SHEN Xiaolin. Biosynthesis of flavonoids and their applications in cosmetics [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 373-390. |
| [13] | XIAO Sen, HU Litao, SHI Zhicheng, WANG Fayin, YU Siting, DU Guocheng, CHEN Jian, KANG Zhen. Research advances in biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid with controlled molecular weights [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 445-460. |
| [14] | WANG Qian, GUO Shiting, XIN Bo, ZHONG Cheng, WANG Yu. Advances in biosynthesis of L-arginine using engineered microorganisms [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 290-305. |
| [15] | ZUO Yimeng, ZHANG Jiaojiao, LIAN Jiazhang. Enabling technology for the biosynthesis of cosmetic raw materials with Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2025, 6(2): 233-253. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||